Visual Function Characteristics in STXBP1 Epileptic Encephalopathy Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Recruitment and Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Ophthalmological Examination
2.4. Orthoptic Examination
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Demographics
4.2. Pregnancy and Perinatal History
4.3. Initial Symptoms and Diagnosis
4.4. Ophthalmological Findings
4.5. Refractive Errors
4.6. Orthoptic Parameters
4.7. Analysis of the Relationship Between Selected Visual Parameters and Age
4.8. Mobility Status and Accommodative Parameters
4.9. Antiepileptic Treatment and Visual Parameters
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spoto, G.; Valentini, G.; Saia, M.C.; Butera, A.; Amore, G.; Salpietro, V.; Nicotera, A.G.; Di Rosa, G. Synaptopathies in developmental and epileptic encephalopathies: A focus on pre-synaptic dysfunction. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 826211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindley, N.; Sanchez Avila, A.; Henstridge, C. Bringing synapses into focus: Recent advances in synaptic imaging and mass-spectrometry for studying synaptopathy. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1130198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michetti, C.; Falace, A.; Benfenati, F.; Fassio, A. Synaptic genes and neurodevelopmental disorders: From molecular mechanisms to developmental strategies of behavioral testing. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 173, 105856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamberger, H.; Nikanorova, M.; Willemsen, M.H.; Accorsi, P.; Angriman, M.; Baier, H.; Benkel-Herrenbrueck, I.; Benoit, V.; Budetta, M.; Caliebe, A.; et al. STXBP1 encephalopathy. A neurodevelopmental disorder including epilepsy. Neurology 2016, 86, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanoue, V.; Chai, Y.J.; Brouillet, J.Z.; Weckhuysen, S.; Palmer, E.E.; Collins, B.M.; Meunier, F.A. STXBP1 encephalopathy. Connecting neurodevelopmental disorders with α-synucleinopathies? Neurology 2019, 93, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhage, M.; Maia, A.S.; Plomp, J.J.; Brussaard, A.B.; Heeroma, J.H.; Vermeer, H.; Toonen, R.F.; Hammer, R.E.; van den, T.K.; Berg Missler, M.; et al. Synaptic assembly of the brain in the absence of neurotransmitter secretion. Science 2000, 287, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, J.; Parthasarathy, S.; Ruggiero, S.M. Assessing the landscape of STXBP1-related disorders in 534 individuals. Brain 2021, 145, 1668–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, D.; Guiberson, N.G.L.; Burré, J. STXBP1 encephalopathies: Clinical spectrum, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic strategies. J. Neurochem. 2020, 157, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Palmero, A.; Boerrigter, M.M.; Gómez-Andrés, D.; Aldinger, K.A.; Marcos-Alcalde, Í.; Popp, B.; Everman, D.B.; Lovgren, A.K.; Arpin, S.; Bahrambeigi, V.; et al. DLG4-related synaptopathy: A new rare brain disorder. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakakhel, M.; Tebbe, L.; Makia, M.S.; Conley, S.M.; Sherry, D.M.; Al-Ubaidi, M.R.; Naash, M.I. Syntaxin 3 is essential for photoreceptor outer segment protein trafficking and survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 20615–20624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Guo, A.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X. p.His16Arg of STXBP1 (MUNC18-1) associated with syntaxin 3B causes autosomal dominant congenital nystagmus. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 591781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simiera, J.; Loba, P. Cyclocheck: A new web-based software for the assessment of objective cyclodeviation. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2017, 21, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, D.A.; Steel, J.M.; Valle, D. Identification and characterization of the human ortholog of rat STXBP1, a protein implicated in vesicle trafficking and neurotransmitter release. Genomics 1998, 48, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piro-Mégy, C.; Sarzi, E.; Tarrés-Solé, A.; Péquignot, M.; Hensen, F.; Quilès, M.; Manes, G.; Chakraborty, A.; Sénéchal, A.; Bocquet, B.; et al. Dominant mutations in mtDNA maintenance gene SSBP1 cause optic atrophy and foveopathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wutz, K.; Sauer, C.; Zrenner, E.; Lorenz, B.; Alitalo, T.; Broghammer, M.; Hergersberg, M.; Chapelle, A.D.; Weber, B.H.; Wissinger, B.; et al. Thirty distinct CACNA1F mutations in 33 families with incomplete type of XLCSNB and Cacna1f expression profiling in mouse retina. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 10, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, D.; Tom Dieck, S.; Ammermüller, J.; Regus-Leidig, H.; Gundelfinger, E.D.; Brandstätter, J.H. Structural and functional remodeling in the retina of a mouse with a photoreceptor synaptopathy: Plasticity in the rod and degeneration in the cone system. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lim, H.T. Ocular torsion among patients with intermittent exotropia: Relationships with disease severity factors. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 155, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengwiler, F.; Rappoport, D.; Jaggi, G.P.; Landau, K.; Traber, G.L. Reliability of cyclotorsion measurements using scanning laser ophthalmoscopy imaging in healthy subjects: The CySLO study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simiera, J.; Ordon, A.J.; Loba, P. Objective cyclodeviation measurement in normal subjects by means of Cyclocheck® application. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinci, A.; Oner, O.; Bozkurt, O.H.; Guven, A.; Degerliyurt, A.; Munir, K. Refractive errors and ocular findings in children with intellectual disability: A controlled study. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2008, 12, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, T.; Lawrence, L.; Mayo-Ortega, L.; Oyama-Ganiko, R.; Schroeder, S. Refractive error and ocular findings among infants and young children with severe problem behavior and developmental disabilities. J. Ment. Health Res. Intellect. Disabil. 2018, 11, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mao, J.; Luo, R.; Li, F.; Munoz, S.R.; Ellwein, L.B. The progression of refractive error in school-age children: Shunyi district, China. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 134, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, E.; Czepita, D. Eye development in children. Part I. Eyeball dimensions. Acta Ophthalmol. Pol. 2010, 112, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, S.C.; Kifley, A.; Rose, K.A.; Morgan, I.; Heller, G.Z.; Mitchell, P. Astigmatism and its components in 6-year-old children. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czepita, D.; Mojsa, A.; Ustianowska, M. Prevalence of myopia and hyperopia in a population of Polish schoolchildren. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2001, 27, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, A.R.; Stephenson, T.J.; Johnson, A.; Tobin, M.J.; Ratib, S.; Fielder, A.R. Change of refractive state and eye size in children of birth weight less than 1701 g. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 90, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrado, P.; Suárez, J.; García-Sánchez, F.A.; Usón, E. Refractive errors in children with cerebral palsy, psychomotor retardation, and other non-cerebral palsy neuromotor disabilities. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 1999, 41, 396–403. [Google Scholar]
- Levinsen, M.; Børresen, M.L.; Roos, L.; Grønskov, K.; Kessel, L. Causes of poor eye contact in infants: A population-based study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021, 21, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bagdady, M.; Stewart, R.E.; Watts, P.; Murphy, P.J.; Woodhouse, J.M. Bifocals and Down’s syndrome: Correction or treatment? Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2009, 29, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullaj, R.; Dyet, L.; Mitra, S.; Bunce, C.; Clarke, C.S.; Saunders, K.; Dale, N.; Horwood, A.; Williams, C.; Tracy, H.S.; et al. Effectiveness of early spectacle intervention on visual outcomes in babies at risk of cerebral visual impairment: A parallel group, open-label, randomized clinical feasibility trial protocol. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e059946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, U.H.; Shetty, N.; Anhar, S.; Mayya, R. Peripheral visual field defect of vigabatrin in pediatric epilepsy: A review. Egypt J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2023, 59, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, J.M.; Robson, C.R.; Jones, A.L.; Cunliffe, I.A.; Smith, P.E. Detecting vigabatrin toxicity by imaging of the retinal nerve fiber layer. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, D. Attenuation of retinal nerve fibre layer in people with epilepsy receiving valproate: An observational study using OCT. Epilepsy Res. 2019, 154, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H.E.; Jain, P.; RamachandranNair, R.; Jones, K.C.; Whitney, R. Genetic Advancements in Infantile Epileptic Spasms Syndrome and Opportunities for Precision Medicine. Genes 2024, 15, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.A.; Knupp, K.G. Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome: Current Treatments, Novel Therapeutics, and Future Directions. Neurotherapeutics 2023, 20, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, D.; Kenny, A.; Eley, S.; McKechanie, A.G.; Stanfield, A.C. Visual social attention in SYNGAP1-related intellectual disability. Autism Res. 2024, 17, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tümer, Z.; Dye, T.J.; Prada, C.; White-Brown, A.M.; MacKenzie, A.; Levy, A.M. DLG4-Related Synaptopathy. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993–2025; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK592682/ (accessed on 12 July 2025).

