Sex Differences in Patients with MASLD and Their Association with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: Insights from the Polish Gallstone Surgery Registry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patient Involvement
- -
- BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2;
- -
- Fasting serum glucose ≥ 5.6 mmol/L (100 mg/dL) or 2 h post-load glucose level ≥ 7.8 mmol/L (≥140 mg/dL) or HbA1c ≥ 5.7% (39 mmol/L) or diabetes mellitus type 2 (T2DM) or treatment for T2DM;
- -
- Blood pressure ≥ 130/85 mmHg or specific antihypertensive drug treatment;
- -
- Plasma triglycerides ≥ 1.7 mmol/L (150 mg/dL) or lipid lowering treatment;
- -
- Plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) ≤ 1.0 mmol/L (40 mg/dL)—men and ≤ 1.3 mmol/L (50 mg/dL)—women or lipid lowering treatment.
2.3. Statistical Analyses
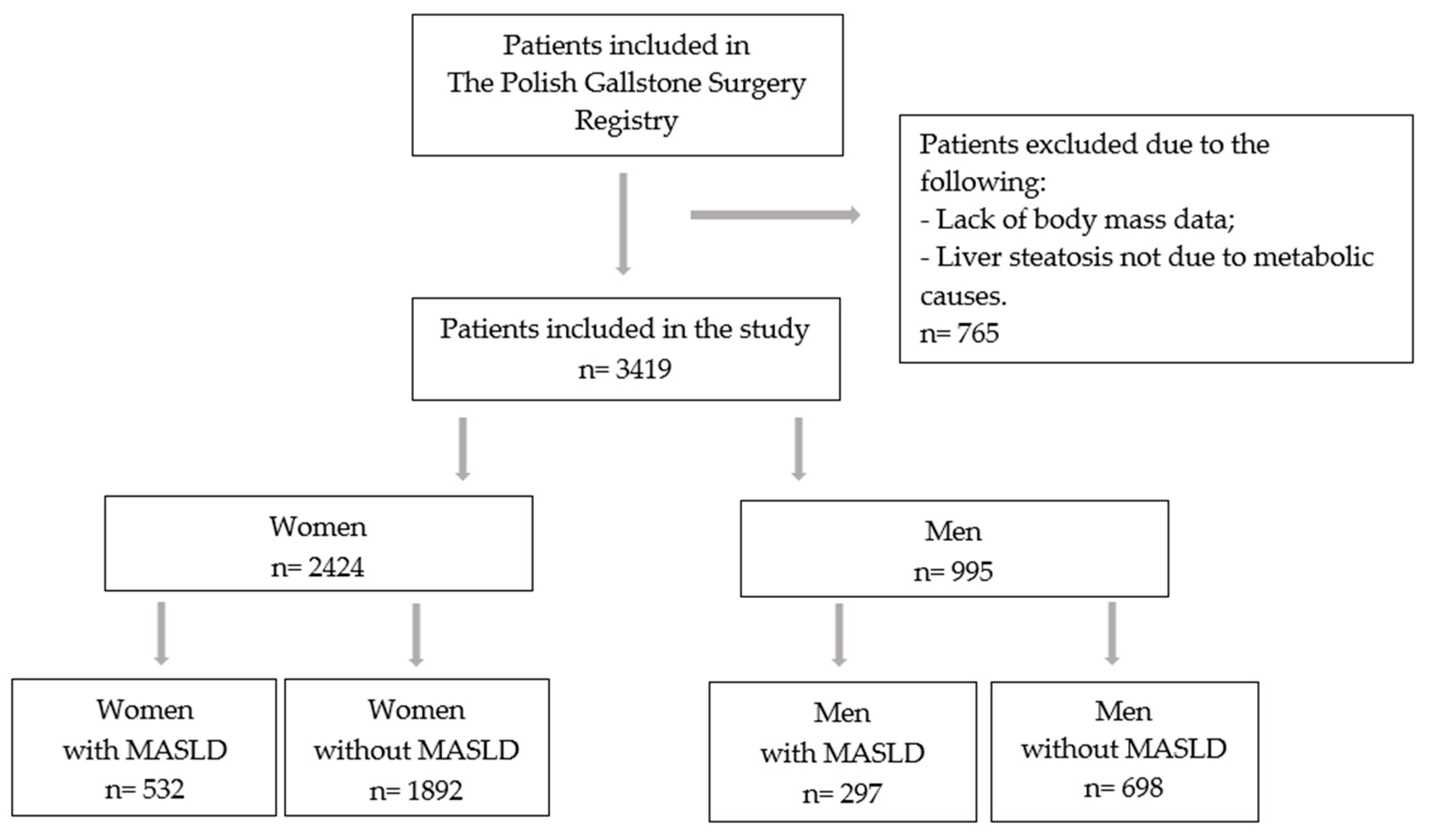
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Prevalence of MASLD in Men and Women
3.3. Prevalence of Cardiometabolic MASLD Diagnostic Criteria in Men and Women According to BMI
3.4. Comparison of Men and Women with MASLD
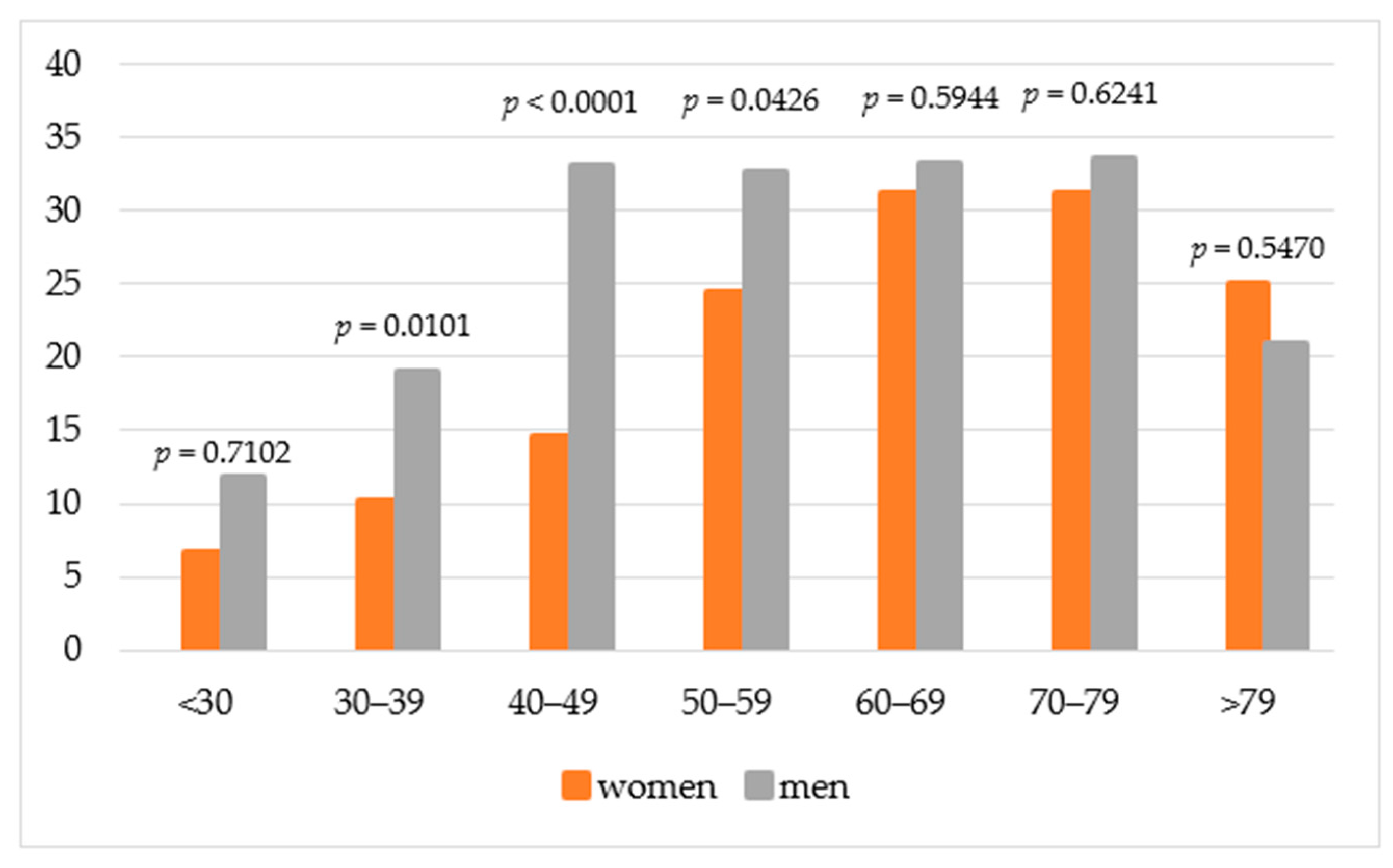
3.5. Prevalence of MASLD and Stratification by Age, BMI, and Metabolic Disorder
3.6. Risk Factors for MASLD
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. NAFLD Nomenclature consensus group. A multi-society Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J. Hepatol. 2023, 6, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janczura, J.; Brzdęk, M.; Dobrowolska, K.; Flisiak, R.; Martonik, D.; Brzdęk, K.; Pleśniak, R.; Kukla-Woźnica, D.; Wajdowicz, M.; Zarębska-Michaluk, D. Steatotic liver disease in patients treated for chronic hepatitis B. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2025, 135, 16942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, W.; Corey, K.E.; Luther, J.; Goodman, R.P.; Schaefer, E.A. Prevalence and Clinical Correlation of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Alcohol-Related Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction and Alcohol Associated Liver Disease (MetALD). J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2025, 15, 102492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimpin, L.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Negro, F.; Corbould, E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Webber, L.; Sheron, N. Burden of liver disease in Europe: Epidemiology and analysis of risk factors to identify prevention policies. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 718–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.H.; Tincopa, M.A.; Tavaglione, F.; Ajmera, V.H.; Richards, L.M.; Amangurbanova, M.; Butcher, C.; Hernandez, C.; Madamba, E.; Singh, S. Prevalence of steatotic liver disease, advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis among community-dwelling overweight and obese individuals in the USA. Gut 2024, 73, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Sun, L.; Hao, Y.; Li, P.