Cervical Epidural Abscess Secondary to a Post-Traumatic Hematoma, Successfully Treated with Adjunctive Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
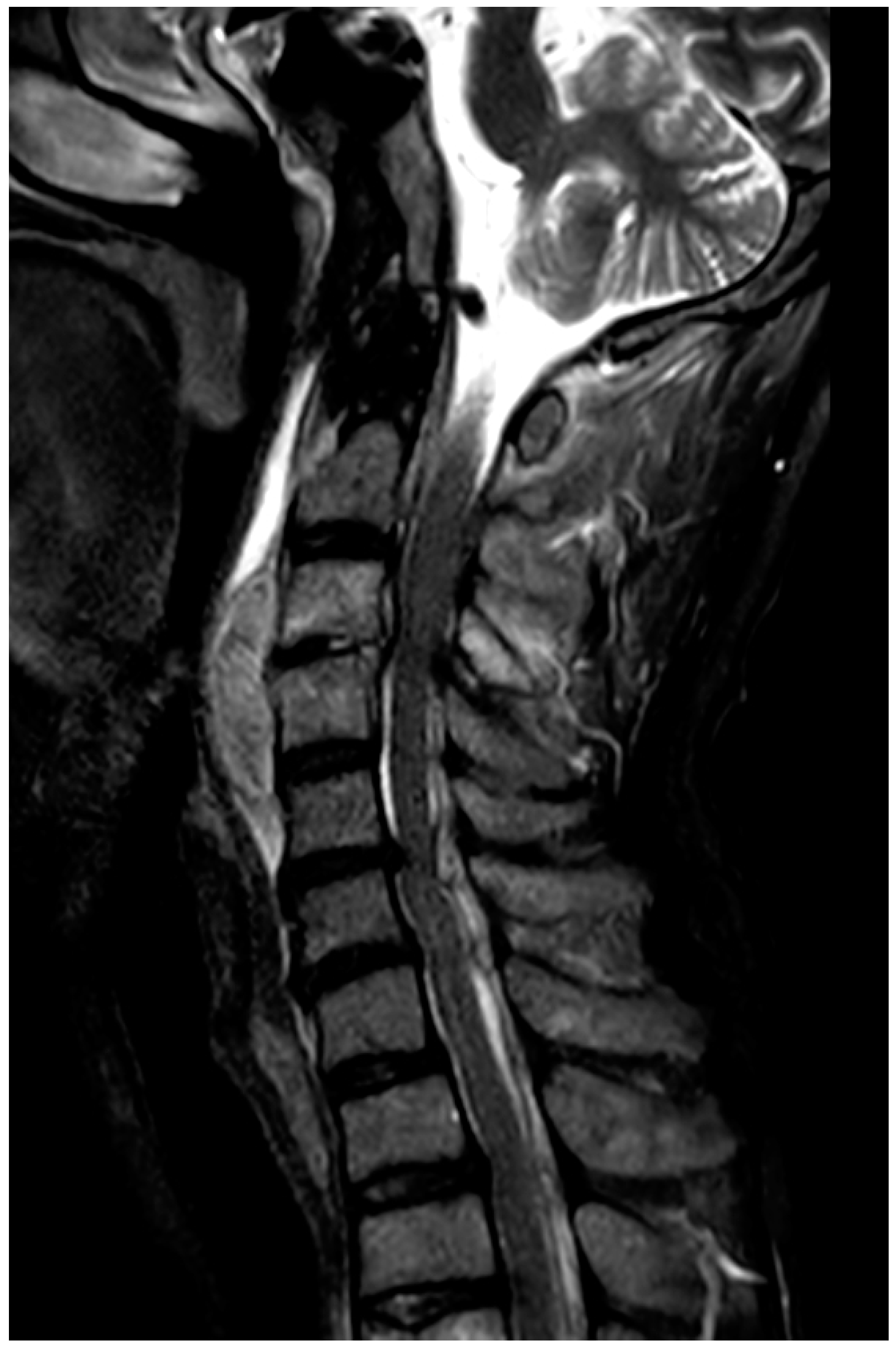
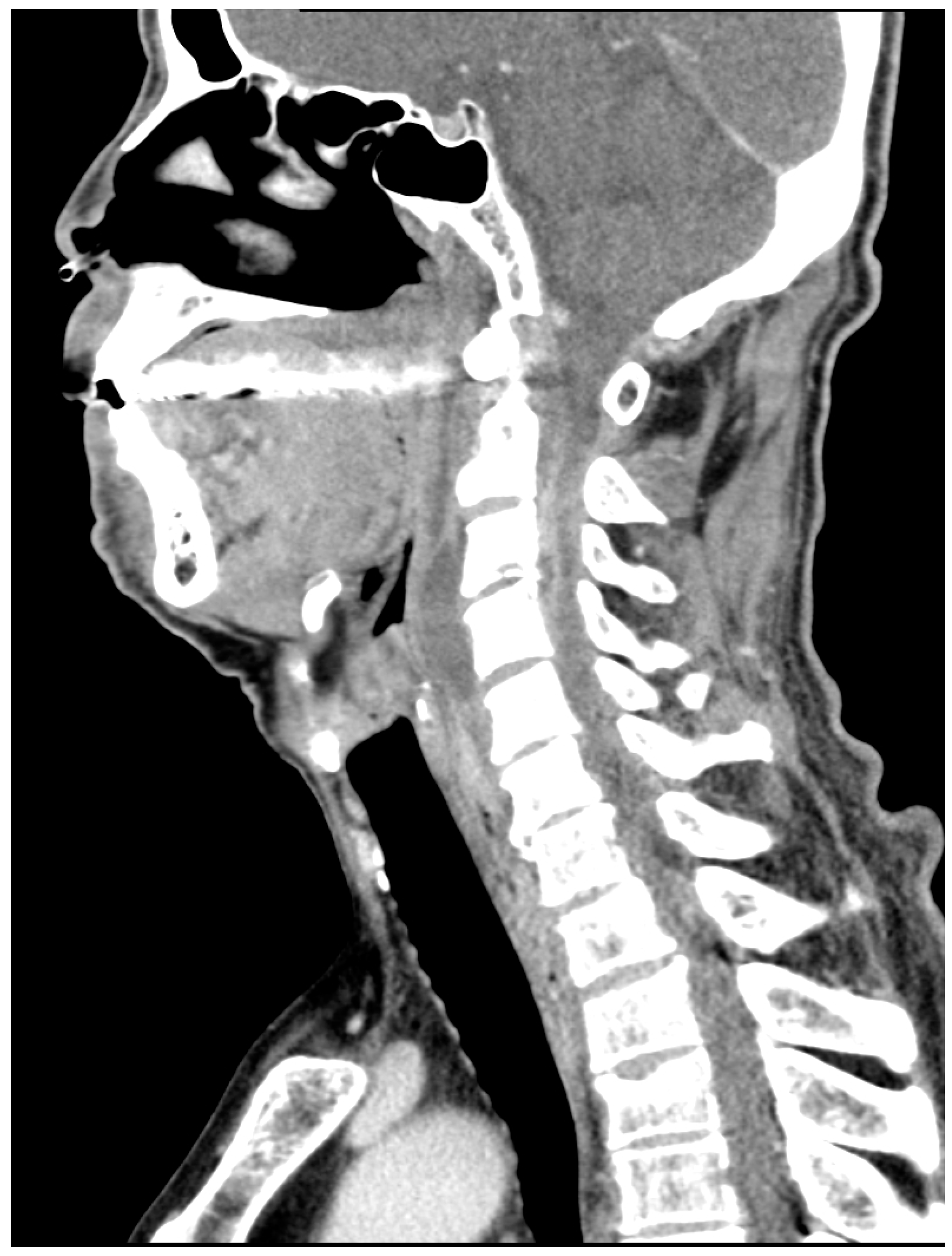
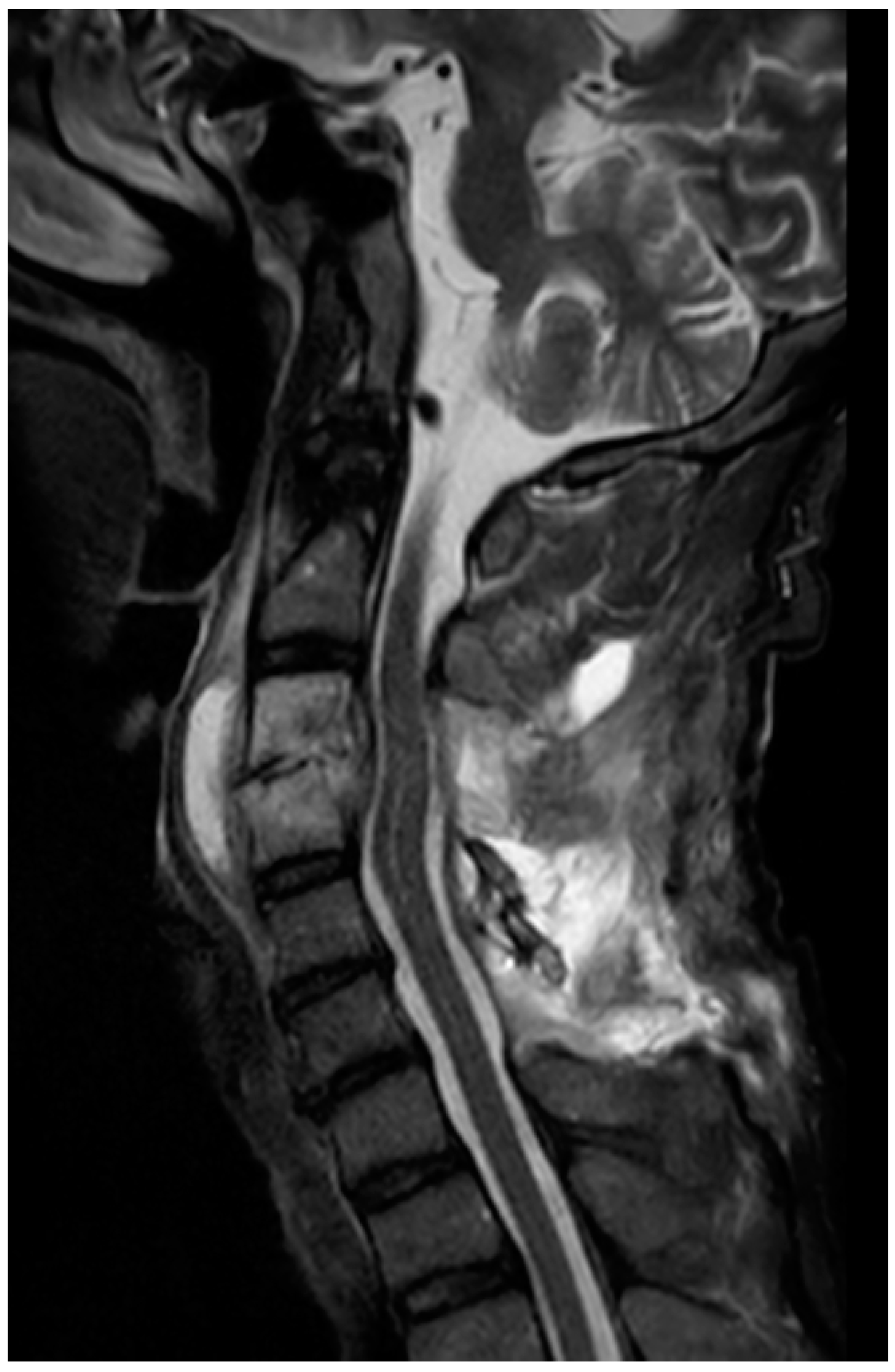
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEA | Spinal epidural abscess |
| HBOT | Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy |
References
- Darouiche, R.O. Spinal Epidural Abscess. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2012–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, D.; Nanda, A. Spinal Epidural Abscess: A Diagnostic Challenge. Am. Fam. Physician 2002, 65, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bodman, A.; Riordan, M.; Chin, L.S. Delayed Presentation of a Cervical Spinal Epidural Abscess of Dental Origin after a Fall in an Elderly Patient. Cureus 2016, 8, e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamasu, J.; Shizu, N.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Hirose, Y. Infected Epidural Hematoma of the Lumbar Spine Associated with Invasive Pneumococcal Disease. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2015, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, R.E. (Ed.) Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Indications, 14th ed.; Undersea & Hyperbaric Medical Society: Durham, NC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ramhmdani, S.; Bydon, A. Streptococcus intermedius: An Unusual Cause of Spinal Epidural Abscess. J. Spine Surg. 2017, 3, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Lu, W.; Huang, W.; Zhai, W.; Ling, Q. Extensive Spinal Epidural Abscess Due to Streptococcus intermedius: A Case Report Treated Conservatively and Literature Review. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1237007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.L.; Wang, H.K. Early decompressive surgery within 72 hours of admission maintains financial advantages for patients with spinal epidural abscess, as evidenced by a retrospective study involving 130 cases. Formos. J. Surg. 2024, 57, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohshi, K.; Abe, H.; Mizoguchi, Y.; Shimokobe, M. Successful Treatment of Cervical Spinal Epidural Abscess by Combined Hyperbaric Oxygenation. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2005, 72, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.C.; Tsou, H.K.; Kao, T.H.; Yang, M.Y.; Shen, C.C. Successful Treatment of Extended Epidural Abscess and Long Segment Osteomyelitis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Surg. Neurol. 2008, 69, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baechli, H.; Schmutz, J.; Mayr, J.M. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of an Epidural Abscess in the Posterior Fossa in an 8-Month-Old Infant. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2008, 44, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunshine, M.D.; Bindi, V.E.; Nguyen, B.L.; Doerr, V.; Boeno, F.P.; Chandran, V.; Smuder, A.J.; Fuller, D.D. Oxygen Therapy Attenuates Neuroinflammation after Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, C.; Liang, Z.; Xiong, F.; He, C.; Wei, Q. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Patients with Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2021, 34, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asamoto, S.; Sugiyama, H.; Doi, H.; Iida, M.; Nagao, T.; Matsumoto, K. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Acute Traumatic Cervical Spinal Cord Injury. Spinal Cord 2000, 38, 538–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iwashita, Y.; Yoshioka, N.; Murakami, K.; Mukoyama, K.; Sato, R.; Kodani, N.; Makiishi, T. Cervical Epidural Abscess Secondary to a Post-Traumatic Hematoma, Successfully Treated with Adjunctive Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: A Case Report. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7346. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207346
Iwashita Y, Yoshioka N, Murakami K, Mukoyama K, Sato R, Kodani N, Makiishi T. Cervical Epidural Abscess Secondary to a Post-Traumatic Hematoma, Successfully Treated with Adjunctive Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: A Case Report. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7346. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207346
Chicago/Turabian StyleIwashita, Yoshiaki, Naho Yoshioka, Kotaro Murakami, Ken Mukoyama, Rie Sato, Nobuhiro Kodani, and Tetsuya Makiishi. 2025. "Cervical Epidural Abscess Secondary to a Post-Traumatic Hematoma, Successfully Treated with Adjunctive Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: A Case Report" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7346. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207346
APA StyleIwashita, Y., Yoshioka, N., Murakami, K., Mukoyama, K., Sato, R., Kodani, N., & Makiishi, T. (2025). Cervical Epidural Abscess Secondary to a Post-Traumatic Hematoma, Successfully Treated with Adjunctive Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: A Case Report. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7346. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207346




