Lipid Profile, Obesity Indicators and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in School-Aged Children and Adolescents: Sex-Specific Associations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
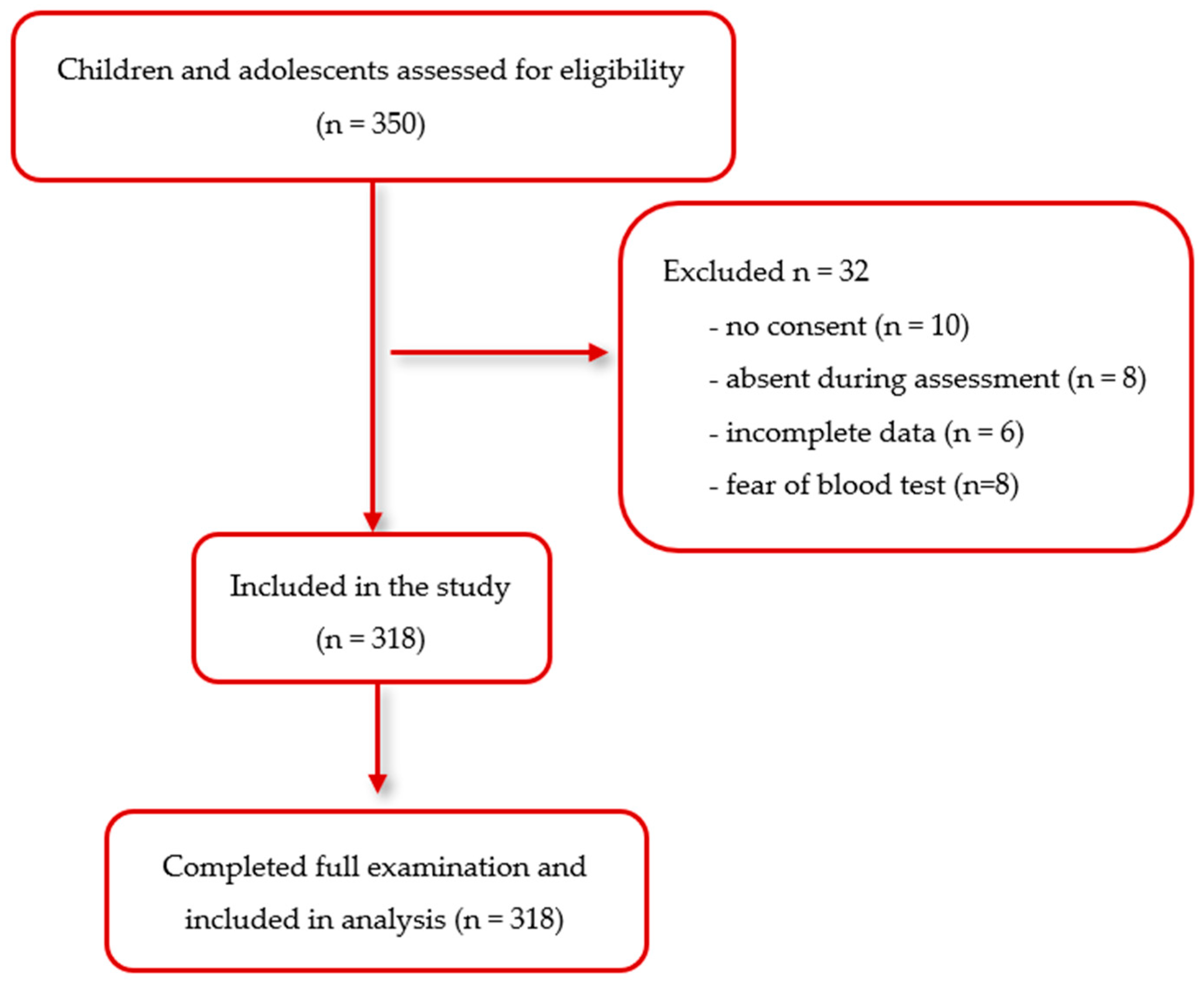
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Blood Profile
2.2.2. Blood Pressure
2.2.3. Anthropometric Measurements and Body Composition
2.2.4. Body Composition
2.2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| OR | odds ratio |
| BMI | body mass index |
| BIA | bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| HC | hip circumference |
| BP | blood pressure |
| SBP | systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | diastolic blood pressure |
| ISAK | International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry |
| WHR | waist-to-hip ratio |
| WC | Waist circumference |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| COSI | Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative |
| WHtR | Waist-to-Height Ratio |
| CI | confidence intervals |
References
- Nader, P.R.; O’Brien, M.; Houts, R.; Bradley, R.; Belsky, J.; Crosnoe, R.; Friedman, S.; Mei, Z.; Susman, E.J. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Early Child Care Research Network. Identifying risk for obesity in early childhood. Pediatrics 2006, 118, e594–e601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight 2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- GBD 2021 Risk Factor Collaborators. Global Burden of 88 Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2162–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundaram, P.; Krishna, S. Obesity Effects on Child Health. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570613/ (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity from 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128.9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fijałkowska, A.; Dzielska, A. (Eds.) Zdrowie Dzieci We Wczesnym Wieku Szkolnym. Raport z Badań 2022–2023; ImiDz: Warszawa, Poland, 2024; Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1lr6RoM7UdZMvhA8-DK6vAqSPaKhTU7AY/view (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Fijałkowska, A.; Oblacińska, A.M.; Dzielska, A.M.; Nałęcz, H.; Korzycka, M. (Eds.) Zdrowie Dzieci w Pandemii COVID-19: Raport z Badań Dotyczących Zdrowia i Zachowań Zdrowotnych Dzieci w Wieku 8 Lat Podczas Pandemii COVID-19; ImiDz: Warszawa, Poland, 2022; Available online: https://imid.med.pl/pl/do-pobrania (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Suligowska, K.; Buczny, J. Obesity in Polish Children and Parents’ Perception of Their Children’s Weight Status: The Results of the SOPKARD-Junior Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonczyk, P.; Potempa-Jeziorowska, M.; Świętochowska, E.; Kucharzewski, M. Analysis of the Nutritional Status of Children Aged 10–13 Years in the Silesian Province, Poland, and Correlation with Sociodemographic Factors. Health Probl. Civiliz. 2021, 15, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenson, G.S.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Bao, W.; Newman, W.P.; Tracy, R.E.; Wattigney, W.A. Association between multiple cardiovascular risk factors and atherosclerosis in children and young adults. The Bogalusa Heart Study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Threefoot, S.A.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Berenson, G.S. Essential hypertension predicted by tracking of elevated blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Am. J. Hypertens. 1995, 8, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidding, S.S.; Bao, W.