Clot Composition and Ischemic Stroke Etiology: A Contemporary Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A Primer on Stroke Etiology and Clot Pathology
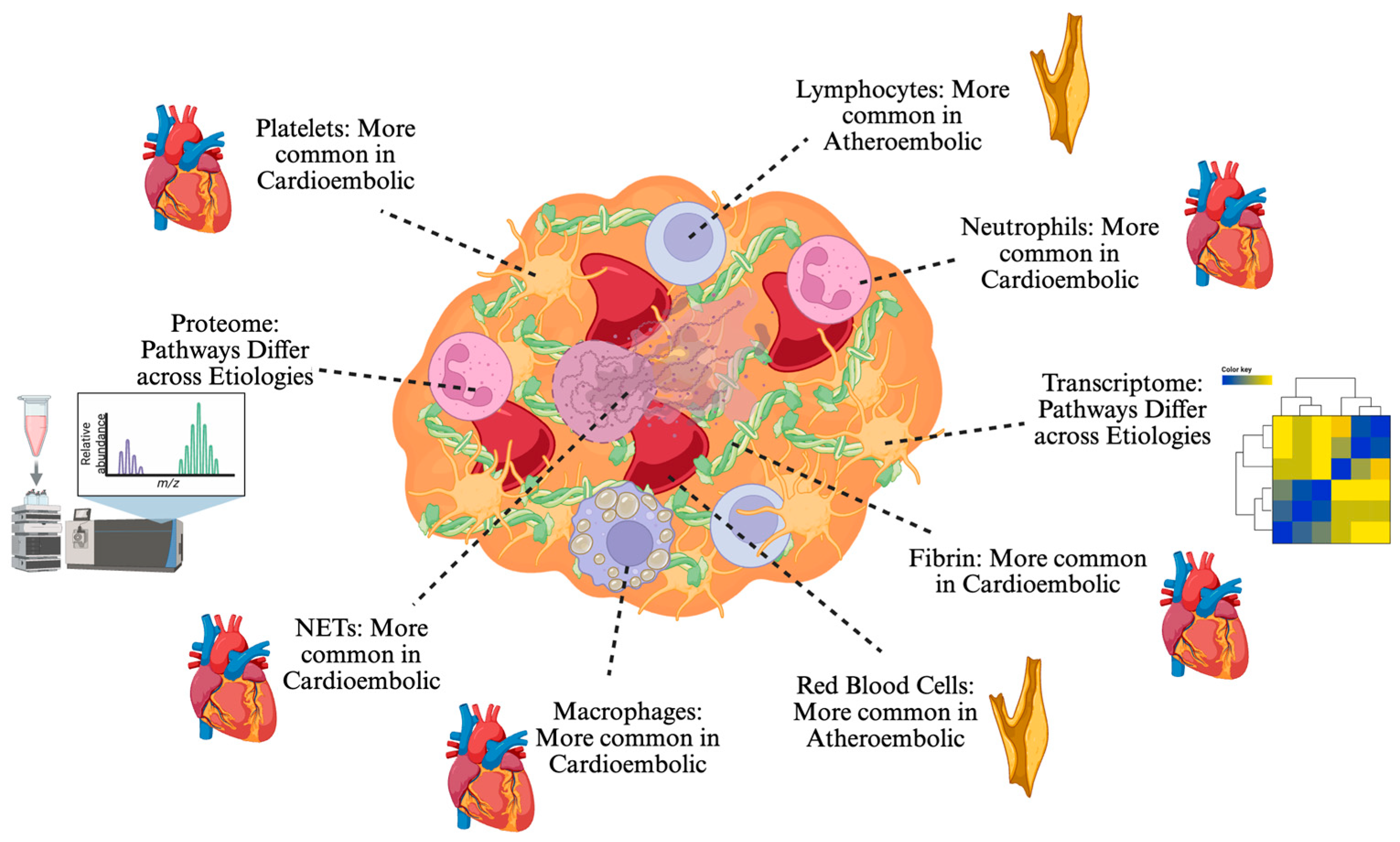
3. Insights from Red Blood Cell, Fibrin, and Platelet Analysis
4. Insights from White Blood Cells and Neutrophil Extracellular Trap
5. Molecular and Next-Generation Analysis
5.1. Proteomics
5.2. Metabolomics
| Reference | Sample Size | Technique | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Darganzanli, 2020 [92] | 60 (32 CE, 28 LAA) | Proteomic with Nano- LC-MS. Dataset then analyzed using support vector machine (SVM) learning method. | Protein trios allowing 88% accuracy of correct classification are coagulation factor XIII +
|
| Specific limitations: Proof-of-concept study. Does not include external validation. | |||
| Suissa, 2021 [99] | 41 (34 CE, 7 LAA) | Multiomic (combined proteomic and metabolomic approach) | Using the combined proteomic and metabolomic signature, the authors’ model achieved 100% sensitivity and 85.7% specificity of predicting CE source. External validation performed on patients initially classified as cryptogenic achieved 100% prediction in the rate of new atrial fibrillation diagnosis at 3 months. |
| Specific limitations: Small validation cohort (7 patients). | |||
| Abbasi, 2021 [100] | 48 (25 CE, 23 LAA) | Proteomic with RPPA | CE clots have more diverse and abundant protein linkages between PPAR-gamma and arginase-1, CD63, CD234, PKCαβ Thr 638/641, and vWF. |
| Specific limitations: Descriptive observational findings only. Does not include predictive modeling. | |||
| Lopez-Pedrera, 2023 [101] | 18 (9 CE, 9 LAA) | Proteomic with nano-LC-MS | 26 proteins were differentially abundant between CE and LAA clots:
|
| Specific limitations: Descriptive observational findings only. Does not include predictive modeling or external validation. | |||
| Li, 2023 [97] | 48 (26 CE, 22 LAA) | Metabolomic with UPLC-QTOF-MS | 6 metabolites were differentially abundant in CE and LAA clots and selected by machine learning model:
|
| Specific limitations: Validation cohort does not include cryptogenic patients, only those with LAA and CE clots. | |||
| Rossi, 2022 [93] | 31 (16 CE, 15 LAA) | Proteomic with LC-MS/MS | 14 proteins were differentially abundant between CE and LAA clots:
|
| Specific limitations: Descriptive observational findings only. Does not include predictive modeling or external validation. | |||
| Kim, 2025 [94] | 27 (17 CE, 6 LAA, 4 CR) | Proteomic with LC-MS/MS |
|
| Specific limitations: Lower PPV, with a small validation cohort (8 patients). |
5.3. Transcriptomics
6. Summary of Current Evidence
7. Limitations and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collaborators, G.B.D.S. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilkens, N.A.; Casolla, B.; Leung, T.W.; de Leeuw, F.-E. Stroke. Lancet 2024, 403, 2820–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Los Rios, F.; Kleindorfer, D.O.; Guzik, A.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Sangha, N.; Kumar, G.; Grotta, J.C.; Lee, J.M.; Meyer, B.C.; Schwamm, L.H.; et al. Intravenous fibrinolysis eligibility: A survey of stroke clinicians’ practice patterns and review of the literature. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 23, 2130–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, N.; Doeppner, T.R.; Hermann, D.M.; Gronewold, J. Efficacy and safety of intravenous tenecteplase compared to alteplase before mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 3928–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019, 50, e344–e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Coote, S.; Pesavento, L.; Churilov, L.; Dewey, H.M.; Davis, S.M.; Campbell, B.C.V. Large Vessel Occlusion Scales Increase Delivery to Endovascular Centers Without Excessive Harm from Misclassifications. Stroke 2017, 48, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dozois, A.; Hampton, L.; Kingston, C.W.; Lambert, G.; Porcelli, T.J.; Sorenson, D.; Templin, M.; VonCannon, S.; Asimos, A.W. PLUMBER Study (Prevalence of Large Vessel Occlusion Strokes in Mecklenburg County Emergency Response). Stroke 2017, 48, 3397–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, A.P.; Desai, S.M.; Jovin, T.G. Indications for Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke: Current Guidelines and Beyond. Neurology 2021, 97 (Suppl. S2), S126–S136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhemer, O.A.; Fransen, P.S.S.; Beumer, D.; van den Berg, L.A.; Lingsma, H.F.; Yoo, A.J.; Schonewille, W.J.; Vos, J.A.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Wermer, M.J.H.; et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, B.C.V.; Mitchell, P.J.; Kleinig, T.J.; Dewey, H.M.; Churilov, L.; Yassi, N.; Yan, B.; Dowling, R.J.; Parsons, M.W.; Oxley, T.J.; et al. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Demchuk, A.M.; Menon, B.K.; Eesa, M.; Rempel, J.L.; Thornton, J.; Roy, D.; Jovin, T.G.; Willinsky, R.A.; Sapkota, B.L.; et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovin, T.G.; Chamorro, A.; Cobo, E.; de Miquel, M.A.; Molina, C.A.; Rovira, A.; San Román, L.; Serena, J.; Abilleira, S.; Ribó, M.; et al. