Percutaneous Biopsy Under Deep Intravenous or Oral Conscious Sedation: Which Is the Best Option for Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
3.2. Comparison Between the IV Sedation Group and the Oral Conscious Sedation Group
3.3. Multiple Linear Regression
3.4. Anesthesiologic Factors and Their Association with Diagnostic Success, Biopsy-Related Complications, and Sedation-Related Complications in the IV Sedation Group
3.5. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| DRGs | Diagnosis-Related Groups |
| ICER | Incremental Cost-Effectiveness Ratio |
| INR | International Normalized Ratio |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| IV | Intravenous |
| NORA | Non-Operating Room Anesthesia |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PICU | Pediatric Intensive Care Unit |
| PT | Prothrombin Time |
| PTT | Partial Thromboplastin Time |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (IBM SPSS® software) |
| TROOPS | Tracking and Reporting Outcomes Of Procedural Sedation |
| US | Ultrasound |
References
- Loupy, A.; Mengel, M.; Haas, M. Thirty years of the International Banff Classification for Allograft Pathology: The past, present, and future of kidney transplant diagnostics. Kidney Int. 2022, 101, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, R.D.; Augustine, J.J. Beyond the Biopsy: Monitoring Immune Status in Kidney Recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.; Yaster, M.; Kudchadkar, S.R. Pediatric Sedation Management. Pediatr. Rev. 2016, 37, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, F.; Mallik, M.; Marks, S.D.; Watson, A.R.; British Association of Paediatric Nephrology. Renal biopsies in children: Current practice and audit of outcomes. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.P.; Ayestaran, F.W.; Gillespie, S.E.; Sanders, R.D.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Simon, H.K.; Stockwell, J.A. Deep procedural sedation by a sedationist team for outpatient pediatric renal biopsies. Pediatr. Transplant. 2016, 20, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rasheed, S.A.; Al Mugeiren, M.M.; Abdurrahman, M.B.; Elidrissy, A.T. The outcome of percutaneous renal biopsy in children: An analysis of 120 consecutive cases. Pediatr. Nephrol. 