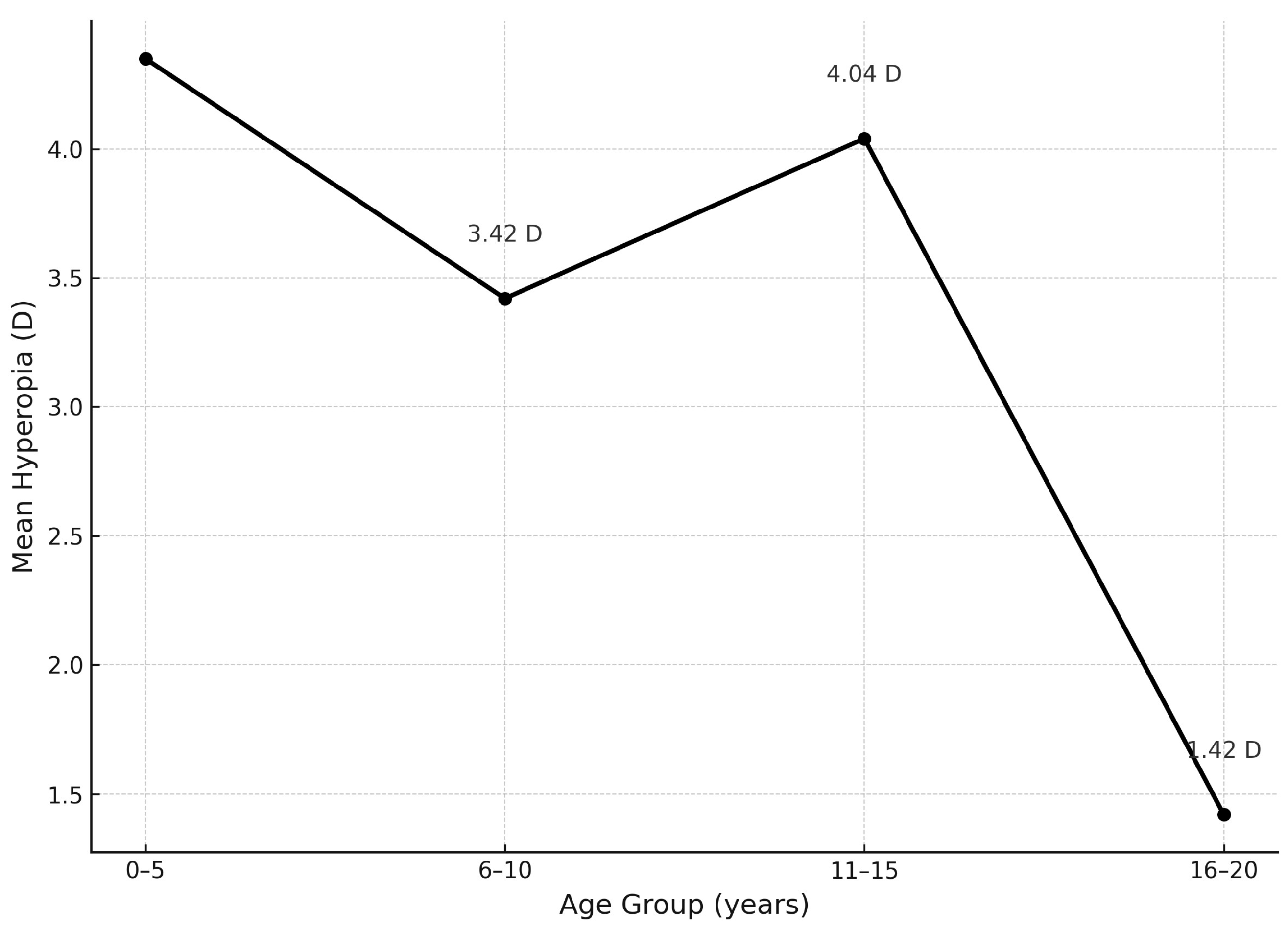
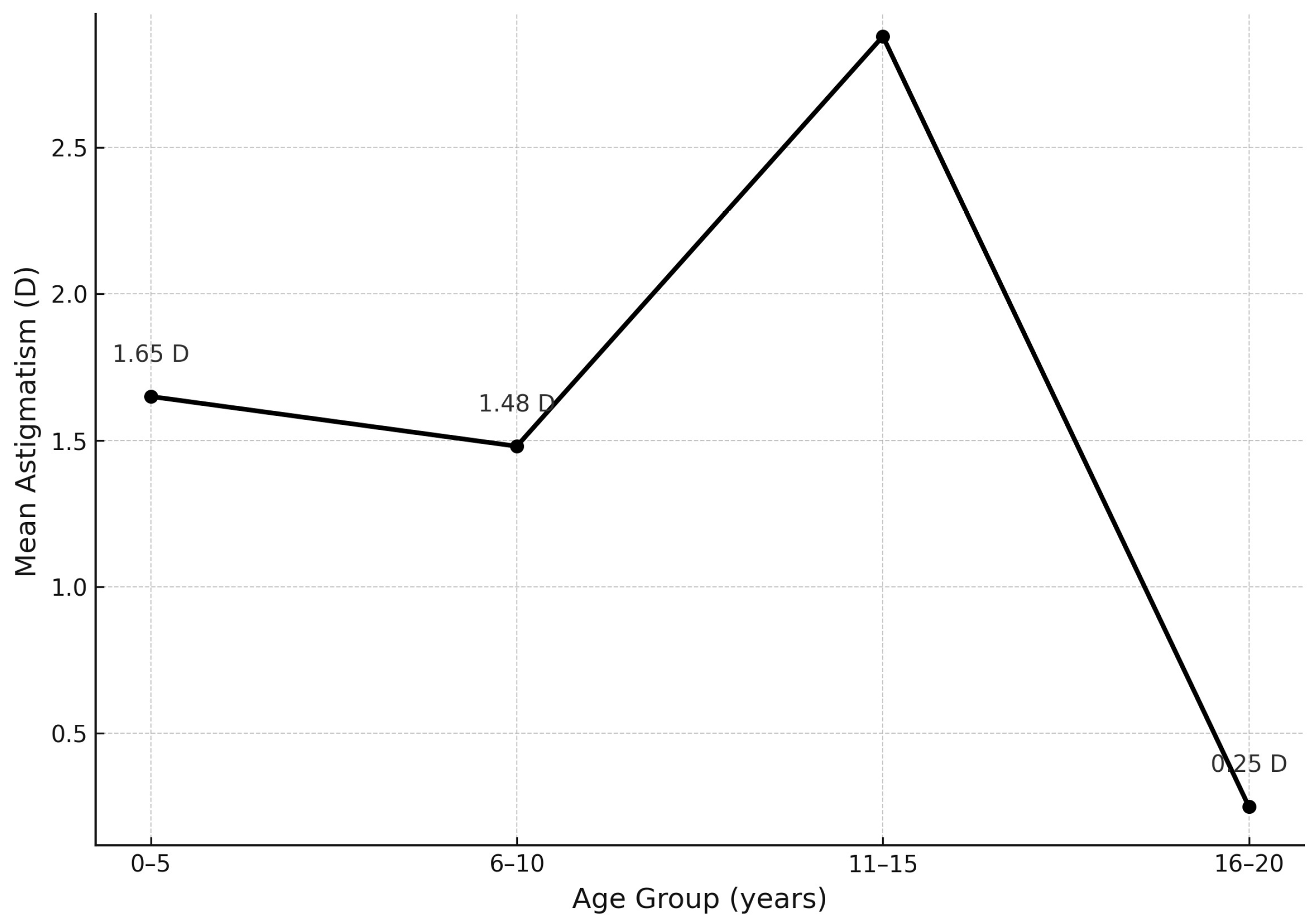
| Refractive Error (D) | Hyperopia OD (%) | Hyperopia OS (%) | Hyperopia Mean OD/OS (%) | Myopia OD (%) | Myopia OS (%) | Myopia Mean OD/OS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 to 2.50 | 26.9% (n = 7) | 38.5% (n = 10) | 32.7% | 3.8% (n = 1) | 3.8% (n = 1) | 3.8% |
| 2.75 to 4.0 | 19.2% (n = 5) | 34.6% (n = 9) | 26.9% | 0% (n = 0) | 3.8% (n = 1) | 1.9% |
| Above 4.25 | 15.4% (n = 4) | 19.2% (n = 5) | 17.3% | 3.8% (n = 1) | 0% (n = 0) | 1.9% |
| Total | 61.5% (n = 16) | 92.3% (n = 24) | 76.9% | 7.7% (n = 2) | 7.7% (n = 2) | 7.7% |
