Antibody Secretion Capacity in CVID Patients: Immunoglobulin Isotypes and Antigen Specificities After T-Cell-Dependent In Vitro Stimulation †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Samples
2.2. Isolation of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
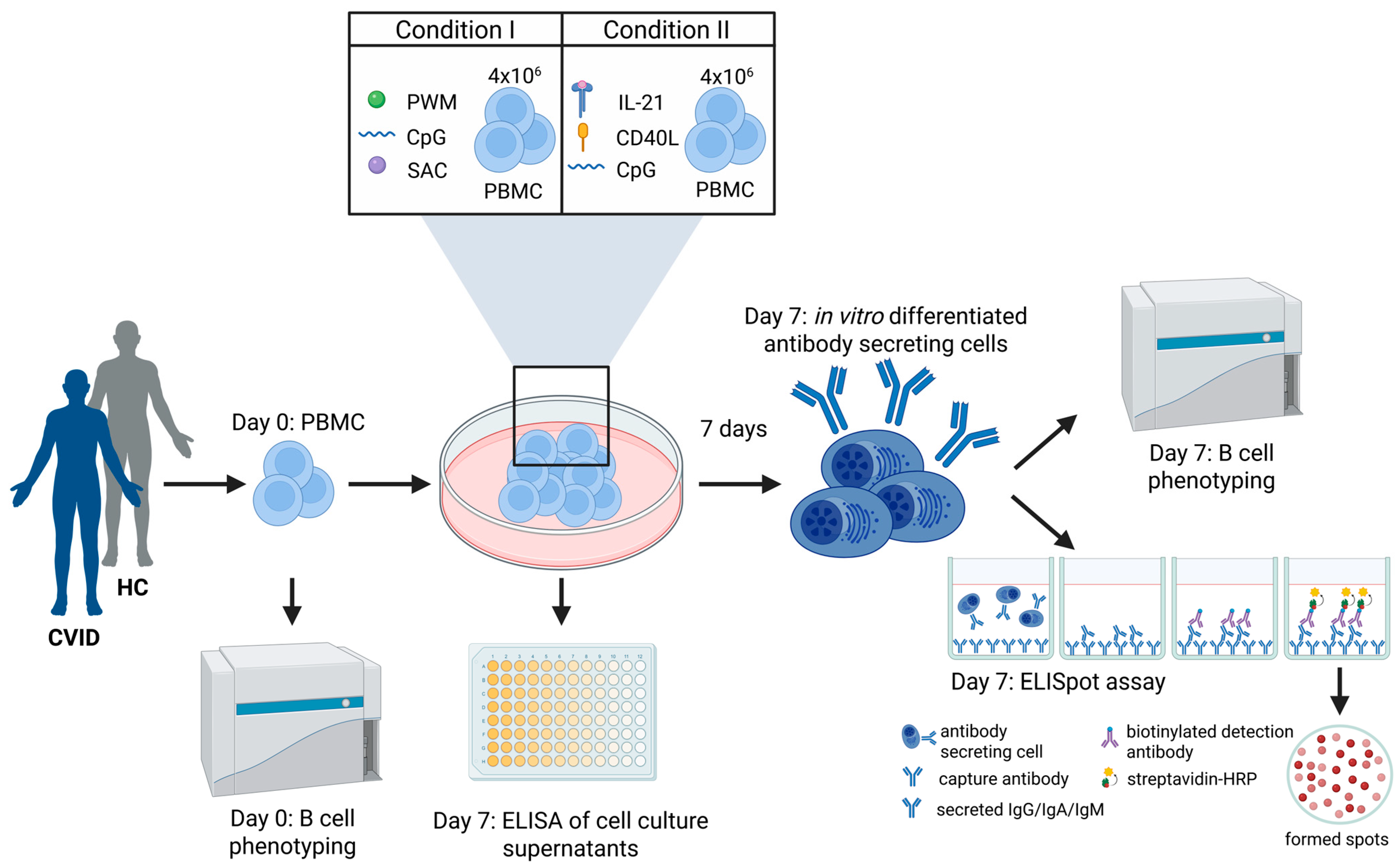
2.3. In Vitro PBMC Cell Culture and Stimulation
2.4. Memory B-Cell ELISpot Assay
2.5. Flow Cytometry B-Cell Phenotyping
2.6. Analysis of In Vitro Differentiation Capacity of Memory B-Cells into Antibody Secreting Cells
2.7. ELISA of Cell Culture Supernatants
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Cohort Characteristics
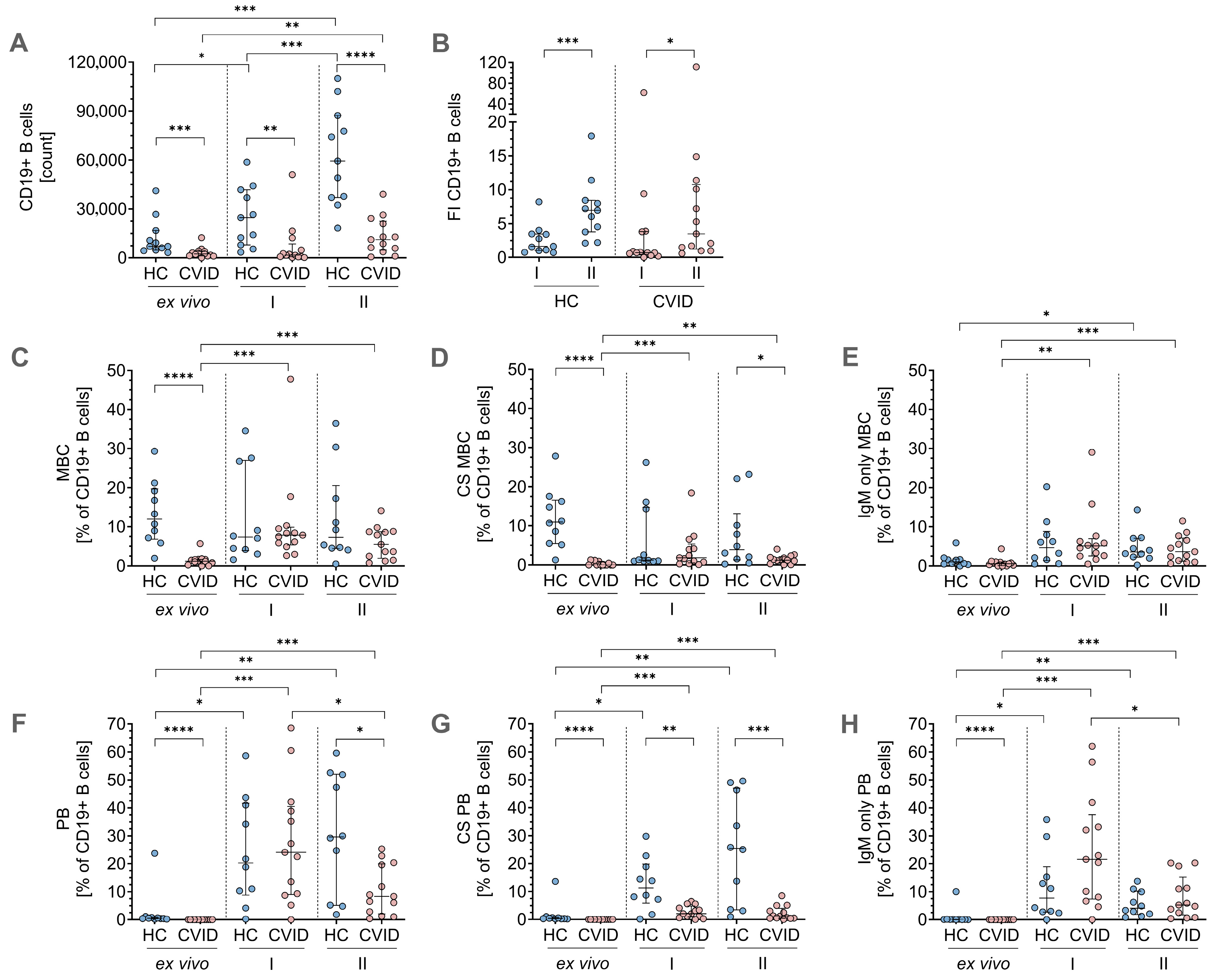
3.2. Phenotypic Flow Cytometry Data for B-Cell Differentiation
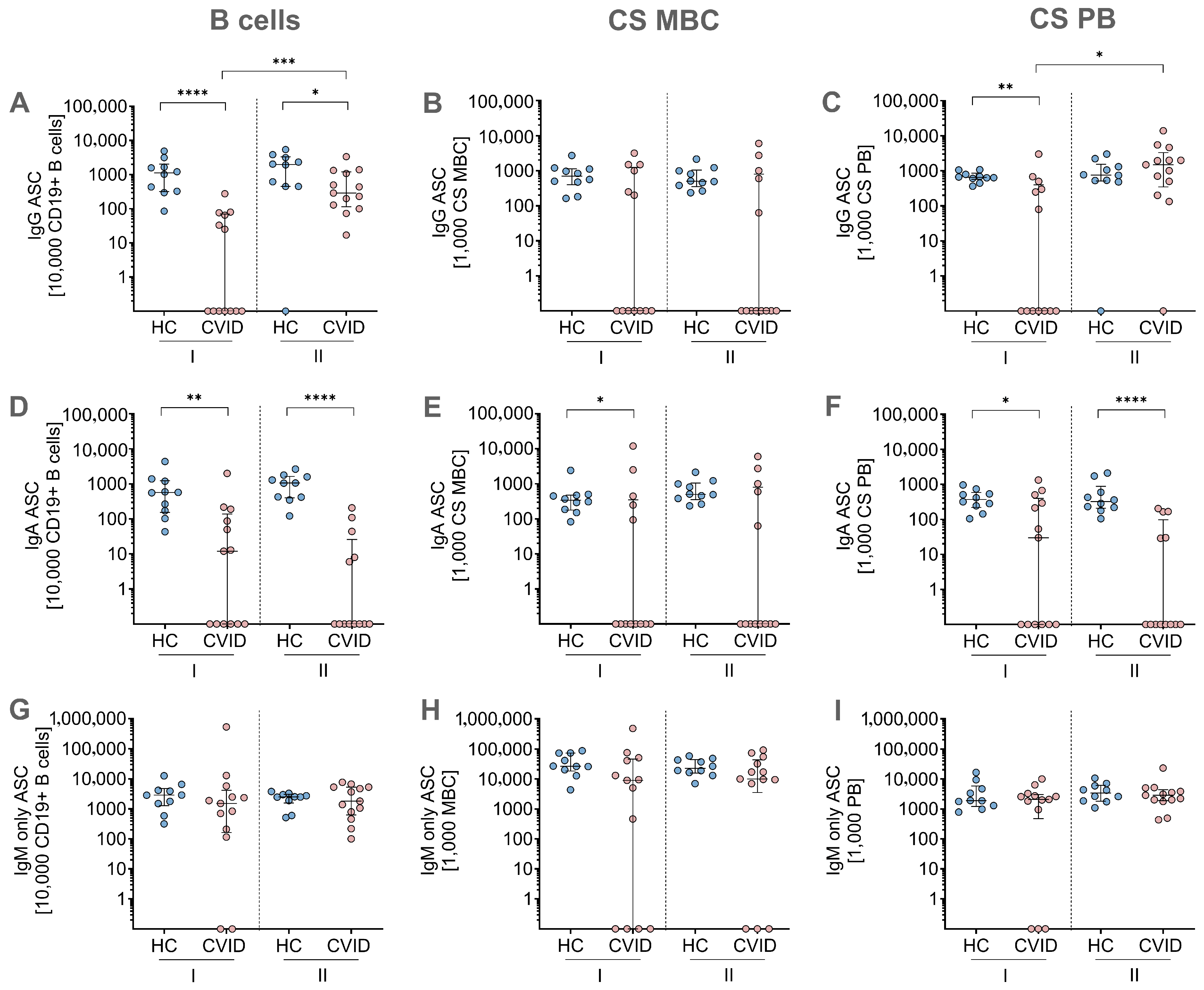
3.3. MBC ELISpot Assay: Immunoglobulin Secretion Capacity After In Vitro Stimulation and Differentiation
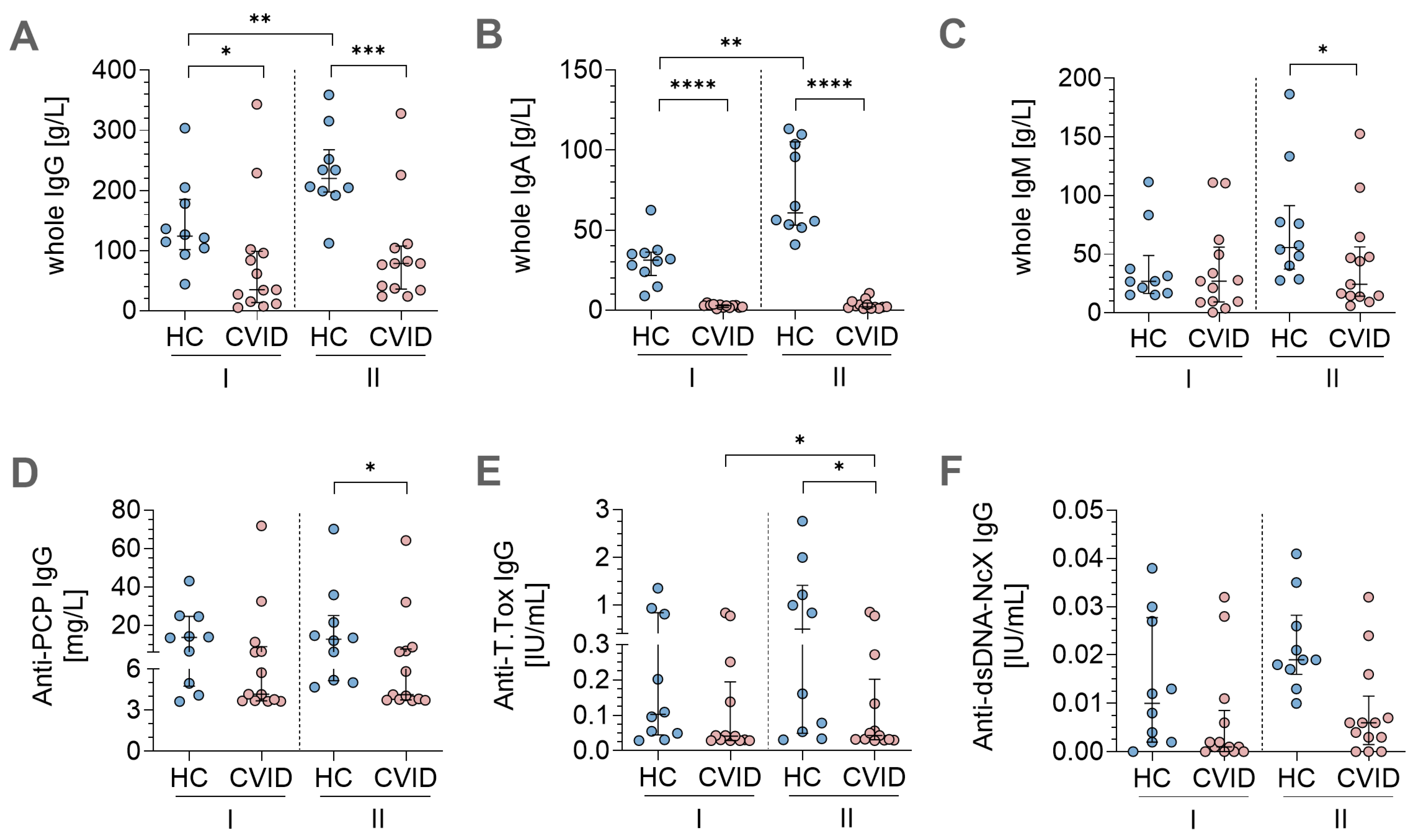
3.4. In Vitro Stimulation Protocols Induced Antigen-Specific Immunoglobulin Secretion
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEC | 3-Amino-9-ethyl-carbazole |
| AID | Activation-induced cytidine deaminase |
| ASC | Antibody-secreting cell |
| BCR | B-cell receptor |
| BLIMP-1 | B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1 |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CD40L | CD40 ligand |
| CPG | Class B CpG oligonucleotide-stimulatory human TLR9 ligand |
| CS | Class-switched |
| CSR | Class-switch recombination |
| CVID | Common variable immunodeficiency disorder |
| DMF | Dimethylformamide |
| dsDNA | Double-stranded desoxyribonucleic acid |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay |
| ELISpot | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot |
| ESID | European Society for Immunodeficiencies |
| FACS | Fluorescence activated cell sorting |
| FCS | Fetal calf serum |
| GC | Germinal center |
| GCP | Good clinical practice |
| GLILD | Granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease |
| HC | Healthy control |
| IEI | Inborn errors of immunity |
| IL-21 | Interleukin 21 |
