Abstract
The FOT is a non-invasive method for assessing respiratory mechanics. It enables the measurement of respiratory system impedance by applying pressure oscillations through a loudspeaker at the subject mouth and then studying its deformation, which is commensurate to the resistance opposed by the respiratory system. The main parameters which can be determined with the FOT are the impedance (Z) and the components of respiratory resistance (Rrs) and reactance (Xrs). The FOT has been predominantly applied to the study of respiratory mechanics for research purposes; however, preclinical experiments and subsequently observational clinical studies have demonstrated that FOT can effectively assess airway obstruction, bronchodilator response, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and the presence of small airways disease. More recently, studies on the FOT in restrictive lung diseases have also been reported. Nonetheless, international guidelines on the precise applications of the FOT in lung diseases are still lacking. The aim of the review was to describe the technical aspects related to the FOT methodology in clinical practice and to provide a concise state of the art on the applications of the FOT in obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
1. Introduction
The Forced Oscillatory Technique (FOT) is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that measures respiratory impedance (Z), and provides information on airway reactance (Xrs) and resistance (Rrs) across different airways’ regions [1].
First described by DuBois et al. in 1956 in the attempt to study the resistive and elastic features of the respiratory system, the FOT has then been applied in research activities, mainly in pre-clinical settings, to characterize the mechanics of the respiratory system [2,3,4]. At the beginning, studies on animals were mainly concentrated on laboratory rodents, then the technique was tried also on larger animals and, finally, on humans [5,6]. The great potential of the FOT to probe the lung mechanics in a very effortless way represented a major advantage which contributed to its wider adoption. Indeed, lung function testing is traditionally based on the use of spirometry, which is an effort-dependent technique. Spirometry can often be challenging to perform by older or very young people. On the contrary, through the application of a defined range of frequencies, the FOT can measure respiratory impedance, resistance, and reactance by superimposing external oscillatory pressure waves over spontaneous breathing [7]. Moreover, central and peripheral airway function can be studied with the FOT frequency-dependent analysis, thus leading to its application both in obstructive and restrictive respiratory syndromes, from asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to interstitial lung disease (ILD) [8,9]. The FOT has proven particularly useful in identifying small airways disease (SAD), especially in severe asthma, where early detection of SAD could help in treatment decisions and, thus, improve outcomes [10,11].
The aim of the review was to describe the technical aspects related to FOT methodology and provide a concise overview on the main clinical applications of the FOT in obstructive and restrictive lung disease (Figure 1).
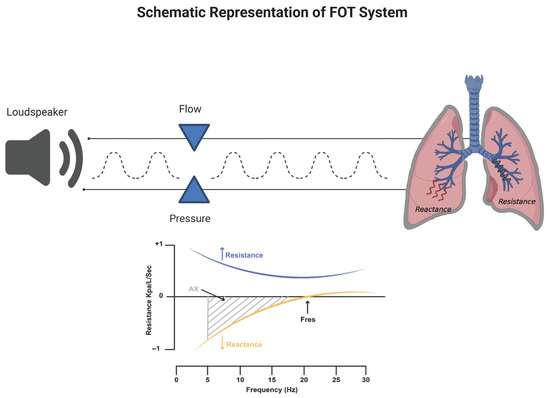
Figure 1.
Applications of the FOT in obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
2. Forced Oscillatory Technique: Methodology and Technical Aspects
The FOT is a non-invasive diagnostic method for assessing respiratory mechanics. It enables the measurement of respiratory system impedance by applying pressure oscillations to the subject during spontaneous breathing with open mouth [12] (Figure 2).
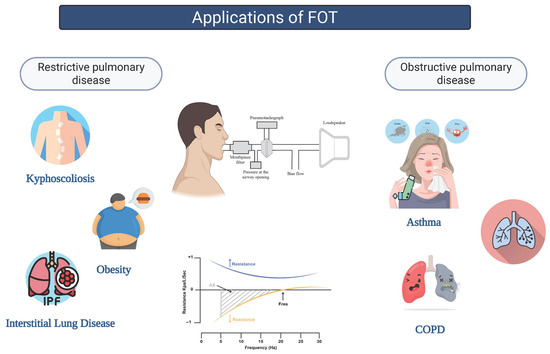
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the Oscillometry system and Oscillometry impedance plot. The plot depicts the Impedance of the respiratory system (Z) versus frequency in hertz (Hz); the upper curve represents the Resistance (Rrs) and the lower curve the Reactance (Xrs) of the respiratory system.
2.1. Methodology
More specifically, mechanical information about the respiratory system can be collected by imposing an oscillatory waveform signal through a loudspeaker at the subject’s mouth and then studying its deformation, which is commensurate with the resistance opposed by the respiratory system.
During the procedure, the patient breathes normally through a mouthpiece connected to a system that both generates and detects oscillatory signals, while supporting their cheeks with their hands to reduce upper airway shunt and interference from orofacial structures [13,14].
An external pressure oscillation, with a typical range of frequencies (i.e., 5–35 Hz), is superimposed on spontaneous breathing through a mouthpiece. The oscillations are then recorded by a transducer system, and the resulting pressure-flow relationship is analyzed (i.e., Fourier transformation) to calculate respiratory impedance.
