Injectable Porcine Collagen in Musculoskeletal Disorders: A Delphi Consensus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
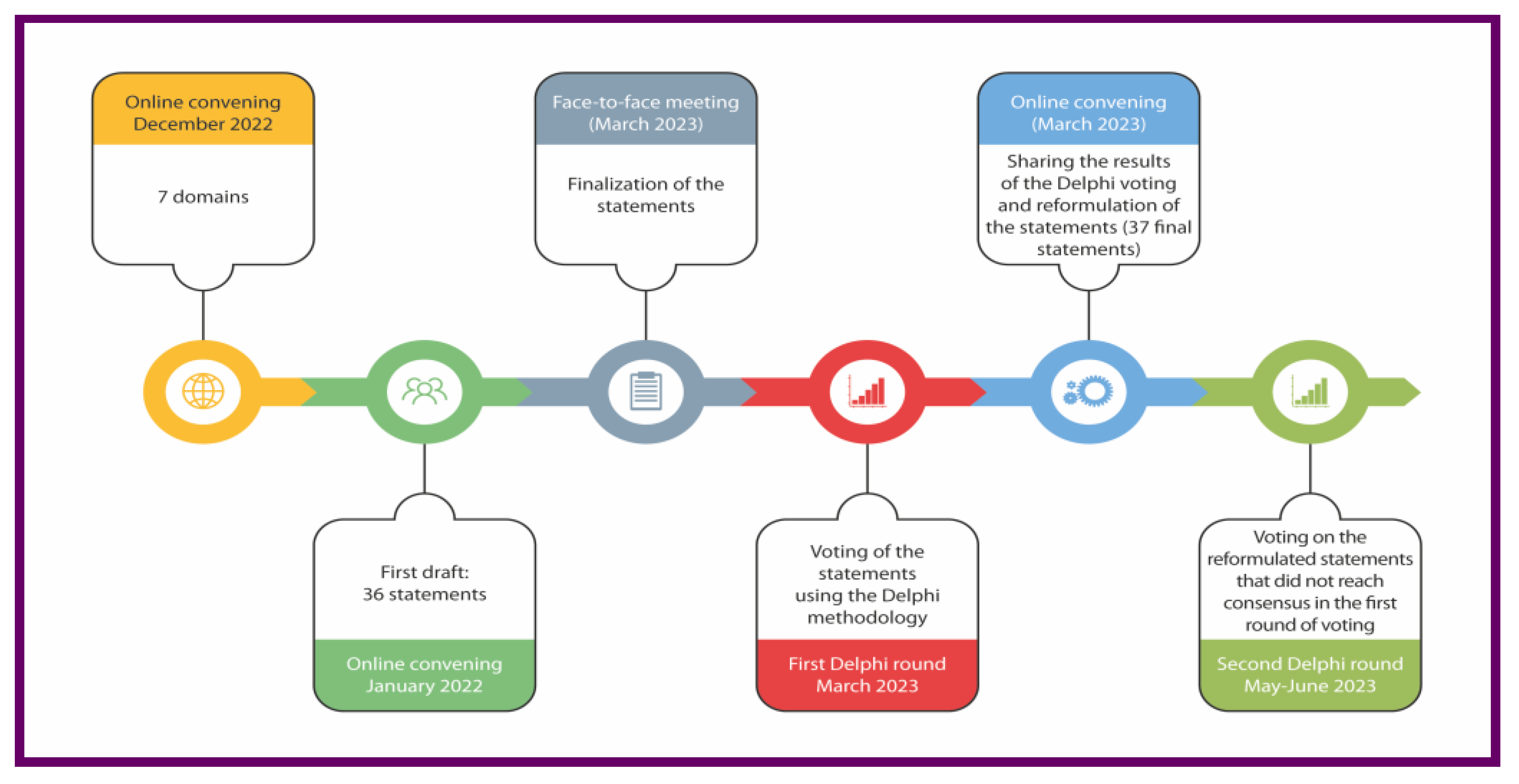
2.1. Delphi Survey and Panel Composition
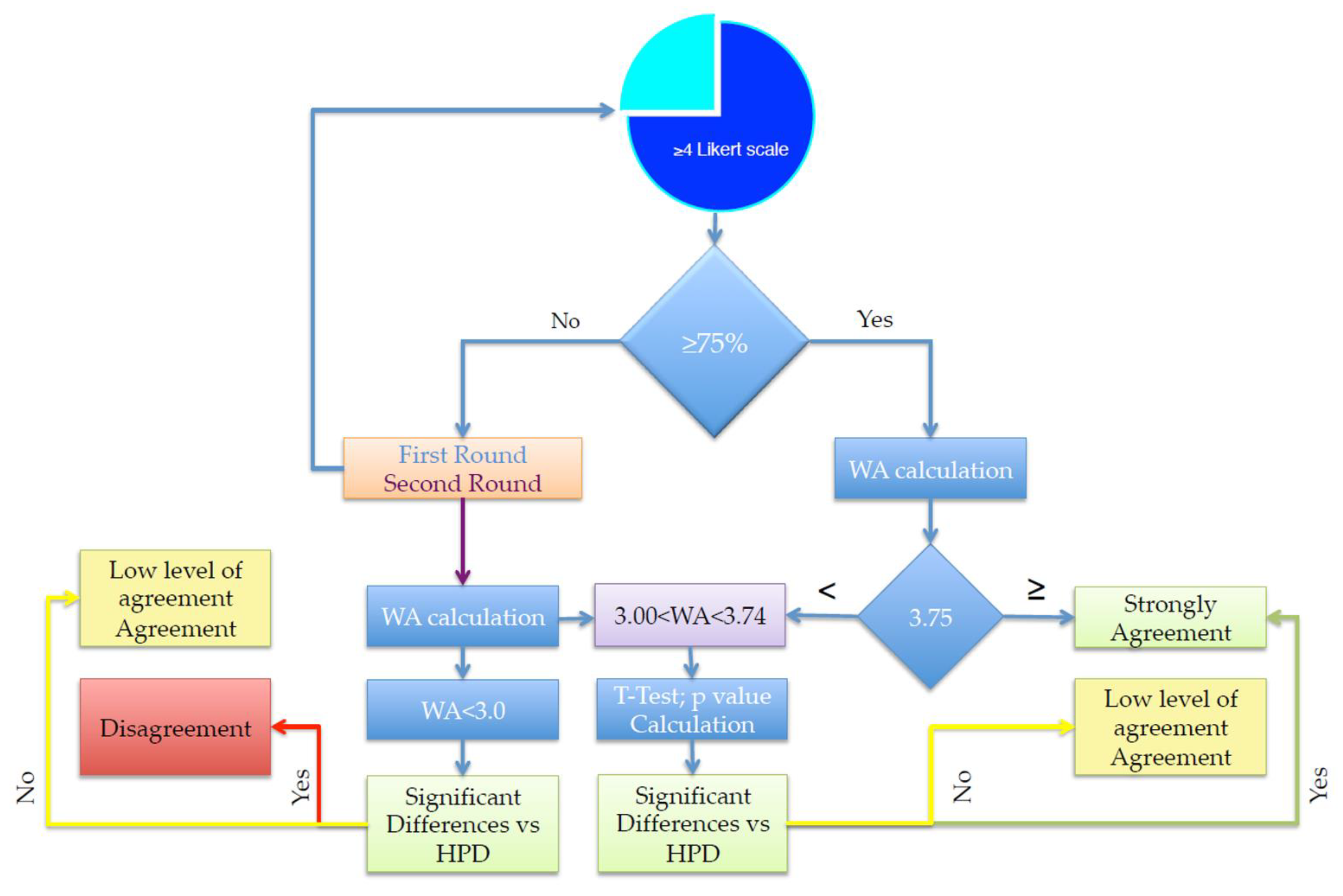
2.2. Opinion Quntification, Threshold Assesment, and Satistical Quntification
