Evaluation of iStent Micro-Bypass vs. Kahook Dual Blade Goniotomy with Phacoemulsification in Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
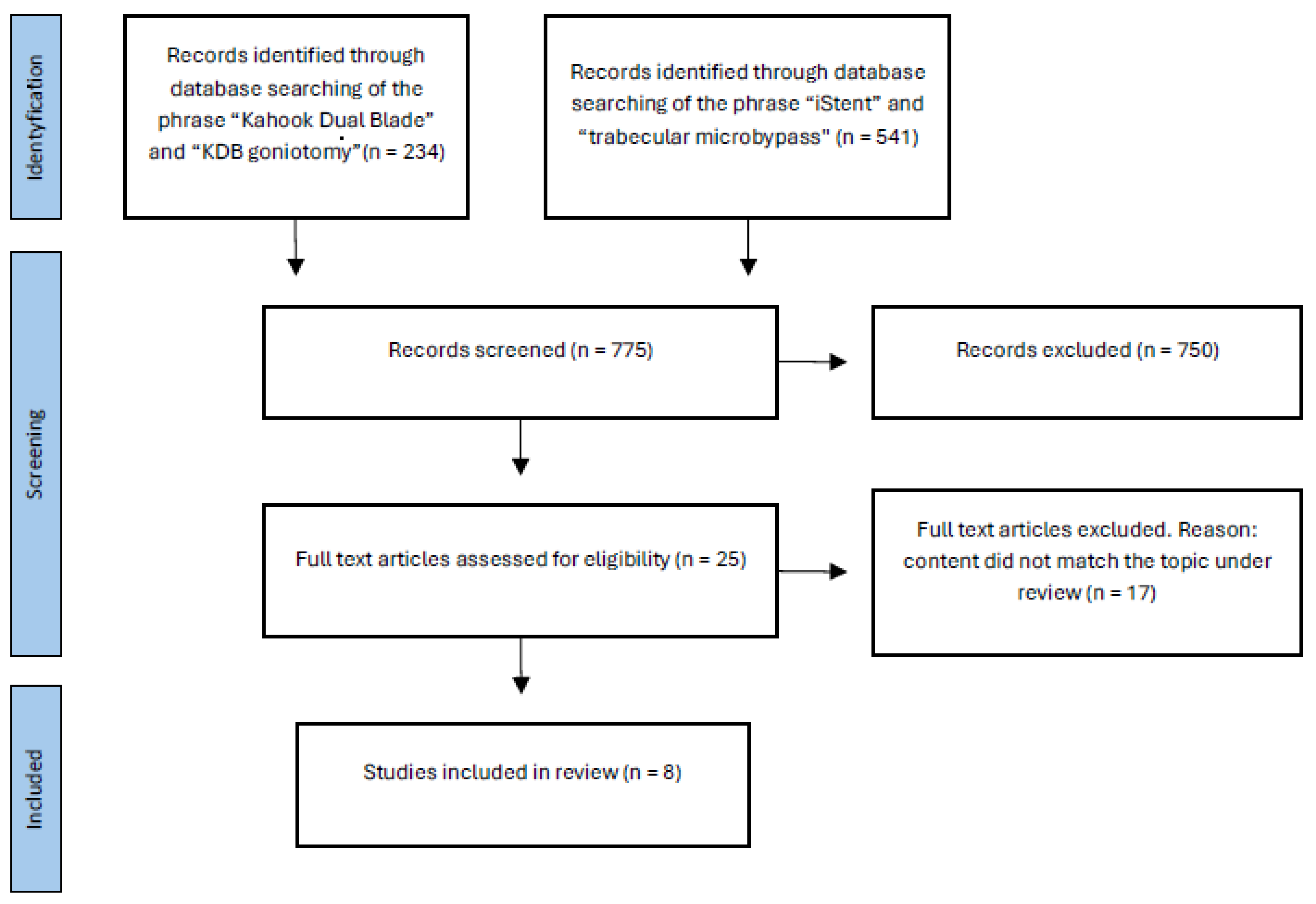
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Procedure and Information Extraction
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
- Prospective or retrospective clinical studies.
- The studies involved patients with OAG.
- Used procedures: iStent micro-bypass implantation with phacoemulsification or KDB goniotomy with phacoemulsification.
- The trial compared the following criteria: baseline IOP, endpoint IOP, baseline number of glaucoma drops, number of endpoint glaucoma drops, and best-corrected visual acuity.
- At least 6 months minimum follow-up period.