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Berenson, G.S. Effects of secular trends in obesity on coronary risk factors in children: The Bogalusa Heart Study. J. Pediatr. 1995, 127, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azab, S.M.; Shanmuganathan, M.; de Souza, R.J.; Kroezen, Z.; Desai, D.; Williams, N.C.; Morrison, K.M.; Atkinson, S.A.; Teo, K.K.; Azad, M.B.; et al. Early sex-dependent differences in metabolic profiles of overweight and adiposity in young children: A cross-sectional analysis. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, C.G.; Wu, Q.; Guo, L.; Liu, G.; Dong, Q.; Li, J.J. Study on the reliability of CardioChek PA for measuring lipid profile. J. Peking Univ. Health Sci. 2016, 48, 523–528. [Google Scholar]
- PTS Diagnostics. CardioChek PA Test System: User Guide. Indianapolis (IN): PTS Diagnostics. 2018. Available online: https://ptsdiagnostics.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/ps-002461-en_rev._4_user_guide_cardiochek_pa.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- World Health Organization. The WHO STEPqise Approach to NCD Risk Factor Surveillance (STEPS). Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/noncommunicable-diseases/surveillance/systems-tools/steps/manuals (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Myśliwiec, M.; Walczak, M.; Małecka-Tendera, E.; Dobrzańska, A.; Cybulska, B.; Filipiak, K.; Mazur, A.; Jarosz-Chobot, P.; Szadkowska, A.; Rynkiewicz, A.; et al. Management of familial hypercholesterolemia in children and adolescents. Position paper of the Polish Lipid Expert Forum. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2014, 8, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polskie Towarzystwo Diabetologiczne. Zalecenia kliniczne dotyczące postępowania u osób z cukrzycą—2024. Stanowisko Polskiego Towarzystwa Diabetologicznego. Curr. Top. Diabetes 2023, 4, 5–155. [Google Scholar]
- Lurbe, E.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Dominiczak, A.; Erdine, S.; Hirth, A.; Invitti, C.; Litwin, M.; Mancia, G.; Pall, D.; et al. 2016 European Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 1887–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kułaga, Z.; Litwin, M.; Grajda, A.; Gurzkowska, B.; Napieralska, E.; Kułaga, K. Distribution of blood pressure in school-aged children and adolescents reference population. Stand. Med. 2010, 7, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Marfell-Jones, M.; Olds, T.; Stewart, A.; Carter, L. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment 2006. Available online: https://books.google.pl/books/about/International_Standards_for_Anthropometri.html?id=n_3ozgEACAAJ&redir_esc=y (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Świąder-Leśniak, A.; Kułaga, Z.; Grajda, A.; Gurzkowska, B.; Góźdź, M.; Wojtyło, M.; Różdżyńska-Świątkowska, A.; Litwin, M. References for waist and hip circumferences in Polish children and adolescents 3–18 year of age. Stand. Med. 2015, 12, 137–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kułaga, Z.; Różdżyńska, A.; Palczewska, I. Percentile charts of height, body mass and body mass index in children and adolescents in Poland—Results of the OLAF study. Stand. Med. 2010, 7, 690–700. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About Child & Teen BMI 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/bmi/child-teen-calculator/bmi-categories.html (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- McCarthy, H.D.; Cole, T.J.; Fry, T.; Jebb, S.A.; Prentice, A.M. Body fat reference curves for children. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Ni, Y.; Yi, C.; Fang, Y.; Ning, Q.; Shen, B.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; et al. Global Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2024, 178, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farbo, D.J.; Rhea, D.J. A Pilot Study Examining Body Composition Classification Differences Between Body Mass Index and Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Children with High Levels of Physical Activity. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 724053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, H.; Gürsoy Koca, T.; Dereci, S.; Akçam, M. Comparison of body composition and body mass index in the determination of obesity in schoolchildren. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2022, 57, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.K.; Yoo, E.G. Hypertriglyceridemia in Obese Children and Adolescents. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 27, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.T.; Kaelber, D.C.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Blowey, D.; Carroll, A.E.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dionne, J.M.; Falkner, B.; Flinn, S.K.; et al. Subcommittee on screening and management of high blood pressure in children. Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20171904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlyshyn, H.; Furdela, V.; Kovalchuk, T.; Haliyash, N.; Luchyshyn, N. Epidemiological aspects of obesity and systemic hypertension amongschool children of Western Ukraine. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2017, 23, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çam, H.H.; Ustuner Top, F. Prevalence of Hypertension and Its Association with Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference Among Adolescents in Turkey: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2021, 57, e29–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meydanlioglu, A.; Akcan, A.; Oncel, S.; Adibelli, D.; Cicek Gumus, E.; Sarvan, S.; Kavla, I. Prevalence of obesity and hypertension in children and determination of associated factors by CHAID analysis. Arch. Pediatr. 2022, 29, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, H.; Juton, C.; Goran, M.I.; Wärnberg, J.; Osés, M.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Gusi, N.; Aznar, S.; Marín-Cascales, E.; González-Valeiro, M.; et al. Twenty-year trend in the prevalence of increased cardiometabolic risk, measured by abdominal obesity, among Spanish children and adolescents across body mass index categories. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manios, Y.; Karatzi, K.; Protogerou, A.D.; Moschonis, G.; Tsirimiagou, C.; Androutsos, O.; Lionis, C.; Chrousos, G.P. Prevalence of childhood hypertension and hypertension phenotypes by weight status and waist circumference: The Healthy Growth Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrodán Serrano, M.D.; Cabañas Armesilla, M.D.; Carmenate Moreno, M.M.; González-Montero de Espinosa, M.; López-Ejeda, N.; Martínez Álvarez, J.R.; Prado Martínez, C.; Romero-Collazos, J.F. Association between adiposity and blood pressure levels between the ages of 6 and 16 years. Analysis in a student population from Madrid, Spain. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2013, 66, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Shi, P.; Luo, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.F.; Yu, H.T.; Guo, C.Y.; Wu, F. Prevalence of hypertension in overweight and obese children from a large school-based population in Shanghai, China. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Pinto, M.A.; Ortiz-Marrón, H.; Ferriz-Vidal, I.; Martínez-Rubio, M.V.; Esteban-Vasallo, M.; Ordobás-Gavin, M.; Galán, I. Association between general and central adiposity and development of hypertension in early childhood. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Shen, W.; Baxter-Jones, A.; Bell, J.D.; Butte, N.F.; Demerath, E.W.; Gilsanz, V.; Goran, M.I.; Hirschler, V.; Hu, H.H.; et al. Adiposity in children and adolescents: Correlates and clinical consequences of fat stored in specific body depots. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, e42–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plachta-Danielzik, S.; Landsberg, B.; Johannsen, M.; Lange, D.; Müller, M.J. Association of different obesity indices with blood pressure and blood lipids in children and adolescents. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.; Twig, G. The Impact of Childhood and Adolescent Obesity on Cardiovascular Risk in Adulthood: A Systematic Review. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syme, C.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Leonard, G.T.; Perron, M.; Richer, L.; Veillette, S.; Xiao, Y.; Gaudet, D.; Paus, T.; Pausova, Z. Sex Differences in Blood Pressure and Its Relationship to Body Composition and Metabolism in Adolescence. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2009, 163, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.L.; Hayman, L.L.; Daniels, S.R.; Robinson, T.N.; Steinberger, J.; Paridon, S.; Bazzarre, T. Cardiovascular health in childhood: A statement for health professionals from the Committee on Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in the Young (AHOY) of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Circulation 2002, 106, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGill, H.C., Jr.; McMahan, C.A.; Gidding, S.S. Preventing heart disease in the 21st century: Implications of the Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis in Youth (PDAY) study. Circulation 2008, 117, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, A.; Sumida, Y.; Urakawa, H.; Gabazza, E.C.; Murashima, S.; Maruyama, N.; Morioka, K.; Nakatani, K.; Yano, Y.; Adachi, Y. Increased visceral fat and serum levels of triglyceride are associated with insulin resistance in Japanese metabolically obese, normal weight subjects with normal glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2341–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriège, P.; Marette, A.; Atgié, C.; Bouchard, C.; Thériault, G.; Bukowiecki, L.K.; Marceau, P.; Biron, S.; Nadeau, A.; Després, J.P. Regional variation in adipose tissue metabolism of severely obese premenopausal women. J. Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Mean ± SD | Me (Q1 Q3) | Mean ± SD | Me (Q1 Q3) | Mean ± SD | Me (Q1 Q3) | p−Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children (6–12 years) | All n = 169 (100.0%) | Boys n = 75 (44.4%) | Girls n = 94 (55.6%) | ||||
| Age (years) | 10.0 ± 1.50 | 10.0 (9.0–11.0) | 10.0 ± 1.49 | 10.0 (9.0–11.0) | 10.0 ± 1.52 | 10.0 (9.0–12.0) | Z = −0.09 0.929 |
| Height (cm) | 144.8 ± 11.69 | 144.5 (135.2–152.5) | 145.5 ± 11.67 | 145.0 (136.0–151.0) | 144.2 ± 11.74 | 143.8 (133.5–152.5) | Z = 0.57 0.571 |
| Body weight (kg) | 39.2 ± 12.35 | 37.4 (30.3–44.5) | 40.3 ± 14.47 | 37.4 (30.1–45.2) | 38.2 ± 10.34 | 37.9 (30.3–44.5) | Z = 0.35 0.729 |