| Refractive Error (D) | Astigmatism OD (%)/n | Astigmatism OS (%)/n | Astigmatism Mean OD/OS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 to 1.00 | 42.3% (n = 11) | 53.8% (n = 14) | 48% |
| 1.25 to 2.5 | 30.8% (n = 8) | 11.5% (n = 3) | 21.2% |
| Above 2.75 | 23.1% (n = 6) | 30.8% (n = 8) | 27% |
| Total | 96.2% (n = 25) | 96.2% (n = 25) | 96.2% |
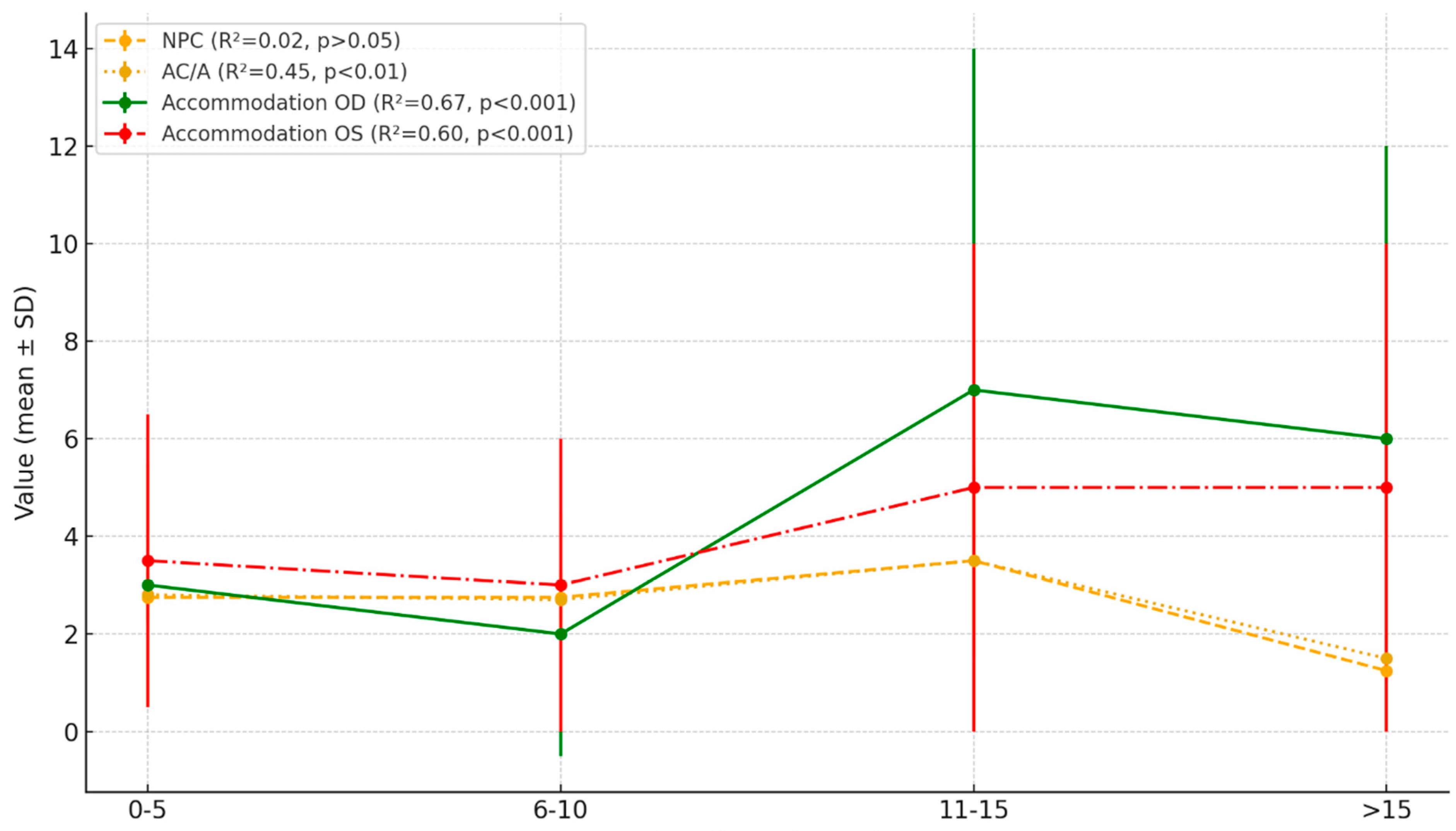
| Parameter | Mean (SD) | Regression Trend | R2 | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPC | 21.43 (15.3) | 0.15 | 0.02 | 1.25 | >0.05 |
| AC/A | 1.16 (1.05) | −0.15 | 0.45 | 7.45 | <0.01 |
| Dynamic Retinoscopy OD | 2.63 (1.24) | −0.13 | 0.67 | 10.23 | <0.001 |