2.2. FOT Parameters
The impedance (usually abbreviated by the letter Z) reflects the overall opposition to the oscillation wave determined by the airways. For clinical applications, the output signal Z is recorded at the same physical location where the input signal is delivered, i.e., the mouth [15,16]. When performing the FOT in humans, it is strictly recommended to adopt oscillation frequencies which are outside the frequency of the subject normal breathing in order to avoid contamination in the spectral content of the input signal. In humans, clinical devices are typically set to adopt 5 Hz as the lowest frequency, because it must be at least an order of magnitude above the frequency of spontaneous breathing (0.2–0.3 Hz) [17]. In very limited conditions, such as anesthetized paralyzed children, mechanical ventilation, voluntary or induced apnea, low-frequency measurements can be used [18,19]. The impedance is composed of respiratory resistance (Rrs) and reactance (Xrs) [13]. These two fundamental parameters can be derived by the FOT as well. While Rrs reflects the total opposition to airflow due to airway caliber and tissue friction, Xrs reflects tissue elasticity and inertance of air [20,21]. Measurements are usually taken over a few breaths, lasting approximately 15–30 s. The technique does not require forced expiratory maneuvers, so it is particularly useful in populations such as young children, elderly individuals, and patients with neuromuscular disorders. Rrs represents the energy dissipative component of impedance and primarily reflects airway resistance [22]. Rrs is commonly measured at standard frequencies such as 5 Hz (R5), representing total airway resistance (central and peripheral), and 20 Hz (R20), which reflects central airway resistance [23,24]. The difference between R5 and R20 (R5–20) is used as an index of ventilation heterogeneity or small airway obstruction [7,24]. Xrs, in contrast, represents the elastic and inertial components of impedance. More negative Xrs values at low frequencies, particularly at 5 Hz (X5), are indicative of increased lung stiffness or reduced compliance of the peripheral lung [7,24]. Additionally derived parameters include the resonant frequency (Fres), which is the frequency at which Xrs crosses zero, and the area under the reactance curve (AX), calculated from X5 to Fres. These parameters provide further insight into the severity of mechanical impairment [13].
2.3. Recommendations for Measurements
The FOT is characterized by high reproducibility and the advantage of being effort-independent, as it does not require maximal respiratory maneuvers from the patient. This makes it particularly well-suited for children, elderly individuals, and patients with severe respiratory impairment [7,14]. Studies have shown that the FOT is feasible in children as young as two years old and demonstrates higher success rates compared to spirometry in young children with asthma [25]. The technique has been applied effectively to assess airway obstruction, bronchodilator response, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness, especially in pediatric populations with asthma, cystic fibrosis, and chronic lung disease of prematurity [14,24]. Furthermore, its sensitivity in detecting peripheral airway dysfunction may exceed that of traditional spirometry, making it a promising tool for both diagnosis and long-term monitoring [14,25]. Despite these advantages, the clinical implementation of the FOT still faces challenges related to standardization across devices and interpretation of parameters. Scientific societies are developing standardized methods to perform and interpret FOT measurements so as to promote wider use of the FOT in routine clinical practice [24,25].
A schematic summary of the trends in FOT parameters together with FOT clinical and research applications in obstructive and restrictive lung diseases are displayed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Schematic comparison of the main FOT parameters alterations and FOT applications in obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
3. Application of the Forced Oscillatory Technique in Obstructive Lung Diseases
The FOT has been thoroughly studied in the context of obstructive lung diseases, i.e., asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The typical FOT pattern includes increased respiratory system resistance (Rrs) and decreased reactance (Xrs), both of which correlate with the degree of airflow obstruction as assessed by spirometry [26,27].
3.1. Asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and airway hyperresponsiveness [28]. Clinical manifestations typically include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and dyspnea. These symptoms may vary in frequency and severity, often worsening at night or during physical exertion. Acute exacerbations may be triggered by inhaled allergens, pollutants, or irritants, leading to bronchoconstriction, mucus hypersecretion, and impaired oxygen exchange [29]. Diagnosis is primarily based on a characteristic pattern of symptoms and their response to treatment, and spirometry serves as the gold standard for diagnostic confirmation by demonstrating reversible airflow limitation. However, in children under six years of age, spirometry is often unreliable due to poor technique, necessitating alternative diagnostic tools. The FOT has emerged as a valuable adjunct to spirometry. Unlike spirometry, which requires forced expiratory maneuvers, the FOT measures respiratory impedance during tidal breathing, making it especially suitable for pediatric and elderly people where standard spirometry is challenging.