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saver, J.L.; Goyal, M.; Bonafe, A.; Diener, H.-C.; Levy, E.I.; Pereira, V.M.; Albers, G.W.; Cognard, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Hacke, W.; et al. Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, G.W.; Marks, M.P.; Kemp, S.; Christensen, S.; Tsai, J.P.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Torbey, M.T.; Kim-Tenser, M.; Leslie-Mazwi, T.; et al. Thrombectomy for Stroke at 6 to 16 Hours with Selection by Perfusion Imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthuis, S.G.H.; Pirson, F.A.V.; Pinckaers, F.M.E.; Hinsenveld, W.H.; Nieboer, D.; Ceulemans, A.; Knapen, R.R.M.M.; Robbe, M.M.Q.; Berkhemer, O.A.; van Walderveen, M.A.A.; et al. Endovascular treatment versus no endovascular treatment after 6–24 h in patients with ischaemic stroke and collateral flow on CT angiography (MR CLEAN-LATE) in the Netherlands: A multicentre, open-label, blinded-endpoint, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E., 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight-Greenfield, A.; Nario, J.J.Q.; Gupta, A. Causes of Acute Stroke: A Patterned Approach. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 57, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibeh, C.; Elkind, M.S.V. Stroke Prevention After Cryptogenic Stroke. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacigaluppi, M.; Semerano, A.; Gullotta, G.S.; Strambo, D. Insights from thrombi retrieved in stroke due to large vessel occlusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2019, 39, 1433–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliena-Valero, A.; Baixauli-Martín, J.; Torregrosa, G.; Tembl, J.I.; Salom, J.B. Clot Composition Analysis as a Diagnostic Tool to Gain Insight into Ischemic Stroke Etiology: A Systematic Review. J. Stroke 2021, 23, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhtman, O.; Sioutas, G.S.; Piavchenko, G.; Bhalla, S.; Cooke, D.L.; Winkler, E.; Burkhardt, J.-K.; Srinivasan, V.M. Endovascular biopsy in neurointerventional surgery: A systematic review. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2024, 15910199241240508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Li, D.; Lin, J.; Thomas, A.M.; Miao, J.; Chen, D.; Li, S.; Chu, C. Cerebral small vessel disease: Pathological mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 961661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wardlaw, J.M. Update on cerebral small vessel disease: A dynamic whole-brain disease. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2016, 1, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, M.S.; O’Brien, J.T.; Perry, R.H.; English, P.; Forster, G.; McMeekin, W.; Slade, J.Y.; Golkhar, A.; Matthews, F.E.; Barber, R.; et al. Comparison of the pathology of cerebral white matter with post-mortem magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the elderly brain. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2004, 30, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.E.; Fernando, M.S.; Clark, L.; Ince, P.G.; Matthews, F.; Forster, G.; O’Brien, J.T.; Barber, R.; Kalaria, R.N.; Brayne, C.; et al. White matter lesions in an unselected cohort of the elderly: Astrocytic, microglial and oligodendrocyte precursor cell responses. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2007, 33, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.E.; Ince, P.G.; Higham, C.E.; Gelsthorpe, C.H.; Fernando, M.S.; Matthews, F.; Forster, G.; O’Brien, J.T.; Barber, R.; Kalaria, R.N.; et al. Microglial activation in white matter lesions and nonlesional white matter of ageing brains. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2007, 33, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, E. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, C7–C12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature 2021, 592, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, J.W.; Litvinov, R.I. Exploring the thrombus niche: Lessons learned and potential therapeutic opportunities. Blood 2025, 2024025319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spronk, H.M.H.; Padro, T.; Siland, J.E.; Prochaska, J.H.; Winters, J.; van der Wal, A.C.; Posthuma, J.J.; Lowe, G.; d’Alessandro, E.; Wenzel, P.; et al. Atherothrombosis and Thromboembolism: Position Paper from the Second Maastricht Consensus Conference on Thrombosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedt, S.; Buchan, A.M.; Dichgans, M.; Lizasoain, I.; Moro, M.A.; Lo, E.H. The neurovascular unit and systemic biology in stroke—Implications for translation and treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.Y.; Gupta, D.; Lip, G.Y.H. Atrial fibrillation and the prothrombotic state: Revisiting Virchow’s triad in 2020. Heart (British Cardiac Society) 2020, 106, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-J.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-A. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinod, K.; Claessen, A.; Martens, C.; Krauel, K.; Velásquez Pereira, L.C.; Witsch, J.; Witsch, T. NET burden in left atrial blood is associated with biomarkers of thrombosis and cardiac injury in patients with enlarged left atria. Clin. Res. Cardiol. Off. J. Ger. Card. Soc. 2025, 114, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereuta, O.M.; Agarwal, T.; Ghozy, S.; Dai, D.; Arul, S.; Brinjikji, W.; Kallmes, D.F.; Kadirvel, R. Shell Versus Core Architecture and Biology of Thrombi in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2023, 29, 10760296231213632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta-Enguita, J.; Machado, F.J.D.; Orbe, J.; Muñoz, R. Thrombus composition and its implication in ischemic stroke assessment and revascularization treatments. Neurol. (Engl. Ed.) 2025, 40, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.H.; Hong, R.; Choo, I.S.; Heo, J.H.; Nam, H.S.; Kang, H.G.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, J.H. Histologic features of acute thrombi retrieved from stroke patients during mechanical reperfusion therapy. Int. J. Stroke 2016, 11, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sujijantarat, N.; Templeton, K.A.; Antonios, J.P.; Renedo, D.; Koo, A.B.; Haynes, J.O.; Fathima, B.; Amllay, A.; Nowicki, K.; Huttner, A.; et al. Is Clot Composition Associated with Cause of Stroke? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke Vasc. Interv. Neurol. 2024, 4, e001426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessens, S.; Vandelanotte, S.; François, O.; Boulleaux, E.; Bretzner, M.; Casolla, B.; Corseaux, D.; Puy, L.; Denorme, F.; De Wilde, M.; et al. Association Between Thrombus Composition and Etiology in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Treated by Thrombectomy. Stroke 2025, 56, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Funatsu, N.; Yamagami, H.; Satow, T.; Takahashi, J.C.; Nagatsuka, K.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Kira, J.-i.; Toyoda, K. Histopathologic Analysis of Retrieved Thrombi Associated with Successful Reperfusion After Acute Stroke Thrombectomy. Stroke 2016, 47, 3035–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, C.; Yang, J. No Histological Difference between Large Atherosclerotic and Cardiogenic Embolic Thrombus. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 4845264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Killingsworth, M.C.; Bhaskar, S.M.M. Is Composition of Brain Clot Retrieved by Mechanical Thrombectomy Associated with Stroke Aetiology and Clinical Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke?—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 748–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, P.B.; Hanning, U.; Schwindt, W.; Velasco, A.; Minnerup, J.; Zoubi, T.; Heindel, W.; Jeibmann, A.; Niederstadt, T.U. Ischemic Stroke: What Does the Histological Composition Tell Us About the Origin of the Thrombus? Stroke 2017, 48, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckh-Behrens, T.; Kleine, J.F.; Zimmer, C.; Neff, F.; Scheipl, F.; Pelisek, J.; Schirmer, L.; Nguyen, K.; Karatas, D.; Poppert, H. Thrombus Histology Suggests Cardioembolic Cause in Cryptogenic Stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinjikji, W.; Nogueira, R.G.; Kvamme, P.; Layton, K.F.; Delgado Almandoz, J.E.; Hanel, R.A.; Mendes Pereira, V.; Almekhlafi, M.A.; Yoo, A.J.; Jahromi, B.S.; et al. Association between clot composition and stroke origin in mechanical thrombectomy patients: Analysis of the Stroke Thromboembolism Registry of Imaging and Pathology. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2021, 13, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laridan, E.; Denorme, F.; Desender, L.; François, O.; Andersson, T.; Deckmyn, H.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; De Meyer, S.F. Neutrophil extracellular traps in ischemic stroke thrombi. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, S.; Wang, S.; Dai, D.; Murphree, D.H., Jr.; Pandit, A.; Douglas, A.; Rizvi, A.; Kadirvel, R.; Gilvarry, M.; McCarthy, R.; et al. Orbit image analysis machine learning software can be used for the histological quantification of acute ischemic stroke blood clots. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.H.; Park, G.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, J.M. Erythrocyte Fraction Within Retrieved Thrombi Contributes to Thrombolytic Response in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Meglio, L.; Desilles, J.P.; Ollivier, V.; Nomenjanahary, M.S.; Di Meglio, S.; Deschildre, C.; Loyau, S.; Olivot, J.M.; Blanc, R.; Piotin, M.; et al. Acute ischemic stroke thrombi have an outer shell that impairs fibrinolysis. Neurology 2019, 93, e1686–e1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, J.; Ha, J.; Hwang, I.G.; Song, T.J.; Yoo, J.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Histological features of intracranial thrombi in stroke patients with cancer. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, J.; Gaida, B.J.; Wanke, I.