Prevalence of Obesity After Living Kidney Donation and Associated Risk Factors: Cardiovascular and Renal Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Donor Variables
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
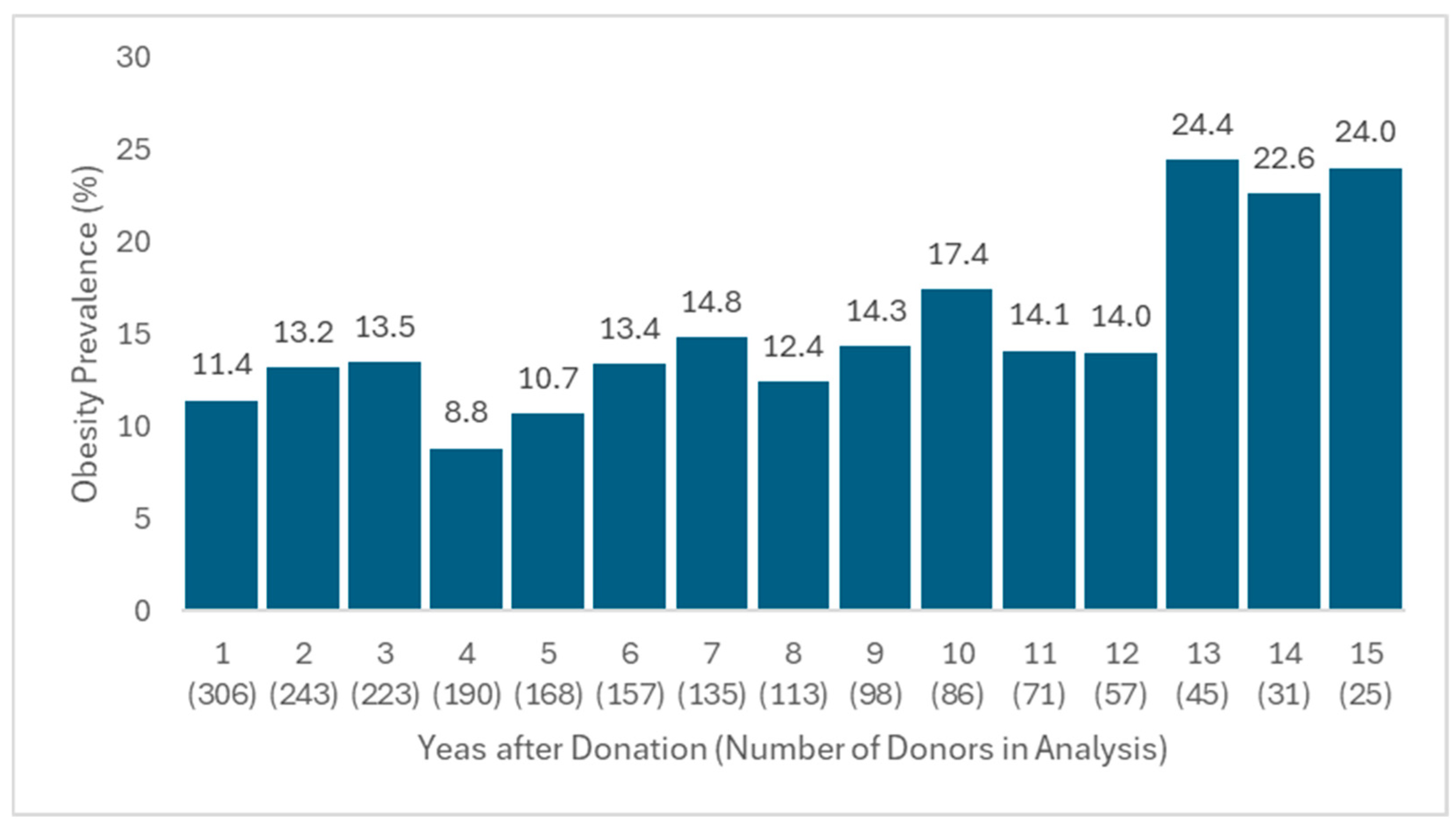
3.2. Evaluation of Obesity Prevalence and Predictors
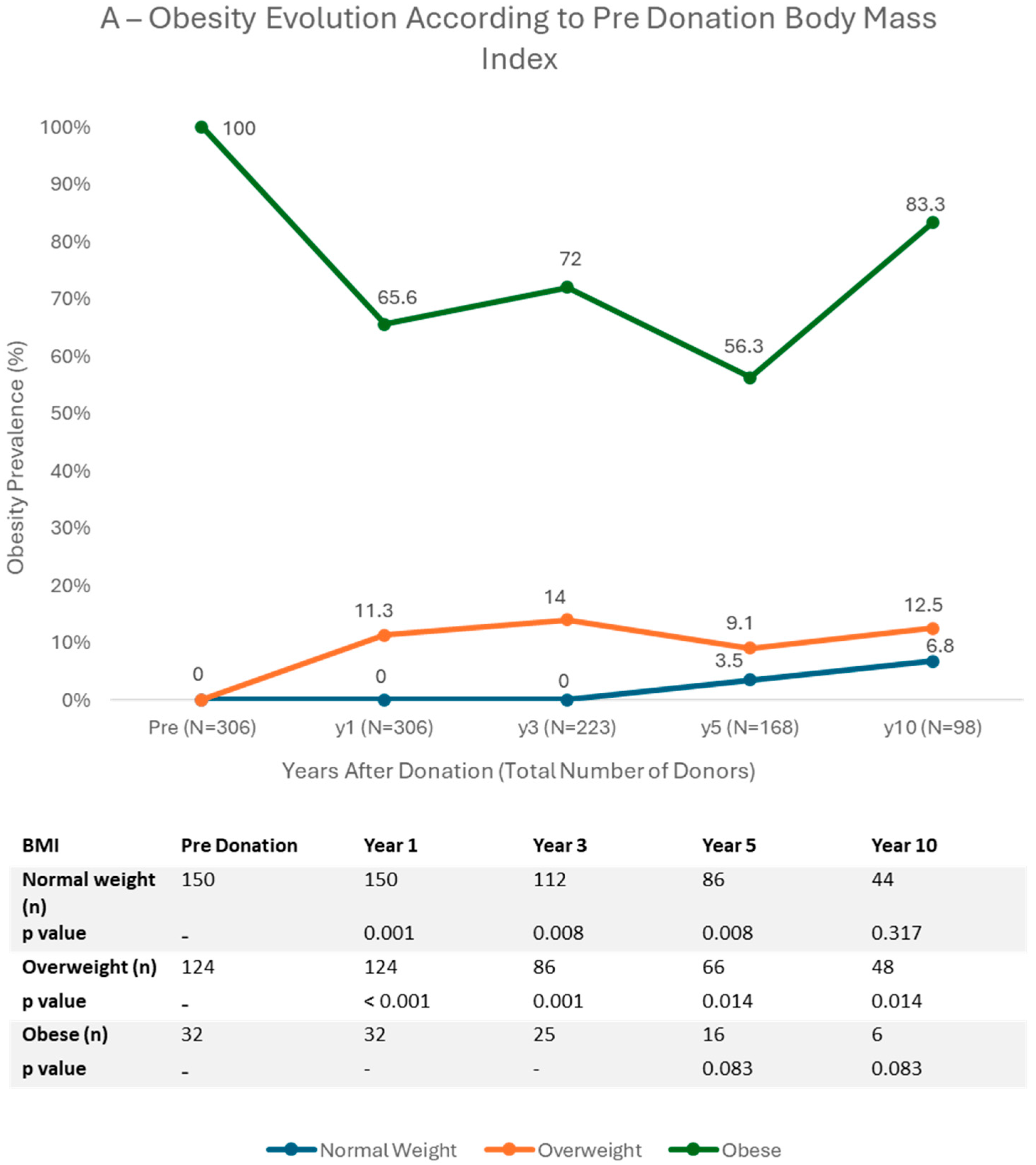
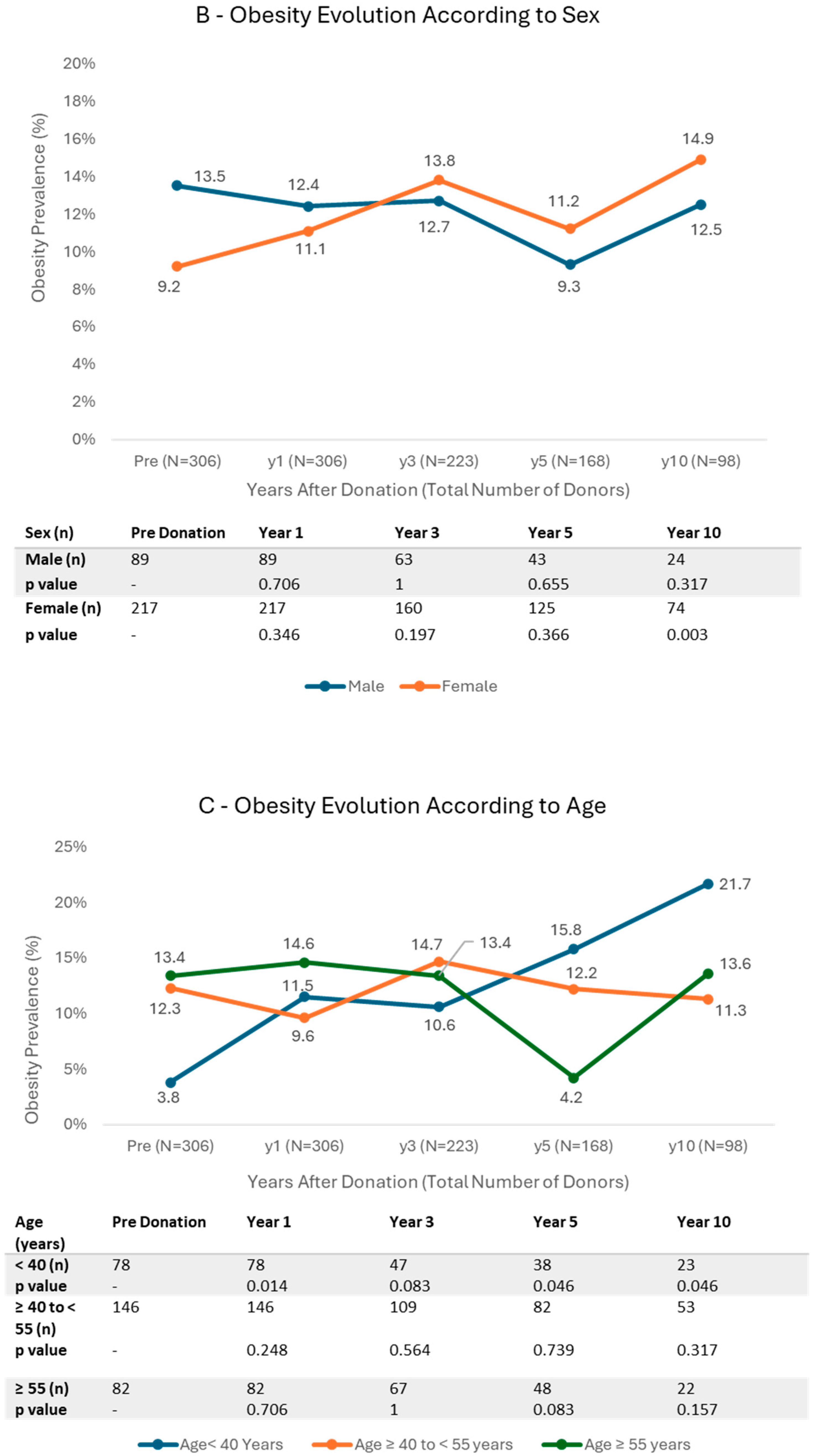
3.3. Trends in BMI Categories
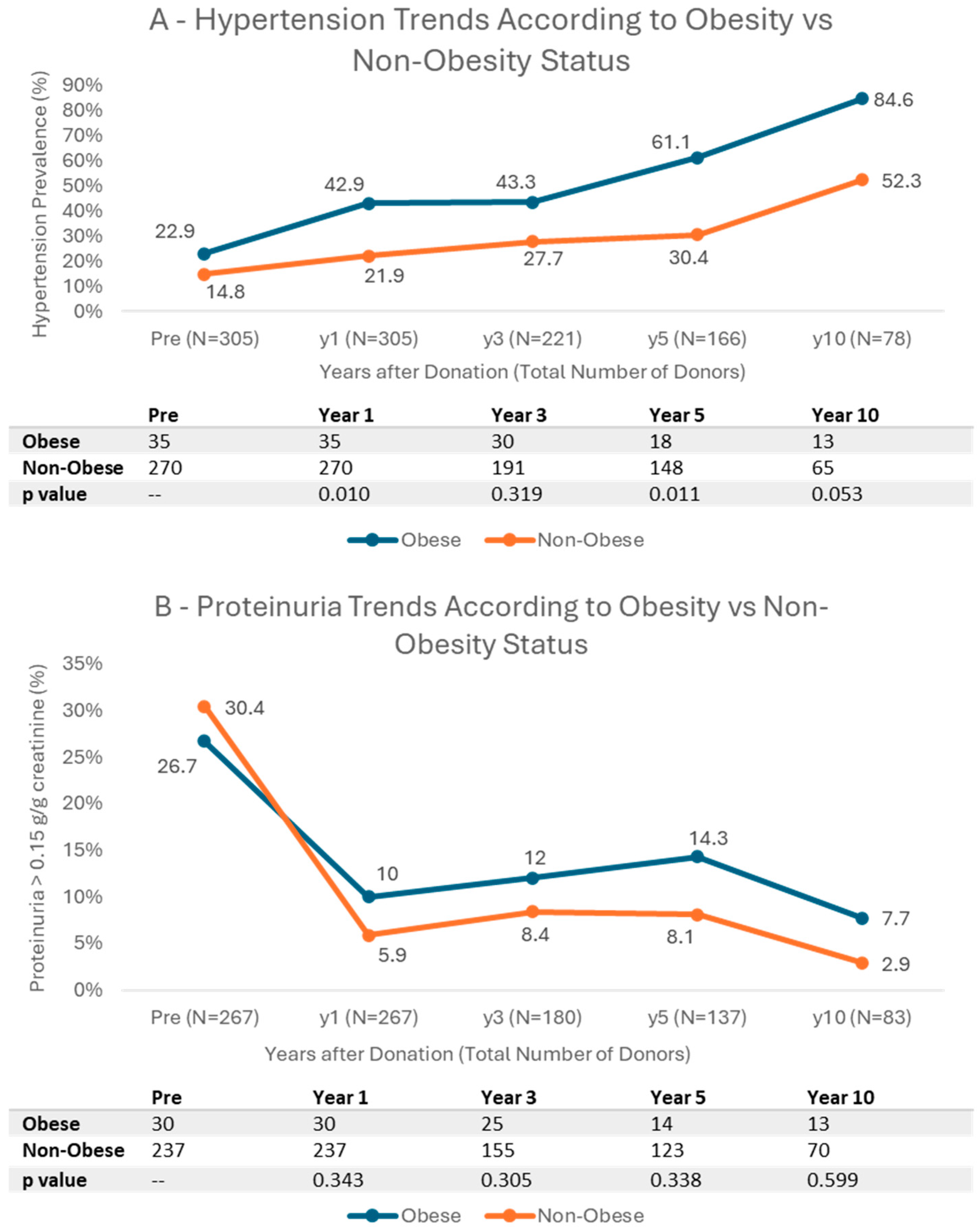
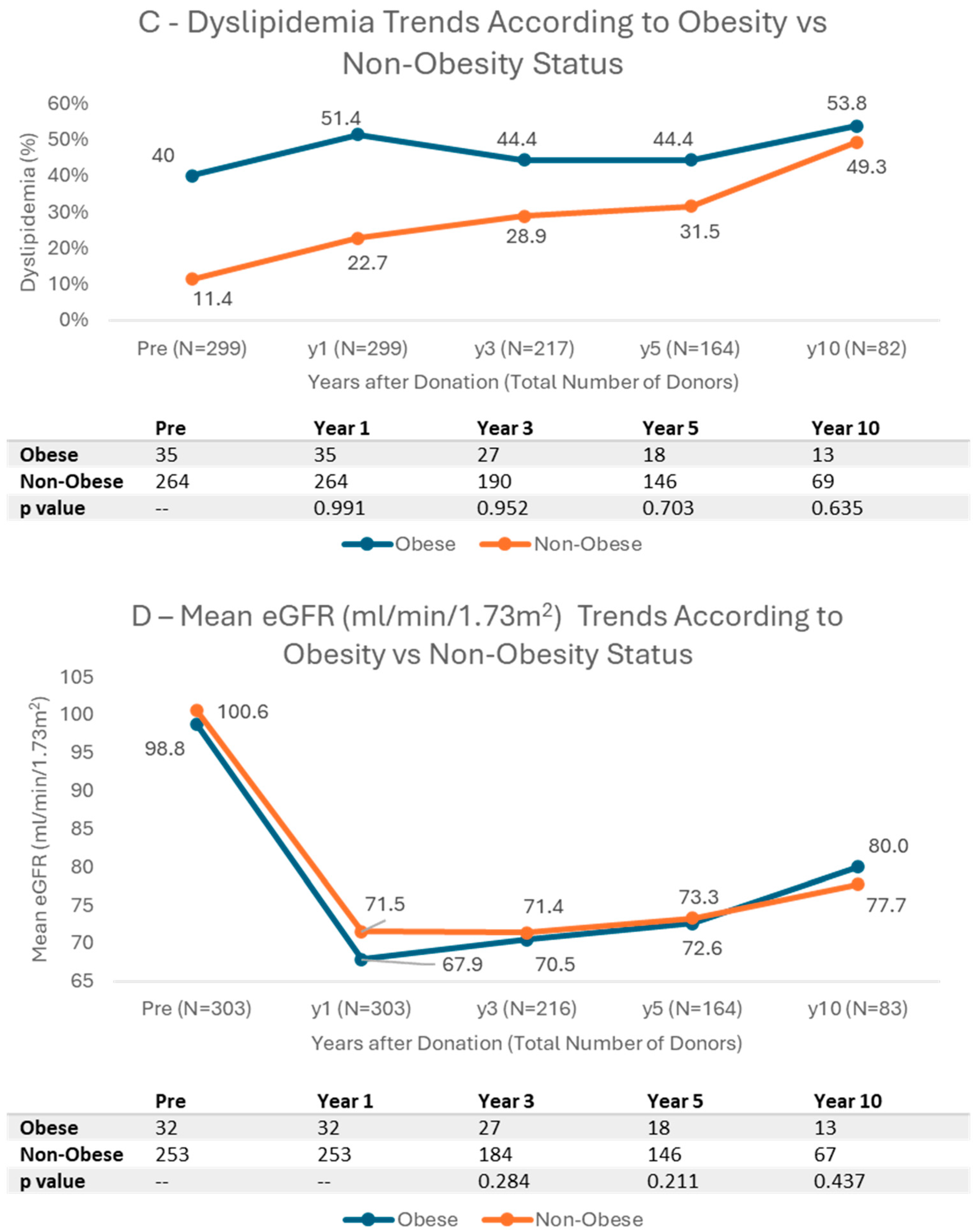
3.4. Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Kidney Function Trends According to BMI
4. Discussion
4.1. Obesity and Age
4.2. Pre Donation Body Mass Index
4.3. Pre Donation Dyslipidemia
4.4. Cardiovascular Risk
4.5. Kidney Function and Proteinuria
4.6. Limitations
4.7. Clinical Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BP | Blood Pressure |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| eGFR | Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| ESKD | End-Stage Kidney Disease |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| KDIGO | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes |
| LKD | Living Kidney Donor |
| LKDT | Living Kidney Donor Transplantation |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
References
- Kovesdy, C.P. Epidemiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: An Update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2022, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, R.A.; Ashby, V.B.; Milford, E.L.; Ojo, A.O.; Ettenger, R.E.; Agodoa, L.Y.C.; Held, P.J.; Port, F.K. Comparison of Mortality in All Patients on Dialysis, Patients on Dialysis Awaiting Transplantation, and Recipients of a First Cadaveric Transplant. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, A.R.; Lafranca, J.A.; Claessens, L.A.; Imamdi, R.M.S.; Ijzermans, J.N.M.; Betjes, M.G.H.; Dor, F.J.M.F. Shifting Paradigms in Eligibility Criteria for Live Kidney Donation: A Systematic Review. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atividade Nacional Annual. 2021. Available online: https://www.ipst.pt/files/TRANSPLANTACAO/DOACAOETRANSPLANTACAO/Dados_Anuais_Atividade_Doacao_Transplantacao2021.