3. Results
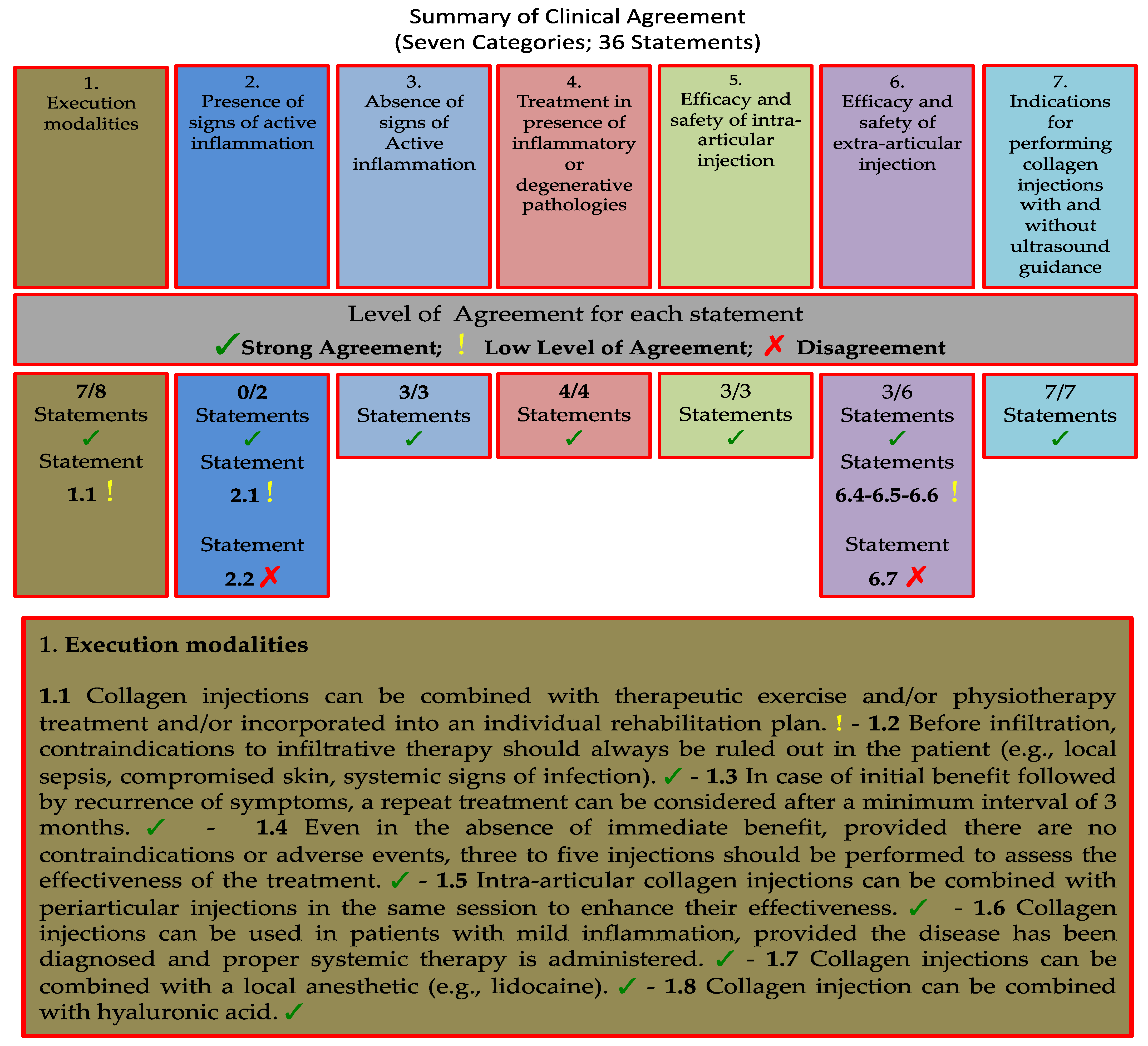
3.1. Category 1: Execution Modalities of Collagen Injections in Musculoskeletal Disorders
- STATEMENTS
- 1.1 Collagen injections can be combined with therapeutic exercise and/or physiotherapy treatment and/or incorporated into an individual rehabilitation plan.
