Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Cell Communication and Novel Biomarkers in Sepsis
Abstract
1. Introduction
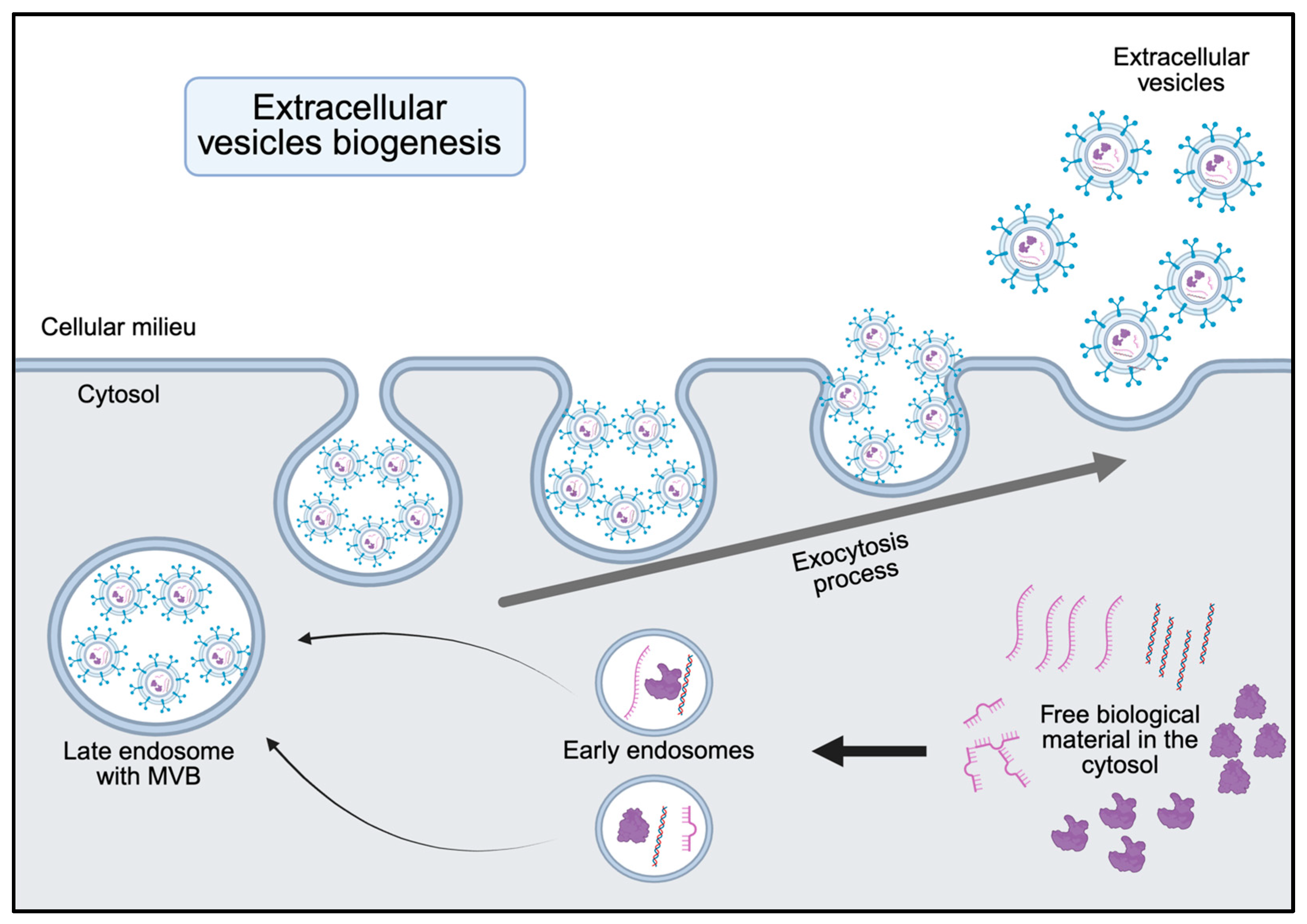
2. Biogenesis and Functional Cargo of sEVs
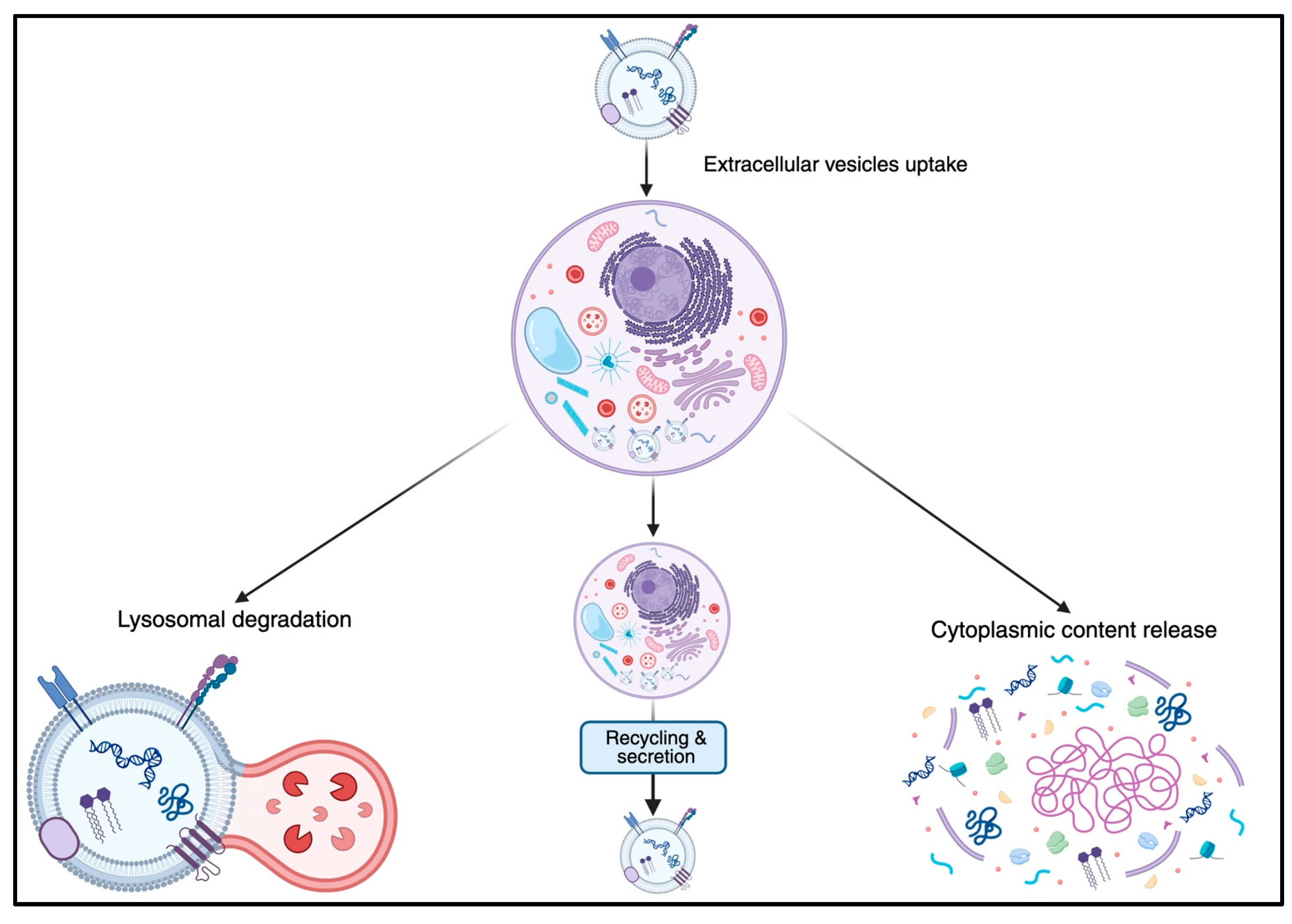
3. Function in Cell–Cell Communication
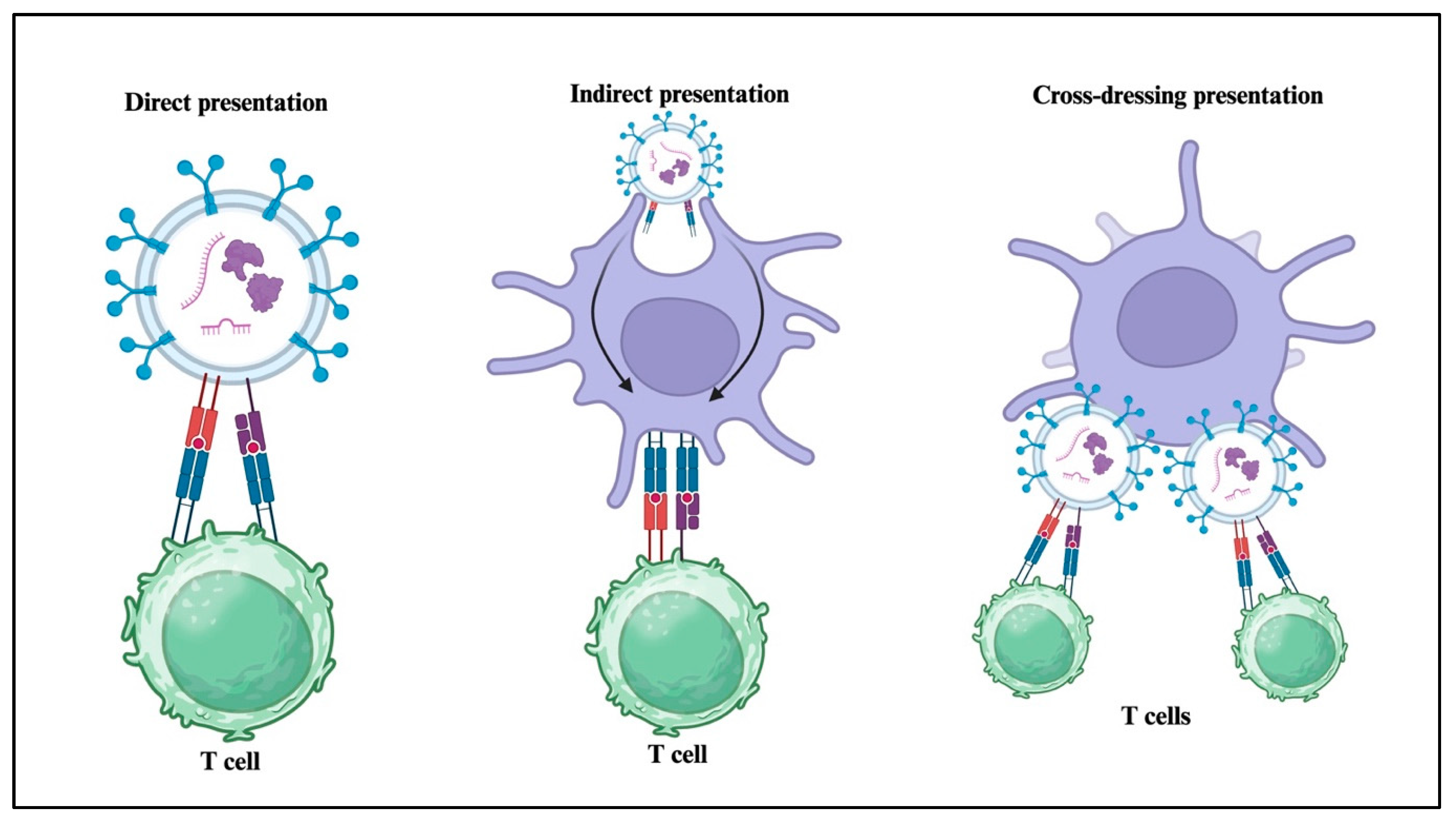
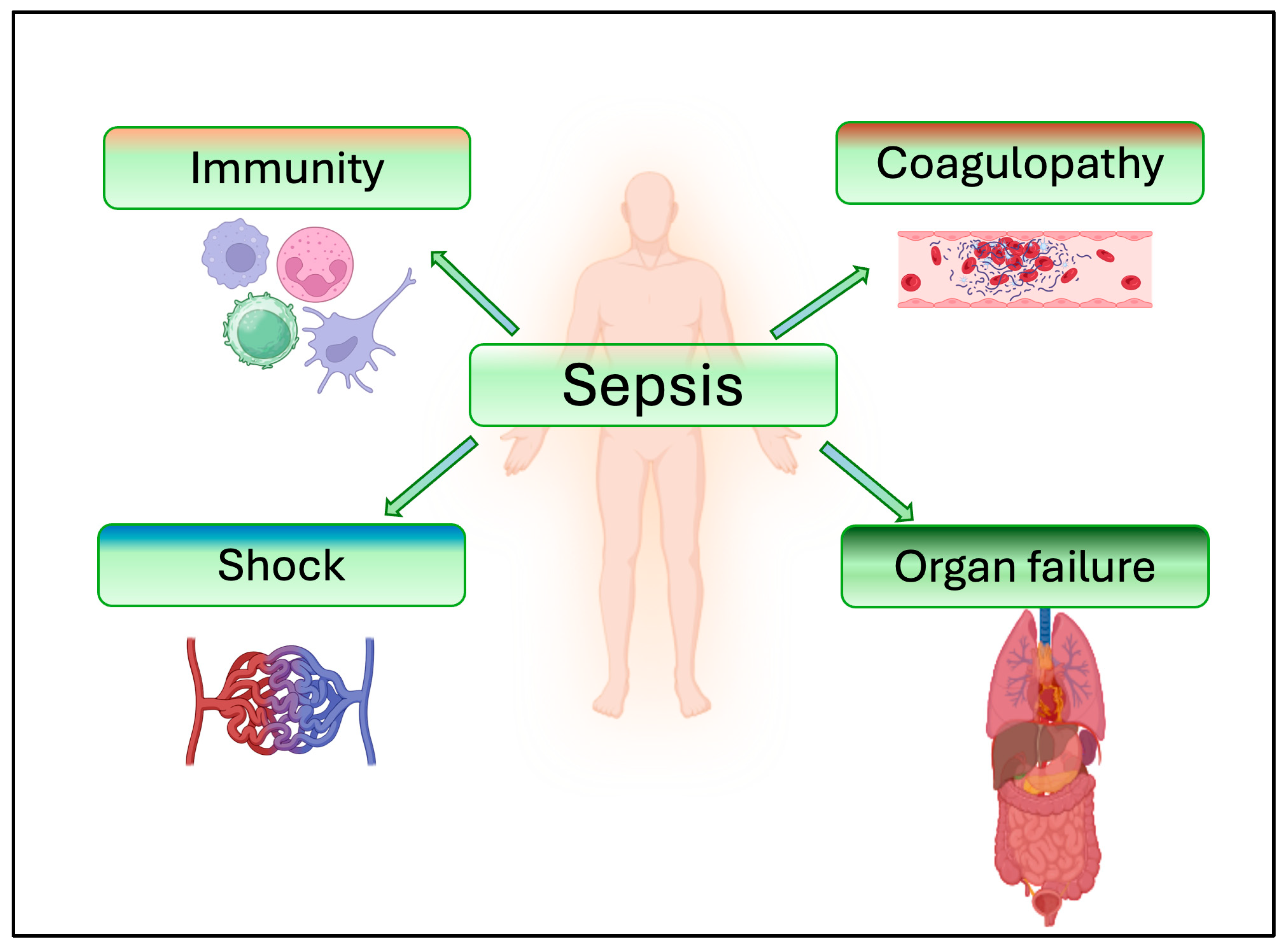
4. Role of sEVs in Immune and Inflammatory Responses
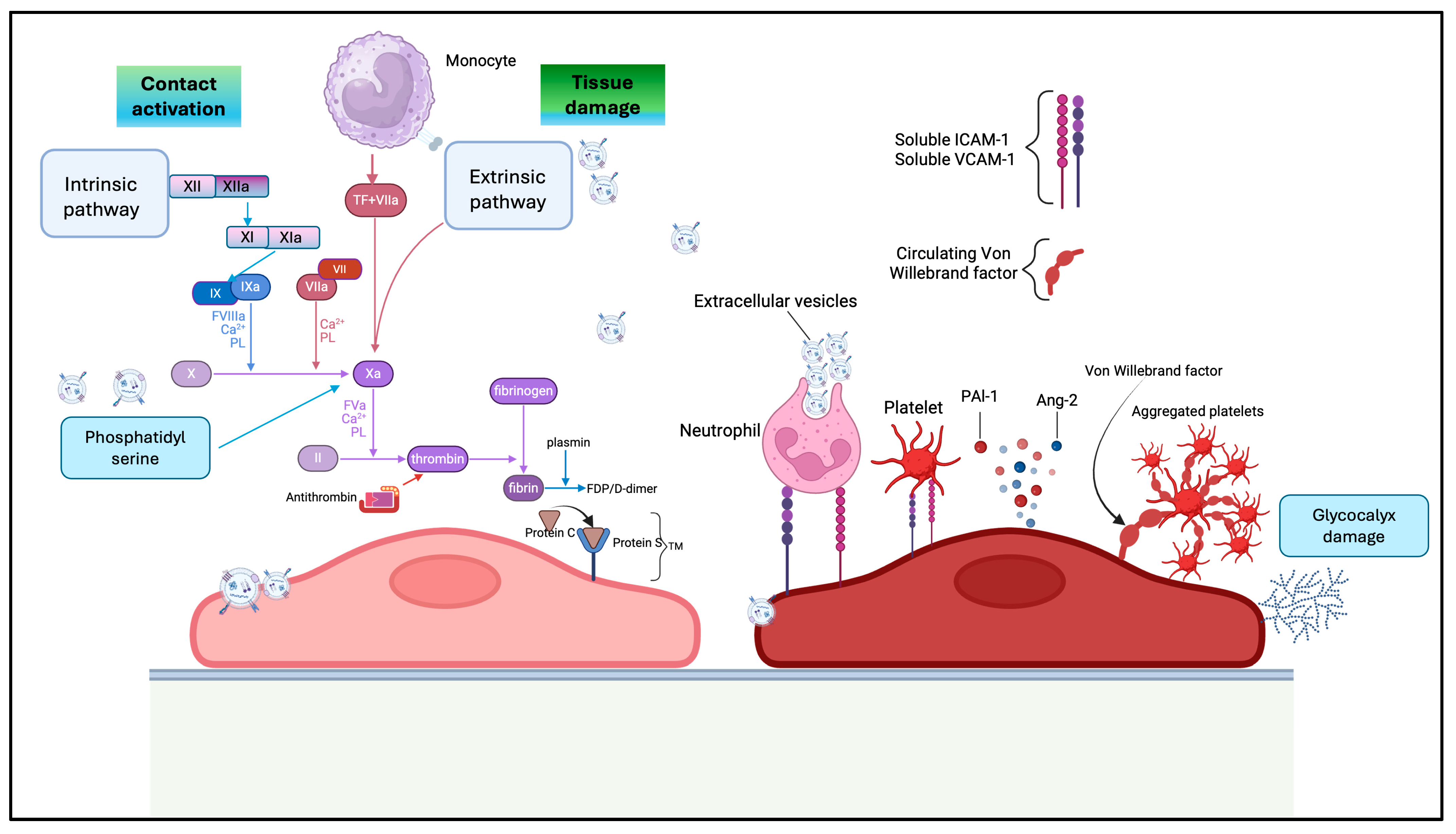
5. Role of sEVs in Coagulation and Coagulopathy in Sepsis
6. Role of sEVs in Organ Failure
7. Role of sEVs in Burn-Related Sepsis
8. Standard and Novel Methods of sEVs Extraction and Isolation
9. Modern Systems of sEV-Based Drug Delivery and Experimental Therapy
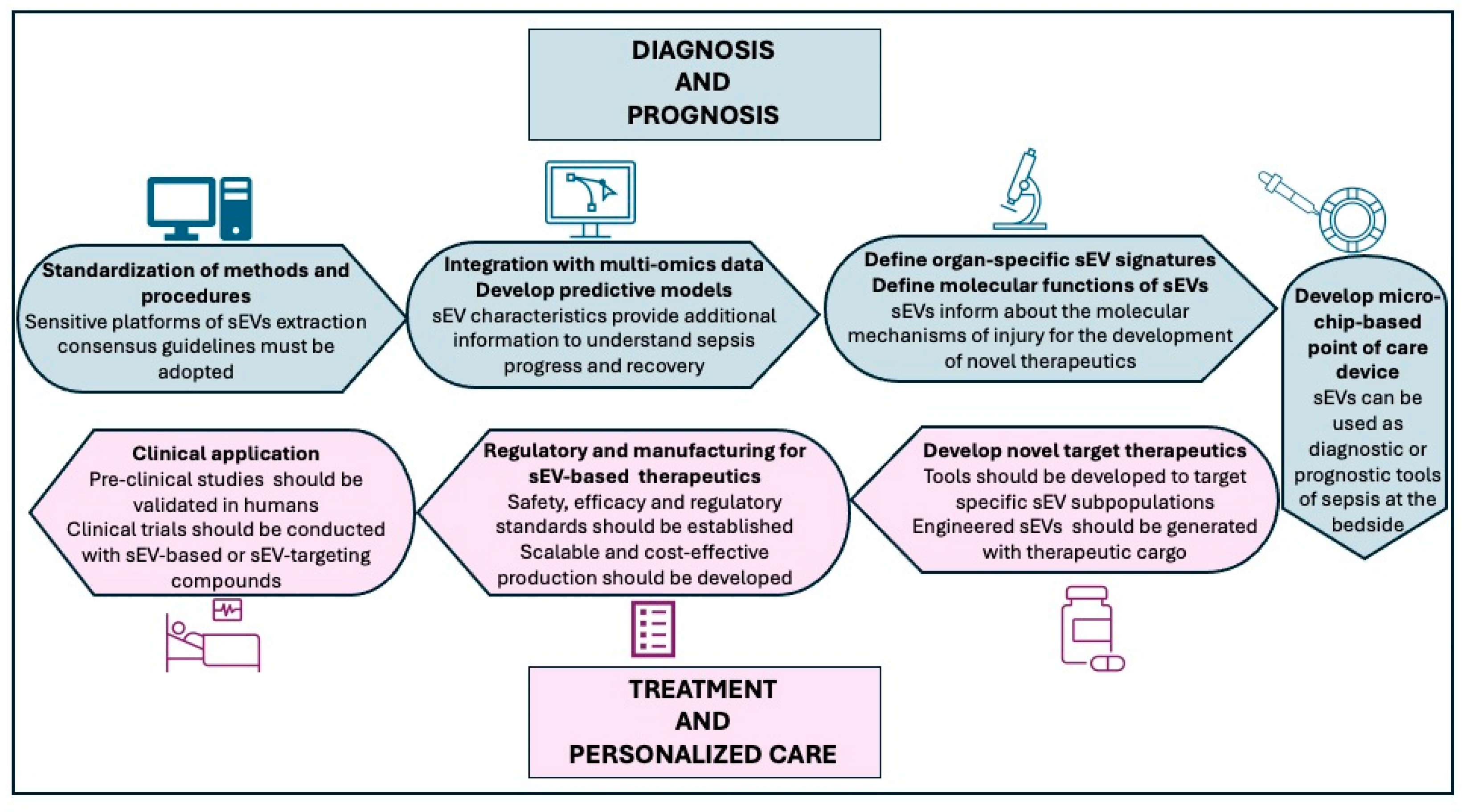
10. Future Directions for Bridging the Bench to Bedside
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, B.; Ramakrishna, K.; Dhamoon, A.S. Sepsis: The evolution in definition, pathophysiology, and management. SAGE Open Med. 2019, 7, 2050312119835043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborowski, M.P.; Balaj, L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lai, C.P. Extracellular Vesicles: Composition, Biological Relevance, and Methods of Study. Bioscience 2015, 65, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoorvogel, W.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Geuze, H.J.; Raposo, G. The biogenesis and functions of exosomes. Traffic 2002, 3, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanov, A.; Shtam, T.; Kamyshinsky, R.; Garaeva, L.; Verlov, N.; Miliukhina, I.; Kudrevatykh, A.; Gavrilov, G.; Zabrodskaya, Y.; Pchelina, S.; et al. Cryo-electron microscopy of extracellular vesicles from cerebrospinal fluid. PLoS ONE 2020, 5, e0227949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Schwarz, H.; Nanda, H.S.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Y. Exosomes, a New Star for Targeted Delivery. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 751079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Fenix, A.M.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell 2019, 177, 428–445.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourcade, O.; Simon, M.F.; Viodé, C.; Rugani, N.; Leballe, F.; Ragab, A.; Fournié, B.; Sarda, L.; Chap, H. Secretory phospholipase A2 generates the novel lipid mediator lysophosphatidic acid in membrane microvesicles shed from activated cells. Cell 1995, 80, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescitelli, R.; Lässer, C.; Szabó, T.G.; Kittel, A.; Eldh, M.; Dianzani, I.; Buzás, E.I.; Lötvall, J. Distinct RNA profiles in subpopulations of extracellular vesicles: Apoptotic bodies, microvesicles and exosomes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzas, E.I. The roles of extracellular vesicles in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgwick, A.E.; D’Souza-Schorey, C. The biology of extracellular microvesicles. Traffic 2018, 19, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheta, M.; Taha, E.A.; Lu, Y.; Eguchi, T. Extracellular Vesicles: New Classification and Tumor Immunosuppression. Biology 2023, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. Role of exosomes in cellular communication between tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidaro, A.; Delitala, A.P.; Manetti, R.; Caccia, S.; Soloski, M.J.; Lambertenghi Deliliers, G.; Castro, D.; Donadoni, M.; Bartoli, A.; Sanna, G.; et al. Platelet Microvesicles, Inflammation, and Coagulation Markers: A Pilot Study. Hematol. Rep. 2023, 15, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midekessa, G.; Godakumara, K.; Ord, J.; Viil, J.; Lättekivi, F.; Dissanayake, K.; Kopanchuk, S.; Rinken, A.; Andronowska, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; et al. Zeta Potential of Extracellular Vesicles: Toward Understanding the Attributes that Determine Colloidal Stability. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16701–16710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamrin, S.H.; Phelps, J.; Nezhad, A.S.; Sen, A. Critical considerations in determining the surface charge of small extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicle 2023, 12, e12353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuana, Y.; Koning, R.I.; Kuil, M.E.; Rensen, P.C.; Koster, A.J.; Bertina, R.M.; Osanto, S. Cryo-electron microscopy of extracellular vesicles in fresh plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 21494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penaloza, C.; Lin, L.; Lockshin, R.A.; Zakeri, Z. Cell death in development: Shaping the embryo. