The Role of Cognitive Functioning in the ICF Framework: A Systematic Review of Its Influence on Activities and Participation and Environmental Factors in People with Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
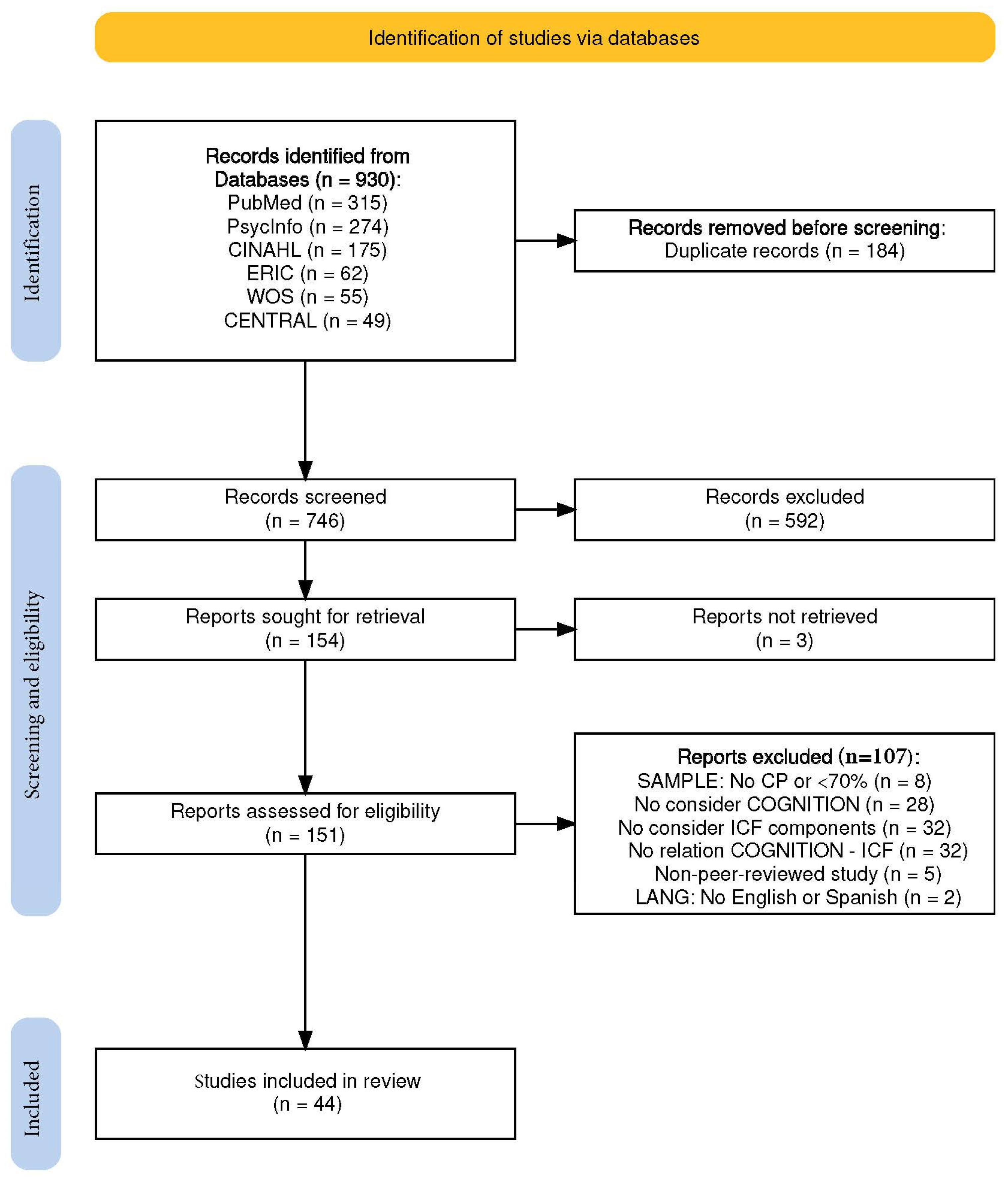
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility of Studies
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Quality Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
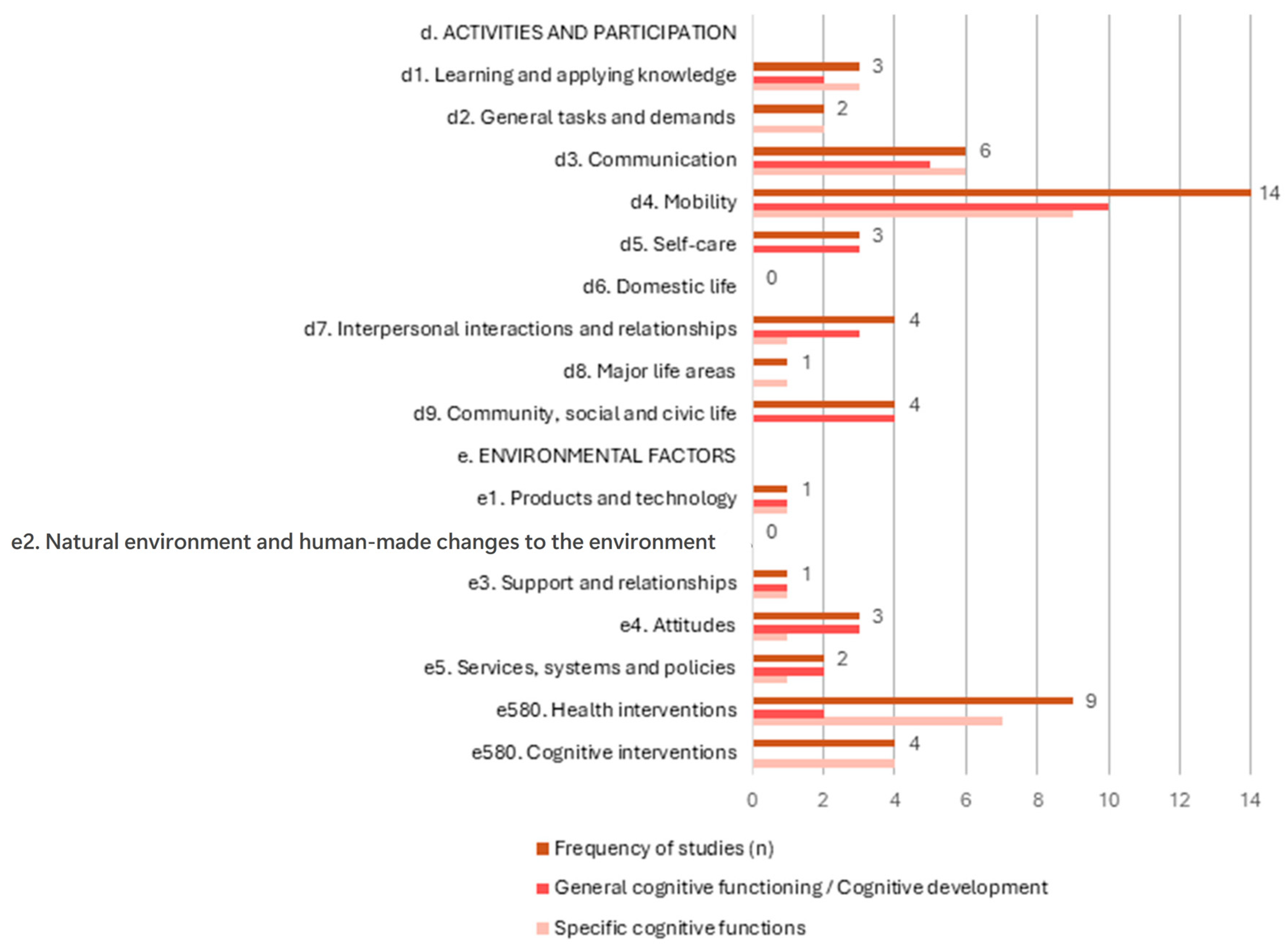
3.2. Distribution of ICF Chapters in Included Studies
3.3. Activities and Participation
3.3.1. Learning and Applying Knowledge (d1)
| ICF | Cognitive Assessment | Demographic Data | Main Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICF chapter | ICF second level Assessment | Cognitive domain Instrument | n Age range (years:months) n females n type CP n pattern CP Motor ability | + (significative) − (significative) n.s. Author (year)—LOE |
| d1 Learning and applying knowledge | d166 Reading Five parent questionnaires regarding Home Literacy Variables Questionnaire about emergent literacy activities | General intellectual functioning Raven Coloured Progressive Matrices (RCPM) | 92 5:0–6:3 years, 40 unk 36 females 78 spastic, 3 ataxic, 11 mixed 16 unilateral, 66 bilateral, 10 unk Mobility ability unk | + (significative) Peeters et al. (2009) [26]—LOE 4 Peeters et al. (2011) [25]—LOE 4 n.s. Peeters et al. (2009) [26]—LOE 4 Peeters et al. (2011) [25]—LOE 4 |
| d166 Reading Five parent questionnaires regarding Home Literacy Variables Four self-administrated parent questionnaires Questionnaire about emergent literacy activities | Language Dutch Language Proficiency Test Dutch Specific Language Impairment (SLI) Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test—3rd edition (PPVT-III) Reading Technology Test, Shortened Version | 127 5:0–7:0 years, 40 unk 57 females 112 spastic, 4 ataxic, 11 mixed 21 unilateral, 91 bilateral, 15 unk Mobility ability unk | + (significative) Peeters et al. (2009) [27]—LOE 3 Peeters et al. (2011) [25]—LOE 4 n.s. Peeters et al. (2009) [26]—LOE 4 Peeters et al. (2009) [27]—LOE 3 Peeters et al. (2011) [25]—LOE 4 | |
3.3.2. General Tasks and Demands (d2)
| ICF | Cognitive Assessment | Demographic Data | Main Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICF chapter | ICF second level Assessment | Cognitive domain Instrument | n Age range (years:months) n females n type CP n pattern CP Motor ability | + (significative) − (significative) n.s. Author (year)—LOE |
| d2 General tasks and demands | d230 Carrying out daily routine Behaviour Rating Inventory of Executive Function (BRIEF) | Executive functions Delis–Kaplan Executive Function System (D-KEFS) Rey Complex Figure Test (RCFT) Test of Everyday Attention for Children (TEA-Ch) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—4th edition (WISC-IV) | 46 8:0–16:0 years 21 females CP type unk 46 unilateral GMFCS: 35 I, 11 II MACS: 6 I, 40 II | − (significative) Whittingham et al. (2014) [28]—LOE 4 |
| d230 Carrying out daily routine Assessment of Motor and Process Skills–7th edition (AMPS) | Visual perception Test of Visual Perceptual Skills (Non-Motor)—3rd edition (TVPS-3) | 101 8:0–17:0 years 50 females 101 spastic 101 unilateral GMFCS: 45 I, 56 II MACS: 24 I, 76 II, 1 III | + (significative) James et al. (2015) [29]—LOE 4 | |
3.3.3. Communication (d3)
| ICF | Cognitive Assessment | Demographic Data | Main Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICF chapter | ICF second level Assessment | Cognitive domain Instrument | n Age range (years:months) n females n type CP n pattern CP Motor ability | + (significative) − (significative) n.s. Author (year)—LOE |
| d3 Communication | d310–d329 Communicating—receiving d330–d349 Communicating—producing d350–d369 Conversation and use of communication devices and techniques Communication Function Classification System (CFCS) Functional Communication Classification Scale (FCCS) d330 Speaking Bus Story Test (BST) Narrative Assessment Profile (NAP) d331 Non-speech vocal expression d335 Producing nonverbal messages Material from Dahlgren, Sandberg, and Hjelmquist 1996 | General intellectual functioning Leiter International Performance Scale—Revised (Leiter-R) Mullen Scales of Early Learning (MSEL) Raven’s Coloured Progressive Matrices (RCPM) | 179 2:0–18:1 years 68 females 131 spastic, 27 dyskinetic, 9 ataxic, 3 mixed, 2 other, 7 unk 37 unilateral, 94 bilateral, 48 unk GMFCS: 55 I, 35 II, 27 III, 24 IV, 31 V, 7 unk MACS: 30 I, 66 II, 24 III, 22 IV, 15 V, 22 unk | − (significative) Asano et al. (2023) [33]—LOE 4 Koopmans et al. (2022) [32]—LOE 4 Nordberg et al. (2015) [34]—LOE 4 Pennington et al. (2020) [35]—LOE 3 n.s. Falkman et al. (2002) [30]—LOE 4 Nordberg et al. (2015) [34]—LOE 4 |
| d310–d329 Communicating—receiving d330–d349 Communicating—producing d350–d369 Conversation and use of communication devices and techniques Communication Function Classification System (CFCS) Functional Communication Classification Scale (FCCS) d310–d329 Communicating—receiving Children’s Communication Checklist (CCC) d330 Speaking Bus Story Test (BST) Narrative Assessment Profile (NAP) d331 Non-speech vocal expression d335 Producing nonverbal messages Material from Dahlgren, Sandberg, and Hjelmquist 1996 | Language MacArthur Communicative Development Inventory (MCDI) Material from Bishop and Adams (1992; translated and adapted to Swedish by the authors) Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test—4th edition (PPVT-4) Picture Vocabulary Test (PVT) Preschool Language Scales—4th edition (PLS-4) Språkligt Impressivt Test (SIT) Syntactic acceptability Test for Auditory Comprehension of Language—4th edition (TACL-4) Test for Reception of Grammar—2nd edition (TROG-2) | 189 2:0–18:1 years 71 females 141 spastic, 27 dyskinetic, 9 ataxic, 3 mixed, 2 other, 7 unk 47 unilateral, 94 bilateral, 48 unk GMFCS: 55 I, 35 II, 27 III, 24 IV, 31 V, 17 unk MACS: 30 I, 66 II, 24 III, 22 IV, 15 V, 32 unk | + (significative) Asano et al. (2023) [33]—LOE 4 Nordberg et al. (2015) [34]—LOE 4 Pennington et al. (2020) [35]—LOE 3 − (significative) Holck et al. (2010) [31]—LOE 4 n.s. Falkman et al. (2002) [30]—LOE 4 Holck et al. (2010) [31]—LOE 4 Koopmans et al. (2022) [32]—LOE 4 | |