To date, limited studies have demonstrated clear diagnostic superiority of either technique in asthma. Notably, one recent investigation reported that oscillometry outperformed spirometry in both diagnosing asthma and assessing response to treatment over a three-month period [30]. Conversely, another study involving military personnel found that spirometry was more effective than oscillometry in diagnosing obstructive lung disease [31]. Such variability may stem from heterogeneity in device types and the lack of universally accepted abnormal threshold values for oscillometric parameters. The use of oscillometry for bronchodilator and bronchoprovocation testing in asthma is an area of investigation. According to current technical standards, a significant bronchodilator response (BDR) is considererd by a 40% decrease in R5, a 50% increase in X5, and an 80% decrease in the area under the reactance curve (Ax) in both adults and children [20]. A recent study assessing the predictive value of different oscillometric BDR thresholds found that resonant frequency (Fres) demonstrated the strongest correlation with positive BDR by spirometry and was more sensitive in identifying uncontrolled asthma [32]. Due to considerable variability in reported outcomes, the technical standards document does not currently provide definitive cut-off values for bronchoprovocation testing [20]. One of the major advantages of oscillometry lies in its heightened sensitivity for detecting bronchoconstriction [33]. This has been corroborated by recent studies demonstrating that oscillometry requires lower methacholine doses to achieve a positive response, and that baseline abnormal oscillometric measurements predict positive methacholine challenge results, as determined by spirometry [34]. In children undergoing evaluation for exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, only modest increases in R5 were observed following exercise challenge [35]. At present, bronchoprovocation thresholds for clinically meaningful interpretation in both adults and children should be considered in the context of scientific research and optimal and shared thresholds must be validated in further dedicated studies. While bronchodilator testing using oscillometry holds promise, further research is necessary to fully elucidate the clinical utility of bronchoprovocation testing. The FOT has proven particularly useful in preschool-aged children, a population in which spirometry is often unreliable. Grell et al. (2023) [36] found that abnormal FOT parameters, specifically R5, R5–20, R20, and Fres, measured in children under 5 years of age were predictive of spirometric impairment at school age. These findings suggest that the FOT may serve as a predictive tool for early asthma diagnosis [36]. Numerous studies have demonstrated the clinical utility of the FOT in the context of pediatric asthma. Improvements in X5 and R5–20 have been documented in children with uncontrolled asthma after one year of treatment, although these values remained inferior compared to healthy controls [37]. Similar findings were reported by Chaiwong who observed elevated R5 and R5–20 values in poorly controlled asthmatic children [38]. Furthermore, increases in R5, R5–20, X5, and Fres have been associated with poor asthma control in several studies [39,40]. Conversely, in adults, FOT findings have not consistently correlated with asthma control status [41]. The FOT not only complements spirometry but also provides a nuanced understanding of airway mechanics. Parameters such as R5 and low-frequency Xrs offer insights into both central and peripheral airway function. The FOT has shown high sensitivity in detecting bronchodilator responsiveness, though it should not be interpreted in isolation, particularly with regard to R5–20, which may not fully capture the complexity of airway obstruction. Although the FOT has not demonstrated a significant correlation with fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO), it has shown considerable promise in the detection of small airway dysfunction (SAD). SAD, which contributes to poor asthma control and increased exacerbation risk, often occurs even in mild asthma and may coexist with normal spirometry. Oscillometric parameters such as R5, X5, and Fres are particularly effective in identifying and quantifying SAD [42]. In a recent study, SAD was present in 73% of asthma patients and was associated with a higher rate of exacerbations, despite no differences in spirometry indices [8]. These findings align with evidence suggesting that the FOT may be superior to spirometry in diagnosing asthma and evaluating short-term treatment outcomes [30]. The FOT may play an essential role in monitoring treatment efficacy. It has been utilized to evaluate changes in airway resistance and reactance following initiation of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) and long-acting β-agonists (LABA) [43]. Furthermore, therapies targeting small airways—such as extrafine-particle ICS/LABA combinations and biologic agents like dupilumab and benralizumab—have demonstrated measurable improvements in the FOT parameters [42]. the FOT parameters may even guide personalized therapy. Sugawara et al. demonstrated that selection of ICS based on the FOT determined airflow obstruction type (central vs. peripheral) improved therapeutic outcomes. For instance, mometasone furoate was more effective in patients with central-type obstruction, whereas fluticasone propionate yielded better results in those with peripheral-type disease, as evidenced by improvements in the Leicester Cough Questionnaire [44]. More recently, we described that in a cohort of eosinophilic severe asthma patients, FOT R5–19 values correlate with FEV1/FVC and are significantly higher in obstruction [45].
Of notice, while for individuals aged 6 years and older spirometry, whenever feasible, is still considered the primary lung function test suggested by international guidelines, Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) recognizes that spirometry may be challenging in younger children who cannot perform forced expiratory maneuvers. GINA acknowledges that alternative methods—including the FOT/oscillometry—are increasingly available and can be considered, especially in children of preschool age who are unable to reliably perform spirometry [46,47].
3.2. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a chronic respiratory disorder characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation due to airway and/or alveolar abnormalities, typically caused by significant exposure to noxious particles or gases. According to the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD), the hallmark features of COPD include chronic cough, sputum production, dyspnea, and recurrent respiratory infections, often associated with bronchitis, bronchiolitis, and emphysematous destruction [48]. The diagnosis of COPD is primarily based on spirometry, which demonstrates a post-bronchodilator ratio of forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) to forced vital capacity (FVC) of less than 0.70 or below the lower limit of normal, indicating persistent airflow limitation [49]. The FOT has emerged as a valuable non-invasive tool to complement spirometry in the assessment of COPD. As known, the FOT is particularly useful for detecting early changes in peripheral airways, which are often involved before spirometry abnormalities become evident. Parameters such as R5, the difference between resistance at 5 and 20 Hz (R5–20), and the area under the reactance curve (AX) have shown strong correlations with disease severity, symptom burden, and exacerbated risk in COPD patients [50]. For example, Baba et al. (2022) demonstrated that patients with smoking-related COPD exhibit greater impairment in oscillometric indices of small airways and a reduced bronchodilator response compared to non-smokers [51]. Furthermore, the FOT has shown promising results in identifying subclinical airway impairment in asymptomatic smokers with normal spirometry, supporting its potential role in screening high-risk populations for early COPD detection [38]. The frequency-dependent nature of oscillometry measurements allows for the detection of subtle changes in small airways, which are often the earliest site of pathology in COPD. This makes the FOT particularly valuable in the early stages of disease, when traditional spirometry may still appear normal. Several studies have also highlighted the ability of the FOT to differentiate between COPD and other obstructive lung diseases such as asthma. Notably, Desai and Joshi reported a significant association between increased ΔX and COPD severity, suggesting its utility in distinguishing COPD from asthma [52]. Brashier and Salvi further observed that in asthma, resistance (R) is more prominently affected, while in COPD, reactance (X) and parameters reflecting peripheral airway involvement (e.g., R5–20 and AX) are more consistently impaired. This was corroborated by studies showing that even at similar levels of FEV1, COPD patients tend to show greater abnormalities in peripheral airway indices compared to asthmatic patients [53]. Incorporating the FOT into the routine assessment of COPD patients might thus offer a more comprehensive evaluation of disease burden.
