AI-Assisted 3D Intracardiac Echocardiography for Pulsed Field Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Novel Variable Loop Circular Catheter: A Multicenter Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Settings and Groups
2.2. The PFA VARIPULSE Platform
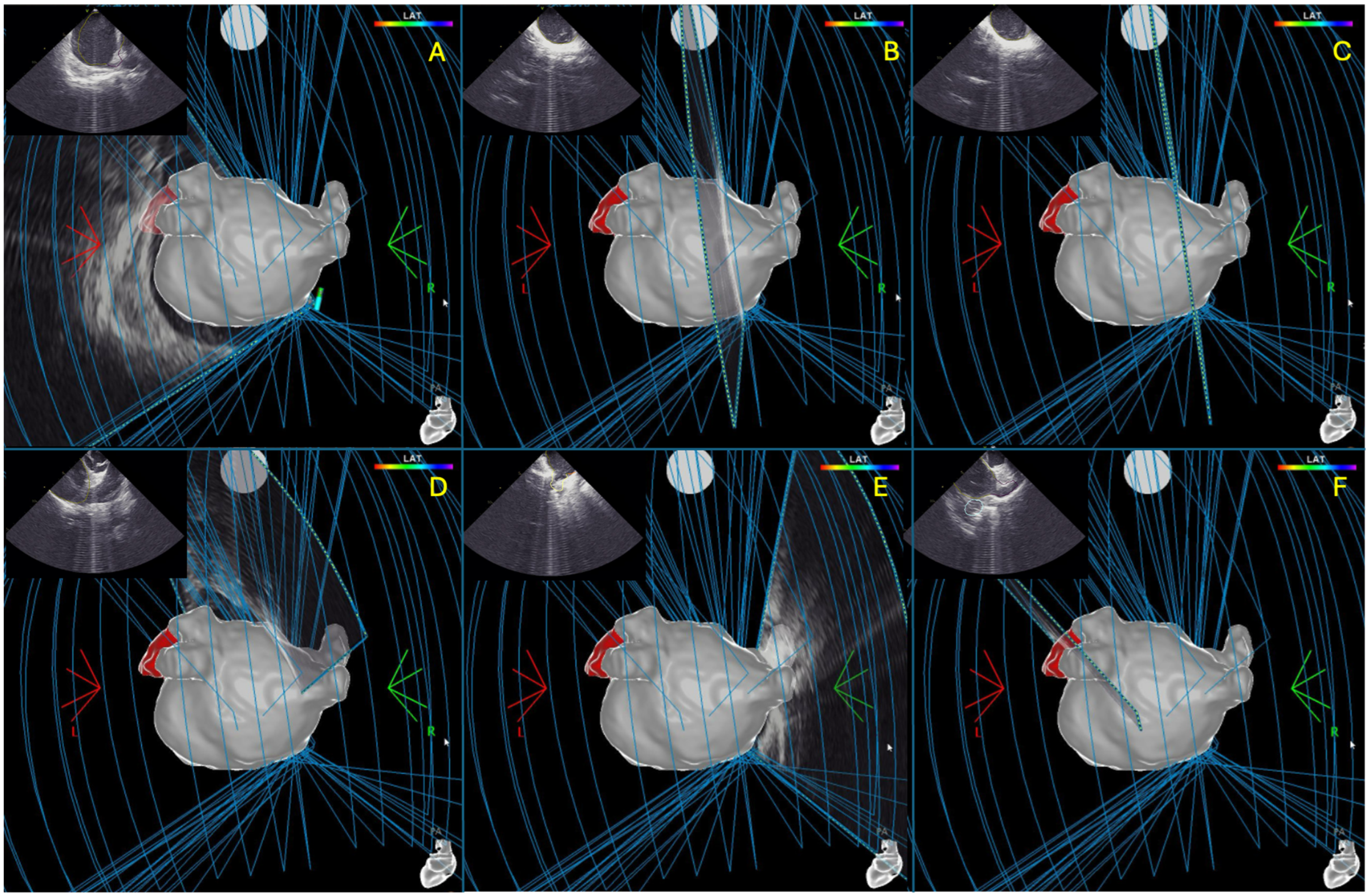
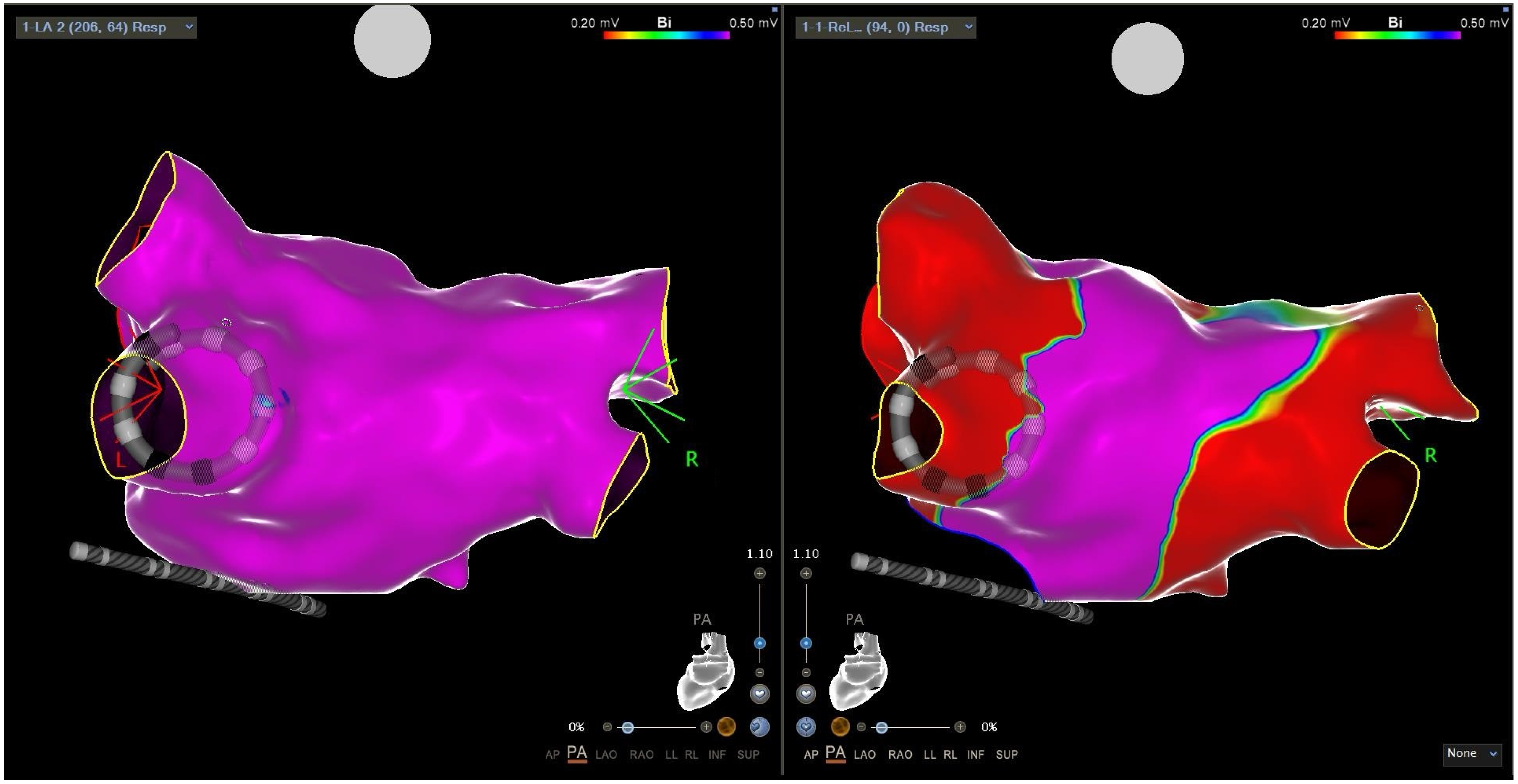
