Virtual Reality Exergaming in Outpatient Stroke Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review and Clinician Roadmap
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Information Sources, Search Strategy, and Screening
2.4. Data Extraction and Synthesis
3. Results
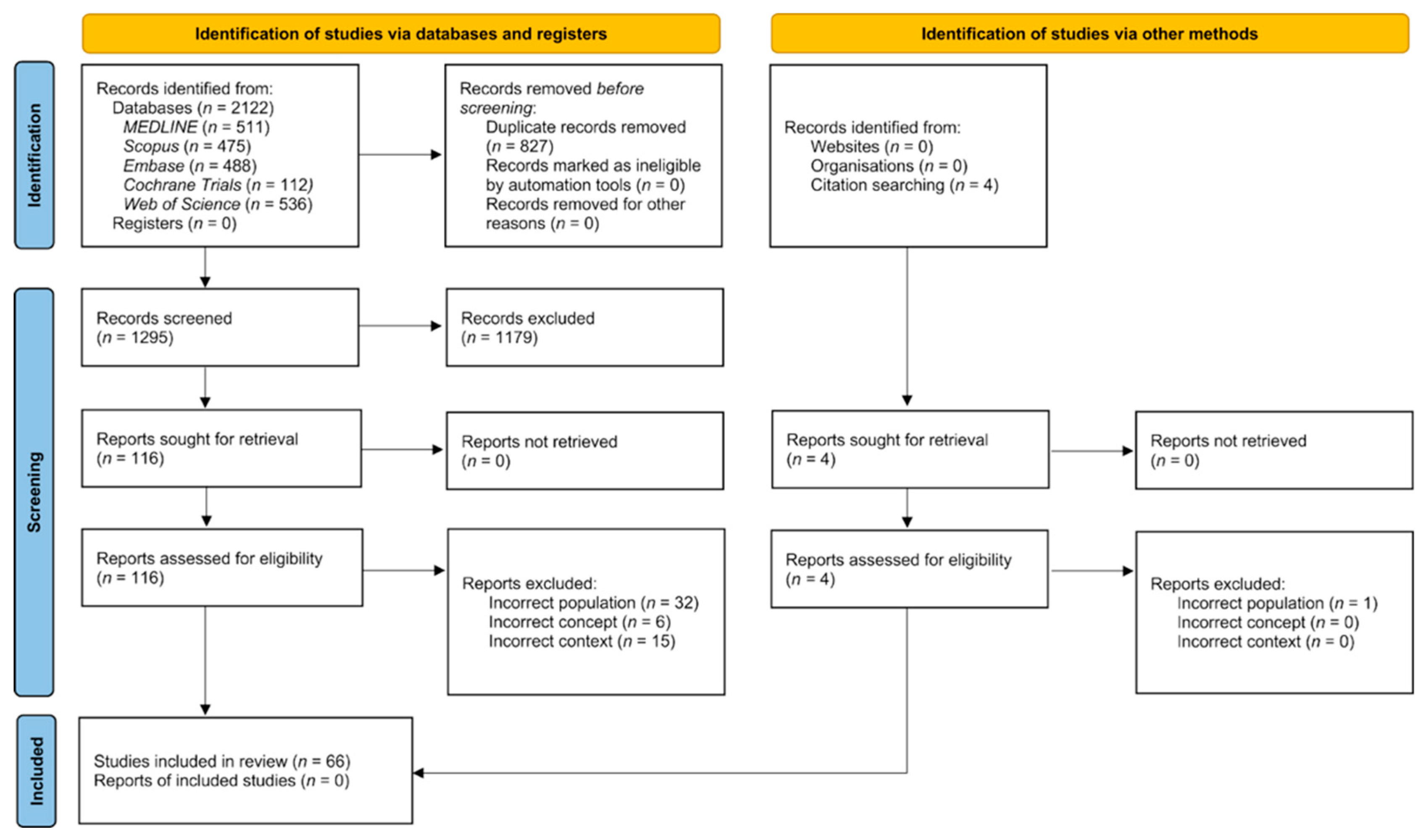
3.1. Search Results
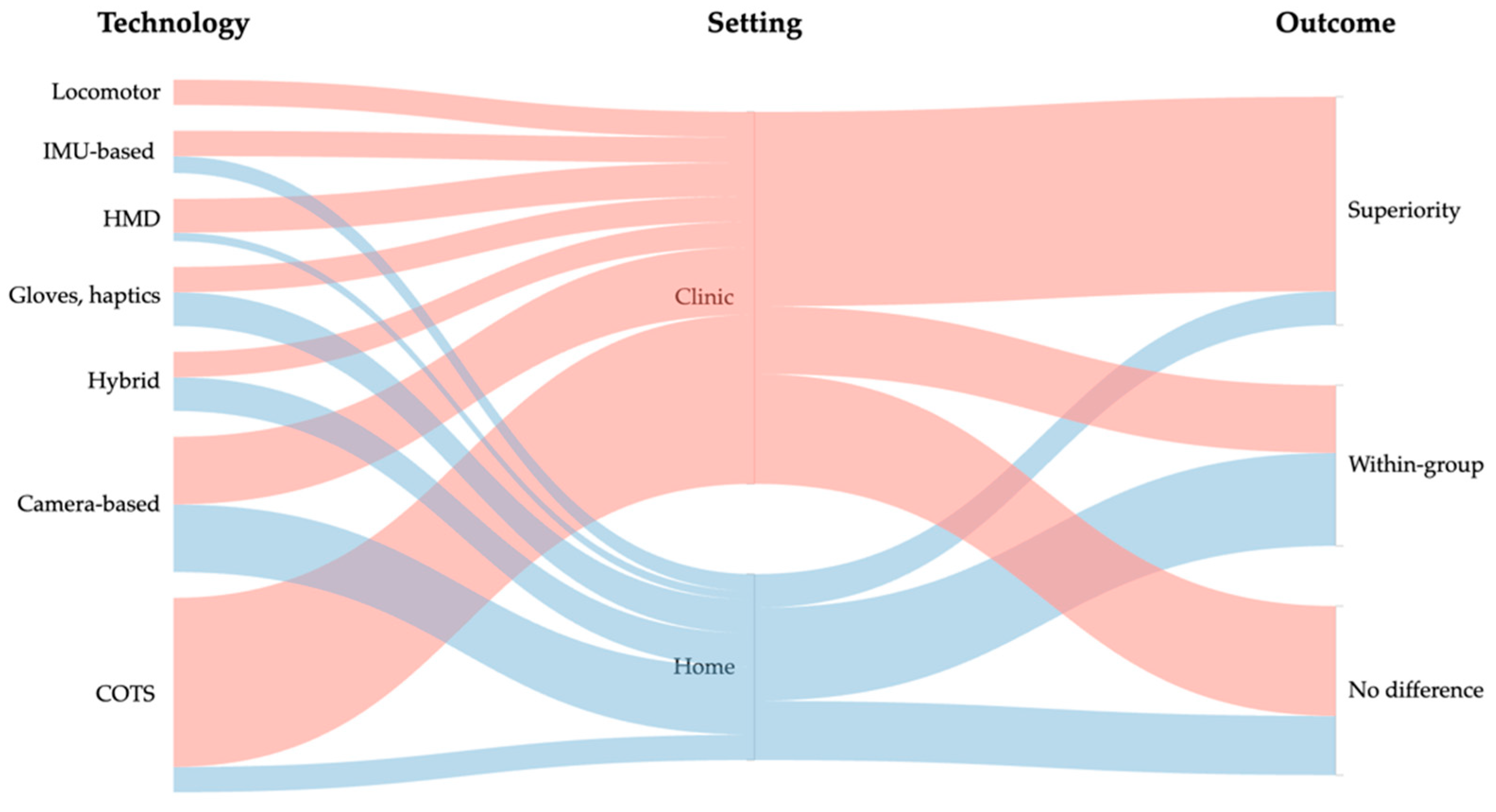
3.2. Types of VR Interventions
3.3. Narrative Effectiveness Overview
3.3.1. Upper Limb
3.3.2. Lower Limb Balance and Gait
3.3.3. Adherence and Acceptability
3.4. Potential Barriers and Facilitators to Implementation
4. Discussion
4.1. Bigger Picture
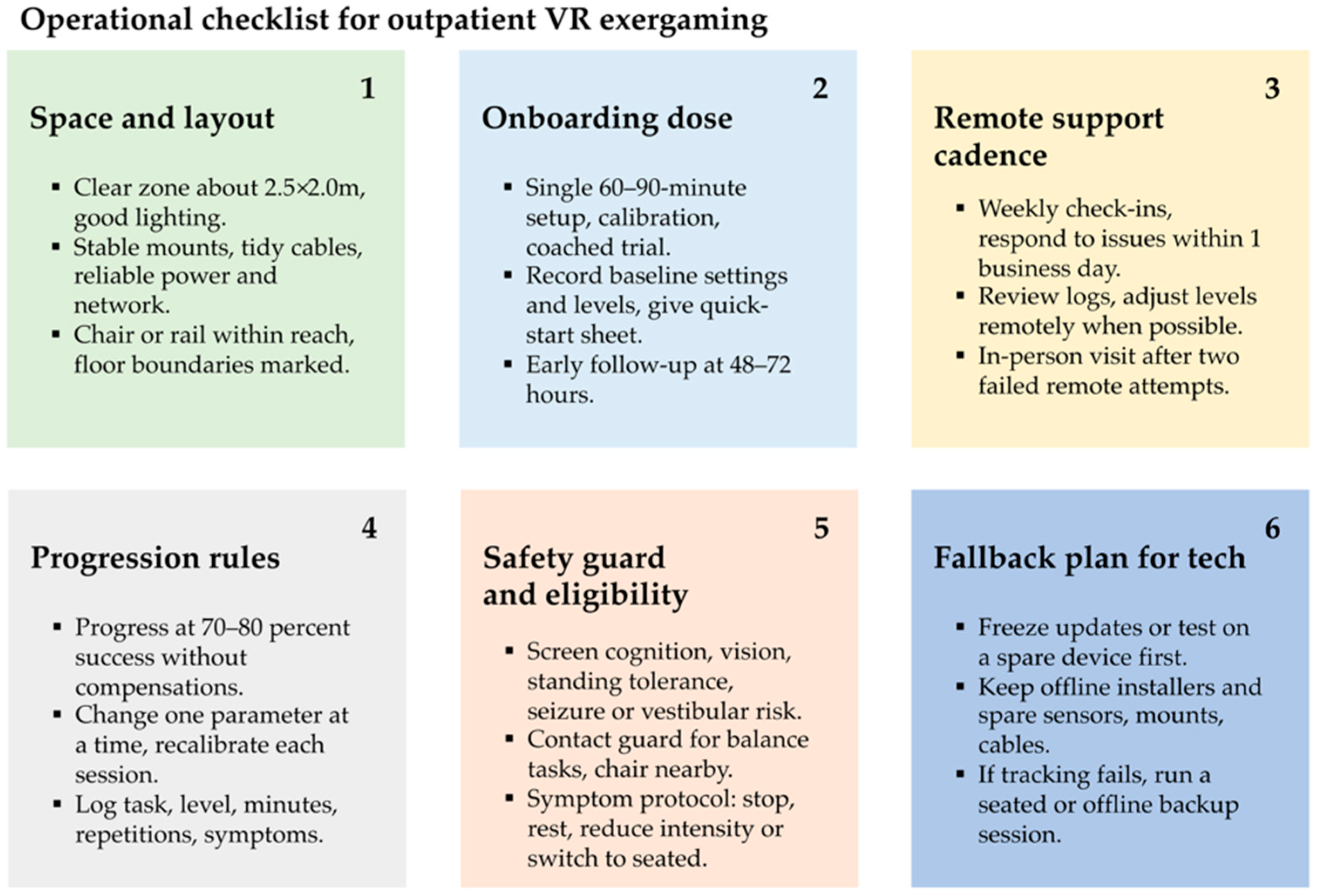
4.2. Clinical Implications and Future Studies Directions
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burdea, G.C.; Coiffet, P. Virtual Reality Technology, 3rd ed.; Wiley-IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; ISBN 978-1-118-01480-6. [Google Scholar]
- Carl, E.; Stein, A.T.; Levihn-Coon, A.; Pogue, J.R.; Rothbaum, B.; Emmelkamp, P.; Asmundson, G.J.G.; Carlbring, P.; Powers, M.B. Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy for Anxiety and Related Disorders: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Anxiety Disord. 2019, 61, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijlers, R.; Utens, E.M.W.J.; Staals, L.M.; de Nijs, P.F.A.; Berghmans, J.M.; Wijnen, R.M.H.; Hillegers, M.H.J.; Dierckx, B.; Legerstee, J.S. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Virtual Reality in Pediatrics: Effects on Pain and Anxiety. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tene, T.; Vique López, D.F.; Valverde Aguirre, P.E.; Orna Puente, L.M.; Vacacela Gomez, C. Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality in Medical Education: An Umbrella Review. Front. Digit. Health 2024, 6, 1365345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viderman, D.; Tapinova, K.; Dossov, M.; Seitenov, S.; Abdildin, Y.G. Virtual Reality for Pain Management: An Umbrella Review. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1203670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, J.R.; O’Connor, A.; Ganapathy, E.; Isba, R.; Payton, A.; McGrath, B.; Tolley, N.; Bruce, I.A. What Is Virtual Reality? A Healthcare-Focused Systematic Review of Definitions. Health Policy Technol. 2023, 12, 100741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caserman, P.; Hoffmann, K.; Müller, P.; Schaub, M.; Straßburg, K.; Wiemeyer, J.; Bruder, R.; Göbel, S. Quality Criteria for Serious Games: Serious Part, Game Part, and Balance. JMIR Serious Games 2020, 8, e19037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.; Ferreira da Silva Pais-Vieira, C.; Novais, J.; Perrotta, A. Serious Game Design and Clinical Improvement in Physical Rehabilitation: Systematic Review. JMIR Serious Games 2021, 9, e20066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüth, M.; Schmelzer, M.; Burtniak, K.; Kaspar, K. Commercial Exergames for Rehabilitation of Physical Health and Quality of Life: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials with Adults in Unsupervised Home Environments. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1155569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.C.; Killen, L.G.; Green, J.M.; Waldman, H.S.; Renfroe, L.G. Exergaming for Physical Activity: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Coll. Health 2024, 72, 2090–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.O.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P.; Grupper, M.F.; Rautalin, I. World Stroke Organization: Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2025. Int. J. Stroke 2025, 20, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo-Fernandez, R.; Violato, M.; Candio, P.; Leal, J. Economic Burden of Stroke across Europe: A Population-Based Cost Analysis. Eur. Stroke J. 2020, 5, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Noll, J.; Clua-Espuny, J.L.; Lleixà-Fortuño, M.; Gavaldà-Espelta, E.; Queralt-Tomas, L.; Panisello-Tafalla, A.; Carles-Lavila, M. The