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- McCormick, F.; Held, P.J.; Chertow, G.M. The Terrible Toll of the Kidney Shortage. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 2775–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.; Escoli, R.; Eusébio, C.; Dias, L.; Almeida, M.; Martins, L.S.; Pedroso, S.; Henriques, A.C.; Cabrita, A. A Survival Analysis of Living Donor Kidney Transplant. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, M. Weight Trends in United States Living Kidney Donors: Analysis of the UNOS Database. World J. Transplant. 2015, 5, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardinha, L.B.; Santos, D.A.; Silva, A.M.; Coelho-e-Silva, M.J.; Raimundo, A.M.; Moreira, H.; Santos, R.; Vale, S.; Baptista, F.; Mota, J. Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity, and Abdominal Obesity in a Representative Sample of Portuguese Adults. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, K.; Kuah, R.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Lam, T.K.T. Obesity and the Kidney: Mechanistic Links and Therapeutic Advances. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Chang, T.I.; Joo, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, C.; Yun, H.; Park, J.T.; Yoo, T.; Sung, S.A.; et al. Association Between Serum High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: Results from the KNOW-CKD. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agati, V.D.; Chagnac, A.; de Vries, A.P.J.; Levi, M.; Porrini, E.; Herman-Edelstein, M.; Praga, M. Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy: Clinical and Pathologic Characteristics and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, F.; Deprele, C.; Sassolas, A.; Moulin, P.; Alamartine, E.; Berthezène, F.; Berthoux, F. Excessive Body Weight as a New Independent Risk Factor for Clinical and Pathological Progression in Primary IgA Nephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 37, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, K.A.; Kramer, H.; Bidani, A.K. Adverse Renal Consequences of Obesity. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2008, 294, F685–F696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazzullo, P.; Barba, G.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Siani, A.; Trevisan, M.; Farinaro, E.; Pagano, E.; Barbato, A.; Iacone, R.; Galletti, F. Altered Renal Sodium Handling in Men with Abdominal Adiposity: A Link to Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeli, S.; Böhnke, J.; Gorzelniak, K.; Janke, J.; Schling, P.; Bader, M.; Luft, F.C.; Sharma, A.M. Weight Loss and the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System. Hypertension 2005, 45, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, N.; Okabayashi, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Yokoo, T. The Renal Pathology of Obesity. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, A.P.J.; Ruggenenti, P.; Ruan, X.Z.; Praga, M.; Cruzado, J.M.; Bajema, I.M.; D’Agati, V.D.; Lamb, H.J.; Barlovic, D.P.; Hojs, R.; et al. Fatty Kidney: Emerging Role of Ectopic Lipid in Obesity-Related Renal Disease. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbay, M.; Copur, S.; Ucku, D.; Zoccali, C. Donor Obesity and Weight Gain after Transplantation: Two Still Overlooked Threats to Long-Term Graft Survival. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, M. Should Obesity Affect Suitability for Kidney Donation? Semin. Dial. 2018, 31, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.I.; Harraz, A.M.; Shokeir, A.A. Controversies related to living kidney donors. Arab. J. Urol. 2011, 9, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, J.E.; Reed, R.D.; Massie, A.; MacLennan, P.A.; Sawinski, D.; Kumar, V.; Mehta, S.; Mannon, R.B.; Gaston, R.; Lewis, C.E.; et al. Obesity Increases the Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease among Living Kidney Donors. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.N.; Foley, R.N.; Reule, S.A.; Spong, R.; Kukla, A.; Issa, N.; Berglund, D.M.; Sieger, G.K.; Matas, A.J. Renal Function Profile in White Kidney Donors: The First 4 Decades. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massie, A.B.; Muzaale, A.D.; Luo, X.; Chow, E.K.H.; Locke, J.E.; Nguyen, A.Q.; Henderson, M.L.; Snyder, J.J.; Segev, D.L. Quantifying Postdonation Risk of ESRD in Living Kidney Donors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2749–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzaale, A.D.; Massie, A.B.; Wang, M.-C.; Montgomery, R.A.; McBride, M.A.; Wainright, J.L.; Segev, D.L. Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease Following Live Kidney Donation. JAMA 2014, 311, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjøen, G.; Hallan, S.; Hartmann, A.; Foss, A.; Midtvedt, K.; Øyen, O.; Reisæter, A.; Pfeffer, P.; Jenssen, T.; Leivestad, T.; et al. Long-Term Risks for Kidney Donors. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, N.N.; Lentine, K.L.; Garg, A.X. End-Stage Renal Disease Risk in Live Kidney Donors. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, P.P.; Boudville, N.; Garg, A.X. Living Kidney Donation: Outcomes, Ethics, and Uncertainty. Lancet 2015, 385, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentine, K.L.; Kasiske, B.L.; Levey, A.S.; Adams, P.L.; Alberú, J.; Bakr, M.A.; Gallon, L.; Garvey, C.A.; Guleria, S.; Li, P.K.-T.; et al. Summary of Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Clinical Practice Guideline on the Evaluation and Care of Living Kidney Donors. Transplantation 2017, 101, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, P.A.; Burnapp, L. British Transplantation Society/Renal Association UK Guidelines for Living Donor Kidney Transplantation 2018: Summary of Updated Guidance. Transplantation 2018, 102, e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A New Equation to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.; Calheiros Cruz, G.; Sousa, C.; Figueiredo, C.; Ventura, S.; Silvano, J.; Pedroso, S.; Martins, L.S.; Ramos, M.; Malheiro, J. External Validation of the Toulouse-Rangueil Predictive Model to Estimate Donor Renal Function After Living Donor Nephrectomy. Transpl. Int. 2023, 36, 11151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Ribeiro, C.; Silvano, J.; Pedroso, S.; Tafulo, S.; Martins, L.S.; Ramos, M.; Malheiro, J. Living Donors’ Age Modifies the Impact of Pre-Donation Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate on Graft Survival. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, D.B.; Arnold, M.; Bakris, G.L.; Bruns, D.E.; Horvath, A.R.; Kirkman, M.S.; Lernmark, A.; Metzger, B.E.; Nathan, D.M. Position Statement Executive Summary: Guidelines and Recommendations for Laboratory Analysis in the Diagnosis and Management of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1419–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Liu, T.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Ruan, G.; Xie, H.; Song, M.; Lin, S.; Yao, Q.; et al. The Age-related Obesity Paradigm: Results from Two Large Prospective Cohort Studies. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2024, 15, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugeja, A.; Harris, S.; Ernst, J.; Burns, K.D.; Knoll, G.; Clark, E.G. Changes in Body Weight Before and After Kidney Donation. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2019, 6, 2054358119847203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punjala, S.R.; Adamjee, Q.; Silas, L.; Gökmen, R.; Karydis, N. Weight Trends in Living Kidney Donors Suggest Predonation Counselling Alone Lacks a Sustainable Effect on Weight Loss: A Single Centre Cohort Study. Transpl. Int. 2021, 34, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, N.; Sánchez, O.A.; Kukla, A.; Riad, S.M.; Berglund, D.M.; Ibrahim, H.N.; Matas, A.J. Weight Gain after Kidney Donation: Association with Increased Risks of Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertension. Clin. Transpl. 2018, 32, e13360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, O.A.; Ferrara, L.K.; Rein, S.; Berglund, D.; Matas, A.J.; Ibrahim, H.N. Hypertension after Kidney Donation: Incidence, Predictors, and Correlates. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Hwang, H.S.; Yoon, H.E.; Kim, Y.K.; Choi, B.S.; Moon, I.S.; Kim, J.C.; Hwang, T.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Yang, C.W. Long-Term Risk of Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease in Living Kidney Donors. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, G.T.; Nolte, C.; Tsinalis, D.; Steiger, J.; Bachmann, L.M. Investigating Kidney Donation as a Risk Factor for Hypertension and Microalbuminuria: Findings from the Swiss Prospective Follow-up of Living Kidney Donors. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Reis Pereira, P.; Silvano, J.; Ribeiro, C.; Pedroso, S.; Tafulo, S.; Martins, L.S.; Silva Ramos, M.; Malheiro, J. Longitudinal Trajectories of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in a European Population of Living Kidney Donors. Transpl. Int. 2024, 37, 13356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grams, M.E.; Sang, Y.; Levey, A.S.; Matsushita, K.; Ballew, S.; Chang, A.R.; Chow, E.K.H.; Kasiske, B.L.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Nadkarni, G.N.; et al. Kidney-Failure Risk Projection for the Living Kidney-Donor Candidate. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentine, K.L.; Kasiske, B.L.; Levey, A.S.; Adams, P.L.; Alberú, J.; Bakr, M.A.; Gallon, L.; Garvey, C.A.; Guleria, S.; Li, P.K.-T.; et al. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline on the Evaluation and Care of Living Kidney Donors. Transplantation 2017, 101, S7–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praga, M.; Hernández, E.; Herrero, J.C.; Morales, E.; Revilla, Y.; Díaz-González, R.; Rodicio, J.L. Influence of Obesity on the Appearance of Proteinuria and Renal Insufficiency after Unilateral Nephrectomy. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, O.K.; Sengupta, B.; Bangdiwala, A.; Vock, D.M.; Dunn, T.B.; Finger, E.B.; Pruett, T.L.; Matas, A.J.; Kandaswamy, R. Implications of Excess Weight on Kidney Donation: Long-Term Consequences of Donor Nephrectomy in Obese Donors. Surgery 2018, 164, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frutos, M.Á.; Crespo, M.; de la Oliva Valentín, M.; Hernández, D.; de Sequera, P.; Domínguez-Gil, B.; Pascual, J. Living-Donor Kidney Transplant: Guidelines with Updated Evidence. Nefrología 2022, 42, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J.; Cruzado, J.M.; Alonso, Á.; Diekman, F.; Gallego, R.J.; Gutiérrez-Dalmau, Á.; Hernández, D.; Morales, J.M.; Rodrigo, E.; Zárraga, S. Kidney