| d330 Speaking Bus Story Test (BST) Narrative Assessment Profile (NAP) | Executive functions Corsi block-tapping test (CB) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—3rd edition (WISC-III) | 15 9:2–12:9 years 7 females 10 spastic, 2 dyskinetic, 3 ataxic 8 unilateral, 2 bilateral, 5 unk GMFCS: 9 I, 1 II, 2 III, 3 IV | n.s. Nordberg et al. (2015) [34]—LOE 4 | |
| d330 Speaking Bus Story Test (BST) Narrative Assessment Profile (NAP) | Memory Corsi block-tapping test (CB): forward Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—3rd edition (WISC-III) | 15 9:2–12:9 years 7 females 10 spastic, 2 dyskinetic, 3 ataxic 8 unilateral, 2 bilateral, 5 unk GMFCS: 9 I, 1 II, 2 III, 3 IV | + (significative) Nordberg et al. (2015) [34]—LOE 4 n.s. Nordberg et al. (2015) [34]—LOE 4 | |
| d330 Speaking Bus Story Test (BST) | Social cognition False belief items of 2 story tests: “Kiki and the cat” and “Birthday puppy” | 15 9:2–12:9 years 7 females 10 spastic, 2 dyskinetic, 3 ataxic 8 unilateral, 2 bilateral, 5 unk GMFCS: 9 I, 1 II, 2 III, 3 IV | + (significative) Nordberg et al. (2015) [34]—LOE 4 | |
3.3.4. Mobility (d4)
| ICF | Cognitive Assessment | Demographic Data | Main Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICF chapter | ICF second level Assessment | Cognitive domain Instrument | n Age range (years:months) n females n type CP n pattern CP Motor ability | + (significative) − (significative) ? (significative) n.s. Author (year)—LOE |
| d4 Mobility (Gross motor functions) | d410–d429 Changing and maintaining body position d430–d449 Carrying, moving, and handling objects d450–d469 Walking and moving Bayley Infant Development Screening Test—2nd edition (BSID-II) Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) Gross Motor Function Classification System Family Report Questionnaire (GMFCS-FR) Gross Motor Function Classification System, Expanded and Revised (GMFCS E&R) Gross Motor Function Measure (GMFM) Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI) Selective Motor Control (SMC) | General intelligence functioning Raven’s Coloured Progressive Matrices (RCPM) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—4th edition (WISC-IV) Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (WPPSI) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—Revised (WISC-R) Comprehensive Developmental Inventory for Infants and Toddlers (CDIIT) Cognitive development Bayley Infant Development Screening Test—2nd edition (BSID-II) Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory—Computer Adaptive Test, Speedy Version (PEDI-CAT) | 1223 0:1–18:0 years, 49 unk 503 females 760 spastic, 77 dyskinetic, 25 ataxic, 63 mixed, 30 other, 268 unk 183 unilateral, 805 bilateral, 232 unk GMFCS: 197 I, 198 II, 205 III, 212 IV, 294 V, 117 unk MACS: 48 I, 63 II, 20 III, 9 IV, 11 V, 1072 unk | + (significative) Asano et al. (2023) [33]—LOE 4 Dalvand et al. (2012) [36]—LOE 4 Song (2013) [37]—LOE 4 n.s. Chen et al. (2013) [38]—LOE 2 Fontes et al. (2025) [39]—LOE 4 Muriel et al. (2014) [40]—LOE 4 Peeters et al. (2009) [41]—LOE 4 Smits et al. (2011) [42]—LOE 3 |
| d410–d429 Changing and maintaining body position d450–d469 Walking and moving Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) Gross Motor Limitation Scale Selective Motor Control (SMC) | Language Dutch Language Proficiency Test Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test—3rd edition (PPVT-III) Reynell Developmental Language Scale—Revised (RDLS-R) Comprehensive Developmental Inventory for Infants and Toddlers (CDIIT) Bo Ege Test Verbal Language Development Scale Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—4th edition (WISC-IV) Picture Vocabulary Test (PVT) | 223 1:0–18:0 years, 49 unk 85 females 127 spastic, 1 dyskinetic, 3 ataxic, 92 unk 25 unilateral, 154 bilateral, 44 unk GMFCS: 39 I, 32 II, 33 III, 21 IV, 20 V, 12 I–II, 17 IV–V, 49 unk MACS: 15 I, 23 II, 6 III, 1 IV, 178 unk | + (significative) Chen et al. (2013) [38]—LOE 3 Peeters et al. (2009) [41]—LOE 4 Pirila et al. (2007) [46]—LOE 4 n.s. Asano et al. (2023) [33]—LOE 4 Muriel et al. (2014) [40]—LOE 4 | |
| d410–d429 Changing and maintaining body position d450–d469 Walking and moving Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) | Executive functions Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—4th edition (WISC-IV) Corsi Block-tapping test (CBT) Walking Corsi Test (WalCT) | 55 5:0–17:0 years 23 females 51 spastic, 3 dyskinetic, 1 ataxic 11 unilateral, 41 bilateral, 3 unk GMFCS: 23 I, 16 II, 2 III, 3 V, 11 III–IV | ? (significative) Bartonek et al. (2021) [45]—LOE 4 n.s. Bartonek et al. (2021) [45]—LOE 4 Muriel et al. (2014) [40]—LOE 4 | |
| d410–d429 Changing and maintaining body position d450–d469 Walking and moving Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) d410–d429 Changing and maintaining body position d430–d449 Carrying, moving, and handling objects Assessment of Motor and Process Skills—7th edition (AMPS) | Visual perception Raven’s Coloured Progressive Matrices (RCPM) Test of Visual Perceptual Skills (Non-Motor)—3rd edition (TVPS-3) | 141 5:0–17:0 years 66 females 138 spastic, 3 dyskinetic 105 unilateral, 33 bilateral, 3 unk GMFCS: 62 I, 68 II, 11 III-IV MACS: 24 I, 76 II, 1 III, 40 unk | + (significative) James et al. (2015) [29]—LOE 4 n.s. Bartonek et al. (2021) [45]—LOE 4 James et al. (2015) [29]—LOE 4 | |
| d410–d429 Changing and maintaining body position d450–d469 Walking and moving Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) | Processing speed Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—4th edition (WISC-IV) | 15 7:0–14:0 years 7 females 14 spastic, 1 ataxic 7 unilateral, 8 bilateral GMFCS: 6 I, 4 II, 2 III, 3 V | n.s. Muriel et al. (2014) [40]—LOE 4 | |
| d4 Mobility (Manual ability) | d440 Fine hand use d430–d449 Carrying, moving, and handling objects Both Hands Assessment (BoHA) Computerised Peg Moving Task (CPMT) Kids Assisting Hand Assessment (AHA) Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) | General intelligence functioning Raven’s Coloured Progressive Matrices (RCPM) | 198 4:0–18:0 years, 49 unk 71 females 187 spastic, 5 dyskinetic, 5 ataxic, 1 mixed 63 unilateral, 124 bilateral, 11 unk GMFCS: 57 I, 30 II, 21 III, 11 IV, 79 unk MACS: 45 I, 51 II, 22 III, 1 IV, 79 unk | + (significative) Asano et al. (2023) [33]—LOE 4 Burgess et al. (2021) [43]—LOE 4 Dellatolas et al. (2005) [44]—LOE 4 n.s. Burgess et al. (2021) [43]—LOE 4 Dellatolas et al. (2005) [44]—LOE 4 Peeters et al. (2009) [41]—LOE 4 |
