Outcomes of Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
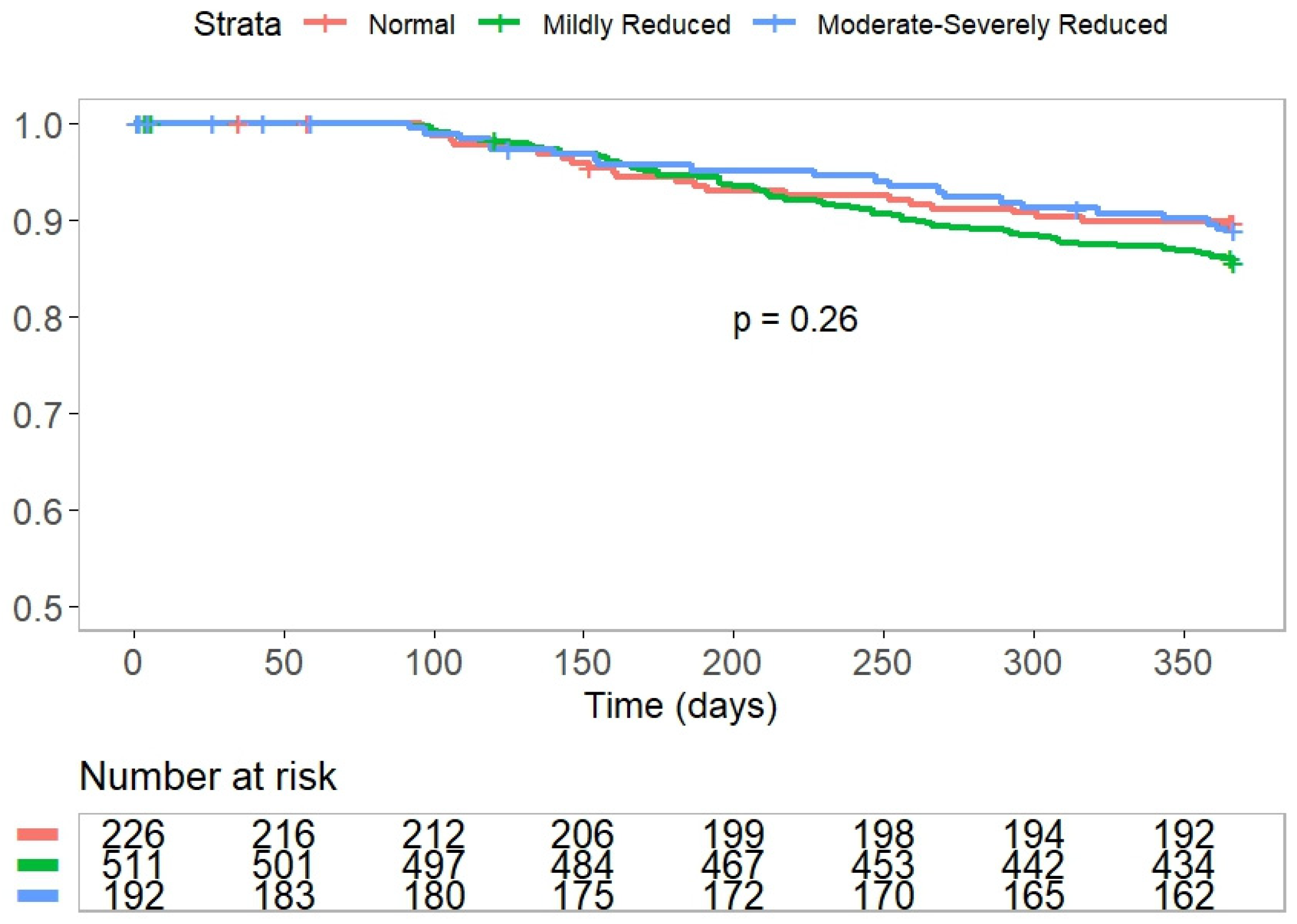
3. Results
4. Study Outcomes
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawaji, T.; Shizuta, S.; Aizawa, T.; Yamagami, S.; Takeji, Y.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Kato, M.; Yokomatsu, T.; Miki, S.; Ono, K.; et al. Renal function and outcomes in atrial fibrillation patients after catheter ablation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, K.C.; Trespalacios, F.C.; Taylor, A.J.; Agodoa, L.Y. Atrial fibrillation in chronic dialysis patients in the United States: Risk factors for hospitalization and mortality. BMC Nephrol. 2003, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.; Robinson, B.; Abbott, K.C.; Agodoa, L.Y.C.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Balkrishnan, R.; Bhave, N.; Dietrich, X.; Ding, Z.; Eggers, P.W.; et al. US Renal Data System 2018 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, A7–A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovesi, S.; Pogliani, D.; Faini, A.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Riva, A.; Stefani, F.; Acquistapace, I.; Stella, A.; Bonforte, G.; DeVecchi, A.; et al. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation and associated factors in a population of long-term hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Murakoshi, N.; Sairenchi, T.; Irie, F.; Igarashi, M.; Nogami, A.; Tomizawa, T.; Yamaguchi, I.; Yamagishi, K.; Iso, H.; et al. Anemia and reduced kidney function as risk factors for new onset of atrial fibrillation (from the Ibaraki prefectural health study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, E.Z.; Prineas, R.J.; Go, A.S.; Xie, D.; Lash, J.P.; Rahman, M.; Ojo, A.; Teal, V.L.; Jensvold, N.G.; Robinson, N.L.; et al. Chronic kidney disease and prevalent atrial fibrillation: The Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC). Am. Heart J. 2010, 159, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turakhia, M.P.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Carrero, J.J.; Clase, C.M.; Deo, R.; Herzog, C.A.; Kasner, S.E.; Passman, R.S.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Reinecke, H.; et al. Chronic kidney disease and arrhythmias: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, Y.; Takahashi, W.; Takizawa, S.; Kawada, S.; Takagi, S. Chronic kidney disease in patients with ischemic stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012, 21, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.J.; Patel, A.; Agnihotri, K.; Pau, D.; Patel, S.; Thakkar, B.; Nalluri, N.; Asti, D.; Kanotra, R.; Kadavath, S.; et al. Prognostic impact of atrial fibrillation on clinical outcomes of acute coronary syndromes, heart failure and chronic kidney disease. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liampas, E.; Kartas, A.; Samaras, A.; Papazoglou, A.S.; Moysidis, D.V.; Vrana, E.; Botis, M.; Papanastasiou, A.; Baroutidou, A.; Vouloagkas, I.; et al. Renal function and mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airy, M.; Schold, J.D.; Jolly, S.E.; Arrigain, S.; Bansal, N.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; Nally, J.V., Jr.; Navaneethan, S.D. Cause-Specific Mortality in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 48, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Watanabe, T.; Sasaki, S.; Nagai, K.; Roden, D.M.; Aizawa, Y. Close bidirectional relationship between chronic kidney disease and atrial fibrillation: The Niigata preventive medicine study. Am. Heart J. 2009, 158, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Providencia, R.; Ali, H.; Creta, A.; Barra, S.; Kanagaratnam, P.; Schilling, R.J.; Farkowski, M.; Cappato, R. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation and impact on clinical outcomes. Eur. Heart J. Open 2024, 4, oeae058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrouche, N.F.; Brachmann, J.; Andresen, D.; Siebels, J.; Boersma, L.; Jordaens, L.; Merkely, B.; Pokushalov, E.; Sanders, P.; Proff, J.; et al. Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation with Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Shantsila, A.; Xue, Y.; Bai, Y.; Guo, P.; Potpara, T.S.; Zhan, X.; Fang, X.; Liao, H.; Wu, S.; et al. Renal function and outcomes after catheter ablation of patients with atrial fibrillation: The Guangzhou atrial fibrillation ablation registry. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 112, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriani, G.; Iacopino, S.; Arena, G.; Pieragnoli, P.; Verlato, R.; Manfrin, M.; Molon, G.; Rovaris, G.; Curnis, A.; Perego, G.B.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease with Mild and Mild to Moderate Reduction in Renal Function and Long-Term Recurrences of Atrial Fibrillation after Pulmonary Vein Cryoballoon Ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullal, A.J.; Kaiser, D.W.; Fan, J.; Schmitt, S.K.; Than, C.T.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; Heidenreich, P.A.; Piccini, J.P.; Perez, M.V.; Wang, P.J.; et al. Safety and Clinical Outcomes of Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2017, 28, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inf. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.S. How to perform pulmonary vein isolation. Europace 2004, 6, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuck, K.H.; Brugada, J.; Furnkranz, A.; Metzner, A.; Ouyang, F.; Chun, K.R.; Elvan, A.; Arentz, T.; Bestehorn, K.; Pocock, S.J.; et al. Cryoballoon or Radiofrequency Ablation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2235–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.G.; Wazni, O.M.; Kuniss, M.; Hawkins, N.M.; Deyell, M.W.; Chierchia, G.B.; Nissen, S.; Verma, A.; Wells, G.A.; Turgeon, R.D. Cryoballoon Ablation as Initial Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 914–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappato, R.; Ali, H. Long-Term Results of Cryoballoon Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: Confirmation of an Early Promise. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 5, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar]
- Charytan, D.; Kuntz, R.E. The exclusion of patients with chronic kidney disease from clinical trials in coronary artery disease. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.B.; Lip, G.Y.; Kamper, A.L.; Hommel, K.; Kober, L.; Lane, D.A.; Lindhardsen, J.; Gislason, G.H.; Torp-Pedersen, C. Stroke and bleeding in atrial fibrillation with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, D.L.; Mark, D.B.; Robb, R.A.; Monahan, K.H.; Bahnson, T.D.; Poole, J.E.