Transplantation Group of the Spanish Society of Nephrology. Nefrología 2013, 33, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafranca, J.A.; Spoon, E.Q.W.; van de Wetering, J.; IJzermans, J.N.M.; Dor, F.J.M.F. Attitudes among Transplant Professionals Regarding Shifting Paradigms in Eligibility Criteria for Live Kidney Donation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total | Normal Weight (BMI < 25 kg/m2) | Overweight (BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2) | Obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 306 (100%) | 150 (49%) | 124 (41%) | 32 (10%) | - |
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 47.2 ± 10.7 | 45.4 ± 11.3 | 48.4 ± 10.2 | 50.8 ± 8.8 | 0.009 |
| Age (years), n (%) | |||||
| <40 | 78 (25) | 50 (33) | 25 (20) | 3 (9) | 0.021 |
| 40–55 | 146 (48) | 65 (43) | 63 (51) | 18 (56) | |
| ≥55 | 82 (27) | 35 (23) | 36 (29) | 11 (34) | |
| Sex F, n (%) | 217 (71) | 114 (76) | 83 (67) | 20 (63) | 0.140 |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean ± SD | 25.3 ± 3.4 | 22.5 ± 1.7 | 27.3 ± 1.4 | 31.2 ± 1.1 | - |
| Smoking habits, n (%) | 49 (16) | 32 (21) | 13 (10) | 4 (13) | 0.045 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 44 (14) | 13 (9) | 18 (15) | 13 (41) | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL), mean ± SD | 194.3 ± 37.2 | 188.2 ± 36.0 | 196.5 ± 36.2 | 214.3 ± 40.2 | 0.001 |
| HT, n (%) | 48 (16) | 11 (7) | 24 (19) | 13 (41) | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg), mean ± SD | 122.5 ± 13.4 | 118.8 ± 12.0 | 125.0 ± 13.3 | 130.0 ± 14.3 | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg), mean ± SD | 73.2 ± 8.7 | 71.6 ± 8.2 | 74.2 ± 8.9 | 76.8 ± 8.8 | 0.002 |
| ProtU 0.15–0.5 g/g, n (%) | 87 (28) | 43 (29) | 33 (27) | 11 (34) | 0.683 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL), mean ± SD | 0.75 ± 0.16 | 0.73 ± 0.15 | 0.76 ± 0.17 | 0.78 ± 0.15 | 0.115 |
| Pre- donation eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2), mean ± SD | 100.3 ± 14.6 | 102.4 ± 15.0 | 98.9 ± 13.9 | 96.3 ± 14.5 | 0.038 |
| Pre- donation eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2), n (%) | 0.278 | ||||
