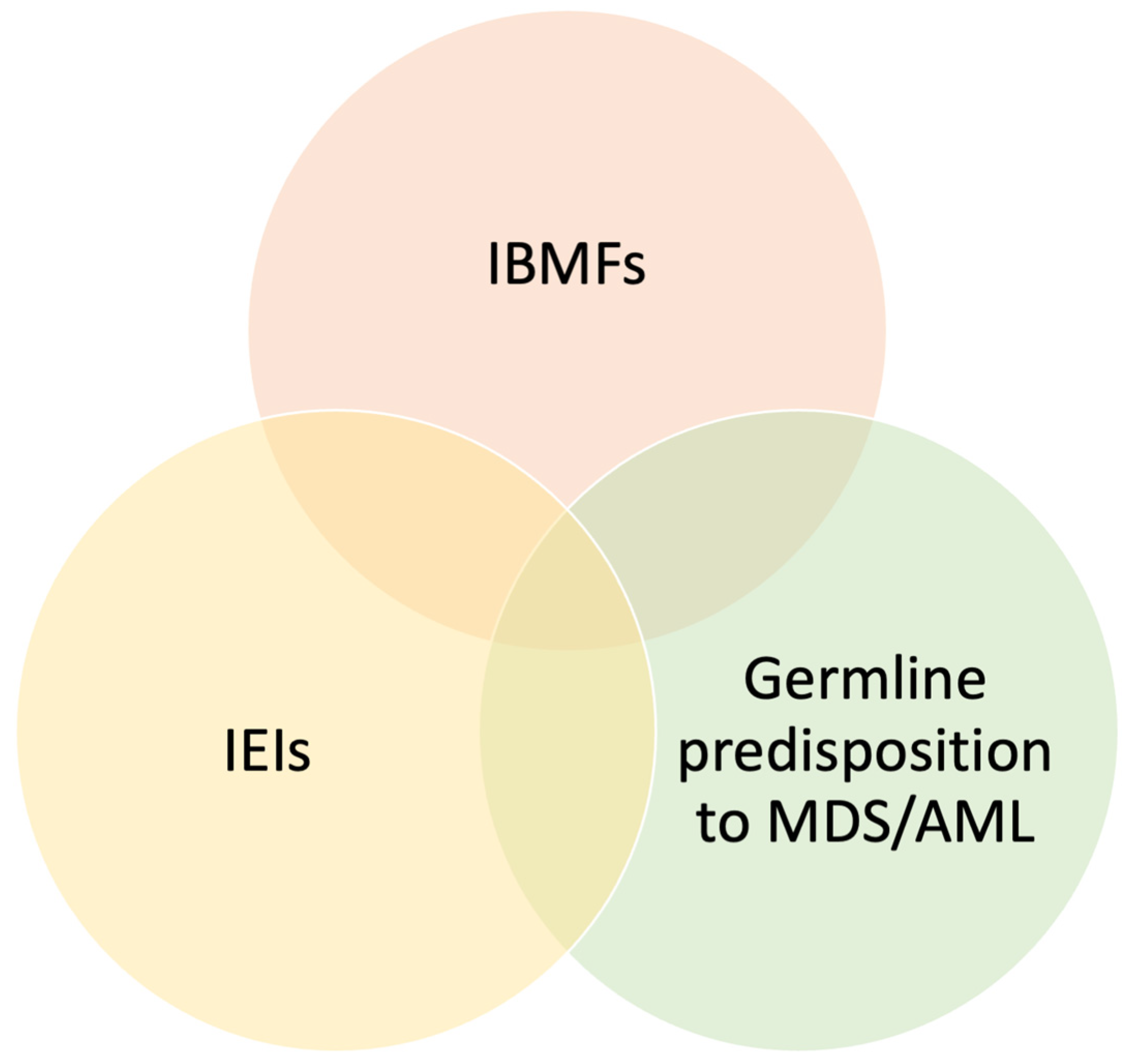
Inborn Errors of Immunity in Pediatric Hematology and Oncology: Diagnostic Principles for Clinical Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Autoimmune Cytopenia and IEIs
3. Polyclonal Lymphoproliferation and IEIs
| Associated Feature | Indicative of/Frequently Found in | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Autoimmune cytopenias | ALPS, CVID, DADA2, CTLA-4/LRBA haploinsufficiency, STAT3 GOF | Frequent early clue; particularly if multilineage |
| Enteropathy | IPEX, CVID, CTLA-4/LRBA d haploinsufficiency, STAT3 GOF | Suggests immune dysregulation |
| Endocrinopathy (e.g., type 1 diabetes, thyroiditis) | IPEX, CTLA-4/LRBA haploinsufficiency | Especially if in association with cytopenias or lymphadenopathy |
| Recurrent/severe infections | CVID, APDS, XMEN, CTLA-4 haploinsufficiency | Suggests impaired immune protection |
| Eczema or eczematous dermatitis | STAT3 GOF, IPEX, WAS, | Particularly if early-onset and severe |
| Granulomatous disease (lung, spleen, liver) | CVID (GLILD), CTLA-4 haploinsufficiency | Often coexists with lymphadenopathy or splenomegaly |
| Neurological involvement | CTLA-4 haploinsufficiency, STAT1 GOF, STAT3 GOF, APDS | Uncommon in infection-driven lymphoproliferation |
| Family history of immunodeficiency/autoimmunity | ALPS, STAT3 GOF, CVID, CTLA-4/LRBA haploinsufficiency, APDS | Strong clue; especially in early-onset presentations |
| Marked hypergammaglobulinemia or hypogammaglobulinemia | CVID, ALPS, APDS, DADA2, CTLA-4 haploinsufficiency | Quantitative immunoglobulin abnormalities support IEI suspicion |
| Elevated αβ double-negative T cells (DNTs) | ALPS (and other diseases of the ALPID spectrum), RALD | Key diagnostic biomarker |
4. Malignancy and IEIs
| IEI Category | Most Common Diseases | Overall Risk of Malignancy | Association with Malignancies |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNA repair disorders | Ataxia–telangiectasia | 16% | Lymphomas (>NHL, MALT lymphomas, extranodal marginal zone lymphomas); breast cancer, liver cancer, gastrointestinal malignancies |
| Nijmegen breakage syndrome | 50% | Lymphomas (>NHL), ALL | |
| AML | |||
| Bloom syndrome | 25% | Leukemia, lymphoma, skin cancers | |
| Primary antibody deficiencies | CVID | 9% | NHL, HL, gastric cancer, breast cancer |
| XLA | 2–6% | NHL, gastrointestinal malignancies | |
| Immune dysregulation disorders and combined immunodeficiencies | Disorders of the ALPID spectrum | Variable, depending on the genetic background (5–17%) | Lymphomas (>HL) |
| APDS | 13–28% | Lymphomas (>NHL) | |
| XLP-1 and other EBV-associated disorders | 30% (for XLP) | EBV-associated lymphoma | |
| Inherited bone marrow failure syndromes and phagocyte disorders | Severe congenital neutropenia | 6–7% | MDS, AML |
| Fanconi Anemia | 27% | MDS, AML, ALL, head and neck malignancies, liver malignancies | |
| GATA2 deficiency | >50% | MDS, AML | |
| IEI with syndromes | WAS | 12% | Lymphomas (>NHL), leukemia |
5. Bone Marrow Failure, Myelodysplastic Syndromes, and IEIs
6. HLH and IEIs
7. Eosinophilia and IEIs
| Clinical Phenotype | Specific Disease | Most Relevant Associated Signs |
|---|---|---|
| HIES | STAT3-HIES | Severe eczema Fungal infections Skin abscesses Recurrent pneumonia Scoliosis Tooth retention High palate |
| DOCK8-HIES | Severe eczema Skin abscesses and recurrent cutaneous infections Recurrent sinopulmonary infections Fungal infections Allergies Risk of malignancy Risk of neurological complications (i.e., cerebral vasculitis) | |
| IPEX and related phenotypes | IPEX | Endocrinopathy Enteropathy Eczema Autoimmune cytopenia |
| STAT3 GOF | Autoimmune cytopenia Lymphoproliferation Multiorgan autoimmunity Enteropathy | |
| STAT1 GOF | IPEX-like phenotype Autoimmunity (endocrinopathy, arthritis) Predisposition to mucocutaneous candidiasis | |
| CTLA4 haploinsufficiency | Autoimmune cytopenia Lymphoproliferation GLILD Enteropathy Respiratory infection Other autoimmune diseases (thyroiditis, arthritis, uveitis) | |
| LRBA haploinsufficiency | Autoimmune cytopenia Lymphoproliferation Enteropathy Autoimmunity (hepatitis, uveitis, diabetes) Respiratory infections, bronchiectasis GLILD | |
| Syndromic IEIs | Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome | Thrombocytopenia Eczema Lymphopenia |
| Combined immunodeficiencies | Omenn syndrome | Early onset of life-threatening infections Splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, Generalized erythroderma |
| Cutaneous diseases | Comel–Netherton syndrome | Severe eczema Congenital ichthyosis Bamboo hair |
8. Practical Implications
8.1. Diagnosing IEIs in Patients with Hematological Diseases
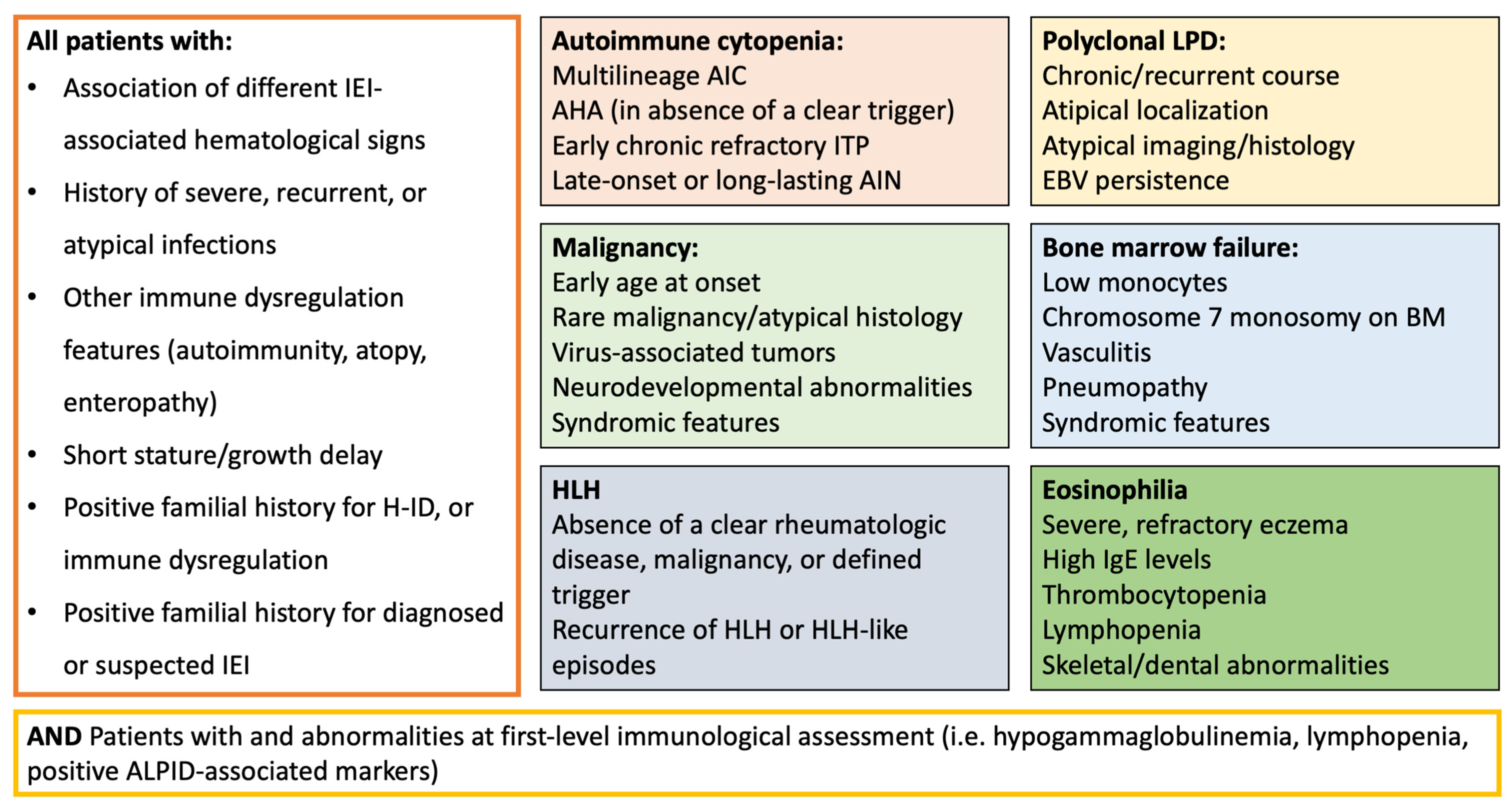
8.1.1. Warning Signs for IEIs in Patients with Hematological Diseases