- 1.2 Before infiltration, contraindications to infiltrative therapy should always be ruled out in the patient (e.g., local sepsis, compromised skin, systemic signs of infection).
- 1.3 In case of initial benefits followed by a recurrence of symptoms, a repeat treatment can be considered after a minimum interval of 3 months.
- 1.4 Even in the absence of immediate benefit, provided there are no contraindications or adverse events, three to five injections should be performed to assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
- 1.5 Intra-articular collagen injections can be combined with periarticular injections in the same session to enhance their effectiveness.
- 1.6 Collagen injections can be used in patients with mild inflammation, provided the disease has been diagnosed and proper systemic therapy is administered.
- 1.7 Collagen injections can be combined with a local anesthetic (e.g., lidocaine).
- 1.8 Collagen injection can be combined with hyaluronic acid.
3.2. Category 2: Collagen Injections in the Treatment of Joint Pathologies with Signs of Active Inflammation at the Joint Level (Intra-Articular, Both in Large and Small Joints)
- STATEMENTS
- 2.1 Up to two injections per week can be performed in a patient with mild inflammation, considering the absolute contraindications of injection therapies.
- 2.2 In the case of mild joint inflammation, it is possible to combine intra-articular injections of steroids and collagen in the same session and injection site.
3.3. Category 3: Collagen Injections in the Treatment of Joint Pathologies in the Absence of Signs of Inflammation at the Joint Level (Intra-Articular. Both in Large and Small Joints)
- STATEMENTS
- 3.1 In the presence of chondropathy, infiltrative therapy with collagen can be a therapeutic option.
- 3.2 Collagen injections can be performed for degenerative joint pathologies.
- 3.3 Collagen treatment can be performed intra-articularly and/or peri-articularly, even simultaneously.
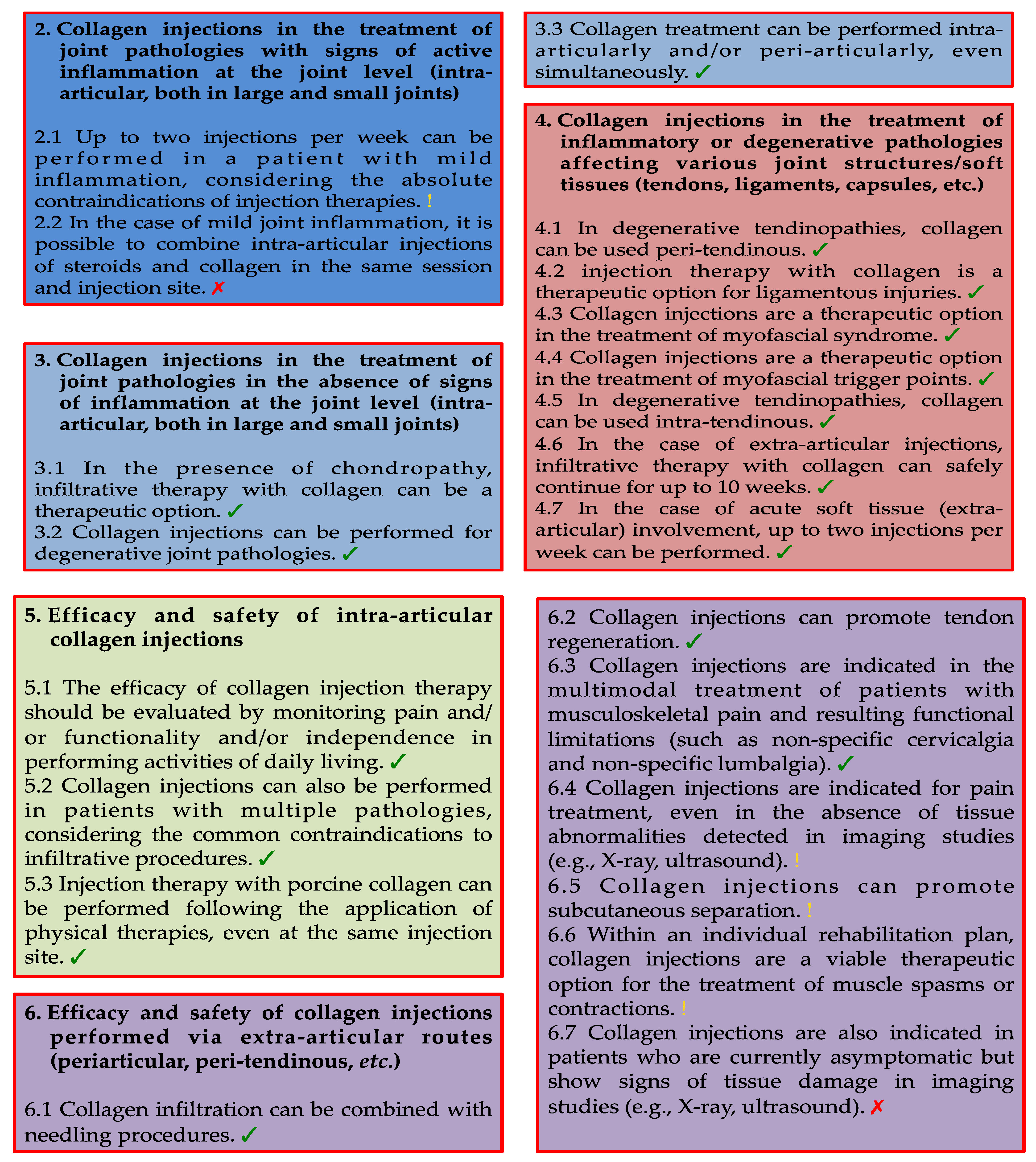
3.4. Category 4: Collagen Injections in the Treatment of Inflammatory or Degenerative Pathologies Affecting Various Joint Structures/Soft Tissues (Tendons, Ligaments. Capsules, etc.)
