Artificial Intelligence in Atrial Fibrillation: From Early Detection to Precision Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
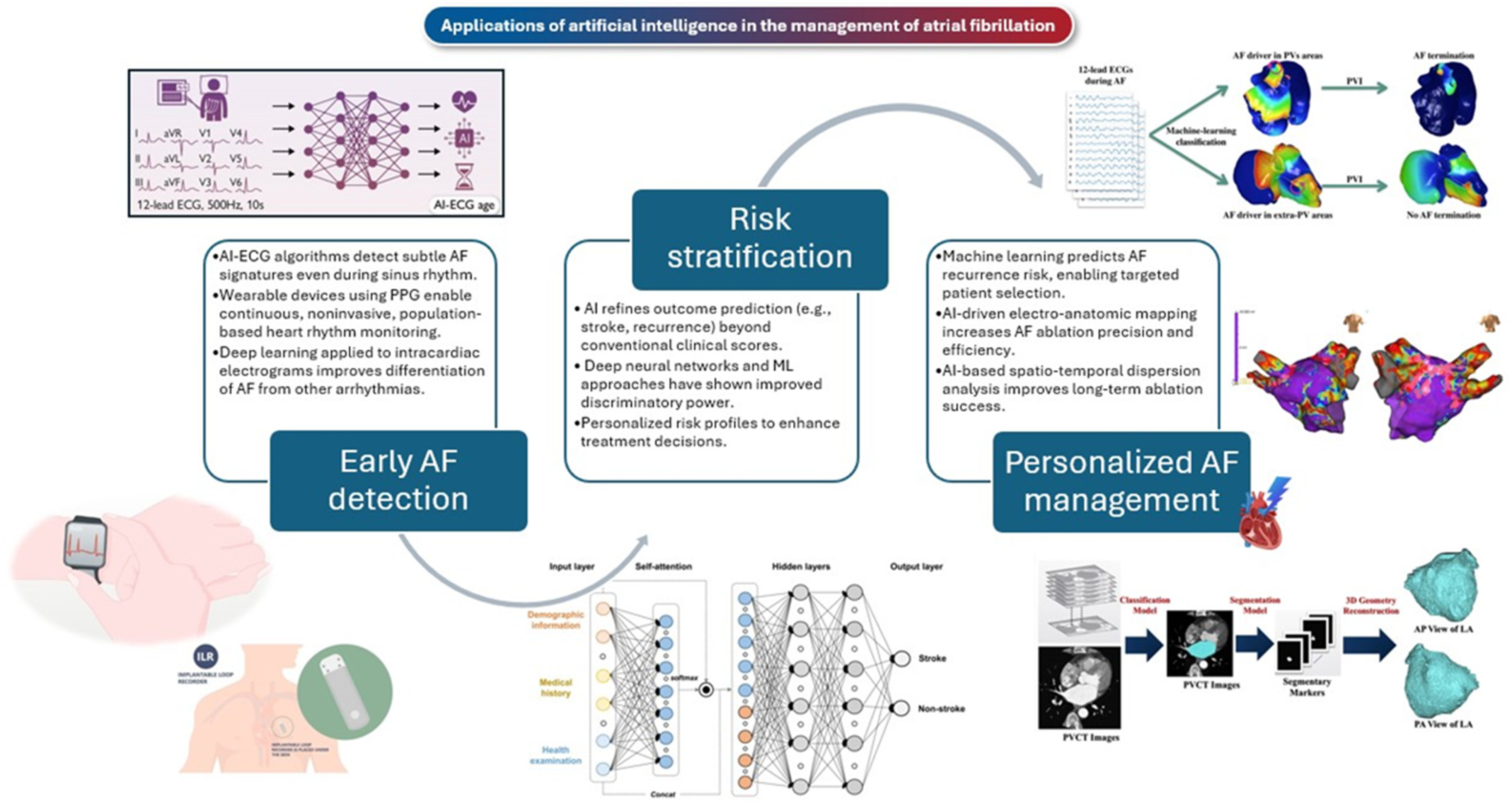
2. AI-Powered Electrocardiographic Screening for the Early Detection of AF
3. AI in Wearable Photoplethysmography for Real-Time AF Detection
4. AI-Based Detection of AF in Patients with Implantable Devices
5. AI-Based Prediction of AF Utilizing Clinical Characteristics
6. AI for Risk Stratification in Atrial Fibrillation
7. AI for Personalized AF Management
7.1. Medical Therapy
7.2. Catheter Ablation Therapy
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, S.; Zhou, J.; Veang, T.; Lin, Q.; Liu, Q. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter from 1990 to 2021: Sex Differences and Global Burden Projections to 2046-A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Europace 2025, 27, euaf027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornej, J.; Börschel, C.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; Schnabel, R.B. Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation in the 21st Century: Novel Methods and New Insights. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linz, D.; Gawalko, M.; Betz, K.; Hendriks, J.M.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Vinter, N.; Guo, Y.; Johnsen, S. Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology, Screening and Digital Health. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 37, 100786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; Bengtson, L.G.S. A Rising Tide: The Global Epidemic of Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2014, 129, 829–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.; Andrade, J.G.; Arbelo, E.; Boriani, G.; Breithardt, G.; Camm, A.J.; Caso, V.; Nielsen, J.C.; De Melis, M.; De Potter, T.; et al. Longer and Better Lives for Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: The 9th AFNET/EHRA Consensus Conference. Europace 2024, 26, euae070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdett, P.; Lip, G.Y.H. Atrial Fibrillation in the UK: Predicting Costs of an Emerging Epidemic Recognizing and Forecasting the Cost Drivers of Atrial Fibrillation-Related Costs. Eur. Heart J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2022, 8, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Chou, K.; Yeung, S.; Naik, N.; Madani, A.; Mottaghi, A.; Liu, Y.; Topol, E.; Dean, J.; Socher, R. Deep Learning-Enabled Medical Computer Vision. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.Y.T.; Cheung, M.F.K.; Munro, Y.L.; Lim, K.M.; Shung, D.; Sung, J.J.Y. Randomized Controlled Trials of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Practice: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e37188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plana, D.; Shung, D.L.; Grimshaw, A.A.; Saraf, A.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Kann, B.H. Randomized Clinical Trials of Machine Learning Interventions in Health Care: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2233946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Xing, W.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Pu, Y.; Xin, F.; Jiang, H.; Yin, Z.; Tao, D.; et al. Robust Artificial Intelligence Tool for Atrial Fibrillation Diagnosis: Novel Development Approach Incorporating Both Atrial Electrograms and Surface ECG and Evaluation by Head-to-Head Comparison With Hospital-Based Physician ECG Readers. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e032100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamporis, K.; Karakasis, P.; Sagris, M.; Theofilis, P.; Milaras, N.; Pantelidaki, A.; Mourouzis, I.; Fragakis, N.; Vlachos, K.; Kordalis, A.; et al. Prevalence of Asymptomatic Atrial Fibrillation and Risk Factors Associated with Asymptomatic Status: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2025, zwaf138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakasis, P.; Pamporis, K.; Siontis, K.C.; Theofilis, P.; Samaras, A.; Patoulias, D.; Stachteas, P.; Karagiannidis, E.; Stavropoulos, G.; Tzikas, A.; et al. Major Clinical Outcomes in Symptomatic vs. Asymptomatic Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 46, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noseworthy, P.A.; Attia, Z.I.; Behnken, E.M.; Giblon, R.E.; Bews, K.A.; Liu, S.; Gosse, T.A.; Linn, Z.D.; Deng, Y.; Yin, J.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Guided Screening for Atrial Fibrillation Using Electrocardiogram during Sinus Rhythm: A Prospective Non-Randomised Interventional Trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shajari, S.; Kuruvinashetti, K.; Komeili, A.; Sundararaj, U. The Emergence of AI-Based Wearable Sensors for Digital Health Technology: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 9498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Song, M.