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Koehrmann, M.; Forsting, M.; Moenninghoff, C.; Radbruch, A.; Junker, A. Is Histologic Thrombus Composition in Acute Stroke Linked to Stroke Etiology or to Interventional Parameters? AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Martinez, C.; Duran-Laforet, V.; Garcia-Culebras, A.; Ostos, F.; Hernandez-Jimenez, M.; Bravo-Ferrer, I.; Perez-Ruiz, A.; Ballenilla, F.; Diaz-Guzman, J.; Pradillo, J.M.; et al. Pharmacological Modulation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Reverses Thrombotic Stroke tPA (Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator) Resistance. Stroke 2019, 50, 3228–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.H.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Lee, C.W.; Tsai, L.K.; Tang, S.C.; Shun, C.T.; Jeng, J.S. Fibrin and Platelet-Rich Composition in Retrieved Thrombi Hallmarks Stroke with Active Cancer. Stroke 2020, 51, 3723–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, S.T.; Wang, S.; Dai, D.; Douglas, A.; Kadirvel, R.; Gounis, M.J.; Chueh, J.; Puri, A.S.; Layton, K.F.; Thacker, I.C.; et al. Platelet-rich clots as identified by Martius Scarlet Blue staining are isodense on NCCT. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2019, 11, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereuta, O.M.; Fitzgerald, S.; Christensen, T.A.; Jaspersen, A.L.; Dai, D.; Abbasi, M.; Puttappa, T.; Kadirvel, R.; Kallmes, D.F.; Doyle, K.M.; et al. High-resolution scanning electron microscopy for the analysis of three-dimensional ultrastructure of clots in acute ischemic stroke. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2021, 13, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouh, A.; Mehta, T.; Hussain, M.; Song, X.; Ollenschleger, M. Clot composition of embolic strokes of undetermined source: A feasibility study. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, J.; Oberdieck, P.; Titova, A.; Pelisek, J.; Chandraratne, S.; Nicol, P.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Joner, M.; Maegdefessel, L.; Poppert, H.; et al. Thrombus NET content is associated with clinical outcome in stroke and myocardial infarction. Neurology 2020, 94, e2346–e2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, P.B.; Hanning, U.; Schwindt, W.; Velasco, A.; Buerke, B.; Cnyrim, C.; Minnerup, J.; Heindel, W.; Jeibmann, A.; Niederstadt, T. Ischemic Stroke: Histological Thrombus Composition and Pre-Interventional CT Attenuation Are Associated with Intervention Time and Rate of Secondary Embolism. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 44, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Neutrophil extracellular traps increased by hyperglycemia exacerbate ischemic brain damage. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 738, 135383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochazka, V.; Jonszta, T.; Czerny, D.; Krajca, J.; Roubec, M.; Macak, J.; Kovar, P.; Kovarova, P.; Pulcer, M.; Zoubkova, R.; et al. The Role of von Willebrand Factor, ADAMTS13, and Cerebral Artery Thrombus Composition in Patient Outcome Following Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 3929–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, A.; Schwarz, G.; Semerano, A.; Callea, M.; Sanvito, F.; Simionato, F.; Panni, P.; Scomazzoni, F.; Doglioni, C.; Comi, G.; et al. Large vessel occlusion stroke due to dislodged aortic valve calcification revealed by imaging and histopathology. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 408, 116573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmann, M.K.; Gunreben, I.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Kraft, P. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Cerebral Thrombi Retrieved by Mechanical Thrombectomy from Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essig, F.; Kollikowski, A.M.; Pham, M.; Solymosi, L.; Stoll, G.; Haeusler, K.G.; Kraft, P.; Schuhmann, M.K. Immunohistological Analysis of Neutrophils and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Human Thrombemboli Causing Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Scott, X.O.; Ferrer Marcelo, Y.; Almeida, V.W.; Blackwelder, P.L.; Yavagal, D.R.; Peterson, E.C.; Starke, R.M.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W.; et al. Netosis and Inflammasomes in Large Vessel Occlusion Thrombi. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 607287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dargazanli, C.; Rigau, V.; Eker, O.; Riquelme Bareiro, C.; Machi, P.; Gascou, G.; Arquizan, C.; Ayrignac, X.; Mourand, I.; Corlobé, A.; et al. High CD3+ Cells in Intracranial Thrombi Represent a Biomarker of Atherothrombotic Stroke. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.; Fitzgerald, S.; Mereuta, O.M.; Rossi, R.; O’Leary, S.; Pandit, A.; McCarthy, R.; Gilvarry, M.; Holmegaard, L.; Abrahamsson, M.; et al. Platelet-rich emboli are associated with von Willebrand factor levels and have poorer revascularization outcomes. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2020, 12, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Doostkam, S.; Reinhard, M.; Ivanovas, V.; Taschner, C.A. Immunohistochemical analysis of thrombi retrieved during treatment of acute ischemic stroke: Does stent-retriever cause intimal damage? Stroke 2013, 44, 1720–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.W.; Jeong, H.S.; Kwon, H.