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 126, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorente, A.; Skotland, T.; Sylvänne, T.; Kauhanen, D.; Róg, T.; Orłowski, A.; Vattulainen, I.; Ekroos, K.; Sandvig, K. Molecular lipidomics of exosomes released by PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yan, J.; Shen, X.; Sun, Y.; Thulin, M.; Cai, Y.; Wik, L.; Shen, Q.; Oelrich, J.; Qian, X.; et al. Profiling surface proteins on individual exosomes using a proximity barcoding assay. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.L.; Sun, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.S.; Lu, Y. Exosomes as critical mediators of cell-to-cell communication in cancer pathogenesis and their potential clinical application. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Ortega, L.; Laso-García, F.; Gómez-de Frutos, M.; Fuentes, B.; Diekhorst, L.; Díez-Tejedor, E.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, M. Role of Exosomes as a Treatment and Potential Biomarker for Stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019, 10, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhong, W.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Qin, Z.; Shi, A.; Xu, W.; Zheng, C.; et al. ICAM-1-mediated adhesion is a prerequisite for exosome-induced T cell suppression. Dev. Cell 2022, 57, 329–343.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, M.; Carmo, N.B.; Krumeich, S.; Fanget, I.; Raposo, G.; Savina, A.; Moita, C.F.; Schauer, K.; Hume, A.N.; Freitas, R.P.; et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monypenny, J.; Milewicz, H.; Flores-Borja, F.; Weitsman, G.; Cheung, A.; Chowdhury, R.; Burgoyne, T.; Arulappu, A.; Lawler, K.; Barber, P.R.; et al. ALIX Regulates Tumor-Mediated Immunosuppression by Controlling EGFR Activity and PD-L1 Presentation. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Roake, C.M.; Galati, A.; Bavasso, F.; Micheli, E.; Saggio, I.; Schoeftner, S.; Cacchione, S.; Gatti, M.; Artandi, S.E.; et al. Loss of Human TGS1 Hypermethylase Promotes Increased Telomerase RNA and Telomere Elongation. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1358–1372.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, E.A.; Ono, K.; Eguchi, T. Roles of Extracellular HSPs as Biomarkers in Immune Surveillance and Immune Evasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltbrunner, S.; Larssen, P.; Eldh, M.; Martinez-Bravo, M.J.; Wagner, A.K.; Karlsson, M.C.; Gabrielsson, S. Exosomal cancer immunotherapy is independent of MHC molecules on exosomes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38707–38717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.G.; Grizzle, W.E. Exosomes: A novel pathway of local and distant intercellular communication that facilitates the growth and metastasis of neoplastic lesions. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Park, D.J.; Eliceiri, B.P. Defining tropism and activity of natural and engineered extracellular vesicles. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1363185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixson, A.C.; Dawson, T.R.; Di Vizio, D.; Weaver, A.M. Context-specific regulation of extracellular vesicle biogenesis and cargo selection. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 454–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga-Lagache, S.; Buchs, N.; Iacovache, M.I.; Zuber, B.; Jackson, C.B.; Heller, M. Robust label-free, quantitative profiling of circulating Plasma Microparticle (MP) associated proteins. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 3640–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Wang, C.A. Review of the regulatory mechanisms of extracellular vesicles-mediated intercellular communication. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Su, H.; Li, J.; Lyon, C.; Tang, W.; Wan, M.; Hu, T.Y. Clinical applications of exosome membrane proteins. Precis. Clin. Med. 2020, 3, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Xiao, F.