Abstract
Background: This study evaluated the effects of veno-arterial (V-A) and veno-venoarterial (V-VA) ECMO in a porcine model of septic endotoxemia-induced acute pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Our hypotheses were as follows: (1) V-VA ECMO lowers pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) by delivering oxygenated blood to the pulmonary circulation, and (2) both V-A and V-VA ECMO improve perfusion to vital organs while simultaneously unloading the right ventricle (RV). Methods: Acute PAH was induced with Salmonella abortus equi lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in 34 pigs. Animals were randomized to either a control group without ECMO or to two groups receiving V-A or V-VA ECMO. Results: All animals developed PAH after one hour of LPS infusion: mean pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) increased significantly from 26 (24–30) mmHg to 40 (34–46) mmHg (p < 0.0001), and PVR increased from 314 (221–390) to 787 (549–1073) (p < 0.0001). Neither V-A nor V-VA ECMO significantly reduced PVR compared to controls. RV end-diastolic area increased in the control group [6.1 (4.3–8.6) cm vs. 8.5 (7.8–9.7) cm, p = 0.2], but not in the V-A [4.7 (3.3–7.6) cm] and V-VA [4.3 (2.5–8.3) cm] ECMO groups. Blood flow in the cranial mesenteric artery and celiac trunk did not differ significantly with or without ECMO. Conclusions: Elevating pulmonary artery oxygen tension through V-A or V-VA ECMO did not reduce PVR or PAP. However, both ECMO configurations effectively unloaded the RV and maintained perfusion to abdominal organs.
1. Introduction
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), defined as a mean pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) exceeding 20 mmHg at rest [1], has been observed in both experimental animal models [2,3] and critically ill patients with sepsis [2]. The resulting right ventricular (RV) dysfunction and dilation is multifactorial, caused by increased afterload due to pulmonary hypertension, the effects of positive pressure ventilation, and the direct impact of inflammatory cytokines on the myocardium [3]. It occurs in 30–60% of patients with sepsis and septic shock and is associated with more than a twofold increase in short- and long-term mortality [4] and is especially prevalent in patients with severe respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) [5]. Notably, in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, acute PAH and RV dysfunction have also been reported in less advanced stages of disease, with prevalences of 12.0% and 14.5% among non-ICU patients, respectively [6]. In critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, a dysregulated host response, involving hyperinflammation, coagulopathy, and pulmonary vascular dysfunction, further contributes to multiple organ failure [7].
In neonatal and pediatric patients, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is recommended as a last-resort therapy for refractory septic shock [8]. In this setting, veno-arterial (V-A) ECMO may improve perfusion pressure and oxygen delivery to vital organs while simultaneously unloading the RV by reducing preload. This approach may significantly reduce catecholamine requirements, thereby limiting their adverse effects on the stressed myocardium. Additionally, veno-venoarterial (V-VA) ECMO may lower pulmonary vascular resistance by delivering oxygenated blood to the pulmonary circulation, thereby improving pulmonary hypertension and specifically addressing hypoxemia due to ARDS [9,10]. However, to date, the role of ECMO in general and the ideal cannulation modality in critically ill patients with acute pulmonary arterial hypertension remains uncertain.
This study aims to evaluate the cardiocirculatory effects of V-A and V-VA ECMO in a standardized porcine model of sepsis-induced acute pulmonary hypertension. We hypothesized that V-VA ECMO, compared to V-A ECMO, significantly reduces pulmonary artery pressure by delivering oxygen-rich blood to the pulmonary circulation. The primary endpoint was a reduction in mean PAP in the presence of a significant increase in pulmonary artery oxygen tension (PpaO2). Secondary endpoints included the ability of both ECMO modalities to maintain perfusion pressure to vital abdominal organs while simultaneously unloading the RV.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board for the care of animal subjects (Baden-Wuerttemberg Regional Council Karlsruhe, Department of Agriculture, Rural Areas, Veterinary and Food Affairs, Karlsruhe, Germany, 35-9185.81/G-9/22). All animals received humane care in compliance with the “Principles of Laboratory Animal Care” formulated by the National Society for Medical Research and the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” prepared by the National Academy of Sciences, USA.