-J.; Song, K.S.; Kim, J. High red blood cell composition in clots is associated with successful recanalization during intra-arterial thrombectomy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woock, M.; Rossi, R.; Jabrah, D.; Douglas, A.; Redfors, P.; Nordanstig, A.; Tatlisumak, T.; Ceder, E.; Dunker, D.; Carlqvist, J.; et al. Clot signature in patients with large vessel occlusion stroke and concomitant active cancer. Eur. J. Neurol. 2025, 32, e70037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Bartolomé, L.; Payá, M.; Barbella-Aponte, R.; Restrepo Carvajal, L.; García-García, J.; Ayo-Martín, O.; Molina-Nuevo, J.D.; Serrano-Heras, G.; Juliá-Molla, E.; Pedrosa-Jiménez, M.J.; et al. Histopathological composition of thrombus material in a large cohort of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A study of atypical clots. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1563371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juega, J.; Pagola, J.; Palacio, C.; Camacho, J.; Cardona, P.; Quesada, H.; Dorado, L.; Hernandez, M.; De la Torre, C.; Muchada, M.; et al. Abstract WMP70: Etiology of Stroke Based on Early Analysis of Clot Cytometry Obtained Through First Pass Technique for Mechanical Thrombectomy. Stroke 2019, 50, AWMP70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagola, J.; Juega, J.; Dorado, L.; Hernandez-Perez, M.; Lazaro, C.; Garcia-Tornel, A.; Olive, M.; Requena, M.; Rubiera, M.; Muchada, M.; et al. Platelet Analysis in the Thrombus Plus Serum BNP for Detecting Clot-Related Atrial Fibrillation. Results from the ITACAT Multicentric Registry. Transl. Stroke Res. 2023, 16, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabrah, D.; Rossi, R.; Molina, S.; Douglas, A.; Pandit, A.; McCarthy, R.; Gilvarry, M.; Ceder, E.; Fitzgerald, S.; Dunker, D.; et al. White blood cell subtypes and neutrophil extracellular traps content as biomarkers for stroke etiology in acute ischemic stroke clots retrieved by mechanical thrombectomy. Thromb. Res. 2024, 234, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Choudhri, T.F.; Winfree, C.J.; McTaggart, R.A.; Kiss, S.; Mocco, J.; Kim, L.J.; Protopsaltis, T.S.; Zhang, Y.; Pinsky, D.J.; et al. Postischemic Cerebrovascular E-Selectin Expression Mediates Tissue Injury in Murine Stroke. Stroke 2000, 31, 3047–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merten, M.; Thiagarajan, P. P-selectin expression on platelets determines size and stability of platelet aggregates. Circulation 2000, 102, 1931–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbig, B.A.; Diamond, S.L. Thrombi produced in stagnation point flows have a core-shell structure. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2017, 10, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, O.E.; Surblyte, M.; Chandran, V.D.; Voronov, R.S. Is the endothelial cell responsible for the thrombus core and shell architecture? Med. Hypotheses 2019, 129, 109244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ma, G.; Zhang, W.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; Du, G. Neutrophil extracellular traps: A novel target for the treatment of stroke. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 241, 108328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massberg, S.; Grahl, L.; von Bruehl, M.-L.; Manukyan, D.; Pfeiler, S.; Goosmann, C.; Brinkmann, V.; Lorenz, M.; Bidzhekov, K.; Khandagale, A.B.; et al. Reciprocal coupling of coagulation and innate immunity via neutrophil serine proteases. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Brill, A.; Duerschmied, D.; Schatzberg, D.; Monestier, M.; Myers, D.D.; Wrobleski, S.K.; Wakefield, T.W.; Hartwig, J.H.; Wagner, D.D. Extracellular DNA traps promote thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15880–15885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, A.S.; Obi, A.T.; Diaz, J.A.; Henke, P.K. The Emerging Role of NETs in Venous Thrombosis and Immunothrombosis. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D. The role of P-selectin/PSGL-1 in regulating NETs as a novel mechanism in cerebral ischemic injury. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1442613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, R.; Yue, H.; Zhang, X.; Pan, X.; Sun, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, C.; Guo, Y. Interaction between neutrophil extracellular traps and cardiomyocytes contributes to atrial fibrillation progression. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Shao, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Tang, B. Neutrophil extracellular traps and neutrophil extracellular traps-related genes are involved in new-onset atrial fibrillation in LPS-induced sepsis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 138, 112550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Roth, S.; Zhang, S.; Kopczak, A.; Mami, S.; Asare, Y.; Georgakis, M.K.; Messerer, D.; Horn, A.; Shemer, R.; et al. DNA-sensing inflammasomes cause recurrent atherosclerotic stroke. Nature 2024, 633, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengozzi, L.; Barison, I.; Malý, M.; Lorenzoni, G.; Fedrigo, M.; Castellani, C.; Gregori, D.; Malý, P.; Matěj, R.; Toušek, P.