| BMI percentile | 52.8 ± 28.94 | 52.0 (26.0–78.0) | 52.0 ± 30.14 | 54.0 (23.0–77.0) | 53.4 ± 28.10 | 51.0 (28.0–79.0) | Z = −0.27 0.790 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 64.9 ± 8.64 | 64.0 (59.0–69.0) | 65.8 ± 10.27 | 65.0 (58.0–68.0) | 64.2 ± 7.06 | 64.0 (59.0–69.0) | Z = 0.35 0.723 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 79.1 ± 9.38 | 78.0 (73.0–84.0) | 79.3 ± 10.55 | 78.0 (72.0–83.0) | 78.9 ± 8.38 | 78.5 (73.0–86.0) | Z = −0.34 0.735 |
| Waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) | 0.8 ± 0.06 | 0.8 (0.8–0.9) | 0.8 ± 0.05 | 0.8 (0.8–0.9) | 0.8 ± 0.06 | 0.8 (0.8–0.9) | t = 1.44 0.151 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 114.1 ± 12.22 | 113.5 (104.5–121.0) | 115.2 ± 12.35 | 114.0 (106.0–124.0) | 113.2 ± 12.10 | 112.3 (104.5–121.0) | t = 1.08 0.282 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 67.6 ± 10.02 | 67.5 (61.0–74.0) | 67.5 ± 9.99 | 68.5 (59.0–75.5) | 67.6 ± 10.10 | 67.3 (62.0–73.0) | t = −0.07 0.947 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 74.7 ± 9.32 | 74.0 (69.0–80.0) | 75.5 ± 9.15 | 75.0 (70.0–81.0) | 74.0 ± 9.44 | 73.5 (68.0–80.0) | t = 1.07 0.286 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 149.6 ± 25.59 | 147.0 (133.0–165.0) | 149.8 ± 27.09 | 147.0 (127.0–167.0) | 149.4 ± 24.48 | 147.5 (133.0–165.0) | t = 0.11 0.916 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 51.2 ± 9.89 | 52.0 (44.0–58.0) | 51.6 ± 10.19 | 52.0 (45.0–59.0) | 51.0 ± 9.69 | 51.0 (44.0–57.0) | t = 0.40 0.688 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 98.3 ± 22.35 | 96.0 (83.0–113.0) | 98.2 ± 23.59 | 94.0 (84.0–114.0) | 98.4 ± 21.44 | 97.0 (82.0–109.0) | t = −0.06 0.955 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 88.5 ± 34.00 | 80.0 (70.0–94.0) | 86.6 ± 31.61 | 79.0 (69.0–93.0) | 90.1 ± 35.89 | 80.0 (70.0–95.0) | Z = −0.49 0.622 |
| Adolescents (13–17 years) | All n = 149 (100.0%) | Boys n = 70 (47.0%) | Girls n = 79 (53.0%) | p-Value | |||
| Age (years) | 15.3 ± 1.48 | 15.0 (14.0–17.0) | 15.4 ± 1.57 | 16.0 (14.0–17.0) | 15.2 ± 1.40 | 15.0 (14.0–17.0) | Z = 0.64 0.524 |
| Height (cm) | 169.0 ± 8.77 | 168.0 (162.0–175.0) | 174.8 ± 8.45 | 175.6 (169.0–181.5) | 163.8 ± 5.03 | 163.0 (160.5–167.0) | t * = 9.50 <0.001 |
| Body weight (kg) | 60.5 ± 13.02 | 57.9 (51.2–67.9) | 66.3 ± 14.34 | 66.2 (55.5–72.1) | 55.4 ± 9.13 | 53.0 (49.0–60.5) | Z = 5.19 <0.001 |
| BMI percentile | 52.0 ± 28.76 | 55.0 (30.0–74.0) | 55.2 ± 28.70 | 58.5 (31.0–79.0) | 49.2 ± 28.70 | 50.0 (26.0–74.0) | Z = 1.35 0.177 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 71.1 ± 9.54 | 69.0 (64.0–76.0) | 74.9 ± 9.78 | 73.5 (68.0–79.0) | 67.6 ± 7.89 | 66.0 (62.0–72.0) | Z = 5.01 <0.001 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 92.9 ± 7.72 | 92.0 (88.0–98.0) | 94.9 ± 8.24 | 94.5 (89.0–99.0) | 91.2 ± 6.84 | 90.0 (87.0–95.0) | Z = 2.82 0.005 |
| Waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) | 0.8 ± 0.07 | 0.8 (0.7–0.8) | 0.8 ± 0.05 | 0.8 (0.8–0.8) | 0.7 ± 0.08 | 0.7 (0.7–0.8) | Z = 5.77 <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 117.3 ± 12.66 | 115.5 (109.0–127.5) | 122.8 ± 13.58 | 122.3 (113.5–133.0) | 112.3 ± 9.41 | 112.0 (105.0–117.0) | t * = 5.43 <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 68.3 ± 7.72 | 68.5 (64.5–72.5) | 68.1 ± 8.12 | 68.5 (63.5–73.0) | 68.5 ± 7.39 | 68.5 (64.5–72.5) | t = −0.30 0.761 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 75.5 ± 13.04 | 72.0 (67.0–84.0) | 75.8 ± 13.14 | 73.5 (68.0–85.0) | 75.2 ± 13.02 | 71.0 (66.0–84.0) | Z = 0.54 0.589 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 140.3 ± 24.59 | 137.0 (122.0–151.0) | 133.5 ± 18.65 | 134.0 (118.0–147.0) | 146.3 ± 27.60 | 143.0 (126.0–159.0) | Z = −2.94 0.003 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 50.3 ± 12.14 | 48.0 (44.0–56.0) | 46.6 ± 12.34 | 45.0 (39.0–53.0) | 53.5 ± 11.07 | 52.0 (45.0–59.0) | Z = −3.75 <0.001 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 90.0 ± 22.39 | 88.0 (76.0–102.0) | 86.9 ± 16.87 | 87.5 (76.0–97.0) | 92.8 ± 26.13 | 89.0 (74.0–107.0) | Z = −0.95 0.340 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 93.3 ± 35.89 | 87.0 (70.0–101.0) | 99.4 ± 41.22 | 87.0 (73.0–118.0) | 87.8 ± 29.62 | 85.0 (68.0–100.0) | Z = 1.24 0.214 |