1990, 4, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Sedation and Analgesia by Non-Anesthesiologists. Practice guidelines for sedation and analgesia by non-anesthesiologists. Anesthesiology 2002, 84, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravero, J.P.; Askins, N.; Sriswasdi, P.; Tsze, D.S.; Zurakowski, D.; Sinnott, S. Validation of the Pediatric Sedation State Scale. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20162897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufosse, C.; Simmonds, N.; Clahsen-van Groningen, M.; Haas, M.; Henriksen, K.J.; Horsfield, C.; Loupy, A.; Mengel, M.; Perkowska-Ptasińska, A.; Rabant, M.; et al. A 2018 Reference Guide to the Banff Classification of Renal Allograft Pathology. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1795–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roback, M.G.; Green, S.M.; Andolfatto, G.; Leroy, P.L.; Mason, K.P. Tracking and Reporting Outcomes of Procedural Sedation (TROOPS): Standardized Quality Improvement and Research Tools from the International Committee for the Advancement of Procedural Sedation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, J.S.; Briggs, A.H.; Willan, A.R. Something old, something new, something borrowed, something blue: A framework for the marriage of health econometrics and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Econ. 2002, 11, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, R.S.; Cappelen-Smith, J.; al Suhaibani, H.; Alfurayh, O.; Shakweer, W.; Akhtar, M. Yield and complications in percutaneous renal biopsy: A comparison between ultrasound-guided gun-biopsy and manual techniques in native and transplant kidneys. Acta Radiol. 1997, 38, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Park, S.Y. Diagnostic efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided kidney transplant biopsy using cortex-only view: A retrospective single-center study. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 5272–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bux, K.I.; Moorani, K.N.; Qureshi, H.; Kumari, U.; Khan, F.; Farooq, F.; Abbas, F.; Aman, M.; Sahito, A.M.; Musharraff, F.; et al. Safety and Adequacy of Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Renal Biopsy in Children: A Single-Center Experience. Cureus 2022, 14, e24452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, L.K.; Lai, W.M.; Lau, S.C.; Tong, P.C.; Tse, K.C.; Chiu, M.C. Ten-year review of disease pattern from percutaneous renal biopsy: An experience from a paediatric tertiary