-K.; Lee, E.; Bae, S.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Lee, D.; Lee, M.J.; Yoo, S. Predicting Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Using Machine Learning. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labovitz, D.L.; Shafner, L.; Reyes Gil, M.; Virmani, D.; Hanina, A. Using Artificial Intelligence to Reduce the Risk of Nonadherence in Patients on Anticoagulation Therapy. Stroke 2017, 48, 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deisenhofer, I.; Albenque, J.-P.; Busch, S.; Gitenay, E.; Mountantonakis, S.E.; Roux, A.; Horvilleur, J.; Bakouboula, B.; Oza, S.; Abbey, S.; et al. Artificial Intelligence for Individualized Treatment of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nat. Med. 2025, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, J.; Mohr Durdez, T.; Lotteau, S.; Bars, C.; Pisapia, A.; Gitenay, E.; Monteau, J.; Reist, M.; Serdi, M.; Dayot, A.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Adjudicated Spatiotemporal Dispersion: A Patient-Unique Fingerprint of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2024, 21, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, J.; Durdez, T.M.; Albenque, J.P.; Pisapia, A.; Gitenay, E.; Durand, C.; Monteau, J.; Moubarak, G.; Théodore, G.; Lepillier, A.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Software Standardizes Electrogram-Based Ablation Outcome for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 2250–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahlke, F.; Englert, F.; Popa, M.; Bourier, F.; Reents, T.; Lennerz, C.; Kraft, H.; Martinez, A.T.; Kottmaier, M.; Syväri, J.; et al. First Clinical Data on Artificial Intelligence-Guided Catheter Ablation in Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2024, 35, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Z.I.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Deshmukh, A.J.; Gersh, B.J.; Carter, R.E.; Yao, X.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Erickson, B.J.; et al. An Artificial Intelligence-Enabled ECG Algorithm for the Identification of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation during Sinus Rhythm: A Retrospective Analysis of Outcome Prediction. Lancet 2019, 394, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehrawat, O.; Kashou, A.H.; Noseworthy, P.A. Artificial Intelligence and Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 1932–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopoulos, G.; Graff-Radford, J.; Lopez, C.L.; Yao, X.; Attia, Z.I.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Petersen, R.C.; Knopman, D.S.; Mielke, M.M.; Kremers, W.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Electrocardiography to Predict Incident Atrial Fibrillation: A Population-Based Study. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e009355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurshid, S.; Friedman, S.; Reeder, C.; Di Achille, P.; Diamant, N.; Singh, P.; Harrington, L.X.; Wang, X.; Al-Alusi, M.A.; Sarma, G.; et al. ECG-Based Deep Learning and Clinical Risk Factors to Predict Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2022, 145, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Hwang, M.; Huang, T.-H.; Chen, Y.-M.J.; Chang, Y.-J.; Ho, T.-H.; Huang, J.; Hwang, K.-S.; Ho, W.-H. Application of Artificial Intelligence Ensemble Learning Model in Early Prediction of Atrial Fibrillation. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinstein, A.A.; Yost, M.D.; Faust, L.; Kashou, A.H.; Latif, O.S.; Graff-Radford, J.; Attia, I.Z.; Yao, X.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Friedman, P.A. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled ECG to Identify Silent Atrial Fibrillation in Embolic Stroke of Unknown Source. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Attia, Z.I.; Behnken, E.M.; Walvatne, K.; Giblon, R.E.; Liu, S.; Siontis, K.C.; Gersh, B.J.; Graff-Radford, J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; et al. Batch Enrollment for an Artificial Intelligence-Guided Intervention to Lower Neurologic Events in Patients with Undiagnosed Atrial Fibrillation: Rationale and Design of a Digital Clinical Trial. Am. Heart J. 2021, 239, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosman, L.; Lampert, R.; Zhuo, S.; Li, Q.; Varma, N.; Burg, M.; Gaffey, A.E.; Armbruster, T.; Gehi, A. Wearable Devices, Health Care Use, and Psychological Well-Being in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e033750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manetas-Stavrakakis, N.; Sotiropoulou, I.M.; Paraskevas, T.; Maneta Stavrakaki, S.; Bampatsias, D.; Xanthopoulos, A.; Papageorgiou, N.; Briasoulis, A. Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence-Based Technologies for the Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, Y.; Song, D.; Sarvepalli, D.; Zaidi, S.R.; Ullah, W.; Arshad, J.; Mir, T.; Zghouzi, M.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Qureshi, W.; et al. Accuracy of Pulsatile Photoplethysmography Applications or Handheld Devices vs. 12-Lead ECG for Atrial Fibrillation Screening: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2022, 65, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.; Tran, N.; Gadhoumi, K.; Pelter, M.M.; Do, D.H.; Lee, R.J.; Colorado, R.; Meisel, K.; Hu, X. Photoplethysmography Based Atrial Fibrillation Detection: A Review. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitajima, H.; Takeda, K.; Ishizawa, M.; Aihara, K.; Minamino, T. Detection of Atrial Fibrillation from Pulse Waves Using Convolution Neural Networks and Recurrence-Based Plots. Chaos 2025, 35, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, M.V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Hedlin, H.; Rumsfeld, J.S.; Garcia, A.; Ferris, T.; Balasubramanian, V.; Russo, A.M.; Rajmane, A.; Cheung, L.; et al. Large-Scale Assessment of a Smartwatch to Identify Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Liang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Yan, L.; Xing, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, S.; et al. Mobile Photoplethysmographic Technology to Detect Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2365–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannhart, D.; Lischer, M.; Knecht, S.; du Fay de Lavallaz, J.; Strebel, I.; Serban, T.; Vögeli, D.; Schaer, B.; Osswald, S.; Mueller, C.; et al. Clinical Validation of 5 Direct-to-Consumer Wearable Smart Devices to Detect Atrial Fibrillation: BASEL Wearable Study. JACC. Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallet, S.; Lemay, M.; Renevey, P.; Leupi, C.; Pruvot, E.; Vesin, J.-M. Can One Detect Atrial Fibrillation Using a Wrist-Type Photoplethysmographic Device? Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2019, 57, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schack, T.; Safi Harb, Y.; Muma, M.; Zoubir, A.M. Computationally Efficient Algorithm for Photoplethysmography-Based Atrial Fibrillation Detection Using Smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turakhia, M.P.; Desai, M.; Hedlin, H.; Rajmane, A.; Talati, N.; Ferris, T.; Desai, S.; Nag, D.; Patel, M.; Kowey, P.; et al. Rationale and Design of a Large-Scale, App-Based Study to Identify Cardiac Arrhythmias Using a Smartwatch: The Apple Heart Study. Am. Heart J. 2019, 207, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, J.; Branan, K.L.; Rodriguez, A.J.; Boonya-Ananta, T.; Ajmal; Ramella-Roman, J.C.; McShane, M.J.; Coté, G.L. Sources of Inaccuracy in Photoplethysmography for Continuous Cardiovascular Monitoring. Biosensors 2021, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizas, K.D.; Freyer, L.; Sappler, N.; von Stülpnagel, L.; Spielbichler, P.; Krasniqi, A.; Schreinlechner, M.; Wenner, F.N.; Theurl, F.; Behroz, A.; et al. Smartphone-Based Screening for Atrial Fibrillation: A Pragmatic Randomized Clinical Trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, M.; Alhusseini, M.I.; Rogers, A.J.; Krittanawong, C.; Thakur, S.; Feng, R.; Ganesan, P.; Narayan, S.M. Atrial Fibrillation Signatures on Intracardiac Electrograms Identified by Deep Learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 145, 105451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-G.; Pastori, D.; Farcomeni, A.; Yang, P.-S.; Jang, E.; Joung, B.; Wang, Y.-T.; Guo, Y.-T.; Lip, G.Y.H. A Simple Clinical Risk Score (C(2)HEST) for Predicting Incident Atrial Fibrillation in Asian Subjects: Derivation in 471,446 Chinese Subjects, With Internal Validation and External Application in 451,199 Korean Subjects. Chest 2019, 155, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; Krijthe, B.P.; Aspelund, T.; Stepas, K.A.; Pencina, M.J.; Moser, C.B.; Sinner, M.F.; Sotoodehnia, N.; Fontes, J.D.; Janssens, A.C.J.W.; et al. Simple Risk Model Predicts Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation in a Racially and Geographically Diverse Population: The CHARGE-AF Consortium. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crijns, H.J.G.M. Refining Clinical Risk Stratification for Predicting Stroke and Thromboembolism in Atrial Fibrillation Using a Novel Risk Factor-Based Approach: The Euro Heart Survey on Atrial Fibrillation. Chest 2010, 137, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Liu, S.; Kingsbury, P.; Sohn, S.; Storlie, C.B.; Habermann, E.B.; Naessens, J.M.; Larson, D.W.; Liu, H. Deep Learning and Alternative Learning Strategies for Retrospective Real-World Clinical Data. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Colborn, K.L.; Smith, D.E.; Xing, F.; Ghosh, D.; Rosenberg, M.A. Assessment of a Machine Learning Model Applied to Harmonized Electronic Health Record Data for the Prediction of Incident Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1919396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenari, K.; Chao, T.-F.; Liu, C.-J.; Kihara, Y.; Chen, T.-J.; Chen, S.-A. Usefulness of HATCH Score in the Prediction of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation for Asians. Medicine 2017, 96, e5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, A.M.; Agarwal, S.K.; Folsom, A.R.; Soliman, E.Z.; Chambless, L.E.; Crow, R.; Ambrose, M.; Alonso, A. A Clinical Risk Score for Atrial Fibrillation in a Biracial Prospective Cohort (from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities [ARIC] Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 107, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, R.B.; Sullivan, L.M.; Levy, D.; Pencina, M.J.; Massaro, J.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.S.; Newton-Cheh, C.; Yamamoto, J.F.; Magnani, J.W.; Tadros, T.M.; et al. Development of a Risk Score for Atrial Fibrillation (Framingham Heart Study): A Community-Based Cohort Study. Lancet 2009, 373, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.R.; Ayoubkhani, D.; McEwan, P.; Sugrue, D.M.; Farooqui, U.; Lister, S.; Lumley, M.; Bakhai, A.; Cohen, A.T.; O’Neill, M.; et al. Predicting Atrial Fibrillation in Primary Care Using Machine Learning. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekelj, S.; Sandler, B.; Johnston, E.; Pollock, K.G.; Hill, N.R.; Gordon, J.; Tsang, C.; Khan, S.; Ng, F.S.; Farooqui, U. Detecting Undiagnosed Atrial Fibrillation in UK Primary Care: Validation of a Machine Learning Prediction Algorithm in a Retrospective Cohort Study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, A.S.; Noseworthy, P.A. Prediction of Atrial Fibrillation Using Machine Learning: A Review. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 752317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadarajah, R.; Wu, J.; Frangi, A.F.; Hogg, D.; Cowan, C.; Gale, C. Predicting Patient-Level New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation from Population-Based Nationwide Electronic Health Records: Protocol of FIND-AF for Developing a Precision Medicine Prediction Model Using Artificial Intelligence. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e052887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadarajah, R.; Wahab, A.; Reynolds, C.; Raveendra, K.; Askham, D.; Dawson, R.; Keene, J.; Shanghavi, S.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Hogg, D.; et al. Future Innovations in Novel Detection for Atrial Fibrillation (FIND-AF): Pilot Study of an Electronic Health Record Machine Learning Algorithm-Guided Intervention to Identify Undiagnosed Atrial Fibrillation. Open Heart 2023, 10, e002447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gao, M.; Song, H.; Wu, X.; Li, G.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, H. Predicting Ischemic Stroke Risk from Atrial Fibrillation Based on Multi-Spectral Fundus Images Using Deep Learning. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1185890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seners, P.; Turc, G.; Oppenheim, C.; Baron, J.-C. Incidence, Causes and Predictors of Neurological Deterioration Occurring within 24 h Following Acute Ischaemic Stroke: A Systematic Review with Pathophysiological Implications. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegler, J.E.; Martin-Schild, S. Early Neurological Deterioration (END) after Stroke: The END Depends on the Definition. Int. J. Stroke 2011, 6, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Jeon, E.-T.; Yu, S.; Oh, K.; Kim, C.K.; Song, T.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Heo, S.H.; Park, K.-Y.; Kim, J.-M.; et al. Interpretable Machine Learning for Early Neurological Deterioration Prediction in Atrial Fibrillation-Related Stroke. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinter, N.; Frederiksen, A.S.; Albertsen, A.E.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Fenger-Grøn, M.; Trinquart, L.; Frost, L.; Møller, D.S. Role for Machine Learning in Sex-Specific Prediction of Successful Electrical Cardioversion in Atrial Fibrillation? Open Heart 2020, 7, e001297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emren, S.V.; Kocabaş, U.; Duygu, H.; Levent, F.; Şimşek, E.