2.3. Intracardiac Echocardiography and CARTOSOUNDFAM MAP Module
2.4. Ablation Procedure
2.4.1. Mapping Phase in ICE-Guided Cohort
2.4.2. Mapping Phase in Non-ICE-Guided Cohort
2.4.3. Ablation Phase
2.5. Study Endpoints
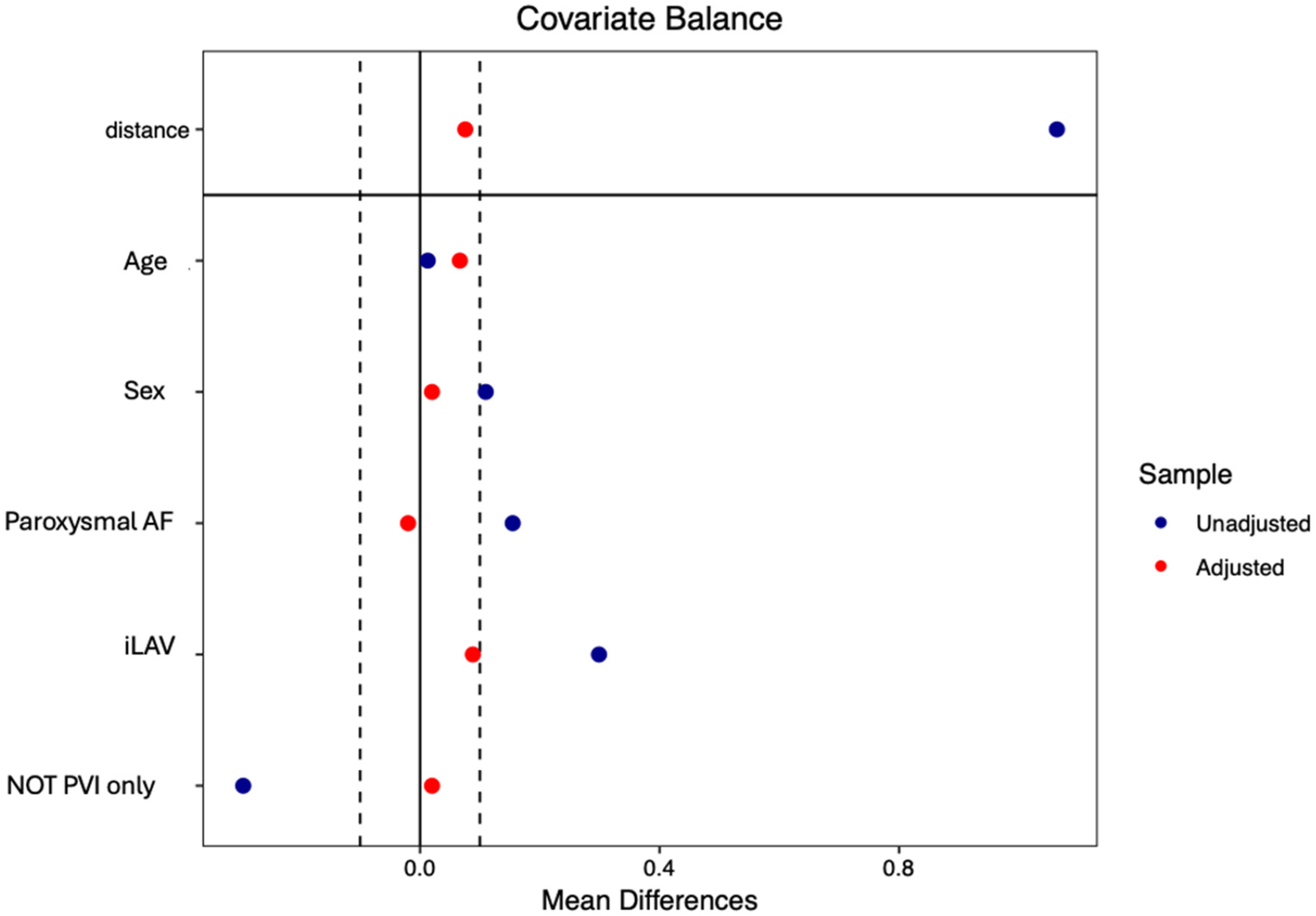
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population
3.2. Feasibility and Safety
3.3. Procedural Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
- The 3D reconstruction of the LA, performed using both the new AI-assisted ICE Module and electroanatomic mapping with high-density mapping catheters, was found to be feasible. Both techniques enable a clear anatomical reconstruction of the LA with short mapping times.