| Parameters | All n (%) | Boys n (%) | Girls n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Children (6–12 years) | |||
| Body weight status (CDC) | χ2 = 6.36 0.095 | |||
| Underweight | 5 (3.0) | 3 (4.0) | 2 (2.1) | |
| Normal | 129 (76.3) | 58 (77.3) | 71 (75.5) | |
| Overweight | 21 (12.4) | 5 (6.7) | 16 (17.0) | |
| Obesity | 14 (8.3) | 9 (6.7) | 5 (5.3) | |
| Body fat status (McCarthy) | χ2 = 5.39 0.146 | |||
| Underfat | 1 (0.6) | 1 (1.3) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Normal | 118 (69.8) | 46 (61.3) | 72 (76.6) | |
| Overfat | 27 (16.0) | 15 (20.0) | 12 (12.8) | |
| Obesity | 23 (13.6) | 13 (17.3) | 10 (10.6) | |
| Blood pressure category | χ2 = 3.04 0.219 | |||
| Normal | 87 (51.5) | 54 (57.4) | 33 (44.0) | |
| High normal | 24 (14.2) | 12 (12.8) | 12 (16.0) | |
| Stage I and II hypertension | 58 (34.3) | 28 (29.8) | 30 (40.0) | |
| Fasting glucose status | χ2 = 0.71 0.401 | |||
| Normal | 123 (72.8) | 57 (76.0) | 66 (70.2) | |
| Low/High | 46 (27.2) | 18 (24.0) | 28 (29.8) | |
| Abdominal obesity | χ2 = 2.44 0.118 | |||
| Yes | 51 (30.2) | 18 (24.0) | 33 (35.1) | |
| No | 118 (69.8) | 57 (76.0) | 61 (64.9) | |
| TG level | χ2 = 0.41 0.523 | |||
| Acceptable | 90 (53.3) | 42 (56.0) | 48 (51.1) | |
| Borderline/high | 79 (46.7) | 33 (44.0) | 46 (48.9) | |
| HDL cholesterol level | χ2 = 0.37 0.542 | |||
| Acceptable | 113 (66.9) | 52 (69.3) | 61 (64.9) | |
| Borderline/low | 56 (33.1) | 23 (30.7) | 33 (35.1) | |
| LDL cholesterol level | χ2 = 0.81 0.368 | |||
| Acceptable | 123 (72.8) | 52 (69.3) | 71 (75.5) | |
| Borderline/high | 46 (27.2) | 23 (30.7) | 23 (24.5) | |
| Total cholesterol level | χ2 = 0.59 0.444 | |||
| Acceptable | 133 (78.7) | 57 (76.0) | 76 (80.9) | |
| Borderline/high | 36 (21.3) | 18 (24.0) | 18 (19.1) | |
| Adolescents (13–17 years) | ||||
| Body weight status (CDC) | χ2 = 1.22 0.748 | |||
| Underweight | 7 (4.7) | 2 (2.9) | 5 (6.3) | |
| Normal | 118 (79.2) | 56 (80.0) | 62 (78.5) | |
| Overweight | 13 (8.7) | 7 (10.0) | 6 (7.6) | |
| Obesity | 11 (7.4) | 5 (7.1) | 6 (7.6) | |
| Body fat status (McCarthy) | χ2 = 1.48 0.687 | |||
| Underfat | 2 (1.3) | 1 (1.4) | 1 (1.3) | |
| Normal | 114 (76.5) | 55 (78.6) | 59 (74.7) | |
| Overfat | 20 (13.4) | 7 (10.0) | 13 (16.5) | |
| Obesity | 13 (8.8) | 7 (10.0) | 6 (7.6) | |
| Blood pressure category | χ2 = 12.89 0.002 C = 0.13 | |||
| Normal | 106 (71.1) | 40 (57.1) | 66 (83.5) | |
| High normal | 26 (17.5) | 19 (27.1) | 7 (8.9) | |
| Stage I and II hypertension | 17 (11.4) | 11 (15.7) | 6 (7.6) | |
| Fasting glucose status | χ2 = 2.05 0.153 | |||
| Normal | 91 (61.1) | 47 (67.1) | 44 (55.7) | |
| Low/high | 58 (38.9) | 23 (32.9) | 35 (44.3) | |
| Abdominal obesity | χ2 = 0.02 0.893 | |||
| Yes | 27 (18.1) | 13 (18.6) | 14 (17.7) | |
| No | 122 (81.9) | 57 (81.4) | 65 (82.3) | |
| TG level | χ2 = 0.01 0.909 | |||
| Acceptable | 88 (59.1) | 41 (58.6) | 47 (59.5) | |
| Borderline/high | 61 (40.9) | 29 (41.4) | 32 (40.5) | |
| HDL cholesterol level | χ2 = 9.71 0.002 C = 0.25 | |||
| Acceptable | 90 (60.4) | 33 (47.1) | 57 (72.2) | |
| Borderline/low | 59 (39.6) | 37 (52.9) | 22 (27.8) | |
| LDL cholesterol level | χ2 = 7.85 0.005 C = 0.22 | |||