Ç.; Yapan Emren, Z.; Tülüce, S. The Role of HATCH Score in Predicting the Success Rate of Sinus Rhythm Following Electrical Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation. Kardiol. Pol. 2016, 74, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, F.; Serenelli, M.; Airaksinen, J.; Pavasini, R.; Tomaszuk-Kazberuk, A.; Mlodawska, E.; Jaakkola, S.; Balla, C.; Falsetti, L.; Tarquinio, N.; et al. CHA2DS2-VASc Score Predicts Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence after Cardioversion: Systematic Review and Individual Patient Pooled Meta-Analysis. Clin. Cardiol. 2019, 42, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez-Garcia, J.C.; Sánchez-Puente, A.; Sampedro-Gómez, J.; Vicente-Palacios, V.; Jiménez-Navarro, M.; Oterino-Manzanas, A.; Jiménez-Candil, J.; Dorado-Diaz, P.I.; Sánchez, P.L. Outcome Analysis in Elective Electrical Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation Patients: Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Prognostic Model. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Baker, E.; Collins, R.; Merino, J.L.; Desteghe, L.; Heidbuchel, H. The Challenge of Managing Multimorbid Atrial Fibrillation: A Pan-European European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) Member Survey of Current Management Practices and Clinical Priorities. Europace 2022, 24, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, J.M.; Moreno Weidmann, Z.; Perrotta, L.; Sultan, A.; Anic, A.; Metzner, A.; Providencia, R.; Boveda, S.; Chun, J. Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation in Routine Practice According to the Last ESC Guidelines: An EHRA Physician Survey-How Are We Dealing with Controversial Approaches? Europace 2024, 26, euae012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakasis, P.; Patoulias, D.; Popovic, D.S.; Pamporis, K.; Theofilis, P.; Nasoufidou, A.; Stachteas, P.; Samaras, A.; Tzikas, A.; Giannakoulas, G.; et al. Effects of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists on New-Onset or Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation: A Bayesian and Frequentist Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachteas, P.; Nasoufidou, A.; Karagiannidis, E.; Patoulias, D.; Karakasis, P.; Alexiou, S.; Samaras, A.; Zormpas, G.; Stavropoulos, G.; Tsalikakis, D.; et al. The Role of Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Atrial Fibrillation: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakasis, P.; Fragakis, N.; Patoulias, D.; Theofilis, P.; Kassimis, G.; Karamitsos, T.; El-Tanani, M.; Rizzo, M. Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists on Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Ther. 2024, 41, 3749–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.J.; Nichols, D.J.; Oliver, S.D. The Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Oral Dofetilide after Twice Daily and Three Times Daily Dosing. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 50, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgwick, M.L.; Rasmussen, H.S.; Cobbe, S.M. Effects of the Class III Antiarrhythmic Drug Dofetilide on Ventricular Monophasic Action Potential Duration and QT Interval Dispersion in Stable Angina Pectoris. Am. J. Cardiol. 1992, 70, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Z.I.; Sugrue, A.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Ackerman, M.J.; Kapa, S.; Friedman, P.A.; Noseworthy, P.A. Noninvasive Assessment of Dofetilide Plasma Concentration Using a Deep Learning (Neural Network) Analysis of the Surface Electrocardiogram: A Proof of Concept Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, H.W.; Kim, D.J.; Mo, J.; Kim, J.-E. Development of a System to Support Warfarin Dose Decisions Using Deep Neural Networks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yin, C.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wang, S.; Bao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, T.; Fan, J.; Liu, X. XGBoost-Based Machine Learning Test Improves the Accuracy of Hemorrhage Prediction among Geriatric Patients with Long-Term Administration of Rivaroxaban. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Abraham, N.S.; Alexander, G.C.; Crown, W.; Montori, V.M.; Sangaralingham, L.R.; Gersh, B.J.; Shah, N.D.; Noseworthy, P.A. Effect of Adherence to Oral Anticoagulants on Risk of Stroke and Major Bleeding Among Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Q. A Novel Network with Enhanced Edge Information for Left Atrium Segmentation from LGE-MRI. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1478347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakasis, P.; Theofilis, P.; Vlachakis, P.K.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Patoulias, D.; Antoniadis, A.P.; Fragakis, N. Atrial Fibrosis in Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanistic Insights, Diagnostic Challenges, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Ammirati, G.; Ventrella, N.; Aguilera, J.; Marazzato, J.; Freilich, M.; Serna, J.C.; Lin, A.N.; La Fazia, V.M.; Mohanty, S.; et al. PO-03-147 Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Using A 3D Artificial Intelligence Module Integration With Intracardiac Echocardiography. Heart Rhythm. 