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
- Meta-analyses and reviews.
- Studies describing partial results.
- Studies omitting certain analyzed factors.
- Case reports.
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Quality Assessment
3. Results
3.1. iStent Micro-Bypass Implantation vs. Kahook Dual Blade Goniotomy
3.2. iStent Micro-Bypass Implantation
3.3. Kahook Dual Blade Goniotomy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IOP | intraocular pressure |
| KDB | Kahook Dual Blade |
| MIGS | microinvasive glaucoma surgery |
| OAG | open-angle glaucoma |
| PCO | posterior capsular opacification |
| PEXG | pseudo-exfoliation glaucoma |
| PG | pigmentary glaucoma |
| POAG | primary open-angle glaucoma |
| SC | Schlemm’s canal |
| TM | trabecular meshwork |
References
- Ansari, E. An update on implants for minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS). Ophthalmol. Ther. 2017, 6, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBry, P.W.; Perkins, T.W.; Heatley, G.; Kaufman, P.; Brumback, L.C. Incidence of late-onset bleb-related complications following trabeculectomy with mitomycin. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheb, H.; Ahmed, I.I.K. Micro-invasive glaucoma surgery: Current perspectives and future directions. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2012, 23, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillunat, L.E.; Erb, C.; Jünemann, A.G.; Kimmich, F. Micro-invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS): A review of surgical procedures using stents. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 11, 1583–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, D.A.; Seibold, L.K.; Kahook, M.Y. Preclinical investigation of goniotomy using four different techniques. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 3519–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkander, A.; Economou, M.A.; Jóhannesson, G. Outcomes of iStent inject versus Kahook Dual Blade surgery in glaucoma patients undergoing cataract surgery. J. Glaucoma 2023, 32, e121–e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorairaj, S.K.; Kahook, M.Y.; Williamson, B.K.; Seibold, L.K.; ElMallah, M.K.; Singh, I.P. A multicenter retrospective comparison of goniotomy versus trabecular bypass device implantation in glaucoma patients undergoing cataract extraction. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 12, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMallah, M.K.; Seibold, L.K.; Kahook, M.Y.; Williamson, B.K.; Singh, I.P.; Dorairaj, S.K.; KDB Goniotomy Study Group. 12-month retrospective comparison of Kahook Dual Blade excisional goniotomy with iStent trabecular bypass device implantation in glaucomatous eyes at the time of cataract surgery. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 2515–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; King, J.; Thomsen, S.; Hirabayashi, M.; An, J. Comparison of surgical outcomes between excisional goniotomy using the Kahook Dual Blade and iStent trabecular micro-bypass stent in combination with phacoemulsification. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2019, 13, 2097–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, K.; Takamura, Y.; Orii, Y.; Arimura, S.; Inatani, M. Performances of glaucoma operations with Kahook Dual Blade or iStent combined with phacoemulsification in Japanese open-angle glaucoma patients. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 13, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan Gaskin, J.C.; Bigirimana, D.; Kong, G.Y.X.; McGuinness, M.B.; Atik, A.; Liu, L.; Brooks, A.M.V.; Ang, G.S.; Glaucoma Investigation and Research Unit, Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital. Prospective, randomized controlled trial of cataract surgery vs combined cataract surgery with insertion of iStent inject. Ophthalmol. Glaucoma 2024, 7, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, C.; Howes, F.; Ioannidis, A.; Shiu, M.; Manning, D.; Lusthaus, J.A.; Skalicky, S.E.; Goodwin, T.W. Multicenter effectiveness and disease stability through 3 years after iStent trabecular micro-bypass with phacoemulsification in glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2022, 16, 2955–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozera, M.; Konopińska, J.; Mariak, Z.; Rękas, M. Effectiveness of iStent trabecular microbypass system combined with phacoemulsification versus phacoemulsification alone in patients with glaucoma and cataract depending on the initial intraocular pressure. Ophthalmic Res. 2021, 64, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkander, A.; Economou, M.A.; Jóhannesson, G. Kahook Dual-Blade goniotomy with and without phacoemulsification in medically uncontrolled glaucoma. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 17, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, K.; Kakimoto, H.; Orii, Y.; Arimura, S.; Takamura, Y.; Inatani, M. Long-term outcomes of a Kahook Dual Blade procedure combined with phacoemulsification in Japanese patients with open-angle glaucoma. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorairaj, S.K.; Seibold, L.K.; Radcliffe, N.M.; Aref, A.A.; Jimenez-Román, J.; Lazcano-Gomez, G.S.; Darlington, J.K.; Mansouri, K.; Berdahl, J.P. 12-month outcomes of goniotomy performed using the Kahook Dual Blade combined with cataract surgery in eyes with medically treated glaucoma. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.M., Jr.; Ko, M.K.; Hong, Y.K.; Weigert, R.; Tan, J.C.H. Deep tissue analysis of distal aqueous drainage structures and contractile features. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreon, T.; van der Merwe, E.; Fellman, R.L.; Johnstone, M.; Bhattacharya, S.K. Aqueous outflow—A continuum from trabecular meshwork to episcleral veins. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 57, 108–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriola-Villalobos, P.; Martínez-de-la-Casa, J.M.; Díaz-Valle, D.; García-Vidal, S.E.; Fernández-Pérez, C.; García-Sánchez, J.; García-Feijoó, J. Mid-term evaluation of the new Glaukos iStent with phacoemulsification in coexistent open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension and cataract. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 97, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.J.; Wasiuta, T.; Kiatos, E.; Malvankar-Mehta, M.; Hutnik, C.M.L. The effects of phacoemulsification on intraocular pressure and topical medication use in patients with glaucoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 3-year data. J. Glaucoma 2017, 26, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.P.; Lin, S.C.; Junk, A.K.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Singh, K.; Chen, T.C. The effect of phacoemulsification on intraocular pressure in glaucoma patients: A report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 1294–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, G.M.; Coleman, A.L. Minimally invasive glaucoma surgery: Current status and future prospects. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2016, 10, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bias Category/Study | Barkander et al., 2023 [6] | Dorairaj et al., 2018 [7] | ElMallah et al., 2019 [8] | Lee et al., 2019 [9] | Iwasaki et al., 2019 [10] | Gaskin et al., 2024 [11] | Clement et al., 2022 [12] | Kozera et al., 2021 [13] | Barkander et al., 2023 [14] | Iwasaki et al., 2022 [15] | Dorairaj et al., 2018 [16] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random sequence generation | ||||||||||||
| Allocation concealment | ||||||||||||
| Groups similar at baseline or were differences controlled for? | ||||||||||||
| Were conditions controlled so effects could be attributed to mobile application? | ||||||||||||
| Were outcomes prespecified and reported? | ||||||||||||
| Were participants analyzed based on originally-assigned group across timepoints? | ||||||||||||
| Were outcome assessors and data analysts masked? | ||||||||||||
