Are We Ready for Pseudotumors in Total Ankle Arthroplasty? A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
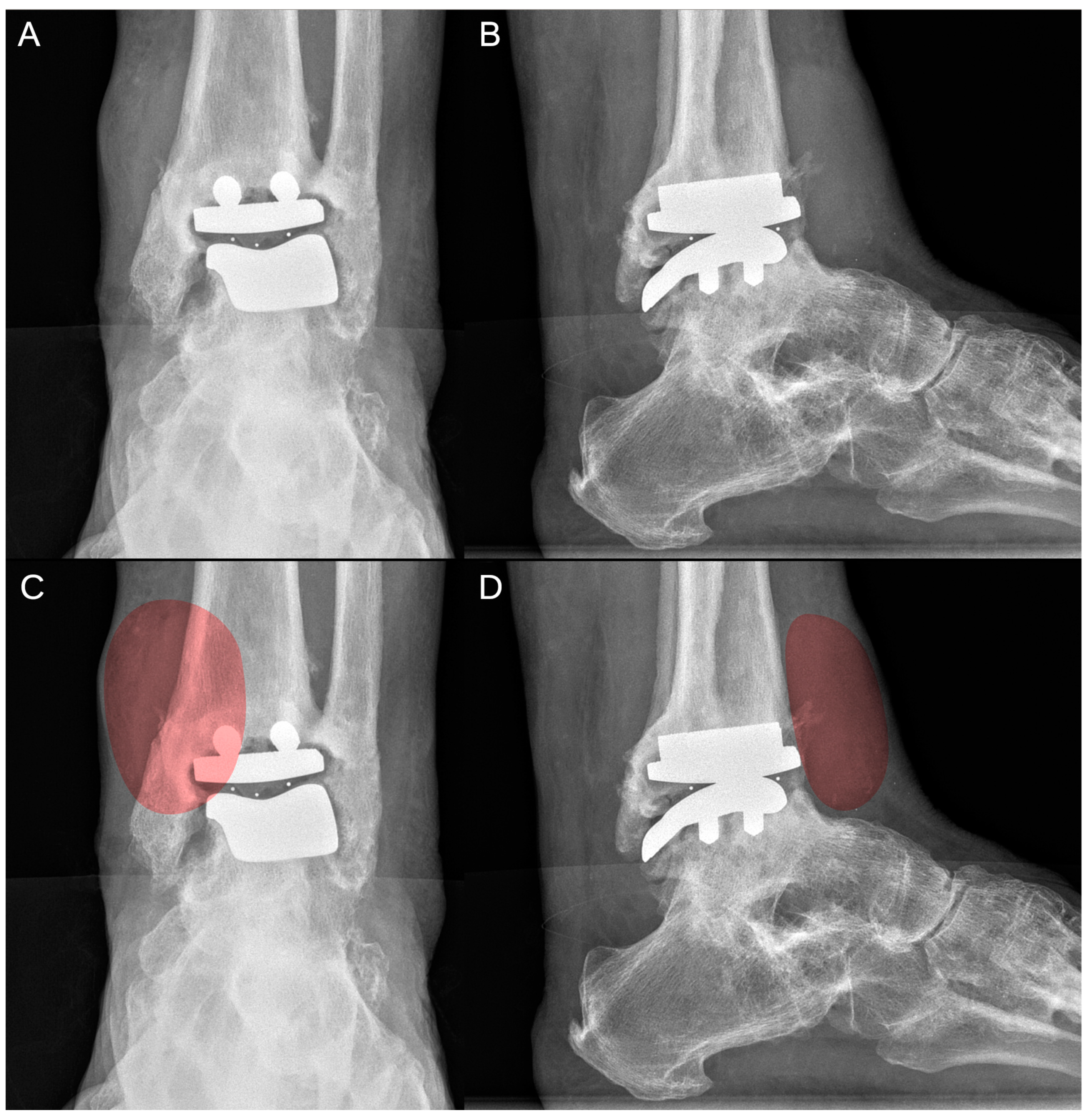
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
3.1. Diagnosis
3.2. Terminology and Pathogenesis
3.3. Pseudotumor-Related Factor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, M.S.; Mathson, L.; Andrews, C.; Wiese, D.; Fritz, J.M.; Jimenez, A.E.; Law, B. Long-term Outcomes After Total Ankle Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2024, 9, 24730114241294070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielli, S.O.; Mazzotti, A.; Artioli, E.; Arceri, A.; Sgubbi, F.; Langone, L.; Abdi, P.; Faldini, C. Radiological Landmarks for Joint Line Level in Challenging Total Ankle Arthroplasty. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faldini, C.; Mazzotti, A.; Langone, L.; Arceri, A.; Bonelli, S.; Zielli, S.O.; Artioli, E. Custom-made total ankle arthroplasty with patient-specific instrumentation for severe bone loss conditions: A case series. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2023, 34, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzotti, A.; Arceri, A.; Zielli, S.; Bonelli, S.; Viglione, V.; Faldini, C. Patient-specific instrumentation in total ankle arthroplasty. World J. Orthop. 2022, 13, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arceri, A.; Abdi, P.; Mazzotti, A.; Zielli, S.O.; Artioli, E.; Langone, L.; Sgubbi, F.; Faldini, C. Standard Total Ankle Arthroplasty vs. Patient-Specific Instrumentation: A Comparative Study. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermus, J.P.; Voesenek, J.A.; Van Gansewinkel, E.H.E.; Witlox, M.A.; Poeze, M.; Arts, J.J. Complications following total ankle arthroplasty: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Foot Ankle Surg. 2022, 28, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catelas, I.; Lehoux, E.A.; Ning, Z.; Figeys, D.; Baskey, S.J.; Beaulé, P.E. Differential proteomic analysis of synovial fluid from hip arthroplasty patients with a pseudotumor vs. Periprosthetic osteolysis. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, H.; Glyn-Jones, S.; McLardy-Smith, P.; Gundle, R.; Whitwell, D.; Gibbons, C.L.M.; Ostlere, S.; Athanasou, N.; Gill, H.S.; Murray, D.W. Pseudotumours associated with metal-on-metal hip resurfacings. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2008, 90, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrogenis, A.F.; Nomikos, G.N.; Sakellariou, V.I.; Karaliotas, G.I.; Kontovazenitis, P.; Papagelopoulos, P.J. Wear debris pseudotumor following total knee arthroplasty: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2009, 3, 9304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, H.; Vlychou, M.; Whitwell, D.; Crook, D.; Luqmani, R.; Ostlere, S.; Murray, D.W.; Athanasou, N.A. Necrotic granulomatous pseudotumours in bilateral resurfacing hip arthoplasties: Evidence for a type IV immune response. Virchows Arch. 2008, 453, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendra, G.; Pandit, H.; Kliskey, K.; Murray, D.; Gill, H.S.; Athanasou, N. Necrotic and inflammatory changes in metal-on-metal resurfacing hip arthroplasties: Relation to implant failure and pseudotumor formation. Acta Orthop. 2009, 80, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Veen, H.C.; Reininga, I.H.F.; Zijlstra, W.P.; Boomsma, M.F.; Bulstra, S.K.; Van Raay, J.J.A.M. Pseudotumour incidence, cobalt levels and clinical outcome after large head metal-on-metal and conventional metal-on-polyethylene total hip arthroplasty: Mid-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Bone Jt. J. 2015, 97, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benevenia, J.; Lee, F.Y.