Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Diagnostic and Pathogenic Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
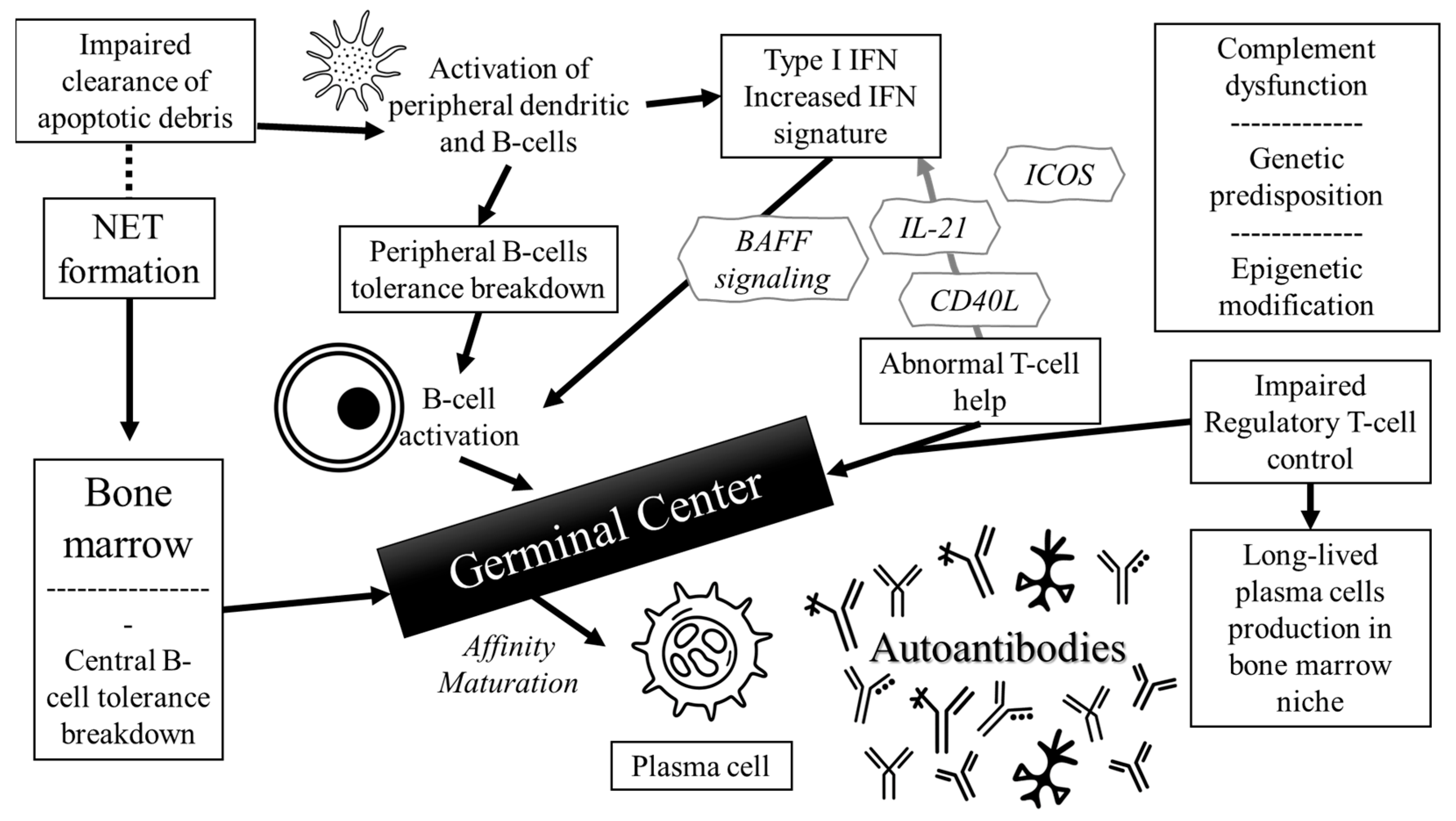
2. Pathophysiology of Autoantibodies in SLE
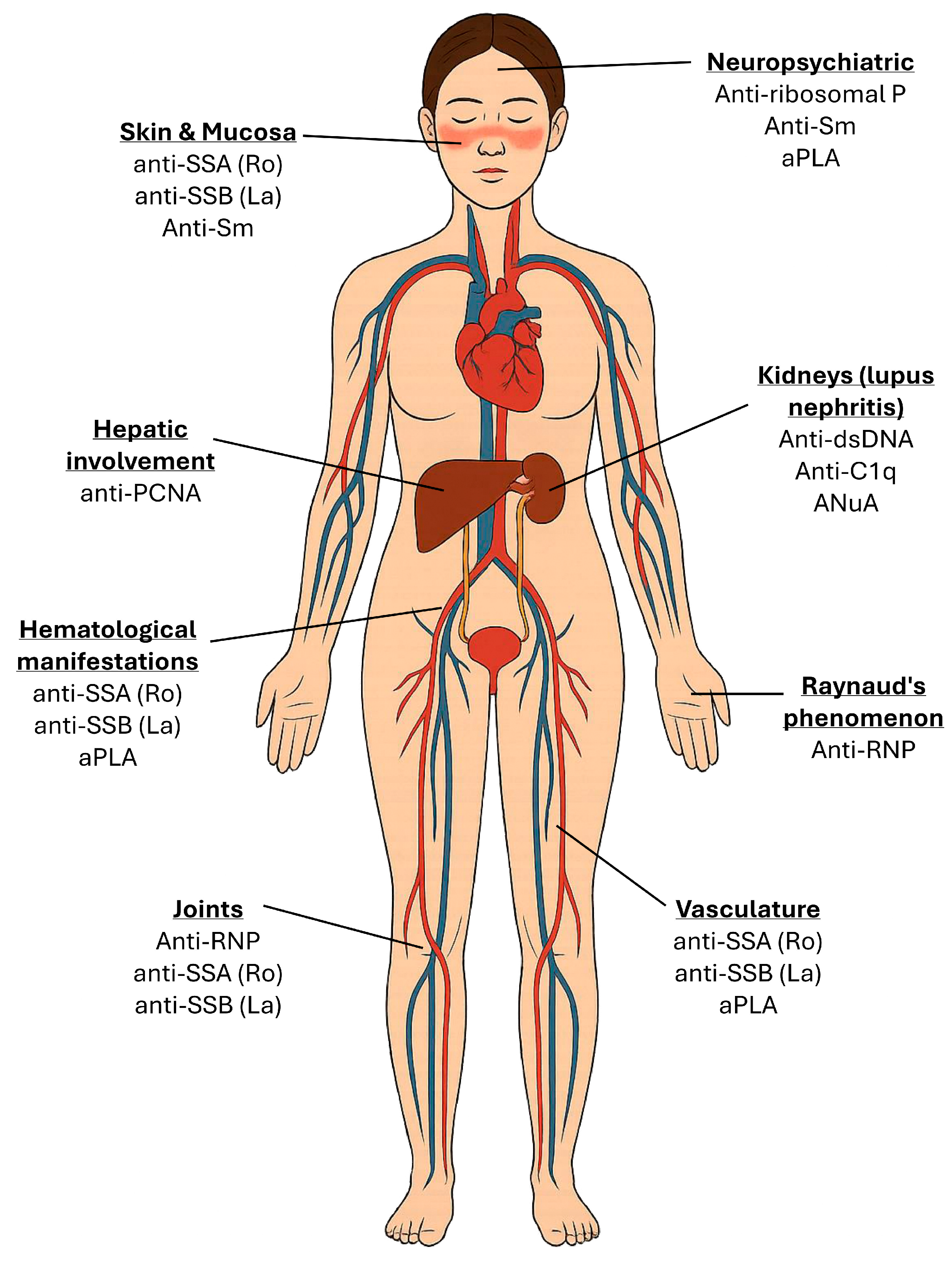
3. Clinical Significance of Key Autoantibodies
| Autoantibody | Prevalence | Associated Clinical Features | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANA | >95% | Screening; entry criterion in 2019 EULAR/ACR; non-specific | Bind nuclear antigens, activate innate immunity via Fc and TLR signaling [43]. |
| Anti-dsDNA | 50–70% | Lupus nephritis; flares; complement consumption | Bind double-stranded DNA forming nephritogenic immune complexes, activate complement, and deposit in glomeruli, triggering inflammation and tissue damage [44]. |
| Anti-Sm | 25–30% | Highly specific for SLE; systemic disease; NPSLE | Target snRNPs interfering with RNA splicing; form immune complexes that activate dendritic cells via TLRs, promoting type I IFN production and systemic autoimmunity; contribute to neurotoxicity via CNS penetration [45]. |
| Anti-RNP | ~40% | Raynaud’s; arthritis; overlap syndromes | Bind U1-RNP forming immune complexes that activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells via TLR7, enhancing type I IFN production [46]. |
| Anti-Ro/SSA | 30–40% | Cutaneous lupus; photosensitivity; neonatal lupus; hematologic involvement | Target Ro52/Ro60 ribonucleoproteins, forming immune complexes that activate dendritic cells via TLRs; cross placenta; bind cardiac tissue [47]. |
| Anti-La/SSB | 10–15% | Cutaneous lupus; neonatal lupus; hematologic involvement | Bind RNA-associated proteins forming immune complexes that activate Toll-like receptors and type I interferon pathways; mediate immune dysregulation [47]. |
| Anti-ribosomal P | 10–20% | Psychosis; depression; neuropsychiatric lupus | Target ribosomal P proteins; potential CNS penetration, disrupt neuronal function, and trigger neuroinflammation via cytokine release and immune complex formation [48]. |
| ANuA | 70–90% | Early SLE; lupus nephritis | Bind nucleosome complexes; promote immune complex formation, activate complement, and mediate glomerular deposition and glomerular inflammation [49]. |
| Anti-histone | ~30% | Drug-induced lupus | Bind to histone proteins within chromatin forming immune complexes; activate complement [50]. |
| Anti-C1q | 15–45% | Lupus nephritis | Bind the collagen-like region of C1q, impair apoptotic cell clearance, activate complement, and promote immune complex-mediated inflammation [51]. |
| aPLA (LA, aCL, anti-β2GPI) | 30–40% | Thrombosis; pregnancy loss; antiphospholipid syndrome | Bind phospholipid-bound proteins; activate endothelial cells, platelets, and complement; activate procoagulant and autoimmune mechanisms [52]. |
4. Autoantibodies in Clinical Diagnosis
5. Lupus Nephritis and Autoantibodies
6. Therapeutic Implications and Emerging Targets
| Agent | Target | Mechanism | Indications | Clinical Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rituximab | CD20+ B cells | Depletes mature B cells; reduces autoantibody production | Refractory SLE/LN/NPSLE | Similar to placebo effects in the EXPLORER [122] and the LUNAR [123] trials. Off-label use supported in refractory NPSLE (85% response, 45% relapse), reduces anti-dsDNA, steroid-sparing [124]. |
| Belimumab | BAFF inhibition | Inhibits B cell survival | Non-renal and renal SLE | Improved SRI-4 and renal response in BLISS-52/76 and BLISS-LN trials; FDA-approved; steroid-sparing [125,126,127]. Significant improvement in refractory SLE and efficacy in pediatric SLE [128,129]. |