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, H. Surface Phosphatidylserine Is Responsible for the Internalization on Microvesicles Derived from Hypoxia-Induced Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Human Endothelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.P.; Mardini, O.; Ericsson, M.; Prabhakar, S.; Maguire, C.; Chen, J.W.; Tannous, B.A.; Breakefield, X.O. Dynamic Biodistribution of Extracellular Vesicles In Vivo Using a Multimodal Imaging Reporter. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaram, S.; Sen, A.; Singh, V.; Raj Ps, M.; Dwivedi, S.; Bansal, A. T Role of Exosomal miRNAs and Epigenetic Modifications in Diabetic Nephropathy: Insights into Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies. Curr. Gene Ther. 2025; advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, R.N.; Alghazali, K.M.; Biris, A.S.; Griffin, R.J. Exosome Traceability and Cell Source Dependence on Composition and Cell-Cell Cross Talk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Liu, Y.T.; Fan, J. Exosomal mediators in sepsis and inflammatory organ injury: Unraveling the role of exosomes in intercellular crosstalk and organ dysfunction. Mil. Med. Res. 2024, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Ji, P. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells regulate M1/M2 macrophage phenotypic polarization to promote bone healing via miR-451a/MIF. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, T.; Hu, S.; Du, K.; Ren, A.; Jia, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Lai, S. Mammary epithelial cell derived exosomal MiR-221 mediates M1 macrophage polarization via SOCS1/STATs to promote inflammatory response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Ji, H.; Tong, X.; Xia, R.; Wang, W.; Ma, Z.; Shi, X. Exosomal miR-30d-5p of neutrophils induces M1 macrophage polarization and primes macrophage pyroptosis in sepsis-related acute lung injury. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Yang, J.; Guo, S.; Zhao, G.; Wu, H.; Deng, G. Peripheral Circulating Exosome-Mediated Delivery of miR-155 as a Novel Mechanism for Acute Lung Inflammation. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1758–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.; Shen, X.; Sprent, J. Direct stimulation of naive T cells by membrane vesicles from antigen-presenting cells: Distinct roles for CD54 and B7 molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6670–6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y. Exosome: The Regulator of the Immune System in Sepsis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 671164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, E.; Nicco, C.; Lombard, B.; Véron, P.; Raposo, G.; Batteux, F.; Amigorena, S.; Théry, C. ICAM-1 on exosomes from mature dendritic cells is critical for efficient naive T-cell priming. Blood 2005, 106, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkach, M.; Kowal, J.; Zucchetti, A.E.; Enserink, L.; Jouve, M.; Lankar, D.; Saitakis, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Théry, C. Qualitative differences in T-cell activation by dendritic cell-derived extracellular vesicle subtypes. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 3012–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecalvo, A.; Shufesky, W.J.; Stolz, D.B.; Sullivan, M.G.; Wang, Z.; Divito, S.J.; Papworth, G.D.; Watkins, S.C.; Robbins, P.D.; Larregina, A.T.; et al. Exosomes as a short-range mechanism to spread alloantigen between dendritic cells during T cell allorecognition. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, P.D.; Dorronsoro, A.; Booker, C.N. Regulation of chronic inflammatory and immune processes by extracellular vesicles. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, N.T.; Kageyama, R.; Ansel, K.M. Selective Export into Extracellular Vesicles and Function of tRNA Fragments during T Cell Activation. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 3356–3370.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralba, D.; Baixauli, F.; Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Fernández-Delgado, I.; Latorre-Pellicer, A.; Acín-Pérez, R.; Martín-Cófreces, N.B.; Jaso-Tamame, Á.L.; Iborra, S.; Jorge, I.; et al. Priming of dendritic cells by DNA-containing extracellular vesicles from activated T cells through antigen-driven contacts. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Jin, J.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; Luo, H.