2.1. Animal Preparation
A total of 34 pigs (22 females, 12 males) weighing 25–35 kg (29.6 ± 2.6 kg) were fasted overnight with unrestricted access to water. Anesthesia was induced by i.m. injection of azaperone (120 mg), midazolam (45 mg), and ketamine (200 mg). The animals were then intubated with a cuffed 6.0 mm endotracheal tube and general anesthesia was maintained with 300 mg/h propofol (10 mg/kg/h) and 0.5 mg/h fentanyl (17 µg/kg/h) throughout the experiment. Animals were placed in the supine position and monitored via continuous ECG and pulse oximetry. Core temperature was maintained at 36–37 °C using a heating mat, stand heater, and pre-warmed infusions. The animals were mechanically ventilated in a volume-controlled mode with a positive end-expiratory pressure of 5 cm H2O, a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg, and a respiratory rate of 20–30 breaths per minute, adjusted to maintain a target PaCO2 of 35–45 mmHg. To control for potential confounders, the fraction of inspired oxygen, PEEP, and tidal volume were kept constant throughout the entire experiment. Mean arterial pressure was maintained at 60–70 mmHg; persistent hypotension was initially managed with a 300 mL bolus of pre-warmed balanced electrolyte solution. In case of volume refractory hypotension, norepinephrine was continuously infused.
All catheters and cannulas were inserted via direct puncture following atraumatic surgical exposure of the arteries and veins (for details see Appendix A) after administration of heparin (100 I.E./kg body weight). Correct catheter positions were verified through direct visualization at the end of the experiment.
The abdomen was accessed through a midline laparotomy extending from the xiphoid to approximately 4–5 cm above the symphysis. Urinary output was measured through bladder catheterization under direct visualization. The most distal parts of the inferior vena cava and abdominal aorta were exposed for ECMO cannulation. Further, the cranial mesenteric artery, celiac trunk, and infradiaphragmatic aorta were surgically exposed. To quantify arterial blood flow, appropriately sized flow probes (PS series, Transonic Systems Inc., Ithaca, NY, USA) were placed on these three vessels. To minimize fluid and heat loss, the abdominal wall was closed.
Thoracic access was gained via a median sternotomy. An appropriately sized flow probe (PAU series, Transonic Systems Inc., Ithaca, NY, USA) was placed on the pulmonary trunk to directly quantify cardiac output. To facilitate epicardial echocardiography, the sternal retractor was left in place, and the pericardial cavity was covered with surgical towels.
2.2. Experimental Design
Following instrumentation and baseline measurements, all animals received a continuous intravenous infusion of Salmonella abortus equi lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (L5886, Sigma-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany) at a constant rate of 2.5 µg/kg/h. The experimental timeline is outlined in Figure 1.
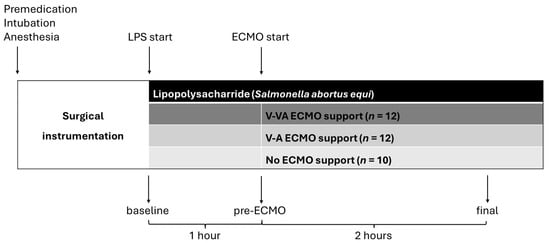
Figure 1.
Experimental timeline. Hemodynamic measurements, echocardiography, and blood sampling were conducted at baseline, after one hour of continuous LPS infusion (pre-ECMO), and after a further two hours of LPS infusion with or without ECMO support (final). ECMO: extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; V-A: veno-arterial; V-VA veno-venoarterial.
The animals were randomly assigned to three groups: V-VA ECMO group (n = 12), V-A ECMO group (n = 12), and control group (n = 10) with either V-VA or V-A cannulation (5 per cannulation type) but no ECMO support. After one hour of continuous LPS infusion, ECMO support was initiated in the V-A and V-VA groups, based on the protocol established in our previous study [11].
As one of the aims of our study was to assess the ability of both ECMO modalities to maintain perfusion pressure to vital abdominal organs, V-A ECMO flow rate was set to 50% of baseline cardiac output. With preserved LV function, arterial support at ~50% of cardiac output was sufficient to sustain a watershed point between the thoracic and abdominal aorta, as demonstrated in our pilot study. In the V-VA configuration, an additional flow of ~1 L/min (30–40% of cardiac output) was returned through the jugular cannula, which was estimated to provide adequate oxygen delivery to the upper body circulation.
ECMO support was limited to 2 h, as this duration was considered sufficient to demonstrate a significant reduction in PAP and PVR. According to the literature, significant reductions in PAP and PVR can be expected within minutes of improved pulmonary artery oxygen tension [12,13]. In both ECMO groups, the final evaluation was performed under ongoing ECMO support.
