Predictability of Lower Incisor Intrusion with Clear Aligners: A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Influencing Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
- -
- Studies involving patients with mixed or deciduous dentition.
- -
- Studies that did not directly analyze lower incisor intrusion.
- -
- Studies lacking quantitative data.
- -
- Studies involving orthodontic treatments with extractions.
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.3. Selection Process
2.4. Data Collection
- (a)
- Author and Year of Publication
- (b)
- Country
- (c)
- Study Design
- (d)
- Number of Patients
- (e)
- Mean Age of Patients
- (f)
- Gender (M/F)
- (g)
- Treatment Duration
- (h)
- Main Conclusions
- (1)
- Aligner Brand
- (2)
- Intrusion Measurement System
- (3)
- Refinement
- (4)
- Aligner Change Frequency
- (5)
- Predictability of Movement (%)
- (6)
- Intrusion Amount (mm)
- (7)
- Auxiliary Elements and Attachments
2.5. Quality Assessment
3. Results
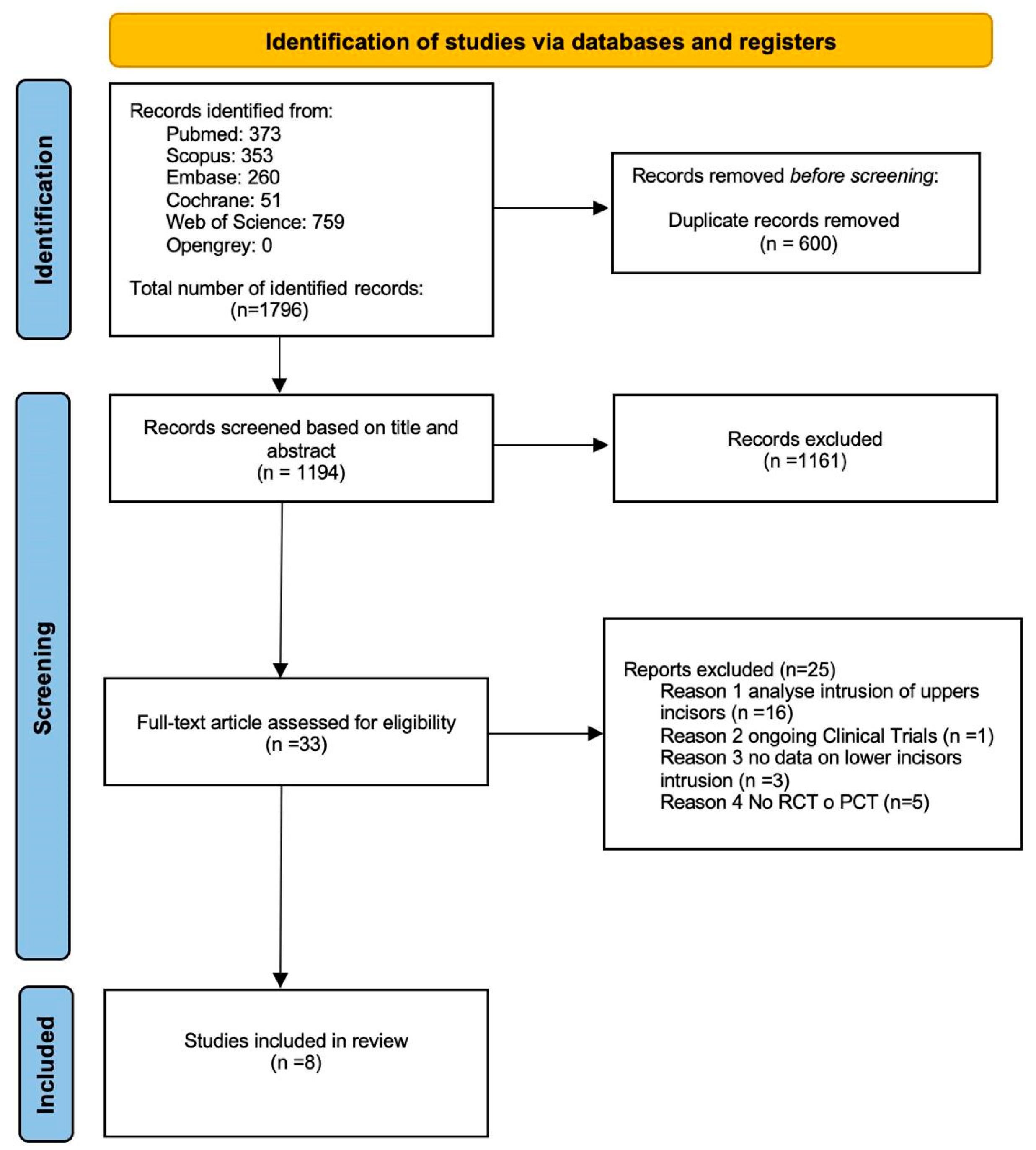
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Primary Outcomes
3.3.1. Predictability of Movement (%)
3.3.2. Intrusion Amount (mm)
3.4. Secondary Outcomes: Influencing Factors
3.4.1. Intrusion Measurement System
3.4.2. Refinement
3.4.3. Aligner Change Frequency
3.4.4. Auxiliary Elements and Attachments
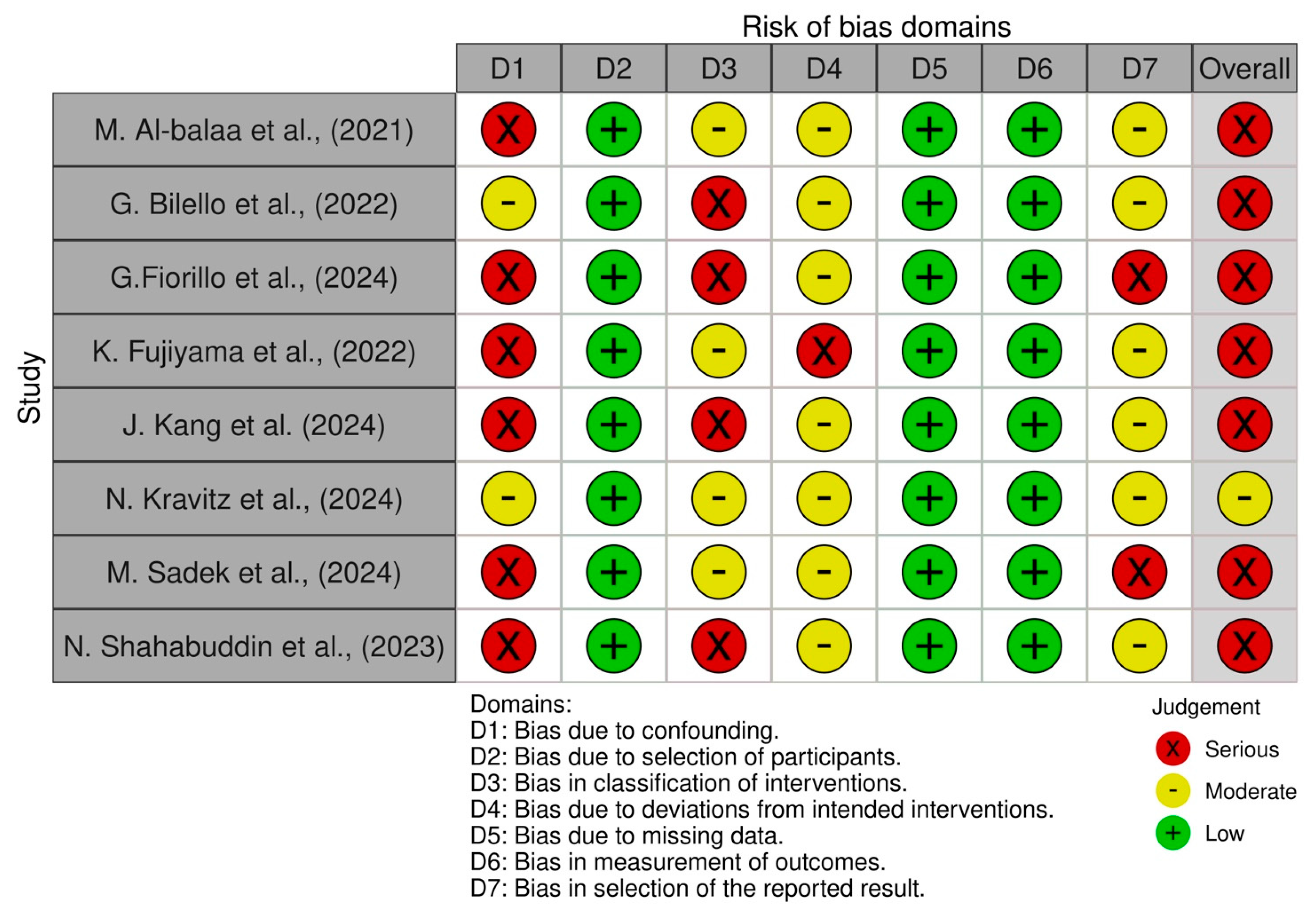
3.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Certainty of Assessment | Certainty | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Risk of Bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other Considerations | |
| M. Al-balaa et al. (2021) [26] | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate | None | Moderate |
| G. Bilello et al. (2022) [27] | Low | Low | Low | Low | None | High |
| G. Fiorillo et al. (2024) [28] | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | None | Moderate |
| K. Fujiyama et al. (2022) [29] | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate | None | Moderate |
| J. Kang et al. (2024) [30] | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | None | Moderate |
| N. Kravitz et al. (2024) [31] | Low | Low | Low | Low | None | High |
| M. Sadek et al. (2024) [32] | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | None | Moderate |
| N. Shahabuddin et al. (2023) [33] | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | None | Moderate |
References
- Fujiyama, K.; Honjo, T.; Suzuki, M.; Matsuoka, S.; Deguchi, T. Analysis of pain level in cases treated with Invisalign aligner: Comparison with fixed edgewise appliance therapy. Prog. Orthod. 2014, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azaripour, A.; Weusmann, B.; Mahmoodi, D.; Peppas, A.; Gerhold-Ay, C.J.; Van Noorden, C.J.F.; Willershausen, B. Braces versus Invisalign®: Gingival parameters and patients’ satisfaction during treatment: A cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.W.; Julien, K.C.; Jacob, H.; Campbell, P.M.; Buschang, P.H. Discomfort associated with Invisalign and traditional brackets: A randomized, prospective trial. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan-Lopez, L.; Barcia-Gonzalez, J.; Plasencia, E. A systematic review of the accuracy and efficiency of dental movements with Invisalign®. Korean J. Orthod. 2019, 49, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesling, H.D. The philosophy of the tooth positioning appliance. Am. J. Orthod. Oral Surg. 1945, 31, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponitz, R.J. Invisible retainers. Am. J. Orthod. 1971, 59, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modlin, S.S. Realignment of incisors with vacuum-formed appliances. J. Clin. Orthod. 1974, 8, 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, J.A.; Kramer, K.L.; Juenker, J.P. Invisible retainers. Clin. Orthod. 1985, 19, 570–578. [Google Scholar]
- Rossini, G.; Parrini, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Deregibus, A.; Debernardi, C.L. Efficacy of clear aligners in controlling orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic review. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepedino, M.; Colasante, P.; Staderini, E.; Masedu, F.; Ciavarella, D. Short-term effect of orthodontic clear aligners on muscular activity and occlusal contacts: A cohort study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2023, 164, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haouili, N.; Kravitz, N.D.; Vaid, N.R.; Ferguson, D.J.; Makki, L. Has Invisalign improved? A prospective follow-up study on the efficacy of tooth movement with Invisalign. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 158, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagravère, M.O.; Flores-Mir, C. The treatment effects of Invisalign orthodontic aligners: A systematic review. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2005, 136, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, M. A comparison of treatment effectiveness between clear aligner and fixed appliance therapies. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, S.N.; Koletsi, D.; Iliadi, A.; Peltomaki, T.; Eliades, T. Treatment outcome with orthodontic aligners and fixed appliances: A systematic review with meta-analyses. Eur. J. Orthod. 2020, 42, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pithon, M.M.; Baiao, F.C.S.; Anna, L.; Paranhos, L.R.; Maia, L.C. Assessment of the effectiveness of invisible aligners compared with conventional appliance in aesthetic and functional orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2019, 10, e12455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.; Kaur, H.; Fagundes, N.C.F.; Romanyk, D.; Major, P.; Flores Mir, C. Effectiveness of clear aligner therapy for orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 23, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletsi, D.; Iliadi, A.; Eliades, T. Predictability of rotational tooth movement with orthodontic aligners comparing software-based and achieved data: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Orthod. 2021, 48, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, A.; Mousoulea, S.; Gkantidis, N.; Kloukos, D. Clinical effectiveness of Invisalign® orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. Prog. Orthod. 