| d430–d449 Carrying, moving, and handling objects Computerised Peg Moving Task (CPMT) Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) | Language Dutch Language Proficiency Test Neuropsychological battery Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test—3rd edition (PPVT-III) Picture Vocabulary Test (PVT) | 124 4:0–18:0 years, 49 unk 45 females 120 spastic, 1 dyskinetic, 2 ataxic, 1 mixed 33 unilateral, 87 bilateral, 4 unk GMFCS: 13 I, 12 II, 13 III, 7 IV, 79 unk MACS: 15 I, 23 II, 6 III, 1 IV, 79 unk | + (significative) Peeters et al. (2009) [41]—LOE 4 n.s. Asano et al. (2023) [33]—LOE 4 Dellatolas et al. (2005) [44]—LOE 4 | |
| d445 Hand and arm use Object hit and avoid task using the Kinarm exoskeleton robot | Attention Behavioural Inattention Test (BIT) | 45 6:5–19:6 years 15 females CP type unk 45 unilateral MACS: 11 I, 18 II, 16 unk | + (significative) Hawe et al. (2020) [47]—LOE 4 | |
| d440 Fine hand use Computerised Peg Moving Task (CPMT) | Visual perception Neuropsychological battery | 30 7:0–8:0 years 12 females 29 spastic, 1 mixed 20 unilateral, 10 bilateral Motor ability unk | + (significative) Dellatolas et al. (2005) [44]—LOE 4 | |
3.3.5. Self-Care (d5)
| ICF | Cognitive Assessment | Demographic Data | Main Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICF chapter | ICF second level Assessment | Cognitive domain Instrument | n Age range (years:months) n females n type CP n pattern CP Motor ability | + (significative) − (significative) n.s. Author (year)—LOE |
| d5 Self-care | d510–d599 Self-care Participation and Environment Measure for Children and Youth (PEM-CY) Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory–Computer Adaptive Test, Speedy Version (PEDI-CAT) d510 Washing oneself d520 Caring for body parts d530 Toileting d540 Dressing d550 Eating d560 Drinking Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI) | General intellectual functioning Raven Coloured Progressive Matrices (RCPM) Revised Scale for Measuring Intelligence according to Wechsler principles (REVISK) | 300 7:0–18:0 years 115 females 242 spastic, 30 dyskinetic, 18 ataxic, 10 mixed 87 unilateral, 155 bilateral, 58 unk GMFCS: 115 I, 67 II, 47 III, 42 IV, 29 V MACS: 75 I, 103 II, 49 III, 36 IV, 27 V, 10 unk | + (significative) Burgess et al. (2021) [43]—LOE 4 Milićević (2020) [48]—LOE 4 Smits et al. (2011) [42]—LOE 3 n.s. Milićević (2020) [48]—LOE 4 |
3.3.6. Interpersonal Interactions and Relationships (d7)
| ICF | Cognitive Assessment | Demographic Data | Main Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICF chapter | ICF second level Assessment | Cognitive domain Instrument | n Age range (years:months) n females n type CP n pattern CP Motor ability | + (significative) − (significative) n.s. Author (year)—LOE |
| d7 Interpersonal interactions and relationships | d710–d729 General interpersonal interactions Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI) d710 Basic interpersonal interactions Friendship Quality Questionnaire (FQQ) Personality Inventory for Children—2nd edition (PIC-2) d720 Complex interpersonal interactions Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) | General intellectual functioning Leiter International Performance Scale—Revised (Leiter-R) Raven Coloured Progressive Matrices (RCPM) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—3rd edition (WISC-III) | 317 4:8–19:0 years 123 females 255 spastic, 20 dyskinetic, 4 ataxic, 38 unk 94 unilateral, 161 bilateral, 62 unk GMFCS: 61 I, 21 II, 34 III, 14 IV, 15 V, 111 I–III, 49 IV–V, 12 unk MACS: 80 I, 80 II, 14 III, 8 IV, 11 V, 124 unk | + (significative) Brossard-Racine et al. (2013) [50]—LOE 4 Cunningham et al. (2009) [49]—LOE 4 Smits et al. (2011) [42]—LOE 3 − (significative) Brossard-Racine et al. (2013) [50]—LOE 4 n.s. Brossard-Racine et al. (2013) [50]—LOE 4 Cunningham et al. (2009) [49]—LOE 4 |
| d720 Complex interpersonal interactions Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) | Executive functions Delis–Kaplan Executive Function System (D-KEFS) Rey Complex Figure Test (RCFT) Test of Everyday Attention for Children (TEA-Ch) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—4th edition (WISC-IV) | 46 8:0–16:0 years 21 females CP type unk 46 unilateral GMFCS: 35 I, 11 II MACS: 6 I, 40 II | − (significative) Whittingham et al. (2014) [28]—LOE 4 n.s. Whittingham et al. (2014) [28]—LOE 4 | |
3.3.7. Major Life Areas (d8)
3.3.8. Community, Social and Civic Life (d9)
| ICF | Cognitive Assessment | Demographic Data | Main Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICF chapter | ICF second level Assessment | Cognitive domain Instrument | n Age range (years:months) n females n type CP n pattern CP Motor ability | + (significative) − (significative) n.s. Author (year)—LOE |
| d9 Community, social and civic life | d920 Recreation and leisure Assessment of Preschool Children’s Participation (APCP) Children’s Assessment of Participation and Enjoyment (CAPE) Participation and Environment Measure for Children and Youth (PEM-CY) Preferences for Activities of Children (PAC) | General intellectual functioning Leiter International Performance Scale—Revised (Leiter-R) Revised Scale for Measuring Intelligence according to Wechsler principles (REVISK) Cognitive development Comprehensive Developmental Inventory for Infants and Toddlers (CDIIT) | 312 2:0–18:0 years 123 females 181 spastic, 12 dyskinetic, 11 ataxic, 10 mixed, 11 other, 87 unk 71 unilateral, 190 bilateral, 11 other, 40 unk GMFCS: 112 I, 72 II, 34 III, 41 IV, 36 V, 5 III–IV, 12 III–V MACS: 12 I, 35 II, 19 III, 28 IV, 16 V, 202 unk | + (significative) Majnemer et al. (2008) [52]—LOE 4 Majnemer et al. (2010) [53]—LOE 4 Milićević (2020) [48]—LOE 4 − (significative) Majnemer et al. (2008) [52]—LOE 4 Milićević (2020) [48]—LOE 4 Wu et al. (2015) [54]—LOE 3 |
3.4. Environmental Factors
3.4.1. Products and Technology (e1)
| ICF | Cognitive Assessment | Demographic Data | Main Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICF chapter | ICF second level Assessment | Cognitive domain Instrument | n Age range (years:months) n females n type CP n pattern CP Motor ability | + (significative) − (significative) n.s. Author (year)—LOE |