Extracorporeal gas flow was kept constant at a rate of 0.5 L/min with 100% oxygen throughout the experiment. Arterial (SaO2) and mixed venous (SvO2) blood samples were collected at baseline, one hour after the initiation of LPS infusion (pre-ECMO), and two hours thereafter (final). Samples were drawn into heparinized blood gas syringes and immediately analyzed, with all values corrected for core body temperature (Siemens RAPIDPoint 500, Siemens Healthineers AG, Forchheim, Germany). Pulmonary artery oxygen tension (PpaO2) was measured from pulmonary artery blood samples in all groups. Mixed venous blood (SvO2) samples were collected from the pulmonary artery in the control group, whereas in the V-A and V-VA ECMO groups, samples were obtained from the pre-oxygenator site. Systemic arterial, left ventricular, pulmonary arterial, and central venous pressures were continuously monitored. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure was obtained intermittently.
Using cardiac output (CO) measured at the pulmonary trunk, pulmonary and systemic vascular resistance (PVR and SVR) were then calculated as follows:
where mPAP is mean pulmonary artery pressure, PCWP is pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, and MAP is mean arterial pressure; CVP is central venous pressure.
The heart was imaged using parasternal and apical-equivalent echocardiographic planes. Direct epicardial echocardiography was performed by placing a standard echocardiographic transducer, enclosed in a sterile sheath, directly on the epicardial surface. Two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiographic assessments were conducted to evaluate basal end-diastolic diameters of both ventricles, septal bowing or paradoxical septal motion, significant valvular regurgitation or stenosis, and intracardiac shunts. RV function was assessed using tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) and RV fractional area change, while left ventricular (LV) function was evaluated using Doppler mitral inflow, tissue Doppler imaging of the mitral annulus, and LV velocity–time integral. Due to significant LV shortening, ejection fraction could not be measured reliably.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Based on data from the LPS model used in our previous study [11], an estimated sample size of twelve animals was required to measure differences in pulmonary artery pressure between ECMO groups with a power of 0.8 and a significance level of 0.05. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation for normally distributed values and as median with interquartile range for values without a normal distribution. The within-subject effect of time (differences between baseline and pre-ECMO) was assessed using analysis of variance (F-test) with correction for repeated measurements. As various values at final evaluation were not normally distributed, between-group differences were analyzed using the non-parametric Steel–Dwass method for multiple comparisons. Data were analyzed using JMP Version 16 (JMP Statistical Discovery LLC., Cary, NC, USA).
3. Results
There were no significant differences in relevant physiological parameters at baseline and at pre-ECMO (after 1 h of LPS infusion) between the V-VA ECMO, V-A ECMO, and control groups.
All animals developed PAH at pre-ECMO. Mean PAP increased significantly from baseline to pre-ECMO (26 (24–30) mmHg vs. 40 (34–46) mmHg, p < 0.0001). We found no differences between the two ECMO modalities (Figure 2).
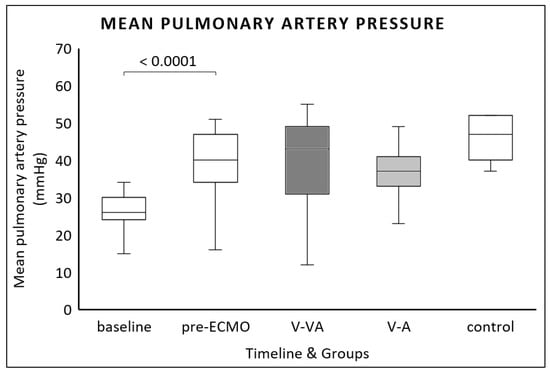
Figure 2.
Mean pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) measured at baseline, after one hour of continuous LPS infusion (pre-ECMO), and at the final evaluation in the V-VA ECMO group (dark gray), the V-A ECMO group (light gray), and the control group without ECMO support (white).
PVR increased from baseline to pre-ECMO (314 (221–390) dynes.s.cm−5 vs. 787 (549–1073) dynes.s.cm−5, p < 0.0001). Compared to the control group, neither V-A nor V-VA ECMO reduced PVR at the final evaluation (Figure 3). Furthermore, we found no differences between the ECMO modalities.
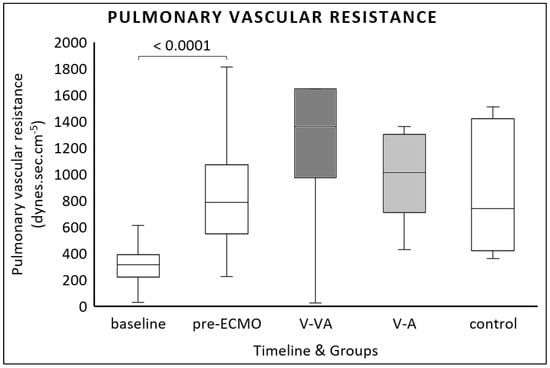
Figure 3.
Pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) calculated at baseline, after one hour of continuous LPS infusion (pre-ECMO), and at the final evaluation in the V-VA ECMO group (dark gray), the V-A ECMO group (light gray), and the control group without ECMO support (white).
