Effective Conservative Management of Severe Scoliosis in a Girl with Prader–Willi Syndrome: A 20-Year Case Study Follow-Up
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PWS | Prader–Willi syndrome |
| SSE | Scoliosis-specific exercises |
| ATR | Angle of trunk rotation |
| TRACE | Trunk Aesthetic Clinical Evaluation |
References
- Butler, M.G.; Miller, J.L.; Forster, J.L. Prader-Willi Syndrome—Clinical Genetics, Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches: An Update. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2019, 15, 207–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.G.; Hanchett, J.M.; Thompson, T. Clinical Findings and Natural History of Prader-Willi Syndrome. In Management of Prader-Willi Syndrome; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 3–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Seo, S.W.; Koo, K.H.; Jin, D.K. The Musculoskeletal Manifestations of Prader-Willi Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2010, 30, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bosse, H.J.P.; Butler, M.G. Clinical Observations and Treatment Approaches for Scoliosis in Prader–Willi Syndrome. Genes 2020, 11, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Murakami, N.; Iida, T.; Ozeki, S.; Asano, S.; Nohara, Y.; Nagai, T. The Characteristics of Scoliosis in Prader–Willi Syndrome (PWS): Analysis of 58 Scoliosis Patients with PWS. J. Orthop. Sci. 2015, 20, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crinò, A.; Armando, M.; Crostelli, M.; Mazza, O.; Bruzzese, D.; Convertino, A.; Fintini, D.; Bocchini, S.; Ciccone, S.; Sartorio, A.; et al. High Prevalence of Scoliosis in a Large Cohort of Patients with Prader-Willi Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bosse, H.J.P. Role of Body Cast Application for Scoliosis Associated With Prader-Willi Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2021, 41, e321–e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odent, T.; Accadbled, F.; Koureas, G.; Cournot, M.; Moine, A.; Diene, G.; Molinas, C.; Pinto, G.; Tauber, M.; Gomes, B.; et al. Scoliosis in Patients with Prader-Willi Syndrome. Pediatrics 2008, 122, e499–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lind van Wijngaarden, R.F.A.; de Klerk, L.W.L.; Festen, D.A.M.; Hokken-Koelega, A.C.S. Scoliosis in Prader-Willi Syndrome: Prevalence, Effects of Age, Gender, Body Mass Index, Lean Body Mass and Genotype. Arch. Dis. Child. 