| <80 | 27 (9) | 14 (9) | 10 (8) | 3 (9) | |
| 80–90 | 47 (15) | 17 (11) | 22 (18) | 8 (25) | |
| ≥90 | 232 (76) | 119 (79) | 92 (74) | 21 (66) | |
| Related donor, n (%) | 104 (34) | 52 (35) | 40 (32) | 12 (38) | 0.830 |
| Donation of left kidney | 251 (82) | 115 (77) | 108 (87) | 28 (88) | 0.624 |
| Multivariable OR (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Time post-donation | 0.985 (0.844–1.150) | 0.848 |
| Age | 0.882 (0.808–0.963) | 0.005 |
| Female Sex | 3.250 (0.731–14.453) | 0.122 |
| Pre-donation BMI kg/m2 | 5.324 (3.471–8.168) | <0.001 |
| Smoking habits | 0.450 (0.055–3.647) | 0.454 |
| HT | 0.182 (0.030–1.094) | 0.063 |
| Dyslipidemia | 6.048 (1.065–34.348) | 0.042 |
| ProtU 0.15–0.5 g/g | 0.361 (0.083–1.560) | 0.172 |
| Pre-donation eGFR mL/min/1.73 m2 | 0.951 (0.899–1.006) | 0.080 |
| Related donor | 0.745 (0.194–2.831) | 0.668 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cunha, A.; Almeida, M.; Braga, B.G.; Sousa, S.; Silvano, J.; Ribeiro, C.; Pedroso, S.; Martins, L.S.; Malheiro, J. Prevalence of Obesity After Living Kidney Donation and Associated Risk Factors: Cardiovascular and Renal Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186411
Cunha A, Almeida M, Braga BG, Sousa S, Silvano J, Ribeiro C, Pedroso S, Martins LS, Malheiro J. Prevalence of Obesity After Living Kidney Donation and Associated Risk Factors: Cardiovascular and Renal Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186411
Chicago/Turabian StyleCunha, Ana, Manuela Almeida, Beatriz Gil Braga, Sofia Sousa, José Silvano, Catarina Ribeiro, Sofia Pedroso, La Salete Martins, and Jorge Malheiro. 2025. "Prevalence of Obesity After Living Kidney Donation and Associated Risk Factors: Cardiovascular and Renal Implications" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186411
APA StyleCunha, A., Almeida, M., Braga, B. G., Sousa, S., Silvano, J., Ribeiro, C., Pedroso, S., Martins, L. S., & Malheiro, J. (2025). Prevalence of Obesity After Living Kidney Donation and Associated Risk Factors: Cardiovascular and Renal Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186411