| ITP | Immune thrombocytopenia |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| MBC | Memory B-cell |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| ON | Overnight |
| PB | Plasmablast |
| PBMC | Peripheral blood mononuclear cell |
| PCP | Pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide |
| PRDM1 | PR domain zinc finger protein 1 |
| PWM | Pokweed mitogen |
| Rec. | Recurrent |
| RT | Room temperature |
| SAC | Staphylococcus aureus Cowan |
| SHM | Somatic hypermutation |
| T.Tox | Tetanus toxoid |
| TLR9 | Toll-like receptor 9 |
| WES | Whole exome sequencing |
| β-ME | β-Mercaptoethanol |
References
- Lee, E.Y.; Betschel, S.; Grunebaum, E. Monitoring patients with uncomplicated common variable immunodeficiency: A systematic review. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2022, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Role of B cells in common variable immune deficiency. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 5, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangye, S.G.; Al-Herz, W.; Bousfiha, A.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Franco, J.L.; Holland, S.M.; Klein, C.; Morio, T.; Oksenhendler, E.; Picard, C.; et al. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: 2022 Update on the Classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 1473–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirdag, Y.Y.; Gupta, S. Update on Infections in Primary Antibody Deficiencies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 634181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksenhendler, E.; Gérard, L.; Fieschi, C.; Malphettes, M.; Mouillot, G.; Jaussaud, R.; Viallard, J.-F.; Gardembas, M.; Galicier, L.; Schleinitz, N.; et al. Infections in 252 Patients with Common Variable Immunodeficiency. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.E.