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Rosenberg, Y.D.; Jeffries, N.; Mitchell, L.B.; et al. Effect of Catheter Ablation vs Antiarrhythmic Drug Therapy on Mortality, Stroke, Bleeding, and Cardiac Arrest Among Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: The CABANA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasitlumkum, N.; Chokesuwattanaskul, R.; Kaewput, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Tokavanich, N.; Bathini, T.; Boonpheng, B.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Jongnarangsin, K. Temporal trends and in-hospital complications of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation among patients with moderate and advanced chronic kidney diseases: 2005–2018. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27042964 (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Khouri, Y.; Stephens, T.; Ayuba, G.; AlAmeri, H.; Juratli, N.; McCullough, P.A. Understanding and Managing Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Kidney Disease. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2015, 7, 1069. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaitman, M.; Dixit, D.; Bridgeman, M.B. Potassium-Binding Agents for the Clinical Management of Hyperkalemia. Pharm. Ther. 2016, 41, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhof, P.; Camm, A.J.; Goette, A.; Brandes, A.; Eckardt, L.; Elvan, A.; Breithardt, G. Early rhythm-control therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbo, A.; Arow, Z.; Eyal, A.; Elias, A.; Beinart, R.; Nof, E.; Michowitz, Y.; Glikson, M.; Haim, M.; Luria, D.; et al. Outcomes of atrial fibrillation ablation in patients with chronic kidney disease. EP Eur. 2025, 27, euaf085.392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Baseline Characteristics | * eGFR Level | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Mildly Reduced | Moderately to Severely Reduced | ||
| n (929) | 226 (24%) | 511 (55%) | 192 (21%) | |
| Age, years (median) | 61 | 66 | 70 | <0.001 |
| Gender, male, n (%) | 162 (71) | 316 (62) | 103 (53) | <0.001 |
| CHA2DS2-VASC, median [IQR] | 2 [1, 3] | 2 [2, 3] | 3 [2, 4] | <0.01 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 105 (46) | 251 (49) | 123 (64) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 110 (49) | 324 (63) | 157 (82) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 55 (24) | 107 (21) | 73 (38) | <0.001 |
| AF duration (median) | 3.0 (1.0–4.8) | 3.0 (1.0–6.0) | 3.0 (1.0–5.0) | 0.54 |
| eGFR median | 102 (96–112) | 74 (68–82) | 51 (44–55) | <0.001 |
| Prior MI, n (%) | 10 (4) | 44 (9) | 33 (17) | <0.001 |
| Prior CABG, n (%) | 6 (2) | 13 (2) | 12 (6) | 0.04 |
| Prior CVA/TIA, n (%) | 19 (8) | 40 (8) | 26 (13) | 0.05 |
| LV dysfunction, n (%) | ||||
| Mild | 20 (10) | 44 (10) | 19 (11) | 0.01 |
| Moderate | 8 (4) | 28 (6) | 18 (10) | 0.01 |
| Severe | 5 (3) | 19 (4) | 16 (9) | 0.01 |
| LA size, mm (median) | 42 | 42 | 43 | 0.1 |
| LA volume, cc (median) | 58 | 62 | 65 | 0.6 |
| AF classification, n (%) | ||||
| Paroxysmal | 165 (73) | 337 (66) | 106 (56) | <0.001 |
| Persistent | 52 (23) | 165 (32) | 73 (38) | <0.001 |
| Long-standing persistent | 8 (4) | 7 (1) | 10 (5) | 0.2 |
| Permanent | 0 (0) | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.5) | 0.2 |
| Anticoagulant and antiarrhythmic therapies, n (%) | ||||
| AAD drugs (baseline) | 134 (59) | 349 (68) | 133 (69) | 0.03 |
| AAD drugs (after ablation) | 150 (66) | 361 (70) | 139 (72) | 0.3 |
| Prior anticoagulant therapy | 177 (78) | 453 (89) | 183 (96) | <0.001 |
| Apixaban | 110 (62) | 279 (62) | 109 (60) | 0.2 |
| Dabigatran | 18 (10) | 55 (12) | 19 (10) | 0.2 |