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Exosomes Derived From Septic Mouse Serum Modulate Immune Responses via Exosome-Associated Cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essandoh, K.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Qin, D.; Hao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zingarelli, B.; Peng, T.; Fan, G.C. Blockade of exosome generation with GW4869 dampens the sepsis-induced inflammation and cardiac dysfunction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 2362–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, Y.; Goodwin, A.J.; Wolf, B.; Halushka, P.V.; Wang, H.; Zingarelli, B.; Fan, H. Circulating extracellular vesicles are associated with the clinical outcomes of sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1150564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, H.; Qin, D.; Yang, L.; Huang, W.; Essandoh, K.; Wang, Y.; Caldwell, C.C.; Peng, T.; Zingarelli, B.; et al. Exosomal miR-223 Contributes to Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Elicited Cardioprotection in Polymicrobial Sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Goodwin, A.J.; Cook, J.A.; Halushka, P.V.; Chang, E.; Fan, H. Exosomes from Endothelial Progenitor Cells Improve the Outcome of a Murine Model of Sepsis. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, R.; Hou, Y.; Lin, A. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes prevent sepsis-induced myocardial injury by a CircRTN4/miR-497-5p/MG53 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 618, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnegris, H.M.; Abdelrahman, A.A.; El-Roghy, E.S. The potential therapeutic effects of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ileum injury of a rat sepsis model (histological and immunohistochemical study). Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2024, 48, 274–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachetto, A.T.A.; Archibald, S.J.; Hisada, Y.; Rosell, A.; Havervall, S.; van Es, N.; Nieuwland, R.; Campbell, R.A.; Middleton, E.A.; Rondina, M.T.; et al. Tissue factor activity of small and large extracellular vesicles in different diseases. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 7, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, A.P.; Mackman, N. Microparticles in hemostasis and thrombosis. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackman, N. The role of tissue factor and factor VIIa in hemostasis. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 108, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Deng, Q.J. Role of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles in traumatic brain injury-induced coagulopathy and inflammation. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 2102–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiasch, A.K.; Lehner, G.F.; Feistritzer, C.; Peer, A.; Zassler, B.; Neumair, V.M.; Klein, S.J.; Joannidis, M. Extracellular vesicle tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor are independent discriminators of sepsis-induced coagulopathy. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2024, 8, 102596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Ryu, T.; Mohamed-Hinds, R.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.H.; Zou, L.; Williams, B.; Na, C.H.; Chao, W. Proteomic profiling of plasma extracellular vesicles identifies signatures of innate immunity, coagulation, and endothelial activation in septic patients. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 21871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Chen, H.; Qi, B.; Jiang, Y.; Lian, N.; Zhuang, X.; Yu, Y. Brain-derived extracellular vesicles mediated coagulopathy, inflammation and apoptosis after sepsis. Thromb. Res. 2021, 207, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.; Lin, Q.; Xiao, W.; Mao, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, L.; Wu, X.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. miR-150-5p in neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles associated with sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy in septic patients. Cell Death. Discov. 