2008, 93, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.G.; Manzardo, A.M.; Heinemann, J.; Loker, C.; Loker, J. Causes of Death in Prader-Willi Syndrome: Prader-Willi Syndrome Association (USA) 40-Year Mortality Survey. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proffitt, J.; Osann, K.; McManus, B.; Kimonis, V.E.; Heinemann, J.; Butler, M.G.; Stevenson, D.A.; Gold, J.-A. Contributing Factors of Mortality in Prader-Willi Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2019, 179, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.-L.; Urquhart, D.S. Respiratory Complications in Children with Prader Willi Syndrome. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2017, 22, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Hosoe, H.; Mizutani, M.; Shimizu, K. Scoliosis Associated with Prader-Willi Syndrome. Spine J. 2007, 7, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andaloro, A.A.; Bari, L.J.; Becchetti, F.; Formica, M.; Michelis, M.B.; Nasto, L.A. Scoliosis and Rare Diseases: Our Experience with the Prader–Willi Syndrome. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 2463–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greggi, T.; Martikos, K.; Lolli, F.; Bakaloudis, G.; Di Silvestre, M.; Cioni, A.; Bròdano, G.B.; Giacomini, S. Treatment of Scoliosis in Patients Affected with Prader-Willi Syndrome Using Various Techniques. Scoliosis 2010, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helenius, I.J. Standard and Magnetically Controlled Growing Rods for the Treatment of Early Onset Scoliosis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshavardhana, N.S.; Lonstein, J.E. Results of Bracing for Juvenile Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine Deform. 2018, 6, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnier, J.J.; Kienle, G.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; Sox, H.; Riley, D. The CARE Guidelines: Consensus-Based Clinical Case Reporting Guideline Development. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2013, 2, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, V.; Memari, A.H.; Saeedi, M.; Nadernejad, S.; Kordi, R. Brace-Related Stress and Quality-of-Life Parameters in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine Surg. Relat. Res. 2022, 6, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, S.; Aulisa, A.G.; Cerny, P.; de Mauroy, J.C.; McAviney, J.; Mills, A.; Donzelli, S.; Grivas, T.B.; Hresko, M.T.; Kotwicki, T.; et al. The Classification of Scoliosis Braces Developed by SOSORT with SRS, ISPO, and POSNA and Approved by ESPRM. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, S.; Donzelli, S.; Aulisa, A.G.; Czaprowski, D.; Schreiber, S.; de Mauroy, J.C.; Diers, H.; Grivas, T.B.; Knott, P.; Kotwicki, T.; et al. 2016 SOSORT Guidelines: Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Treatment of Idiopathic Scoliosis during Growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, S.; Donzelli, S.; Jurenaite, G.; Negrini, F.; Zaina, F. Efficacy of Bracing in Early Infantile Scoliosis: A 5-Year Prospective Cohort Shows That Idiopathic Respond Better than Secondary—2021 SOSORT Award Winner. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 3498–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côté, P.; Kreitz, B.G.; Cassidy, J.D.; Dzus, A.K.; Martel, J. A Study of the Diagnostic Accuracy and Reliability of the Scoliometer and Adam’s Forward Bend Test. Spine (Phila. PA 1976) 1998, 23, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrini, S.; Donzelli, S.; Di Felice, F.; Zaina, F.; Caronni, A. Construct Validity of the Trunk Aesthetic Clinical Evaluation (TRACE) in Young People with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 63, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, H.-R.; Goodall, D. Scoliosis in Patients with Prader Willi Syndrome—Comparisons of Conservative and Surgical Treatment. Scoliosis 2009, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Shi, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, P.; Yao, H.; Tan, X.; Yu, X.; Shao, Y.; Liu, X. Impact of Growth Hormone on Scoliosis. Pediatr. Discov. 2023, 1, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, S.; Donzelli, S.; Zaina, F.; Strube, P.; Lindemann, C.; Bahrke, M.; Brodt, S.; Sachse, A.; Reich, L.I.; Hoelzl, A.; et al. Improvement of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Primary Correction by Brace Design Optimization. Children 2022, 9, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S.; Kiaghadi, A.; Fallahian, N. Effective Factors on Brace Compliance in Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Literature Review. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2020, 15, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S.L. The Natural History of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2019, 39, S44–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
