The Role of IOS in Identification of Specific Treatable Traits in Pediatric Asthma: Current Limitations and Future Perspectives—Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Impulse Oscillometry
2.1. Overview and Clinical Relevance
2.2. Technical Aspects of IOS
2.3. IOS Parameters and Interpretation
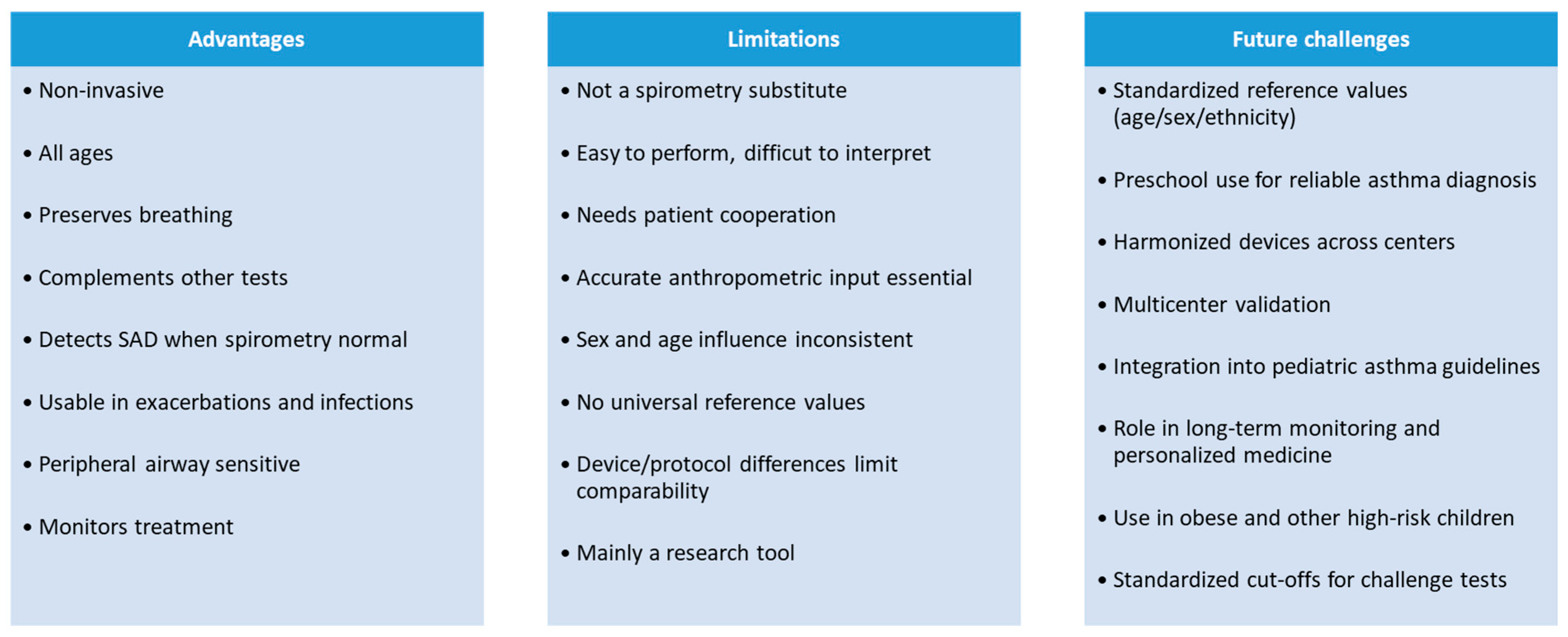
2.4. Clinical Relevance and Limitations
3. Small Airway Disease
3.1. Overview
3.2. SAD and Asthma Control
3.3. Treatable Asthma Traits and SAD
4. IOS in Diagnosis and Therapeutic Management of SAD
4.1. IOS in Adults
4.2. IOS in Children (School-Aged and Older)
4.3. IOS in Preschoolers and Infants
4.4. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papi, A.; Brightling, C.; Pedersen, S.E.; Reddel, H.K. Asthma. Lancet 2018, 391, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacharier, L.B.; Guilbert, T.W. Diagnosis and management of early asthma in preschool-aged children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manti, S.; Magri, P.; De Silvestri, A.; De Filippo, M.; Votto, M.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. Epidemiology of severe asthma in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2024, 33, 240095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bacharier, L.B.; Strunk, R.C.; Mauger, D.; White, D.; Lemanske, R.F., Jr.; Sorkness, C.A. Classifying asthma severity in children: Mismatch between symptoms, medication use, and lung function. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, R.; Gochicoa-Rangel, L.; Cottini, M.; Comberiati, P.; Gaillard, E.A.; Ducharme, F.M.; Galant, S.P. Ascertainment of Small Airways Dysfunction Using Oscillometry to Better Define Asthma Control and Future Risk: Are We Ready to Implement It in Clinical Practice? Chest 2025, 167, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bar-Yishay, E.; Matyashchuk, E.; Mussaffi, H.; Mei-Zahav, M.; Prais, D.; Hananya, S.; Steuer, G.; Blau, H. Use of the forced oscillation technique to detect bronchodilation in children: Experience from the Schneider Children’s Medical Center of Israel. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2009, 11, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Postma, D.S.; Brightling, C.; Baldi, S.; Van den Berge, M.; Fabbri, L.M.; Gagnatelli, A.; Papi, A.; Van der Molen, T.; Rabe, K.F.; Siddiqui, S.; et al. Exploring the relevance and extent of small airways dysfunction in asthma (ATLANTIS): Baseline data fra prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 402–416, Erratum in Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, e28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30242-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.G.; Bates, J.; Berger, K.I.; Calverley, P.; de Melo, P.L.; Dellacà, R.L.; Farré, R.; Hall, G.L.; Ioan, I.; Irvin, C.G.; et al. Technical standards for respiratory oscillometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauberghs, M.; Van de Woestijne, K.P. Effect of upper airway shunt and series properties on respiratory impedance measurements. J. Appl. Physiol. 1989, 66, 2274–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellinckx, J.; De Boeck, K.; Bande-Knops, J.; van der Poel, M.; Demedts, M. Bronchodilator response in 3–6.5 years old healthy and stable asthmatic children. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 12, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calogero, C.; Simpson, S.J.; Lombardi, E.; Parri, N.; Cuomo, B.; Palumbo, M.; de Martino, M.; Shackleton, C.; Verheggen, M.; Gavidia, T.; et al. Respiratory impedance and bronchodilator responsiveness in healthy children aged 2–13 years. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2013, 48, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, J.; Jutla, J.; Kramer, G.; Hatzakis, G.E.; Ducharme, F.M.; Davis, G.M. Impulse oscillometry: Reference values in children 100 to 150 cm in height and 3 to 10 years of age. Chest 2005, 128, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dencker, M.; Malmberg, L.P.; Valind, S.; Thorsson, O.; Karlsson, M.K.; Pelkonen, A.; Pohjanpalo, A.; Haahtela, T.; Turpeinen, M.; Wollmer, P. Reference values for respiratory system impedance by using impulse oscillometry in children aged 2–11 years. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2006, 26, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminsky, D.A.; Simpson, S.J.; Berger, K.I.; Calverley, P.; de Melo, P.L.; Dandurand, R.; Dellacà, R.L.; Farah, C.S.; Farré, R.; Hall, G.L.; et al. Clinical significance and applications of oscillometry. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 210208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McNulty, W.; Usmani, O.S. Techniques of assessing small airways dysfunction. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2014, 1, 25898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hansen, J.E.; Sun, X.G.; Wasserman, K. Discriminating measures and normal values for expiratory obstruction. Chest 2006, 129, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgel, P.R.; de Blic, J.; Chanez, P.; Delacourt, C.; Devillier, P.; Didier, A.; Dubus, J.C.; Frachon, I.; Garcia, G.; Humbert, M.; et al. Update on the roles of distal airways in asthma. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2009, 18, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Wiel, E.; ten Hacken, N.H.; Postma, D.S.; van den Berge, M. Small-airways dysfunction associates with respiratory symptoms and clinical features of asthma: A systematic review. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepak, D.; Prasad, A.; Atwal, S.S.; Agarwal, K. Recognition of Small Airways Obstruction in Asthma and COPD—The Road Less Travelled. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, TE01–TE05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cottini, M.; Lombardi, C.; Berti, A.; Comberiati, P. Small-airway dysfunction in paediatric asthma. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 21, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottini, M.; Lombardi, C.; Comberiati, P.; Berti, A.; Menzella, F.; Dandurand, R.J.; Diamant, Z.; Chan, R. Oscillometry-defined small airways dysfunction as a treatable trait in asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025, 134, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetta, A.; Facciolongo, N.; Franco, C.; Franzini, L.; Piraino, A.; Rossi, C. Impulse Oscillometry, Small Airways Disease, and Extra-Fine Formulations in Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Windows for New Opportunities. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2022, 18, 965–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ducharme, F.M.; Chan, R. Oscillometry in the diagnosis, assessment, and monitoring of asthma in children and adults. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025, 134, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, V.M.; Fingleton, J.; Agusti, A.; Hiles, S.A.; Clark, V.L.; Holland, A.E.; Marks, G.B.; Bardin, P.P.; Beasley, R.; Pavord, I.D.; et al. Treatable Traits Down Under International Workshop report. Treatable Traits Down Under International Workshop participants: Treatable traits: A new paradigm for 21st century management of chronic airway diseases: Treatable Traits Down Under International Workshop report. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1802058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottini, M.; Licini, A.; Lombardi, C.; Berti, A. Prevalence and features of IOS-defined small airway disease across asthma severities. Respir. Med. 2021, 176, 106243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Main Report. 2024. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/2024-report/ (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Cottini, M.; Bondi, B.; Bagnasco, D.; Braido, F.; Passalacqua, G.; Licini, A.; Lombardi, C.; Berti, A.; Comberiati, P.; Landi, M.; et al. Impulse oscillometry defined small airway dysfunction in asthmatic patients with normal spirometry: Prevalence, clinical associations, and impact on asthma control. Respir. Med. 2023, 218, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, T.; Oga, T.; Niimi, A.; Matsumoto, H.; Ito, I.; Yamaguchi, M.; Matsuoka, H.; Jinnai, M.; Otsuka, K.; Oguma, T.; et al. Relationship between small airway function and health status, dyspnea and disease control in asthma. Respiration 2010, 80, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Liu, L.; Ali, K.; Wu, S.; Chen, J. Impulse Oscillometry Combined to FeNO in Relation to Asthma Control Among Preschool Children. J. Asthma Allergy 2024, 17, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Leiria-Pinto, P.; Carreiro-Martins, P.; Peralta, I.; Marques, J.; Finelli, E.; Alves, C.; Belo, J.; Alves, M.; Papoila, A.; Neuparth, N. Factors associated with asthma control in 121 preschool children. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 31, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-M.; Chang, Y.-J.; Yang, K.D.; Lin, C.-H.; Chien, J.-W.; Kao, J.-K.; Lee, M.-S.; Chiang, T.-I.; Lin, C.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-G. Small airway dysfunction measured by IOS and fractional exhaled nitric oxide is associated with asthma control in children. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 877681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, A.; Pamies, R.; Oliver, F.; Medina, A.; Caballero, L.; Mazon, A. Montelukast improves pulmonary function measured by impulse oscillometry in children with asthma (Mio study). Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipworth, B. Targeting the small airways asthma phenotype: If we can reach it, should we treat it? Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 110, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottini, M.; Licini, A.; Lombardi, C.; Berti, A. Clinical Characterization and Predictors of IOS-Defined Small-Airway Dysfunction in Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 997–1004.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, U.; Dixon, A.E.; Forno, E. Obesity and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Forno, E.; Weiner, D.J.; Mullen, J.; Sawicki, G.; Kurland, G.; Han, Y.Y.; Cloutier, M.M.; Canino, G.; Weiss, S.T.; Litonjua, A.A.; et al. Obesity and Airway Dysanapsis in Children with and without Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ringbaek, T.; Froelund, L.; Mortensen, J.; El Ali, H.H. The influence of obesity on IOS parameters in asthma, COPD, and other lung diseases: Analyzed by random forest. BMC Pulm. Med. 2025, 25, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Klubdaeng, A.; Udomittipong, K.; Palamit, A.; Charoensittisup, P.; Mahoran, K. Impact of obesity on pulmonary function of preschool children: An impulse oscillometry study. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2025, 68, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pijnenburg, M.W.; Baraldi, E.; Brand, P.L.; Carlsen, K.H.; Eber, E.; Frischer, T.; Hedlin, G.; Kulkarni, N.; Lex, C.; Mäkelä, M.J.; et al. Monitoring asthma in children. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 906–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, G.L.; Hantos, Z.; Wildhaber, J.H.; Sly, P.D. Contribution of nasal pathways to low frequency respiratory impedance in infants. Thorax 2002, 57, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Graham, B.L.; Steenbruggen, I.; Miller, M.R.; Barjaktarevic, I.Z.; Cooper, B.G.; Hall, G.L.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; McCarthy, K.; McCormack, M.C.; et al. Standardization of Spirometry 2019 Update. An Official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society Technical Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e70–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Quanjer, P.H.; Stanojevic, S.; Cole, T.J.; Baur, X.; Hall, G.L.; Culver, B.H.; Enright, P.L.; Hankinson, J.L.; Ip, M.S.M.; Zheng, J.; et al. ERSG lobal Lung Function Initiative Multi-ethnic reference values for spirometry for the 3-95-year age range: The global lung function 2012 equations. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 1324–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chan, R.; Stewart, K.; Kuo, C.R.; Lipworth, B. Evaluation of dupilumab and benralizumab on peripheral airway resistance and reactance. Allergy 2024, 79, 2862–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Error related to height, sex |
| Inadequate measurement duration for each recording |
| Insufficient number of repetitions |
| Absence of nose clip during measurement |
| Lack of manual cheek stabilization |
| Incorrect head and body positioning |
| Saliva swallowing interfering with data acquisition |
| Breath-holds during testing |
| Glottic closure events |
| Air leak around the mouth |