Costs Associated with Stroke Care Continuum: A Systematic Review. Health Econ. Rev. 2023, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laver, K.E.; Lange, B.; George, S.; Deutsch, J.E.; Saposnik, G.; Chapman, M.; Crotty, M. Virtual Reality for Stroke Rehabilitation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2025, 6, CD008349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Imam, Y.Z.; Muneer, M.; Al Jerdi, S.; Gill, S.K. Virtual Reality in Stroke Recovery: A Meta-Review of Systematic Reviews. Bioelectron. Med. 2024, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Jia, Y. Effects of Virtual Reality-Based Intervention on Depression in Stroke Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Crum, G.; Siu, K. Effects of Virtual Reality on Stroke Rehabilitation: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e70082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, F.; Lin, S.; Yu, L.; Lin, R. Effects of Virtual Reality Rehabilitation Training on Cognitive Function and Activities of Daily Living of Patients With Poststroke Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 103, 1422–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salbach, N.M.; Mountain, A.; Lindsay, M.P.; Blacquiere, D.; McGuff, R.; Foley, N.; Corriveau, H.; Fung, J.; Gierman, N.; Inness, E.; et al. Canadian Stroke Best Practice Recommendations: Virtual Stroke Rehabilitation Interim Consensus Statement 2022. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 101, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt Murphy, M.; Pradhan, S.; Levin, M.F.; Hancock, N.J. Uptake of Technology for Neurorehabilitation in Clinical Practice: A Scoping Review. Phys. Ther. 2023, 104, pzad140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Physical Therapy Association Virtual Reality. Available online: https://www.apta.org/patient-care/interventions/virtual-reality (accessed on 29 August 2025).