RV end-diastolic area remained stable from baseline to pre-ECMO (6.1 (4.3–8.6) cm vs. 5.8 (4.5–8.1) cm, p = 0.7). Both ECMO strategies were equally effective in limiting RV distension compared to control at the final evaluation (4.7 (3.3–7.6) vs. 8.5 (7.8–9.7), p = 0.02 for V-A ECMO vs. control, respectively; and 4.3 (2.5–8.3) vs. 8.5 (7.8–9.7), p = 0.04 for V-VA ECMO vs. control) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Physiological parameters.
From baseline to pre-ECMO, SvO2 decreased (75 (72–80)% vs. 71 (63–74)%, p = 0.0003). At the end of the experiment, SvO2 was significantly lower in the control group compared to both ECMO strategies (V-A ECMO, 72 (65–81)% vs. 54 (38–68)%, p = 0.002; V-VA ECMO, 70 (67–82)% vs. 54 (38–68)%, p = 0.002).
At the end of the experiment, both ECMO modalities significantly increased pulmonary arterial oxygen tension (PpaO2) compared to pre-ECMO values [46 mmHg (42–50 mmHg) vs. 58 mmHg (47–68 mmHg) for V-A ECMO; p = 0.001 and 82 mmHg (72–102 mmHg) for V-VA ECMO; p = 0.0004] (Figure 4). Additionally, V-VA ECMO resulted in significantly higher PpaO2 at the end of the study compared to V-A ECMO [82 mmHg (72–102 mmHg) vs. 58 mmHg (47–68 mmHg); p = 0.002] (Figure 4).
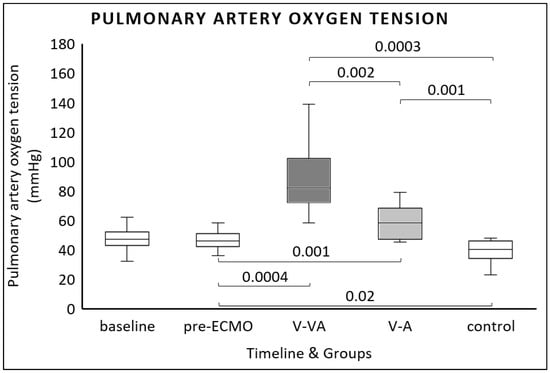
Figure 4.
Pulmonary artery oxygen tension (PpaO2) measured at baseline, after one hour of continuous LPS infusion (pre-ECMO), and at the final evaluation in the V-VA ECMO group (dark gray), the V-A ECMO group (light gray), and the control group without ECMO support (white).
Arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) decreased from baseline to pre-ECMO (220 mmHg (206–230 mmHg) vs. 195 mmHg (147–223 mmHg), p = 0.0001) (Table 2). In the control group, PaO2 declined further at the end of the experiment (99 mmHg (74–127 mmHg) vs. 208 (146–242) and 190 (148–246) for V-VA and V-A ECMO, respectively, p = 0.002 and p = 0.02) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Blood gas analyses.
Blood flow in the cranial mesenteric artery remained stable throughout the experiment (Table 3). At the celiac trunk, blood flow increased from baseline to pre-ECMO (0.15 L/min (0.1–0.3) vs. 0.4 (0.1–0.6, p = 0.0001). Thereafter, no significant changes in blood flow were observed (Table 3).

Table 3.
Abdominal perfusion.
From baseline to pre-ECMO, blood flow in the infradiaphragmatic aorta decreased (1.8 L/min (1.3–2.9 L/min) vs. 1.7 L/min (1.1–2.1 L/min), p = 0.03). V-A and V-VA ECMO induced comparable retrograde flow in the infradiaphragmatic aorta (Table 3).
4. Discussion
In this study, we evaluated the cardiocirculatory effects of veno-arterial (V-A) and veno-venoarterial (V-VA) ECMO cannulation strategies in a standardized porcine model of LPS-induced acute PAH. Our main findings demonstrated that (1) neither V-VA nor V-A ECMO effectively reduced PVR or PAP; and (2) both ECMO modalities maintained abdominal blood flow while effectively unloading the RV.
In ARDS, PVR is typically increased by low PpaO2, hypercapnia, acidosis, and high airway pressures [14]. On the other hand, endotoxin inhibits hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction, leading to a right-to-left intrapulmonary shunt and systemic hypoxia [14]. The primary advantage of V-VA ECMO over V-A ECMO is its ability to prevent low PpaO2 and differential hypoxia if cardiac function recovers before pulmonary function, thereby protecting critical organs such as the heart and brain [15,16].