- Although both LA reconstruction techniques demonstrated short LA dwell time, these times were significantly shorter in ICE-guided cohort. Additionally, ICE-guided cohort was associated with approximately half the radiation exposure compared to non-ICE-guided cohort. These advantages were confirmed even after propensity matching, employed to account for potential heterogeneity in baseline clinical characteristics of the patients.
- In a large real-world cohort, despite these being the initial cases performed with this new technology, both techniques exhibited a high safety profile, with a major complication rate of 0% and a minor complication rate of less than 1% (single non-surgical vascular complication).
4.2. Procedure Efficiency and AI-Assisted ICE Module
4.3. Safety
4.4. Study Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oikawa, J.; Fukaya, H.; Kanaoda, K.; Niwano, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Iwanaga, Y.; Iwasaki, Y.; Nagashima, K.; Masuda, M.; Yamashita, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: A comparison of first-line vs second-line therapy. Heart Rhythm, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Tzeis, S.; Gerstenfeld, E.P.; Kalman, J.; Saad, E.B.; Shamloo, A.S.; Andrade, J.G.; Barbhaiya, C.R.; Baykaner, T.; Boveda, S.; Calkins, H.; et al. 2024 European Heart Rhythm Association/Heart Rhythm Society/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Europace 2024, 26, euae043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Asivatham, S.J.; Deneke, T.; Castellvi, Q. Neal RE Primer on pulsed electrical field ablation: Understanding the benefits and limitations. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2021, 14, e010086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanem, E.; Reddy, V.Y.; Schmidt, B.; Reichlin, T.; Neven, K.; Metzner, A.; Hansen, J.; Blaauw, Y.; Maury, P.; Arentz, T.; et al. Multinational survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety on the post-approval clinical use of pulsed field ablation (MANIFEST-PF). Europace 2022, 24, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.; Bordignon, S.; Neven, K.; Reichlin, T.; Blaauw, Y.; Hansen, J.; Adelino, R.; Ouss, A.; Futing, A.; Roten, L.; et al. EUropean realworld outcomes with pulsed field ablatiOn in patients with symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation: Lessons from the multicentre EU-PORIA registry. Europace 2023, 25, euad185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, H.; Reynolds, M.R.; Spector, P.; Sondhi, M.; Xu, Y.; Martin, A.; Williams, C.J.; Sledge, I. Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation with antiarrhythmic drugs or radiofrequency ablation: Two systematic literature reviews and meta-analyses. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, D.G.; Gomez, T.; De Potter, T. VARIPULSE: A step-by-step guide to pulmonary vein isolation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2024, 35, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Biase, L.; Zou, F.; Lin, A.N.; Grupposo, V.; Marazzato, J.; Tarantino, N.; Della Rocca, D.; Mohanty, S.; Natale, A.; Alhuarrat, M.A.D.; et al. Feasibility of 3D artificial intelligence algorithm integration with intracardiac echocardiography for LA imaging during Atrial Fibrillation catheter ablation. Europace 2023, 25, euad211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerström, F.; Drca, N.; Jensen-Urstad, M.; Braunschweig, F. Feasibility of a novel algorithm for automated reconstruction of the LA anatomy based on intracardiac echocardiography. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 45, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guangan, L.; Bo, S.; Wanglong, W.; Linxiao, Z.; Jing, C.; Wenxue, C.; Ruoxi, Z.; Feng, L. Safety and efficacy of intracardiac echocardiography-guided zero-fluoroscopy ablation in atrial fibrillation patients: A comparative study of high-power short-duration and low-power long-duration strategies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1510889. [Google Scholar]
