Virtual Reality Training for Balance in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Quality Assessment and Risk of Bias
2.4. Evidence Certainity Assessment (GRADE)
2.5. Data Extraction and Synthesis
3. Statistical Analysis
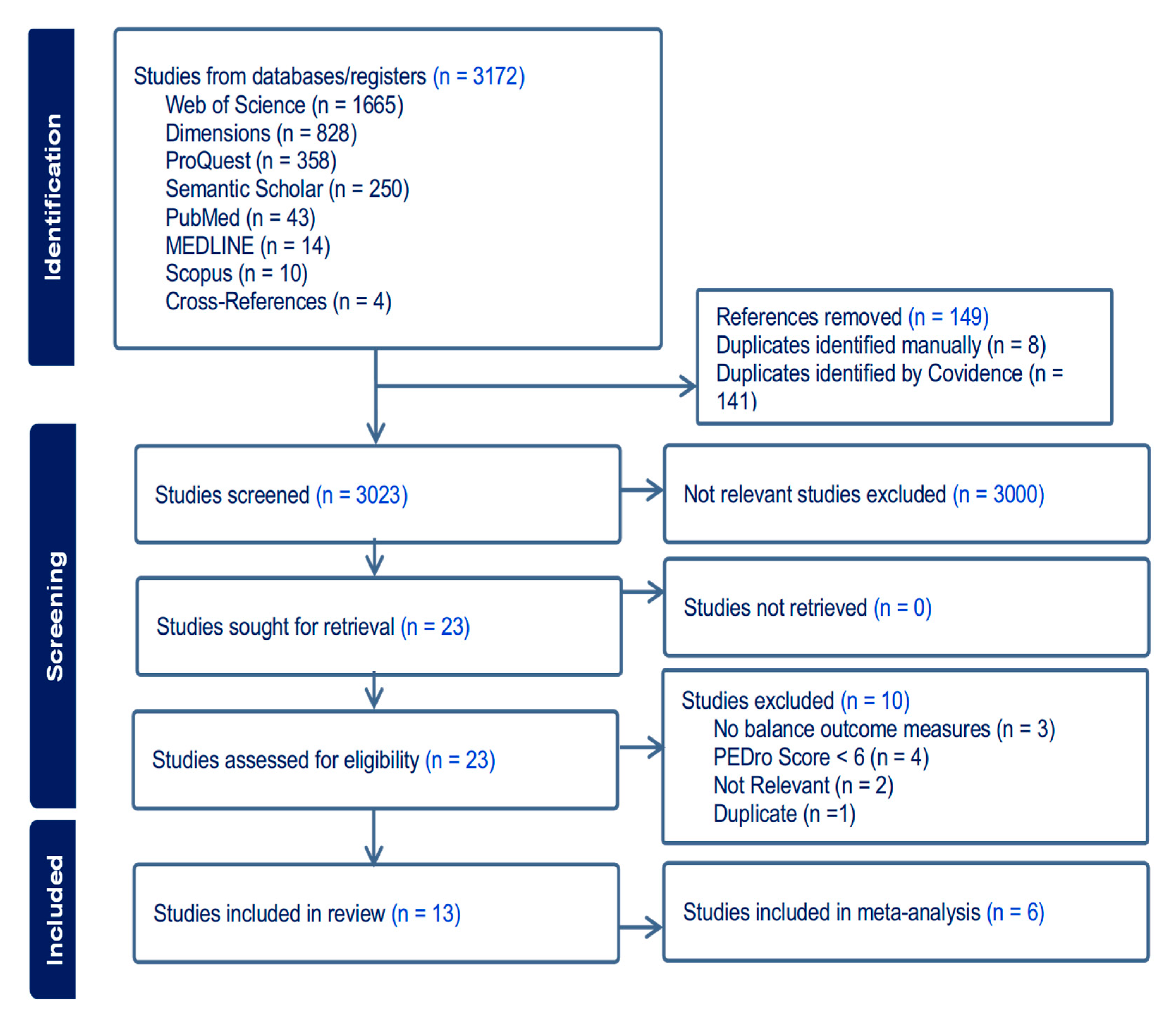
4. Results
4.1. Article Selection
4.2. Study Characteristics
4.3. Characteristics of Meta-Analysis Studies
4.4. Quality and Risk of Bias Assessment
| Author, Year | Country | Population Group (N): Subgroups (n), % Male | Age (Mean ± SD) | Environment (Level of Immersion) | Device (Type of Feedback) | Intervention | Dose | Balance Outcome Measure(s) | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdelraouf et al., 2020 [18] | Egypt | NSLBP in collegiate male athletes (50): EG (25) CG (25), 100% | EG: 20.9 ± 5.2 CG: 22.1 ± 2.6 | Lightweight headset with 2 games: (No Limits 2 Roller Coaster) and (Euro Truck 2 simulations). (high) | Oculus Rift DK2 (audiovisual) | EG: core stability exercises and virtual reality CG: core stability exercises | 6 weeks (2 sets × 20 repetitions with 15 s hold for each exercise, 5 days/week) | Dynamic Balance (SEBT) | EG was significantly better than CG in anterior (p = 0.031), posterolateral (p = 0.034), and posteromedial (p = 0.037) directions. |
| Chen et al., 2016 [30] | Korea | NSLBP (19): EG (10) CG (9), NIA | Overall: between 19 and 30 years EG: NIA CG: NIA | VR-based horse-riding simulator (moderate) | Indoor riding machine (Hongjin Leports) and 2D screen (visual, motion haptic) | EG: lumbar strengthening exercise (15 min) + horse riding simulator exercise (15 min). CG: lumbar strengthening exercise (30 min) | 4 weeks (12 sessions of 30 min) | Forward and backward LoS | Significant improvement in both groups (p < 0.05). No significant difference between the groups (p > 0.05) |
| Cikajlo et al., 2016 [20] | Slovenia | CLBP expanding into the lower limb (11): EG (6) CG (5), 27.3% | EG: 56.8 ± 12.4 CG: 56.8 ± 12.4 | Graphical computing environment with ball rolling on virtual path + weight (COG) shift (moderate) | Gamma trainer (PHU Technomex Sp., Gliwice, Poland (visual) | EG: balance training with Gamma device. CG: balance training with a wobble board | 2 weeks (5 consecutive days/week) | Postural perturbation response (overshoot and latency) Functional reaching Single Leg standing | No significant differences between both groups (p > 0.05). |
| Li et al., 2021 [34] | China | CNLBP (34): EG (11) CG (11) MCE (12), 26.47% | EG: 21.9 ± 2.4 CG: 25.4 ± 3.7 MCE: 23.8 ± 4.1 | VR-based Kinect games: Fruit Ninja game (moderate) | Kinect Xbox 360 systems (audiovisual) | EG: thermal magnetic therapy + VR training CG: thermal magnetic therapy MCE: Thermal magnetic therapy + MCE training | EG: 5 weeks (MT + 6 game sessions/day × 5 days/week) CG: two weeks (20 min × 5 days/week). MCE: 5 weeks (10 repetitions × 3 sessions of ultrasound-guided ADIM + 4-point kneeling 5 days/week). | Activation Time: APAs CPAs | EG: MF muscle activated later (p = 0.001) Significant decrease in TrA (p = 0.002) and TA (p = 0.007) muscle activity during 1st CPA. The IEMGs of TrA (p = 0.002) and TA (p = 0.007) during 1st CPA CG: No significant changes (p > 0.05). |
