Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Biparametric MRI for Detecting Prostate Cancer—A Comparative Multireader Multicase Accuracy Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. MRI Protocol
2.3. AI Decision
2.4. Network Training and Evaluation
2.5. Radiological Assessment
2.6. Reference Standard
2.7. Study End Points
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
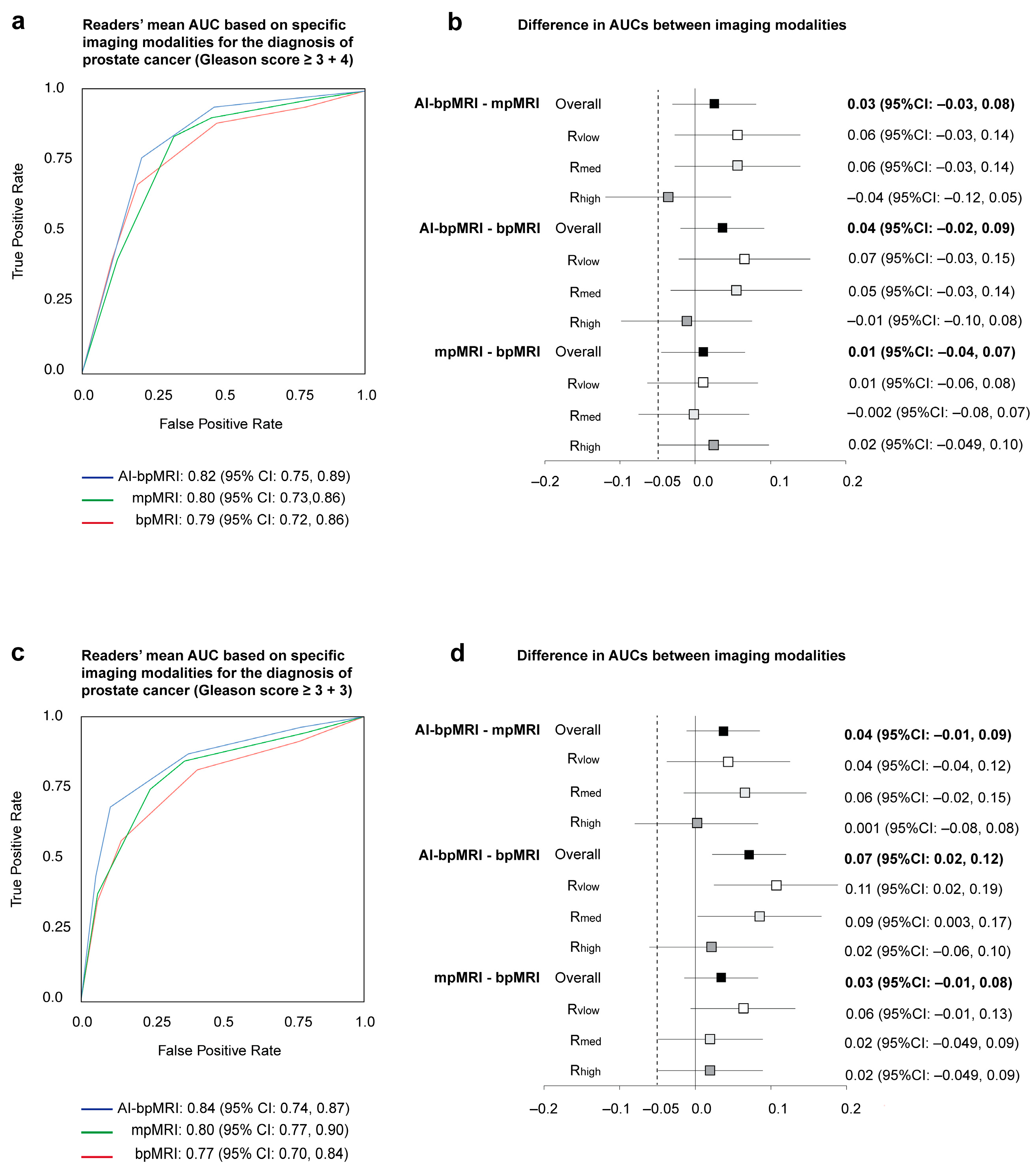
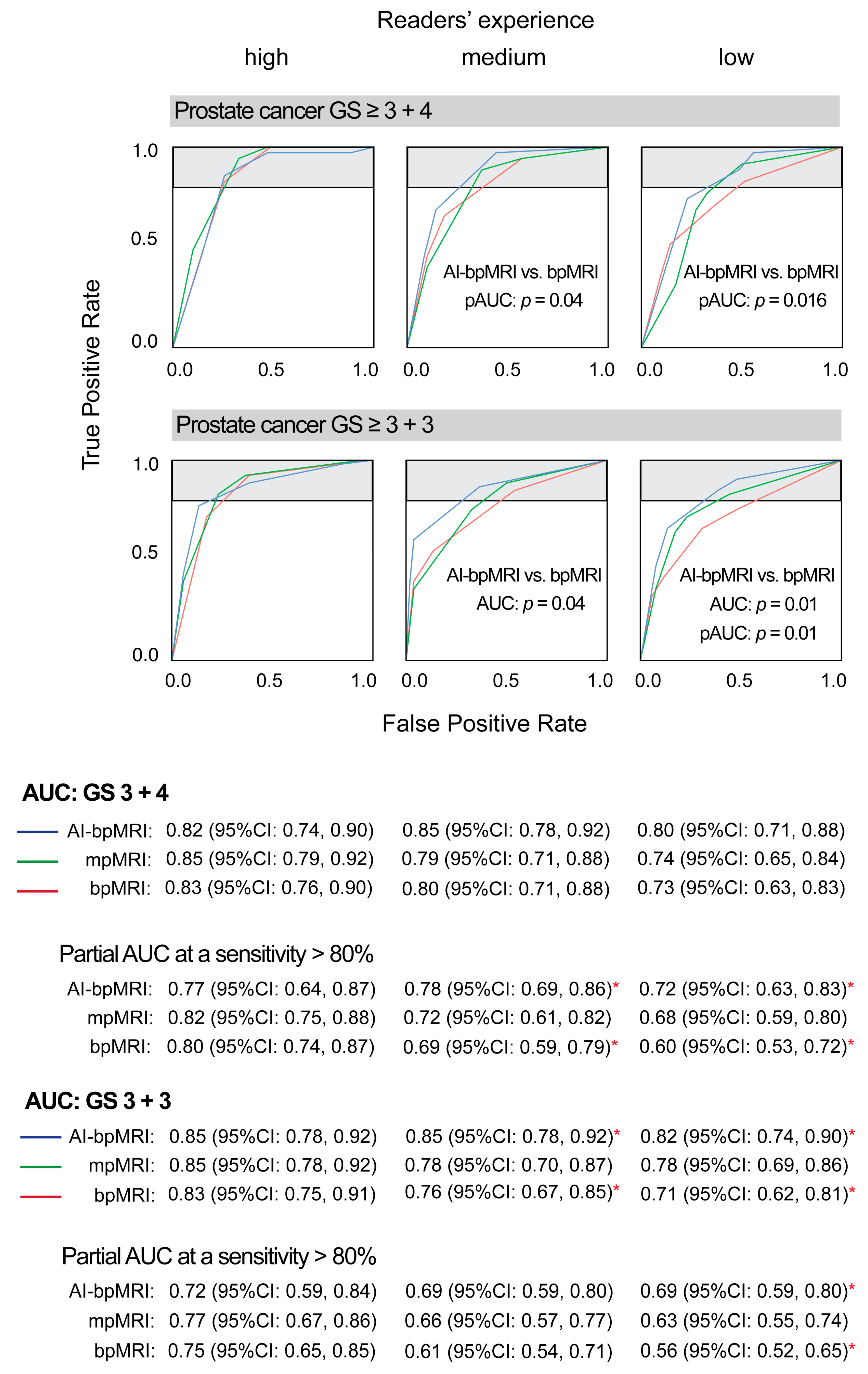
3.1. Area Under the ROC Curve
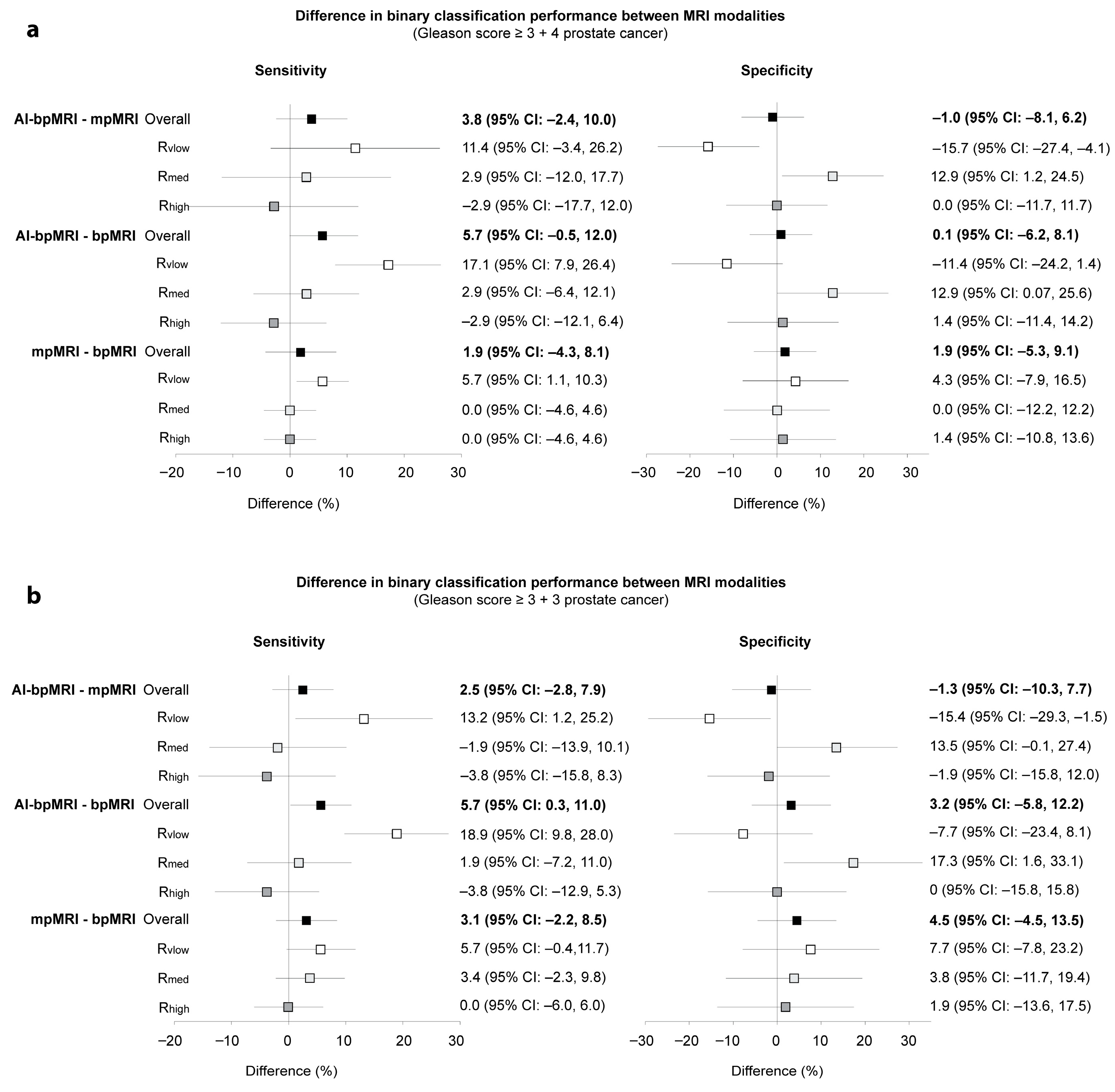
3.2. Binary Accuracy Measures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI-bpMRI | AI-assisted biparametric MRI |
| PCa | prostate cancer |
| mpMRI | multiparametric MRI |
| bpMRI | biparametric MRI |
| AUC | area under the receiver operating characteristic curves |
| pAUCs | partial AUCs |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| GS | Gleason score |
| T2w | T2-weighted |
| DWI | diffusion-weighted imaging |
| DCE | dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging |
| PI-RADS | Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System |
| VGG | Visual Geometry Group |
| BCE | binary cross entropy |
| CCE | categorical cross entropy |
| MRMC | multireader multicase |
| FFPE | formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded |
| H&E | haematoxilin and eosin |
| CI | confidence interval |
| LR+ | likelihood ratio for a positive test result |
| LR− | likelihood ratio for a negative test result |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornford, P.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Brunckhorst, O.; Darraugh, J.; Eberli, D.; De Meerleer, G.; De Santis, M.; Farolfi, A.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-ISUP-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2024 Update. Part I: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2024, 86, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjurlin, M.A.; Carroll, P.R.; Eggener, S.; Fulgham, P.F.; Margolis, D.J.; Pinto, P.A.