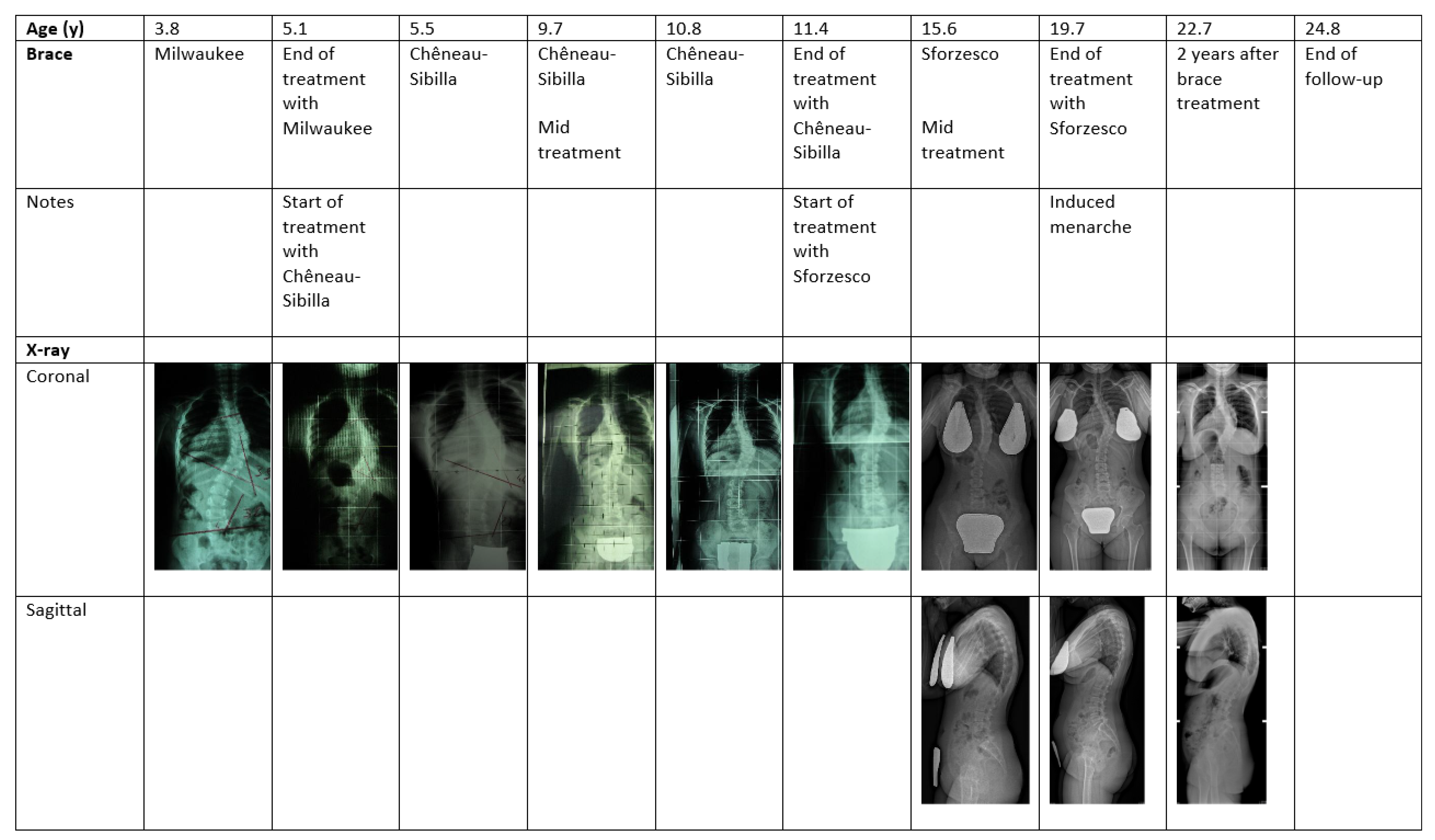
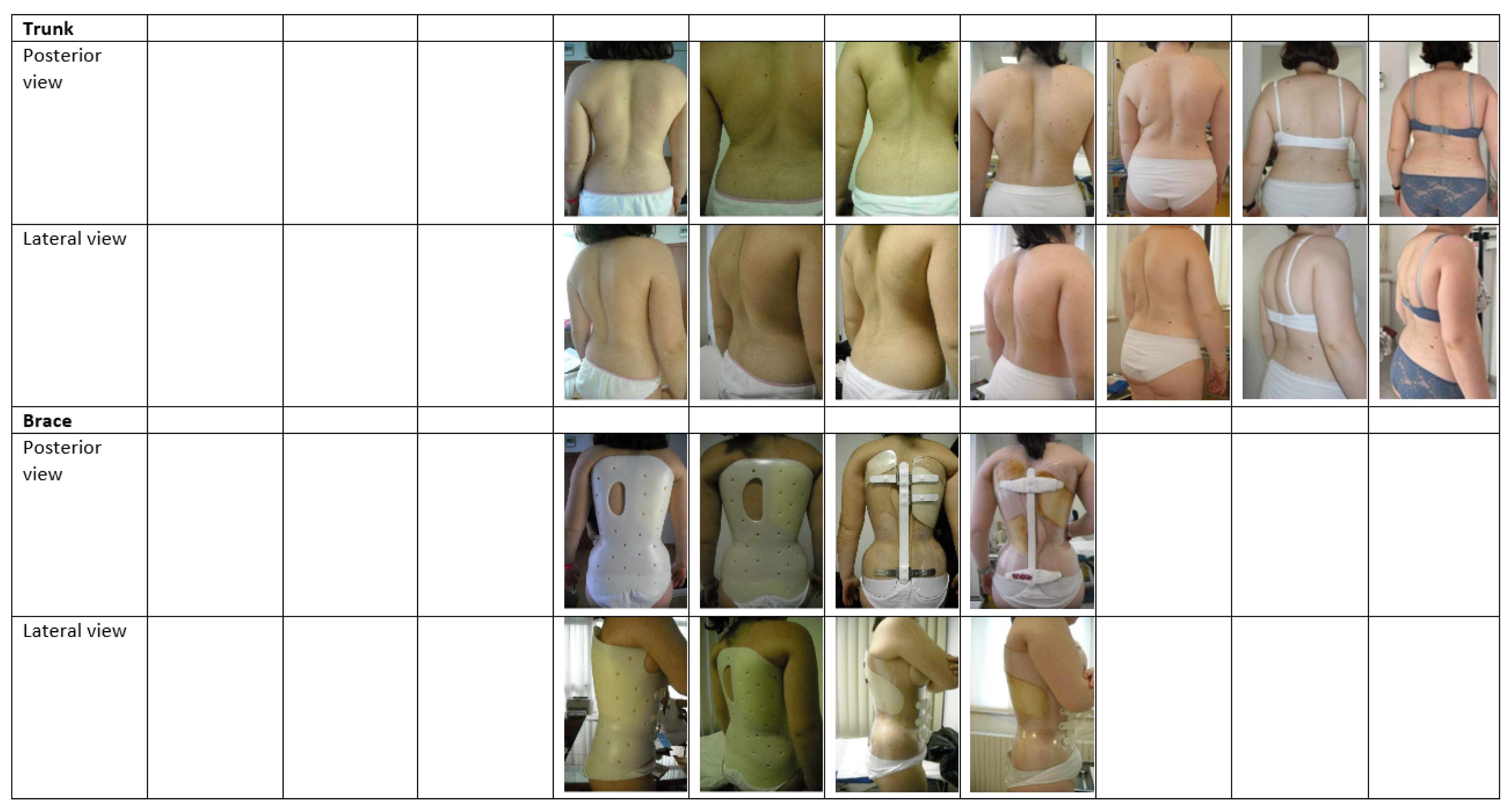
| Demographic Data | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Age (y) | 3.8 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.3 | 7.8 | 8.7 | 9.7 | 10.8 | 11.4 | 12.4 | 13.1 | 13.8 | 14.8 | 15.6 | 17.0 | 17.9 | 18.3 | 19.7 | 20.8 | 22.7 | 24.8 |
| Height (cm) | 102 | 106 | 110 | 121 | 125 | 132.5 | 137.5 | 140 | 144 | 148 | 150 | 150 | 151.5 | 150 | 151 | 150 | 150.5 | 151.5 | 151 | 151 | |
| Weight (kg) | 21 | 21 | 24 | 30 | 32.5 | 37.5 | 41.5 | 42.5 | 46.5 | 48 | 50 | 53.5 | 58 | 58.5 | 58.5 | 59.5 | 60.5 | 62.5 | 61 | 63.5 | |
| Treatment | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brace (hours per day) | MB (18) | CSB (23) | CSB (23) | CSB (23) | CSB (23) | CSB (22) | CSB (20) | CSB (20) | SB (22) | SB (20) | SB (21) | SB (20) | SB (18) | SB (16) | SB (14) | SB (12) | SB (8) | No | No | No | |
| SSE: Times per week (minutes) | 4 (45) | 2 (45) | 2 (45) | 2 (45) | 2 (45) | 2 (45) | 2 (45) | 3 (30) | 2 (30) | 2 (45) | 2 (45) | 2 (45) | 2 (45) | 2 (45) | |||||||
| Sport (times/week) | swim (2) | swim (2) | swim (2) | swim (2) | swim (2) | swim (2) | TR (2) | TR (2) | TR (2) | TR (5) | TR (2) | dance (1) | FB (2) | ||||||||
| Notes | GH therapy ongoing from 3.1 | Stop GH therapy | Induced menarche | ||||||||||||||||||
| X-ray | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Right thoracic curve (°) | 39 | 50 | 44 | 37 | 32 | 32 | 41 | 35 | 26 | 34 | 40 | 41 | 40 | 43 | 45 | 45 | 50 | 50 | 48 | 53 | |
| Left lumbar curve (°) | 42 | 34 | 27 | 19 | 20 | 22 | 26 | 23 | 18 | 18 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 25 | 25 | 19 | 24 | 24 | 22 | 27 | |
| Thoracic kyphotic (°) | 40 | 21 | 67 | 53 | 59 | 46 | 48 | 45 | 58 | ||||||||||||
| Lumbar lordosis (°) | 36 | 42 | 53 | 49 | 55 | 51 | 53 | 53 | 58 | ||||||||||||
| Sacral slope (°) | 38 | 42 | 28 | 31 | 39 | 41 | 38 | 32 | 25 | ||||||||||||
| Pelvic tilt (°) | 8 | 25 | 22 | 19 | 18 | 19 | 32 | 25 | |||||||||||||
| Pelvic incidence (°) | 50 | 53 | 53 | 58 | 59 | 57 | 51 | 58 | |||||||||||||
| Risser | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Clinical data | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Right thoracic ATR (°) | 15 | 9 | 12 | 12 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 12 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 14 | |