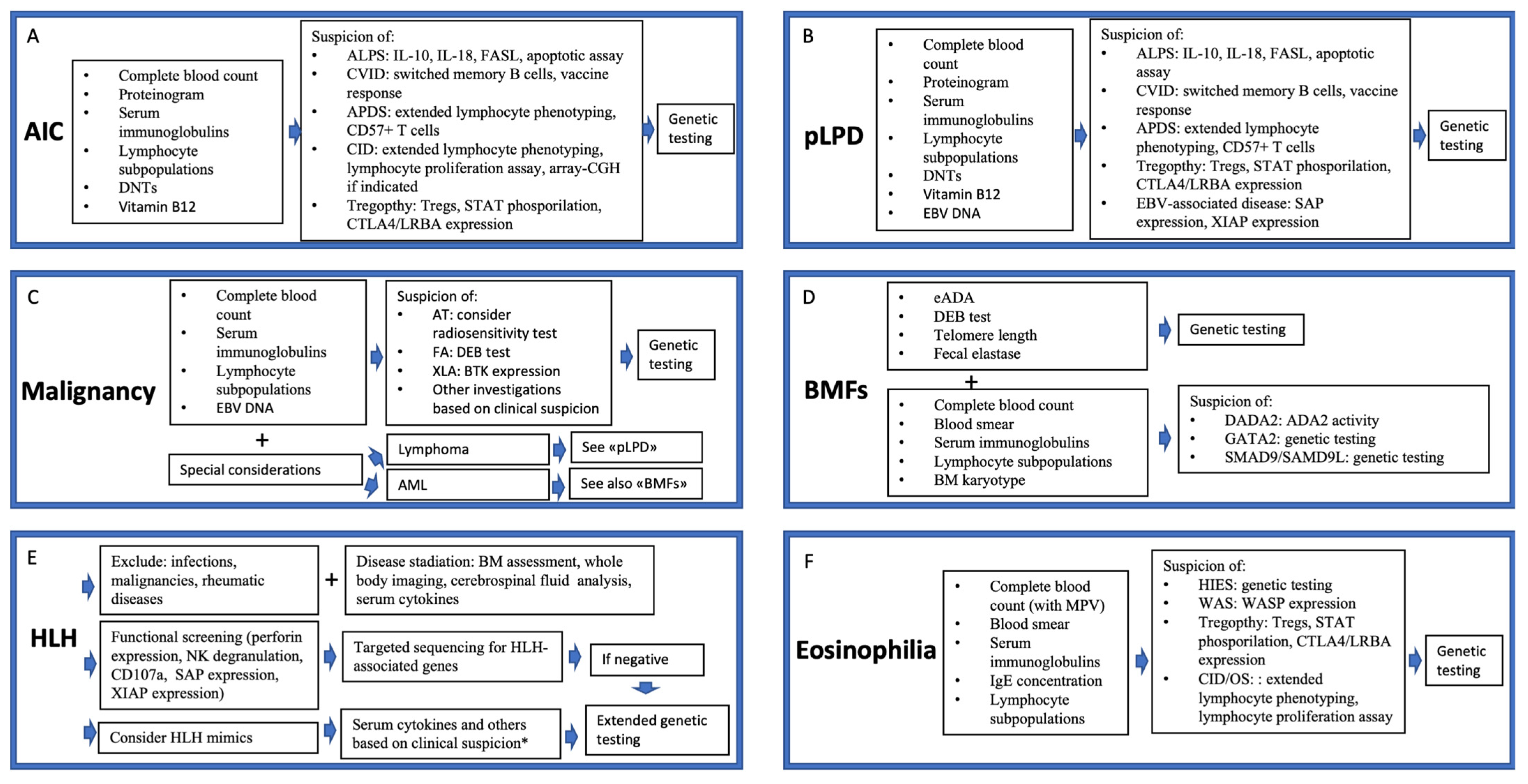
8.1.2. An Overview of the Diagnostic Approach
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADA2 | Adenosine Deaminase 2 |
| AIC | Autoimmune Cytopenia |
| AIHA | Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia |
| AIN | Autoimmune Neutropenia |
| ALPID | Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Immunodeficiencies |
| AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
| AP3B1 | Adaptor-Related Protein Complex 3 Subunit Beta 1 |
| AP3D1 | Adaptor-Related Protein Complex 3 Subunit Delta 1 |
| APDS | Activated PI3K-Delta Syndrome |
| AT | Ataxia–Telangiectasia |
| BIRC4 | Baculoviral IAP Repeat Containing 4 |
| BMF | Bone Marrow Failure |
| CASP10 | Caspase 10 |
| CD25 | Cluster of Differentiation 25 |
| CD27 | Cluster of Differentiation 27 |
| CD137 | Cluster of Differentiation 137 |
| CD57+ CD8+ | Differentiated Cytotoxic CD8+ T Cells expressing CD57 |
| CECR1 | Cat Eye Syndrome Chromosome Region, Candidate 1 |
| CID | Combined Immunodeficiency |
| CTLA4 | Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4 |
| CVID | Common Variable Immunodeficiency |
| DADA2 | Deficiency of Adenosine Deaminase 2 |
| DNTs | Double-Negative T Cells |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| DOCK8 | Dedicator of Cytokinesis 8 |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr Virus |
| ES | Evans Syndrome |
| FAAP24 | Fanconi Anemia-Associated Protein 24 |
| FAS | Fas Cell Surface Death Receptor |
| FASL | Fas Ligand |
| FHL | Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis |
| FOXP3 | Forkhead Box P3 |
| GATA2 | GATA Binding Protein 2 |
| GIMAP6 | GTPase IMAP Family Member 6 |
| GLILD | Granulomatous–Lymphocytic Interstitial Lung Disease |
| GOF | Gain of Function |
| H-ID | Hematologic Immune Dysregulation |
| HIES | Hyper-IgE Syndrome |
| HLH | Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis |
| HPV | Human Papillomavirus |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation |
| IBMF | Inherited Bone Marrow Failure |
| IEIs | Inborn Errors of Immunity |
| IgA | Immunoglobulin A |
| IgE | Immunoglobulin E |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IgM | Immunoglobulin M |
| IL-2 | Interleukin 2 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 |
| IL-18 | Interleukin 18 |
| IPEX | Immune Dysregulation, Polyendocrinopathy, Enteropathy, X-Linked Syndrome |
| ITP | Immune Thrombocytopenia |
| ITK | IL-2-Inducible T-cell Kinase |
| IUIS | International Union of Immunological Societies |
| JAK | Janus Kinase |
| KRAS | Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog |
| LOF | Loss of Function |
| LPD | Lymphoproliferative Disease |
| LRBA | Lipopolysaccharide-Responsive Beige-Like Anchor |
| LYST | Lysosomal Trafficking Regulator |
| MALT | Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue |
| MDS | Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
| MIRAGE Syndrome | Myelodysplasia, Infection, Restriction of Growth, Adrenal Hypoplasia, Genital Anomalies, Enteropathy |
| NFKB1 | Nuclear Factor Kappa B Subunit 1 |
| NHL | Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma |
| NK | Natural Killer |
| NRAS | Neuroblastoma RAS Viral Oncogene Homolog |
| OS | Omenn Syndrome |
| PET/CT | Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| PI3Kδ | PI3K Delta Isoform |
| PKCD | Protein Kinase C Delta |
| pLPD | Polyclonal Lymphoproliferative Disease |
| PRF1 | Perforin 1 |
| RAB27A | RAS-Related Protein Rab-27A |
| RALD | RAS-Associated Autoimmune Leukoproliferative Disease |
| RASGRP1 | RAS Guanyl Releasing Protein 1 |
| RHOG | Ras Homolog Family Member G |
| SAM | Severe Dermatitis, Multiple Allergies, and Metabolic Wasting Syndrome |
| SAMD9/SAMD9L | Sterile Alpha Motif Domain Containing 9/Like |
| SCID | Severe Combined Immunodeficiency |
| SH2D1A | SH2 Domain Containing 1A |
| SLC7A7 | Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 7 |
| STAT1 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 1 |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| STAT5b | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 5b |
| STK4 | Serine/Threonine Kinase 4 |
| STX1 | Syntaxin 1 |
| STXBP2 | Syntaxin Binding Protein 2 |
| TACI | Transmembrane Activator and CAML Interactor |
| T-LGLL | T-cell Large Granular Lymphocytic Leukemia |
| TIM3 | T-cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin-domain Containing-3 |
| Treg | Regulatory T Cells |
| UNC13D | Unc-13 Homolog D |
| unPAD | Unclassified Primary Antibody Deficiency |
| WAS | Wiskott–Aldrich Syndrome |
| XLP | X-Linked Lymphoproliferative Syndrome |
| XLP-1 | X-Linked Lymphoproliferative Syndrome Type 1 |
| XLP-2 | X-Linked Lymphoproliferative Syndrome Type 2 |