2018, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, A.F.; Garfinkle, J.S.; Covell, D.A.; Wang, M.; Doyle, L.; Sedgley, C.M. Outcome assessment of orthodontic clear aligner vs fixed appliance treatment in a teenage population with mild malocclusions. Angle Orthod. 2020, 90, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassir, Y.A.; Nabbat, S.A.; McIntyre, G.T.; Bearn, D.R. Clinical effectiveness of clear aligner treatment compared to fixed appliance treatment: An overview of systematic reviews. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 2353–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Del Castillo McGrath, M.; Araujo-Monsalvo, V.M.; Murayama, N.; Martínez-Cruz, M.; Justus-Doczi, R.; Domínguez-Hernández, V.M.; Ondarza-Rovira, R. Mandibular anterior intrusion using miniscrews for skeletal anchorage: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2018, 154, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Sugawara, Y.; Balam, T.A.; Takano-Yamamoto, T.; Yamashiro, T. Indirect usage of miniscrew anchorage to intrude overerupted mandibular incisors in a Class II patient with a deep overbite. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2013, 143 (Suppl. S4), S113–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Balaa, M.; Li, H.; Ma Mohamed, A.; Xia, L.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Omran, T.; Li, S.; Hua, X. Predicted and actual outcome of anterior intrusion with Invisalign assessed with cone-beam computed tomography. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 159, e275–e280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilello, G.; Fazio, M.; Amato, E.; Crivello, L.; Galvano, A.; Currò, G. Accuracy evaluation of orthodontic movements with aligners: A prospective observational study. Prog. Orthod. 2022, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, G.; Campobasso, A.; Garrisi, L.; Battista, G.; D’Antò, V.; Mandelli, A.; Mandelli, G.; Ambrosi, A.; Gastaldi, G. The accuracy of biomechanical mechanisms for dental deep bite correction using the Invisalign system. Australas. Orthod. J. 2024, 40, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiyama, K.; Honjo, T.; Suzuki, M.; Matsuoka, S.; Deguchi, T. Comparison of clinical outcomes between Invisalign and conventional fixed appliance therapies in adult patients with severe deep overbite treated with non extraction. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 161, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Jeon, H.H.; Shahabuddin, N. Does aligner refinement have the same efficiency in deep bite correction: A retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, N.D.; Hansa, I.; Vaid, N.R.; Moshiri, M.; Adel, S.M. Does age influence deep overbite correction with Invisalign? A prospective study evaluating mandibular incisor intrusion in adolescents vs. adults. Angle Orthod. 2024, 94, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadek, M.M.; Alhashmi, R. Unplanned tooth movement in deepbite correction with Invisalign: A retrospective study. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2024, 13, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahabuddin, N.; Kang, J.; Jeon, H.H. Predictability of the deep overbite correction using clear aligners. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2023, 163, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Ren, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Jian, F.; Long, H.; Lai, W. Effectiveness of clear aligners in achieving proclination and intrusion of incisors among Class II division 2 patients: A multivariate analysis. Prog. Orthod. 2023, 24, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Cheng, C.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Shen, C.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Duan, Y.; Xia, L.; Chu, F.; et al. Biomechanical analysis of clear aligners for mandibular anterior teeth intrusion and its clinical application in the design of new aligner attachment. Prog. Orthod. 2025, 26, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiarui, S.; Chaoran, X.; Hui, X. Seeking orderness out of the orderless movements: An up-to-date review of the biomechanics in clear aligners. Prog. Orthod. 2024, 25, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Sun, B.; Gong, Z.; Wei, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W.; Wu, H.; Zhao, B. The tooth movement efficiency of different orthodontic thermoplastics for clear aligners: Study protocol for a randomized controlled clinical trial. Trials 2023, 24, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, D.; Fanelli, C.; Suriano, C.; Campobasso, A.; Lorusso, M.; Ferrara, D.; Maci, M.; Esposito, R.; Tepedino, M. Curve of Spee modification in different vertical skeletal patterns after clear aligner therapy: A 3D set-up retrospective study. Prog. Orthod. 2024, 25, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, W.; Deng, W.W. Effects of different patterns of movement for correcting a deep curve of Spee with clear aligners on the anterior teeth: A finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, W.; Li, S. Force changes associated with differential activation of en-masse retraction and/or intrusion with clear aligners. Korean J. Orthod. 2021, 51, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, R.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, R.; Xia, L.; Fang, B. Stress and movement trend of lower incisors with different IMPA intruded by clear aligner: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Prog. Orthod. 2023, 24, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geramy, A.; Ebrahimi, S. Evaluation of different models of intrusive force application and temporary anchorage device (TAD) placement in total arch intrusion using clear aligners; a finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Su, J.Y.; Lei, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Nie, X.P.; Ying, Q.H.; Hou, J.X.; Guo, J. Effectiveness of different intrusion modes of maxillary anterior teeth with mini-implants in clear aligner treatment: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosly, R.; Mohammed, H.; Rizk, M.Z.; Jamous, E.; Qaisi, A.G.; Bearn, D.R. Effectiveness of miniscrew-supported maxillary incisor intrusion in deep-bite correction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Angle Orthod. 