4. Application of the Forced Oscillatory Technique in Restrictive Lung Diseases
4.1. Interstitial Lung Diseases
Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILDs) encompass a heterogeneous group of pulmonary disorders characterized by varying degrees of inflammation and fibrosis of the lung interstitium [54]. Spirometric evaluation typically reveals a restrictive ventilatory defect, with reductions in forced vital capacity (FVC), total lung capacity (TLC), and diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO), reflecting impaired lung compliance and parenchymal distortion.
The FOT has emerged as a promising, non-invasive modality for assessing respiratory mechanics in ILDs. Although the FOT has been primarily adopted in the evaluation of obstructive airway diseases, its applicability has expanded to restrictive pathologies, offering insight into SAD, lung stiffness, and ventilation heterogeneity.
Recent histopathological and imaging studies have demonstrated that early small airway involvement—such as loss of terminal bronchioles and fibrotic remodeling—is a fundamental feature of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), the prototypical form of ILD [55]. This has stimulated interest in the FOT as a tool for early detection and phenotyping of ILD. Several studies have investigated correlations between FOT-derived parameters, conventional pulmonary function tests (PFTs), and high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) findings. The FOT’s key advantage lies in its effort-independent nature, making it especially useful in elderly or debilitated patients who may be unable to perform reliable spirometry [56]. A retrospective analysis by Takeichi et al. involving 29 patients with various respiratory conditions indicated that oscillometric indices of impedance primarily reflect small airway alterations and ventilation inhomogeneities rather than gross parenchymal destruction. Notably, increased resistance (Rrs) and more negative reactance (Xrs) values were significantly associated with SAD in ILD patients [57]. Complementary findings by Mikamo et al. revealed significant alterations in R5–20, X5, resonant frequency (Fres), and area of reactance (AX) in ILD patients with SAD [58]. In a comparative study, Miyoshi et al. evaluated FOT parameters across ILD, asthma, and COPD cohorts. ILD patients exhibited lower resistance values (R5, R20) than those with asthma yet showed more negative reactance and higher Fres and ALX values than COPD patients. These findings underscore the potential of the FOT in distinguishing restrictive from obstructive phenotypes [59]. Further, Xrs has emerged as a sensitive marker of restrictive impairment. Tatsuru Ishikawa et al. identified a significant association between baseline Xrs and survival in patients with IPF, with specific cut-off values proposed to predict three-year mortality. Their study highlights the prognostic potential of the FOT in longitudinal disease monitoring [9]. Changes in inspiratory X5 have been associated with FVC and DLCO, as shown by Matesanz-López et al., reinforcing the role of the FOT as a surrogate marker of disease severity. Notably, unlike in COPD, where expiratory reactance dominates oscillometric profiles due to dynamic airway collapse, ILD is characterized by more pronounced abnormalities during inspiration, an important distinction with potential diagnostic implications [56]. The FOT has also shown utility in the assessment of connective tissue disease-associated ILD (CTD-ILD). In rheumatoid arthritis-related ILD, a resonant frequency above 14.14 Hz was significantly associated with greater disease burden on HRCT and served as an independent predictor of pulmonary involvement [60]. Additionally, Panagopoulos et al. demonstrated that in systemic sclerosis-associated ILD (SSc-ILD), SAD could be detected via the FOT even in the absence of HRCT abnormalities, with the R5–20 gradient serving as a sensitive marker of subclinical airway involvement [61,62].
Finally, application of the FOT might be relevant to assess lung function in rare and ultra-rare diseases with lung involvement, such as Acid Sphingomyelinase Disease (ASMD) which can manifest from childhood and which can be characterized by restrictive as well as mixed respiratory pattern [63,64].
4.2. Obesity and Kyphoscoliosis
Restrictive respiratory patterns are also observed in extrapulmonary conditions such as obesity and kyphoscoliosis, wherein thoracic mechanics are altered due to anatomical or functional constraints.
In obesity (defined as BMI > 30), increased body mass results in reduced functional residual capacity (FRC), leading to elevated airway resistance. Miura et al. demonstrated that R5 values increase proportionally with BMI, influenced both by reduced lung volumes and upper airway narrowing due to adipose tissue accumulation. The study emphasized the importance of adjusting oscillometric reference values for BMI and sex, especially when interpreting results in epidemiological or clinical settings [65]. Similarly, in kyphoscoliosis and ankylosing spondylitis, thoracic cage deformities reduce chest wall compliance and lung expansion. Using the FOT across a frequency range of 2–26 Hz, Van Noord et al. found elevated Rrs and mildly reduced Xrs in both conditions, with negative frequency dependence, reflecting mechanical restriction and inhomogeneous impedance distribution [22].