- STATEMENTS
- 4.1 In degenerative tendinopathies, collagen can be used as peri-tendinous.
- 4.2 Injection therapy with collagen is a therapeutic option for ligamentous injuries.
- 4.3 Collagen injections are a therapeutic option in the treatment of myofascial syndrome.
- 4.4 Collagen injections are a therapeutic option in the treatment of myofascial trigger points.
- 4.5 In degenerative tendinopathies, collagen can be used intra-tendinous.
- 4.6 In the case of extra-articular injections, infiltrative therapy with collagen can safely continue for up to 10 weeks.
- 4.7 In the case of acute soft tissue (extra-articular) involvement, up to two injections per week can be performed.
3.5. Category 5: Efficacy and Safety of Intra-Articular Collagen Injections
- STATEMENTS
- 5.1 The efficacy of collagen injection therapy should be evaluated by monitoring pain and/or functionality and/or independence in performing activities of daily living.
- 5.2 Collagen injections can also be performed in patients with multiple pathologies, considering the common contraindications to infiltrative procedures.
- 5.3 Injection therapy with porcine collagen can be performed following the application of physical therapies, even at the same injection site.
3.6. Category 6: Efficacy and Safety of Collagen Injections Performed via Extra-Articular Routes (Periarticular, Peri-Tendinous, etc.)
- STATEMENTS
- 6.1 Collagen infiltration can be combined with needling procedures.
- 6.2 Collagen injections can promote tendon regeneration.
- 6.3 Collagen injections are indicated in the multimodal treatment of patients with musculoskeletal pain and resulting functional limitations (such as non-specific cervicalgia and non-specific lumbalgia).
- 6.4 Collagen injections are indicated for pain treatment, even in the absence of tissue abnormalities detected in imaging studies (e.g., X-ray, ultrasound).
- 6.5 Collagen injections can promote subcutaneous separation.
- 6.6 Within an individual rehabilitation plan, collagen injections are a viable therapeutic option for the treatment of muscle spasms or contractions.
- 6.7 Collagen injections are also indicated in patients who are currently asymptomatic but show signs of tissue damage in imaging studies (e.g., X-ray, ultrasound).
3.7. Category 7: Indications for Performing Collagen Injections with and Without Ultrasound Guidance
- STATEMENTS
- 7.1 The use of ultrasound guidance is recommended for intra-articular injections in cases where joint-periarticular degeneration has altered the anatomy or reduced the joint space and/or to avoid structures that should not be involved (large blood vessels, pleura).
- 7.2 For peri-tendinous injections, ultrasound guidance is recommended to improve the accuracy of injection placement.
- 7.3 Ultrasound guidance for peri-tendinous and intra-tendinous collagen injections allows for the performance of tendon delamination and needling maneuvers as well.
- 7.4 The use of direct ultrasound guidance is particularly recommended for intra-articular hip injections.
- 7.5 Intra-articular knee infiltration can be performed without ultrasound guidance, although ultrasound guidance is recommended if available.
- 7.6 Ultrasound guidance is recommended for the treatment of muscle injuries, including those involving the muscle-tendon junction and the muscle belly.
- 7.7 Mesotherapy with collagen can be performed freehand.
- −
- For intra-articular injections when there are alterations in the joint space anatomy or dimensions or to avoid structures that should not be involved (e.g., large blood vessels of pleura; 23 out of 23; 100% agreement);
- −
- For peri-tendinous injections to improve the accuracy of injection placement (22 out of 23; 96%);
- −
- To perform tendon delamination and needling maneuvers in both peri-tendinous and intra-tendinous collagen injections (22 out of 23; 96%);
- −
- To perform intra-articular hip injections (22 out of 23; 96%);
- −
- For the treatment of muscle injuries, including those involving the muscle-tendon junction and the muscle belly (20 out of 23; 87%).
4. Discussion
4.1. Category 1: Execution Modalities of Collagen Injections in Musculoskeletal Disorders
4.2. Category 2: Collagen Injections in the Treatment of Joint Pathologies with Signs of Active Inflammation at the Joint Level (Intra-Articular. Both in Large and Small Joints)
4.3. Category 3: Collagen Injections in the Treatment of Joint Pathologies in the Absence of Signs of Inflammation at the Joint Level (Intra-Articular, Both in Large and Small Joints)
4.4. Category 4: Collagen Injections in the Treatment of Inflammatory or Degenerative Pathologies Affecting Various Joint Structures/Soft Tissues (Tendons, Ligaments, Capsules, etc.)
4.5. Category 5: Efficacy and Safety of Intra-Articular Collagen Injections
4.6. Category 6: Efficacy and Safety of Collagen Injections Performed via Extra-Articular Routes (Periarticular, Peri-Tendinous, etc.)