2020, 90, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini-Pereira, S.A.; Almeida, J.; Aliaga-Del Castillo, A.; Dos Santos, C.C.O.; Henriques, J.F.C.; Janson, G. Evaluation of root resorption following orthodontic intrusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Euro J. Orthod. 2020, 43, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Feng, G.; Wang, C.; Song, J.; Fan, Y. Comparative assessment of orthodontic clear aligner versus fixed appliance for anterior retraction: A finite element study. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mario, P.; de Villagomez, S.S.; Federica, P.; Cremonini, F.; Salvatore, R.; Lombardo, L. Evaluation of Tooth Movement Accuracy with the F22 Aligner System: A Retrospective Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucera, R.; Dolci, C.; Bellocchio, A.M.; Costa, S.; Barbera, S.; Rustico, L.; Farronato, M.; Militi, A.; Portelli, M. Effects of Composite Attachments on Orthodontic Clear Aligners Therapy: A Systematic Review. Materials 2022, 15, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, W. Force changes associated with different intrusion strategies for deep-bite correction by clear aligners. Angle Orthod. 2018, 88, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| PICOS | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Participant | Adult and adolescent patients with permanent dentition | Patients with mixed or deciduous dentition |
| Intervention | Use of clear aligners for the intrusion of lower incisors without extractions | Treatments with clear aligners without lower incisor intrusion, treatments with extractions. |
| Comparison | Studies analyzing the effectiveness of clear aligners in lower incisors intrusion, with or without comparison to other orthodontic methodologies | Studies that do not include any analysis of the effectiveness of lower incisor intrusion with clear aligners. |
| Outcome | Effectiveness of lower incisor intrusion measured through CBCT, setup software, or cephalometric analysis. | Studies without measurable quantitative data. |
| Study design | R&PCTs | Case–control, cohort, cross-sectional, Nr-RCTs 2; reviews; case reports; case series; in vitro; and animal studies |
| Database | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| PubMed | (“Tooth Movement Techniques”[MeSH Terms] OR “Orthodontic Anchorage Procedures”[MeSH Terms]) AND (“Clear Aligners”[All Fields] OR “Invisalign”[All Fields]) |
| Scopus | (TITLE-ABS-KEY (“tooth movement techniques” OR “orthodontic anchorage procedures”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (“clear aligners” OR “Invisalign” OR “removable aligners”)) |
| Embase | (‘Tooth movement’/exp OR ‘orthodontic anchorage’/exp) AND (‘clear aligner’/exp OR ‘invisalign’ OR ‘removable orthodontic appliance’) |
| Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials | (“Tooth movement” OR “orthodontic anchorage”) AND (“clear aligner” OR “Invisalign” OR “removable orthodontic appliance”) |
| Web of Science | (((TS = (“Tooth Movement Techniques”)) OR TS = (“Orthodontic Anchorage Procedures”)) AND TS = (“Clear Aligners”)) OR TS = (“Invisalign”) |
| Author (Year) | Country | Study Design | Number of Patients | Mean Age (Years) | Gender (M/F) | Treatment Duration (Months) | Main Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-balaa et al. (2021) [26] | China | RCT | 22 | 23.74 | 10/12 | Average 19.27 | The mandibular incisors exhibited the least precise tooth movement, with an intrusion predictability of 44.71%. |
| Bilello et al. (2022) [27] | Italy | PCT | 10 | 34.8 ± 14 | 3/7 | Not specified | The mandibular incisors demonstrated a high predictability of intrusion (92.2%), but accuracy decreased for movements exceeding 2 mm. |
| Fiorillo et al. (2024) [28] | Italy | RCT | 25 | 32.28 | 12/13 | Not specified | Larger vertical changes were correlated with larger errors. |
| Fujiyama et al. (2022) [29] | Japan | RCT | 25 Invisalign 23 fixed appliances | 23.3 ± 8.5 | 7/18 | 31.9 ± 8.6 | Deep overbite correction was primarily achieved through 2.0 mm mandibular incisor intrusion, along with 1.0 mm maxillary incisor intrusion. Treatment duration was comparable to fixed appliances. |
| Kang et al. (2024) [30] | USA | RCT | 20 | 32.63 ± 11.88 | 7/13 | 22.96 ± 12.34 | The vertical movement of lower incisors has moderate predictability in the first set of aligners but decreases in refinements. |
| Kravitz et al. (2024) [31] | USA | PCT | 58 (29 adolescents, 29 adults) | -Adolescents: 15.1 -Adults: 40.7 | 16/42 | Not specified | Mandibular incisor intrusion was more accurate in adolescents (63.5%) than adults (45.3%), with greater intrusion (1.7 mm vs. 0.9 mm). Accuracy decreased with age. |
| Sadek et al. (2024) [32] | UAE | RCT | 34 | 30.65 ± 11.80 | Not specified | 16.14 ± 6.42 | Lower incisor intrusion with aligners shows limited predictability, with unplanned vertical movements being more pronounced in anterior teeth compared to posterior teeth. |
| Shahabuddin et al. (2023) [33] | USA | RCT | 24 | 32.8 ± 11.9 | 10/14 | 11.04 ± 4.14 | Intrusion success increased slightly with bite ramps and elastics, but not significantly. Planned vs. achieved movements showed significant discrepancies. Overcorrection and refinements are needed. |
| Study | Planned (mm) | Achieved (mm) | Predictability (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al-balaa et al. (2021) [26] | 1.8 | 0.82 | 51.2 |
| Bilello et al. (2022) [27] | ≤2.0 | NR | 92 |
| Fiorillo et al. (2024) [28] | NR | 1.15–2.11 diff. | 41–51 |
| Fujiyama et al. (2022) [29] | NR | ~2.0 | NR |
| Kang et al. (2024) [30] | NR | 1.48–1.59 | 27–42 |
| Kravitz et al. (2024) [31] | NR | 0.9–1.7 | 45–64 |
| Sadek et al. (2024) [32] | NR | NR | NR |
| Shahabuddin et al. (2023) [33] | NR | 1.02–1.09 | 42.5 |
| Author (Year) | Aligner Brand | Intrusion Measurement System | Refinement | Aligner Change Frequency | Auxiliary Elements and Attachments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-balaa et al. (2021) [26] | Invisalign | CBCT | No | 14 days | Pressure areas, no bite ramps |