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, X.; Hu, J.; Wei, H. From NAFLD to MASLD: When metabolic comorbidity matters. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zheng, X.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Overlap prevalence and interaction effect of cardiometabolic risk factors for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Nutr. Metab. 2025, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Heterogeneous pathomechanisms and effectiveness of metabolism-based treatment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayén, A.L.; Sabra, M.; Aglago, E.K.; Perlemuter, G.; Voican, C.; Ramos, I.; Debras, C.; Blanco, J.; Viallon, V.; Ferrari, P.; et al. Hepatic steatosis, metabolic dysfunction and risk of mortality: Findings from a multinational prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Ballestri, S.; Fairweather, D.; Win, S.; Than, T.A.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A. Sex differences in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: State of the art and identification of research gaps. Hepatology. 2019, 70, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.L.; Madak-Erdogan, Z. Estrogens and female liver health. Steroids. 2018, 133, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosimo, S.; Mitra, S.K.; Chaudhury, T.; Marchesini, G. Insulin resistance and metabolic flexibility as drivers of liver and cardiac disease in T2DM. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 206, 111016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, K.; Abrams, G.A. Metabolic liver disease of obesity and role of adipose tissue in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 3540–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yu, W.; Jiang, G.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Xie, L.; Bai, X.; Cui, P.; Chen, Q.; Lou, Y.; et al. Global Epidemiology of Gallstones in the 21st Century: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Rydqvist, P.; Ramezani, T.; Haas, J.S.; Bantel, H.; Buggisch, P.; Geier, A.; Hofmann, W.P.; Mauss, S.; Roeb, E.; et al. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis Diagnosis and Management in Germany: Insights From an Expert Consensus Panel. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e70225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesch-Dietlen, F.; Pérez-Morales, A.G.; Grube-Pagola, P.; González-Santes, M.; Díaz-Roesch, F.; Triana-Romero, A.; Roesch-Ramos, L.; Remes-Troche, J.M.; Cruz-Aguilar, M. Prevalence of metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) in patients with gallstone disease. Study on a cohort of cases in South-Southeastern Mexico. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2023, 88, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Shi, R.; Ma, M.; Lin, H.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, B. Elevated LDL-c may warn of the risk of gallbladder stones in the patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A case-control study. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2024, 48, 102363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, H.J. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and gallstone risk in nonobese and lean individuals. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 36, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanzadeh, D.M.; Holmboe, S.A.; Sørensen, L.T.; Linneberg, A.; Andersson, A.M.; Jørgensen, T. Are incident gallstones associated to sex-dependent changes with age? A cohort study. Andrology 2017, 5, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogabe, M.; Okahisa, T.; Kagawa, M.; Kashihara, T.; Fujmoto, S.; Kawaguchi, T.; Yokoyama, R.; Kagemoto, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kida, Y.; et al. Association of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease with gallstone development: A longitudinal study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 39, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, F.; Pasdar, Y.; Nazar, M.M.; Darbandi, M. Association between obesity phenotypes and non-alcoholic fatty liver: A large population-based study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresneda, S.; Abbate, M.; Busquets-Cortés, C.; López-González, A.; Fuster-Parra, P.; Bennasar-Veny, M.; Yáñez, A.M. Sex and age differences in the association of fatty liver index-defined non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiometabolic risk factors: A cross-sectional study. Biol. Sex. Differ. 2022, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Cheng, S. Heart-Liver Axis Research Collaboration: Sex differences in prevalence and prognosis of steatotic liver disease phenotypes: Biological sex matters. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, e68–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.; Shao, Z.; Wei, W.; Shen, P.; Shen, G. Sex-specific prevalence and risk factors of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease among 75,570 individuals in eastern China. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1241169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Tian, S.; Wu, J.; Liang, X.Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.L.; Xiao, J.; et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for metabolic associated fatty liver disease in an urban population in China: A cross-sectional comparative study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Qin, J.J.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, M.M.; Sun, T.; Huang, X.; Deng, K.Q.; Zuo, X.; Yao, D.; et al. The prevalence of MAFLD and its association with atrial fibrillation in a nationwide health check-up population in China. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1007171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Gong, M.; Yuan, G.; Wang, Z. Sex Hormone: A Potential Target at Treating Female Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease? J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2025, 15, 102459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.S.; Santos, J.D.M.; Cruz, A.G.; Camargo, F.N.; Talarico, C.H.Z.; Santos, A.R.M.; Silva, C.A.A.; Morgan, H.J.N.; Matos, S.L.; Araujo, L.C.C.; et al. Hepatic Estrogen Receptor Alpha Overexpression Protects Against Hepatic Insulin Resistance and MASLD. Pathophysiology 2025, 32, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubini, A.; Della Torre, S.; Pelusi, S.; Valenti, L. Sexual dimorphism of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Trends. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.M.; Guo, Y.M.; Jiang, S.Y.; Li, K.X.; Zheng, Y.F.; Guo, X.G.; Ren, Z.Y. Potential predictive role of Non-HDL to HDL Cholesterol Ratio (NHHR) in MASLD: Focus on obese and type 2 diabetic populations. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025, 25, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhou, F.; Shen, J. Trends in the prevalence of cardiometabolic diseases in US adults with newly diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes, 1988–2020. Public Health 2025, 239, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Husain, M.; Ahima, R.; Arca, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Diehl, A.M.; Fontana, L.; Foo, R.; Frühbeck, G.; et al. Clinical staging to guide management of metabolic disorders and their sequelae: A European Atherosclerosis Society consensus statement. Eur. Heart J. 2025, ehaf314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinical Characteristic | Women n = 2424 | Men n = 995 | p MASLD Women vs. MASLD Men | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MASLD n = 532 | Non-MASLD n = 1892 | p | MASLD n = 297 | Non-MASLD n = 698 | p | ||
| Age, years, mean (SD) | 59.6 (13.0) | 52.4 (15.5) | <0.0001 | 58.5 (13.2) | 56.1 (15.6) | 0.0150 | 0.2383 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | |||||||
| <18.5 | 1 (0.2) | 23 (1.2) | <0.0001 | 0 (0.0) | 3 (0.4) | <0.0001 | 0.0762 |
| 18.5–24.9 | 61 (11.5) | 613 (32.4) | 31 (10.4) | 144 (20.6) | |||
| 25.0–29.9 | 164 (30.8) | 686 (36.3) | 116 (39.1) | 344 (49.3) | |||