4.3. Neuromuscular Disorders
The FOT is emerging as a valuable, non-invasive tool for assessing respiratory mechanics in patients with neuromuscular disorders (NMDs), including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), where traditional spirometry may be limited by poor patient cooperation or bulbar dysfunction. FOT indices, particularly low-frequency reactance (X5), showed significant correlations with conventional measures such as FVC and maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP), highlighting the FOT’s sensitivity to early respiratory muscle weakness even when spirometric values remain within normal limits. This supports its role as a screening and monitoring tool in NMDs, especially for detecting subclinical respiratory decline.
Furthermore, the FOT may help differentiate between upper and lower airway contributions to respiratory dysfunction and could be particularly beneficial in longitudinal monitoring or in individuals with bulbar involvement who are unable to perform forced maneuvers reliably.
Although standardization is still evolving, the FOT holds promise for incorporation into routine respiratory surveillance in NMD populations and may complement conventional tools in assessing the impact of interventions such as non-invasive ventilation or respiratory muscle training [66].
5. Future Perspectives
The FOT has transitioned from an ancillary assessment tool to a potentially key component in the diagnostic and prognostic functional evaluation of both obstructive and restrictive lung disease. Its ability to capture subtle alterations in peripheral airway function, particularly in early or subclinical disease stages, makes it highly attractive for clinical integration.
Recent studies have proposed the use of oscillometric indices such as Fres and Xrs not only for detection but also for the prognostic purposes. For instance, Fres > 14.14 Hz correlates with both HRCT-based disease extent and spirometric impairment, offering predictive accuracy superior to traditional PFTs in early rheumatoid arthritis-ILD [60]. In IPF, inspiratory Fres and ALX have been linked to disease progression and composite physiological indices [67].
Moreover, a limited number of Clinical Trials so far have focused on the FOT or impulse oscillometry outcomes as primary/secondary endpoints or biomarkers. Table 2 includes trial identifiers, target population, interventions, the FOT parameters measured, outcome role, and current status.

Table 2.
Ongoing or recent trials incorporating FOT parameters.
Standardization of the FOT thresholds, integration into multidimensional scoring systems, and validation through longitudinal cohorts will be essential for a wider adoption of this technique. Moreover, the use of machine learning algorithms could unlock the full diagnostic potential of the multifrequency, intra-breath data generated by the FOT, enabling early stratification and personalized treatment pathways.
As respiratory medicine moves toward more personalized and noninvasive diagnostic tools, the FOT might play a growing role in future guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma and COPD. As already evidenced, since the FOT allows for sensitive assessment of respiratory mechanics during tidal breathing without requiring patient effort or forced maneuvers, the technique might be especially beneficial in the diagnosis and follow up of elderly, pediatric, or severely ill populations. Future guidelines are expected to incorporate the FOT not only as a diagnostic adjunct but also as a tool for ongoing disease management, especially as normative reference values become standardized and device accessibility improves. Integration of the FOT into clinical pathways may enhance objective assessment in patients who are unable to perform reliable spirometry, ultimately contributing to a more inclusive and effective approach to chronic airway disease management.
6. Limitations of the Forced Oscillation Technique
Despite its promising advantages, the FOT still has several limitations which restrict its widespread clinical adoption. Particularly, one of the main challenges lies in the lack of universally accepted reference values and standardized protocols, which might limit the comparison of results across different devices and populations.
Furthermore, while the FOT is highly sensitive to describe peripheral airway mechanics, no standardized comparability to volumetric spirometry data limit its standalone diagnostic value in current guideline-based classifications.
Interpretation of the FOT parameters requires specialized expertise and remains less intuitive to many clinicians compared to traditional spirometry.
Large-scale, prospective trials validating the FOT impact on outcomes are needed before it can be fully integrated into routine practice or guidelines.
7. Economic Considerations and Global Availability of the Forced Oscillation Technique
From an economic perspective, although the initial investment in the FOT devices can be substantial, improved disease monitoring, earlier diagnosis of SAD, and consequently better disease management might reduce the costs related to disease therapy. Unfortunately, at the moment, to the best of our knowledge, no studies on the economic impact of the wide-scale adoption of the FOT are available.
The current lack of standardized reimbursement pathways and limited guideline endorsement in many health systems may hinder widespread adoption of the FOT, especially in resource-limited environments. Additionally, clinicians need to be specifically trained in the use of the FOT and the relative unfamiliarity with the FOT among general practitioners could result in FOT underutilization.
Moreover, the availability and clinical use of the FOT vary widely across countries, reflecting differences in healthcare infrastructure, guideline adoption, economic resources, and diagnostic priorities. While in high-income countries the FOT has started to be used, particularly in academic centers, as a complement to common lung function tests, both in research and selected clinical use, in low- and middle-income countries, access to the FOT is very limited. The high cost of equipment, lack of trained personnel, and focus on acute respiratory infections and tuberculosis often push chronic disease diagnostics like the FOT to a lower priority.