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Rubenstein, J.N.; Rukstalis, D.B.; Taneja, S.S.; et al. Update of the Standard Operating Procedure on the Use of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Diagnosis, Staging and Management of Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2020, 203, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkbey, B.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Haider, M.A.; Padhani, A.R.; Villeirs, G.; Macura, K.J.; Tempany, C.M.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Margolis, D.J.; et al. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2.1: 2019 Update of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosaily, A.E.; Frangou, E.; Ahmed, H.U.; Emberton, M.; Punwani, S.; Kaplan, R.; Brown, L.C.; Freeman, A.; Jameson, C.; Hindley, R.; et al. Additional Value of Dynamic Contrast-enhanced Sequences in Multiparametric Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data from the PROMIS Study. Eur. Urol. 2020, 78, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapisarda, S.; Bada, M.; Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; Arcaniolo, D.; Polara, A.; Imbimbo, C.; Grosso, G. The role of multiparametric resonance and biopsy in prostate cancer detection: Comparison with definitive histological report after laparoscopic/robotic radical prostatectomy. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 4178–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieda, N.; Krishna, S.; Davenport, M.S. Update on Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent-Enhanced Imaging in the Genitourinary System. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabile, A.; Giganti, F.; Kasivisvanathan, V.; Giannarini, G.; Moore, C.M.; Padhani, A.R.; Panebianco, V.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Salomon, G.; Turkbey, B.; et al. Factors Influencing Variability in the Performance of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Detecting Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 145–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Bosma, J.S.; Twilt, J.J.; van Ginneken, B.; Bjartell, A.; Padhani, A.R.; Bonekamp, D.; Villeirs, G.; Salomon, G.; Giannarini, G.; et al. Artificial intelligence and radiologists in prostate cancer detection on MRI (PI-CAI): An international, paired, non-inferiority, confirmatory study. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, N.D.; Tannock, I.; N’Dow, J.; Feng, F.; Gillessen, S.; Ali, S.A.; Trujillo, B.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Attard, G.; Bray, F.; et al. The Lancet Commission on prostate cancer: Planning for the surge in cases. Lancet 2024, 403, 1683–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, K.; Kong, Z.; Xing, Z.; Chen, Y.; Luo, N.; Yu, Y.; Song, B.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; et al. A multicenter study of artificial intelligence-aided software for detecting visible clinically significant prostate cancer on mpMRI. Insights Imaging 2023, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, C.A.; Baumgärtner, G.L.; Biessmann, F.; Beetz, N.L.; Hartenstein, A.; Savic, L.J.; Froböse, K.; Dräger, F.; Schallenberg, S.; Rudolph, M.; et al. Interactive Explainable Deep Learning Model Informs Prostate Cancer Diagnosis at MRI. Radiology 2023, 307, e222276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roest, C.; Kwee, T.C.; Saha, A.; Fütterer, J.J.; Yakar, D.; Huisman, H. AI-assisted biparametric MRI surveillance of prostate cancer: Feasibility study. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labus, S.; Altmann, M.M.; Huisman, H.; Tong, A.; Penzkofer, T.; Choi, M.H.; Shabunin, I.; Winkel, D.J.; Xing, P.; Szolar, D.H.; et al. A concurrent, deep learning-based computer-aided detection system for prostate multiparametric MRI: A performance study involving experienced and less-experienced radiologists. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransen, S.J.; Kwee, T.C.; Rouw, D.; Roest, C.; van Lohuizen, Q.Y.; Simonis, F.F.J.; van Leeuwen, P.J.; Heijmink, S.; Ongena, Y.P.; Haan, M.; et al. Patient perspectives on the use of artificial intelligence in prostate cancer diagnosis on MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2025, 35, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooij, G.; Bagulho, I.; Huisman, H. Automatic segmentation of prostate zones. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.07146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.N.I.; Ryu, S.; Song, J.