| Anifrolumab | IFNAR1 | Blocks type I IFN receptor, inhibiting IFN signaling | Non-renal SLE | MUSE: increased SRI-4 (34.3% vs. 17.6%, p = 0.014), benefit in IFN-high [131]. TULIP-1: no SRI-4 benefit, signal in BICLA and CLASI [133]. TULIP-2: ↑BICLA (47.8% vs. 31.5%, p = 0.001), steroid-sparing, skin benefits [134]. |
| Obinutuzumab | CD20+ B cells | Type II anti-CD20 antibody; induces enhanced B cell apoptosis | Refractory LN post-rituximab | NOBILITY: improved CRR (41% vs. 23%, p = 0.026) with improvements from baseline in C3, C4 anti-dsDNA and eGFR (adjusted mean difference, 9.7 mL/min/1.73 m2 (95% CI 1.7–18), p = 0.017) [138]. |
| Rontalizumab | IFN-α | Neutralizes all 12 IFN-α subtypes | SLE (low ISG subset) | ROSE: no overall benefit vs. placebo; ISM-low subgroup: improved SRI, reduced flares (HR 0.61, p = 0.004), steroid-sparing [140]. |
| Sifalimumab | IFN-α | Neutralizes most IFN-α subtypes | SLE | Phase IIb: improved SRI-4 at week 52 (58–60% vs. 45%), broad disease activity improvement, increased occurrence of herpes zoster infection [141]. |
| Abatacept | CD80/CD86 | Inhibits CD28 co-stimulation on T cells | SLE, LN | ACCESS: no improvement in CRR at 24 weeks (33% vs. 31%); 50% of abatacept responders sustained remission after stopping immunosuppressants [144]. |
| Dapirolizumab | PEGylated anti-CD40L Fab | Inhibits T cell–B cell interaction via CD40–CD40L axis | SLE | Phase II: modest improvement in BICLA, SRI-4, and serologic markers vs. placebo; dose–response not met (p = 0.07) [146]. |
| Baricitinib | JAK 1/2 | Inhibits JAK-STAT signaling; reduces inflammatory cytokine signaling | Cutaneous/articular SLE | Improvement in arthritis/rash resolution at week 24 (67% vs. 53%, p = 0.041); preclinical data support renoprotection via JAK/STAT modulation [154,155]. |
| Tofacitinib | JAK 1/3 | Modulates type I IFN responses and T cell activation | Investigational | Phase I: improved HDL profile, vascular function, and IFN signature in SLE; benefits stronger in STAT4-risk carriers [156]. |
7. Challenges and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANA | Anti-nuclear antibodies |
| aCL | Anti-cardiolipin antibody |
| ANuA | Anti-nucleosome antibodies |
| anti-dsDNA | Anti-double-stranded DNA antibody |
| anti-C1q | Anti-C1q antibody |
| anti-Jo-1 | Anti-histidyl-tRNA synthetase |
| anti-Ku | Antibodies to Ku protein |
| anti-La | Anti-La/SSB antibody |
| anti-PCNA | Anti-proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
| anti-PM-Scl | Anti-polymyositis/scleroderma antibodies |
| aPLA | Antiphospholipid antibodies |
| APS | Antiphospholipid syndrome |
| anti-RBP | Anti-RNA binding protein |
| anti-RNP | Anti-ribonucleoprotein |
| anti-Ro, | Anti-Ro/SSA antibody |
| anti-Sm | Anti-Smith antibody |
| anti-SSA | Anti-Sjogren’s syndrome A |
| anti-SSB | Anti-Sjogren’s syndrome B |
| BAFF | B cell-activating factor |
| BILAG | British Isles Lupus Assessment Group |
| CD | Cluster of differentiation |
| CLASI | Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays |
| ENA | Extractable nuclear antigen |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| ICOS | Inducible T cell costimulator |
| IFN | Type I interferon |
| IFNAR | Interferon-alpha receptor |
| IIFA | Indirect immunofluorescence assay |
| IL-21 | Interleukin-21 |
| JAKs | Janus kinases |
| LLADAS | Lupus low disease activity state |
| MMF | Mycophenolate mofetil |