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Stroke Rehabilitation in Adults; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: Clinical Guidelines; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): London, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-4731-5481-0. [Google Scholar]
- Slatman, S.; Staal, J.B.; van Goor, H.; Ostelo, R.; Soer, R.; Knoop, J. Limited Use of Virtual Reality in Primary Care Physiotherapy for Patients with Chronic Pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobaigy, A.; Alshehri, M.A.; Timmons, S.; Helal, O.F. The Feasibility of Using Exergames as a Rehabilitation Tool: The Attitudes, Awareness, Opinions and Experiences of Physiotherapists, and Older People towards Exergames. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouijzer, M.M.T.E.; Kip, H.; Bouman, Y.H.A.; Kelders, S.M. Implementation of Virtual Reality in Healthcare: A Scoping Review on the Implementation Process of Virtual Reality in Various Healthcare Settings. Implement. Sci. Commun. 2023, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Marnie, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Pollock, D.; Munn, Z.; Alexander, L.; McInerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H. Updated Methodological Guidance for the Conduct of Scoping Reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.L.; Ho, C.Z.H.; Khaing, N.E.E.; Ho, E.; Pong, C.; Guan, J.S.; Chua, C.; Li, Z.; Lim, T.; Lam, S.S.W.; et al. Frameworks for Measuring Population Health: A Scoping Review. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0278434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, C.; Greenwood, H.; Carter, M.; Clark, J. Automation of Duplicate Record Detection for Systematic Reviews: Deduplicator. Syst. Rev. 2024, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan-a Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, M.; Wilbur, S. A Framework for Immersive Virtual Environments Five: Speculations on the Role of Presence in Virtual Environments. Presence Teleoper. Virtual Env. 1997, 6, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Jang, H.; Kim, H.; Song, C. 360° Immersive Virtual Reality-Based Mirror Therapy for Upper Extremity Function and Satisfaction among Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2024, 60, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-Y.; Kuo, L.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Su, F.-C.; Yang, T.-H.; Lin, C.-W. Effects of a Virtual Reality-Based Mirror Therapy Program on Improving Sensorimotor Function of Hands in Chronic Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair. 2022, 36, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-H.; Kreidler, T.; Ochsenfahrt, A. Rehago—A Home-Based Training App Using Virtual Reality to Improve Functional Performance of Stroke Patients with Mirror Therapy and Gamification Concept: A Pilot Study. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2022, 292, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosbie, J.; Lennon, S.; McGoldrick, M.; McNeill, M.; McDonough, S. Virtual Reality in the Rehabilitation of the Arm after Hemiplegic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Clin. Rehabil. 2012, 26, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peláez-Vélez, F.-J.; Eckert, M.; Gacto-Sánchez, M.; Martínez-Carrasco, Á. Use of Virtual Reality and Videogames in the Physiotherapy Treatment of Stroke Patients: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.; Bird, M.-L.; Muthalib, M.; Teo, W.-P. An Innovative STRoke Interactive Virtual thErapy (STRIVE) Online Platform for Community-Dwelling Stroke Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 101, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi-Gheidari, N.; Hernandez, A.; Archambault, P.S.; Higgins, J.; Poissant, L.; Kairy, D. Feasibility, Safety and Efficacy of a Virtual Reality Exergame System to Supplement Upper Extremity Rehabilitation Post-Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial and Proof of Principle. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehy, L.; Taillon-Hobson, A.; Sveistrup, H.; Bilodeau, M.; Yang, C.; Welch, V.; Finestone, H. Home-Based Nonimmersive Virtual Reality Training After Discharge From Inpatient or Outpatient Stroke Rehabilitation: Parallel Feasibility Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2025, 12, e64729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, J.-W.; Chou, C.-X.; Chang, Y.-J.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chang, K.-C.; Wu, W.-C.; Howell, S. Comparison of Kinect2Scratch Game-Based Training and Therapist-Based Training for the Improvement of Upper Extremity Functions of Patients with Chronic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Single-Blinded Trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 55, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrique, P.P.B.; Colussi, E.L.; De Marchi, A.C.B. Effects of Exergame on Patients’ Balance and Upper Limb Motor Function after Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2019, 28, 2351–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, K.; Prabhakaran, B.; Ifejika, N.; Annaswamy, T.M. Personalized 3D Exergames for In-Home Rehabilitation after Stroke: A Pilot Study. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2023, 18, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielbar, K.O.; Triandafilou, K.M.; Barry, A.J.; Yuan, N.; Nishimoto, A.; Johnson, J.; Stoykov, M.E.; Tsoupikova, D.; Kamper, D.G. Home-Based Upper Extremity Stroke Therapy Using a Multiuser Virtual Reality Environment: A Randomized Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 101, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tong, M.; Ming, W.-K.; Lin, Y.; Mai, W.; Huang, W.; Chen, Z. A Depth Camera–Based, Task-Specific Virtual Reality Rehabilitation Game for Patients With Stroke: Pilot Usability Study. JMIR Serious Games 2021, 9, e20916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.F.; Snir, O.; Liebermann, D.G.; Weingarden, H.; Weiss, P.L. Virtual Reality Versus Conventional Treatment of Reaching Ability in Chronic Stroke: Clinical Feasibility Study. Neurol. Ther. 2012, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jang, S.H.; Kim, C.S.; Jung, J.H.; You, J.H. Use of Virtual Reality to Enhance Balance and Ambulation in Chronic Stroke: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 88, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junata, M.; Cheng, K.C.-C.; Man, H.S.; Lai, C.W.-K.; Soo, Y.O.-Y.; Tong, R.K.-Y. Kinect-Based Rapid Movement Training to Improve Balance Recovery for Stroke Fall Prevention: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, C.; Lau, C.C.