renal centre in Hong Kong. Hong Kong Med. J. 2008, 14, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Varnell, C.D., Jr.; Stone, H.K.; Welge, J.A. Bleeding complications after pediatric kidney biopsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.J.; Lin, S.H.; Huang, J.L.; Wu, T.W.; Hsia, S.H.; Lin, J.J.; Chou, Y.C.; Tseng, M.H. Risk factors for complications of percutaneous ultrasound-guided renal biopsy in children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Q.Y.; Lim, C.C.; Tan, H.Z.; Sultana, R.; Kee, T.; Htay, H. Complications of Percutaneous Kidney Allograft Biopsy: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Transplantation 2022, 106, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwah, D.S.; Korbet, S.M. Timing of complications in percutaneous renal biopsy: What is the optimal period of observation? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1996, 28, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnoli, L.; Italian Society of Nephrology. Instructions and implementations for percutaneous renal biopsy. Guidelines for the therapy of glomerular nephropaties. G. Ital. Nefrol. 2003, 20 (Suppl. S24), S3–S47. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, K.D.; Madden, S.; Taylor, B.W.; Rees, L. Psychological and clinical effects of renal biopsy performed using sedation. Pediatr. Nephrol. 1996, 10, 693–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, C.; Kanagaratnam, R.; Coughlan, F.; Graf, N.; Hahn, D.; Durkan, A. Kidney biopsy adequacy and complications in children—Does technique matter? Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, A.; Ikeda Kurakawa, K.; Harita, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Yamaguchi, S.; Aso, S.; Ono, S.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kumazawa, R.; Michihata, N.; et al. Comparison of bleeding complications after pediatric kidney biopsy between intravenous sedation and general anesthesia: A nationwide cohort study. BMC Pediatr. 2023, 23, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelianova, D.; Prikis, M.; Morris, C.S.; Gibson, P.C.; Solomon, R.; Scriver, G.; Smith, Z.T.; Bhave, A.; Shields, J.; DeSarno, M.; et al. The evolution of performing a kidney biopsy: A single center experience comparing native and transplant kidney biopsies performed by interventional radiologists and nephrologists. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Chen, H. Comparison of complications between total intravenous anaesthesia and combined intravenous and inhalation anaesthesia after renal biopsy in children. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2024, 77, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitu, M.; Hicks, S.; Hedlund, L.; Slaven, J.E.; Rigby, M.R. Propofol-based procedural sedation with or without low-dose ketamine in children. J. Pediatr. Intensive Care 2016, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Das, S.; Chauhan, S.; Kiran, U.; Satapathy, S. Perioperative Anxiety and Stress in Children Undergoing Congenital Cardiac Surgery and Their Parents: Effect of Brief Intervention—A Randomized Control Trial. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2019, 33, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.L.; Baker, C.M. Pain in children: Comparison of assessment scales. Pediatr. Nurs. 1988, 14, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McMurtry, C.M.; Noel, M.; Chambers, C.T.; McGrath, P.J. Children’s fear during procedural pain: Preliminary investigation of the Children’s Fear Scale. Health Psychol. 2011, 30, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patients | n = 251 |
|---|---|
| Biopsies | n = 711 |
| Mean age of patients | 12 ± 5.8 years |
| Sex | Male 143 (57%), Female 108 (43%) |
| For-cause biopsy | n = 225 (31.6%) |
| Protocol biopsy | n = 486 (68.4%) |
| Technical difficulties during sampling | n = 150 (21.1%) |
| Length of the cortical part of the specimen | 1.6 cm (IQR 1.2–2.0) |
| Median number of glomeruli | 13 (IQR 7–20) |
| n = 711 | IV Sedation | Oral Sedation | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biopsies | n = 548 | n = 163 | |
| Mean age | 10.1 ± 5.0 years | 18 ± 2.3 years | <0.001 |
| For-cause biopsy | n = 172 (31.4%) | n = 53 (32.5%) | 0.91 |
| Protocol biopsy | n = 376 (68.6%) | n = 110 (67.5%) | 0.90 |
| Technical difficulties in sampling | n = 127 (23.2%) | n = 23 (14.1%) | <0.001 |
| Length of the cortical part of the specimen | 1.8 cm (IQR 1.2–2.0) | 1.5 cm (IQR 1.0–2.0) | <0.001 |
| Median number of glomeruli | 16 (IQR 8–16) | 8 (IQR 6–15) | <0.001 |
| IV Sedation | Oral Sedation | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
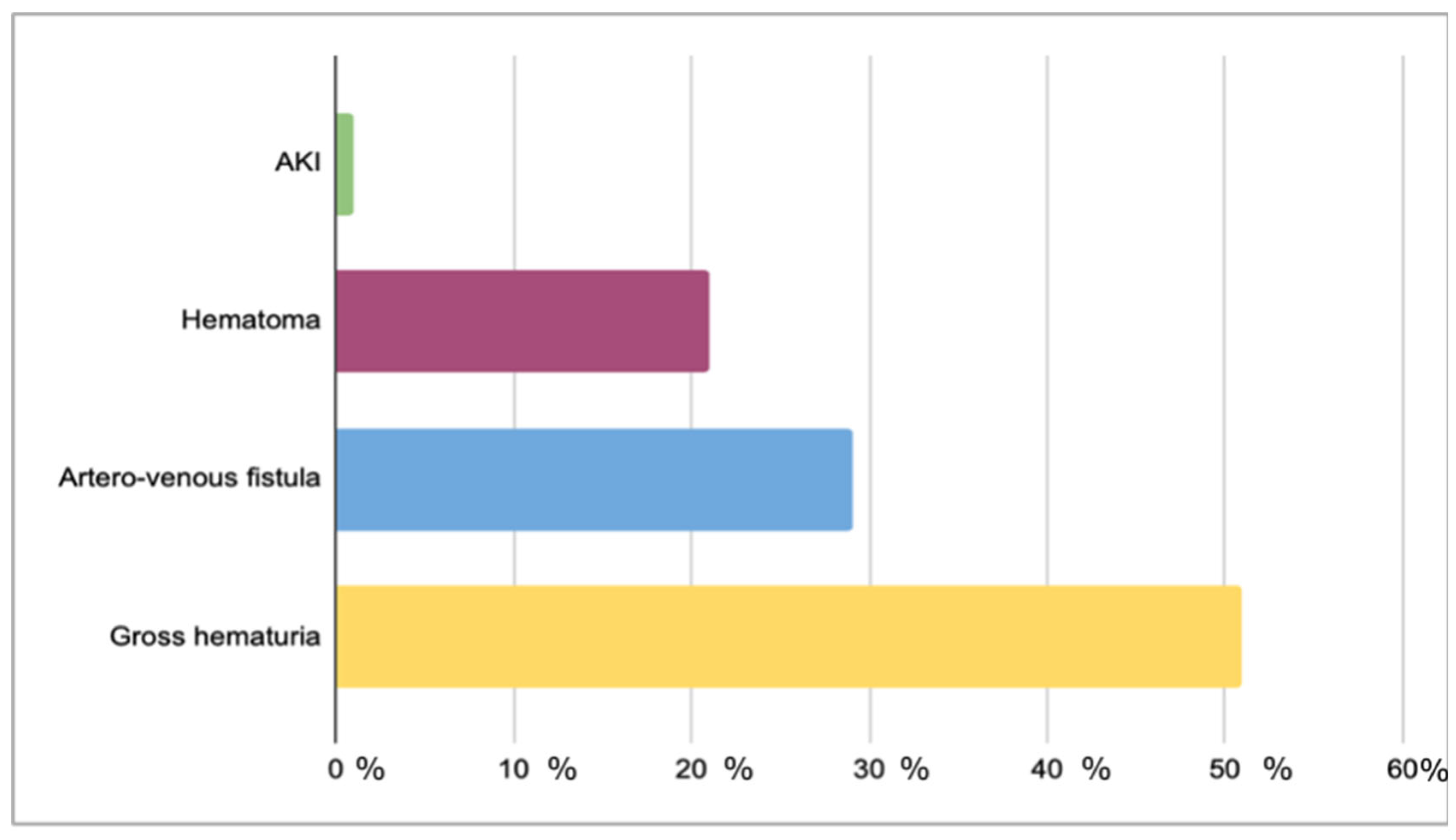
| Biopsy-related complications | n = 73 (13.3%) | n = 19 (11.6%) | 0.58 |
| Sedation-related complications | n = 27 (4.9%) | n = 1 (0.1%) | 0.01 |