- Saliba, W.; Thomas, J. Intracardiac echocardiography during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Europace 2008, 10, iii42–iii47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isabelle, C.G.; Michiel, R.; Karina, V.B.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.; De Potter, T.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414. [Google Scholar]
- Duytschaever, M.; De Potter, T.; Grimaldi, M.; Anic, A.; Vijgen, J.; Neuzil, P.; Van Herendael, H.; Verma, A.; Skanes, A.; Scherr, D.; et al. Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Using a Novel Variable-Loop Biphasic Pulsed Field Ablation Catheter Integrated With a 3-Dimensional Mapping System: 1-Year Outcomes of the Multicenter inspIRE Study. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2023, 16, e011780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek, Y.; Reddy, V.Y.; Calkins, H.; Mansour, M.; Wazni, O.; Di Biase, L.; Bahu, M.; Newton, D.; Liu, C.F.; Sauer, W.H.; et al. Pulsed Field Ablation to Treat Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: Safety and Effectiveness in the AdmIRE Pivotal Trial. Circulation 2024, 150, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnucci, P.; Volpato, G.; Cipolletta, L.; Parisi, Q.; Valeri, Y.; Campanelli, F.; D’Angelo, L.; Ciliberti, G.; Stronati, G.; Carboni, L.; et al. Posterior wall ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation: Very-high-power short-duration versus standard-power radiofrequency ablation. Heart Rhythm O2 2024, 5, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dello Russo, A.; Compagnucci, P.; Anselmino, M.; Schillaci, V.; Campanelli, F.; Ascione, M.R.; Volpato, G.; Cipolletta, L.; Parisi, Q.; Valeri, Y.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation: Results of a multicenter, real-world experience. Heart Rhythm 2024, 21, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, S.; Nagashima, K.; Watanabe, R. Workflow of the zero-fluoro pulsed field ablation. J. Arrhythm. 2024, 40, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.C.; Gibson, D.; Banker, R.; Doshi, S.K.; Gidney, B.; Gomez, T.; Berman, D.; Datta, K.; Govari, A.; Natale, A.; et al. In vivo porcine characterization ofatrial lesion safety and efficacy utilizing a circular pulsed-fieldablation catheter including assessment of collateral damage toadjacent tissue in supratherapeutic ablation applications. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 1480–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koruth, J.; Kuroki, K.; Iwasawa, J.; Enomoto, Y.; Viswanathan, R.; Brose, R.; Buck, E.D.; Speltz, M.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Reddy, V.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of pulsedfield ablation: Electrophysiological and histological assessment ofthoracic vein isolation. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e007781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Nagashima, K.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Byun, E.; Chen, Q.; Gomez, T. In vivo assessment of catheter-tissue contact using tissue proximity indication and its impact on lesion formation in pulsed field ablation. Heart Rhythm 2024, 22, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, B.; Verma, A.; Tzou, W.S.; Mattison, L.; Kos, B.; Miklavcic, D.; Onal, B.; Stewart, M.T.; Sigg, D.C. Effects of electrode-tissueproximity on cardiac lesion formation using pulsed field ablation. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2022, 15, e011110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, M.T.; Haines, D.E.; Verma, A.; Kirchhof, N.; Barka, N.; Grassl, E.; Howard, B. Intracardiac pulsed fieldablation: Proof of feasibility in a chronic porcine model. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.F. The Evolving Utility of Intracardiac Echocardiography in Cardiac Procedures. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2014, 6, 1055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| ICE-Guided Cohort (N = 64) | Non-ICE-Guided Cohort (N = 93) | p Value | Matched ICE-Guided Cohort (N = 50) | Matched Non-ICE-Guided Cohort (N = 50) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age—Median [IQR] | 62 [59.5–69] | 62 [58–67] | p = 0.453 | 62 [58–69] | 61.5 [55.3–61] | p = 0.347 |
| Male Sex—N (%) | 49 (77) | 61 (66) | p = 0.194 | 35 (70) | 34 (68) | p = 0.829 |
| Paroxysmal AF—N (%) | 45 (70) | 51 (55) | p = 0.074 | 38 (76) | 39 (78) | p = 0.812 |
| First therapy AF ablation—N (%) | 17 (27) | 14 (15) | p = 0.115 | 14 (28) | 8 (16) | p = 0.148 |
| Months AAD Therapy—Median [IQR] | 12 [6.5–15] | 13 [6–36] | p = 0.082 | 12 [6–36] | 16.5 [7–16] | p = 0.276 |
| Previous Ablation—N (%) | 9 (14) | 25 (27) | p = 0.085 | 8 (16) | 16 (32) | p = 0.061 |
| CHA2DSVA—Median [IQR] | 1 [1–2.25] | 1 [0–2] | p = 0.459 | 1 [0–2] | 1 [0–1] | p = 0.711 |
| Hypertension—N (%) | 36 (56) | 56 (60) | p = 0.740 | 26 (52) | 30 (60) | p = 0.420 |
| Dyslipidaemia—N (%) | 36 (65) | 41 (44) | p = 0.182 | 28 (56) | 21 (42) | p = 0.194 |
| Diabetes Mellitus—N (%) | 8 (13) | 6 (7) | p = 0.307 | 6 (12) | 3 (6) | p = 0.480 |
| EGFR < 45 mL/min/m2—N (%) | 1 (2) | 5 (5) | p = 0.423 | 1 (2) | 3 (6) | p = 0.208 |
| Smoke—N (%) | 7 (11) | 18 (19) | p = 0.232 | 7 (14) | 11 (22) | p = 0.299 |
| COPD—N (%) | 2 (3) | 6 (7) | p = 0.574 | 2 (4) | 2 (4) | p = 0.400 |
| Vascular Disease/CAD—N (%) | 8 (13) | 9 (10) | p = 0.766 | 7 (14) | 7 (14) | p = 1 |
| Osas—N (%) | 11 (17) | 14 (15) | p = 0.890 | 8 (16) | 6 (12) | p = 0.564 |
| Stroke/TIA—N (%) | 1 (2) | 3 (3) | p = 0.892 | 1 (2) | 2 (4) | p = 0.558 |
| Tachycardiomyiopathy—N (%) | 4 (6) | 1 (1) | p = 0.176 | 4 (8) | 1 (2) | p = 0.169 |
| BMI—Median [iqr] | 26.6 [25.4–28.4] | 27.9 [24.6–31] | p = 0.197 | 26 [25–28] | 25.5 [23.3–25] | p = 0.728 |
| LVEF %—Median [IQR] | 60 [55.7–61] | 60 [56–63] | p = 0.202 | 60 [55–60] | 60 [56–60] | p = 0.390 |
| Severe IM—N (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | p = 1 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | p = 1 |
| ILAV (ml/m2)—Mean (st) | 38.4 (12.7) | 34.6 (9.3) | p = 0.009 | 36 (11.6) | 34.8 (9.6) | p = 0.212 |
| TAPSE (mm)—Median [iqr] | 22 [20–24] | 22 [20–24] | p = 0.689 | 22 [20–24] | 22 [20–22] | p = 0.617 |
| Pre-Ablation AAD therapy - Beta-Blocker—N (%) - Flacainide/Propafenone—N (%) - Amiodarone—N (%) - NOAC—N (%) | 39 (61) 23 (36) 9 (14) 55 (86) | 42 (45) 37 (40) 23 (25) 80 (86) | p = 0.075 p = 0.748 p = 0.153 p = 0.826 | 27 (54) 21 (42) 5 (10) 41 (82) | 21 (42) 19 (38) 12 (24) 38 (76) | p = 0.230 p = 0.683 p = 0.064 p = 0.461 |
| ICE-Guided Cohort (N = 64) | Non-ICE-Guided Cohort (N = 93) | p Value | Matched ICE-Guided Cohort (N = 50) | Matched Non ICE-Guided Cohort (N = 50) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICE—N (%) | 64 (100) | 12 (13) | p < 0.001 | 50 (100) | 11 (22) | p < 0.001 |