| ≥30 | 306 (57.5) | 570 (30.1) | 150 (50.5) | 207 (29.7) | |||
| BMI, kg/m2, mean (SD) | 31.5 (5.7) | 27.7 (5.2) | <0.0001 | 30.4 (4.8) | 28.1 (4.3) | <0.0001 | 0.0032 |
| Comorbidities | |||||||
| Hypertension | 292 (54.9) | 662 (35) | <0.0001 | 169 (56.9) | 310 (44.4) | 0.0003 | 0.5755 |
| T2DM | 115 (21.6) | 153 (8.1) | <0.0001 | 60 (20.2) | 87 (12.5) | 0.0016 | 0.6323 |
| Prediabetes | 29 (5.5) | 59 (3.1) | 0.0110 | 7 (2.4) | 9 (1.3) | 0.2697 | 0.0361 |
| T2DM or prediabetes | 144 (27.1) | 212 (11.2) | <0.0001 | 67 (22.6) | 96 (13.8) | 0.0006 | 0.1530 |
| Atherogenic dyslipidemia | 255 (47.9) | 30 (1.6) | <0.0001 | 125 (42.1) | 22 (3.2) | <0.0001 | 0.1054 |
| Chronic coronary syndrome | 29 (5.5) | 88 (4.7) | 0.4469 | 30 (10.1) | 57 (8.2) | 0.3228 | 0.0125 |
| Previous myocardial infarction | 13 (2.4) | 32 (1.7) | 0.2561 | 16 (5.4) | 26 (3.7) | 0.2328 | 0.0270 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 80 (15) | 135 (7.1) | <0.0001 | 39 (13.1) | 48 (6.9) | 0.0014 | 0.4529 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 21 (3.9) | 47 (2.5) | 0.0710 | 20 (6.7) | 35 (5) | 0.2774 | 0.0760 |
| Thromboembolism events | 7 (1.3) | 18 (1) | 0.4623 | 15 (5.1) | 25 (3.6) | 0.2804 | 0.0013 |
| Venous thromboembolism | 14 (2.6) | 31 (1.4) | 0.1343 | 10 (3.4) | 20 (2.9) | 0.6720 | 0.5448 |
| Heart failure | 12 (2.3) | 41 (2.2) | 0.9017 | 14 (4.7) | 27 (3.9) | 0.5392 | 0.0515 |
| Acute pancreatitis previous | 29 (5.5) | 76 (4.0) | 0.1511 | 16 (5.4) | 43 (6.2) | 0.6365 | 0.9689 |
| Chronic pancreatitis | 3 (0.6) | 9 (0.5) | 0.7328 | 2 (0.7) | 5 (0.7) | 1 | 1 |
| Malignancy | 47 (8.8) | 113 (6) | 0.0188 | 16 (5.4) | 47 (6.7) | 0.4249 | 0.0725 |
| Criteria of MASLD Diagnosis | All MASLD n = 829 | Women with MASLD n = 532 | Men with MASLD n = 297 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 criterion | 162 (19.5) | 99 (18.6) | 63 (21.2) | 0.3648 |
| 2 criteria | 493 (59.5) | 318 (59.8) | 175 (58.9) | 0.8107 |
| 3 criteria | 147 (17.7) | 98 (18.4) | 49 (16.5) | 0.4871 |
| 4 criteria | 27 (3.3) | 17 (3.2) | 10 (3.4) | 0.8939 |
| BMI ≤ 24.9 kg/m2 n = 876 | BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2 n = 1310 | BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 n = 1233 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women n = 698 | Men n = 178 | p | Women n = 850 | Men n = 460 | p | Women n = 876 | Men n = 357 | p | |
| MASLD | 62 (8.9) | 31 (17.4) | 0.0010 | 164 (19.3) | 116 (25.2) | 0.0126 | 306 (34.9) | 150 (42.0) | 0.0194 |
| Hypertension | 163 (23.4) | 67 (37.6) | 0.0001 | 353 (41.5) | 198 (43.0) | 0.5962 | 438 (50.0) | 214 (59.9) | 0.0015 |
| T2DM or prediabetes | 40 (5.7) | 20 (11.2) | 0.0094 | 117 (13.8) | 57 (12.4) | 0.4845 | 199 (22.7) | 86 (24.1) | 0.6040 |