-Y.; Tong, R.K.-Y. Home-Based Guidance Training System with Interactive Visual Feedback Using Kinect on Stroke Survivors with Moderate to Severe Motor Impairment. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2024, 21, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Cronce, A.; Patel, J.; Fluet, G.G.; Mont, A.J.; Merians, A.S.; Adamovich, S.V. Development of the Home Based Virtual Rehabilitation System (HoVRS) to Remotely Deliver an Intense and Customized Upper Extremity Training. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluet, G.; Qiu, Q.; Gross, A.; Gorin, H.; Patel, J.; Merians, A.; Adamovich, S. The Influence of Scaffolding on Intrinsic Motivation and Autonomous Adherence to a Game-Based, Sparsely Supervised Home Rehabilitation Program for People with Upper Extremity Hemiparesis Due to Stroke. A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2024, 21, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsdottir, J.; Baglio, F.; Gindri, P.; Isernia, S.; Castiglioni, C.; Gramigna, C.; Palumbo, G.; Pagliari, C.; Di Tella, S.; Perini, G.; et al. Virtual Reality for Motor and Cognitive Rehabilitation From Clinic to Home: A Pilot Feasibility and Efficacy Study for Persons With Chronic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 601131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, F.; Hancock, N.; Kennedy, N.; Clark, A.; Wells, J.; Chandler, E.; Payne, D.; Pomeroy, V.M. Consideration-of-Concept of EvolvRehab-Body for Upper Limb Virtual Rehabilitation at Home for People Late after Stroke. Physiotherapy 2022, 116, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-S.; Lim, J.-H.; Jeon, B.-H.; Song, C.-S. Non-Immersive Virtual Reality Rehabilitation Applied to a Task-Oriented Approach for Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2020, 38, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansberg, M.G.; Legault, C.; MacLellan, A.; Parikh, A.; Muccini, J.; Mlynash, M.; Kemp, S.; Buckwalter, M.S.; Flavin, K. Home-Based Virtual Reality Therapy for Hand Recovery after Stroke. PMR 2022, 14, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ase, H.; Honaga, K.; Tani, M.; Takakura, T.; Wada, F.; Murakami, Y.; Isayama, R.; Tanuma, A.; Fujiwara, T. Effects of Home-Based Virtual Reality Upper Extremity Rehabilitation in Persons with Chronic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2025, 22, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zondervan, D.K.; Friedman, N.; Chang, E.; Zhao, X.; Augsburger, R.; Reinkensmeyer, D.J.; Cramer, S.C. Home-Based Hand Rehabilitation after Chronic Stroke: Randomized, Controlled Single-Blind Trial Comparing the MusicGlove with a Conventional Exercise Program. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2016, 53, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockley, R.C.; O’Connor, D.A.; Smith, P.; Moss, S.; Allsop, L.; Edge, W. A Mixed Methods Small Pilot Study to Describe the Effects of Upper Limb Training Using a Virtual Reality Gaming System in People with Chronic Stroke. Rehabil. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 9569178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broeren, J.; Claesson, L.; Goude, D.; Rydmark, M.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Virtual Rehabilitation in an Activity Centre for Community-Dwelling Persons with Stroke: The Possibilities of 3-Dimensional Computer Games. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2008, 26, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standen, P.J.; Threapleton, K.; Richardson, A.; Connell, L.; Brown, D.J.; Battersby, S.; Platts, F.; Burton, A. A Low Cost Virtual Reality System for Home Based Rehabilitation of the Arm Following Stroke: A Randomised Controlled Feasibility Trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittmann, F.; Held, J.P.; Lambercy, O.; Starkey, M.L.; Curt, A.; Höver, R.; Gassert, R.; Luft, A.R.; Gonzenbach, R.R. Self-Directed Arm Therapy at Home after Stroke with a Sensor-Based Virtual Reality Training System. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2016, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilbride, C.; Scott, D.J.M.; Butcher, T.; Norris, M.; Warland, A.; Anokye, N.; Cassidy, E.; Baker, K.; Athanasiou, D.A.; Singla-Buxarrais, G.; et al. Safety, Feasibility, Acceptability and Preliminary Effects of the Neurofenix Platform for Rehabilitation via HOMe Based Gaming Exercise for the Upper-Limb Post Stroke (RHOMBUS): Results of a Feasibility Intervention Study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e052555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, A.; Cinnera, A.M.; Pucello, A.; Iosa, M.; Coiro, P.; Personeni, S.; Gimigliano, F.; Iolascon, G.; Paolucci, S.; Morone, G. Effects on Balance Skills and Patient Compliance of Biofeedback Training with Inertial Measurement Units and Exergaming in Subacute Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Funct. Neurol. 2018, 33, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Noveletto, F.; Soares, A.V.; Mello, B.A.; Sevegnani, C.N.; Eichinger, F.L.F.; Hounsell, M.D.S.; Bertemes-Filho, P. Biomedical Serious Game System for Balance Rehabilitation of Hemiparetic Stroke Patients. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 2179–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Singh, D.K.A.; Mohd Nordin, N.A.; Hooi Nee, K.; Ibrahim, N. Virtual Reality Games as an Adjunct in Improving Upper Limb Function and General Health among Stroke Survivors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 16, 5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adie, K.; Schofield, C.; Berrow, M.; Wingham, J.; Humfryes, J.; Pritchard, C.; James, M.; Allison, R. Does the Use of Nintendo Wii SportsTM Improve Arm Function? Trial of WiiTM in Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial and Economics Analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carregosa, A.A.; Santos, L.R.A.d.; Masruha, M.R.; Coêlho, M.L.d.S.; Machado, T.C.; Souza, D.C.B.; Passos, G.L.L.; Fonseca, E.P.; Ribeiro, N.M.d.S.; Melo, A.d.S. Virtual Rehabilitation through Nintendo Wii in Poststroke Patients: Follow-Up. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinthal, A.; Szirony, K.; Clark, C.; Swiers, J.; Kellicker, M.; Linder, S. ENGAGE: Guided Activity-Based Gaming in Neurorehabilitation after Stroke: A Pilot Study. Stroke Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 784232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmand, S.; Ghasemi, M.; Basiri, K.; Ghasemi, E. Investigating the Effects of Nintendo Wii on Ankle Spasticity in Patients with Stroke: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Mod. Rehabil. 