| Rivaroxaban | 46 (26) | 104 (23) | 42 (23) | 0.3 |
| Warfarin | 3 (2) | 15 (3) | 12 (7) | 0.2 |
| * eGFR Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preserved | Mildly Reduced | Moderately to Severely Reduced | p-Value | |
| n (929) | 226 | 511 | 192 | |
| Procedure performed | 0.88 | |||
| Cryoablation, n (%) | 194 (86) | 428 (84) | 162 (84) | |
| RF Ablation, n (%) | 15 (7) | 45 (9) | 17 (9) | |
| Cryo- and RF ablation, n (%) | 17 (7) | 38 (7) | 13 (7) | |
| Procedure duration, minutes (median) | 90 | 85 | 80 | 0.3 |
| Fluoroscopy time, minutes (median) | 23 | 21 | 21 | 0.7 |
| General anesthesia, n (%) | 120 (53) | 269 (53) | 112 (59) | 0.2 |
| Cardiac CT, n (%) | 104 (46) | 233 (46) | 78 (42) | 0.5 |
| TEE (before/during), n (%) | 95 (42) | 199 (39) | 93 (49) | 0.06 |
| Use of ICE, n (%) | 59 (26) | 114 (22) | 39 (20) | 0.3 |
| * eGFR Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preserved | Mildly Reduced | Moderately to Severely Reduced | p-Value | |
| n (929) | 226 | 511 | 192 | |
| AF recurrence **, n (%) | 63 (30) | 150 (32) | 69 (40) | 0.1 |
| Repeat ablation for recurrent AF, n (%) | 13 (6) | 47 (10) | 22 (13) | 0.09 |
| Time to first re-AF, months (median) | 4.8 | 5.2 | 2.4 | 0.4 |
| Time to first re-ablation, months (median) | 9.8 | 7.9 | 10 | 0.9 |
| 1-year all-cause mortality, n (%) | 0 (0) | 4 (0.8) | 5 (2.7) | 0.02 |
| 1-year cardiac mortality, n (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.1) | 2 (1) | N/A |
| Rehospitalizations (12 months), n (%) | 39 (19) | 111 (24) | 55 (32) | 0.01 |
| Cause of rehospitalizations, n (%) | ||||
| Heart failure | 2 (5) | 4 (4) | 10 (18) | <0.01 |
| Cardiac | 26 (72) | 85 (78) | 36 (69) | 0.4 |
| Scheduled | 12 (30) | 37 (34) | 22 (40) | 0.6 |
| * eGFR Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preserved | Mildly Reduced | Moderately to Severely Reduced | p-Value | |
| n (929) | 226 | 511 | 192 | |
| Pericardial effusion, n (%) | 1 (0.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.2 |
| Tamponade, n (%) | 1 (0.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.2 |
| Cardiac arrest, n (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.2) | 0 (0) | 0.6 |
| Thromboembolic events, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.5) | 0.1 |
| Neurological events, n (%) | 1 (0.4) | 3 (0.6) | 3 (0.6) | 0.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbo, A.; Arow, Z.; Eyal, A.; Glueck, R.M.; Elias, A.; Beinart, R.; Nof, E.; Haskiah, F.; Michowitz, Y.; Glikson, M.; et al. Outcomes of Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176227
Abbo A, Arow Z, Eyal A, Glueck RM, Elias A, Beinart R, Nof E, Haskiah F, Michowitz Y, Glikson M, et al. Outcomes of Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176227
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbo, Aharon (Ronnie), Ziad Arow, Allon Eyal, Robert M. Glueck, Adi Elias, Roy Beinart, Eyal Nof, Feras Haskiah, Yoav Michowitz, Michael Glikson, and et al. 2025. "Outcomes of Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176227
APA StyleAbbo, A., Arow, Z., Eyal, A., Glueck, R. M., Elias, A., Beinart, R., Nof, E., Haskiah, F., Michowitz, Y., Glikson, M., Konstantino, Y., Haim, M., Luria, D., Omelchenko, A., Cohen-Hagai, K., Shehab, M., Marai, I., Laish-Farkash, A., & Suleiman, M., on behalf of the Israeli Working Group on Pacing and Electrophysiology. (2025). Outcomes of Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176227