4.7. Category 7: Indications for Performing Collagen Injections with and Without Ultrasound Guidance
4.8. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Cieza, A.; Causey, K.; Kamenov, K.; Hanson, S.W.; Chatterji, S.; Vos, T. Global Estimates of the Need for Rehabilitation Based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-T.; Chiang, C.-F.; Wu, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-T.; Tu, Y.-K.; Wang, T.-G. Comparative Effectiveness of Injection Therapies in Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review, Pairwise and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 336–349.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Lima, G.; Llorente, L.; Nuñez-Álvarez, C.; Ruiz-Ordaz, B.H.; Echevarría-Zuno, S.; Hernández-Cuevas, V. Polymerized-Type I Collagen Downregulates Inflammation and Improves Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis Following Arthroscopic Lavage: A Randomized, Double-Blind, and Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 342854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin Martin, L.S.; Massafra, U.; Bizzi, E.; Migliore, A. A Double Blind Randomized Active-Controlled Clinical Trial on the Intra-Articular Use of Md-Knee versus Sodium Hyaluronate in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis (“Joint”). BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitecka-Buchta, A.; Walczynska-Dragon, K.; Batko-Kapustecka, J.; Wieckiewicz, M. Comparison between Collagen and Lidocaine Intramuscular Injections in Terms of Their Efficiency in Decreasing Myofascial Pain within Masseter Muscles: A Randomized, Single-Blind Controlled Trial. Pain Res. Manag. 2018, 2018, 8261090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricard-Blum, S. The Collagen Family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grounds, M.D. Complexity of Extracellular Matrix and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. In Skeletal Muscle Repair and Regeneration; Advances in Muscle Research; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 3, pp. 269–302. ISBN 978-1-4020-6767-9. [Google Scholar]
- Myllyharju, J. Collagens, Modifying Enzymes and Their Mutations in Humans, Flies and Worms. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randelli, F.; Menon, A.; Giai Via, A.; Mazzoleni, M.; Sciancalepore, F.; Brioschi, M.; Gagliano, N. Effect of a Collagen-Based Compound on Morpho-Functional Properties of Cultured Human Tenocytes. Cells 2018, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randelli, F.; Fioruzzi, A.; Mazzoleni, M.G.; Radaelli, A.; Rahali, L.; Verga, L.; Menon, A. Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Injections of Type I Collagen-Based Medical Device for Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: A Pilot Study. Life 2025, 15, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koszela, K.; Woldańska-Okońska, M.; Słupiński, M.; Gasik, R. The Role of Injection Collagen Therapy in Greater Trochanter Pain Syndrome. A New Therapeutic Approach? Rheumatology 2025, 63, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, D.; Mottola, R.; Palermi, S.; Sirico, F.; Corrado, B.; Gnasso, R. Intra-Articular Collagen Injections for Osteoarthritis: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borja-Flores, A.; Macías-Hernández, S.I.; Hernández-Molina, G.; Perez-Ortiz, A.; Reyes-Martínez, E.; Belzazar-Castillo De La Torre, J.; Ávila-Jiménez, L.; Vázquez-Bello, M.C.; León-Mazón, M.A.; Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; et al. Long-Term Effectiveness of Polymerized-Type I Collagen Intra-Articular Injections in Patients with Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis: Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation in a Cohort Study. Adv. Orthop. 2020, 2020, 9398274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Oh, K.J.; Moon, Y.W.; In, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Kwon, S.Y. Intra-Articular Injection of Type I Atelocollagen to Alleviate Knee Pain: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Cartilage 2021, 13, 342S–350S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aicale, R.; Savarese, E.; Mottola, R.; Corrado, B.; Sirico, F.; Pellegrino, R.; Donati, D.; Tedeschi, R.; Ruosi, L.; Tarantino, D. Collagen Injections for Rotator Cuff Diseases: A Systematic Review. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, B.; Bonini, I.; Chirico, V.A.; Filippini, E.; Liguori, L.; Magliulo, G.; Mazzuoccolo, G.; Rosano, N.; Gisonni, P. Ultrasound-Guided Collagen Injections in the Treatment of Supraspinatus Tendinopathy: A Case Series Pilot Study. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Corrado, B.; Bonini, I.; Alessio Chirico, V.; Rosano, N.; Gisonni, P. Use of Injectable Collagen in Partial-Thickness Tears of the Supraspinatus Tendon: A Case Report. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 2020, omaa103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvipriya, K.; Kumar, K.; Bhat, A.; Kumar, B.; John, A.; Lakshmanan, P. Collagen: Animal Sources and Biomedical Application. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsworth, L.R.; DeLustro, F.; Brennan, J.E.; Sawamura, S.; McPherson, J. The Human Immune Response to Reconstituted Bovine Collagen. J. Immunol. 1986, 136, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, R.A.C.S.; Costa, B.S.; Dellaretti, M.A.; De Carvalho, G.T.C.; Faria, M.P.; De Sousa, A.A. Efficacy and Safety of a Porcine Collagen Sponge for Cranial Neurosurgery: A Prospective Case-Control Study. World Neurosurg. 2013, 79, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, B.; Mazzuoccolo, G.; Liguori, L.; Chirico, V.A.; Costanzo, M.; Bonini, I.; Bove, G.; Curci, L. Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis with Collagen Injections: A Pilot Study. Muscle Ligaments Tendons J. 2019, 09, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, P.; Colombini, A.; Carimati, G.; Beggio, M.; De Girolamo, L.; Volpi, P. Intra-Articular Injection of Hydrolyzed Collagen to Treat Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis. A Functional In Vitro Investigation and a Pilot Retrospective Clinical Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giarda, F.; Agostini, A.; Colonna, S.; Sciumè, L.; Meroni, A.; Beretta, G.; Dalla Costa, D. Infiltrative Type I Collagen in the Treatment of Morton’s Neuroma: A Mini-Series. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.A. Local Injections in Pain Management. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 1995, 6, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, M.; Dlimi, S.; Parisi, M.; Benoni, A.; Bisinella, G.; Di Fabio, S. Subacromial Injection of Hydrolyzed Collagen in the Symptomatic Treatment of Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: An Observational Multicentric Prospective Study on 71 Patients. JSES Int. 2023, 7, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damjanov, N.; Micu, M.C. Ultrasound Guided Injection with Collagen-Based Medical Device: Real-Life Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety in Hip Osteoarthritis. Med. Ultrason. 2024, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, D.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, B.-K.; Kim, Y.-S. Atelocollagen Injection Improves Tendon Integrity in Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: A Prospective Comparative Study. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2020, 8, 2325967120904012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pascalis, M.; Mulas, S.; Sgarbi, L. Combined Oxygen–Ozone and Porcine Injectable Collagen Therapies Boosting Efficacy in Low Back Pain and Disability. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayhan, E. Intraarticular Injections (Corticosteroid, Hyaluronic Acid, Platelet Rich Plasma) for the Knee Osteoarthritis. World J. Orthop. 2014, 5, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernetti, A.; Mangone, M.; Villani, C.; Alviti, F.; Valeo, M.; Grassi, M.C.; Migliore, A.; Viora, U.; Adriani, E.; Quirino, N.; et al. Appropriateness of Clinical Criteria for the Use of SYmptomatic Slow-Acting Drug for OsteoArthritis (SYSADOA). A Delphi Method Consensus Initiative among Experts in Italy. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 55, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eysenbach, G. Improving the Quality of Web Surveys: The Checklist for Reporting Results of Internet E-Surveys (CHERRIES). J. Med. Internet Res. 2004, 6, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onu, I.; Matei, D.; Sardaru, D.-P.; Cascaval, D.; Onu, A.; Gherghel, R.; Serban, I.L.; Mocanu, G.D.; Iordan, D.A.; Murariu, G.; et al. Rehabilitation of Patients with Moderate Knee Osteoarthritis Using Hyaluronic Acid Viscosupplementation and Physiotherapy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M.B.; Beutler, A.I.; O’Connor, F.G. Musculoskeletal Injections: A Review of the Evidence. Am. Fam. Physician 2008, 78, 971–976. [Google Scholar]
- Amiel, D.; Toyoguchi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Bowden, K.; Amiel, M.E.; Healey, R.M. Long-Term Effect of Sodium Hyaluronate (Hyalgan®) on Osteoarthritis Progression in a Rabbit Model. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2003, 11, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Goomer, R.S.; Harwood, F.; Kubo, T.; Hirasawa, Y.; Amiel, D. The Effects of Hyaluronan on Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), Interleukin-1β(IL-1β), and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) Gene Expression during the Development of Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 1999, 7, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, E. Collagen Medical Device Lumbar nel Trattamento Combinato del Dolore da Instabilità del Rachide Lombare. La Med. Biol. 2019, 3, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka, N.; Takahashi, K.A.; Arai, Y.; Sakao, K.; Mazda, O.; Kishida, T.; Honjo, K.; Tanaka, S.; Kubo, T. Intra-articular Injection of Hyaluronan Restores the Aberrant Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 in Osteoarthritic Subchondral Bone. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randelli, F.; Sartori, P.; Carlomagno, C.; Bedoni, M.; Menon, A.; Vezzoli, E.; Sommariva, M.; Gagliano, N. The Collagen-Based Medical Device MD-Tissue Acts as a Mechanical Scaffold Influencing Morpho-Functional Properties of Cultured Human Tenocytes. Cells 2020, 9, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsiko, A.; Levingstone, T.J.; O’Brien, F.J.; Gleeson, J.P. Addition of Hyaluronic Acid Improves Cellular Infiltration and Promotes Early-Stage Chondrogenesis in a Collagen-Based Scaffold for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 11, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muran, A.C.; Schaffler, B.C.; Wong, A.; Neufeld, E.; Swami, P.; Pianka, M.; Grande, D. Effect of Increasing Hyaluronic Acid Content in Collagen Scaffolds on the Maintenance of Chondrogenic Phenotype in Chondrocytes and Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Cartil. Jt. Preserv. 2023, 3, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshkova, V.; Rashkov, R.; Nestorova, R. Efficacy and Safety Evaluation of Guna Collagen MDs Injections in Knee Osteoarthritis—A Case Series of 30 Patients. Available online: https://medicomfort.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/EWALUA1.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2017).
- Volpi, P.; Zini, R.; Erschbaumer, F.; Beggio, M.; Busilacchi, A.; Carimati, G. Effectiveness of a Novel Hydrolyzed Collagen Formulation in Treating Patients with Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis: A Multicentric Retrospective Clinical Study. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco-Bonora, P.M.; Martín-Pintado-Zugasti, A. Effects of Myofascial Trigger Point Dry Needling in Patients with Sleep Bruxism and Temporomandibular Disorders: A Prospective Case Series. Acupunct. Med. 2017, 35, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalichman, L.; Vulfsons, S. Dry Needling in the Management of Musculoskeletal Pain. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2010, 23, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Choi, Y.S.; You, M.-W.; Kim, J.S.; Young, K.W. Sonoelastography in the Evaluation of Plantar Fasciitis Treatment: 3-Month Follow-Up After Collagen Injection. Ultrasound Q. 2016, 32, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestorova, R.; Rashkov, R.; Petranova, T. Clinical and Sonographic Assessment of the Effectiveness of Guna Collagen MDs Injections in Patients with Partial Thickness Tear of The Rotator Cuff. Physiol. Regul. Med. 2017, 35–37. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317236542_clinical_and_sonographic_assessment_of_the_effectiveness_of_guna_collagen_mds_injections_in_patients_with_partial_thickness_tear_of_the_rotator_cuff (accessed on 30 June 2017).