| NET | Neutrophil extracellular trap |
| pDCs | Plasmacytoid dendritic cells |
| SELENA-SLEDAI | Safety of Estrogens in Lupus Erythematosus National Assessment-Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| STAT | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TLR | Toll-like receptors |
References
- Tsokos, G.C.; Lo, M.S.; Reis, P.C.; Sullivan, K.E. New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Isenberg, D.A. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, C.H.; Hiraki, L.T.; Liu, J.; Fischer, M.A.; Solomon, D.H.; Alarcón, G.S.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; Costenbader, K.H. Epidemiology and sociodemographics of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis among US adults with Medicaid coverage, 2000–2004. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2013, 65, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.R.W.; Drenkard, C.; Falasinnu, T.; Hoi, A.; Mak, A.; Kow, N.Y.; Svenungsson, E.; Peterson, J.; Clarke, A.E.; Ramsey-Goldman, R. Global epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekvig, O.P.; van der Vlag, J.; Seredkina, N. Review: Antinucleosome antibodies: A critical reflection on their specificities and diagnostic impact. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dema, B.; Charles, N. Autoantibodies in SLE: Specificities, Isotypes and Receptors. Antibodies 2016, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurasov, S.; Wardemann, H.; Hammersen, J.; Tsuiji, M.; Meffre, E.; Pascual, V.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Defective B cell tolerance checkpoints in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holers, V.M. Systemic lupus erythematosus as the paradigm for understanding the complex immune relationships and therapeutic opportunities for targeting complement in autoimmune diseases. Immunobiology 2025, 230, 152915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekvig, O.P. Anti-dsDNA antibodies as a classification criterion and a diagnostic marker for systemic lupus erythematosus: Critical remarks. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 179, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, K.; Fismen, S.; Hedberg, A.; Seredkina, N.; Fenton, C.; Mortensen, E.S.; Rekvig, O.P. Anti-dsDNA antibodies promote initiation, and acquired loss of renal Dnase1 promotes progression of lupus nephritis in autoimmune (NZBxNZW)F1 mice. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.; Derk, C.T. Anti-ribosomal-P antibodies in lupus nephritis, neuropsychiatric lupus, lupus hepatitis, and Chagas’ disease: Promising yet limited in clinical utility. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Mackay, M.; Aranow, C.; Diamond, B. Phenotypic characterization of autoreactive B cells—Checkpoints of B cell tolerance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurasov, S.; Tiller, T.; Tsuiji, M.; Velinzon, K.; Pascual, V.; Wardemann, H.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Persistent expression of autoantibodies in SLE patients in remission. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odendahl, M.; Mei, H.; Hoyer, B.F.; Jacobi, A.M.; Hansen, A.; Muehlinghaus, G.; Berek, C.; Hiepe, F.; Manz, R.; Radbruch, A.; et al. Generation of migratory antigen-specific plasma blasts and mobilization of resident plasma cells in a secondary immune response. Blood 2005, 105, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullal, A.J.; Reich, C.F., 3rd; Clowse, M.; Criscione-Schreiber, L.G.; Tochacek, M.; Monestier, M.; Pisetsky, D.S. Microparticles as antigenic targets of antibodies to DNA and nucleosomes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Autoimmun. 