| 3D Anatomical Mapping - Varipulse—N (%) - Pentaray—N (%) - Octaray—N (%) - ICE Soundfam—N (%) | 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 64 (100) | 93 (100) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) | p < 0.001 p = 1 p = 1 p < 0.001 | 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 50 (100) | 50 (100) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) | p < 0.001 p = 1 p = 1 p < 0.001 |
| Pre-ABL. Point—Median [IQR] | 401 [171–725] | 2100 [1221–2834] | p < 0.001 | 401 [190–725] | 1970 [1110–1901] | p < 0.001 |
| - Left Common PV—N (%) - Right Common PV—N (%) | 25 (39) 0 (0) | 7 (8) 2 (2) | p < 0.001 p = 0.147 | 21 (42) 0 (0) | 4 (8) 1 (2) | p < 0.001 p = 0.315 |
| PW Ablation—N (%) | 22 (34) | 39 (42) | p = 0.430 | 17 (33) | 10 (20) | p = 0.115 |
| Extra PV/PW Ablation - MI—N (%) - CTI—N (%) - AW—N (%) - SVC—N (%) | 3 (5) 5 (8) 3 (5) 0 (0) | 2 (2) 3 (3) 16 (17) 2 (2) | p = 0.374 p = 0.360 p = 0.018 p = 0.147 | 2 (4) 6 (12) 2 (4) 0 (0) | 2 (2) 2 (4) 7 (14) 2 (4) | p = 1 p = 0.140 p = 0.081 p = 0.153 |
| N° TOT Application—Median [IQR] | 66 [56–96] | 60 [54–87] | p = 0.136 | 64.5 [57–87.7] | 54 [51–54] | p = 0.004 |
| Complete PVI During Remap—N (%) | 62 (97) | 93 (100) | p = 0.165 | 52 (100) | 52 (100) | p = 1 |
| Mapping Time (Min)—Median [IQR] | 5 [4–5] | 8 [6–11] | p < 0.001 | 5 [4–5] | 7 [6–7] | p < 0.001 |
| Time in LA (Min)—Median [IQR] | 33.5 [26–35] | 38.5 [30–46] | p = 0.001 [171–725 | 30.5 [25.5–35] | 35 [28–35] | p = 0.035 |
| PROC. TIME (Min)—Median [IQR] | 65 [60–75] | 60 [60–75] | p = 0.535 | 65 [60–77] | 60 [60–60] | p = 0.424 |
| Fluoro Time (Min)—Median [IQR] | 7.5 [6–9] | 14 [9.2–18.3] | p < 0.001 | 7 [6–9] | 14 [13–14] | p < 0.001 |
| AF Recurrence During Hospitalizations—N (%) | 4 (6) | 4 (4) | p = 0.860 | 4 (8) | 2 (4) | p = 0.400 |
| Minor Complication—N (%) | 1 (2) | 2 (2) | p = 0.742 | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | p = 1 |
| Major Complication—N (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | p = 1 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | p = 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dello Russo, A.; Valeri, Y.; Ciconte, G.; Schiavone, M.; Compagnucci, P.; Di Monaco, A.; Riva, S.; Salerno, R.; Volpato, G.; Cipolletta, L.; et al. AI-Assisted 3D Intracardiac Echocardiography for Pulsed Field Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Novel Variable Loop Circular Catheter: A Multicenter Evaluation. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207249
Dello Russo A, Valeri Y, Ciconte G, Schiavone M, Compagnucci P, Di Monaco A, Riva S, Salerno R, Volpato G, Cipolletta L, et al. AI-Assisted 3D Intracardiac Echocardiography for Pulsed Field Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Novel Variable Loop Circular Catheter: A Multicenter Evaluation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207249
Chicago/Turabian StyleDello Russo, Antonio, Yari Valeri, Giuseppe Ciconte, Marco Schiavone, Paolo Compagnucci, Antonio Di Monaco, Stefania Riva, Raffaele Salerno, Giovanni Volpato, Laura Cipolletta, and et al. 2025. "AI-Assisted 3D Intracardiac Echocardiography for Pulsed Field Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Novel Variable Loop Circular Catheter: A Multicenter Evaluation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207249
APA StyleDello Russo, A., Valeri, Y., Ciconte, G., Schiavone, M., Compagnucci, P., Di Monaco, A., Riva, S., Salerno, R., Volpato, G., Cipolletta, L., Parisi, Q., Casella, M., Grimaldi, M., Tondo, C., & Pappone, C. (2025). AI-Assisted 3D Intracardiac Echocardiography for Pulsed Field Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Novel Variable Loop Circular Catheter: A Multicenter Evaluation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207249