- Vetrano, M.; d’Alessandro, F.; Torrisi, M.R.; Ferretti, A.; Vulpiani, M.C.; Visco, V. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Promotes Cell Proliferation and Collagen Synthesis of Primary Cultured Human Tenocytes. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2011, 19, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, G.; De Mos, M.; van Binsbergen, R.; van Schie, H.T.M.; van de Lest, C.H.A.; Van Weeren, P.R. The Effect of Focused Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Collagen Matrix and Gene Expression in Normal Tendons and Ligaments. Equine Vet. J. 2009, 41, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, V.T.; Pinfildi, C.E.; Neves, M.A.I.; Parizoto, N.A.; Hochman, B.; Ferreira, L.M. Collagen Changes and Realignment Induced by Low-level Laser Therapy and Low-intensity Ultrasound in the Calcaneal Tendon. Lasers Surg. Med. 2010, 42, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirri, C.; Fede, C.; Petrelli, L.; De Rose, E.; Biz, C.; Guidolin, D.; De Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Immediate Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Fascial Fibroblasts: An In Vitro Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, F.; Akkus, O.; King, M.W. A Collagen/PLA Hybrid Scaffold Supports Tendon-derived Cell Growth for Tendon Repair and Regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 2624–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, B.S.; Ruan, R.; Vahabli, E.; Chen, P.; De-Juan-Pardo, E.M.; Zheng, M.; Doyle, B. Natural, Synthetic and Commercially-Available Biopolymers Used to Regenerate Tendons and Ligaments. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 19, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joines, M.; Motamedi, K.; Seeger, L.; DiFiori, J. Musculoskeletal Interventional Ultrasound. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2007, 11, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Smith, M.; Hasan, K. Accuracy of Intraarticular Injections: Blind vs. Image Guided Techniques—A Review of Literature. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardowski, E.A.; Byrd, J.W.T. Piriformis Injection: An Ultrasound-Guided Technique. Arthrosc. Tech. 2019, 8, e1457–e1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernetti, A.; Agostini, F.; Alviti, F.; Giordan, N.; Martella, F.; Santilli, V.; Paoloni, M.; Mangone, M. New Viscoelastic Hydrogel Hymovis MO.RE. Single Intra-Articular Injection for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis in Sportsmen: Safety and Efficacy Study Results. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 673988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Categories | Number of Statements |
|---|---|
| 8 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 6 |
| 3 |
| 7 |
| 7 |
| Sum (%) | Weighted Average | Analyses | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 + 2 L-LSV | 4 + 5 H-LSV | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | HPD | Delta (%) LSVs | Delta WA Value | WA Value | p Value | Statement |
| 13.04 | 30.43 | 0.000 | 0.130 | 1.696 | 0.696 | 0.652 | 3.00 | 17.39 | 0.17 | 3.17 | 0.1309 | 1.1 |
| 4.35 | 65.22 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.913 | 1.217 | 1.739 | 3.00 | 60.87 | 0.91 | 3.91 | 0.0003 | 1.2 |
| 8.70 | 82.61 | 0.000 | 0.087 | 0.261 | 1.391 | 2.391 | 3.00 | 73.91 | 1.13 | 4.13 | 0.0001 | 1.3 |
| 0.00 | 78.26 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.652 | 1.217 | 2.391 | 3.00 | 78.26 | 1.26 | 4.26 | 0.0001 | 1.4 |
| 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.870 | 3.913 | 3.00 | 100.00 | 1.78 | 4.78 | 0.0001 | 1.5 |
| 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 5.000 | 3.00 | 100.00 | 2.00 | 5.00 | 0.0001 | 1.6 |
| 0.00 | 86.96 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.391 | 1.739 | 2.174 | 3.00 | 86.96 | 1.30 | 4.30 | 0.0001 | 1.7 |
| 4.35 | 86.96 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.261 | 1.739 | 2.174 | 3.00 | 82.61 | 1.22 | 4.22 | 0.0001 | 1.8 |
| Sum (%) | Weighted Average | Analyses | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 + 2 L-LSV | 4 + 5 H-LSV | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | HPD | Delta (%) LSV | Delta WA Value | WA Value | p Value | Statement |
| 52.17 | 30.43 | 0.043 | 0.478 | 0.522 | 0.696 | 0.652 | 3.00 | −21.74 | −0.61 | 2.39 | 0.7232 | 2.1 |
| 17.39 | 43.48 | 0.087 | 0.087 | 1.174 | 1.043 | 0.870 | 3.00 | 26.09 | 0.26 | 3.26 | 0.2183 | 2.2 |
| Sum (%) | Weighted Average | Analyses | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 + 2 L-LSV | 4 + 5 H-LSV | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | HPD | Delta (%) LSV | Delta WA Value | WA Value | p Value | Statement |
| 0.00 | 91.30 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.261 | 1.391 | 2.826 | 3.00 | 91.30 | 1.48 | 4.48 | 0.0001 | 3.1 |
| 4.35 | 95.65 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.000 | 1.739 | 2.609 | 3.00 | 91.30 | 1.39 | 4.39 | 0.0001 | 3.2 |
| 4.35 | 91.30 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.130 | 1.565 | 2.609 | 3.00 | 86.96 | 1.35 | 4.35 | 0.0001 | 3.3 |