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Non-infectious Complications of Common Variable Immunodeficiency: Updated Clinical Spectrum, Sequelae, and Insights to Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Valles-Ibáñez, G.; Esteve-Solé, A.; Piquer, M.; González-Navarro, E.A.; Hernandez-Rodriguez, J.; Laayouni, H.; González-Roca, E.; Plaza-Martin, A.M.; Deyà-Martínez, Á.; Martín-Nalda, A.; et al. Evaluating the Genetics of Common Variable Immunodeficiency: Monogenetic Model and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangye, S.G.; Nguyen, T.; Deenick, E.K.; Bryant, V.L.; Ma, C.S. Inborn errors of human B cell development, differentiation, and function. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20221105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Schouwenburg, P.A.; IJspeert, H.; Pico-Knijnenburg, I.; Dalm, V.A.S.H.; van Hagen, P.M.; van Zessen, D.; Stubbs, A.P.; Patel, S.Y.; van der Burg, M. Identification of CVID Patients With Defects in Immune Repertoire Formation or Specification. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchelli, C.; Buckridge, S.; Thrasher, A.J.; Gaspar, H.B. Translational mini-review series on immunodeficiency: Molecular defects in common variable immunodeficiency. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 149, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.B.; Wolf, H.M.; Eggenbauer, H.; Thon, V.; Vogel, E.; Lokaj, J.; Litzman, J.; Mannhalter, J.W.; Eibl, M.M. The costimulatory signal CD28 is fully functional but cannot correct the impaired antigen response in T cells of patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1994, 95, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gast, G.C.; Wilkins, S.R.; Webster, A.D.; Rickinson, A.; Platts-Mills, T.A. Functional ‘immaturity’ of isolated B cells from patients with hypogammaglobulinaemia. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1980, 42, 535–544. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, M.B.; Wolf, H.M.; Hauber, I.; Eggenbauer, H.; Thon, V.; Sasgary, M.; Eibl, M.M. Activation via the antigen receptor is impaired in T cells, but not in B cells from patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.B.; Hauber, I.; Eggenbauer, H.; Thon, V.; Vogel, E.; Schaffer, E.; Lokaj, J.; Litzman, J.; Wolf, H.M.; Mannhalter, J.W.; et al. A defect in the early phase of T-cell receptor-mediated T-cell activation in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Blood 1994, 84, 4234–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, A.; Calver, N.C.; Toubi, E.; Webster, A.D.; Farrant, J. Classification of patients with common variable immunodeficiency by B cell secretion of IgM and IgG in response to anti-IgM and interleukin-2. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1990, 56, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösel, A.L.; Scheibenbogen, C.; Schliesser, U.; Sollwedel, A.; Hoffmeister, B.; Hanitsch, L.; von Bernuth, H.; Krüger, R.; Warnatz, K.; Volk, H.D.; et al. Classification of common variable immunodeficiencies using flow cytometry and a memory B-cell functionality assay. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonoyama, S.; Farrington, M.; Ishida, H.; Howard, M.; Ochs, H.D. Activated B cells from patients with common variable immunodeficiency proliferate and synthesize immunoglobulin. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 1282–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehr, C.; Kivioja, T.; Schmitt, C.; Ferry, B.; Witte, T.; Eren, E.; Vlkova, M.; Hernandez, M.; Detkova, D.; Bos, P.R.; et al. The EUROclass trial: Defining subgroups in common variable immunodeficiency. Blood 2008, 111, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.E.; Yoshida, T.; Muehlinghaus, G.; Hiepe, F.; Dörner, T.; Radbruch, A.; Hoyer, B.F. Phenotypic analysis of B-cells and plasma cells. Methods Mol. Med. 2007, 136, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, M.E.; Notarangelo, L.D.; Etzioni, A. Diagnostic Criteria for Primary Immunodeficiencies. Clin. Immunol. 1999, 93, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, S.; Aubert, R.D.; Glidewell, J.; Ahmed, R. Tracking human antigen-specific memory B cells: A sensitive and generalized ELISPOT system. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 286, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeda, M.Z.; Hong, T.; Huang, C.; Huang, W.; Mu, Q. B cell memory: From generation to reactivation: A multipronged defense wall against pathogens. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schouwenburg, P.; Unger, S.; Payne, K.J.; Kaiser, F.M.P.; Pico-Knijnenburg, I.; Pfeiffer, J.; Hausmann, O.; Friedmann, D.; Erbel, M.; Seidl, M.; et al. Deciphering imprints of impaired memory B-cell maturation in germinal centers of three patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 959002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.P.; Caballero-Oteyza, A.; Grimbacher, B. Common Variable Immunodeficiency: More Pathways than Roads to Rome. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2023, 18, 283–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgueta, R.; Benson, M.J.; de Vries, V.C.; Wasiuk, A.; Guo, Y.; Noelle, R.J. Molecular mechanism and function of CD40/CD40L engagement in the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 152–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnell, J.; Ettinger, R. The Interplay of IL-21 and BAFF in the Formation and Maintenance of Human B Cell Memory. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbach, H.; Schickel, J.-N.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Conley, M.E.; Reisli, I.; Franco, J.L.; Meffre, E. CD19 controls Toll-like receptor 9 responses in human B cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 889–898.e886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allman, D.; Wilmore, J.R.; Gaudette, B.T. The continuing story of T-cell independent antibodies. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 288, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsman, C.; Verhoeven, D.; Koers, J.; Rispens, T.; Ten Brinke, A.; van Ham, S.M.; Kuijpers, T.W. Optimized Protocols for In-Vitro T-Cell-Dependent and T-Cell-Independent Activation for B-Cell Differentiation Studies Using Limited Cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 815449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoenkhoen, S.; Ádori, M.; Pedersen, G.K.; Karlsson Hedestam, G.B. Flow Cytometry-Based Protocols for the Analysis of Human Plasma Cell Differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 571321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, E.; Farroni, C.; Cascioli, S.; Marcellini, V.; Scarsella, M.; Giorda, E.; Piano Mortari, E.; Leonardi, L.; Scarselli, A.; Valentini, D.; et al. B-cell activation with CD40L or CpG measures the function of B-cell subsets and identifies specific defects in immunodeficient patients. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, M.; Béland, M.; Dembele, M.; Lejtenyi, D.; Drolet, J.P.; Lemire, M.; Tsoukas, C.; Ben-Shoshan, M.; Noya, F.J.D.; Alizadehfar, R.; et al. Modulation of the Interleukin-21 Pathway with Interleukin-4 Distinguishes Common Variable Immunodeficiency Patients with More Non-infectious Clinical Complications. J. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gómez, A.; Clemente, A.; Cunill, V.; Pons, J.; Ferrer, J.M. IL-21 and anti-CD40 restore Bcl-2 family protein imbalance in vitro in low-survival CD27(+) B cells from CVID patients. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borte, S.; Pan-Hammarström, Q.; Liu, C.; Sack, U.; Borte, M.; Wagner, U.; Graf, D.; Hammarström, L. Interleukin-21 restores immunoglobulin production ex vivo in patients with common variable immunodeficiency and selective IgA deficiency. Blood 2009, 114, 4089–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, P.A.; Verstegen, N.J.M.; Marsman, C.; Jorritsma, T.; Rispens, T.; Ten Brinke, A.; van Ham, S.M. Minimalistic In Vitro Culture to Drive Human Naive B Cell Differentiation into Antibody-Secreting Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, S.; Schwarz, T.; Corman, V.M.; Jeworowski, L.M.; Bauer, S.; Drosten, C.; Scheibenbogen, C.; Hanitsch, L.G. Impaired B Cell Recall Memory and Reduced Antibody Avidity but Robust T Cell Response in CVID Patients After COVID-19 Vaccination. J. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 43, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Hatchette, T.; Yue, F.; Liu, J.; Song, H.; Zhao, H.; Betschel, S.; Ostrowski, M. Impaired Memory B-Cell Response to Influenza Immunization in Patients With Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID). Pathog. Immun. 2021, 6, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, S.; Wittke, K.; Scheibenbogen, S.; Hanitsch, L. Conference Poster: The in vitro functional memory B cell response is intact in most patients with Common Variable Immunodeficiency Disorder. In Proceedings of the 7th European Congress of Immunology (ECI), Dublin, Ireland, 1–4 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