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Thrombolysis Resistance: New Insights for Targeting Therapies. Stroke 2024, 55, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costamagna, G.; Bonato, S.; Corti, S.; Meneri, M. Advancing Stroke Research on Cerebral Thrombi with Omic Technologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, F.; Geddes-McAlister, J.; Mann, M.; Bantscheff, M. The emerging role of mass spectrometry-based proteomics in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunica, N.; Van Den Helm, S.; McCafferty, C.; Swaney, E.; Cai, T.; Attard, C.; Karlaftis, V.; Monagle, P.; Ignjatovic, V. Proteomics in Thrombosis and Hemostasis. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 122, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doche, E.; Sulowski, C.; Guigonis, J.-M.; Graslin, F.; Casolla, B.; Hak, J.-F.; Carle, X.; Brunel, H.; Lindenthal, S.; Martin, J.-C.; et al. How Clot Composition Influences Fibrinolysis in the Acute Phase of Stroke: A Proteomic Study of Cerebral Thrombi. Stroke 2024, 55, 1818–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargazanli, C.; Zub, E.; Deverdun, J.; Decourcelle, M.; de Bock, F.; Labreuche, J.; Lefèvre, P.-H.; Gascou, G.; Derraz, I.; Riquelme Bareiro, C.; et al. Machine Learning Analysis of the Cerebrovascular Thrombi Proteome in Human Ischemic Stroke: An Exploratory Study. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 575376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.; Mereuta, O.M.; Barbachan e Silva, M.; Molina Gil, S.; Douglas, A.; Pandit, A.; Gilvarry, M.; McCarthy, R.; O’Connell, S.; Tierney, C.; et al. Potential Biomarkers of Acute Ischemic Stroke Etiology Revealed by Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomic Characterization of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Blood Clots. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 854846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Jung, J.W.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yoon, B.-W.; Han, D.; Ko, S.-B. Proteomic Analyses of Clots Identify Stroke Etiologies in Patients Undergoing Endovascular Therapy. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2025, 31, e70340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul, S.; Ghozy, S.; Mereuta, O.M.; Senol, Y.C.; Orscelik, A.; Kobeissi, H.; Gupta, R.; Brinjikji, W.; Kallmes, D.F.; Kadirvel, R. Metabolite signature in acute ischemic stroke thrombi: A systematic review. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2023, 56, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martha, S.R.; Levy, S.H.; Federico, E.; Levitt, M.R.; Walker, M. Machine Learning Analysis of the Cerebrovascular Thrombi Lipidome in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2023, 55, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Bai, X.; Hao, J.; Xu, X.; Lin, F.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, C.; Dai, G.; Peng, F.; Zhang, M.; et al. Thrombosis origin identification of cardioembolism and large artery atherosclerosis by distinct metabolites. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2023, 15, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osakada, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Morihara, R.; Matsumoto, N.; Sasaki, R.; Tadokoro, K.; Nomura, E.; Kawahara, Y.; Omote, Y.; Hishikawa, N.; et al. 4-Hydroxyl-2-Nonenal Localized Expression Pattern in Retrieved Clots is Associated with Large Artery Atherosclerosis in Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suissa, L.; Guigonis, J.-M.; Graslin, F.; Robinet-Borgomano, E.; Chau, Y.; Sedat, J.; Lindenthal, S.; Pourcher, T. Combined Omic Analyzes of Cerebral Thrombi: A New Molecular Approach to Identify Cardioembolic Stroke Origin. Stroke 2021, 52, 2892–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Fitzgerald, S.; Ayers-Ringler, J.; Espina, V.; Mueller, C.; Rucker, S.; Kadirvel, R.; Kallmes, D.; Brinjikji, W. Proteomic Analysis of Cardioembolic and Large Artery Atherosclerotic Clots Using Reverse Phase Protein Array Technology Reveals Key Cellular Interactions Within Clot Microenvironments. Cureus 2021, 13, e13499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Pedrera, C.; Oteros, R.; Ibáñez-Costa, A.; Luque-Tévar, M.; Muñoz-Barrera, L.; Barbarroja, N.; Chicano-Gálvez, E.; Marta-Enguita, J.; Orbe, J.; Velasco, F.; et al. The thrombus proteome in stroke reveals a key role of the innate immune system and new insights associated with its etiology, severity, and prognosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 2894–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Chauhan, G.; Traylor, M.; Sargurupremraj, M.; Okada, Y.; Mishra, A.; Rutten-Jacobs, L.; Giese, A.-K.; van der Laan, S.W.; Gretarsdottir, S.; et al. Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traylor, M.; Farrall, M.; Holliday, E.G.; Sudlow, C.; Hopewell, J.C.