Our results indicate that increasing PpaO2 via ECMO while maintaining normocapnia did not reduce the LPS-induced increase in PVR. However, this approach prevented a significant decline in PaO2 associated with right-to-left intrapulmonary shunting, as observed in the control group.
Experimental lung injury models with atelectatic lungs have shown that increasing PpaO2 above 100 mmHg can effectively reduce PVR [12]. Accordingly, some authors propose that V-V ECMO might lower PVR by increasing PpaO2 during severe ARDS, thereby reducing RV afterload and improving RV function [17,18]. This effect could be mediated by improved PpaO2, increased CO2 elimination, correction of respiratory acidosis, and reduced airway pressures [19,20]. In a porcine model of endotoxin shock, Mu et al. reported a return of PVR to baseline levels under V-A ECMO support [21]. However, in this study, a lung-rest strategy was employed, including a reduced respiratory rate, making it unclear whether the observed PVR reduction was attributable to increased PpaO2 or to changes in ventilator settings. In contrast, Holzgraefe et al. found that increasing PpaO2 via peripheral V-V ECMO, without altering ventilator settings, failed to reduce mean pulmonary artery pressure or lessen hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in a porcine model of global alveolar hypoxia [16]. Thus, based on the existing literature and our findings, increasing PpaO2 via peripheral V-VA ECMO ensures adequate oxygenation but does not necessarily decrease PVR.
Sudden, sustained elevations in PVR may compromise RV contractility, leading to rapid RV distension and failure [22]. RV failure has been reported in 22.5% of patients with septic shock [23] and in 25% of ARDS patients, a condition linked to decreased survival in those requiring V-V ECMO [22,24]. In our study, both V-A and V-VA ECMO facilitated RV unloading through venous-arterial shunting. After two hours of ECMO support, epicardial echocardiography showed a significantly smaller RV end-diastolic diameter in both ECMO groups compared to the control group, but no difference between V-A and V-VA ECMO.
Both V-A and V-VA ECMO strategies effectively maintained perfusion pressure to vital abdominal organs and allowed partial weaning from catecholamines [25,26], thereby reducing their adverse effects on the myocardium, PVR, and overall organ function [25,27,28]. Mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2), a surrogate marker for assessing the adequacy of systemic oxygen delivery, declined in the control group to levels that, from a clinical perspective, would be considered inadequate in critically ill patients [29]. In contrast, SvO2 was significantly higher in both the V-VA and V-A ECMO groups, indicating that both ECMO modalities effectively maintained global oxygen delivery.
However, these findings should be interpreted with caution, as SvO2 was measured from the pre-oxygenator site in both ECMO groups [15]. In the V-VA configuration, arterialized blood is partially returned to the venous circulation, potentially leading to an overestimation of true SvO2 values if measured directly from pulmonary artery blood samples. In V-A ECMO, blood is primarily drained from the inferior vena cava, while venous return from the superior vena cava largely bypasses the drainage cannula [15]. Since the primary focus of this study was on perfusion and oxygen delivery to abdominal organs, SvO2 was specifically measured at the pre-oxygenator site.
The adequacy of abdominal perfusion could also be confirmed by sustained blood flow in the cranial mesenteric artery and celiac trunk, with no statistical differences between the study groups. The slight negative blood flow observed at the proximal abdominal aorta in both ECMO groups suggests that, with arterial ECMO flow set at 50% of baseline cardiac output and preserved left ventricular function, the mixing point between native and retrograde ECMO circulations (the watershed region) is located between the thoracic and abdominal aorta.
Using continuous intravenous infusion of Salmonella abortus equi LPS, we established a reproducible model of acute precapillary PAH. After one hour, mean PAP consistently exceeded 30 mmHg, confirming this timeframe as sufficient to reach the experimental target. The pulmonary hypertension was precapillary in nature, driven by endotoxin-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction and reflected by elevated mean PAP and PVR, with low pulmonary capillary wedge pressure and LVEDP. During V-A ECMO, additional venous return through a jugular cannula raises pulmonary artery oxygen tension and should theoretically reduce PAP and PVR in precapillary PAH [12]. However, our study failed to demonstrate such an effect, as discussed previously. This mechanism must be clearly differentiated from LV venting with an additional ECMO drainage cannula [30,31], which addresses postcapillary PAH and cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Postcapillary PAH typically arises from cardiogenic shock and left-sided heart disease, characterized by elevated LVEDP and pulmonary venous pressure [32]. While LV venting reduces LVEDP and prevents pulmonary congestion [30,33], it does not target the underlying pathophysiology of precapillary PAH.