2024, 18, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.S.; Oliveira, T.d.P.; Gouvêa, J.X.M.; Perez, D.B.; Marques, A.P.; Piemonte, M.E.P. Balance Training in Virtual Reality Promotes Performance Improvement but Not Transfer to Postural Control in People with Chronic Stroke. Games Health J. 2019, 8, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, L.; Vora, J.; Bhatt, T.; Hughes, S.L. Cognitive-Motor Exergaming for Reducing Fall Risk in People with Chronic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. NeuroRehabilitation 2019, 44, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, E.P.d.; Silva, N.M.R.d.; Pinto, E.B. Therapeutic Effect of Virtual Reality on Post-Stroke Patients: Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Ribeiro, N.M.; Ferraz, D.D.; Pedreira, É.; Pinheiro, Í.; da Silva Pinto, A.C.; Neto, M.G.; Dos Santos, L.R.A.; Pozzato, M.G.G.; Pinho, R.S.; Masruha, M.R. Virtual Rehabilitation via Nintendo Wii® and Conventional Physical Therapy Effectively Treat Post-Stroke Hemiparetic Patients. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2015, 22, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, N.; Karimi, H.; Ahmad, A.; Mumtaz, N.; Saqulain, G.; Gilani, S.A. A Novel Virtual Reality Training Strategy for Poststroke Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6598726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, N.; Karimi, H.; Ahmad, A.; Gilani, S.A.; Khalid, K.; Aslam, A.S.; Hanif, A. Virtual Reality Training Using Nintendo Wii Games for Patients With Stroke: Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Serious Games 2022, 10, e29830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Shendy, W.; Hassan, A.; Abdelmonem, K.; El Khatib, A. The Impact of Virtual Reality Training with a Cognitive Load on Falling in Stroke Cases. NeuroQuantology 2022, 20, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, J.-W.; Chou, C.-X.; Hsieh, Y.-W.; Wu, W.-C.; Yu, M.-Y.; Chen, P.-C.; Chang, H.-F.; Ding, S.-E. Randomized Comparison Trial of Balance Training by Using Exergaming and Conventional Weight-Shift Therapy in Patients with Chronic Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, S.L.; Peters, D.M.; Merlo, A.M.; Donley, J. Active Video-Gaming Effects on Balance and Mobility in Individuals with Chronic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2013, 20, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golla, A.; Müller, T.; Wohlfarth, K.; Jahn, P.; Mattukat, K.; Mau, W. Home-Based Balance Training Using Wii FitTM: A Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial with Mobile Older Stroke Survivors. Pilot. Feasibility Stud. 2018, 4, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Sule, E.; Arnal-Gómez, A.; Buitrago-Jiménez, G.; Suso-Martí, L.; Cuenca-Martínez, F.; Espí-López, G.V. Effectiveness of Nintendo Wii and Physical Therapy in Functionality, Balance, and Daily Activities in Chronic Stroke Patients. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand, D.; Weingarden, H.; Weiss, R.; Yacoby, A.; Reif, S.; Malka, R.; Shiller, D.A.; Zeilig, G. Self-Training to Improve UE Function at the Chronic Stage Post-Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, Q.U.; Khan, S.; Ilyas, S.; Yaseen, A.; Tariq, I.; Liu, T.; Wang, J. Additional Effects of Xbox Kinect Training on Upper Limb Function in Chronic Stroke Patients: A Randomized Control Trial. Healthcare 2021, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul, A.Q.; Khan, S.; Ishtiaq, S.; Alsaied, A.; Liu, T.; Wang, J. Therapeutic Benefits of Xbox Kinect Training on Upper Limb Motor Function in Chronic Stroke Patients. In Proceedings of the 2022 8th International Conference on Virtual Reality (ICVR), Nanjing, China, 26–28 May 2022; pp. 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam, S.; Bhatt, T. Dance-Based Exergaming for Upper Extremity Rehabilitation and Reducing Fall-Risk in Community-Dwelling Individuals with Chronic Stroke. A Preliminary Study. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2019, 26, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.N.; Masood, T. Task-Oriented Training and Exer-Gaming for Improving Mobility after Stroke: A Randomized Trial. JPMA J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2021, 71, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkusuz, S.; Taşkın, G.; Korkusuz, B.S.; Özen, M.S.; Yürük, Z.Ö. Examining the Effects of Non-Immersive Virtual Reality Game-Based Training on Knee Hyperextension Control and Balance in Chronic Stroke Patients: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Study. Neurol. Sci. Off. J. Ital. Neurol. Soc. Ital. Soc. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2025, 46, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.K.A.; Mohd Nordin, N.A.; Aziz, N.A.A.; Lim, B.K.; Soh, L.C. Effects of Substituting a Portion of Standard Physiotherapy Time with Virtual Reality Games among Community-Dwelling Stroke Survivors. BMC Neurol. 2013, 13, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, N.; Khushnood, K.; Qureshi, S.; Altaf, S.; Khan, M.K.; Malik, A.N.; Mehmood, R.; Awan, M.M.A. Effects of Virtual Reality Training Using Xbox Kinect on Balance, Postural Control, and Functional Independence in Subjects with Stroke. Games Health J. 2023, 12, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Marcos, D.; Chevalley, O.; Schmidlin, T.; Garipelli, G.; Serino, A.; Vuadens, P.; Tadi, T.; Blanke, O.; Millán, J.D.R. Increasing Upper Limb Training Intensity in Chronic Stroke Using Embodied Virtual Reality: A Pilot Study. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, B.R.; Nirme, J.; Camacho, I.; Duarte, E.; Rodríguez, S.; Cuxart, A.; Duff, A.; Verschure, P.F.M.J. Domiciliary VR-Based Therapy for Functional Recovery and Cortical Reorganization: Randomized Controlled Trial in Participants at the Chronic Stage Post Stroke. JMIR Serious Games 2017, 5, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slijper, A.; Svensson, K.E.; Backlund, P.; Engström, H.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Computer Game-Based Upper Extremity Training in the Home Environment in Stroke Persons: A Single Subject Design. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borstad, A.L.; Crawfis, R.; Phillips, K.; Lowes, L.P.; Maung, D.; McPherson, R.; Siles, A.; Worthen-Chaudhari, L.; Gauthier, L.V. In-Home Delivery of Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy via Virtual Reality Gaming. J. Patient-Centered Res. Rev. 2018, 5, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoupikova, D.; Stoykov, N.S.; Corrigan, M.; Thielbar, K.; Vick, R.; Li, Y.; Triandafilou, K.; Preuss, F.; Kamper, D. Virtual Immersion for Post-Stroke Hand Rehabilitation Therapy. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijenhuis, S.M.; Prange-Lasonder, G.B.; Stienen, A.H.; Rietman, J.S.; Buurke, J.H. Effects of Training with a Passive Hand Orthosis and Games at Home in Chronic Stroke: A Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escalante-Gonzalbo, A.M.; Ramírez-Graullera, Y.S.; Pasantes, H.; Aguilar-Chalé, J.J.; Sánchez-Castillo, G.I.; Escutia-Macedo, X.A.; Briseño-Soriano, T.M.; Franco-Castro, P.; Estrada-Rosales, A.L.; Vázquez-Abundes, S.E.; et al. Safety, Feasibility, and Acceptability of a New Virtual Rehabilitation Platform: A Supervised Pilot Study. Rehabil. Process Outcome 2021, 10, 11795727211033279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesmana, I.P.D.; Destarianto, P.; Widiawan, B.; Suryana, A.L.; Hossain, F.S. Effectiveness of Virtual Reality Cycling Exercise towards the Motoric and Cardiorespiratory Functions of Post-Stroke Patients. Physiother. Q. 2024, 32, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloréns, R.; Gil-Gómez, J.-A.; Alcañiz, M.; Colomer, C.; Noé, E. Improvement in Balance Using a Virtual Reality-Based Stepping Exercise: A Randomized Controlled Trial Involving Individuals with Chronic Stroke. Clin. Rehabil. 2015, 29, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-R.; Tsai, M.-P.; Chuang, T.-Y.; Sung, W.-H.; Wang, R.-Y. Virtual Reality-Based Training Improves Community Ambulation in Individuals with Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelineau, A.; Perrochon, A.; Robin, L.; Daviet, J.-C.; Mandigout, S. Measured and Perceived Effects of Upper Limb Home-Based Exergaming Interventions on Activity after Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazavi Dozin, S.M.; Mohammad Rahimi, N.; Aminzadeh, R. Wii Fit-Based Biofeedback Rehabilitation Among Post-Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2024, 26, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.S.; Magalhães, B.; Gonçalves, F.; Lima, A.; Silva, M.; Moreira, M.T.; Santos, C.; Ferreira, S. Exergames for Rehabilitation in Stroke Survivors: Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2025, 34, 108161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; He, Z.; Yu, X.; Remis, A. Comparison of Immersive and Non-Immersive Virtual Reality for Upper Extremity Functional Recovery in Patients with Stroke: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Neurol. Sci. Off. J. Ital. Neurol. Soc. Ital. Soc. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2023, 44, 2679–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjipanayi, C.; Banakou, D.; Michael-Grigoriou, D. Virtual Reality Exergames for Enhancing Engagement in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Narrative Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudri, N.A. Adherence to Long-Term Therapies Evidence for Action. Ann. Saudi Med. 2004, 24, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favetta, M.; Romano, A.; Valè, N.; Cieslik, B.; Federico, S.; Girolami, A.; Mazzarotto, D.; Pregnolato, G.; Righetti, A.; Salvalaggio, S.; et al. A Scoping Review of Scientific Concepts Concerning Motor Recovery after Stroke as Employed in Clinical Trials. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1221656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.F.; Weiss, P.L.; Keshner, E.A. Emergence of Virtual Reality as a Tool for Upper Limb Rehabilitation: Incorporation of Motor Control and Motor Learning Principles. Phys. Ther. 2015, 95, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramia, F.; D’Angelantonio, E.; Lucangeli, L.; Camomilla, V. Validation of Low-Cost IMUs for Telerehabilitation Exercises. Sensors 2025, 25, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.J.; Parnandi, A.; Eva, S.; Schambra, H. The Use of Wearable Sensors to Assess and Treat the Upper Extremity after Stroke: A Scoping Review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2022, 44, 6119–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigrist, R.; Rauter, G.; Riener, R.; Wolf, P. Augmented Visual, Auditory, Haptic, and Multimodal Feedback in Motor Learning: A Review. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2013, 20, 21–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuena, C.; Borghesi, F.; Bruni, F.; Cavedoni, S.; Maestri, S.; Riva, G.; Tettamanti, M.; Liperoti, R.; Rossi, L.; Ferrarin, M.; et al. Technology-Assisted Cognitive Motor Dual-Task Rehabilitation in Chronic Age-Related Conditions: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e44484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, N.E.; Cheek, F.M.; Nichols-Larsen, D.S. Motor-Cognitive Dual-Task Training in Persons With Neurologic Disorders: A Systematic Review. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. JNPT 2015, 39, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloréns, R.; Noé, E.; Colomer, C.; Alcañiz, M. Effectiveness, Usability, and Cost-Benefit of a Virtual Reality–Based Telerehabilitation Program for Balance Recovery After Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 418–425.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-de-la-Cuerda, R.; Blázquez-Fernández, A.; Marcos-Antón, S.; Sánchez-Herrera-Baeza, P.; Fernández-González, P.; Collado-Vázquez, S.; Jiménez-Antona, C.; Laguarta-Val, S. Economic Cost of Rehabilitation with Robotic and Virtual Reality Systems in People with Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agbemanyole, K.A.; Agbohessou, K.G.; Pons, C.; Lenca, P.; Rémy-Néris, O.; Goff-Pronost, M.L. Economic Analysis of Digital Motor Rehabilitation Technologies: A Systematic Review. Health Econ. Rev. 2024, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Evidence Reviews for the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness of Telerehabilitation for Adults after a Stroke. In Stroke Rehabilitation in Adults (Update); Evidence Review G (NICE Guideline No. 236); NICE: London, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-4731-5456-8. [Google Scholar]