| e1 Products and technology | e125 Products and technology for communication Augmentative and Alternative Communication(AAC) | General intellectual functioning Griffiths Scales of Mental Development (GSMD) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—Revised (WISC-R) Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scales of Intelligence—Revised (WPPSI-R) | 36 1:10–9:0 years 16 females 22 spastic, 14 unk 5 unilateral, 31 bilateral GMFCS: 7 III, 12 I–II, 17 IV–V | + (significative) Pirila et al. (2007) [46]—LOE 4 |
| e3 Support and relationships | e320 Friends Social Network Inventory for Children (SNIC) | General intellectual functioning Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—3rd edition (WISC-III) | 41 6:0–12:0 years 18 females 38 spastic, 3 unk 10 unilateral, 28 bilateral, 3 unk GMFCS: 5 I, 1 II, 17 III, 5 IV, 1 V, 12 unk | + (significative) Cunningham et al. (2009) [49]—LOE 4 |
| e4 Attitudes | e410 Individual attitudes of immediate family members Family Empowerment Scale (FES) Parenting Dimensions Inventory (PDI) | General intellectual functioning Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—3rd edition (WISC-III) Cognitive development Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development—3rd edition (BSID-III) | 82 1:1–12:0 years 36 females 38 spastic, 44 unk 10 unilateral, 28 bilateral, 44 unk GMFCS: 9 I, 20 II, 26 III, 14 IV, 1 V, 12 unk | + (significative) Pierce et al. (2023) [55]—LOE 4 n.s. Cunningham et al. (2009) [49]—LOE 4 |
| e430 Individual attitudes of people in positions of authority Teacher reading expectations Teacher writing expectations | General intellectual functioning Raven Coloured Progressive Matrices (RCPM) | 49 71.88 ± 5.82 months ‡ 18 females 48 spastic, 1 ataxic 7 unilateral, 40 bilateral, 2 unk Motor ability unk | + (significative) Peeters et al. (2009) [41]—LOE 4 | |
| e430 Individual attitudes of people in positions of authority Teacher reading expectations Teacher writing expectations | Language Dutch Language Proficiency Test Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test—3rd edition (PPVT-III) | 49 71.88 ± 5.82 months ‡ 18 females 48 spastic, 1 ataxic 7 unilateral, 40 bilateral, 2 unk Motor ability unk | + (significative) Peeters et al. (2009) [41]—LOE 4 n.s. Peeters et al. (2009) [41]—LOE 4 | |
| e5 Services, systems, and policies | e580 Health services, systems, and policies Formal questionnaire regarding current educational and rehabilitation services Speech therapy | General intellectual functioning Griffiths Scales of Mental Development (GSMD) Leiter International Performance Scale—Revised (Leiter-R) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—Revised (WISC-R) Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scales of Intelligence—Revised (WPPSI-R) | 294 1:10–19:0 years 118 females 22 spastic, 272 unk 5 unilateral, 31 bilateral, 258 unk GMFCS: 94 I, 7 III, 8 IV, 24 V, 12 I–II, 71 II–III, 70 IV-V, 8 unk | − (significative) Pirila et al. (2007) [46]—LOE 4 Majnemer et al. (2014) [56]—LOE 4 |
3.4.2. Support and Relationships (e3)
3.4.3. Attitudes (e4)
3.4.4. Services, Systems, and Policies (e5)
Health Services, Systems, and Policies (e580)
| Intervention | Cognitive Assessment | Demographic Data | Main Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Intervention’s name Characteristics | Cognitive domain Instrument | n (IG/CG) Age range (years:months) n females (IG/CG) n type CP n pattern CP Motor ability | + (significative) − (significative) n.s. Author (year)—LOE |
| Physical | Intense exercise Intense aerobic exercise that consists of a shuttle run and walk test 1 session | Executive functions/Processing speed Stroop-like test, modified and designed for children | 17 (8/9) 6:0–14:8 years 7 females (3/4) 8 spastic CP pattern unk GMFCS: 8 I | + (significative) Maltais et al. (2016) [60]—LOE 4 − (significative) Maltais et al. (2016) [60]—LOE 4 n.s. Maltais et al. (2016) [60]—LOE 4 |
| Dance intervention Physical intervention (coordination movements of upper and lower limbs, body image interaction between subject and environment, skill and agility sequential components of the movement, and trunk and head movements for spatial orientation and equilibrium) 2 sessions of 60 min, twice per week, for 3 months | Cognitive development Functional Independence Measure (FIM) | 26 (13/13) 15:0–29:0 years 15 females (8/7) CP type unk CP pattern unk GMFCS: 3 II, 5 III, 4 IV, 1 V | + (significative) Teixeira-Machado et al. (2017) [24]—LOE 2 | |
| MiYoga Mindfulness and mindful movement techniques based on hatha yoga principles 6 sessions of 90 min, for 6 weeks, with 2 follow-up consultations via phone or Skype over the following 2 weeks | Attention Conners’ Continuous Performance Test—2nd edition (CPT-II) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—4th edition (WISC-IV) Executive functions Delis–Kaplan Executive Function System (D-KEFS) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—4th edition (WISC-IV) | 42 (21/21) 6:0–16:0 years 18 females (7/11) 21 spastic 7 unilateral, 14 bilateral GMFCS: 11 I, 4 II, 6 III | + (significative) Mak et al. (2018) [58]—LOE 2 n.s. Mak et al. (2018) [58]—LOE 2 | |
| MiYoga Mindfulness and mindful movement techniques based on hatha yoga principles 6 sessions of 90 min, for 6 weeks, with 2 follow-up consultations via phone or Skype over the following 2 weeks | Attention Conners’ Continuous Performance Test—2nd edition (CPT-II) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—4th edition (WISC-IV) Executive functions Delis–Kaplan Executive Function System (D-KEFS) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—4th edition (WISC-IV) | 23 6:0–16:0 years 0 females 23 spastic 10 unilateral, 13 bilateral GMFCS: 14 I, 6 II, 3 III | n.s. Mak et al. (2022)—[59] LOE 2 | |
| Functional Strength Training (FST) Functional strength training for lower limbs followed by conventional physical therapy 3 sessions of 90 min each per week, for 6 months | Attention/Processing speed/Memory/Executive functions Computer-based RehaCom software (version 5) | 32 (16/16) 8:0–12:0 years 14 females (9/5) 16 spastic 16 bilateral GMFCS: 6 II, 10 III | + (significative) AL-Nemr (2024) [57]—LOE 2 n.s. AL-Nemr (2024) [57]—LOE 2 | |