| Bilello et al. (2022) [27] | Invisalign | Rhinoceros® software (Robert McNeel & Associates, USA) | Yes | 7 days | Bite ramps, power ridges, elastics, optimized root control attachments |
| Fiorillo et al. (2024) [28] | Invisalign | Geomagic Control X software (Rock Hill, SC, USA). | No | Not specified | Standardized horizontal attachments on premolars and molars, no bite ramps or elastics used |
| Fujiyama et al. (2022) [29] | Invisalign | Cephalometric radiographs | Not specified | Not specified | No auxiliary appliances other than elastics were used |
| Kang et al. (2024) [30] | Invisalign | 3D Slicer software via the SlicerCMF project (cmf.slicer.org, open-source, version 4.11.2). | Yes | 7–14 days | Bite ramps, optimized rotation attachments, optimized deep bite attachments, and conventional rectangular attachments |
| Kravitz et al. (2024) [31] | Invisalign Teen (Adolescents), Invisalign Full (Adults) | Compare (version 8.1; GeoDigm, Falcon Heights, Minn) | No | 7 days | Maxillary incisor bite ramps, G5 attachments on mandibular premolars and first molars, 4.0 mm beveled attachments on mandibular lateral incisors and canines. Mandibular premolars and first molars extruded 0.5 mm, canines and incisors intruded progressively. Final: 0.0 mm overbite, heavy posterior contacts, no interproximal reduction. |
| Sadek et al. (2024) [32] | Invisalign | eModel 9.0 software (GeoDigm Corporation, Falcon Heights, MN) | Not specified | 14 days | Optimized deep bite attachments, precision bite ramps, pressure areas |
| Shahabuddin et al. (2023) [33] | Invisalign | 3D Slicer via the SlicerCMF project (version 4.9.0; cmf.slicer.org)) | No | 7–14 days | Precision bite ramps, optimized deepbite attachments, new pressure areas on lingual surfaces |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fracchia, D.E.; Bignotti, D.; Lai, S.; Battista, E.; Verdecchia, A.; Spinas, E. Predictability of Lower Incisor Intrusion with Clear Aligners: A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Influencing Factors. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176339
Fracchia DE, Bignotti D, Lai S, Battista E, Verdecchia A, Spinas E. Predictability of Lower Incisor Intrusion with Clear Aligners: A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Influencing Factors. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176339
Chicago/Turabian StyleFracchia, David Emilio, Denis Bignotti, Stefano Lai, Eric Battista, Alessio Verdecchia, and Enrico Spinas. 2025. "Predictability of Lower Incisor Intrusion with Clear Aligners: A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Influencing Factors" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176339
APA StyleFracchia, D. E., Bignotti, D., Lai, S., Battista, E., Verdecchia, A., & Spinas, E. (2025). Predictability of Lower Incisor Intrusion with Clear Aligners: A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Influencing Factors. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176339