- Elser, A.; Lange, M.; Kopkow, C.; Schäfer, A.G. Barriers and Facilitators to the Implementation of Virtual Reality Interventions for People With Chronic Pain: Scoping Review. JMIR XR Spat. Comput. JMXR 2024, 1, e53129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhorne, P.; Baylan, S. Early Supported Discharge Trialists Early Supported Discharge Services for People with Acute Stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 7, CD000443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, S.; Jeong, M.; Paik, N.-J.; Kim, W.-S.; Shin, Y.-I.; Ko, S.-H.; Kwon, I.S.; Choi, B.M.; Jung, Y.; Chang, W.; et al. Early Supported Discharge and Transitional Care Management After Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 755316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose Sin Yi, L.; Jing Jing, S.; Hammoda, A.-O.; Jonathan, B.; Ladislav, B.; Jing, Q. Effects of Virtual Reality-Based Cognitive Interventions on Cognitive Function and Activity of Daily Living among Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Nurs. 2024, 33, 1169–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, M.; Yim, J. A New Approach to Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Improving Cognitive Motor Learning and Hand Function with the Nintendo Switch in Stroke Survivors. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2019, 25, 9555–9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Gómez, A.; Martín-Díaz, P.; Sánchez-Herrera Baeza, P.; Martínez-Medina, A.; Ortiz-Comino, C.; Cano-de-la-Cuerda, R. Nintendo Switch Joy-Cons’ Infrared Motion Camera Sensor for Training Manual Dexterity in People with Multiple Sclerosis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, A.D.; Roth, N.; Yehoshua, T.; Itah, D.; Braun Benyamin, O.; Dahan, A. Personalized Rehabilitation Approach for Reaching Movement Using Reinforcement Learning. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waffenschmidt, S.; Knelangen, M.; Sieben, W.; Bühn, S.; Pieper, D. Single Screening versus Conventional Double Screening for Study Selection in Systematic Reviews: A Methodological Systematic Review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2019, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, G. Effect Size Guidelines for Individual and Group Differences in Physiotherapy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
| Characteristics of Studies | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Publication year | |
| 2025–2021 | 27 (41) |
| 2020–2016 | 26 (39) |
| 2015–2011 | 10 (15) |
| ≤2010 | 3 (5) |
| Design | |
| RCTs | 45 (68) |
| Non-randomized controlled studies | 4 (6) |
| Single-group pre–post | 17 (26) |
| Type of VR | |
| Serious exergame | 43 (65) |
| Commercial exergame | 23 (35) |
| Environment | |
| Clinic-based outpatient | 44 (67) |
| Home-based outpatient | 22 (33) |
| Experimental intervention | |
| HMD | 5 (8) |
| Camera-based | 16 (24) |
| Gloves, haptics | 7 (11) |
| IMU-based systems | 5 (8) |
| COTS | 23 (35) |
| Hybrid | 7 (11) |
| Locomotor | 3 (5) |
| Category | Technology | Area | Setting | CA | Sample Size | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMD | HMD VR mirror therapy | Upper limb | Clinic | No | 45 | [31] |
| HMD VR mirror therapy + Leap Motion, | Upper limb | Clinic | No | 52 | [32] | |
| Pico Neo 2 HMD + REHAGO software | Upper limb | Home | No | 48 | [33] | |
| Custom immersive VR HMD with IMU | Upper limb | Clinic | No | 18 | [34] | |
| Oculus Quest 2 HMD + Kinect sensor | Multiple | Clinic | No | 24 | [35] | |
| Camera-based | Jintronix (Kinect) | Upper limb | Both | Yes | 98 | [36,37,38] |
| Kinect2Scratch (custom PC games) | Upper limb | Clinic | No | 18 | [39] | |
| Motion Rehab AVE 3D (Kinect + projection) | Upper limb | Clinic | No | 31 | [40] | |
| PIXER home (Kinect v2) | Upper limb | Home | No | 10 | [41] | |
| VERGE tele-exergame (Kinect) | Upper limb | Home | No | 20 | [42] | |
| Stomp Joy | Lower limb | Clinic | No | 22 | [43] | |
| GestureTek IREX | Upper limb | Clinic | Yes | 36 | [44,45] | |
| Kinect Rapid Movement Training platform | Lower limb | Both | No | 30 | [46] | |
| Kinect v2 home guidance system | Upper limb | Home | No | 12 | [47] | |
| HoVRS, home platform using Leap Motion | Upper limb | Home | No | 43 | [48,49] | |
| HEAD platform (Kinect plus Leap Motion) | Upper limb | Home | No | 34 | [50] | |
| EvolvRehab Body (Kinect v2 plus Leap Motion) | Upper limb | Home | Yes | 8 | [51] | |
| Gloves, haptics | RAPAEL or Neofect Smart Glove | Upper limb | Both | Yes | 70 | [52,53,54] |
| MusicGlove (Flint Rehab) | Upper limb | Home | Yes | 17 | [55] | |
| YouGrabber sensor gloves (YouRehab) | Upper limb | Clinic | No | 12 | [56] | |
| Workbench VR with Phantom Omni stylus | Upper limb | Clinic | No | 22 | [57] | |
| Virtual Glove (infrared glove) | Upper limb | Home | No | 27 | [58] | |
| IMU-based systems | ArmeoSenso (home) | Upper limb | Home | Yes | 11 | [59] |
| Neurofenix NeuroBall/NeuroBands | Upper limb | Home | Yes | 30 | [60] | |
| RIABLO (wireless IMUs + force platform) | Lower limb | Clinic | Yes | 15 | [61] | |
| myBalance IMU balance board (custom) | Lower limb | Clinic | No | 6 | [62] | |
| PC games with CyWee Z motion controller | Upper limb | Clinic | No | 36 | [63] | |
| COTS | Nintendo Wii/Wii Fit | Multiple | Both | Yes | 660 | [64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78] |
| PlayStation 2 EyeToy | Multiple | Clinic | Yes | 68 | [66,76,79] | |
| Xbox 360 Kinect | Multiple | Both | Yes | 283 | [79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86] | |
| Hybrid | MindMotion PRO (motion camera + wrist IMUs) | Upper limb | Clinic | Yes | 10 | [87] |
| Rehabilitation Gaming System (Eodyne) | Upper limb | Home | No | 35 | [88] | |
| Custom home gaming system | Upper limb | Home | No | 11 | [89] | |
| Recovery Rapids: Kinect + glove | Upper limb | Home | No | 14 | [90] | |
| Dual 3D displays with PneuGlove, IMUs | Upper limb | Clinic | No | 6 | [91] | |
| Passive hand orthosis, SaeboMAS software | Upper limb | Home | No | 19 | [92] | |
| LANR platform (Kinect plus Leap Motion) | Upper limb | Home | No | 9 | [93] | |
| Locomotor | VR cycling system (recumbent bike + screen VR) | Lower limb | Clinic | No | 8 | [94] |
| VR stepping exercise (screen-based) | Balance | Clinic | No | 20 | [95] | |
| CAVE-style VR treadmill | Lower limb | Clinic | No | 20 | [96] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cieślik, B. Virtual Reality Exergaming in Outpatient Stroke Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review and Clinician Roadmap. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207227
Cieślik B. Virtual Reality Exergaming in Outpatient Stroke Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review and Clinician Roadmap. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207227
Chicago/Turabian StyleCieślik, Błażej. 2025. "Virtual Reality Exergaming in Outpatient Stroke Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review and Clinician Roadmap" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207227
APA StyleCieślik, B. (2025). Virtual Reality Exergaming in Outpatient Stroke Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review and Clinician Roadmap. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207227