| Biofeedback and brain stimulation | Augmented biofeedback E-Link Upper Limb Exerciser, a computerized graded interactive system Physical training Exercises facilitating hand–eye coordination and fine motor skills 1 session of 60 min per day, three times per week, for 3 months | Visual perception Beery–Buktenica Developmental Test of Visual–Motor Integration—6th edition (Beery) | 45 (15/30) 5:5–7:9 years 22 females (5/17) 15 spastic 15 unilateral MACS: 15 I–II | + (significative) Alwhaibi et al. (2020) [61]—LOE 2 |
| Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) tDCS combined with treadmill training and training in intellectual activities 10 sessions | General intelligence functioning Raven’s Coloured Progressive Matrices (RCPM) | 30 (15/15) 6:0–12:0 years unk females 15 spastic 6 unilateral, 9 bilateral GMFCS: 4 I, 7 II, 4 III | + (significative) Collange-Grecco et al. (2023) [63]—LOE 2 n.s. Collange-Grecco et al. (2023) [63]—LOE 2 | |
| EEG Neurofeedback training Neurofeedback 2 sessions of approximately 1 h each, for 10 weeks | Attention Conners Continuous Performance Test—2nd edition (CPT-II) Visual perception Test of Visual–Perceptual Skills—3rd edition (TVPS-3) | 19 (8/11) 4:0–12:0 years 2 females (1/1) CP type unk 4 unilateral, 4 bilateral GMFCS: 4 I, 1 II, 3 III MACS: 3 I, 5 II | + (significative) Chen et al. (2024) [62]—LOE 2 n.s. Chen et al. (2024) [62]—LOE 2 | |
| Medical | Hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBO2) IG: 100% oxygen at 1.75 atmospheres absolute (HBO2) CG: air (21% oxygen) at 1.3 atmospheres absolute (Sham) 40 sessions of 1 h of either HBO2 or Sham treatment, for 2 months | Executive functions Corsi Blocks (CB) Picture Span Tests Test of Variables of Attention (TOVA), 10.8-min vigilant condition Word Span Test Attention Test of Variables of Attention (TOVA), 10.8-min vigilant condition | 75 (40/35) 4:0–12:0 years 41 females (21/20) 40 spastic 1 unilateral, 38 bilateral, 1 unk Motor ability unk | + (significative) Hardy et al. (2002) [64]—LOE 2 n.s. Hardy et al. (2002) [64]—LOE 2 |
| Intervention | ICF Assessment | Demographic Data | Main Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Intervention’s name Characteristics | ICF component ICF chapter; ICF second level Assessment | n (IG/CG) Age range (years:months) n females (IG/CG) n type CP n pattern CP Motor ability | + (significative) − (significative) n.s. Author (year)—LOE |
| Cognitive | Guttman NeuroPersonalTrainer, Child Version Online and individual intervention, adapted depending on the cognitive function baseline level 16 sessions of 1 h, 2 days a week, for 8 weeks | d Activities and Participation d2 General tasks and demands; d230 Carrying out daily routine Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function (BRIEF) Conners rating scales (CPRS-48/CTRS-28) | 15 7:0–14:0 years 7 females 14 spastic, 1 ataxic 7 unilateral, 8 bilateral GMFCS: 6 I, 4 II, 2 III, 3 V | n.s. Muriel et al. (2014) [40]—LOE 4 |
| CogMed RM computer program Computerized cognitive training Around 25 sessions of 30–40 min, 5 days a week, for 5 weeks | d Activities and Participation d2 General tasks and demands; d230 Carrying out daily routine ADHD rating scale IV Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function (BRIEF) | 66 (32/34) 11.4 ± 3.1/9.4 ± 2.6 years ‡ 25 females (13/12) CP type unk CP pattern unk Motor ability unk | n.s. Beneventi et al. (2023) [65]—LOE 3 | |
| Strengthening Mental Abilities Through Relational Training (SMART) Online cognitive training program Participants could complete 5 modules per day, with a total of 55 modules to complete up to 12 weeks | d Activities and Participation d2 General tasks and demands; d230 Carrying out daily routine Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function (BRIEF) Conners-3 Rating Scale d3 Communication; d350–369 Conversation and use of communication devices and techniques Social Communication Questionnaire–Current (SCQ–Current–Parent form) d7 Interpersonal interactions and relationships; d720 Complex interpersonal interactions Behavior Assessment System for Children—3rd edition (BASC-3) Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) | 21 (9/12) 4 females (whole sample) 8:3–12:6 years CP type unk CP pattern unk Motor ability unk | n.s. Wotherspoon et al. (2024) [67]—LOE 2 | |
| Neuronup Home-based computerized executive function intervention 10 sessions of 15 min per week, for 12 weeks | d Activities and Participation d9 Community, social and civic life; d920 Recreation and leisure Participation and Environment Measure for Children and Youth Questionnaire (PEM-CY) | 60 (30/30) 8:11–12:11 years 30 females (15/15) 27 spastic, 3 dyskinetic 17 unilateral, 10 bilateral, 3 unk GMFCS: 20 I, 6 II, 4 III MACS: 11 I, 16 II, 3 III | n.s. Blasco et al. (2025) [66]—LOE 2 | |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McIntyre, S.; Goldsmith, S.; Webb, A.; Ehlinger, V.; Hollung, S.J.; McConnell, K.; Arnaud, C.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Oskoui, M.; Khandaker, G.; et al. Global Prevalence of Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2022, 64, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, A.S. Recent Advances in the Neuroimaging and Neuropsychology of Cerebral Palsy. Appl. Neuropsychol. Child 2017, 6, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadskleiv, K. Cognitive Functioning in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, I.; Hines, M.; Goldsmith, S.; Barclay, R. Clinical Prognostic Messages from a Systematic Review on Cerebral Palsy. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e1285–e1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ego, A.; Lidzba, K.; Brovedani, P.; Belmonti, V.; Gonzalez-Monge, S.; Boudia, B.; Ritz, A.; Cans, C. Visual-Perceptual Impairment in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluss, J.; Lidzba, K. Cognitive and Academic Profiles in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Narrative Review. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 63, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikako-Thomas, K.; Majnemer, A.; Law, M.; Lach, L. Determinants of Participation in Leisure Activities in Children and Youth with Cerebral Palsy: Systematic Review. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2008, 28, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health: ICF; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; ISBN 9241545429.