| Acceptable | 125 (83.9) | 65 (92.9) | 60 (75.9) | |
| Borderline/high | 24 (16.1) | 5 (7.1) | 19 (24.1) | |
| Total cholesterol level | χ2 = 4.21 0.040 * C = 0.17 | |||
| Acceptable | 132 (88.6) | 66 (94.3) | 66 (83.5) | |
| Borderline/high | 17 (11.4) | 4 (5.7) | 13 (16.5) | |
| Total sample | ||||
| Body weight status (CDC) | χ2 = 2.65 0.449 | |||
| Underweight | 12 (3.8) | 5 (3.4) | 7 (4.0) | |
| Normal | 247 (77.7) | 114 (78.6) | 133 (76.9) | |
| Overweight | 34 (10.7) | 12 (8.3) | 22 (12.7) | |
| Obesity | 25 (7.8) | 14 (9.7) | 11 (6.4) | |
| Body fat status (McCarthy) | χ2 = 2.40 0.493 | |||
| Underfat | 3 (0.9) | 2 (1.4) | 1 (0.6) | |
| Normal | 232 (73.0) | 101 (69.7) | 131 (75.7) | |
| Overfat | 47 (14.8) | 22 (15.2) | 25 (14.5) | |
| Obesity | 36 (11.3) | 20 (13.8) | 16 (9.2) | |
| Blood pressure category | χ2 = 12.61 0.002 C = 0.20 | |||
| Normal | 193 (60.7) | 73 (50.3) | 120 (69.4) | |
| High normal | 50 (15.7) | 31 (21.4) | 19 (11.0) | |
| Stage I and II hypertension | 75 (23.6) | 41 (28.3) | 34 (19.7) | |
| Fasting glucose status | χ2 = 2.38 0.123 | |||
| Normal | 214 (67.3) | 104 (71.7) | 110 (63.6) | |
| Low/high | 104 (32.7) | 41 (28.3) | 63 (36.4) | |
| Abdominal obesity | χ2 = 1.43 0.232 | |||
| Yes | 78 (24.5) | 31 (21.4) | 47 (27.2) | |
| No | 240 (75.5) | 114 (78.6) | 126 (72.8) | |
| TG level | χ2 = 0.17 0.677 | |||
| Acceptable | 178 (56.0) | 83 (57.2) | 95 (54.9) | |
| Borderline/high | 140 (44.0) | 62 (42.8) | 78 (45.1) | |
| HDL cholesterol level | χ2 = 3.14 0.076 | |||
| Acceptable | 203 (63.8) | 85 (58.6) | 118 (68.2) | |
| Borderline/low | 115 (36.2) | 60 (41.4) | 55 (31.8) | |
| LDL cholesterol level | χ2 = 1.13 0.287 | |||
| Acceptable | 248 (78.0) | 117 (80.7) | 131 (75.7) | |
| Borderline/high | 70 (22.0) | 28 (19.3) | 42 (24.3) | |
| Total cholesterol level | χ2 = 0.43 0.513 | |||
| Acceptable | 265 (83.3) | 123 (84.8) | 142 (82.1) | |
| Borderline/high | 53 (16.7) | 22 (15.2) | 31 (17.9) | |
| Variable | Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) | LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) | TG (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | |
| Body weight status (CDC) | ||||
| Underweight and normal weight | 145.0 ± 24.85 | 51.3 ± 11.11 | 93.7 ± 22.07 | 88.6 ± 32.28 |
| Overweight and obesity | 146.3 ± 28.43 | 48.4 ± 10.26 | 97.9 ± 25.27 | 100.3 ± 43.78 |
| p | Z = 0.07 0.944 | Z = 1.72 0.085 | Z = −0.90 0.368 | Z = −1.91 0.055 |
| Body fat status (McCarthy) | ||||
| Underfat and normal body fat | 146.0 ± 24.54 | 51.6 ± 11.45 | 94.4 ± 21.90 | 89.0 ± 32.48 |
| Overfat and obesity | 143.2 ± 28.15 | 48.4 ± 9.25 | 94.7 ± 25.03 | 95.6 ± 40.92 |
| p | Z = 1.10 0.273 | Z = 2.01 0.045 | Z = 0.19 0.846 | Z = −0.85 0.393 |
| Abdominal obesity | ||||
| Yes | 144.9 ± 24.62 | 48.9 ± 10.92 | 96.1 ± 20.89 | 101.9 ± 46.07 |
| No | 145.3 ± 25.84 | 51.4 ± 10.97 | 93.9 ± 23.30 | 87.1 ± 29.67 |
| p | Z = −0.18 0.859 | Z = 1.88 0.061 | Z = −0.82 0.415 | Z = −2.25 0.025 |
| Blood pressure category | ||||
| Normal | 144.4 ± 26.07 | 50.8 ± 10.56 | 93.6 ± 23.83 | 88.8 ± 34.07 |
| High normal | 148.3 ± 28.05 | 51.3 ± 13.64 | 97.0 ± 21.58 | 93.3 ± 34.76 |
| Stage I and II hypertension | 145.3 ± 22.25 | 50.4 ± 10.27 | 94.9 ± 20.54 | 93.9 ± 37.29 |
| p | H = 0.98 0.613 | H = 0.35 0.841 | H = 1.37 0.505 | H = 2.02 0.363 |
| Girls | Boys | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Acceptable | Borderline/High | p | Acceptable | Borderline/High | p | ||
| n (%) | n (%) | OR (95% p.u.) | n (%) | n (%) | OR (95% p.u.) | |||
| TG level | TG level | |||||||