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campello, E.; Radu, C.M.; Simion, C.; Spiezia, L.; Bulato, C.; Gavasso, S.; Tormene, D.; Perin, N.; Turatti, G.; Simioni, P. Longitudinal Trend of Plasma Concentrations of Extracellular Vesicles in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 770463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helin, T.; Palviainen, M.; Lemponen, M.; Maaninka, K.; Siljander, P.; Joutsi-Korhonen, L. Increased circulating platelet-derived extracellular vesicles in severe COVID-19 disease. Platelets 2024, 35, 2313362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Słomka, A.; Urban, S.K.; Lukacs-Kornek, V.; Żekanowska, E.; Kornek, M. Large Extracellular Vesicles: Have We Found the Holy Grail of Inflammation? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepesch, C.; Nitzsche, R.; Glass, A.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Schubert, J.K.; Oehmcke-Hecht, S. High intravascular tissue factor-but not extracellular microvesicles-in septic patients is associated with a high SAPS II score. J. Intensive Care 2016, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canzano, P.; Brambilla, M.; Porro, B.; Cosentino, N.; Tortorici, E.; Vicini, S.; Poggio, P.; Cascella, A.; Pengo, M.F.; Veglia, F.; et al. Platelet and Endothelial Activation as Potential Mechanisms Behind the Thrombotic Complications of COVID-19 Patients. JACC Basic. Transl. Sci. 2021, 6, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, M.; Frigerio, R.; Becchetti, A.; Gori, A.; Cretich, M.; Conti, M.; Mazza, A.; Pengo, M.; Camera, M. Head-to-Head Comparison of Tissue Factor-Dependent Procoagulant Potential of Small and Large Extracellular Vesicles in Healthy Subjects and in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Biology 2023, 12, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, Y.; Yoo, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.; Suh, G.Y.; Jeon, K. Association of plasma exosomes with severity of organ failure and mortality in patients with sepsis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9439–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahida, R.Y.; Price, J.; Lugg, S.T.; Li, H.; Parekh, D.; Scott, A.; Harrison, P.; Matthay, M.A.; Thickett, D.R. CD14-positive extracellular vesicles in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid as a new biomarker of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2022, 322, L617–L624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, H.; Furuya, S.; Amemiya, H.; Hosomura, N.; Ichikawa, D. Exosomes isolated from blood induce acute lung injury in a rat septic peritonitis model. Shock, 2025; advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, J. Neutrophil-derived exosomal S100A8 aggravates lung injury in sepsis by inducing pyroptosis. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 181, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, M.F.; Ferreira, L.R.P.; Vieira Junior, J.M.; Deheinzelin, D.; Aparecida Santos Nussbaum, A.C.; Toshihiro Sakamoto, L.H.; Vasconcelos, R.O.; Salomao, R.; Waisberg, J.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles as potential biomarkers and mediators of acute respiratory distress syndrome in sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taggart, C.; Wereski, R.; Mills, N.L.; Chapman, A.R. Diagnosis, Investigation and Management of Patients with Acute and Chronic Myocardial Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Geng, H.; Sun, Y.; Feng, W.; Tian, T.; Ye, L.; Lei, M. Exosomes derived from the blood of patients with sepsis regulate apoptosis and aerobic glycolysis in human myocardial cells via the hsa-miR-1262/SLC2A1 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, M.; Tu, F.; Yang, K.; Ha, T.; Liu, L.; Kalbfleisch, J.; Williams, D.; Li, C. Endothelial HSPA12B Exerts Protection Against Sepsis-Induced Severe Cardiomyopathy via Suppression of Adhesion Molecule Expression by miR-126. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Liao, H.; Hao, S.; Hou, D.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Song, R.; Tan, X.; Luo, Z.; et al. TSPO exacerbates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction by inhibiting p62-Mediated autophagic flux via the ROS-RIP1/RIP3-exosome axis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 226, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegyesi, H.; Pallinger, É.; Mecsei, S.; Hornyák, B.; Kovácsházi, C.; Brenner, G.B.; Giricz, Z.; Pálóczi, K.; Kittel, Á.; Tóvári, J.; et al. Circulating cardiomyocyte-derived extracellular vesicles reflect cardiac injury during systemic inflammatory response syndrome in mice. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, H.; Yue, L. Endothelial progenitor cells-secreted extracellular vesicles containing microRNA-93-5p confer protection against sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via the KDM6B/H3K27me3/TNF-α axis. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 395, 112173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, P.; Tan, X.; Sheng, M.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, P.; Yu, M. Platelet Exosome-Derived miR-223-3p Regulates Pyroptosis in the Cell Model of Sepsis-Induced Acute Renal Injury by Targeting Mediates NLRP3. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 44, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panich, T.; Chancharoenthana, W.; Somparn, P.; Issara-Amphorn, J.; Hirankarn, N.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Urinary exosomal activating transcriptional factor 3 as the early diagnostic biomarker for sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zou, B.; Liou, Y.C.; Huang, C. The pathogenesis and diagnosis of sepsis post burn injury. Burns Trauma 2021, 9, tkaa047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dea, K.P.; Porter, J.R.; Tirlapur, N.; Katbeh, U.; Singh, S.; Handy, J.M.; Takata, M. Circulating Microvesicles Are Elevated Acutely following Major Burns Injury and Associated with Clinical Severity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chatterjee, V.; Zheng, E.; Reynolds, A.; Ma, Y.; Villalba, N.; Tran, T.; Jung, M.; Smith, D.J.; Wu, M.H.; et al. Burn Injury-Induced Extracellular Vesicle Production and Characteristics. Shock 2022, 57, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, M.L.; Seim, R.F.; Herring, L.E.; Mordant, A.L.; Webb, T.S.; Upchurch, G.R.; Sharma, A.K.; Cairns, B.A.; Efron, P.A.; Wallet, S.M.; et al. Temporal changes in the protein cargo of extracellular vesicles and resultant immune reprogramming after severe burn injury in humans and mice. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1596598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavello, M.; Bosco, O.; Vizio, B.; Sciarrillo, A.; Pensa, A.; Pivetta, E.; Morello, F.; Risso, D.; Montrucchio, G.; Mariano, F.; et al. Profiling of miRNAs Contained in Circulating Extracellular Vesicles and Associated with Sepsis Development in Burn Patients: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, H.J.; Lowe, N.M.; Arun, V.; Kolesov, A.V.; Palmieri, T.L.; Tran, N.K.; Carney, R.P. Plasma-derived Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) as Biomarkers of Sepsis in Burn Patients via Label-free Raman Spectroscopy. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter-Ovanesyan, D.; Norman, M.; Lazarovits, R.; Trieu, W.; Lee, J.H.; Church, G.M.; Walt, D.R. Framework for rapid comparison of extracellular vesicle isolation methods. Elife 2021, 10, e70725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, C.; Bruce, K.D.; Burgy, O.; Boyd, T.D.; Michel, C.R.; Garcia-Perez, J.E.; Adame, V.; Anton, P.; Bettcher, B.M.; Chial, H.J.; et al. Exosome Isolation by Ultracentrifugation and Precipitation and Techniques for Downstream Analyses. Curr. Protoc. Cell. Biol. 2020, 88, e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Arntz, O.J.; Husch, J.F.A.; Kraan, P.M.V.; Beucken, J.J.J.P.V.D.; van de Loo, F.A.J. Polyethylene glycol precipitation is an efficient method to obtain extracellular vesicle-depleted fetal bovine serum. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, G.; Qadri, S.; Parray, A.; Akhthar, N.; Shuaib, A.; Haik, Y. Exosomes Derived Neuronal Markers: Immunoaffinity Isolation and Characterization. Neuromol. Med. 2022, 24, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshi, Q.U.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Dissanayake, K.; Fazeli, A. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) Using Benchtop Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) Columns. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2273, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, S.E.; van de Wakker, S.I.; Phillips, W.; Willms, E.