| Dynamic Retinoscopy OS | 2.68 (1.31) | −0.12 | 0.60 | 8.15 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosa, A.; Nowakowska, D.; Rosa, P.; Simiera, J.; Gliniany, A.; Zawadka, M.; Szczałuba, K.; Przyslo, L.; Szymańska, K.; Loba, P.; et al. Visual Function Characteristics in STXBP1 Epileptic Encephalopathy Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196840
Rosa A, Nowakowska D, Rosa P, Simiera J, Gliniany A, Zawadka M, Szczałuba K, Przyslo L, Szymańska K, Loba P, et al. Visual Function Characteristics in STXBP1 Epileptic Encephalopathy Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196840
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosa, Agnieszka, Dominika Nowakowska, Piotr Rosa, Justyna Simiera, Andrzej Gliniany, Michał Zawadka, Krzysztof Szczałuba, Lukasz Przyslo, Krystyna Szymańska, Piotr Loba, and et al. 2025. "Visual Function Characteristics in STXBP1 Epileptic Encephalopathy Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196840
APA StyleRosa, A., Nowakowska, D., Rosa, P., Simiera, J., Gliniany, A., Zawadka, M., Szczałuba, K., Przyslo, L., Szymańska, K., Loba, P., Gawęcki, M., & Pojda-Wilczek, D. (2025). Visual Function Characteristics in STXBP1 Epileptic Encephalopathy Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196840