2024, 21, S345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbomo-Harmitt, S.; Muffoletto, M.; Zeidan, A.; Qureshi, A.; King, A.; Aslanidi, O. Can Artificial Intelligence Prediction of Successful Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation Therapy Be Interpretable? Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2022, 3, ztac076.2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kwon, O.-S.; Shim, J.; Kim, D.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, Y.-G.; Yu, H.T.; Kim, T.-H.; Uhm, J.-S.; Choi, J.-I.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Estimated Electrocardiographic Age as a Recurrence Predictor after Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation. NPJ Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruwez, H.; Barthels, M.; Dhont, S.; Meekers, E.; Wouters, F.; Pierlet, N.; Nuyens, D.; Rivero-Ayerza, M.; Van Herendael, H.; Pison, L.; et al. Predicting Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence after Catheter Ablation Using an Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Electrocardiogram Algorithm. EP Eur. 2024, 26, euae102.167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Fox, S.R.; Toomu, A.; Gu, K.; Kang, J.; Sung, K.; Han, F.T.; Hoffmayer, K.S.; Hsu, J.C.; Raissi, F.; Feld, G.K.; et al. Impact of Artificial Intelligence Arrhythmia Mapping on Time to First Ablation, Procedure Duration, and Fluoroscopy Use. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2024, 35, 916–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaeikheybari, G.; El-Harasis, M.; Gupta, A.; Shoemaker, M.B.; Barnard, J.; Hunter, J.; Passman, R.S.; Sun, H.; Kim, H.S.; Schilling, T.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Based Feature Analysis of Pulmonary Vein Morphology on Computed Tomography Scans and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation: A Multi-Site Study. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2024, 17, e012679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Sotomi, Y.; Hikoso, S.; Kitamura, T.; Nakatani, D.; Okada, K.; Dohi, T.; Sunaga, A.; Kida, H.; Matsuoka, Y.; et al. Uplift Modeling to Identify Patients Who Require Extensive Catheter Ablation Procedures among Patients with Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-M.; Chang, S.-L.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, W.-S.; Lin, Y.-J.; Lo, L.-W.; Hu, Y.-F.; Chung, F.-P.; Chao, T.-F.; Tuan, T.-C.; et al. The Clinical Application of the Deep Learning Technique for Predicting Trigger Origins in Patients With Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation With Catheter Ablation. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e008518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-H.; Liu, C.-M.; Chang, S.-L.; Chang, P.Y.-C.; Chen, W.-S.; Pan, Y.-M.; Fang, S.-T.; Zhan, S.-Q.; Chuang, C.-M.; Lin, Y.-J.; et al. Automated Extraction of Left Atrial Volumes from Two-Dimensional Computer Tomography Images Using a Deep Learning Technique. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 316, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X. Segmentation of Left Atrium Through Combination of Deep Convolutional and Recurrent Neural Networks. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2018, 8, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muffoletto, M.; Fu, X.; Roy, A.; Varela, M.; Bates, P.A.; Aslanidi, O.V. Development of a Deep Learning Method to Predict Optimal Ablation Patterns for Atrial Fibrillation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), Siena, Italy, 9–11 July 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.; Metzner, A.; Wohlmuth, P.; Lin, T.; Wissner, E.; Tilz, R.; Rillig, A.; Mathew, S.; Saguner, A.; Heeger, C.; et al. Insights into Ablation of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Lessons from 6-Year Clinical Outcomes. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-E.; Naditch-Brûlé, L.; Murin, J.; Goethals, M.; Inoue, H.; O’Neill, J.; Silva-Cardoso, J.; Zharinov, O.; Gamra, H.; Alam, S.; et al. Distribution and Risk Profile of Paroxysmal, Persistent, and Permanent Atrial Fibrillation in Routine Clinical Practice: Insight from the Real-Life Global Survey Evaluating Patients with Atrial Fibrillation International Registry. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2012, 5, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrábano, M.; Peterson, L.E.; Swarup, V.; Schurmann, P.A.; Makkar, A.; Doshi, R.N.; DeLurgio, D.; Athill, C.A.