Outcomes of Strabismus Surgery in Patients with Cranial Nerve Palsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
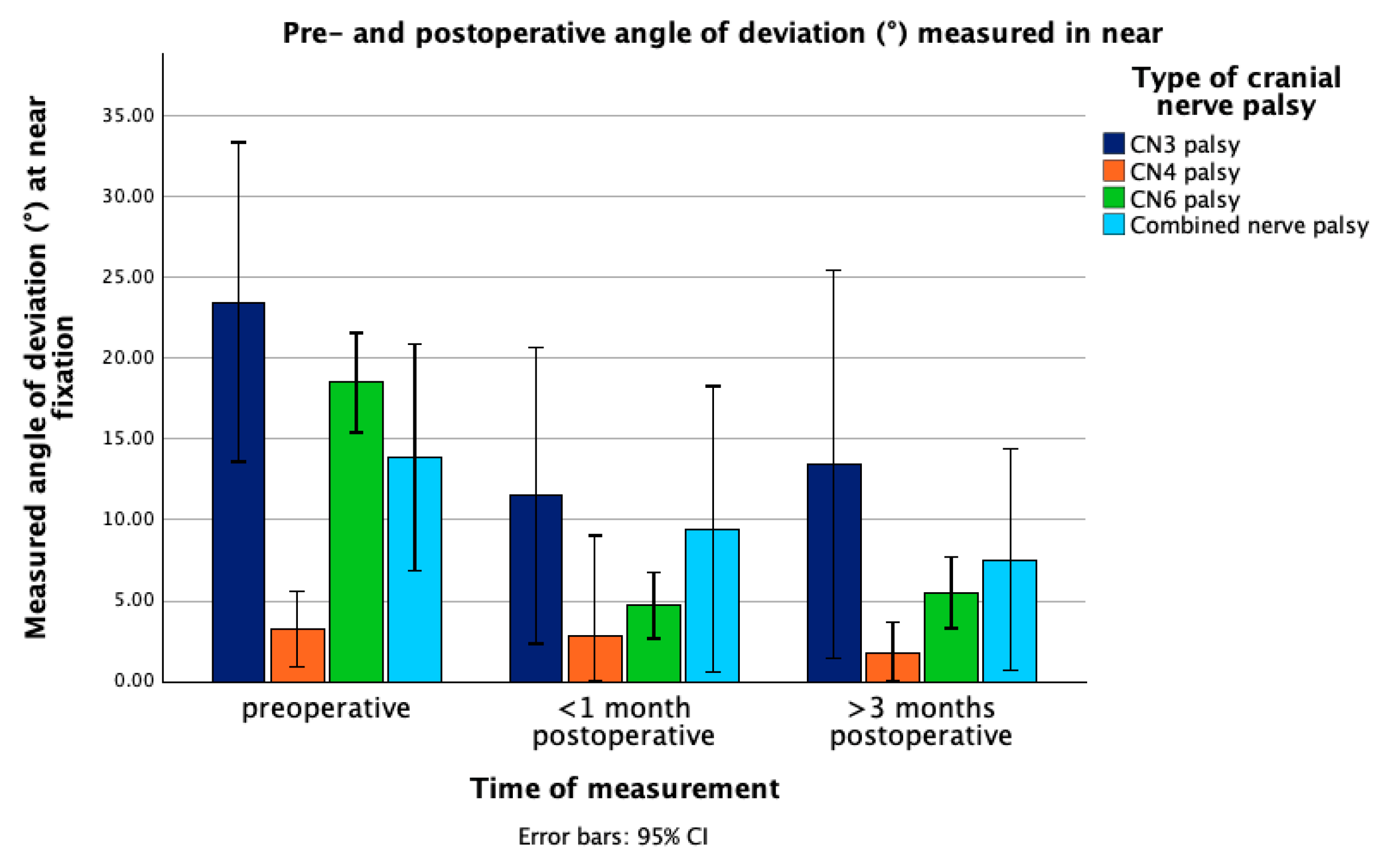
3.2. Change in Angle of Deviation
3.3. Change in Vertical Deviation
3.4. Change in Refractive Error
3.5. Change in Visual Acuity
3.6. Additional Operations
3.7. Multivariable Logistic Regression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOD | Angle of deviation |
| BCVA | Best-corrected visual acuity |
| CN3 | Third cranial nerve |
| CN4 | Fourth cranial nerve |
| CN6 | Sixth cranial nerve |
| D | Diopters |
| IO | Inferior oblique |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| LL | Lower limit |
| logMAR | logarithm of the minimal angle of resolution |
| LR | Lateral rectus |
| MR | Medial rectus |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PD | Prism diopters |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SO | Super oblique |
| UL | Upper limit |
| VA | Visual acuity |
| VD | Vertical deviation |
References
- Mocan, M.C.; Pastapur, A.; Kaufman, L. Etiology-Based Strabismus Classification Scheme for Pediatricians. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2022, 64, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.-H.; Lin, H.-S.; Lin, M.-C.; Sheu, S.-J. Acquired Paralytic Strabismus in Southern Taiwan. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2013, 76, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, A.V.; Repka, M.X. Ophthalmologic Outcome after Third Cranial Nerve Palsy or Paresis in Childhood. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 1999, 3, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, M.; Kido, A.; Miyake, M.; Tamura, H.; Kamei, T.; Wada, S.; Ueshima, H.; Nakao, S.; Yamamoto, A.; Suda, K.; et al. Lifetime Risk, Sex and Age Differences in Annual Incidence of Ocular Motor Cranial Nerve Palsy in Japan for 2019. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.H.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, J.Y.; Cho, B.-J. The Incidence and Etiology of Sixth Cranial Nerve Palsy in Koreans: A 10-Year Nationwide Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Borhani, M.; Tavakoli, M.; Salehirad, S. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Strabismus Treatment in Third Cranial Nerve Palsy during a 10-Year Period. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2014, 9, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yahalom, C.; Hunter, D.G.; Dagi, L.R. Strategies for Managing Strabismus from Oculomotor Nerve Palsy. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2023, 27, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farvardin, H.; Farvardin, M.; Koohestani, S. Combined Lateral Rectus Myectomy and Maximal Medial Rectus Resection in Complete Third Cranial Nerve Palsy. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. 2018, 7, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Merino, P.; Gutierrez, C.; de Liaño, P.G.; Srur, M. Long Term Outcomes of Strabismus Surgery for Third Nerve Palsy. J. Optom. 2019, 12, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Motlagh, M.; Naqvi, I.A. Neuroanatomy, Cranial Nerve 4 (Trochlear). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Brazis, P. Isolated Palsies of Cranial Nerves III, IV, and VI. Semin. Neurol. 