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Fornage, M.; Ikram, M.A.; Malik, R.; Bevan, S.; et al. Genetic risk factors for ischaemic stroke and its subtypes (the METASTROKE Collaboration): A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagodic, A.; Zivalj, D.; Krsek, A.; Baticic, L. Genetic Architecture of Ischemic Stroke: Insights from Genome-Wide Association Studies and Beyond. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, B.H.; Kim, H.S.; Yoon, W.; Lee, Y.Y.; Baek, J.M.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, S.K. Inflammatory mediator expression within retrieved clots in acute ischemic stroke. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukurba, K.R.; Montgomery, S.B. RNA Sequencing and Analysis. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2015, 2015, 951–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutino, V.M.; Fricano, S.; Chien, A.; Patel, T.R.; Monteiro, A.; Rai, H.H.; Dmytriw, A.A.; Chaves, L.D.; Waqas, M.; Levy, E.I.; et al. Gene expression profiles of ischemic stroke clots retrieved by mechanical thrombectomy are associated with disease etiology. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2023, 15, e33–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renedo, D.; Barak, T.; DeLong, J.; Acosta, J.N.; Sujijantarat, N.; Koo, A.; Antonios, J.; Rivier, C.; Clocchiatti-Tuozzo, S.; Huo, S.; et al. Characterizing Stroke Clots Using Single-Cell Sequencing. medRxiv 2025, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, B.A.; Poppenberg, K.E.; Ciecierska, S.-S.; Lim, J.; Baig, A.A.; Jaikumar, V.; Raygor, K.P.; Patel, T.R.; Shah, M.; Levy, E.I.; et al. Decoding Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Outcomes After Ischemic Stroke Thrombectomy by RNA Sequencing of Retrieved Clots. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2024, 28, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, B.A.; Poppenberg, K.E.; Ciecierska, S.-S.K.; Baig, A.A.; Raygor, K.P.; Patel, T.R.; Shah, M.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Tutino, V.M. Hybrid Clot Histomic–Transcriptomic Models Predict Functional Outcome After Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurosurgery 2024, 95, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, K.; Philippou, H.; Ariëns, R.A.S. Ischaemic Stroke, Thromboembolism and Clot Structure. Neuroscience 2024, 550, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaGrange, D.D.; Reymond, P.; Brina, O.; Zboray, R.; Neels, A.; Wanke, I.; Lövblad, K.-O. Spatial heterogeneity of occlusive thrombus in acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review. J. Neuroradiol. 2023, 50, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinjikji, W.; Mereuta, O.M.; Dai, D.; Kallmes, D.F.; Savastano, L.; Liu, Y.; Nimjee, S.M.; Nogueira, R.G.; Abbasi, M.; Kadirvel, R. Mechanisms of fibrinolysis resistance and potential targets for thrombolysis in acute ischaemic stroke: Lessons from retrieved stroke emboli. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2021, 6, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denorme, F.; Langhauser, F.; Desender, L.; Vandenbulcke, A.; Rottensteiner, H.; Plaimauer, B.; François, O.; Andersson, T.; Deckmyn, H.; Scheiflinger, F.; et al. ADAMTS13-mediated thrombolysis of t-PA-resistant occlusions in ischemic stroke in mice. Blood 2016, 127, 2337–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesten, J.M.; van der Schaaf, I.C.; van der Graaf, Y.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biessels, G.J.; Horsch, A.D.; Dankbaar, J.W.; Luitse, M.J.; van Seeters, T.; Smit, E.J.; et al. Predictive value of thrombus attenuation on thin-slice non-contrast CT for persistent occlusion after intravenous thrombolysis. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 37, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, J.; Pedraza, S.; Demchuk, A.; Daunis, I.E.J.; Termes, H.; Blasco, G.; Soria, G.; Boada, I.; Remollo, S.; Baños, J.; et al. Quantification of thrombus hounsfield units on noncontrast CT predicts stroke subtype and early recanalization after intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, P.B.; Jeibmann, A.; Minnerup, J.; Broocks, G.; Nawabi, J.; Schön, G.; Fiehler, J.; Wildgruber, M.; Heindel, W.; Kemmling, A.; et al. Histological Clot Composition Is Associated with Preinterventional Clot Migration in Acute Stroke Patients. Stroke 2019, 50, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, S.; Mereuta, O.M.; Doyle, K.M.; Dai, D.; Kadirvel, R.; Kallmes, D.F.; Brinjikji, W. Correlation of imaging and histopathology of thrombi in acute ischemic stroke with etiology and outcome. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2019, 63, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Brinjikji, W.; Abbasi, M.; Dai, D.; Arturo Larco, J.L.; Madhani, S.I.; Shahid, A.H.; Mereuta, O.M.; Nogueira, R.G.; Kvamme, P.; et al. Quantification of clot spatial heterogeneity and its impact on thrombectomy. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2022, 14, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Pinheiro, A.; Brinjikji, W.; Abbasi, M.; Al-Bayati, A.R.; Mohammaden, M.H.; Viana, L.S.; Ferreira, F.; Abdelhamid, H.; Bhatt, N.R.; et al. Clot composition and recanalization outcomes in mechanical thrombectomy. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2024, 16, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y.; Kan, H.; Kano, Y.; Onda, K.; Sakurai, K.; Takada, K.; Ueki, Y.; Matsukawa, N.; Hillis, A.E.; Oishi, K. Longitudinal Changes in Iron and Myelination Within Ischemic Lesions Associate with Neurological Outcomes: A Pilot Study. Stroke 2024, 55, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baysoy, A.; Bai, Z.; Satija, R.; Fan, R. The technological landscape and applications of single-cell multi-omics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 695–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| 1 | Large-artery atherosclerosis (embolus/thrombosis) |
| 2 | Cardioembolism (high-risk/medium-risk) |
| 3 | Small-vessel occlusion (lacune) |
| 4 | Stroke of other determined etiology |
| 5 | Stroke of undetermined etiology (“cryptogenic stroke”) |
| a. Two or more causes identified | |
| b. Negative evaluation | |
| c. Incomplete evaluation |
| Component | Staining Technique |
|---|---|
| Red blood cells | H&E staining [48], MSB (selective quantification) [49], IHC CD235a antigen [50,51] |
| Fibrin | H&E staining [48], MSB (selective quantification) [49], Picro-Mallory (can also detect fibrin maturity in thrombi) [21], Ladewig trichrome [52] |
| Platelets | MSB [49], CD41 [53], CD42b [38,54,55,56], CD61 [57] |
| White blood cells | H&E staining [48], IHC CD45 antigen [58,59], neutrophil elastase [58], neutrophil myeloperoxidase [51] |
| Monocytes | Ly6G [60], CD14 [58], CD15 [61], CD68 [44,62,63] |
| Granulocytes | Ly6G [60] |
| Neutrophils | Ly6G [60], CD15 [61], CD66b [47,64] NET-associated: citrullinated histones, caspase-1, and apoptosis-associated speck-like protein [65], granular neutrophil proteins (MPO), extracellular DNA [47] |
| Eosinophil | CD15 [61] |
| T-lymphocyte | CD3 [66], CD4 [63] |
| B-lymphocyte | CD20 [44] |
| Coagulation proteins | antibodies against vWF [50,56,61,63,67] |
| tPA | plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 [50], protease nexin-1 [50] |
| Elastic collagen fibers | Elastica van Gieson [52,68] |
| Hemosiderin/iron | Prussian blue [52] |
| Calcifications | Von Kossa [52,68] |
| Collagen | Masson’s trichrome [21] |
| WBC Type | LAA Clot | CE Clot | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Innate Immune Cells | ↓ (less enriched) | ↑ (more enriched) | [44,52,58,64,74] |
CD68+ (Macrophages) | ↓ | ↑ | [44,52] |
NE+ MPO+ Neutrophils | ↓ | ↑ | [58,64,74] |
| Adaptive Immune Cells | ↑ | ↓ | [66,72,73,74] |
CD3+ (lymphocytes) | ↑ | ↓ | [66,74] |
CD4+ (Helper T cells) | ↑ | ↓ | [72,73] |
| Reference | Sample Size | Technique | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tutino, 2023 [107] | 38 (21 CE, 6 LAA, 5 other determined cause, 6 cryptogenic) | Paired-end RNA-seq |
|
| Specific limitations: Descriptive observational findings only. Does not include predictive modeling or external validation. Validation cohort contained low RNA concentrations, and only 3 DEGs could be tested. | |||
| Renedo, 2025 [108] | 12 (6 CE, 4 LAA, 2 venous) | scRNA-seq |
|
| Specific limitations: Small sample size. Descriptive observational findings only. Does not include predictive modeling or external validation. |
| Clot Components | LAA Clot | CE Clot |
|---|---|---|
| RBCs | ↑ (more enriched) | ↓ (less enriched) |
| Platelets/Fibrin | ↓ | ↑ |
| Innate Immune Cells | ↓ | ↑ |
| Adaptive Immune Cells | ↑ | ↓ |
| Multiomic pathways | Multiple unique associations | Multiple unique associations |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosyakovsky, J.; Rossitto, C.P.; Antonios, J.P.; Renedo, D.; Stapleton, C.J.; Sansing, L.H.; Navaratnam, D.S.; Giles, J.A.; Patel, A.B.; Matouk, C.C.; et al. Clot Composition and Ischemic Stroke Etiology: A Contemporary Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6203. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176203
Kosyakovsky J, Rossitto CP, Antonios JP, Renedo D, Stapleton CJ, Sansing LH, Navaratnam DS, Giles JA, Patel AB, Matouk CC, et al. Clot Composition and Ischemic Stroke Etiology: A Contemporary Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6203. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176203
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosyakovsky, Jacob, Christina P. Rossitto, Joseph P. Antonios, Daniela Renedo, Christopher J. Stapleton, Lauren H. Sansing, Dhasakumar S. Navaratnam, James A. Giles, Aman B. Patel, Charles C. Matouk, and et al. 2025. "Clot Composition and Ischemic Stroke Etiology: A Contemporary Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6203. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176203
APA StyleKosyakovsky, J., Rossitto, C. P., Antonios, J. P., Renedo, D., Stapleton, C. J., Sansing, L. H., Navaratnam, D. S., Giles, J. A., Patel, A. B., Matouk, C. C., & Sujijantarat, N. (2025). Clot Composition and Ischemic Stroke Etiology: A Contemporary Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6203. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176203