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Natale, A.; et al. Effect of Catheter Ablation With Vein of Marshall Ethanol Infusion vs Catheter Ablation Alone on Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: The VENUS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrouche, N.F.; Wazni, O.; McGann, C.; Greene, T.; Dean, J.M.; Dagher, L.; Kholmovski, E.; Mansour, M.; Marchlinski, F.; Wilber, D.; et al. Effect of MRI-Guided Fibrosis Ablation vs Conventional Catheter Ablation on Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence in Patients With Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: The DECAAF II Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 2296–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, P.M.; Chieng, D.; Sugumar, H.; Ling, L.-H.; Segan, L.; Azzopardi, S.; Al-Kaisey, A.; Parameswaran, R.; Anderson, R.D.; Hawson, J.; et al. Effect of Catheter Ablation Using Pulmonary Vein Isolation With vs Without Posterior Left Atrial Wall Isolation on Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence in Patients With Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: The CAPLA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 329, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebert, J.; Ravi, N.; Fenton, F.H.; Christoph, J. Rotor Localization and Phase Mapping of Cardiac Excitation Waves Using Deep Neural Networks. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 782176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Ragot, D.; Nayyar, S.; Suszko, A.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Chauhan, V.S. Deep Learning Classification of Unipolar Electrograms in Human Atrial Fibrillation: Application in Focal Source Mapping. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 704122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Razeghi, O.; Kapoor, R.; Alhusseini, M.I.; Fazal, M.; Rogers, A.J.; Rodrigo Bort, M.; Clopton, P.; Wang, P.J.; Rubin, D.L.; et al. Machine Learning-Enabled Multimodal Fusion of Intra-Atrial and Body Surface Signals in Prediction of Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Outcomes. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2022, 15, e010850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, J.; Bars, C.; Théodore, G.; Beurtheret, S.; Lellouche, N.; Bremondy, M.; Ferracci, A.; Faure, J.; Penaranda, G.; Yamazaki, M.; et al. AF Ablation Guided by Spatiotemporal Electrogram Dispersion Without Pulmonary Vein Isolation: A Wholly Patient-Tailored Approach. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study (Year) | Patient Population | Sample Size | AI Technique | Findings | Clinical Implications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bahlke et al. (2024) [20] | Patients with long-standing persistent AF | 50 | Volta VX1 software for AI-guided ablation of spatio-temporal dispersions | 82% of patients remained in stable sinus rhythm after an average of 1.46 procedures; 52% experienced arrhythmia recurrence; AF cycle length prolonged significantly; low complication rate. | AI-guided ablation of spatio-temporal dispersions may improve outcomes for persistent AF patients, but randomized trials are needed to confirm long-term efficacy. |
| Zou et al. (2024) [76] | Patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation for AF | 118 | CARTOSOUND FAM AI-based ICE module for 3D LA reconstruction | 98% acute ablation success rate; no immediate complications; mean procedure time: 136.9 min; mean RF time: 29.6 min; 92% received PVI, 68% received posterior wall isolation. | AI-integrated ICE module enables accurate LA reconstruction without a multipolar mapping catheter, demonstrating high acute success and safety; long-term AF recurrence needs further study. |
| Ogbomo-Harmitt et al. (2022) [77] | Persistent AF patients undergoing simulated RF catheter ablation | 122 | Deep learning (CNN) for predicting success of fibrosis-based and rotor-based ablation | For fibrosis-based ablation: AUC 0.92, recall 0.89, precision 0.82; for rotor-based ablation: AUC 0.77, recall 0.93, precision 0.76; saliency maps identified ablation lesions in 62–71% of cases. | DL-based prediction models can identify proarrhythmogenic regions and improve AI interpretability for AF ablation, potentially aiding clinical decision making. |
| Park et al. (2024) [78] | Patients undergoing de novo AF catheter ablation | 5466 | AI-estimated electrocardiographic age (AI-ECG) using ResNet-based model | AI-ECG age gap (≥10 years) associated with higher AF recurrence risk; 5-year recurrence HR 1.44 (95% CI 1.31–1.59); each year increase in AI-ECG age gap increased recurrence risk by 1%. | AI-ECG age gap is a potential predictor of AF recurrence after ablation, offering a simple and interpretable risk marker for clinical use. |