| Were reliable measures of outcomes used consistently across all participants? | ||||||||||||
| Overall quality (Moderate risk or Low risk of bias) | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Low | |
| Author/Year | Region | Form of the Procedure of the Studied Group (Control Group) | Size of Studied Group (Control Group) | Follow-Up (Months) | Age of the Patient (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barkander et al., 2023 [6] | Sweden | KDB Goniotomy + Phacoemulsification | 97 | 24 | 74.6 ± 5.5 |
| iStent + Phacoemulsification | 56 | 75.7 ± 7.8 | |||
| Dorairaj et al., 2018 [7] | Multicenter | KDB Goniotomy + Phacoemulsification | 237 | 6 | 70.1 ± 8.9 |
| iStent + Phacoemulsification | 198 | 71.3 ± 8.1 | |||
| ElMallah et al., 2019 [8] | USA | KDB Goniotomy + Phacoemulsification | 190 | 12 | 69.6 ± 0.8 |
| iStent + Phacoemulsification | 125 | 72.4 ± 0.8 | |||
| Lee et al., 2019 [9] | USA | KDB Goniotomy + Phacoemulsification | 44 | 6 | 69.1 ± 1.6 |
| iStent + Phacoemulsification | 58 | 69.5 ± 1.4 | |||
| Iwasaki et al., 2019 [10] | Japan | KDB Goniotomy + Phacoemulsification | 129 | 12 | 76.8 ± 7.5 |
| iStent + Phacoemulsification | 44 | 75.4 ± 7.8 | |||
| Gaskin et al., 2024 [11] | Australia | iStent + Phacoemulsification | 56 | 24 | 73.3 ± 7.5 |
| (Phacoemulsification Solo) | (48) | ||||
| Clement et al., 2022 [12] | Multicenter | iStent + Phacoemulsification | 273 | 36 | 72.4 ± 8.3 |
| Kozera et al., 2021 [13] | Poland | iStent + Phacoemulsification | 44 | 24 | 70.1 ± 8.5 |
| (Phacoemulsification Solo) | (36) | ||||
| Barkander et al., 2023 [14] | Sweden | KDB Goniotomy + Phacoemulsification | 51 | 24 | 7.6 ± 6.0 |
| KDB Goniotomy Solo | 39 | ||||
| Iwasaki et al., 2022 [15] | Japan | KDB Goniotomy + Phacoemulsification | 148 | 31.3 ± 14.8 | 76.9 ± 7.2 |
| Dorairaj et al., 2018 [16] | North America | KDB Goniotomy + Phacoemulsification | 52 | 12 | ≥18 |
| Author/ Year | Number of Eyes: Studied Group (Control Group) | Baseline IOP (mmHg) | Endpoint IOP (mmHg) | Number of Baseline Medication | Number of Endpoint Medications | Mean Preoperative BCVA | Endpoint BCVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barkander et al., 2023 [6] | 56 | 20.3 ± 6.1 | 14.2 ± 4.1 | 3.0 ± 0.9 | 2.6 ± 1.1 | LOD | LOD |
| Dorairaj et al., 2018 [7] | 198 | 16.7 ± 4.4 | 13.9 ± 2.7 | 1.9 ± 0.9 | 1.0 ± 1.0 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.1 ± 0.2 |
| ElMallah et al., 2019 [8] | 125 | 16.7 ± 0.3 | 14.4 ± 0.3 | 1.51 ± 0.06 | 0.56 ± 0.07 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 0.1 ± 0.01 |
| Lee et al., 2019 [9] | 40 | 16.7 ± 0.4 | 14.2 ± 0.4 | 1.4 ± 0.14 | 1.4 ± 0.14 | LOD | LOD |
| Iwasaki et al., 2019 [10] | 44 | 17.8 ± 2.9 | 14.3 ± 2.3 | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 0.9 ± 1.4 | LOD | LOD |
| Gaskin et al., 2024 [11] | 56 (48) | 17.7 ± 4.0 | 15.2 ± 5.8 | 1.69 ± 1.05 | 0.7 ± 0.9 | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 0.06 ± 0.35 |
| Clement et al., 2022 [12] | 273 | 16.4 ± 4.6 | 13.9 ± 3.5 | 1.51 ± 1.17 | 0.48 ± 0.89 | LOD | LOD |
| Kozera et al., 2021 [13] | 44 (36) | 22.04 ± 1.64 | 15.57 ± 2.13 | 1.32 ± 0.55 | 0.32 ± 0.55 | 0.56 ± 0.23 | 0.95 ± 0.12 |
| Author/Year | iStent Generation | Number of Implants | Number of Eyes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barkander et al., 2023 [6] | second | 2 | 56 |
| Dorairaj et al., 2018 [7] | first | 1 | 198 |
| ElMallah et al., 2019 [8] | first | 1 | 125 |
| Lee et al., 2019 [9] | first | 1 | 40 |
| Iwasaki et al., 2019 [10] | first | 1 | 44 |
| Gaskin et al., 2024 [11] | second | 3 | 1 |
| 2 | 54 | ||
| 1 | 1 | ||
| Clement et al., 2022 [12] | second | 2 | 271 |
| 1 | 2 | ||
| Kozera et al., 2021 [13] | first | 1 | 44 |
| Author/ Year | Number of Eyes: Studied Group (Control Group) | Baseline IOP (mmHg) | Endpoint IOP (mmHg) | Number of Baseline Medications | Number of Endpoint Medications | Mean Preoperative BCVA | Endpoint BCVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barkander et al., 2023 [6] | 97 | 20.1 ± 6.1 | 14.7 ± 3.6 | 2.3 ± 1.0 | 1.5 ± 1.3 | LOD | LOD |