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, B. Evaluation of Functional Decline in Alzheimer’s Dementia Using 3D Deep Learning and Group ICA for rs-fMRI Measurements. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isensee, F.; Jäger, P.; Wasserthal, J.; Zimmerer, D.; Petersen, J.; Kohl, S.; Schock, J.; Klein, A.; Roß, T.; Wirkert, S.; et al. Batchgenerators—A Phyton Framework for Data Augmentation; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Available online: https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/batchgenerators?tab=readme-ov-file (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Litjens, G.; Toth, R.; van de Ven, W.; Hoeks, C.; Kerkstra, S.; van Ginneken, B.; Vincent, G.; Guillard, G.; Birbeck, N.; Zhang, J.; et al. Evaluation of prostate segmentation algorithms for MRI: The PROMISE12 challenge. Med. Image Anal. 2014, 18, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armato, S.G., 3rd; Huisman, H.; Drukker, K.; Hadjiiski, L.; Kirby, J.S.; Petrick, N.; Redmond, G.; Giger, M.L.; Cha, K.; Mamonov, A.; et al. PROSTATEx Challenges for computerized classification of prostate lesions from multiparametric magnetic resonance images. J. Med. Imaging 2018, 5, 044501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.; Reinke, A.; Bakas, S.; Farahani, K.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Landman, B.A.; Litjens, G.; Menze, B.; Ronneberger, O.; Summers, R.M.; et al. The Medical Segmentation Decathlon. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obuchowski, N.A.; Gallas, B.D.; Hillis, S.L. Multi-reader ROC studies with split-plot designs: A comparison of statistical methods. Acad. Radiol. 2012, 19, 1508–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obuchowski, N.A.; Bullen, J. Multireader Diagnostic Accuracy Imaging Studies: Fundamentals of Design and Analysis. Radiology 2022, 303, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franiel, T.; Röthke, M. PI-RADS 2.0 for Prostate MRI. Radiologe 2017, 57, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, Q. The evolving Gleason grading system. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 28, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Short, E.; Warren, A.Y.; Varma, M. Gleason grading of prostate cancer: A pragmatic approach. Diagn. Histopathol. 2019, 25, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obuchowski, N.A., Jr.; Rockette, H.E., Jr. Hypothesis testing of diagnostic accuracy for multiple readers and multiple tests an anova approach with dependent observations. Commun. Stat.—Simul. Comput. 1995, 24, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, D.; Sathyamurthy, S.; Putha, P. MRMCsamplesize: An R Package for Estimating Sample Sizes for Multi-Reader Multi-Case Studies. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Ahn, H.; Hwang, S.I.; Lee, H.J.; Choe, G.; Byun, S.S.; Hong, S.K. Biparametric versus multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate: Detection of clinically significant cancer in a perfect match group. Prostate Int. 2020, 8, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.; Hillis, S.; Pesce, L. MCMCaov: Multi-Reader Multi-Case Analysis of Variance. R Package Version 0.3.0. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/brian-j-smith/MRMCaov (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Smith, B.J.; Hillis, S.L. Multi-reader multi-case analysis of variance software for diagnostic performance comparison of imaging modalities. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2020, 11316, 113160K. [Google Scholar]
- Hillis, S.L.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Schartz, K.M.; Berbaum, K.S. A comparison of the Dorfman-Berbaum-Metz and Obuchowski-Rockette methods for receiver operating characteristic (ROC) data. Stat. Med. 2005, 24, 1579–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakrour, N.; Cochran, R.L.; Mercaldo, N.D.; Bradley, W.; Tsai, L.L.; Prajapati, P.; Grimm, R.; von Busch, H.; Lo, W.C.; Harisinghani, M.G. Impact of artificial intelligence assisted lesion detection on radiologists’ interpretation at multiparametric prostate MRI. Clin. Imaging 2025, 122, 110484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoots, I.G.; Barentsz, J.O.; Bittencourt, L.K.; Haider, M.A.; Macura, K.J.; Margolis, D.J.A.; Moore, C.M.; Oto, A.; Panebianco, V.; Siddiqui, M.M.; et al. PI-RADS Committee Position on MRI Without Contrast Medium in Biopsy-Naive Men With Suspected Prostate Cancer: Narrative Review. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooij, M.; Allen, C.; Twilt, J.J.; Thijssen, L.C.P.; Asbach, P.; Barrett, T.; Brembilla, G.; Emberton, M.; Gupta, R.T.; Haider, M.A.; et al. PI-QUAL version 2: An update of a standardised scoring system for the assessment of image quality of prostate MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 7068–7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, M.; Faletti, R.; Calleris, G.; Giglio, J.; Berzovini, C.; Gentile, F.; Marra, G.; Misischi, F.; Molinaro, L.; Bergamasco, L.; et al. Prostate cancer detection with biparametric magnetic resonance imaging (bpMRI) by readers with different experience: Performance and comparison with multiparametric (mpMRI). Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Saha, A.; Brand, P.; Slootweg, I.; de Rooij, M.; Huisman, H. Deep learning-assisted prostate cancer detection on bi-parametric MRI: Minimum training data size requirements and effect of prior knowledge. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massanova, M.; Vere, R.; Robertson, S.; Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; Dutto, L.; Ahmad, I.; Underwood, M.; Salmond, J.; Patel, A.; et al. Clinical and prostate multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging findings as predictors of general and clinically significant prostate cancer risk: A retrospective single-center study. Curr. Urol. 2023, 17, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

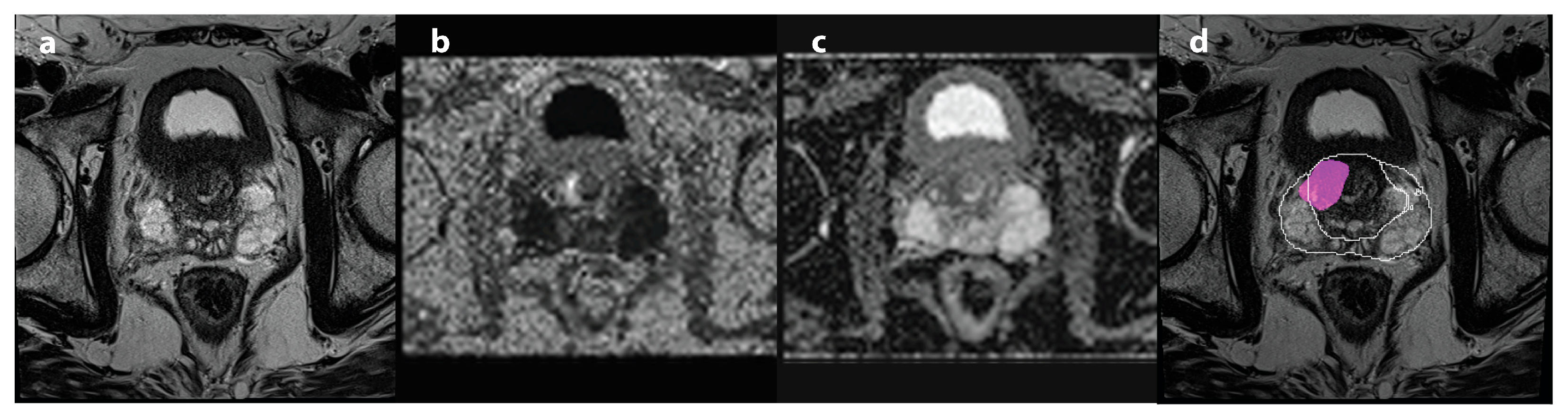
| Characteristic (N = 105) | |
|---|---|
| Age (y) * | 66 ± 7 |
| PSA level (ng/mL) * | 9.4 ± 6.8 |
| Suspiciously elevated PSA level | 38 (36) |
| Abnormal rise in PSA | 59 (56) |
| Suspicious digital rectal examination | 3 (3) |
| Staging following positive biopsy | 2 (2) |
| Active surveillance | 3 (3) |
| Histopathology | |
| No PCa | 52 (50) |
| GS 3 + 3 | 18 (17) |
| GS 3 + 4 | 21 (20) |
| GS 4 + 3 | 3 (3) |
| GS 4 + 4 | 10 (10) |
| GS 4 + 5 | 1 (1) |