| Citation, Author, Year | What Was the Study About? | Study Population |
|---|---|---|
| Bar-Yishay E et al., 2009 [6] | - Detection of bronchodilatation in children - Comparison to spirometry | Preschool children |
| Postma DS et al., 2019 [7] | - Comprehensive assessment of asthma (spirometry, body plethysmography, IOS, multiple breath nitrogen washout, computed tomography in selected participants, questionnaires) - Exploring the relevance and extent of SAD in asthma | Adults with and without asthma |
| Cauberghs M et al., 1989 [9] | - Impact of upper airway shunt on respiratory impedance assessment | Healthy adults and children and patients with obstructive lung disease |
| Hellinckx J et al., 1988 [10] | - Evaluation of baseline lung function and bronchodilator response | Preschool healthy and asthmatic children |
| Calogero C et al., 2013 [11] | - Development of reference values for respiratory impedance | Healthy preschool- and school -aged children |
| Frei J et al., 2005 [12] | - Development of reference equations - Assessment of changes in IOS parameters in relation to anthropometric measures | Healthy preschool- and school-aged children |
| Dencker M et al., 2006 [13] | - The extension of the reference values for IOS variables - Assessment of changes in IOS parameters in relation to anthropometric measures | Preschool and school-aged children |
| Cottini M et al., 2021 [25] | - Evaluation of IOS-defined SAD across treatment steps | Adults with asthma |
| Takeda T et al., 2010 [28] | - Using IOS to evaluate the relationship between central and peripheral airway function and clinical parameters such as health status, dyspnea and asthma control | Adult patients with asthma |
| Xiao J et al., 2024 [29] | - Differences in IOS and FeNO in relation to asthma control - Predictive value of IOS combined with FeNO for uncontrolled asthma | Preschool children with asthma and healthy controls |
| Leiria-Pinto P et al., 2021 [30] | - The association between clinical and functional parameters and the lack of asthma control in preschool children | Preschool children with asthma and healthy controls |
| Lin LM et al., 2022 [31] | - The role of IOS and FeNO for assessing childhood asthma control in terms of SAD and airway inflammation - Comprehensive evaluation of pediatric asthma using FeNO, spirometry, IOS, bronchodilator testing, total IgE measurement and C-ACT | Asthmatic children and healthy participants. |
| Nieto A et al., 2006 [32] | - Evaluation of the effect of oral montelukast on airway resistance | Children with asthma and healthy controls |
| Cottini M et al., 2020 [34] | - Determination of predictors of SAD | Adults with asthma |
| Ringbaek T et al., 2025 [37] | - Analyzing predictors of respiratory dysfunction across Body Mass Index groups | Adult patients with asthma and/or lung-related symptoms |
| Klubdaeng A et al., 2025 [38] | - Identification of obesity indices predictive of impaired lung function | Obese preschool children and healthy controls |
| Hall GL et al., 2002 [40] | - Examining airway resistance changes in nasally breathing infants | Infants |
| Chan R et al., 2024 [43] | - Evaluation of the effect of biological anti-asthmatic therapy on small airway mechanics | Adult with asthma |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Połomska, J.; Sikorska-Szaflik, H.; Sozańska, B. The Role of IOS in Identification of Specific Treatable Traits in Pediatric Asthma: Current Limitations and Future Perspectives—Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207368
Połomska J, Sikorska-Szaflik H, Sozańska B. The Role of IOS in Identification of Specific Treatable Traits in Pediatric Asthma: Current Limitations and Future Perspectives—Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207368
Chicago/Turabian StylePołomska, Joanna, Hanna Sikorska-Szaflik, and Barbara Sozańska. 2025. "The Role of IOS in Identification of Specific Treatable Traits in Pediatric Asthma: Current Limitations and Future Perspectives—Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207368
APA StylePołomska, J., Sikorska-Szaflik, H., & Sozańska, B. (2025). The Role of IOS in Identification of Specific Treatable Traits in Pediatric Asthma: Current Limitations and Future Perspectives—Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207368