| Dorairaj et al., 2018 [7] | 237 | 17.9 ± 4.4 | 13.6 ± 2.7 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 0.6 ± 1.0 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.1 ± 0.2 |
| ElMallah et al., 2019 [8] | 190 | 18.2 ± 0.3 | 13.2 ± 0.1 | 1.45 ± 0.05 | 0.43 ± 0.05 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | 0.1 ± 0.01 |
| Lee et al., 2019 [9] | 34 | 17.2 ± 0.7 | 14.8 ± 0.6 | 1.9 ± 0.17 | 1.0 ± 0.17 | LOD | LOD |
| Iwasaki et al., 2019 [10] | 44 | 19.8 ± 7.3 | 13.0 ± 3.1 | 2.5 ± 1.4 | 1.6 ± 1.6 | LOD | LOD |
| Barkander et al., 2023 [14] | 51 (39) | 22.3 ± 5.8 | 13.9 ± 3.0 | 3.3 ± 0.5 | 2.3 ± 1.1 | 0.25 ± 0.30 | LOD |
| Iwasaki et al., 2022 [15] | 148 | 19.5 ± 6.9 | 11.9 ± 2.7 | 2.4 ± 1.4 | 1.6 ± 1.4 | 0.53 ± 0.46 | 0.35 ± 0.67 |
| Dorairaj et al., 2018 [16] | 52 | 16.8 ± 0.6 | 12.4 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.439 ± 0.041 | 0.137 ± 0.016 |
| Author/ Adverse Event | Barkander et al. n (%) [6] | Dorairaj et al. n (%) [7] | ElMallah et al. n (%) [8] | Lee et al. n (%) [9] | Iwasaki et al. n (%) [10] | Gaskin et al. n (%) [11] | Clement et al. n (%) [12] | Kozera et al. n (%) [13] | Barkander et al. n (%) [14] | Iwasaki et al. n (%) [15] | Dorairaj et al. n (%) [16] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of MIGS | iStent | KDB | iStent | KDB | iStent | KDB | iStent | KDB | iStent | KDB | iStent | iStent | iStent | KDB | KDB | KDB |
| Hyphema | 7 (14%) | 60 (62%) | 1 (0.5%) | 9 (3.8%) | NR | NR | NR | 2 (4.5%) | 1 (2.3%) | 21 (16.3%) | NR | NR | 5 (11.4%) | 2 (4%) | 21 (14.2%) | NR |
| IOP spikes | 2 (5%) | 13 (14%) | 25 (12.6%) | 15 (6.3%) | 1 (0.8%) | 2 (1%) | 1 (1.7%) | 8 (18.2%) | 3 (6.8%) | 18 (14%) | NR | NR | 1 (1.25%) | 4 (8%) | 19 (12.8%) | 2 (3.8%) |
| Stent obstruction | NR | NA | NR | NA | NR | NA | NR | NA | NR | NA | NR | 2 (<1%) | NR | NA | NA | NA |
| Stent malposition | NR | NA | NR | NA | NR | NA | NR | NA | 1 (2.3%) | NA | 2 (3.57%) | NR | NR | NA | NA | NA |
| Macular edema | NR | 1 (1.03%) | NR | NR | NR | NR | 1 (1.7%) | 2 (4.5%) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 1 (2%) | NR | 1 (1.9%) |
| Corneal edema | NR | NR | 3 (1.5%) | 5 (2.1%) | 1 (0.8%) | 2 (1%) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 1 (1.25%) | NR | NR | NR |
| Inflammation | 3 (5%) | 3 (5%) | 4 (2%) | 1 (0.4%) | 3 (2.4%) | 2 (1%) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 1 (2%) | NR | NR |
| Additional procedures | 7 (12.5%) | 4 (4.12%) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 3 (2.3%) | 4 (7.2%) | 23 (8.42%) | NR | 6 (12%) | 6 (4.1%) | NR |
| Pain/ irritation | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 4 (7.7%) |
| PCO | NR | 3 (3.09%) | 5 (2.5%) | 1 (0.4%) | 1 (0.8%) | 3 (1.6%) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 4 (9.1%) | NR | NR | 2 (3.8%) |
| Posterior vitreous detachment | NR | NR | 2 (1%) | 2 (0.8%) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Rebound iritis | NR | NR | 2 (1%) | 2 (0.8%) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charytonowicz, A.; Błażowski, J.; Konopińska, J. Evaluation of iStent Micro-Bypass vs. Kahook Dual Blade Goniotomy with Phacoemulsification in Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165819
Charytonowicz A, Błażowski J, Konopińska J. Evaluation of iStent Micro-Bypass vs. Kahook Dual Blade Goniotomy with Phacoemulsification in Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165819
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharytonowicz, Anna, Jakub Błażowski, and Joanna Konopińska. 2025. "Evaluation of iStent Micro-Bypass vs. Kahook Dual Blade Goniotomy with Phacoemulsification in Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165819
APA StyleCharytonowicz, A., Błażowski, J., & Konopińska, J. (2025). Evaluation of iStent Micro-Bypass vs. Kahook Dual Blade Goniotomy with Phacoemulsification in Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165819