| AI-bpMRI | mpMRI | bpMRI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gleason score ≥ 3 + 4 | |||
| Sensitivity, % | 94.3 (88.0, 100) | 90.5 (85.1, 95.9) | 88.6 (82.6, 94.5) |
| Specificity, % | 53.3 (44.0, 62.7) | 54.3 (45.4, 63.2) | 52.4 (43.5, 61.3) |
| LR+ | 2.0 (1.6, 2.7) | 2.0 (1.6, 2.6) | 1.9 (1.5, 2.4) |
| LR− | 0.1 (0.0, 0.3) | 0.2 (0.1, 0.3) | 0.2 (0.1, 0.4) |
| Gleason score ≥ 3 + 3 | |||
| Sensitivity, % | 86.8 (78.9, 94.7) * | 84.3 (77.3, 91.2) | 81.1 (73.2, 89.1) * |
| Specificity, % | 62.2 (52.3, 72.0) | 63.5 (54.1, 72.8) | 59.0 (49.5, 68.4) |
| LR+ | 2.3 (1.7, 3.2) | 2.3 (1.7, 3.4) | 2.0 (1.5, 3.0) |
| LR− | 0.2 (0.2, 0.4) | 0.2 (0.1, 0.4) | 0.3 (0.1, 0.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nißler, D.; Reimers-Kipping, S.; Ingwersen, M.; Berger, F.; Niekrenz, F.; Theis, B.; Hielscher, F.; Franken, P.; Gaßler, N.; Grimm, M.-O.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Biparametric MRI for Detecting Prostate Cancer—A Comparative Multireader Multicase Accuracy Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176111
Nißler D, Reimers-Kipping S, Ingwersen M, Berger F, Niekrenz F, Theis B, Hielscher F, Franken P, Gaßler N, Grimm M-O, et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Biparametric MRI for Detecting Prostate Cancer—A Comparative Multireader Multicase Accuracy Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176111
Chicago/Turabian StyleNißler, Daniel, Sabrina Reimers-Kipping, Maja Ingwersen, Frank Berger, Felix Niekrenz, Bernhard Theis, Fabian Hielscher, Philipp Franken, Nikolaus Gaßler, Marc-Oliver Grimm, and et al. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Biparametric MRI for Detecting Prostate Cancer—A Comparative Multireader Multicase Accuracy Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176111
APA StyleNißler, D., Reimers-Kipping, S., Ingwersen, M., Berger, F., Niekrenz, F., Theis, B., Hielscher, F., Franken, P., Gaßler, N., Grimm, M.-O., Teichgräber, U., & Franiel, T. (2025). Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Biparametric MRI for Detecting Prostate Cancer—A Comparative Multireader Multicase Accuracy Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176111