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Hill, A.F.; Wood, M.J.A.; Vader, P. Scalable purification of extracellular vesicles with high yield and purity using multimodal flowthrough chromatography. J. Extracell. Biol. 2024, 3, e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, A.; Hu, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, L.; Shen, Z. Recent developments in isolating methods for exosomes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1100892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, W.; Yoshida, T.; Diez, D.; Miyatake, Y.; Nishibu, T.; Imawaka, N.; Naruse, K.; Sadamura, Y.; Hanayama, R. A novel affinity-based method for the isolation of highly purified extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías, M.; Rebmann, V.; Mateos, B.; Varo, N.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Alegre, E.; González, Á. Comparison of six commercial serum exosome isolation methods suitable for clinical laboratories. Effect in cytokine analysis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deregibus, M.C.; Figliolini, F.; D’Antico, S.; Manzini, P.M.; Pasquino, C.; De Lena, M.; Tetta, C.; Brizzi, M.F.; Camussi, G. Charge-based precipitation of extracellular vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Murakami, K.; Borra, V.J.; Ozen, M.O.; Demirci, U.; Nakamura, T.; Esfandiari, L. A Label-Free Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy for Detection of Clusters of Extracellular Vesicles Based on Their Unique Dielectric Properties. Biosensors 2022, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggiolaro, A.; Moccia, V.; Brun, P.; Pierno, M.; Mistura, G.; Zappulli, V.; Ferraro, D. Microfluidic Strategies for Extracellular Vesicle Isolation: Towards Clinical Applications. Biosensors 2022, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, A.; Lim, H.C.; Evander, M.; Lilja, H.; Laurell, T.; Scheding, S.; Ceder, Y. Acoustic Enrichment of Extracellular Vesicles from Biological Fluids. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8011–8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broman, A.; Lenshof, A.; Evander, M.; Happonen, L.; Ku, A.; Malmström, J.; Laurell, T. Multinodal Acoustic Trapping Enables High Capacity and High Throughput Enrichment of Extracellular Vesicles and Microparticles in miRNA and MS Proteomics Studies. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3929–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Cai, N.; Niu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yan, X. Quantitative assessment of lipophilic membrane dye-based labelling of extracellular vesicles by nano-flow cytometry. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görgens, A.; Bremer, M.; Ferrer-Tur, R.; Murke, F.; Tertel, T.; Horn, P.A.; Thalmann, S.; Welsh, J.A.; Probst, C.; Guerin, C.; et al. Optimisation of imaging flow cytometry for the analysis of single extracellular vesicles by using fluorescence-tagged vesicles as biological reference material. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1587567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Shiba, T.; Yoshida, T.; Bolidong, D.; Kato, K.; Sato, Y.; Mochizuki, M.; Seto, T.; Kawashiri, S.; Hanayama, R. Precise analysis of single small extracellular vesicles using flow cytometry. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.N.; Guerreiro, E.M.; Enciso-Martinez, A.; Kruglik, S.G.; Otto, C.; Snir, O.; Ricaud, B.; Hellesø, O.G. Identification of extracellular vesicles from their Raman spectra via self-supervised learning. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, Y.; Mirzaaghasi, A.; Heo, J.; Kim, Y.N.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, N.H.; Cho, E.S.; In Yook, J.; et al. Exosome-based delivery of super-repressor IκBα relieves sepsis-associated organ damage and mortality. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, K.; Wang, F.; Fei, X.; Niu, C.; Li, T.; Liu, L. Neutrophil membrane-engineered Panax ginseng root-derived exosomes loaded miRNA 182-5p targets NOX4/Drp-1/NLRP3 signal pathway to alleviate acute lung injury in sepsis: Experimental studies. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.; Busatto, S.; Pham, A.; Tian, M.; Suh, A.; Carson, K.; Quintero, A.; Lafrence, M.; Malik, H.; Santana, M.X.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Theranostics 2019, 9, 8001–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostyushev, D.; Kostyusheva, A.; Brezgin, S.; Smirnov, V.; Volchkova, E.; Lukashev, A.; Chulanov, V. Gene Editing by Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutaria, D.S.; Badawi, M.; Phelps, M.A.; Schmittgen, T.D. Achieving the Promise of Therapeutic Extracellular Vesicles: The Devil is in Details of Therapeutic Loading. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilahibaks, N.F.; Ardisasmita, A.I.; Xie, S.; Gunnarsson, A.; Brealey, J.; Vader, P.; de Jong, O.G.; de Jager, S.; Dekker, N.; Peacock, B.; et al. TOP-EVs: Technology of Protein delivery through Extracellular Vesicles is a versatile platform for intracellular protein delivery. J. Control. Release 2023, 355, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincela Lins, P.M.; Pirlet, E.; Szymonik, M.; Bronckaers, A.; Nelissen, I. Manufacture of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stromal cells. Trends Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 965–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, J.; Stone, T., Jr.; Wang, Y. Biomaterial-enabled 3D cell culture technologies for extracellular vesicle manufacturing. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 4055–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, A.; Parmar, G.; Kirkham, A.M.; Burger, D.; Allan, D.S. Registered clinical trials investigating treatment with cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A scoping review. Cytotherapy 2023, 25, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, Q. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate sepsis-induced lung injury in mice by inhibiting the secretion of IL-27 in macrophages. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, B.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Hou, L.; Yang, Z. BMSC-Derived Exosomes Alleviate Sepsis-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Activating the Nrf2 Pathway to Reverse Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Stem Cells Int. 2023, 2023, 7072700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, H.; Namjoo, A.R.; Narmi, M.T.; Mardi, N.; Narimani, S.; Naturi, O.; Khosrowshahi, N.D.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Saghebasl, S.; Hashemzadeh, S.; et al. Exosome-bearing hydrogels and cardiac tissue regeneration. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Won, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Choi, M.; Lee, E.; Ryoou, B.; Lee, S.G.; Cho, B.S. Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Pan, C.; Xu, P.; Liu, K. Hydrogel-mediated extracellular vesicles for enhanced wound healing: The latest progress, and their prospects for 3D bioprinting. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Exosomes | Microvesicles | Apoptotic Bodies | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | 30–150 nm | 100–1000 nm | 1–5 μm | [3,4,5,6,7,8,9] |
| Origin | From multivesicular bodies | From plasma membrane | From plasma membrane and cellular fragment | [10,11] |
| Mechanism of formation | Released by fusion with plasma membrane | From swelling towards the outside of the plasma membrane | Apoptotic process byproducts | [12,13] |
| Content | Proteins, lipids, RNA, DNA, mRNA and miRNA | Proteins, lipids, RNA, DNA, mRNA and miRNA | Cytosol portions, degraded proteins, DNA fragments, or organelles | [14] |
| Membrane markers | CD9, CD63 and CD81, and ESCRT proteins Alix and TSG101 | Selectins, flotillin-2, ARF6 and CD40 | Caspase3, CD3 and CD44 | [15] |
| Role | Cell–cell communication | Coagulation | Cell clearance | [16] |
| Charge | Negative | Negative | Not reported | [17,18] |
| Shape at EM | Small and spherical | Small and spherical | Heterogenous in size and shape | [19,20] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Repici, A.; Piraino, G.; Wolfe, V.; Kaplan, J.; Nakamura, T.; Zingarelli, B. Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Cell Communication and Novel Biomarkers in Sepsis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186649
Repici A, Piraino G, Wolfe V, Kaplan J, Nakamura T, Zingarelli B. Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Cell Communication and Novel Biomarkers in Sepsis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186649
Chicago/Turabian StyleRepici, Alberto, Giovanna Piraino, Vivian Wolfe, Jennifer Kaplan, Takahisa Nakamura, and Basilia Zingarelli. 2025. "Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Cell Communication and Novel Biomarkers in Sepsis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186649
APA StyleRepici, A., Piraino, G., Wolfe, V., Kaplan, J., Nakamura, T., & Zingarelli, B. (2025). Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Cell Communication and Novel Biomarkers in Sepsis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186649