| Sum (%) | Weighted Average | Analyses | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 + 2 L-LSV | 4 + 5 H-LSV | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | HPD | Delta (%) LSV | Delta WA Value | WA Value | p Value | Statement |
| 13.04 | 52.17 | 0.000 | 0.130 | 1.043 | 1.217 | 1.087 | 3.00 | 39.13 | 0.48 | 3.48 | 0.0110 | 4.1 |
| 0.00 | 95.65 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.130 | 1.565 | 2.826 | 3.00 | 95.65 | 1.52 | 4.52 | 0.0001 | 4.2 |
| 13.04 | 65.22 | 0.000 | 0.130 | 0.652 | 1.217 | 1.739 | 3.00 | 52.17 | 0.74 | 3.74 | 0.0014 | 4.3 |
| 0.00 | 78.26 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.652 | 1.913 | 1.522 | 3.00 | 78.26 | 1.09 | 4.09 | 0.0001 | 4.4 |
| 4.35 | 73.91 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.652 | 1.913 | 1.304 | 3.00 | 69.57 | 0.91 | 3.91 | 0.0001 | 4.5 |
| 8.70 | 56.52 | 0.000 | 0.087 | 1.043 | 1.565 | 0.870 | 3.00 | 47.83 | 0.57 | 3.57 | 0.0041 | 4.6 |
| Sum (%) | Weighted Average | Analyses | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 + 2 L-LSV | 4 + 5 H-LSV | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | HPD | Delta (%) LSV | Delta WA Value | WA Value | p Value | Statement |
| 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.391 | 3.261 | 3.00 | 100.00 | 1.65 | 4.65 | 0.0001 | 5.1 |
| 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.913 | 2.609 | 3.00 | 100.00 | 1.52 | 4.52 | 0.0001 | 5.2 |
| 8.70 | 82.61 | 0.000 | 0.087 | 0.261 | 1.565 | 2.174 | 3.00 | 73.91 | 1.09 | 4.09 | 0.0001 | 5.3 |
| Sum (%) | Weighted Average | Analyses | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 + 2 L-LSV | 4 + 5 H-LSV | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | HPD | Delta (%) LSV | Delta WA Value | WA Value | p Value | Statement |
| 4.35 | 82.61 | 0.000 | 4.348 | 13.043 | 34.783 | 47.826 | 3.00 | 78.26 | 1.22 | 4.22 | 0.0001 | 6.1 |
| 0.00 | 52.17 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 47.826 | 26.087 | 26.087 | 3.00 | 52.17 | 0.78 | 3.78 | 0.0005 | 6.2 |
| 4.35 | 65.22 | 0.000 | 4.348 | 30.435 | 39.130 | 26.087 | 3.00 | 60.87 | 0.83 | 3.83 | 0.0003 | 6.3 |
| 21.74 | 52.17 | 4.348 | 17.391 | 26.087 | 34.783 | 17.391 | 3.00 | 30.43 | 0.26 | 3.26 | 0.1009 | 6.4 |
| 30.43 | 43.48 | 0.000 | 30.435 | 26.087 | 21.739 | 21.739 | 3.00 | 13.04 | 0.04 | 3.04 | 0.1232 | 6.5 |
| 21.74 | 56.52 | 8.696 | 13.043 | 21.739 | 43.478 | 13.043 | 3.00 | 34.78 | 0.26 | 3.26 | 0.1640 | 6.6 |
| 30.43 | 34.78 | 8.696 | 21.739 | 34.783 | 21.739 | 13.043 | 3.00 | 4.35 | −0.13 | 2.87 | 0.7817 | 6.7 |
| Sum (%) | Weighted Average | Analyses | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 + 2 L-LSV | 4 + 5 H-LSV | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | HPD | Delta (%) LSV | Delta WA Value | WA Value | p Value | Statement |
| 0.00 | 95.65 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.130 | 0.522 | 4.130 | 3.00 | 95.65 | 1.78 | 4.78 | 0.0001 | 7.1 |
| 0.00 | 95.65 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.130 | 1.217 | 3.261 | 3.00 | 95.65 | 1.61 | 4.61 | 0.0001 | 7.2 |
| 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.217 | 3.478 | 3.00 | 100.00 | 1.70 | 4.70 | 0.0001 | 7.3 |
| 4.35 | 86.96 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.261 | 1.217 | 2.826 | 3.00 | 82.61 | 1.35 | 4.35 | 0.0001 | 7.4 |
| 0.00 | 95.65 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.130 | 0.174 | 4.565 | 3.00 | 95.65 | 1.87 | 4.87 | 0.0001 | 7.5 |
| 4.35 | 73.91 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.652 | 0.522 | 3.043 | 3.00 | 69.57 | 1.26 | 4.26 | 0.0001 | 7.6 |
| 0.00 | 95.65 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.130 | 1.565 | 2.826 | 3.00 | 95.65 | 1.52 | 4.52 | 0.0001 | 7.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Lucia, O.; Giarda, F.; Bernetti, A.; Ceccarelli, C.; Mauro, G.L.; Gervasoni, F.; Berti, L.; Robecchi Majnardi, A. Injectable Porcine Collagen in Musculoskeletal Disorders: A Delphi Consensus. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6058. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176058
De Lucia O, Giarda F, Bernetti A, Ceccarelli C, Mauro GL, Gervasoni F, Berti L, Robecchi Majnardi A. Injectable Porcine Collagen in Musculoskeletal Disorders: A Delphi Consensus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6058. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176058
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Lucia, Orazio, Federico Giarda, Andrea Bernetti, Chiara Ceccarelli, Giulia Letizia Mauro, Fabrizio Gervasoni, Lisa Berti, and Antonio Robecchi Majnardi. 2025. "Injectable Porcine Collagen in Musculoskeletal Disorders: A Delphi Consensus" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6058. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176058
APA StyleDe Lucia, O., Giarda, F., Bernetti, A., Ceccarelli, C., Mauro, G. L., Gervasoni, F., Berti, L., & Robecchi Majnardi, A. (2025). Injectable Porcine Collagen in Musculoskeletal Disorders: A Delphi Consensus. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6058. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176058