| Right thoracic Hump height (mm) | 18 | 9 | 15 | 17 | 12 | 13 | 18 | 11 | 11 | 14 | 12 | 11 | 13 | 13 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 23 | 25 | 25 | |
| TRACE ± SD (%) | 51.3 ±7.7 | 45.6 ±7.9 | 51.3 ±7.7 | 39.5 ±8.3 | 0±20.2 | 32.8 ±8.7 | 25.1 ±9.6 | 45.6 ±7.9 | 0±20.2 | 25.1 ±9.6 | 0±20.2 | 25.1 ±9.6 | 32.8 ±8.7 | 39.5 ±8.3 | 39.5 ±8.3 | 56.8 ±7.8 | 45.6 ±7.9 | 45.6 ±7.9 | 51.3 ±7.7 | 51.3 ±7.7 | |
| C7 plumbline (mm) | 25 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 35 | 25 | 25 | 45 | 15 | 50 | 30 | 35 | 25 | 10 | 40 | 40 | 35 | 45 | 40 | 30 | |
| L3 plumbline (mm) | 0 | 30 | 25 | 35 | 35 | 40 | 25 | 30 | 20 | 20 | 35 | 25 | 25 | 35 | 30 | 60 | 30 | 30 | 25 | 40 | |
| Sagittal Index (mm) | 45 | 70 | 55 | 65 | 70 | 65 | 50 | 75 | 35 | 70 | 65 | 60 | 50 | 45 | 70 | 100 | 65 | 75 | 65 | 70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malfitano, C.; Negrini, F.; Palloni, V.; Meggiolaro, M.; Brevi, E.; Benfatti, P.; Zaina, F.; Ferriero, G.; Negrini, S. Effective Conservative Management of Severe Scoliosis in a Girl with Prader–Willi Syndrome: A 20-Year Case Study Follow-Up. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7350. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207350
Malfitano C, Negrini F, Palloni V, Meggiolaro M, Brevi E, Benfatti P, Zaina F, Ferriero G, Negrini S. Effective Conservative Management of Severe Scoliosis in a Girl with Prader–Willi Syndrome: A 20-Year Case Study Follow-Up. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7350. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207350
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalfitano, Calogero, Francesco Negrini, Valentina Palloni, Marcello Meggiolaro, Elena Brevi, Piero Benfatti, Fabio Zaina, Giorgio Ferriero, and Stefano Negrini. 2025. "Effective Conservative Management of Severe Scoliosis in a Girl with Prader–Willi Syndrome: A 20-Year Case Study Follow-Up" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7350. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207350
APA StyleMalfitano, C., Negrini, F., Palloni, V., Meggiolaro, M., Brevi, E., Benfatti, P., Zaina, F., Ferriero, G., & Negrini, S. (2025). Effective Conservative Management of Severe Scoliosis in a Girl with Prader–Willi Syndrome: A 20-Year Case Study Follow-Up. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7350. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207350