In this sense, overall, the global availability of the FOT is expanding, but its use remains primarily concentrated in research settings or specialized care units in wealthier countries.
8. Conclusions
In conclusion, the FOT offers a non-invasive, effort-independent, and highly sensitive modality for the functional characterization of obstructive and restrictive lung diseases. Although, at the moment, the FOT is mainly used for research purposes, its utility has been demonstrated in the diagnosis, monitoring, and prognostication, particularly in patients for whom conventional spirometry might be limiting or inconclusive due to the inability to coordinate or to produce an adequate effort. Future research and standardization of the technique are needed to ensure that the FOT is increasingly considered a core component in respiratory diagnostics of obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.T.; writing—original draft preparation, C.T., S.M. (Sabrina Mira), M.I., S.M. (Sara Maggioni), M.Z., S.C. and C.I.; writing—review and editing, C.T., E.M.P., and M.M.; supervision, M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bhattarai, P.; Myers, S.; Chia, C.; Weber, H.C.; Young, S.; Williams, A.D.; Sohal, S.S. Clinical Application of Forced Oscillation Technique (FOT) in Early Detection of Airway Changes in Smokers. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.B.; Brody, A.W.; Lewis, D.H.; Burgess, B.F., Jr. Oscillation Mechanics of Lungs and Chest in Man. J. Appl. Physiol. 1956, 8, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.H.T. CORP: Measurement of lung function in small animals. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 123, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundblad, L.K.A. Issues determining direct airways hyperresponsiveness in mice. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 32648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.C.; Watson, J.W. Oscillatory mechanics of the respiratory system in normal rats. Respir. Physiol. 1982, 48, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, W.E.; Long, E.C. Respiratory impedance and volume flow at high frequency in dogs. J. Appl. Physiol. 1961, 16, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundblad, L.K.A.; Robichaud, A. Oscillometry of the respiratory system: A translational opportunity not to be missed. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2021, 320, L1038–L1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottini, M.; Lombardi, C.; Comberiati, P.; Berti, A.; Menzella, F.; Dandurand, R.J.; Diamant, Z.; Chan, R. Oscillometry-defined small airways dysfunction as a treatable trait in asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025, 134, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Nishikiori, H.; Mori, Y.; Fujino, K.; Saito, A.; Takahashi, M.; Kuronuma, K.; Hinotsu, S.; Chiba, H. The impact of respiratory reactance in oscillometry on survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. MC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, D.A.; Simpson, S.J.; Berger, K.I.; Calverley, P.; de Melo, P.L.; Dandurand, R.; Dellacà, R.L.; Farah, C.S.; Farré, R.; Hall, G.L.; et al. Clinical significance and applications of oscillometry. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 210208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, A.; Locatelli, F.; Gini, E.; Albicini, F.; Tirelli, C.; Cerveri, I.; Corsico, A.G. The course of asthma during pregnancy in a recent, multicase–control study on respiratory health. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, A.; Jarenbäck, L.; Bjermer, L.; Tufvesson, E. Assessment of expiratory vs inspiratory resistance and reactance using FOT as a measure of air trapping. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54 (Suppl. S63), PA2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Desai, A.; Therkorn, J.H.; Klein-Adams, J.C.; Sotolongo, A.M.; Falvo, M.J. Employing the Forced Oscillation Technique for the Assessment of Respiratory Mechanics in Adults. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 180, e63165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skylogianni, E.; Douros, K.; Anthracopoulos, M.B.; Fouzas, S. The Forced Oscillation Technique in Paediatric Respiratory Practice. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2016, 18, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, J.H.T.; Irvin, C.G.; Farré, R.; Hantos, Z. Oscillation Mechanics of the Respiratory System. In Comprehensive Physiology; Wiley: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 1233–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, J.H.T.; Irvin, C.G. Measuring lung function in mice: The phenotyping uncertainty principle. J Appl Physiol. 2003, 94, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandurand, R.J.; Lavoie, J.P.; Lands, L.C.; Hantos, Z. Comparison of oscillometry devices using active mechanical test loads. ERJ Open Res. 2019, 5, 00160–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sly, P.D.; Hayden, M.J.; Peták, F.; Hantos, Z. Measurement of low-frequency respiratory impedance in infants. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutchen, K.R.; Yang, K.; Kaczka, D.W.; Suki, B. Optimal ventilation waveforms for estimating low-frequency respiratory impedance. J. Appl. Physiol. 1993, 75, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.G.; Bates, J.; Berger, K.I.; Calverley, P.; De Melo, P.L.; Dellacà, R.L.; Farre, R.; Hall, G.; Ioan, I.; Irvin, C.G.; et al. Technical standards for respiratory oscillometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostveen, E.; MacLeod, D.; Lorino, H.; Farré, R.; Hantos, Z.; Desager, K.; Marchal, F. The forced oscillation technique in clinical practice: Methodology, recommendations and future developments. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 1026–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Noord, J.A.; Clément, J.; Van De Woestijne, K.P.; Demedts, M. Total Respiratory Resistance and Reactance in Patients with Asthma, Chronic Bronchitis, and Emphysema. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 143 Pt 1, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatawadekar, S.A.; Leary, D.; Chen, Y.; Ohishi, J.; Hernandez, P.; Brown, T.; McParland, C.; Maksym, G.N. A Study of Artifacts and Their Removal During Forced Oscillation of the Respiratory System. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.; Parakh, A. Forced oscillation technique and impulse oscillometry: An update on current understanding. J. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023, 2, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alblooshi, A.; Alkalbani, A.; Albadi, G.; Narchi, H.; Hall, G. Is forced oscillation technique the next respiratory function test of choice in childhood asthma. World J. Methodol. 2017, 7, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcanti, J.V.; Lopes, A.J.; Jansen, J.M.; Melo, P.L. Detection of changes in respiratory mechanics due to increasing degrees of airway obstruction in asthma by the forced oscillation technique. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mango, A.M.G.T.; Lopes, A.J.; Jansen, J.M.; Melo, P.L. Changes in respiratory mechanics with increasing degrees of airway obstruction in COPD: Detection by forced oscillation technique. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, P. 2023 GINA report for asthma. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsahai, J.M.; Hansbro, P.M.; Wark, P.A.B. Mechanisms and Management of Asthma Exacerbations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandilwar, S.; Thorve, S.M.; Gupta, V.; Prabhudesai, P. Role of impulse oscillometry in diagnosis and follow-up in bronchial asthma. Lung India 2023, 40, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houle, M.C.; Cavacece, C.T.; Gonzales, M.A.; Anderson, J.T.; Hunninghake, J.C.; Holley, A.B.; Morris, M.J. Correlation of Impulse Oscillometry with Spirometry in Deployed Military Personnel with Airway Obstruction. Mil. Med. 2023, 188 (Suppl. S6), 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayasu, H.; Shirai, T.; Hirai, K.; Akamatsu, T.; Kitahara, Y. Bronchodilator response using oscillometry to detect uncontrolled asthma. Allergol. Int. 2023, 72, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostorz-Nosal, S.; Jastrzębski, D.; Błach, A.; Skoczyński, S. Window of opportunity for respiratory oscillometry: A review of recent research. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2023, 316, 104135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corral-Blanco, M.; Díaz Campos, R.M.; Peláez, A.; Melero Moreno, C. Beyond forced exhalation: Impulse oscillometry as a promising tool for bronchial hyperresponsiveness evaluation. J. Asthma 2024, 61, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Gupta, S.; Jat, K.R.; Sankar, J.; Lodha, R.; Kabra, S.K. Impulse oscillometry (IOS) for detection of exercise induced bronchoconstriction in children with asthma ages 6–15 years. J. Asthma 2023, 60, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grell, A.V.; Vera, R.G.; Yarur, A.M.; Castro-Rodriguez, J.A.; Montenegro, M.A.P.; Colodro, O.F.; Elías, S.A.; Bentjerodt, M.S.; Poblete, J.M. Impulse oscillometry in preschool children with persistent asthma can predict spirometry at school age. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023, 58, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Vera, R.; Saavedra Bentjerodt, M.; Vidal Grell, A.; Mackenney Poblete, J. Función pulmonar evolutiva evaluada por oscilometría de impulso en prescolares con asma. Andes Pediatr. 2021, 92, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwong, W.; Namwongprom, S.; Liwsrisakun, C.; Pothirat, C. The roles of impulse oscillometry in detection of poorly controlled asthma in adults with normal spirometry. J. Asthma 2022, 59, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawman, L.; Mukherjee, A.; Sethi, T.; Agrawal, A.; Kabra, S.K.; Lodha, R. Role of Impulse Oscillometry in Assessing Asthma Control in Children. Indian Pediatr. 2020, 57, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.R.; Lipworth, B. Airwave oscillometry and patient-reported outcomes in persistent asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 124, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Palacios, M.Á.; Hervás Marín, D.; Giner Valero, A.; Colomer Hernández, N.; Torán Barona, C.; Hernández Fernández de Rojas, D. Correlation between impulse oscillometry parameters and asthma control in an adult population. J. Asthma Allergy 2019, 12, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, M.; Trinkmann, F.; Kirsten, A.-M.; Pedersen, F.; Herzmann, C.; von Mutius, E.; Kopp, M.V.; Hansen, G.; Waschki, B.; Rabe, K.F.; et al. Small Airway Dysfunction Links Asthma Severity with Physical Activity and Symptom Control. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 3359–3368.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.S.; Rutting, S.; Farrow, C.E.; Tonga, K.O.; Watts, J.; Dame-Carrol, J.R.; Bertolin, A.; King, G.G.; Thamrin, C.; Chapman, D.G. Ventilation heterogeneity and oscillometry predict asthma control improvement following step-up inhaled therapy in uncontrolled asthma. Respirology 2020, 25, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, H.; Saito, A.; Yokoyama, S.; Tsunematsu, K.; Chiba, H.; Takahashi, H. A retrospective analysis of usefulness of impulse oscillometry system in the treatment of asthma. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirelli, C.; Parazzini, E.M.; Sacchi, L.; Carone, G.; Pescol, F.; Maggioni, S.; Belmonte, L.A.; Albrici, C.; Contino, S.; Re, B.; et al. Forced oscillatory technique R5-19 values correlate with spirometry FEV1/FVC in severe eosinophilic asthma. An observational, prospective, cohort study. Respir. Med. 2025, 247, 108260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreetapirom, P.; Kiewngam, P.; Jotikasthira, W.; Kamchaisatian, W.; Benjaponpitak, S.; Manuyakorn, W. Forced oscillation technique as a predictor for loss of control in asthmatic children. Asia Pac. Allergy 2020, 10, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauhkonen, E.; Kaltsakas, G.; Sivagnanasithiyar, S.; Iles, R. Comparison of forced oscillation technique and spirometry in paediatric asthma. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00202–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirelli, C.; Mira, S.; Belmonte, L.A.; De Filippi, F.; De Grassi, M.; Italia, M.; Maggioni, S.; Guido, G.; Mondoni, M.; Canonica, G.W.; et al. Exploring the Potential Role of Metabolomics in COPD: A Concise Review. Cells 2024, 13, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, P. GOLD COPD report: 2024 update. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crim, C.; Celli, B.; Edwards, L.D.; Wouters, E.; Coxson, H.O.; Tal-Singer, R.; Calverley, P.M. Respiratory system impedance with impulse oscillometry in healthy and COPD subjects: ECLIPSE baseline results. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, R.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Berger, K.I.; Goldring, R.M.; Liu, M.; Kazeros, A.; Rosen, R.; Reibman, J. COPD in Smoking and Non-Smoking Community Members Exposed to the World Trade Center Dust and Fumes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, U.; Joshi, J.M. Impulse Oscillometry. Adv. Respir. Med. 2019, 87, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brashier, B.; Salvi, S. Measuring lung function using sound waves: Role of the forced oscillation technique and impulse oscillometry system. Breathe 2015, 11, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirelli, C.; Pesenti, C.; Miozzo, M.; Mondoni, M.; Fontana, L.; Centanni, S. The Genetic and Epigenetic Footprint in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis: A State-of-the-Art Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verleden, S.E.; Tanabe, N.; McDonough, J.E.; Vasilescu, D.M.; Xu, F.; Wuyts, W.A.; Piloni, D.; De Sadeleer, L.; Willems, S.; Mai, C.; et al. Small airways pathology in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matesanz-López, C.; Raboso-Moreno, B.; Saldaña-Pérez, L.E.; Rodríguez-Nieto, M.J.; Río-Ramírez, M.T. Is Lung Function Measured by Oscillometry Useful in Interstitial Lung Diseases? Open Respir. Arch. 2024, 6, 100278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeichi, N.; Yamazaki, H.; Fujimoto, K. Comparison of impedance measured by the forced oscillation technique and pulmonary functions, including static lung compliance, in obstructive and interstitial lung disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2019, 14, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikamo, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Oyama, Y.; Kono, M.; Enomoto, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Inui, N.; Sumikawa, H.; Johkoh, T.; Suda, T. Clinical Significance of Forced Oscillation Technique for Evaluation of Small Airway Disease in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Lung 2016, 194, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, S.; Katayama, H.; Matsubara, M.; Kato, T.; Hamaguchi, N.; Yamaguchi, O. Prediction of Spirometric Indices Using Forced Oscillometric Indices in Patients with Asthma, COPD, and Interstitial Lung Disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2020, 15, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-C.; Chang, S.-H.; Chen, W.-C.; Wu, B.-R.; Chen, C.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Hsu, W.-H.; Lan, J.-L.; Chen, D.-Y. Application of impulse oscillometry to detect interstitial lung disease and airway disease in adults with rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, P.K.; Goules, A.V.; Georgakopoulou, V.E.; Kallianos, A.; Chatzinikita, E.; Pezoulas, V.C.; Malagari, K.; Fotiadis, D.I.; Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.; Vassilakopoulos, T.; et al. Small airways dysfunction in patients with systemic sclerosis and interstitial lung disease. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1016898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirelli, C.; Zanframundo, G.; Valentini, A.; Bortolotto, C.; Dore, R.; Oggionni, T.; Milani, P.; Bravi, E.; Kadija, Z.; Mariani, F.; et al. CT-guided biopsy in the differential diagnosis of Sjogren syndrome associated cystic lung disease: A case of lung nodular AL-k amyloidosis. Radiol. Case Rep. 2020, 15, 2331–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirelli, C.; Rondinone, O.; Italia, M.; Mira, S.; Belmonte, L.A.; De Grassi, M.; Guido, G.; Maggioni, S.; Mondoni, M.; Miozzo, M.R.; et al. The Genetic Basis, Lung Involvement, and Therapeutic Options in Niemann-Pick Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirelli, C.; Arbustini, E.; Meloni, F. Bilateral Cystic Bronchiectasis as Novel Phenotype of Niemann-Pick Disease Type B Successfully Treated With Double Lung Transplantation. Chest 2021, 159, e293–e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, E.; Tsuchiya, N.; Igarashi, Y.; Arakawa, R.; Nikkuni, E.; Tamai, T.; Tabata, M.; Ohkouchi, S.; Irokawa, T.; Ogawa, H.; et al. Respiratory resistance among adults in a population-based cohort study in Northern Japan. Respir. Investig. 2019, 57, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliaz, S.; Yunisova, G.; Cakmak, O.O.; Celebi, O.; Bulus, E.; Duman, A.; Bayraktaroglu, M.; Oflazer, P. The clinical use of impulse oscillometry in neuromuscular diseases. Respir. Med. 2022, 200, 106931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Shirai, T.; Mori, K.; Mikamo, M.; Shishido, Y.; Akita, T.; Morita, S.; Asada, K.; Suda, T. Inspiratory resonant frequency of forced oscillation technique as a predictor of the composite physiologic index in interstitial lung disease. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2015, 207, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).