| Meinke et al., 2022 [32] | Switzerland | NSLBP (24): EG (13) CG (14), 37% | EG: 40.9 ± 15.2 CG:40.1 ± 12.4 | VR-based ValedoMotion Home system (moderate) | Wireless motion sensors Valedo Pro (Hocoma AG), 2D screen (Audiovisual) | EG: movements of the upper body or the pelvis CG: no intervention | 3 weeks (9 sessions of 20 min) | CoP during quiet standing: Medial-lateral displacement Global displacement Anterior–posterior velocity Medial-lateral velocity Global velocity | No changes in any outcomes in any group (p ≥ 0.25) |
| Monteiro-Junior et al., 2015 [29] | Brazil | CLBP (30): EG (16) CG (14), 0% | Overall: 68 ± 4 EG: NIA, CG: NIA | VR-based Nintendo Wii Fit program (moderate) | Nintendo Wii Motion Tracking System/2D screen (Wii balance board (audiovisual) | EG: lower limb strength exercises + core training + Wii-based exercise CG: lower limb strength exercises + core training. | 8 weeks (3×/week) EG: strengthening and core 10–15 s ×3; +30 min of virtual physical training CG: strengthening and core 10–15 s ×3 | Static balance (Wii balance board measuring (EA) of displacement of (CoP) (cm2) | No significant within or between groups differences in balance (p > 0.01) |
| Mueller et al., 2022 [36] | Germany | CLBP (13): cross-over trial: EG-CG (7) CG-EG (6), 38.5% | EG-CG: 2 males: 26.5 ± 4 years, five females: 50 ± 13 years CG-EG: 3 males: 41 ± 25 years, 3 females: 34 ± 11 years | VR-home based (Valedo Home; Hocoma, Switzerland) (moderate) avatar movement in 3 levels (moderate) | Valedo Home System + application-based software with tablet/smartphone (audiovisual) | EG-CG: trunk movements training ⟶ rest CG-EG: rest ⟶ trunk movements training | One session: 12 min intervention and the 12-min-rest-time | Proprioception (angle reproduction) | No significant change in angle reproduction between both groups (p > 0.05) |
| Park et al., 2013 [27] | South Korea | Work related CLBP (24): EG (NWE) (8) Second intervention group of LSE (8); CG (8), 100% | NWE: 44.1 ± 5.5 LSE: 43.4 ± 5.4 CG: 45.5 ± 5.3 | VR-based Nintendo Wii Sports games (moderate) | Nintendo Wii Motion Tracking System/2D screen (audiovisual) | NWE: Conventional + Nintendo Wii exercise program, including wakeboard, Frisbee dog, jet ski, and canoe games LSE: conventional + stabilization exercise CG: conventional only. | 8 weeks (each session: 50 min conventional (all groups) and 30 min exercise program (LSE and NWE) × 3 times/week) | Functional balance (One-legged stand test) | Only CG and LSE groups improved significantly (p < 0.05). |
| Suh et al., 2018 [37] | Korea | CLBP (20): EG (10) CG (10), 0% | EG: 72.3 ± 5.3 CG: 66.7 ± 3.1 | VR-based Nintendo Wii sports games (moderate) | Nintendo Wii Motion Tracking System/2D screen (audiovisual) | EG: Wii Sports Tennis, Bowling, and Golf CG: no exercises | 4 weeks (30 min × 3 times/week) | Berg balance scale | No significant difference between both groups (p > 0.05) |
| Tomruk et al., 2020 [28] | Turkey | CLBP (42): EG (21) CG (21), NIA | Median (IQR) EG: 46 (40.05–50.50) CG: 45 (44–48) | Computer-based stability training (moderate) | Biodex Balance System (visual) | EG: Postural stability, limits of stability, weight shift, and maze control training. CG: Traditional postural training exercises. | 12 weeks (2 times a week; 30 min/session). | Postural control (LoS and PS tests by Biodex Balance System) | Both groups improved significantly (p < 0.05), but EG showed a better effect than CG (p = 0.023). |