Limitations
Our study is an experimental investigation using a porcine model, and its findings should be cautiously translated into clinical practice. We used a continuous LPS infusion to induce an increase in PVR. This represents an artificial model, mimicking only aspects of septic shock and extrapulmonary ARDS [34]. Further, LPS also inhibits hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction, leading to a right-to-left intrapulmonary shunt and systemic hypoxia [14], which might have influenced our findings.
Changes in PVR and PAP are dynamic and often occur over a longer period of time [35]. In our unpublished pilot study, however, one hour of LPS infusion consistently increased mean PAP to values above 30 mmHg, confirming this timeframe as sufficient to establish acute PAH. Accordingly, we investigated a reproducible model of acute PAH, defined by a significant rise in mean PAP compared with baseline [11]. Short-term V-V ECMO support, however, may not be sufficient to achieve a clinically relevant reduction in PAP [36]. In contrast, Reis et al. reported an immediate decrease in PAP following V-V ECMO initiation [18]. Thus, time-dependent effects of ECMO on PAP and PVR might be influenced by the ECMO modality and the underlying disease.
To minimize the influence of ventilator settings and alveolar oxygen tension on PVR, ventilatory parameters were maintained without transitioning to ultraprotective ventilator settings during ECMO support. Traditional ventilator strategies are known to influence respiratory system function and hemodynamics both in experimental ARDS [37] as well as in clinical practice [19,20]. Drugs with alpha- and beta-agonistic effects influence pulmonary vascular tone and consequently PVR [38]. Therefore, we tried to avoid the administration of norepinephrine during our study. Lastly, epicardial echocardiographic assessments in this study cannot be directly compared with standardized transthoracic or transesophageal echocardiography used in clinical practice.
5. Conclusions
In a porcine model with LPS-induced acute PAH, increasing pulmonary artery oxygen tension through either V-A or V-VA ECMO did not reduce PVR or PAP. Nevertheless, both ECMO configurations effectively unloaded the RV and maintained adequate perfusion to vital abdominal organs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S., J.K. and M.T.; methodology, S.S., J.K. and M.T.; animal experiment: S.S., T.S. and P.T.G.; software, S.S. and J.K.; validation, S.S., J.K. and M.T.; formal analysis, S.S. and J.K.; investigation, S.S., J.K., T.S. and P.T.G.; resources, S.S., J.K. and M.T.; data curation, S.S. and T.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S.; writing—review and editing, S.S., J.K., G.B. and M.T.; visualization, S.S. and J.K.; supervision, J.K., G.B. and M.T.; project administration, S.S., J.K. and M.T.; funding acquisition, S.S., J.K. and M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Partial funding for this research was provided by the Medical Faculty Mannheim, University of Heidelberg, Gleichstellungsfoerderung—grant number 90703072.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Baden-Württemberg Regional Council Karlsruhe, Department of Agriculture, Rural Areas, Veterinary and Food Affairs, Karlsruhe, Germany (reference number 35-9185.81/G-9/22; date of approval: 3 March 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analyzed for this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CMA | Cranial mesenteric artery |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| LV | Left ventricle |
| LVEDP | Left ventricular end-diastolic pressure |
| LVESP | Left ventricular end-systolic pressure |
| PAP | Pulmonary artery pressure |
| PAH | Pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| PaO2 | Arterial oxygen tension |
| PpaO2 | Pulmonary arterial oxygen tension |
| PCWP | Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure |
| PEEP | Positive end-expiratory pressure |
| PVR | Pulmonary vascular resistance |
| RV | Right ventricle |
| SaO2 | Arterial oxygen saturation |
| SvO2 | Mixed venous oxygen saturation |
| SVR | Systemic vascular resistance |
| V-A | Veno-arterial |
| V-VA | Veno-venoarterial |
Appendix A
Vascular access sites and utilization:
- 20G peripheral intravenous line in the left auricular vein:
- -
- Induction of anesthesia, fluid administration.
- Central venous catheter in the left internal jugular vein:
- -
- Continuous infusion of anesthetic drugs, norepinephrine, lipopolysaccharide, and fluids;
- -
- Continuous measurement of central venous pressure;
- -
- Transpulmonary thermodilution.
- Pulmonary artery catheter in the right internal jugular vein:
- -
- Continuous pulmonary artery pressure measurement, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure measurement;
- -
- Pulmonary artery thermodilution measurement;
- -
- Central venous and mixed venous blood gas analysis.
- Arterial catheter in the left carotid artery:
- -
- Hemodynamic monitoring;
- -
- Arterial blood gas analysis.
- Left ventricular catheter via the right carotid artery:
- -
- Continuous left ventricular pressure monitoring.