| IV Sedation | Oral Sedation | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 108) | (N = 150) | ||
| Age | 16.8 years (IQR 15.9–18.0) | 18.8 years (IQR 17.2–20.4) | p = 0.013 |
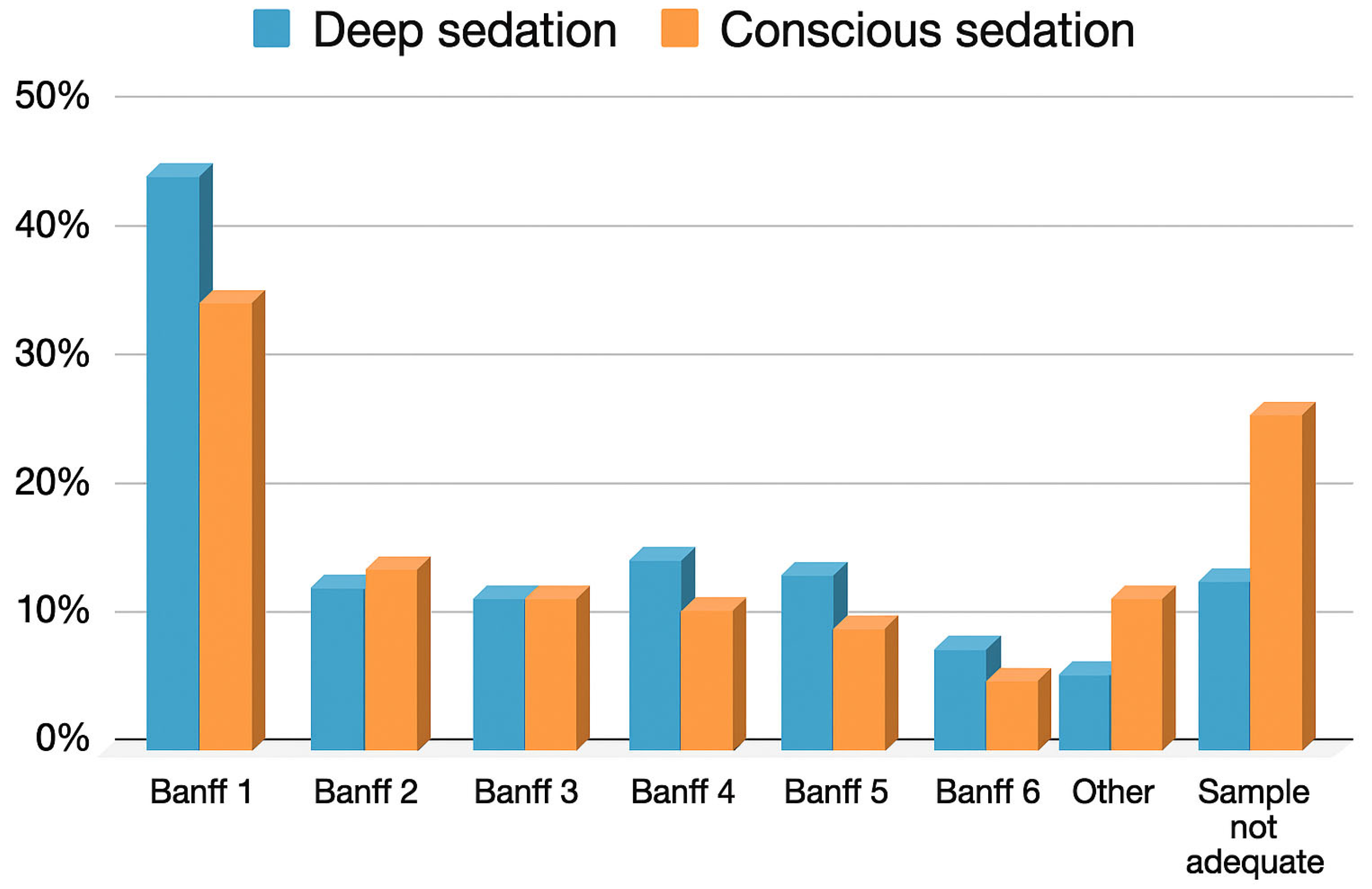
| Protocol biopsy | 64/108 (59%) | 102/150 (68%) | p = 0.152 |
| Technical difficulties | 26/108 (24%) | 22/150 (15%) | p = 0.062 |
| Length of the cortical part of the specimen | 2.0 cm (IQR 1.4–2.1) | 1.5 cm (IQR 1–2) | p < 0.01 |
| Median number of glomeruli | 12. (IQR 7–19) | 8.0 (IQR 5–14) | p < 0.01 |
| Biopsy-related complications | 14/108 (13%) | 0.1 19/150 (13%) | p = 0.942 |
| Diagnostic biopsy | 97/108 (89.8%) | 106/150 (70.6%) | p < 0.01 |
| Variable | Beta (β) | p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | −0.020 | 0.663 | Not significant |
| For cause-biopsy | −0.054 | 0.132 | Not significant |
| Technical difficulties | −0.087 | 0.017 | Significant, negative relationship |
| Length of the cortical part of the specimen | 0.208 | <0.001 | Significant, positive relationship |
| Biopsy-related complications | −0.057 | 0.140 | Not significant |
| Sedation | 0.152 | <0.001 | Significant, positive relationship |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Partigiani, N.B.; Zanin, A.; Martini, B.; Antoniello, B.; Negrisolo, S.; Sangermano, M.; Benini, F.; Benetti, E. Percutaneous Biopsy Under Deep Intravenous or Oral Conscious Sedation: Which Is the Best Option for Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207361
Partigiani NB, Zanin A, Martini B, Antoniello B, Negrisolo S, Sangermano M, Benini F, Benetti E. Percutaneous Biopsy Under Deep Intravenous or Oral Conscious Sedation: Which Is the Best Option for Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207361
Chicago/Turabian StylePartigiani, Nicola Bertazza, Anna Zanin, Beatrice Martini, Benedetta Antoniello, Susanna Negrisolo, Maria Sangermano, Franca Benini, and Elisa Benetti. 2025. "Percutaneous Biopsy Under Deep Intravenous or Oral Conscious Sedation: Which Is the Best Option for Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207361
APA StylePartigiani, N. B., Zanin, A., Martini, B., Antoniello, B., Negrisolo, S., Sangermano, M., Benini, F., & Benetti, E. (2025). Percutaneous Biopsy Under Deep Intravenous or Oral Conscious Sedation: Which Is the Best Option for Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207361