2009, 29, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helveston, E.M.; Mora, J.S.; Lipsky, S.N.; Plager, D.A.; Ellis, F.D.; Sprunger, D.T.; Sondhi, N. Surgical Treatment of Superior Oblique Palsy. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1996, 94, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, C.; Gurnani, B.; Mohseni, M. Abducens Nerve Palsy. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, L.; Shen, T.; Qiu, X.; Yu, X.; Shen, H.; Yan, J. Supramaximal Horizontal Rectus Recession–Resection Surgery for Complete Unilateral Abducens Nerve Palsy. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 795665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, M.; Masoomian, B.; Mirmohammadsadeghi, A.; Sadeghi, M. A Review of Transposition Techniques for Treatment of Complete Abducens Nerve Palsy. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2021, 33, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBain, H.B.; Au, C.K.; Hancox, J.; MacKenzie, K.A.; Ezra, D.G.; Adams, G.G.W.; Newman, S.P. The Impact of Strabismus on Quality of Life in Adults with and without Diplopia: A Systematic Review. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2014, 59, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, O.H.; Nepstad, L. A Standardized Recession of the Inferior Oblique Extraocular Muscle—A Safe and Self-grading Surgical Procedure for Trochlear Nerve Palsy: A 10-year Material. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Zheng, J.; Yu, X. Long-Term Quality of Life in Adult Patients with Strabismus after Corrective Surgery Compared to the General Population. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, S.R.; Leske, D.A.; Kirgis, P.A.; Bradley, E.A.; Holmes, J.M. The Effects of Strabismus on Quality of Life in Adults. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 144, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpak, G.; Coskun, E.; Erbagci, I.; Bez, Y.; Okumus, S.; Oren, B.; Gurler, B. Effects of Corrective Surgery on Social Phobia, Psychological Distress, Disease-Related Disability and Quality of Life in Adult Strabismus Patients. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Congdon, N.; Yam, J.C.S.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, K.; Ma, D.; Chen, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, M. Alcohol Use and Positive Screening Results for Depression and Anxiety Are Highly Prevalent Among Chinese Children With Strabismus. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 157, 894–900.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uretmen, O.; Egrilmez, S.; Kose, S.; Pamukçu, K.; Akkin, C.; Palamar, M. Negative Social Bias against Children with Strabismus. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2003, 81, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, Q.; Capsec, J.; Arsène, S.; Pisella, P.J.; Grammatico-Guillon, L.; Khanna, R.K. Strabismus Outcomes after Surgery: The Nationwide SOS France Study. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2022, 260, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachenmayr, B.; Friedburg, D.; Buser, A. Auge—Brille—Refraktion; Georg Thieme Verlag KG: Stuttgart, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- de Camargo, G.B.; Hida, W.T.; Goldchmit, M.; Uesugui, C.F.; Souza-Dias, C.R. de Estrabismo Paralítico: Revisão de 24 Anos Da Santa Casa de São Paulo. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2007, 70, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.H.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, J.Y.; Cho, B.-J. The Incidence and Etiologies of Third Cranial Nerve Palsy in Koreans: A 10-Year Nationwide Cohort Study. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2020, 27, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörner, R.; Kassubek, J.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Ludolph, A.C. The Spectrum and Differential Diagnosis of Acquired Ocular Motor Nerve Palsies: A Clinical Study of 502 Patients. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 2140–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuljhele, S.; Dhiman, R.; Sharma, M.; Kusiyait, S.K.; Saxena, R.; Mahalingam, K.; Sharma, P. Acquired Ocular Motor Palsy: Current Demographic and Etiological Profile. Asia-Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 9, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.-A.; Oh, S.Y.; Min, J.-H.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, Y. Cause of Acquired Onset of Diplopia Due to Isolated Third, Fourth, and Sixth Cranial Nerve Palsies in Patients Aged 20 to 50 years in Korea: A High Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 407, 116546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, U.-C.; Kim, S.-J.; Hwang, J.-M.; Yu, Y.S. Clinical Features and Natural History of Acquired Third, Fourth, and Sixth Cranial Nerve Palsy. Eye 2008, 22, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srimanan, W. Outcomes and Factors Associated with Successful Strabismus Surgery for Abducens Nerve Palsies: A Retrospective Study and Literature Review. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2024, 18, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSahaf, E.; AlShamlan, F.T. Plication or Resection Combined with Antagonist Recession in Horizontal Strabismus. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. 2024, 13, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonwani, P.; Amitava, A.; Khan, A.; Gupta, S.; Grover, S.; Kumari, N. Plication as an Alternative to Resection in Horizontal Strabismus: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 65, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S. No Split, No Tenotomy Transposition Procedure for Complete Abducens Palsy. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 65, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.; Choi, J.; Kim, S.-J.; Yu, Y.S. Superior Rectus Muscle Recession for Residual Head Tilt after Inferior Oblique Muscle Weakening in Superior Oblique Palsy. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 26, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, P.; Escribano, J.; Gómez de Liaño, P.; Yela, R. Surgical Treatment of Superior Oblique Palsy: Predictors of Outcome. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 65, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y. Clinical Outcomes and Etiology of Acquired Sixth Cranial Nerve Palsy. Medicine 2022, 101, e29102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumuşak, E.; Yolcu, Ü.; Küçükevcilioğlu, M.; Diner, O.; Mutlu, F.M. Outcomes of Unilateral Inferior Oblique Myectomy Surgery in Inferior Oblique Overaction Due to Superior Oblique Palsy. Turk. Oftalmol. Derg. 2016, 46, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, M.R.; Bayat, R.; Mirmohammadsadeghi, A.; Mirshahi, R. Paradoxical Head Tilt in Unilateral Traumatic Superior Oblique Palsy. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2017, 29, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushner, B.J. The Influence of Head Tilt on Ocular Torsion in Patients with Superior Oblique Muscle Palsy. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2009, 13, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghofaili, R.S.; Sesma, G.; Khandekar, R. Strabismus Surgery Outcomes and Their Determinants in Patients with Chronic Sixth Nerve Palsy. Middle East Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 28, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.C.; Melson, A.T.; Bryant, J.C.; Ding, K.; Farris, B.K.; Siatkowski, R.M. Surgical Outcomes Following Strabismus Surgery for Abducens Nerve Palsy. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2023, 27, 142.e1–142.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, A.; Fallahi, M.-R.; Abrishami, M.; Salour, H.; Aletaha, M. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Treatment for Fourth Nerve Palsy. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2010, 5, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, M.M. The Stabilization of Postoperative Exo-Drift in Intermittent Exotropia after Surgical Treatment. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 30, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Etiologies | CN3 Palsy (n = 12) | CN4 Palsy (n = 8) | CN6 Palsy (n = 30) | Combined Palsy (n = 7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congenital | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Acquired | Inflammation | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Trauma | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | |
| Brain neoplasm | 4 | 1 | 12 | 2 | |
| Vascular disease | 4 | 0 | 6 | 4 | |
| Unknown | 1 | 1 | 6 | 0 |
| Surgical Procedure | CN3 Palsy (n = 12) | CN4 Palsy (n = 8) | CN6 Palsy (n = 30) | Combined Palsy (n = 7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR recession & LR plication | 20 | 1 | ||
| LR recession & MR plication | 9 | 1 | ||
| Horizontal 2-muscle surgery with oblique muscle procedure | 2 | 1 | ||
| MR recession | 1 | |||
| LR plication | 5 | 2 | ||
| LR recession with oblique muscle recession | 1 | |||
| LR plication with oblique muscle plication | 2 | |||
| IO recession | 5 | |||
| SO plication | 3 | 1 | ||
| Hummelsheim procedure | 3 |
| Type of Strabismus | Preoperative AOD (°) | MR Recession/Plication * (mm) | LR Recession/Plication * (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN3 palsy | 10 | 5.5 | 8 |
| 15 | 5.5 | 9 | |
| 20 | 6 | 8 | |
| 50 | 6 | 12 | |
| CN4 palsy | 2–14 VD | IO Recession: 11–13 mm with additional anteriorization (1–2 mm) | |
| CN6 palsy | 5 | 4.5 | 9.5 |
| 15 | 3 | 7 | |
| 20 | 4 | 8.5 | |
| 30 | 5 | 10 | |