| Yalfani et al., 2022 [33] | Iran | CLBP (27): EG (13) CG (14), 0% | EG: 68 ± 2.9 CG: 67.1 ± 2.9 | Adrenaline station game center (high) | HTC Vive virtual reality system (audiovisual) | EG: Fisher, Boxing, Tennis, Football, Bowling, Beat Saber, Audio shield, and Skiing) VR training. CG: no intervention | EG: 8 weeks (3 sessions/week, with 30 min for each session) CG: Daily routine. | Fall Risk Index | EG improved better than CG (p = 0.001) |
| Yalfani et al., 2024 [35] | Iran | CLBP (24): EG (12) CG (12), 0% | EG: 68.3 ± 2.9 CG: 67.1 ± 2.9 | Adrenaline Station Game Center (high) | HTC-Vive virtual reality headset system (audiovisual) | EG: Training package 1: fish-catching, boxing, tennis, and football. Training package 2: boxing, skiing, bowling, Beat Saber, and Audio-shield. CG: No rehabilitation | EG: 8 weeks (3× 30 min training sessions/week) | Plantar pressure CoP fluctuations (anterior–posterior, medial-lateral, and sway velocity) -TUG | EG improved in all outcomes compared to CG (p ≤ 0.02) |
| Yelvar et al., 2017 [31] | Turkey | NSLBP (44, 36.4%): EG (22, 54.5%) CG (22, 18.2%). | EG: 46.3 ± 3.4 CG: 52.8 ± 11.5 | Video clip in natural walking down Ireland forest at a speed of 1.0 km/h (moderate) | iPod (Apple Inc., Apple Park, CA, USA) with video glasses (Wrap920, Vuzix Corporation) (visual) | EG: virtual walking + traditional physiotherapy CG: traditional physiotherapy | 5×/2 weeks | Single-Leg Balance Test TUG | No significant difference in single-leg balance between groups (p = 0.099). EG improved better than CG in TUG (p < 0.001). |
| Study | 1. Random Allocation | 2. Concealed Allocation | 3. Baseline Comparability | 4. Blinding Subjects | 5. Blinding Therapists | 6. Blinding Assessor | 7. Outcome Data > 85% | 8. Condition as Allocated or Intention to Treat | 9. Between-Group Results | 10. Variability Measures | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdelraouf, 2020 [18] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8/10 |
| Chen, 2016 [30] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6/10 |
| Cikajlo, 2016 [20] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6/10 |
| Li, 2021 [34] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8/10 |
| Meinke, 2022 [32] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9/10 |
| Monteiro-Junior, 2015 [29] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8/10 |
| Mueller, 2022 [36] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 9/10 |
| Park, 2013 [27] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6/10 |
| Suh, 2018 [37] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6/10 |
| Tomruk, 2020 [28] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8/10 |
| Yalfani, 2022 [33] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7/10 |
| Yalfani, 2024 [35] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8/10 |
| Yilmaz Yelvar, 2017 [31] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7/10 |
4.5. Proof of Efficacy
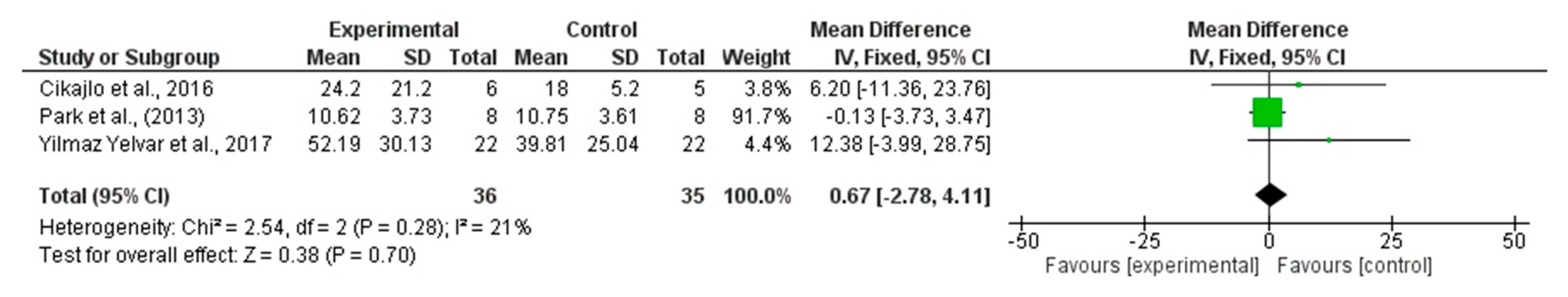
4.5.1. Single Leg Stance
4.5.2. CoP Mean Medio-Lateral Displacement
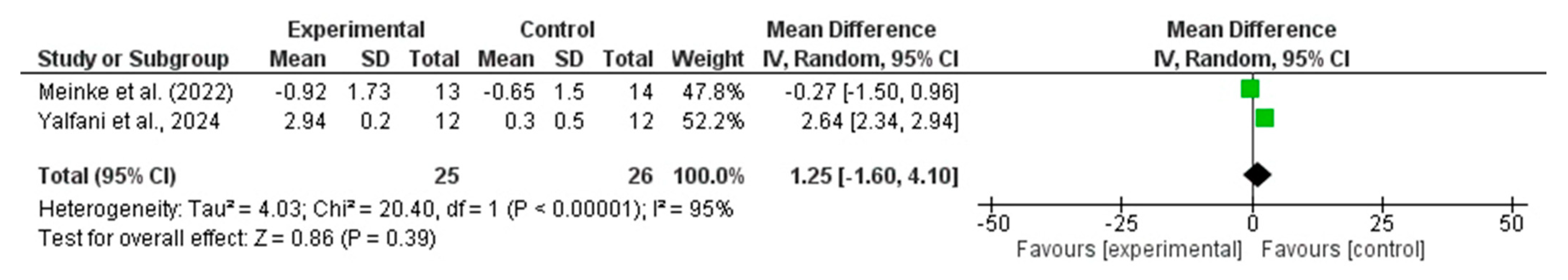
4.5.3. CoP Velocity
4.5.4. Timed Up and Go (TUG)
4.5.5. Dynamic Balance in Reaching