- Venous ECMO drainage cannula in the inferior vena cava.
- Venous ECMO return cannula in the left brachiocephalic vein.
- Arterial ECMO return cannula in the distal abdominal aorta.
References
- Kovacs, G.; Bartolome, S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Gu, S.; Khanna, D.; Badesch, D.; Montani, D. Definition, classification and diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 64, 2401324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spapen, H.; Vincken, W. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Sepsis and the Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Acta Clin. Belg. 1992, 47, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischke, S.E.; Hestenes, S.; Johansen, H.T.; Fure, H.; Bugge, J.F.; Espinoza, A.; Skulstad, H.; Edvardsen, T.; Fosse, E.; Mollnes, T.E.; et al. Sepsis causes right ventricular myocardial inflammation independent of pulmonary hypertension in a porcine sepsis model. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Shankar, A.; Vojjini, R.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Sundaragiri, P.R.; DuBrock, H.M.; Sekiguchi, H.; Frantz, R.P.; Cajigas, H.R.; Kane, G.C.; et al. Impact of Right Ventricular Dysfunction on Short-term and Long-term Mortality in Sepsis: A Meta-analysis of 1373 Patients. Chest 2021, 159, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessap, A.M.; Boissier, F.; Charron, C.; Bégot, E.; Repessé, X.; Legras, A.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Vignon, P.; Vieillard-Baron, A. Acute cor pulmonale during protective ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome: Prevalence, predictors, and clinical impact. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnesi, M.; Baldetti, L.; Beneduce, A.; Calvo, F.; Gramegna, M.; Pazzanese, V.; Ingallina, G.; Napolano, A.; Finazzi, R.; Ruggeri, A.; et al. Pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular involvement in hospitalised patients with COVID-19. Heart 2020, 106, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torge, D.; Bernardi, S.; Arcangeli, M.; Bianchi, S. Histopathological Features of SARS-CoV-2 in Extrapulmonary Organ Infection: A Systematic Review of Literature. Pathogens 2022, 11, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.L.M.; Carcillo, J.A.; Aneja, R.K.; Deymann, A.J.; Lin, J.C.; Nguyen, T.C.; Okhuysen-Cawley, R.S.M.; Relvas, M.S.M.; Rozenfeld, R.A.M.; Skippen, P.W.M.; et al. The American College of Critical Care Medicine Clinical Practice Parameters for Hemodynamic Support of Pediatric and Neonatal Septic Shock: Executive Summary. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 18, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, D.J.; Murray, J.; Czapran, A.Z.; Camporota, L.; Ioannou, N.; Meadows, C.I.S.; Sherren, P.B.; Daly, K.; Gooby, N.; Barrett, N. Veno-arterio-venous ECMO for septic cardiomyopathy: A single-centre experience. Perfusion 2018, 33, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöhr, F.; Emmert, M.Y.; Lachat, M.L.; Stocker, R.; Maggiorini, M.; Falk, V.; Wilhelm, M.J. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for acute respiratory distress syndrome: Is the configuration mode an important predictor for the outcome? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 12, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, M.; Kreimeier, U.; Holzer, K.; Moritz, S.C.M.; Peter, K.; Messmer, K. Effects of adenosine on cardiopulmonary functions and oxygen-derived variables during endotoxemia. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 26, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domino, K.B.; Wetstein, L.; Glasser, S.A.; Lindgren, L.; Marshall, C.; Harken, A.; Marshall, B.E. Influence of Mixed Venous Oxygen Tension (PVO2) on Blood Flow to Atelectatic Lung. Anesthesiology 1983, 59, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, A.; Kula, S.; Olgunturk, R.; Tunaoglu, S.; Oguz, D.; Saylan, B.; Sanli, C. Evaluation of pulmonary vascular resistance and vasoreactivity testing with oxygen in children with congenital heart disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Anadolu Kardiyol. Dergisi/Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2014, 14, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, L.C.; McAuley, D.F.; Marino, P.S.; Finney, S.J.; Griffiths, M.J.; Wort, S.J. Pathophysiology of pulmonary hypertension in acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 302, L803–L815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Shiloh, A.L.; Carlese, A. Monitoring of the Adult Patient on Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 393258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzgraefe, B.; Larsson, A.; Eksborg, S.; Kalzén, H. Does extracorporeal membrane oxygenation attenuate hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in a porcine model of global alveolar hypoxia? Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2020, 64, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunge, J.J.H.; Caliskan, K.; Gommers, D.; Miranda, D.R. Right ventricular dysfunction during acute respiratory distress syndrome and veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S674–S682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, D.R.; van Thiel, R.; Brodie, D.; Bakker, J. Right Ventricular Unloading after Initiation of Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, P.T.; Boesing, C.; Brumm, I.; Biehler, J.; Müller, K.W.; Thiel, M.; Pelosi, P.; Rocco, P.R.M.; Luecke, T.; Krebs, J. Ultraprotective versus apneic ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A physiological study. J. Intensive Care 2022, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesing, C.; Schaefer, L.; Graf, P.T.; Pelosi, P.; Rocco, P.R.; Luecke, T.; Krebs, J. Effects of different positive end-expiratory pressure titration strategies on mechanical power during ultraprotective ventilation in ARDS patients treated with veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A prospective interventional study. J. Crit. Care 2024, 79, 154406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, T.S.; Becker, A.M.; Clark, A.J.; Batts, S.G.; Murata, L.-A.M.; Uyehara, C.F.T.; Bader, M. ECMO with vasopressor use during early endotoxic shock: Can it improve circulatory support and regional microcirculatory blood flow? PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, C.; Richards, J.B.; Frakes, M.; Cohen, J.; Wilcox, S.R. ECMO and Right Ventricular Failure: Review of the Literature. J. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 36, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geri, G.; Vignon, P.; Aubry, A.; Fedou, A.-L.; Charron, C.; Silva, S.; Repessé, X.; Vieillard-Baron, A. Cardiovascular clusters in septic shock combining clinical and echocardiographic parameters: A post hoc analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zochios, V.; Nasa, P.; Yusuff, H.; Schultz, M.J.; Antonini, M.V.; Duggal, A.; Dugar, S.; Ramanathan, K.; Shekar, K.; Schmidt, M. Definition and management of right ventricular injury in adult patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for respiratory support using the Delphi method: A PRORVnet study. Expert position statements. Intensive Care Med. 2024, 50, 1411–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broman, L.M.; Dubrovskaja, O.; Balik, M. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Septic Shock in Adults and Children: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrio, S.; Krebs, J.; Leonardy, E.; Thiel, M.; Schoettler, J.J. Vasoactive Inotropic Score as a Prognostic Factor during (Cardio-) Respiratory ECMO. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittinger, C.A.; Torgersen, C.; Luckner, G.; Schröder, D.C.H.; Lorenz, I.; Dünser, M.W. Adverse cardiac events during catecholamine vasopressor therapy: A prospective observational study. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudiger, A.; Singer, M. Decatecholaminisation during sepsis. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmukhappa, C.; Lokeshwaran, S. Venous Oxygen Saturation. 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564395/ (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Kang, J.; Lee, K.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, H.; Ahn, H.; Han, J.; Yang, H.; Park, K.W.; Lee, H.; Kang, H.; et al. Differential effect of left ventricular unloading according to the aetiology of cardiogenic shock. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrio, S.; Springer, W.; Karck, M.; Gorenflo, M.; Weymann, A.; Ruhparwar, A.; Loukanov, T. Extracorporeal life support with an integrated left ventricular vent in children with a low cardiac output. Cardiol. Young 2014, 24, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeije, R.; Chin, K. Differentiating Precapillary from Postcapillary Pulmonary Hypertension. Circulation 2019, 140, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldetti, L.; Gallone, G. Left ventricular unloading and venting in veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: The importance of cardiogenic shock aetiology in guiding treatment strategies. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.L.; Scharffenberg, M.; Rocco, P.R.M. Understanding the mechanisms of ventilator-induced lung injury using animal models. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2023, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.D.; Bossone, E.; Naeije, R.; Grünig, E.; Saggar, R.; Lancellotti, P.; Ghio, S.; Varga, J.; Rajagopalan, S.; Oudiz, R.; et al. Pulmonary Vascular Hemodynamic Response to Exercise in Cardiopulmonary Diseases. Circulation 2013, 128, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, A.M.; Duerschmied, D.; Boesing, C.; Thiel, M.; Beck, G.; Luecke, T.; Rocco, P.R.M.; Krebs, J.; Loosen, G. Impact of Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation on Right Ventricular Impairment in Severe ARDS: A Prospective Observational Longitudinal Study. J. Intensive Care Med. 2025, 24, 8850666251352445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araos, J.; Alegria, L.; Garcia, P.; Cruces, P.; Soto, D.; Erranz, B.; Amthauer, M.; Salomon, T.; Medina, T.; Rodriguez, F.; et al. Near-Apneic Ventilation Decreases Lung Injury and Fibroproliferation in an Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Model with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, L.C.; Wort, S.J.; Finney, S.J.; Marino, P.S.; Brett, S.J. Pulmonary vascular and right ventricular dysfunction in adult critical care: Current and emerging options for management: A systematic literature review. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).