| Patient | Age | Sex | IgG | IgA | IgM | CD4+ | Anti-PCP Antibody Vaccine Response | CD8+ | CD19+ | CS MBC | NK Cells | Neutrophils |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 29 | F | 1.98 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.49 | no response | 0.69 | 0.19 | 0.820 | 0.2 | 3.2 |
| 2 | 34 | M | 0.71 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.68 | no response | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0.010 | 0.06 | 2.5 |
| 3 | 37 | F | 1.90 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.33 | no response | 0.34 | 0.07 | 0.030 | 0.07 | 1.8 |
| 4 | 56 | F | 1.50 | 0.06 | 0.3 | 0.45 | n.a. | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.960 | 0.33 | 3.7 |
| 5 | 31 | F | 1.00 | 0.06 | 0.1 | 0.74 | no response | 0.21 | 0.06 | 0.010 | 0.05 | 5.1 |
| 6 | 59 | F | 0.30 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.57 | n.a. | 0.38 | 0.01 | 0.000 | 0.08 | 2.0 |
| 7 | 53 | F | 0.40 | 0.08 | 0.38 | 2.36 | n.a. | 3.5 | 1.5 | 0.000 | 0.99 | 7.5 |
| 8 | 55 | M | 0.30 | 0.06 | 0.1 | 0.6 | no response | 0.9 | 0.14 | 0.030 | 0.08 | 3.2 |
| 9 | 51 | M | 0.30 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.64 | n.a. | 0.62 | 0.04 | 0.030 | 0.05 | 7.5 |
| 10 | 62 | F | 2.76 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0.57 | no response | 0.32 | 0.07 | 1.190 | 0.11 | 2.9 |
| 11 | 47 | M | 1.80 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 1.47 | no response | 0.84 | 0.25 | 0.470 | 0.04 | 4.1 |
| 12 | 60 | M | 1.69 | 0.06 | 0.28 | 0.53 | no response | 0.62 | 0.21 | 1.320 | 0.14 | 5.7 |
| 13 | 57 | M | 5.17 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.29 | n.a. | 0.2 | 0.07 | 0.000 | 0.04 | 3.6 |
| median | 53 | 1.5 | 0.06 | 0.1 | 0.57 | 0.38 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 3.6 |