-I.; Buechel, F.; Parsons, J.R. Pathologic supracondylar fracture due to osteolytic pseudotumor of knee following cementless total knee replacement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 43, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivananthan, S.; Pirapat, R.; Goodman, S.B. A Rare Case of Pseudotumor Formation following Total Knee Arthroplasty. Malays. Orthop. J. 2015, 9, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhry, M.; Dipane, M.V.; McPherson, E.J. Periosteal pseudotumor in complex total knee arthroplasty resembling a neoplastic process. World J. Orthop. 2018, 9, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurmis, A.P.; Herman, A.; McIntyre, A.R.; Masri, B.A.; Garbuz, D.S. Pseudotumors and High-Grade Aseptic Lymphocyte-Dominated Vasculitis-Associated Lesions Around Total Knee Replacements Identified at Aseptic Revision Surgery: Findings of a Large-Scale Histologic Review. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 2434–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.J.; Brooke, B.T.; Sturdee, S. A wear debris cyst following S.T.A.R. total ankle replacement—Surgical management. Foot Ankle Surg. 2009, 15, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haston, S.; Langton, D.; Townshend, D.; Bhalekar, R.; Joyce, T. Metal debris release is commonly seen from explanted total ankle replacements. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 144, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadossi, M.; Chiarello, E.; Savarino, L.; Mazzotti, A.; Tedesco, G.; Greco, M.; Giannini, S. Fast growing pseudotumour in a hairdresser after metal-on-metal hip resurfacing: A case report. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cristofaro, C.; Pinsker, E.B.; Halai, F.; Wolfstadt, J.; Daniels, T.R.; Halai, M. Metal hypersensitivity in foot & ankle orthopaedic surgery: A systematic review. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2023, 44, 102249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.Z.W.; Schalock, P.C. Metal Hypersensitivity Reactions to Orthopedic Implants. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 7, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasio, A.T.; Balu, A.R.; Johnson, L.; Crook, B.; Parekh, S.G. Metal Hypersensitivity Following Total Ankle Arthroplasty: Case Series and Literature Review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2023, 23, 19386400231162419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, S.; Romagnoli, M.; O’Connor, J.J.; Catani, F.; Nogarin, L.; Magnan, B.; Malerba, F.; Massari, L.; Guelfi, M.; Milano, L.; et al. Early Clinical Results of the BOX Ankle Replacement Are Satisfactory: A Multicenter Feasibility Study of 158 Ankles. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2011, 50, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.-M.; Ostlere, S.J.; McLardy-Smith, P.; Athanasou, N.A.; Gill, H.S.; Murray, D.W. “Asymptomatic” Pseudotumors After Metal-on-Metal Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2011, 26, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.J.; Satchithananda, K.; Liddle, A.D.; Sabah, S.A.; McRobbie, D.; Henckel, J.; Cobb, J.P.; Skinner, J.A.; Mitchell, A.W. Pseudotumors in Association with Well-Functioning Metal-on-Metal Hip Prostheses: A Case-Control Study Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2012, 94, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grammatopolous, G.; Pandit, H.; Kwon, Y.