| Atherogenic dyslipidemia | 47 (6.7) | 25 (14.0) | 0.0015 | 61 (7.2) | 32 (7.0) | 0.8824 | 177 (20.2) | 90 (25.2) | 0.0530 |
| Overweight or Obesity n = 2543 | Hypertension n = 1433 | T2DM or Prediabetes n = 519 | Atherogenic Dyslipidemia n = 432 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 736 (28.9) | 461 (32.2) | 211 (40.7) | 380 (88) |
| Women | 470/1726 (27.2) | 292/954 (30.6) | 144/356 (40.4) | 255/285 (89.5) |
| Men | 266/817 (32.6) | 169/479 (35.3) | 67/163 (41.1) | 125/147 (85) |
| p value | 0.0057 | 0.0740 | 0.8879 | 0.1791 |
| Age < 50 Years | Age ≥ 50 Years | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multivariable OR | 95% CI | p | Multivariable OR | 95% CI | p | ||
| Gender | Female | Ref. | Ref. | ||||
| Male | 2.55 | 1.83–3.56 | <0.0001 | 1.14 | 0.93–1.4 | 0.2146 | |
| BMI kg/m2 | <25 | Ref. | Ref. | ||||
| 25.0–29.9 | 1.87 | 1.11–3.14 | <0.0186 | 1.99 | 1.48–2.68 | <0.001 | |
| ≥30 | 6.53 | 4.08–10.47 | <0.0001 | 3.90 | 2.92–5.22 | <0.0001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorczyca-Głowacka, I.; Kołomańska, M.; Mazurkiewicz, R.; Niżnik, M.; Ratnicki, K.; Czerniak, M.; Myrcha, P.; Lenarcik, S.; Mitura, K.; Kacprzak, L.; et al. Sex Differences in Patients with MASLD and Their Association with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: Insights from the Polish Gallstone Surgery Registry. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176158
Gorczyca-Głowacka I, Kołomańska M, Mazurkiewicz R, Niżnik M, Ratnicki K, Czerniak M, Myrcha P, Lenarcik S, Mitura K, Kacprzak L, et al. Sex Differences in Patients with MASLD and Their Association with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: Insights from the Polish Gallstone Surgery Registry. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176158
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorczyca-Głowacka, Iwona, Magdalena Kołomańska, Robert Mazurkiewicz, Marcin Niżnik, Krzysztof Ratnicki, Małgorzata Czerniak, Piotr Myrcha, Sebastian Lenarcik, Kryspin Mitura, Laura Kacprzak, and et al. 2025. "Sex Differences in Patients with MASLD and Their Association with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: Insights from the Polish Gallstone Surgery Registry" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176158
APA StyleGorczyca-Głowacka, I., Kołomańska, M., Mazurkiewicz, R., Niżnik, M., Ratnicki, K., Czerniak, M., Myrcha, P., Lenarcik, S., Mitura, K., Kacprzak, L., Pajer, M., Richter, P., Rapacz, K., Sroczyński, M., Szmit, M., & Nawacki, Ł. (2025). Sex Differences in Patients with MASLD and Their Association with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: Insights from the Polish Gallstone Surgery Registry. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176158