| Patient | ITP | GLILD | Splenomegaly | Bronchiectasis | Rec. Pneumonia | Rec. Sinusitis | Genetics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | negative |
| 2 | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | negative |
| 3 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | negative |
| 4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | VUS in PIK3CD |
| 5 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | negative |
| 6 | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | negative |
| 7 | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | negative |
| 8 | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | negative |
| 9 | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | negative |
| 10 | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | negative |
| 11 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | negative |
| 12 | No | No | No | No | No | No | VUS in IRF2BP2 |
| 13 | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | negative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Steiner, S.; Wittke, K.; Bauer, S.; Scheibenbogen, C.; Hanitsch, L.G. Antibody Secretion Capacity in CVID Patients: Immunoglobulin Isotypes and Antigen Specificities After T-Cell-Dependent In Vitro Stimulation. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207246
Steiner S, Wittke K, Bauer S, Scheibenbogen C, Hanitsch LG. Antibody Secretion Capacity in CVID Patients: Immunoglobulin Isotypes and Antigen Specificities After T-Cell-Dependent In Vitro Stimulation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207246
Chicago/Turabian StyleSteiner, Sophie, Kirsten Wittke, Sandra Bauer, Carmen Scheibenbogen, and Leif G. Hanitsch. 2025. "Antibody Secretion Capacity in CVID Patients: Immunoglobulin Isotypes and Antigen Specificities After T-Cell-Dependent In Vitro Stimulation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207246
APA StyleSteiner, S., Wittke, K., Bauer, S., Scheibenbogen, C., & Hanitsch, L. G. (2025). Antibody Secretion Capacity in CVID Patients: Immunoglobulin Isotypes and Antigen Specificities After T-Cell-Dependent In Vitro Stimulation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207246