-M.; Gundle, R.; McLardy-Smith, P.; Beard, D.J.; Murray, D.W.; Gill, H.S. Hip resurfacings revised for inflammatory pseudotumour have a poor outcome. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2009, 91, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.L.; Morrison, J.J. Hip Arthroplasty Pseudotumors: Pathogenesis, Imaging, and Clinical Decision Making. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2016, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaksonen, I.; Galea, V.P.; Donahue, G.S.; Matuszak, S.J.; Muratoglu, O.; Malchau, H. The Cobalt/Chromium Ratio Provides Similar Diagnostic Value to a Low Cobalt Threshold in Predicting Adverse Local Tissue Reactions in Patients With Metal-on-Metal Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 3020–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, P.; Ebramzadeh, E.; Nelson, S.; Takamura, K.; De Smet, K.; Amstutz, H.C. Histological Features of Pseudotumor-like Tissues From Metal-on-Metal Hips. Clin. Orthop. 2010, 468, 2321–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perino, G.; Ricciardi, B.F.; Jerabek, S.A.; Martignoni, G.; Wilner, G.; Maass, D.; Goldring, S.R.; Purdue, P.E. Implant based differences in adverse local tissue reaction in failed total hip arthroplasties: A morphological and immunohistochemical study. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2014, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.-M.; Glyn-Jones, S.; Simpson, D.J.; Kamali, A.; McLardy-Smith, P.; Gill, H.S.; Murray, D.W. Analysis of wear of retrieved metal-on-metal hip resurfacing implants revised due to pseudotumours. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2010, 92, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvie, P.; Giele, H.; Fang, C.; Ansorge, O.; Ostlere, S.; Gibbons, M.; Whitwell, D. The Treatment of Femoral Neuropathy Due to Pseudotumour Caused by Metal-On-Metal Resurfacing Arthroplasty. HIP Int. 2008, 18, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Sun, W.; Shen, J.; Ma, X.; Cai, Z.; Hua, Y. Inflammatory pseudotumor around metal-on-polyethylene total hip arthroplasty in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: Description of two cases and review of literature. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastel, M.; Boisvert, A.; Moore, R.; Sutherland, F.; Powell, J. Metallosis following hip arthroplasty: Two case reports. J. Med. Case Rep. 2022, 16, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langton, D.J.; Jameson, S.S.; Joyce, T.J.; Hallab, N.J.; Natu, S.; Nargol, A.V.F. Early failure of metal-on-metal bearings in hip resurfacing and large-diameter total hip replacement: A CONSEQUENCE OF EXCESS WEAR. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2010, 92, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.H. Osteolysis and particle disease in hip replacement: A review. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1994, 65, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.J.; Shanbhag, A.; Glant, T.T.; Black, J.; Galante, J.O. Wear Debris in Total Joint Replacements. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 1994, 2, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willert, H.