4.6. Evidence Grading for Key Outcomes
5. Discussion
6. Strengths and Limitations
7. Clinical Implication
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CLBP | Chronic Low Back Pain |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| TUG | Timed Up and Go (test) |
| SLS | Single Leg Stance (test) |
| CoP | Center of Pressure |
| LoS | Limits of Stability |
| SEBT | Star Excursion Balance Test |
| PEDro | Physiotherapy Evidence Database |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PROSPERO | International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews |
| EG | Experimental Group |
| CG | Control Group |
| NWE | Nintendo Wii Exercise |
| LSE | Lumbar Stabilization Exercise |
| MCE | Motor Control Exercise |
| ADIM | Abdominal Drawing-In Maneuver |
| AT | Activation Time |
| APA | Anticipatory Postural Adjustment |
| CPA | Compensatory Postural Adjustment |
| TrA | Transversus Abdominis |
| TA | Tibialis Anterior |
| MF | Multifidus |
| IEMG | Integral of Electromyography |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| MD | Mean Difference |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| I2 | I-squared statistic (for heterogeneity) |
| NIA | No Information Available |
| EA | Elliptical Area |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| MT | Magnetic Therapy |
| COG | Center of Gravity |
| IV | Inverse Variance |
References
- Freburger, J.K.; Holmes, G.M.; Agans, R.P.; Jackman, A.M.; Darter, J.D.; Wallace, A.S.; Castel, L.D.; Kalsbeek, W.D.; Carey, T.S. The rising prevalence of chronic low back pain. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 251–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvik, J.G.; Deyo, R.A. Diagnostic evaluation of low back pain with emphasis on imaging. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 137, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducas, J.; Hamel, A.; Vadez, G.; Descarreaux, M.; Abboud, J. Individuals with chronic low back pain show impaired adaptations of lumbar extensor muscle reflex amplitude during unexpected perturbations. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhile, P.; Patil, D.S.; Jaiswal, P.R. An integrated approach to chronic low back pain: Evaluating the impact of consecutive loop theraband training combined with proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation and conventional physiotherapy. Cureus 2024, 16, e58632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shousha, T.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Alayat, M. Effect of mechanical low back pain on postural balance and fall risk. Indian. J. Physiother. Occup. Ther. 2013, 7, 265. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, C.B.; Maher, C.G.; Pinto, R.Z.; Traeger, A.C.; Lin, C.C.; Chenot, J.F.; Van Tulder, M.; Koes, B.W. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-specific low back pain in primary care: An updated overview. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 2791–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.Z.; Fritz, J.M.; Silfies, S.P.; Schneider, M.J.; Beneciuk, J.M.; Lentz, T.A.; Gilliam, J.R.; Hendren, S.; Norman, K.S. Interventions for the management of acute and chronic low back pain: Revision 2021. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2021, 51, CPG1–CPG60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wippert, P.M.; Puschmann, A.K.; Driesslein, D.; Banzer, W.; Beck, H.; Schiltenwolf, M.; Schneider, C.; Mayer, F. Personalized treatment suggestions: The validity and applicability of the risk-prevention-index social in low back pain exercise treatments. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Cheng, X.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Ambrose Lo, W.L.; Yu, Q.; Wang, C. The associations between lumbar proprioception and postural control during and after calf vibration in people with and without chronic low back pain. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1329437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brea-Gomez, B.; Torres-Sanchez, I.; Ortiz-Rubio, A.; Calvache-Mateo, A.; Cabrera-Martos, I.; Lopez-Lopez, L.; Valenza, M.C. Virtual reality in the treatment of adults with chronic low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Kong, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, D.; Fu, C.; Wei, Q. Virtual reality-based training in chronic low back pain: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2024, 26, e45406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Almagro, D.; Achalandabaso-Ochoa, A.; Ibanez-Vera, A.J.; Gongora-Rodriguez, J.; Rodriguez-Huguet, M. Effectiveness of virtual reality therapy on balance and gait in the elderly: A systematic review. Healthcare 2024, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.H.; Park, J.K.; Koh, Y.H. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the effect of virtual reality-based rehabilitation for people with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano-Aguilera, A.; Bivia-Roig, G.; Cuenca-Martinez, F.; Suso-Marti, L.; Calatayud, J.; Blanco-Diaz, M.; Casana, J. Effectiveness of virtual reality on balance and risk of falls in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockx, K.; Bekkers, E.M.; Van den Bergh, V.; Ginis, P.; Rochester, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Mirelman, A.; Nieuwboer, A. Virtual reality for rehabilitation in parkinson’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 12, CD010760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirelman, A.; Maidan, I.; Herman, T.; Deutsch, J.E.; Giladi, N.; Hausdorff, J.M. Virtual reality for gait training: Can it induce motor learning to enhance complex walking and reduce fall risk in patients with Parkinson’s disease? J Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2011, 66, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molhemi, F.; Monjezi, S.; Mehravar, M.; Shaterzadeh-Yazdi, M.J.; Salehi, R.; Hesam, S.; Mohammadianinejad, E. Effects of virtual reality vs. conventional balance training on balance and falls in people with multiple sclerosis: A randomized controlled trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 102, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelraouf, O.R.; Abdel-aziem, A.A.; Selim, A.O.; Ali, O.I. Effects of core stability exercise combined with virtual reality in collegiate athletes with nonspecific low back pain: A randomized clinical trial. Bull. Fac. Phys. Ther. 2020, 25, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Hsu, W.L.; Kantha, P.; Chen, P.J.; Lai, D.M. Virtual reality skateboarding training for balance and functional performance in degenerative lumbar spine disease. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2024, 21, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cikajlo, I.; Bajuk, S. Response latencies to postural disturbances when using a virtual reality balance trainer or wobble board in persons with low back pain. Int. J. Child. Health Hum. Dev. 2016, 9, 323. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; McKenzie, J.E. Introduction to preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses 2020 and implications for research synthesis methodologists. Res. Synth. Methods 2022, 13, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, E.; Butikofer, L.; Armijo-Olivo, S.; Ha, C.; Egger, M. Construct validity of the physiotherapy evidence database (pedro) quality scale for randomized trials: Item response theory and factor analyses. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 11, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, A.M.; Pinheiro, M.B. Research note: Evaluating risk of bias in randomised controlled trials. J. Physiother. 2022, 68, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, M.H.; Mustafa, R.A.; Schünemann, H.J.; Sultan, S.; Santesso, N. Rating the certainty in evidence in the absence of a single estimate of effect. Evid. Based Med. 2017, 22, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, ED000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Ko, D.S. The effects of the Nintendo Wii exercise program on chronic work-related low back pain in industrial workers. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2013, 25, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomruk, M.S.; Kara, B.; Erbayraktar, R.S. The effect of computer-based training on postural control in patients with chronic low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. J. Basic Clin. Health Sci. 2020, 4, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro-Junior, R.S.; de Souza, C.P.; Lattari, E.; Rocha, N.B.; Mura, G.; Machado, S.; Da Silva, E.B. Wii-workouts on chronic pain, physical capabilities and mood of older women: A randomized controlled double-blind trial. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 14, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, I.-S.; Hwangbo, G. Effects of horse riding simulator on pain, oswestry disability index and balance in adults with nonspecific chronic low back pain. J. Korean Soc. Phys. Med. 2016, 11, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz Yelvar, G.D.; Cirak, Y.; Dalkilinc, M.; Parlak Demir, Y.; Guner, Z.; Boydak, A. Is physiotherapy integrated virtual walking effective on pain, function, and kinesiophobia in patients with non-specific low-back pain? Randomised controlled trial. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinke, A.; Peters, R.; Knols, R.H.; Swanenburg, J.; Karlen, W. Feedback on trunk movements from an electronic game to improve postural balance in people with nonspecific low back pain: Pilot randomized controlled trial. JMIR Serious Games 2022, 10, e31685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalfani, A.; Abedi, M.; Raeisi, Z. Effects of an 8-week virtual reality training program on pain, fall risk, and quality of life in elderly women with chronic low back pain: Double-blind randomized clinical trial. Games Health J. 2022, 11, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yu, Q.; Luo, H.; Liang, W.; Li, X.; Ge, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Wang, C. The effect of virtual reality training on anticipatory postural adjustments in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain: A preliminary study. Neural Plast. 2021, 2021, 9975862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalfani, A.; Abedi, M.; Raeisi, Z.; Asgarpour, A. The effects of virtual reality training on postural sway and physical function performance on older women with chronic low back pain: A double-blind randomized clinical trial. J. Back. Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2024, 37, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, J.; Niederer, D.; Tenberg, S.; Oberheim, L.; Moesner, A.; Mueller, S. Acute effects of game-based biofeedback training on trunk motion in chronic low back pain: A randomized cross-over pilot trial. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.R.; Lee, S.Y. A change in the size of the abdominal muscles and balance ability after virtual reality exercise in the elderly with chronic low back pain. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2018, 9, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Na, Y.; Tao, W.; Yu, L.; Jin, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Postural control deficits during static single-leg stance in chronic ankle instability: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Health 2024, 16, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sell, T.C.; Clark, N.C.; Wood, D.; Abt, J.P.; Lovalekar, M.; Lephart, S.M. Single-leg balance impairments persist in fully operational military special forces operators with a previous history of low back pain. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2014, 2, 2325967114532780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Xie, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Characteristics of trunk muscle activation and plantar pressure distribution in patients with chronic low back pain. Chin. J. Rehabil. Theory Pract. 2025, 1, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Marcos, D.; Bieler-Aeschlimann, M.; Serino, A. Virtual reality as a vehicle to empower motor-cognitive neurorehabilitation. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buraschi, R.; Pollet, J.; Villafane, J.H.; Piovanelli, B.; Negrini, S. Temporal and kinematic analyses of timed up and go test in chronic low back pain patients. Gait Posture 2022, 96, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, G.S.; Chhabra, D.; Mrityunjay, K. Efficacy of the star excursion balance test in detecting reach deficits in subjects with chronic low back pain. Physiother. Res. Int. 2015, 20, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachalathiti, R.; Sakulsriprasert, P.; Kingcha, P. Decreased functional capacity in individuals with chronic non-specific low back pain: A cross-sectional comparative study. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedian-Nasab, N.; Jaberi, A.; Shirazi, F.; Kavousipor, S. Effect of virtual reality exercises on balance and fall in elderly people with fall risk: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Phu, S.; Lord, S.R.; Okubo, Y. Effects of immersive virtual reality training on balance, gait and mobility in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gait Posture 2024, 110, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, A.S.; Raghunandan, A.; Tata, F.; Kibler, D.; Mcgeary, D. Virtual reality in the management of chronic low back pain: A scoping review. Front. Pain. Res. 2022, 3, 856935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souchet, A.D.; Lourdeaux, D.; Burkhardt, J.M.; Hancock, P.A. Design guidelines for limiting and eliminating virtual reality-induced symptoms and effects at work: A comprehensive, factor-oriented review. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1161932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horlings, C.G.; Carpenter, M.G.; Küng, U.M.; Honegger, F.; Wiederhold, B.; Allum, J.H. Influence of virtual reality on postural stability during movements of quiet stance. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 451, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldaner, N.; Sosnova, M.; Ziga, M.; Zeitlberger, A.M.; Bozinov, O.; Gautschi, O.P.; Weyerbrock, A.; Regli, L.; Stienen, M.N. External validation of the minimum clinically important difference in the timed-up-and-go test after surgery for lumbar degenerative disc disease. Spine 2022, 47, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautschi, O.P.; Stienen, M.N.; Corniola, M.V.; Joswig, H.; Schaller, K.; Hildebrandt, G.; Smoll, N.R. Assessment of the minimum clinically important difference in the timed up and go test after surgery for lumbar degenerative disc disease. Neurosurgery 2017, 80, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Outcome | Studies (n) | Effect (MD, 95% CI) | I2 | Certainty (GRADE) | Reasons for Downgrading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Leg Stance (s) | 3 RCTs (71) | +0.67 (−2.78 to 4.11) | 21% | Low | Imprecision (−1); Risk of Bias (−1) |
| CoP Medio-Lateral Displacement (mm) | 2 RCTs (51) | +1.42 (−1.43 to 4.27) | 96% | Very low | Inconsistency (−1/−2); Imprecision (−1); Risk of Bias (−1) |
| CoP Velocity (mm/s) | 2 RCTs (51) | +1.25 (−1.60 to 4.10) | 95% | Very low | Inconsistency (−1/−2); Imprecision (−1); Risk of Bias (−1) |
| Timed Up & Go (s) | 2 RCTs (68) | −2.29 (−2.91 to −1.66) | 0% | Moderate | Risk of Bias (−1) |
| Dynamic Balance in Reaching (cm) | 2 RCTs (61) | +7.80 (2.08 to 13.52) | 0% | Moderate | Risk of Bias (−1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlSadiq, A.I.; Abdulla, F.A.; Alshami, A.M. Virtual Reality Training for Balance in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207247
AlSadiq AI, Abdulla FA, Alshami AM. Virtual Reality Training for Balance in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207247
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlSadiq, Abrar I., Fuad A. Abdulla, and Ali M. Alshami. 2025. "Virtual Reality Training for Balance in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207247
APA StyleAlSadiq, A. I., Abdulla, F. A., & Alshami, A. M. (2025). Virtual Reality Training for Balance in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207247