| CN3 Palsy (n = 12) | CN4 Palsy (n = 8) | CN6 Palsy (n = 30) | Combined Palsy (n = 7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic factors | ||||
| Age at time of surgery (years) | 39.36 ± 27.65 | 32.21 ± 21.49 | 43.27 ± 22.38 | 46.49 ± 21.62 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 7 (58.33%) | 5 (62.5%) | 16 (53.33%) | 2 (28.57%) |
| Female | 5 (41.67%) | 3 (37.5%) | 14 (46.67%) | 5 (71.43%) |
| Clinical characteristics | ||||
| Type of palsy | ||||
| Partial | 3 (25%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (3.33%) | 1 (14.29%) |
| Complete | 9 (75%) | 8 (100%) | 29 (96.67%) | 3 (42.86%) |
| Both * | 3 (42.86%) | |||
| Preoperative AOD (°) | ||||
| Near | 23.48 ± 14.7 | 3.24 ± 2.22 | 18.5 ± 8.25 | 13.89 ± 7.57 |
| Distance | 20.93 ± 14.24 | 3.62 ± 2.7 | 18.48 ± 7.19 | 15.77 ± 7.03 |
| Postoperative AOD at first follow-up (°) | ||||
| Near | 11.5 ± 12.8 | 2.86 ± 2.49 | 4.73 ± 4.74 | 9.43 ± 8.44 |
| Distance | 10.57 ± 14.72 | 2 ± 2.02 | 4.35 ± 4.29 | 6.86 ± 5.77 |
| Postoperative AOD at second follow-up (°) | ||||
| Near | 13.44 ± 15.61 | 1.71 ± 1.23 | 5.52 ± 5.12 | 7.54 ± 5.53 |
| Distance | 12.14 ± 17.15 | 1.43 ± 0.4 | 5.97 ± 4.47 | 7.71 ± 7.94 |
| Preoperative refractive error (D) | 0.19 ± 1.99 | −0.97 ± 1.4 | −0.75 ± 2.94 | 0.27 ± 1.01 |
| Preoperative VA (logMAR (IQR)) | 0.09 (0.43) | 0.0 (0.07) | 0.08 (0.15) | 0.05 (0.18) |
| Preoperative Ptosis | 9 (75%) | - | - | 1 (14.29%) |
| Preoperative Diplopia | 8 (66.67%) | 6 (75.00%) | 12 (40%) | 4 (57.14%) |
| Preoperative head tilt | 2 (16.66%) | 4 (50%) | 4 (13.33%) | - |
| Surgical success | 7 (58.33%) | 7 (87.5%) | 27 (90%) | 5 (71.43%) |
| Failure | 5 (41.67%) | 1 (12.5%) | 3 (10%) | 2 (28.57%) |
| Parameters | p-Value | OR | 95% LL | 95% UL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.314 | 1.019 | 0.983 | 1.056 | |
| Gender | 0.902 | 0.894 | 0.150 | 5.322 | |
| Preoperative AOD | 0.149 | 0.912 | 0.804 | 1.034 | |
| Type of nerve palsy (with CN6 palsy as reference) | CN3 palsy | 0.061 | 0.143 | 0.019 | 1.097 |
| CN4 palsy | 0.201 | 0.093 | 0.002 | 3.535 | |
| Combined palsy | 0.123 | 0.138 | 0.011 | 1.708 | |
| Etiology (with neoplasm as reference) | Vascular disease | 0.928 | 0.899 | 0.089 | 9.101 |
| Trauma | 0.880 | 1.191 | 0.123 | 11.509 | |
| Other | 0.628 | 0.545 | 0.047 | 6.345 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hinterhuber, L.; Rezar-Dreindl, S.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Stifter, E. Outcomes of Strabismus Surgery in Patients with Cranial Nerve Palsy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207221
Hinterhuber L, Rezar-Dreindl S, Schmidt-Erfurth U, Stifter E. Outcomes of Strabismus Surgery in Patients with Cranial Nerve Palsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207221
Chicago/Turabian StyleHinterhuber, Laetitia, Sandra Rezar-Dreindl, Ursula Schmidt-Erfurth, and Eva Stifter. 2025. "Outcomes of Strabismus Surgery in Patients with Cranial Nerve Palsy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207221
APA StyleHinterhuber, L., Rezar-Dreindl, S., Schmidt-Erfurth, U., & Stifter, E. (2025). Outcomes of Strabismus Surgery in Patients with Cranial Nerve Palsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207221