-G.; Buchhorn, G.H.; Fayyazi, A.; Flury, R.; Windler, M.; Köster, G.; Lohmann, C.H. Metal-on-Metal Bearings and Hypersensitivity in Patients with Artificial Hip Joints: A Clinical and Histomorphological Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2005, 87, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharplin, P.; Wyatt, M.C.; Rothwell, A.; Frampton, C.; Hooper, G. Which is the best bearing surface for primary total hip replacement? A New Zealand Joint Registry study. HIP Int. 2018, 28, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadossi, M.; Mazzotti, A.; Baldini, N.; Giannini, S.; Savarino, L. New couplings, old problems: Is there a role for ceramic-on-metal hip arthroplasty? J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 104, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadossi, M.; Tedesco, G.; Savarino, L.; Baldini, N.; Mazzotti, A.; Greco, M.; Giannini, S. Effect of acetabular cup design on metal ion release in two designs of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Cooper, H.; Della Valle, C.J.; Berger, R.A.; Tetreault, M.; Paprosky, W.G.; Sporer, S.M.; Jacobs, J.J. Corrosion at the Head-Neck Taper as a Cause for Adverse Local Tissue Reactions After Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg.-Am. Vol. 2012, 94, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.H. Edge Loading Has a Paradoxical Effect on Wear in Metal-on-Polyethylene Total Hip Arthroplasties. Clin. Orthop. 2012, 470, 3077–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.; Rajaee, S.; Brien, E.; Paiement, G.D. Inflammatory pseudotumor after ceramic-on-ceramic total hip arthroplasty. Arthroplast. Today 2017, 3, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thever, Y.; Goh, L.; Yau Li, S.F.; Siu Ling, D.H.; Rong Chia, S.Y.; Ing How, M. Adverse Local Tissue Reaction and Osteolysis After Ceramic-on-Ceramic Total Hip Arthroplasty. Arthroplast. Today 2024, 30, 101584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciatti, C.; Maniscalco, P.; Bosio, S.; Puma Pagliarello, C.; Bianchi, G.; Quattrini, F. Pseudotumor from ceramic-on-ceramic total hip arthroplasty. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2024, 116, 109374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahan, I.; Anagnostakos, K. Metallosis after knee replacement: A review. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2020, 140, 1791–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Lugo, N.J.; Serrano-Boett, P.S.; Acosta-Julbe, J.; Otero-Lopez, A.; Bibiloni-Rodríguez, J. Pseudotumor in total knee revision arthroplasty resembling heterotopic ossification: A case report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2024, 124, 110479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, M.; Xing, C.; Xu, P.; Wei, X.; Fan, L. Case report: Formation and recurrence of inflammatory pseudotumor after metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1422230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Weegen, W.; Smolders, J.M.H.; Sijbesma, T.; Hoekstra, H.J.; Brakel, K.; Van Susante, J.L.C. High Incidence of Pseudotumours after Hip Resurfacing Even in Low Risk Patients; Results from an Intensified MRI Screening Protocol. HIP Int. 2013, 23, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, D.A.; Adams, J.B.; Morris, M.J.; Berend, K.R.; Lombardi, A.V. Revision of Failed Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty: Midterm Outcomes of 203 Consecutive Cases. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoogstraten, S.W.G.; Hermus, J.; Loenen, A.C.Y.; Arts, J.J.; Van Rietbergen, B. Malalignment of the total ankle replacement increases peak contact stresses on the bone-implant interface: A finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, T.E.; Kwan, S.; Skibicki, H.E.; Cheesman, Q.T.; Daniel, J.N. Morbidity After Metal Allergy to a Total Ankle Implant. Foot Ankle Spec. 2020, 13, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encinas-Ullan, C.A.; De La Corte-Rodriguez, H.; Gomez-Cardero, P.; Rodriguez-Merchan, E.C. Orthopedic surgical procedures in people with hemophilia. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2023, 34, S5–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morwood, M.P.; Garrigues, G.E. Shoulder arthroplasty in the patient with metal hypersensitivity. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2015, 24, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, D.; Li, K.; Riegler, V.; Barrack, R.L. Patient-Reported Metal Allergy: A Risk Factor for Poor Outcomes After Total Joint Arthroplasty? J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 1910–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyssen, J.P.; Menné, T.; Schalock, P.C.; Taylor, J.S.; Maibach, H.I. Pragmatic approach to the clinical work-up of patients with putative allergic disease to metallic orthopaedic implants before and after surgery: Clinical work-up of patients with orthopaedic implant failure. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 164, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallab, N.J. Lymphocyte Transformation Testing for Quantifying Metal-Implant-Related Hypersensitivity Responses. Dermat. Former. Am. J. Contact Dermat. 2004, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akil, S.; Newman, J.M.; Shah, N.V.; Ahmed, N.; Deshmukh, A.J.; Maheshwari, A.V. Metal hypersensitivity in total hip and knee arthroplasty: Current concepts. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2018, 9, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Etiology | Pathogenetic Mechanism | Clinical Presentation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallosis | Accumulation of metal debris | Metal ion release (Co/Cr) | Local tissue necrosis, breakdown of implant materials, and systemic reaction |
| Debris Disease | Particulate debris from worn implant materials | Inflammatory response with macrophage activation | Osteolysis around implants |
| ALVAL | Metal hypersensitivity | Immune-mediated reaction characterized by perivascular lymphocyte infiltration | / |
| Pseudotumor | Metallosis, debris, and metal hypersensitivity | Not clear | A non-neoplastic inflammatory mass within the periprosthetic tissue, periprosthetic bone loss, and loosening of prosthetic components |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sgubbi, F.; Mazzotti, A.; Arceri, A.; Zielli, S.O.; Artioli, E.; Langone, L.; Gambarotti, M.; Faldini, C. Are We Ready for Pseudotumors in Total Ankle Arthroplasty? A Case Report. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020649
Sgubbi F, Mazzotti A, Arceri A, Zielli SO, Artioli E, Langone L, Gambarotti M, Faldini C. Are We Ready for Pseudotumors in Total Ankle Arthroplasty? A Case Report. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(2):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020649
Chicago/Turabian StyleSgubbi, Federico, Antonio Mazzotti, Alberto Arceri, Simone Ottavio Zielli, Elena Artioli, Laura Langone, Marco Gambarotti, and Cesare Faldini. 2025. "Are We Ready for Pseudotumors in Total Ankle Arthroplasty? A Case Report" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 2: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020649
APA StyleSgubbi, F., Mazzotti, A., Arceri, A., Zielli, S. O., Artioli, E., Langone, L., Gambarotti, M., & Faldini, C. (2025). Are We Ready for Pseudotumors in Total Ankle Arthroplasty? A Case Report. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(2), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020649