| TAILORED-AF Trial (2025) [17] | Patients with drug-refractory persistent or long-standing persistent AF | 374 | AI algorithm detecting spatio-temporal dispersion for tailored ablation | Freedom from AF at 12 months: 88% (tailored arm) vs. 70% (PVI-only arm); freedom from any arrhythmia: no significant difference after one procedure in the entire population, becoming significant after one or two procedures. Significant difference after a single procedure in the >6 months’ persistent AF pre-specified subgroup; tailored ablation had longer procedure and ablation times but similar safety outcomes. | AI-guided ablation targeting spatio-temporal dispersion improves AF elimination compared to PVI alone; long-term efficacy and need for additional AT ablation require further study. |
| Gruwez et al. (2024) [79] | Patients undergoing AF ablation with pre-procedure sinus rhythm ECG | 53 | Deep neural network (DNN)-based AI-enabled ECG algorithm | AI-ECG predicted AF recurrence with AUC 0.65; patients classified as high-risk had a 2.6-fold higher risk of AF recurrence (HR 2.6, p = 0.037). | AI-enabled ECG analysis may help predict AF recurrence risk post-ablation, potentially improving patient selection and risk stratification. |
| Fox et al. (2024) [80] | Patients undergoing AI-guided arrhythmia mapping for catheter ablation | 28 | Forward-solution AI ECG mapping system | Reduced time to first ablation by 19% (133 vs. 165 min, p = 0.02); reduced procedure duration by 22.6% (233 vs. 301 min, p < 0.001); reduced fluoroscopy time by 43.7% (18.7 vs. 33.2 min, p < 0.001); 6-month arrhythmia-free survival: 73.5% (AI) vs. 63.3% (control, p = 0.56). | AI-guided ECG mapping improves procedural efficiency by reducing mapping time, procedure duration, and radiation exposure without negatively affecting outcomes. |
| Asaeikheybari et al. (2024) [81] | Patients undergoing AF catheter ablation with pre-procedure CT scans | 809 | AI-based segmentation and radiomic analysis of pulmonary vein morphology | Primary PV morphology associated with AF recurrence (AUC 0.73, 0.71, 0.70 across datasets); AF+ cases exhibited greater surface complexity; secondary PV features had weaker association (AUC ~0.61). | AI-extracted pulmonary vein features may serve as predictors of AF recurrence post-ablation; potential for improved patient selection and ablation strategies. |
| Sato et al. (2024) [82] | Patients with persistent AF undergoing catheter ablation | 497 | Uplift modeling with adaptive boosting to predict benefit from extensive ablation | Uplift score ≥ 0.0124 identified patients who benefited from extensive ablation (HR 0.40, p = 0.015); no benefit observed in patients with uplift score < 0.0124 (HR 1.17, p = 0.661); creatinine, LVEF, BNP, hemoglobin among top predictors. | AI-based uplift modeling can stratify patients who require extensive catheter ablation, offering a precision medicine approach to AF ablation strategies. |
| Liu et al. (2020) [83] | Patients with paroxysmal AF undergoing catheter ablation | 521 | Deep learning (ResNet34) for predicting non-pulmonary vein (NPV) triggers | Prediction accuracy for NPV triggers: 88.6%; sensitivity: 75.0%, specificity: 95.7%; AUC for individual images: 0.82, for patients: 0.88. | AI-based prediction of NPV triggers before ablation may enhance procedural planning, helping to reduce AF recurrence and improve ablation strategies. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karakasis, P.; Theofilis, P.; Sagris, M.; Pamporis, K.; Stachteas, P.; Sidiropoulos, G.; Vlachakis, P.K.; Patoulias, D.; Antoniadis, A.P.; Fragakis, N. Artificial Intelligence in Atrial Fibrillation: From Early Detection to Precision Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082627
Karakasis P, Theofilis P, Sagris M, Pamporis K, Stachteas P, Sidiropoulos G, Vlachakis PK, Patoulias D, Antoniadis AP, Fragakis N. Artificial Intelligence in Atrial Fibrillation: From Early Detection to Precision Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082627
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarakasis, Paschalis, Panagiotis Theofilis, Marios Sagris, Konstantinos Pamporis, Panagiotis Stachteas, Georgios Sidiropoulos, Panayotis K. Vlachakis, Dimitrios Patoulias, Antonios P. Antoniadis, and Nikolaos Fragakis. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence in Atrial Fibrillation: From Early Detection to Precision Therapy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082627
APA StyleKarakasis, P., Theofilis, P., Sagris, M., Pamporis, K., Stachteas, P., Sidiropoulos, G., Vlachakis, P. K., Patoulias, D., Antoniadis, A. P., & Fragakis, N. (2025). Artificial Intelligence in Atrial Fibrillation: From Early Detection to Precision Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082627