| XMEN | X-Linked Immunodeficiency with Magnesium Defect, Epstein–Barr Virus Infection, and Neoplasia |
References
- Thalhammer, J.; Kindle, G.; Nieters, A.; Rusch, S.; Seppänen, M.R.J.; Fischer, A.; Grimbacher, B.; Edgar, D.; Buckland, M.; Mahlaoui, N.; et al. Initial presenting manifestations in 16,486 patients with inborn errors of immunity include infections and noninfectious manifestations. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesi, M.; Dotta, L.; Cattalini, M.; Lougaris, V.; Soresina, A.; Badolato, R. Unmasking inborn errors of immunity: Identifying the red flags of immune dysregulation. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1497921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costagliola, G.; Peroni, D.; Consolini, R. Beyond Infections: New Warning Signs for Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 855445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, G.; Romano, R.; Lougaris, V.; Castagnoli, R.; Cillo, F.; Leonardi, L.; La Torre, F.; Soresina, A.; Federici, S.; Cancrini, C.; et al. Immune tolerance breakdown in inborn errors of immunity: Paving the way to novel therapeutic approaches. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 251, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarangelo, L.; Bacchetta, R.; Casanova, J.; Su, H.C. Human inborn errors of immunity: An expanding universe. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabb1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, K.; Stack, M.; Notarangelo, L. Targeted pharmacologic immunomodulation for inborn errors of immunity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya-Uribe, L.; Rojas, M.; Azizi, G.; Anaya, J.M.; Gershwin, M.E. Primary immunodeficiency and autoimmunity: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 99, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Provot, J.; Jais, J.P.; Alcais, A.; Mahlaoui, N.; Members of the CEREDIH French PID Study Group. Autoimmune and inflammatory manifestations occur frequently in patients with primary immunodeficiencies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, M.; Guardo, D.; Grossi, A.; Palmisani, E.; Fioredda, F.; Terranova, P.; Cappelli, E.; Lupia, M.; Traverso, M.; Dell’Orso, G.; et al. Underlying Inborn Errors of Immunity in Patients with Evans Syndrome and Multilineage Cytopenias: A Single-Centre Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 869033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägele, P.; Staus, P.; Scheible, R.; Uhlmann, A.; Heeg, M.; Klemann, C.; Maccari, M.E.; Ritterbusch, H.; Armstrong, M.; Cutcutache, I.; et al. Diagnostic evaluation of paediatric autoimmune lymphoproliferative immunodeficiencies (ALPID): A prospective cohort study. Lancet Haematol. 2024, 11, e114–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioredda, F.; Beccaria, A.; Casartelli, P.; Turrini, E.; Contratto, C.; Giarratana, M.C.; Bagnasco, F.; Saettini, F.; Pillon, M.; Marzollo, A.; et al. Late-onset and long-lasting neutropenias in the young: A new entity anticipating immune-dysregulation disorders. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, M. Autoimmune and other cytopenias in primary immunodeficiencies: Pathomechanisms, novel differential diagnoses, and treatment. Blood 2014, 124, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskin, R.B.; Topyıldız, E.; Edeer Karaca, N.; Aksu, G.; Yılmaz Karapınar, D.; Kutukculer, N. Autoimmune Cytopenias Are Highly Associated with Inborn Errors of Immunity and They May Be the Initial Presentations in Cases without Severe Infections. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2024, 185, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, E.; Martini, B.; Attardi, E.; Consonni, F.; Ciullini Mannurita, S.; Coniglio, M.L.; Tellini, M.; Chiocca, E.; Fotzi, I.; Luti, L.; et al. Autoimmune Cytopenias and Dysregulated Immunophenotype Act as Warning Signs of Inborn Errors of Immunity: Results from a Prospective Study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 790455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, R. How to Evaluate for Immunodeficiency in Patients with Autoimmune Cytopenias: Laboratory Evaluation for the Diagnosis of Inborn Errors of Immunity. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2020, 2020, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consolini, R.; Costagliola, G.; Spatafora, D. The Centenary of Immune Thrombocytopenia-Part 2: Revising Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Pilania, R.K.; Anjani, G.; Sudhakar, M.; Arora, K.; Tyagi, R.; Dhaliwal, M.; Vignesh, P.; Rawat, A.; Singh, S. Lymphoproliferation in Inborn Errors of Immunity: The Eye Does Not See What the Mind Does Not Know. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 856601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costagliola, G.; Consolini, R. Lymphadenopathy at the crossroad between immunodeficiency and autoinflammation: An intriguing challenge. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 205, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, R.; Habibi, S.; Sharifi, L.; Azizi, G.; Abolhassani, H.; Olbrich, P.; Aghamohammadi, A. Common Variable Immunodeficiency: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Classification, and Management. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 30, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Gereige, J.; Maglione, P. State-of-the-art diagnostic evaluation of common variable immunodeficiency. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 127, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gompels, M.M.; Hodges, E.; Lock, R.J.; Angus, B.; White, H.; Larkin, A.; Chapel, H.M.; Spickett, G.P.; Misbah, S.A.; Smith, J.L.; et al. Lymphoproliferative disease in antibody deficiency: A multi-centre study. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 134, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Maglione, P. Common variable immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1425–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakaboski, E.; Fuleihan, R.L.; Sullivan, K.E.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Feuille, E. Lymphoproliferative Disease in CVID: A Report of Types and Frequencies from a US Patient Registry. J. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 40, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, H.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Non-infectious Complications of Common Variable Immunodeficiency: Updated Clinical Spectrum, Sequelae, and Insights to Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglione, P.J. Autoimmune and Lymphoproliferative Complications of Common Variable Immunodeficiency. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costagliola, G.; De Marco, E.; Consonni, F.; Rocchi, V.; Legitimo, A.; Menconi, M.; Gambineri, E.; Casazza, G.; Consolini, R. Inborn errors of immunity presenting with lymphoproliferation: Lessons from a case series. Ann. Hematol. 2025, 104, 3117–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, S.; Seidl, M.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Böhm, J.; Schrenk, K.; Wehr, C.; Goldacker, S.; Dräger, R.; Gärtner, B.C.; Fisch, P.; et al. Ill-defined germinal centers and severely reduced plasma cells are histological hallmarks of lymphadenopathy in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 34, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Stigt, A.C.; Dik, W.A.; Kamphuis, L.S.J.; Smits, B.M.; van Montfrans, J.M.; van Hagen, P.M.; Dalm, V.A.S.H.; Ijspeert, H. What Works When Treating Granulomatous Disease in Genetically Undefined CVID? A Systematic Review. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 606389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.B.; Bleesing, J.J.; Dianzani, U.; Fleisher, T.A.; Jaffe, E.S.; Lenardo, M.J.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Siegel, R.M.; Su, H.C.; Teachey, D.T.; et al. Revised diagnostic criteria and classification for the autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS): Report from the 2009 NIH International Workshop. Blood 2010, 116, e35–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toskov, V.; Ehl, S. Autoimmune lymphoproliferative immunodeficiencies (ALPID) in childhood: Breakdown of immune homeostasis and immune dysregulation. Mol. Cell. Pediatr. 2023, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magerus, A.; Rensing-Ehl, A.; Rao, V.K.; Teachey, D.T.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Ehl, S. Autoimmune lymphoproliferative immunodeficiencies (ALPIDs): A proposed approach to redefining ALPS and other lymphoproliferative immune disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 153, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durandy, A.; Kracker, S. Increased activation of PI3 kinase-δ predisposes to B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2020, 135, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, K.; Uzel, G. Activated PI3K Delta Syndrome. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barzaghi, F.; Moratti, M.; Panza, G.; Rivalta, B.; Giardino, G.; De Rosa, A.; Baselli, L.A.; Chinello, M.; Marzollo, A.; Montin, D.; et al. Report of the Italian Cohort with Activated Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase δ Syndrome in the Target Therapy Era. J. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 45, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.I. Primary Immunodeficiencies Associated with EBV Disease. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 390 Pt 1, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavannaugh, C.; Ochs, H.; Buchbinder, D. Diagnosis and clinical management of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: Current and emerging techniques. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 18, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, K.R.; Price, S.; Braylan, R.C.; Oliveira, J.B.; Lenardo, M.; Fleisher, T.A.; Rao, V.K. JMML and RALD (Ras-associated autoimmune leukoproliferative disorder): Common genetic etiology yet clinically distinct entities. Blood 2015, 125, 2753–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilania, R.K.; Banday, A.Z.; Sharma, S.; Kumrah, R.; Joshi, V.; Loganathan, S.; Dhaliwal, M.; Jindal, A.K.; Vignesh, P.; Suri, D.; et al. Deficiency of Human Adenosine Deaminase Type 2—A Diagnostic Conundrum for the Hematologist. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 869570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsultan, A.; Basher, E.; Alqanatish, J.; Mohammed, R.; Alfadhel, M. Deficiency of ADA2 mimicking autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome in the absence of livedo reticularis and vasculitis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e26912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, M.; Delavari, S.; Salami, F.; Ansari, S.; Rasouli, S.E.; Chavoshzadeh, Z.; Sherkat, R.; Ahanchian, H.; Aleyasin, S.; Esmaeilzadeh, H.; et al. Diversity of malignancies in patients with different types of inborn errors of immunity. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2022, 18, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipambo, N.; Verwey, C.; Moore, D.; Mackinnon, D.; Mopeli, R.; Naidu, G. Inborn errors of immunity and malignancy. Curr. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 37, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mortaz, E.; Tabarsi, P.; Mansouri, D.; Khosravi, A.; Garssen, J.; Velayati, A.; Adcock, I.M. Cancers Related to Immunodeficiencies: Update and Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebudi, R.; Kiykim, A.; Sahin, M. Primary Immunodeficiency and Cancer in Children. A Review of the Literature. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2019, 15, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekrvand, S.; Abolhassani, H.; Esfahani, Z.H.; Fard, N.N.G.; Amiri, M.; Salehi, H.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Saeedi-Boroujeni, A.; Fathi, N.; Mohtashami, M.; et al. Cancer Trends in Inborn Errors of Immunity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 45, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, I.; Faridi, W.; Patnaik, M.; Abraham, R. A systematic review on predisposition to lymphoid (B and T cell) neoplasias in patients with primary immunodeficiencies and immune dysregulatory disorders (inborn errors of immunity). Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiri, A.; Masetti, R.; Conti, F.; Tignanelli, A.; Turrini, E.; Bertolini, P.; Esposito, S.; Pession, A. Inborn Errors of Immunity and Cancer. Biology 2021, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, J.V.W.T.; Hlaváčková, E.; Derpoorter, C.; Fischer, U.; Saettini, F.; Ghosh, S.; Farah, R.; Bogaert, D.; Wagener, R.; Loeffen, J.; et al. How to recognize inborn errors of immunity in a child presenting with a malignancy: Guidelines for the pediatric hemato-oncologist. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 40, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesi, B.; Davidsson, J.; Voss, M.; Rahikkala, E.; Holmes, T.D.; Chiang, S.C.C.; Komulainen-Ebrahim, J.; Gorcenco, S.; Rundberg Nilsson, A.; Ripperger, T.; et al. Gain-of-function SAMD9L mutations cause a syndrome of cytopenia, immunodeficiency, MDS, and neurological symptoms. Blood 2017, 129, 2266–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomken, S.; van der Werff Ten Bosch, J.; Attarbaschi, A.; Bacon, C.M.; Borkhardt, A.; Boztug, K.; Fischer, U.; Hauck, F.; Kuiper, R.P.; Lammens, T.; et al. Current understanding and future research priorities in malignancy associated with inborn errors of immunity and DNA repair disorders: The perspective of an interdisciplinary working group. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska-Kuśnierz, B.; Gregorek, H.; Chrzanowska, K.; Piątosa, B.; Pietrucha, B.; Heropolitańska-Pliszka, E.; Pac, M.; Klaudel-Dreszler, M.; Kostyuchenko, L.; Pasic, S.; et al. Nijmegen breakage syndrome: Clinical and immunological features, long-term outcome and treatment options—A retrospective analysis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koldej, R.M.; Prabahran, A.; Tan, C.W.; Ludford-Menting, M.; Morgan, H.; Holzwart, N.; Davis, M.J.; Ritchie, D.S. Spatial proteomics identifies a spectrum of immune dysregulation in acquired bone marrow failure syndromes. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1213560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousfiha, A.; Jeddane, L.; Moundi, A.; Poli, M.C.; Aksentijevich, I.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Hambleton, S.; Klein, C.; Morio, T.; Picard, C.; et al. The 2024 update of IUIS phenotypic classification of human inborn errors of immunity. J. Hum. Immun. 2025, 1, e20250002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Kozyra, E.; Wlodarski, M. Germline predisposition in myeloid neoplasms: Unique genetic and clinical features of GATA2 deficiency and SAMD9/SAMD9L syndromes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2020, 33, 101197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Eldomery, M.; Maciaszek, J.; Klco, J. Inherited Predispositions to Myeloid Neoplasms: Pathogenesis and Clinical Implications. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2025, 20, 87–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluteau, O.; Sebert, M.; Leblanc, T.; Peffault de Latour, R.; Quentin, S.; Lainey, E.; Hernandez, L.; Dalle, J.H.; Sicre de Fontbrune, F.; Lengline, E.; et al. A landscape of germ line mutations in a cohort of inherited bone marrow failure patients. Blood 2018, 131, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, K.; Hickstein, D. The spectrum of GATA2 deficiency syndrome. Blood 2023, 141, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, A.; McReynolds, L.; Holland, S. GATA2 deficiency. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 15, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukerd, M.R.Z.; Mirkamali, H.; Nakhaie, M.; Alizadeh, S.D. GATA2 deficiency and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH): A systematic review of reported cases. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, M.; Liquori, A.; Such, E.; Zúñiga, Á.; Cervera, J. The Clinical Spectrum, Diagnosis, and Management of GATA2 Deficiency. Cancers 2023, 15, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.S.; Pastor, V.B.; Goodings, C.; Voss, R.K.; Kozyra, E.J.; Szvetnik, A.; Noellke, P.; Dworzak, M.; Starý, J.; Locatelli, F.; et al. Clinical evolution, genetic landscape and trajectories of clonal hematopoiesis in SAMD9/SAMD9L syndromes. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntharalingham, J.P.; Ishida, M.; Del Valle, I.; Stalman, S.E.; Solanky, N.; Wakeling, E.; Moore, G.E.; Achermann, J.C.; Buonocore, F. Emerging phenotypes linked to variants in SAMD9 and MIRAGE syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 953707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Tanase-Nakao, K.; Shima, H.; Shirai, R.; Yoshida, K.; Osumi, T.; Deguchi, T.; Mori, M.; Arakawa, Y.; Takagi, M.; et al. Prevalence of germline GATA2 and SAMD9/9L variants in paediatric haematological disorders with monosomy 7. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 191, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyts, I.; Aksentijevich, I. Deficiency of Adenosine Deaminase 2 (DADA2): Updates on the Phenotype, Genetics, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. J. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.Y.; Davidson, B.A.; Abraham, R.S.; Alter, B.; Arostegui, J.I.; Bell, K.; Belot, A.; Bergerson, J.R.E.; Bernard, T.J.; Brogan, P.A.; et al. Evaluation and Management of Deficiency of Adenosine Deaminase 2: An International Consensus Statement. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grom, A.; Horne, A.; De Benedetti, F. Macrophage activation syndrome in the era of biologic therapy. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canna, S.; Marsh, R. Pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2020, 135, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanegane, H.; Noguchi, A.; Yamada, Y.; Yasumi, T. Rare diseases presenting with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Int. 2023, 65, e15516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benevenuta, C.; Mussinatto, I.; Orsi, C.; Timeus, F. Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in children. Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 26, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naymagon, L.; Roehrs, P.; Hermiston, M.; Connelly, J.; Bednarski, J.; Boelens, J.J.; Chandrakasan, S.; Dávila Saldaña, B.; Henry, M.M.; Satwani, P.; et al. Perspectives on the current diagnostic and treatment paradigms in secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2025, 20, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latour, S.; Fischer, A. Signaling pathways involved in the T-cell-mediated immunity against Epstein-Barr virus: Lessons from genetic diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 291, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyarchuk, O.; Volokha, A.; Yarema, N.; Dyvoniak, O.; Tomashivska, T.; Shymanska, I.; Makukh, H.; Walter, J.E. Fatal HLH in patients with X-linked lymphoproliferative disease 1 due to a novel variant in SH2D1A: Case report. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1602107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachlopnik Schmid, J.; Canioni, D.; Moshous, D.; Touzot, F.; Mahlaoui, N.; Hauck, F.; Kanegane, H.; Lopez-Granados, E.; Mejstrikova, E.; Pellier, I.; et al. Clinical similarities and differences of patients with X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome type 1 (XLP-1/SAP deficiency) versus type 2 (XLP-2/XIAP deficiency). Blood 2011, 117, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, S.; Sarli, W.M.; Lodi, L.; Canessa, C.; Lippi, F.; Dini, D.; Ferrari, M.; Pisano, L.; Sieni, E.; Indolfi, G.; et al. HLH as an additional warning sign of inborn errors of immunity beyond familial-HLH in children: A systematic review. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1282804. [Google Scholar]
- Wegehaupt, O.; Wustrau, K.; Lehmberg, K.; Ehl, S. Cell Versus Cytokine—Directed Therapies for Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in Inborn Errors of Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.B.; Allen, C.E.; Greenberg, J.; Henry, M.; Hermiston, M.L.; Kumar, A.; Hines, M.; Eckstein, O.; Ladisch, S.; Nichols, K.E.; et al. Challenges in the diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Recommendations from the Norh American Consortium for Histiocytosis (NACHO). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taurisano, G.; Ruffi, M.; Canalis, S.; Costanzo, G. Hypereosinophilia: Clinical and therapeutic approach in 2025. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2025, 25, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagnoli, R.; Lougaris, V.; Giardino, G.; Volpi, S.; Leonardi, L.; La Torre, F.; Federici, S.; Corrente, S.; Cinicola, B.L.; Soresina, A.; et al. Inborn errors of immunity with atopic phenotypes: A practical guide for allergists. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 14, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinicola, B.L.; Corrente, S.; Castagnoli, R.; Lougaris, V.; Giardino, G.; Leonardi, L.; Volpi, S.; La Torre, F.; Federici, S.; Soresina, A.; et al. Primary atopic disorders and chronic skin disease. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 33, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.; Milner, J.; Freeman, A. Eosinophilia Associated with Disorders of Immune Deficiency or Immune Dysregulation. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2015, 35, 523–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taietti, I.; Catamerò, F.; Lodi, L.; Giovannini, M.; Castagnoli, R. Inborn errors of immunity with atopic phenotypes in the allergy and immunology clinic: A practical review. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2025, 25, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, H.; Adytia, G.; Fetarayani, D. Hyper IgE Syndrome: Bridging the Gap Between Immunodeficiency, Atopy, and Allergic Diseases. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2025, 25, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilifis, C.; Freeman, A.; Gennery, A. STAT3 Hyper-IgE Syndrome-an Update and Unanswered Questions. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 41, 864–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woellner, C.; Gertz, E.M.; Schäffer, A.A.; Lagos, M.; Perro, M.; Glocker, E.O.; Pietrogrande, M.C.; Cossu, F.; Franco, J.L.; Matamoros, N.; et al. Mutations in STAT3 and diagnostic guidelines for hyper-IgE syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 424–432.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepika, A.M.; Sato, Y.; Liu, J.M.; Uyeda, M.J.; Bacchetta, R.; Roncarolo, M.G. Tregopathies: Monogenic diseases resulting in regulatory T-cell deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1679–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voarino, M.; Consonni, F.; Gambineri, E. Expanding the spectrum of IPEX: From new clinical findings to novel treatments. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 24, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambineri, E.; Ciullini Mannurita, S.; Hagin, D.; Vignoli, M.; Anover-Sombke, S.; DeBoer, S.; Segundo, G.R.S.; Allenspach, E.J.; Favre, C.; Ochs, H.D.; et al. Clinical, Immunological, and Molecular Heterogeneity of 173 Patients with the Phenotype of Immune Dysregulation, Polyendocrinopathy, Enteropathy, X-Linked (IPEX) Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Denton, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Guan, Q.; Dawson, D.B.; Bleesing, J.; Zhang, W. Genetic Testing in Patients with Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Syndrome: Experience of 802 Patients at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. J. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 44, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelling, D.; Bain, B. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 969–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, W.T.; Dunn, E.; Notarangelo, L.D.; Dvorak, C.C.; Puck, J.M.; Logan, B.R.; Griffith, L.M.; Kohn, D.B.; O’Reilly, R.J.; Fleisher, T.A.; et al. Establishing diagnostic criteria for severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID), leaky SCID, and Omenn syndrome: The Primary Immune Deficiency Treatment Consortium experience. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montin, D.; Marolda, A.; Licciardi, F.; Robasto, F.; Di Cesare, S.; Ricotti, E.; Ferro, F.; Scaioli, G.; Giancotta, C.; Amodio, D.; et al. Immunophenotype Anomalies Predict the Development of Autoimmune Cytopenia in 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, M.; Hauck, F. Multilayer concept of autoimmune mechanisms and manifestations in inborn errors of immunity: Relevance for precision therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 153, 615–628.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatter, M.; Lum, S. Personalized hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for inborn errors of immunity. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1162605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costagliola, G.; De Marco, E.; Massei, F.; Roberti, G.; Catena, F.; Casazza, G.; Consolini, R. The Etiologic Landscape of Lymphoproliferation in Childhood: Proposal for a Diagnostic Approach Exploring from Infections to Inborn Errors of Immunity and Metabolic Diseases. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2024, 20, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henter, J.I.; Sieni, E.; Eriksson, J.; Bergsten, E.; Hed Myrberg, I.; Canna, S.W.; Coniglio, M.L.; Cron, R.Q.; Kernan, K.F. Diagnostic guidelines for familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis revisited. Blood 2024, 144, 2308–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, K.; Notarangelo, L.; Delmonte, O. When to suspect inborn errors of immunity in Epstein-Barr virus-related lymphoproliferative disorders. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokal, I.; Tummala, H.; Vulliamy, T. Inherited bone marrow failure in the pediatric patient. Blood 2022, 140, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miano, M.; Grossi, A.; Dell’Orso, G.; Lanciotti, M.; Fioredda, F.; Palmisani, E.; Lanza, T.; Guardo, D.; Beccaria, A.; Ravera, S.; et al. Genetic screening of children with marrow failure. The role of primary Immunodeficiencies. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Immune dysregulation disorders |
|
| Primary antibody deficiencies |
|
| Others |
|
| Primary HLH | Gene |
|---|---|
| FHL without hypopigmentation | |
| FHL-1 | Unknown |
| FHL-2 (Perforin deficiency) | PRF1 |
| FHL-3 (UNC13D deficiency) | UNC13D |
| FHL-4 (Syntaxin 11 deficiency) | STX11 |
| FHL-5 (STXBP2 deficiency) | STXBP2 |
| FHL with hypopigmentation | |
| Griscelli syndrome type 2 | RAB27A |
| Chediak-Higashi syndrome | LYST |
| Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 2 | AP3B1 |
| Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 10 | AP3D1 |
| GIMAP6 deficiency | GIMAP6 |
| Other immune dysregulation disorders associated with HLH | |
| XLP-1 | SH2D1A |
| XLP-2 | BIRC4 |
| CD27 deficiency | CD27 |
| CD137 deficiency | CD137 |
| TIM3 deficiency | HAVCR2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roberti, G.; Maestrini, G.; Polito, B.; Amato, L.; Parolo, E.; Casazza, G.; Consolini, R.; Costagliola, G. Inborn Errors of Immunity in Pediatric Hematology and Oncology: Diagnostic Principles for Clinical Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176295
Roberti G, Maestrini G, Polito B, Amato L, Parolo E, Casazza G, Consolini R, Costagliola G. Inborn Errors of Immunity in Pediatric Hematology and Oncology: Diagnostic Principles for Clinical Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176295
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoberti, Giulia, Giulia Maestrini, Beatrice Polito, Leonardo Amato, Eva Parolo, Gabriella Casazza, Rita Consolini, and Giorgio Costagliola. 2025. "Inborn Errors of Immunity in Pediatric Hematology and Oncology: Diagnostic Principles for Clinical Practice" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176295
APA StyleRoberti, G., Maestrini, G., Polito, B., Amato, L., Parolo, E., Casazza, G., Consolini, R., & Costagliola, G. (2025). Inborn Errors of Immunity in Pediatric Hematology and Oncology: Diagnostic Principles for Clinical Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176295