- Bickenbach, J.; Cieza, A.; Davenport, T.E.; Escorpizo, R.; Finger, M.; Glässel, A.; Lückenkemper, M.; Ptyushkin, P.; Rauch, A.; Rundell, S.D.; et al. ICF Core Sets: Manual for Clinical Practice; Jerome, B., Cieza, A., Rauch, A., Stucki, G., Eds.; Hogrefe Publishing GmbH: Göttingen, Germany, 2012; ISBN 9781616764319. [Google Scholar]
- Noten, S.; Selb, M.; Troenosemito, L.A.A.; Thorpe, D.E.; Rodby-Bousquet, E.; van der Slot, W.M.A.; Roebroeck, M.E. ICF Core Sets for the Assessment of Functioning of Adults with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2022, 64, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiariti, V.; Selb, M.; Cieza, A.; O’Donnell, M. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health Core Sets for Children and Youth with Cerebral Palsy: A Consensus Meeting. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, C.A.S.; Rosenbaum, P.; van der Kemp, J.; de Campos, A.C. Looking beyond Body Structure and Function: ICF Foci and Who Is Being Assessed in Research about Adolescents and Young Adults with Cerebral Palsy—A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.; Reilly, S.; Reddihough, D.; Mensah, F.; Green, J.; Pennington, L.; Morgan, A.T. Activities and Participation of Children with Cerebral Palsy: Parent Perspectives. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 37, 2164–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashmdarfard, M.; Richards, L.G.; Amini, M. Factors Affecting Participation of Children with Cerebral Palsy in Meaningful Activities: Systematic Review. Occup. Ther. Health Care 2021, 35, 442–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottcher, L. Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy, Their Cognitive Functioning, and Social Participation: A Review. Child Neuropsychol. 2010, 16, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-H. Relationship between Gross Motor Function and the Function, Activity and Participation Components of the International Classification of Functioning in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 1732–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, P.M.O.; Haase, V.G.; Oliveira-Ferreira, F. An ICF-Based Approach for Cerebral Palsy from a Biopsychosocial Perspective. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2012, 15, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 Statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towards a Common Language for Functioning, Disability and Health ICF; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- The Oxford 2011 Levels of Evidence; OCEBM Levels of Evidence Working Group: Oxford, UK, 2011.
- Blasco, M.; García-Galant, M.; Berenguer-González, A.; Caldú, X.; Arqué, M.; Laporta-Hoyos, O.; Ballester-Plané, J.; Miralbell, J.; Jurado, M.Á. Roser Pueyo Interventions with an Impact on Cognitive Functions in Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2023, 33, 551–577. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, I.; Mcintyre, S.; Morgan, C.; Campbell, L.; Dark, L.; Morton, N.; Stumbles, E.; Wilson, S.; Goldsmith, S. A Systematic Review of Interventions for Children with Cerebral Palsy: State of the Evidence. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 885–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R Package and Shiny App for Producing PRISMA 2020-Compliant Flow Diagrams, with Interactivity for Optimised Digital Transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Machado, L.; Azevedo-Santos, I.; De Santana, J.M. Dance Improves Functionality and Psychosocial Adjustment in Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 96, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, M.; de Moor, J.; Verhoeven, L. Emergent Literacy Activities, Instructional Adaptations and School Absence of Children with Cerebral Palsy in Special Education. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, M.; Verhoeven, L.; Van Balkom, H.; De Moor, J. Home Literacy Environment: Characteristics of children with Cerebral Palsy. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2009, 44, 917–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Verhoeven, L.; de Moor, J.; van Balkom, H.; van Leeuwe, J. Home Literacy Predictors of Early Reading Development in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2009, 30, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittingham, K.; Bodimeade, H.L.; Lloyd, O.; Boyd, R.N. Everyday Psychological Functioning in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: Does Executive Functioning Play a Role? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.; Ziviani, J.; Ware, R.S.; Boyd, R.N. Relationships between Activities of Daily Living, Upper Limb Function, and Visual Perception in Children and Adolescents with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkman, K.W.; Sandberg, A.D.; Hjelmquist, E. Notes and Discussion Preferred Communication Modes: Prelinguistic and Linguistic Communication in Non-Speaking Preschool Children with Cerebral Palsy. Int. J. Lang. Comm. Dis. 2002, 37, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holck, P.; Sandberg, A.D.; Nettelbladt, U. Inferential Ability in Children with Cerebral Palsy, Spina Bifida and Pragmatic Language Impairment. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2010, 31, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, C.; Sakash, A.; Soriano, J.; Long, H.L.; Hustad, K.C. Functional Communication Abilities in Youth With Cerebral Palsy: Association With Impairment Profiles and School-Based Therapy Goals. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2022, 53, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, D.; Takeda, M.; Nobusako, S.; Morioka, S. Error Analysis of Raven’s Coloured Progressive Matrices in Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2023, 67, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, A.; Dahlgren Sandberg, A.; Miniscalco, C. Story Retelling and Language Ability in School-Aged Children with Cerebral Palsy and Speech Impairment. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2015, 50, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, L.; Dave, M.; Rudd, J.; Hidecker, M.J.C.; Caynes, K.; Pearce, M.S. Communication Disorders in Young Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvand, H.; Dehghan, L.; Hadian, M.R.; Feizy, A.; Hosseini, S.A. Relationship between Gross Motor and Intellectual Function in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Cross-Sectional Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-S. Relationships between Physical and Cognitive Functioning and Activities of Daily Living in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2013, 25, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.M.; Hsu, H.C.; Chen, C.L.; Chung, C.Y.; Chen, K.H.; Liaw, M.Y. Predictors for Changes in Various Developmental Outcomes of Children with Cerebral Palsy-A Longitudinal Study. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 3867–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, D.E.; Ayupe, K.M.A.; Moreira, R.S.; de Souza Morais, R.L.; de Carvalho Chagas, P.S.; Longo, E.; de Campos, A.C.; de Toledo, A.M.; Leite, H.R.; Camargos, A.C.R. Factors Associated with Performance of Activities and Participation of Brazilian Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: A Cross-Sectional Study. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2025, 28, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriel, V.; García-Molina, A.; Aparicio-López, C.; Enseñat, A.; Roig-Rovira, T. Cognitive Stimulation in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 59, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Peeters, M.; Verhoeven, L.; De Moor, J. Teacher Literacy Expectations for Kindergarten Children with Cerebral Palsy in Special Education. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2009, 32, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, D.W.; Ketelaar, M.; Gorter, J.W.; van Schie, P.; Dallmeijer, A.; Jongmans, M.; Lindeman, E. Development of Daily Activities in School-Age Children with Cerebral Palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, A.; Boyd, R.N.; Chatfield, M.D.; Ziviani, J.; Wotherspoon, J.; Sakzewski, L. Hand Function and Self-care in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 63, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellatolas, G.; Nunes Filho, G.; Souza, L.; Nunes, L.G.; Braga, L.W. Manual Skill, Hand Skill Asymmetry, and Neuropsychological Test Performance in Schoolchildren with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Laterality 2005, 10, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartonek, Å.; Piccardi, L.; Guariglia, C. Topographical Working Memory in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Mot. Behav. 2021, 53, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirila, S.; van der Meere, J.; Pentikainen, T.; Ruusu-Niemi, P.; Korpela, R.; Kilpinen, J.; Nieminen, P. Language and Motor Speech Skills in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Commun. Disord. 2007, 40, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawe, R.L.; Kuczynski, A.M.; Kirton, A.; Dukelow, S.P. Robotic Assessment of Rapid Motor Decision Making in Children with Perinatal Stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milićević, M. Home Participation of Children with and without Cerebral Palsy in Serbia: An Exploratory Study. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 42, 3696–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, S.D.; Warschausky, S.; Thomas, P.D. Parenting and Social Functioning of Children With and Without Cerebral Palsy. Rehabil. Psychol. 2009, 54, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brossard-Racine, M.; Waknin, J.; Shikako-Thomas, K.; Shevell, M.; Poulin, C.; Lach, L.; Law, M.; Schmitz, N.; Majnemer, A. Behavioral Difficulties in Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy. J. Child Neurol. 2013, 28, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenker, R.; Coster, W.; Parush, S. Participation and Activity Performance of Students with Cerebral Palsy within the School Environment. Disabil. Rehabil. 2005, 27, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majnemer, A.; Shevell, M.; Law, M.; Birnbaum, R.; Chilingaryan, G.; Rosenbaum, P.; Poulin, C. Participation and Enjoyment of Leisure Activities in School-Aged Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2008, 50, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majnemer, A.; Shikako-Thomas, K.; Chokron, N.; Law, M.; Shevell, M.; Chilingaryan, G.; Poulin, C.; Rosenbaum, P. Leisure Activity Preferences for 6- to 12-Year-Old Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.P.; Chuang, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, I.; Liu, H.; Chen, H. Predictors of Participation Change in Various Areas for Preschool Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Longitudinal Study. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 37, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, S.R.; Skorup, J.; Paremski, A.C.; Prosser, L.A. The Relationship between Family Empowerment and Fine Motor, Gross Motor and Cognitive Skills in Young Children with Cerebral Palsy. Child Care Health Dev. 2023, 49, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majnemer, A.; Shikako-Thomas, K.; Lach, L.; Shevell, M.; Law, M.; Schmitz, N.; Poulin, C. Rehabilitation Service Utilization in Children and Youth with Cerebral Palsy. Child Care Health Dev. 2014, 40, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AL-Nemr, A. Synergistic Effect of Functional Strength Training and Cognitive Intervention on Gross Motor Function in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Appl. Neuropsychol. Child 2024, 13, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, C.; Whittingham, K.; Cunnington, R.; Boyd, R.N. Effect of Mindfulness Yoga Programme MiYoga on Attention, Behaviour, and Physical Outcomes in Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, C.; Whittingham, K.; Cunnington, R.; Chatfield, M.; Boyd, R.N. Six-Month Follow-up of a Mindfulness Yoga Program, MiYoga, on Attention, Executive Function, Behaviour and Physical Outcomes in Cerebral Palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2022, 44, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, D.B.; Gane, C.; Dufour, S.K.; Wyss, D.; Bouyer, L.J.; McFadyen, B.J.; Zabjek, K.; Andrysek, J.; Voisin, J.I.A. Acute Physical Exercise Affects Cognitive Functioning in Children With Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2016, 28, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwhaibi, R.M.; Alsakhawi, R.S.; ElKholi, S.M. Augmented Biofeedback Training with Physical Therapy Improves Visual-Motor Integration, Visual Perception, and Motor Coordination in Children with Spastic Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Randomised Control Trial. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2020, 40, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chang, W.; Liang, K.; Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Chan, P.S. The Effects of Neurofeedback Training for Children with Cerebral Palsy and Co-occurring Attention Deficits: A Pilot Study. Child Care Health Dev. 2024, 50, e13231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collange-Grecco, L.A.; Cosmo, C.; Silva, A.L.S.; Rizzutti, S.; Oliveira, C.S.; Muszkat, M. Effects of Dual Task Training and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Randomized Control Trial. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2023, 26, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, P.; Collet, J.; Goldberg, J.; Vanasse, M.; Lambert, J.; Marois, P.; Amar, M.; Montgomery, D.L.; Lecomte, J.M.; Johnston, K.M.; et al. Neuropsychological Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2002, 44, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneventi, H.; Løhaugen, G.C.; Andersen, G.L.; Sundberg, C.; Østgård, H.F.; Bakkan, E.; Walther, G.; Vik, T.; Skranes, J. Working Memory Training in Norwegian Children with Cerebral Palsy (CP) Show Minimal Evidence of Near and No Far Transfer Effects. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2023, 26, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, M.; García-Galant, M.; Ballester-Plané, J.; Laporta-Hoyos, O.; Caldú, X.; Leiva, D.; Boyd, R.N.; Ortibus, E.; Pueyo, R. Transferability of an Executive Function Intervention in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2025, 67, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotherspoon, J.; Whittingham, K.; Sheffield, J.; Boyd, R.N. Randomised Controlled Trial of an Online Cognitive Training Program in School-Aged Children with Cerebral Palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2024, 150, 104752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benner, J.L.; Noten, S.; Limsakul, C.; Van Der Slot, W.M.A.; Stam, H.J.; Selb, M.; Van Den Berg-Emons, R.J.G.; Roebroeck, M.E. Outcomes in Adults with Cerebral Palsy: Systematic Review Using the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granild-Jensen, J.B.; Rackauskaite, G.; Flachs, E.M.; Uldall, P. Predictors for Early Diagnosis of Cerebral Palsy from National Registry Data. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Adde, L.; Blackman, J.; Boyd, R.N.; Brunstrom-Hernandez, J.; Cioni, G.; Damiano, D.; Darrah, J.; Eliasson, A.C.; et al. Early, Accurate Diagnosis and Early Intervention in Cerebral Palsy: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palisano, R.J.; Di Rezze, B.; Stewart, D.; Freeman, M.; Rosenbaum, P.L.; Hlyva, O.; Wolfe, L.; Gorter, J.W. Promoting Capacities for Future Adult Roles and Healthy Living Using a Lifecourse Health Development Approach. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 42, 2002–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.L.; Gilbert, T.K.; McCormick, A.; Ayling-Campos, A.; Boydell, K.; Law, M.; Fehlings, D.L.; Mukherjee, S.; Wedge, J.H.; Williams, J.I. Youth and Young Adults With Cerebral Palsy: Their Use of Physician and Hospital Services. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljuhani, T.; Alzahrani, S.A.; Aldosary, A.M.; Alzamil, L.A.; Alshehri, R.K.; Gmmash, A.S.; Albesher, R.A. Measuring Community and Home Participation and Environmental Factors in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr. Rep. 2025, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kemp, J.; Ketelaar, M.; Gorter, J.W. Environmental Factors Associated with Participation and Its Related Concepts among Children and Youth with Cerebral Palsy: A Rapid Review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2022, 44, 1571–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Raji, P.; Mousavi, S.T.; Mahmoodian, M.; Baghestani, A.R. Study of Environmental Factors and Quality of Life in Children with Cerebral Palsy Based on International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Br. J. Occup. Ther. 2022, 85, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonsson, R.J.; Leonardi, M.; Lollar, D.; Bjorck-Akesson, E.; Hollenweger, J.; Martinuzzi, A. Applying the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) to Measure Childhood Disability. Disabil. Rehabil. 2003, 25, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnie, K.A.; Richardson, P.A.; Rajagopalan, A.V.; Bhandari, R.P. Factors Related to Agreement Between Child and Caregiver Report of Child Functioning With Chronic Pain. Clin. J. Pain 2020, 36, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramstad, K.; Loge, J.H.; Jahnsen, R.; Diseth, T.H. Self-Reported Mental Health in Youth with Cerebral Palsy and Associations to Recurrent Musculoskeletal Pain. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 37, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester-Plané, J.; Laporta-Hoyos, O.; Macaya, A.; Póo, P.; Meléndez-Plumed, M.; Vázquez, É.; Delgado, I.; Zubiaurre-Elorza, L.; Narberhaus, A.; Toro-Tamargo, E.; et al. Measuring Intellectual Ability in Cerebral Palsy: The Comparison of Three Tests and Their Neuroimaging Correlates. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2016, 56, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, K.; Starrfelt, R.; Robotham, R.J. Cognitive Functioning and Assessment in Adults with Cerebral Palsy: A Scoping Review. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2024, 27, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bøttcher, L.; Stadskleiv, K.; Berntsen, T.; Christensen, K.; Korsfelt, Å.; Kihlgren, M.; Ödman, P. Systematic Cognitive Monitoring of Children with Cerebral Palsy–the Development of an Assessment and Follow-up Protocol. Scand. J. Disabil. Res. 2016, 18, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadskleiv, K.; van Walsem, M.R.; Andersen, G.L.; Bergqvist, L.; Bøttcher, L.; Christensen, K.; Heyerdahl, D.; Hollung, S.J.; Høye, H.; Jahnsen, R.; et al. Systematic Monitoring of Cognition for Adults With Cerebral Palsy—The Rationale Behind the Development of the CPCog-Adult Follow-Up Protocol. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 710440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, P.S.C.; Magalhães, E.D.D.; Sousa Junior, R.R.; Romeros, A.C.S.F.; Palisano, R.J.; Leite, H.R.; Rosenbaum, P. Development of Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults with Cerebral Palsy According to the ICF: A Scoping Review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2023, 65, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelmann, K.; McManus, V.; Hagberg, G.; Uvebrant, P.; Krägeloh-Mann, I.; Cans, C. Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy in Europe: Trends in Prevalence and Severity. Arch. Dis. Child. 2009, 94, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horber, V.; Fares, A.; Platt, M.J.; Arnaud, C.; Krägeloh-Mann, I.; Sellier, E. Severity of Cerebral Palsy-The Impact of Associated Impairments. Neuropediatrics 2020, 51, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monbaliu, E.; Himmelmann, K.; Lin, J.P.; Ortibus, E.; Bonouvrié, L.; Feys, H.; Vermeulen, R.J.; Dan, B. Clinical Presentation and Management of Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delacy, M.J.; Reid, S.M.; Australian Cerebral Palsy Register Group. Profile of associated impairments at age 5 years in Australia by cerebral palsy subtype and Gross Motor Function Classification System level for birth years 1996 to 2005. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58 (Suppl. S2), 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidecker, M.J.C.; Ho, N.T.; Dodge, N.; Hurvitz, E.A.; Slaughter, J.; Workinger, M.S.; Kent, R.D.; Rosenbaum, P.; Lenski, M.; Messaros, B.M.; et al. Inter-Relationships of Functional Status in Cerebral Palsy: Analyzing Gross Motor Function, Manual Ability, and Communication Function Classification Systems in Children. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2012, 54, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodur, M.; Özmen, A.H.; Sait Okan, M. Clinical Phenotypes and Etiological Risk Factors in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Retrospective Study. Iran. J. Pediatr. 2024, 34, e143328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, D.M.; Sini, F.; Brogna, C.; Albamonte, E.; Ricci, D.; Mercuri, E. Sex Differences in Cerebral Palsy on Neuromotor Outcome: A Critical Review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdardottir, S.; Eiriksdottir, A.; Gunnarsdottir, E.; Meintema, M.; Arnadottir, U.; Vik, T. Cognitive Profile in Young Icelandic Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2008, 50, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Population | Neuropsychology/Cognition | ICF Components 1 |
|---|---|---|
| cerebral palsy | neuropsycholog*, cogniti*, intelligence, intellectual, executive func*, language, memory, verbal learning, nonverbal learning, visual percep*, visuospatial ability, spatial processing, attention, cognitive processing speed, social cognition, theory of mind, emotion recognition | literacy, reading, writing, math*, learning, activities of daily living, nonverbal communication, augmentative communication, motor activity, physical mobility, household management, household work, interpersonal relations, interpersonal interaction, interpersonal relationships, education, work, employment, participation, social participation, community participation, community involvement, leisure activities, recreation, technology, social support, community support, attitude, social services, policy, international classification of functioning, disability and health |
| ICF | Cognitive Assessment | Demographic Data | Main Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICF chapter | ICF second level Assessment | Cognitive domain Instrument | n Age range (years:months) n females n type CP n pattern CP Motor ability | + (significative) − (significative) n.s. Author (year)—LOE |
| d8 Major life areas | d820 School education School Function Assessment (SFA) | Memory School Function Assessment (SFA) | 148 6:1–13:6 years 61 females CP type unk CP pattern unk GMFCS: 148 II–IV | + (significative) Schenker et al. (2005) [51]—LOE 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carracedo-Martín, M.; Moral-Salicrú, P.; Blasco, M.; Fernández-Andújar, M.; Pueyo, R.; Ballester-Plané, J. The Role of Cognitive Functioning in the ICF Framework: A Systematic Review of Its Influence on Activities and Participation and Environmental Factors in People with Cerebral Palsy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186393
Carracedo-Martín M, Moral-Salicrú P, Blasco M, Fernández-Andújar M, Pueyo R, Ballester-Plané J. The Role of Cognitive Functioning in the ICF Framework: A Systematic Review of Its Influence on Activities and Participation and Environmental Factors in People with Cerebral Palsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186393
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarracedo-Martín, María, Paula Moral-Salicrú, Montse Blasco, Marina Fernández-Andújar, Roser Pueyo, and Júlia Ballester-Plané. 2025. "The Role of Cognitive Functioning in the ICF Framework: A Systematic Review of Its Influence on Activities and Participation and Environmental Factors in People with Cerebral Palsy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186393
APA StyleCarracedo-Martín, M., Moral-Salicrú, P., Blasco, M., Fernández-Andújar, M., Pueyo, R., & Ballester-Plané, J. (2025). The Role of Cognitive Functioning in the ICF Framework: A Systematic Review of Its Influence on Activities and Participation and Environmental Factors in People with Cerebral Palsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186393