| Abdominal obesity | 19 (21.1) | 28 (35.9) | 2.09 (1.05–4.15) | 0.033 | 17 (20.5) | 14 (22.6) | 1.13 (0.51–2.52) | 0.760 |
| Abnormal glucose level | 30 (31.6) | 33 (42.3) | 1.54 (0.82–2.90) | 0.177 | 27 (32.5) | 14 (22.6) | 0.60 (0.29–1.28) | 0.188 |
| Stage I–II hypertension | 13 (14.4) | 21 (26.9) | 2.18 (1.01–4.72) | 0.045 | 27 (32.5) | 14 (22.6) | 0.60 (0.29–1.28) | 0.188 |
| LDL cholesterol level | LDL cholesterol level | |||||||
| Abdominal obesity | 38 (29.0) | 9 (24.3) | 0.79 (0.34–1.82) | 0.575 | 26 (22.2) | 5 (17.9) | 0.76 (0.26–2.20) | 0.613 |
| Abnormal glucose level | 48 (36.6) | 15 (35.7) | 1.05 (0.50–2.24) | 0.894 | 32 (27.4) | 9 (32.1) | 1.26 (0.52–3.07) | 0.613 |
| Stage I–II hypertension | 28 (21.4) | 6 (16.2) | 0.71 (0.27–1.88) | 0.491 | 33 (28.2) | 8 (28.6) | 1.02 (0.41–2.54) | 0.969 |
| HDL cholesterol level | HDL cholesterol level | |||||||
| Abdominal obesity | 30 (25.4) | 17 (34.0) | 1.51 (0.74–3.10) | 0.258 | 16 (18.8) | 15 (25.0) | 1.44 (0.65–3.19) | 0.372 |
| Abnormal glucose level | 45 (38.1) | 18 (32.7) | 0.84 (0.42–1.67) | 0.612 | 28 (32.9) | 13 (21.7) | 0.56 (0.26–1.21) | 0.138 |
| Stage I–II hypertension | 23 (19.5) | 11 (22.0) | 1.16 (0.52–2.62) | 0.711 | 27 (31.8) | 14 (23.3) | 0.65 (0.31–1.39) | 0.267 |
| Variable | Girls | Boys | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% p.u.) | p | OR (95% p.u.) | p | |
| Abdominal obesity | ||||
| TG level | 2.36 (1.18–4.72) | 0.015 | 1.07 (0.47–2.42) | 0.868 |
| LDL cholesterol level | 0.58 (0.25–1.37) | 0.214 | 0.78 (0.27–2.25) | 0.642 |
| HDL cholesterol level | 1.31 (0.64–2.70) | 0.463 | 1.41 (0.62–3.17) | 0.413 |
| Abnormal glucose level | ||||
| TG level | 1.62 (0.86–3.03) | 0.134 | 0.65 (0.30–1.40) | 0.272 |
| LDL cholesterol level | 0.91 (0.44–1.89) | 0.797 | 1.25 (0.51–3.09) | 0.627 |
| HDL cholesterol level | 0.78 (0.39–1.53) | 0.465 | 0.61 (0.28–1.33) | 0.213 |
| Stage I–II hypertension | ||||
| TG level | 2.47 (1.13–5.38) | 0.023 | 0.64 (0.30–1.38) | 0.255 |
| LDL cholesterol level | 0.54 (0.20–1.43) | 0.215 | 1.02 (0.40–2.56) | 0.971 |
| HDL cholesterol level | 1.02 (0.45–2.32) | 0.956 | 0.71 (0.33–1.52) | 0.373 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baran, R.; Baran, J.; Leszczak, J.; Bartosiewicz, A.; Wyszyńska, J. Lipid Profile, Obesity Indicators and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in School-Aged Children and Adolescents: Sex-Specific Associations. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6677. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186677
Baran R, Baran J, Leszczak J, Bartosiewicz A, Wyszyńska J. Lipid Profile, Obesity Indicators and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in School-Aged Children and Adolescents: Sex-Specific Associations. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6677. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186677
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaran, Rafał, Joanna Baran, Justyna Leszczak, Anna Bartosiewicz, and Justyna Wyszyńska. 2025. "Lipid Profile, Obesity Indicators and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in School-Aged Children and Adolescents: Sex-Specific Associations" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6677. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186677
APA StyleBaran, R., Baran, J., Leszczak, J., Bartosiewicz, A., & Wyszyńska, J. (2025). Lipid Profile, Obesity Indicators and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in School-Aged Children and Adolescents: Sex-Specific Associations. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6677. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186677