2011, 36, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutouzov, S.; Jeronimo, A.L.; Campos, H.; Amoura, Z. Nucleosomes in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 30, 529–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiducci, C.; Tripodo, C.; Gong, M.; Sangaletti, S.; Colombo, M.P.; Coffman, R.L.; Barrat, F.J. Autoimmune skin inflammation is dependent on plasmacytoid dendritic cell activation by nucleic acids via TLR7 and TLR9. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2931–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mande, P.; Zirak, B.; Ko, W.C.; Taravati, K.; Bride, K.L.; Brodeur, T.Y.; Deng, A.; Dresser, K.; Jiang, Z.; Ettinger, R.; et al. Fas ligand promotes an inducible TLR-dependent model of cutaneous lupus–like inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2966–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Z.; Zhou, J.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, B.; Branch, V.K.; Carr-Johnson, F.; Karp, D.R.; Mohan, C.; Wakeland, E.K.; Olsen, N.J. Interferon signature gene expression is correlated with autoantibody profiles in patients with incomplete lupus syndromes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 159, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaan, E.D.; Brunekreef, T.E.; Drylewicz, J.; van den Hoogen, L.L.; van der Linden, M.; Leavis, H.L.; van Laar, J.M.; van der Vlist, M.; Otten, H.G.; Limper, M. Association of autoantibodies with the IFN signature and NETosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2024, 9, 100246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammer, A.C.; Lipsky, P.E. B cell abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2003, 5 (Suppl. S4), S22–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, D.Y.H.; Chan, T.M. B Cell Abnormalities in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis-Role in Pathogenesis and Effect of Immunosuppressive Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, J.V.; Haddon, D.J.; Kemmer, D.; Delepine, G.; Mandelbaum, G.; Jarrell, J.A.; Gupta, R.; Balboni, I.; Chakravarty, E.F.; Sokolove, J.; et al. Protein microarray analysis reveals BAFF-binding autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 5135–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, H.S.; Thong, B.Y.H.; Kong, K.O.; Chng, H.H.; Lian, T.Y.; Chia, F.L.; Tay, K.S.S.; Lau, T.C.; Law, W.G.; Koh, E.T.; et al. Associations of B cell-activating factor (BAFF) and anti-BAFF autoantibodies with disease activity in multi-ethnic Asian systemic lupus erythematosus patients in Singapore. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 189, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiepe, F.; Dörner, T.; Hauser, A.E.; Hoyer, B.F.; Mei, H.; Radbruch, A. Long-lived autoreactive plasma cells drive persistent autoimmune inflammation. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispín, J.C.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Terhorst, C.; Tsokos, G.C. T cells as therapeutic targets in SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, S. Follicular helper CD4 T cells (TFH). Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 621–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nomura, T.; Ono, M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 2008, 133, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrett, C.M.; Anguera, M.C. When the balance is broken: X-linked gene dosage from two X chromosomes and female-biased autoimmunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaton, B.P.; Cotton, A.M.; Brown, C.J. Derivation of consensus inactivation status for X-linked genes from genome-wide studies. Biol. Sex Differ. 2015, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghöfer, B.; Frommer, T.; Haley, G.; Fink, L.; Bein, G.; Hackstein, H. TLR7 ligands induce higher IFN-α production in females. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souyris, M.; Cenac, C.; Azar, P.; Daviaud, D.; Canivet, A.; Grunenwald, S.; Pienkowski, C.; Chaumeil, J.; Mejía, J.E.; Guéry, J.C. TLR7 escapes X chromosome inactivation in immune cells. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaap8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Wu, A.; Tesmer, L.; Ray, D.; Yousif, N.; Richardson, B. Demethylation of CD40LG on the inactive X in T cells from women with lupus. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 6352–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.W.; Jacobs, H.M.; Arkatkar, T.; Dam, E.M.; Scharping, N.E.; Kolhatkar, N.S.; Hou, B.; Buckner, J.H.; Rawlings, D.J. B cell IFN-γ receptor signaling promotes autoimmune germinal centers via cell-intrinsic induction of BCL-6. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, C.M.; Cleary, J.; Dagtas, A.S.; Moussai, D.; Diamond, B. Estrogen alters thresholds for B cell apoptosis and activation. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, X. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Updated insights on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmon-Levin, N.; Damoiseaux, J.; Kallenberg, C.; Sack, U.; Witte, T.; Herold, M.; Bossuyt, X.; Musset, L.; Cervera, R.; Plaza-Lopez, A.; et al. International recommendations for the assessment of autoantibodies to cellular antigens referred to as anti-nuclear antibodies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetsky, D.S. Antinuclear antibody testing—Misunderstood or misbegotten? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, M.; Meroni, P.L.; Bossuyt, X.; Fritzler, M.J. Current concepts and future directions for the assessment of autoantibodies to cellular antigens referred to as anti-nuclear antibodies. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 315179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.M. Antinuclear antibodies: Diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology. Adv. Immunol. 1989, 44, 93–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, K.H.; Burbelo, P.D.; Tipton, C.; Wei, C.; Petri, M.; Sanz, I.; Iadarola, M.J. Two major autoantibody clusters in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, S.T.; Craft, J. The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus—An update. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xia, Y. Anti-double Stranded DNA Antibodies: Origin, Pathogenicity, and Targeted Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beers, J.; Schreurs, M.W.J. Anti-Sm antibodies in the classification criteria of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2022, 5, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarese, E.; Chae, O.W.; Trowitzsch, S.; Weber, G.; Kastner, B.; Akira, S.; Wagner, H.; Schmid, R.M.; Bauer, S.; Krug, A. U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein immune complexes induce type I interferon in plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TLR7. Blood 2006, 107, 3229–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, R.; Ohmura, K.; Higuchi, S.; Nakai, W.; Kohyama, M.; Mimori, T.; Morinobu, A.; Arase, H. Positive and negative regulation of the Fcγ receptor-stimulating activity of RNA-containing immune complexes by RNase. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e167799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubi, E.; Shoenfeld, Y. Clinical and biological aspects of anti-P-ribosomal protein autoantibodies. Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 6, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetsky, D.S. Unique Interplay Between Antinuclear Antibodies and Nuclear Molecules in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbagir, S.; Mohammed, N.A.; Oke, V.; Larsson, A.; Nilsson, J.; Elshafie, A.; Elagib, E.M.; Nur, M.A.M.; Gunnarsson, I.; Svenungsson, E.; et al. Anti-histone and anti-nucleosome rather than anti-dsDNA antibodies associate with IFN-induced biomarkers in Sudanese and Swedish SLE patients. Rheumatology 2025, 64, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Diamond, B.; Santiago-Schwarz, F. Fundamental role of C1q in autoimmunity and inflammation. Immunol. Res. 2015, 63, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.S.; Kanthi, Y. Mechanisms of immunothrombosis and vasculopathy in antiphospholipid syndrome. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A. Autoantibodies, lupus and the science of sabotage. Rheumatology 2004, 43, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, B.H. Antibodies to DNA. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, B.M.; Boackle, S.A. Linking complement and anti-dsDNA antibodies in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol. Res. 2013, 55, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruschi, M.; Angeletti, A.; Prunotto, M.; Meroni, P.L.; Ghiggeri, G.M.; Moroni, G.; Sinico, R.A.; Franceschini, F.; Fredi, M.; Vaglio, A.; et al. A critical view on autoantibodies in lupus nephritis: Concrete knowledge based on evidence. Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetsky, D.S. Anti-DNA antibodies—Quintessential biomarkers of SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, F.; Kalsi, J.; Isenberg, D.A. Analysis of antibodies to RNA in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1991, 86, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Borg, E.J.; Horst, G.; Limburg, P.C.; Kallenberg, C.G. Shifts of anti-Sm-specific antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Analysis by counter-immunoelectrophoresis, immunoblotting and RNA-immunoprecipitation. J. Autoimmun. 1991, 4, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzani, E.; Drosera, M.; Gasparini, G.; Parodi, A. Serology of Lupus Erythematosus: Correlation between Immunopathological Features and Clinical Aspects. Autoimmune Dis. 2014, 2014, 321359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuckle, M.R.; McClain, M.T.; Rubertone, M.V.; Scofield, R.H.; Dennis, G.J.; James, J.A.; Harley, J.B. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirohata, S.; Sakuma, Y.; Yanagida, T.; Yoshio, T. Association of cerebrospinal fluid anti-Sm antibodies with acute confusional state in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhani, I.; Khoy, K.; Mariotte, D.; Comby, E.; Marcelli, C.; Le Mauff, B.; Audemard-Verger, A.; Boutemy, J.; Maigné, G.; Silva, N.M.; et al. The diagnostic challenge of patients with anti-U1-RNP antibodies. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisetsky, D.S. Evolving story of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routsias, J.G.; Tzioufas, A.G. B-cell epitopes of the intracellular autoantigens Ro/SSA and La/SSB: Tools to study the regulation of the autoimmune response. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 35, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauliffe, D.P. Cutaneous diseases in adults associated with anti-Ro/SS-A autoantibody production. Lupus 1997, 6, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, M.V.; Lo, S.C.; de Almeida, C.S.; Shinjo, S.K. Anti-Ro antibody and cutaneous vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 28, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurien, B.T.; Newland, J.; Paczkowski, C.; Moore, K.L.; Scofield, R.H. Association of neutropenia in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) with anti-Ro and binding of an immunologically cross-reactive neutrophil membrane antigen. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 120, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Fu, C.; Jin, X.; Lei, C.; Zhu, X. Neonatal lupus erythematosus: An acquired autoimmune disease to be taken seriously. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2476049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.K.; Hamel, J.C.; Buyon, J.P.; Tan, E.M. Molecular definition and sequence motifs of the 52-kD component of human SS-A/Ro autoantigen. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlü, O.; Zuily, S.; Erkan, D. The clinical significance of antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 3, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.S.; Branch, D.W.; Rauch, J. The antiphospholipid syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hasbani, G.; Saliba, A.N.; Uthman, I.; Taher, A.T. Hematological manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome: Going beyond thrombosis. Blood Rev. 2023, 58, 101015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.S.; Branch, D.W.; Ortel, T.L. Antiphospholipid syndrome: Advances in diagnosis, pathogenesis, and management. BMJ 2023, 380, e069717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Rato, M.; Bandeira, M.; Romão, V.C.; de Sousa, D.A. Neurologic Manifestations of the Antiphospholipid Syndrome—An Update. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2021, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, A.; Knight, J.S.; Zuo, Y. Antiphospholipid syndrome management: A 2023 update and practical algorithm-based approach. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2023, 35, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastori, D.; Menichelli, D.; Cammisotto, V.; Pignatelli, P. Use of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients With Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Comparison of the International Guidelines. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 715878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briani, C.; Lucchetta, M.; Ghirardello, A.; Toffanin, E.; Zampieri, S.; Ruggero, S.; Scarlato, M.; Quattrini, A.; Bassi, N.; Ermani, M.; et al. Neurolupus is associated with anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies: An inception cohort study. J. Autoimmun. 2009, 32, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.Y.; FitzPatrick, R.D.; Buhler, K.; Mahler, M.; Fritzler, M.J. A review and meta-analysis of anti-ribosomal P autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, A.; Bläss, S.; Hausdorf, G.; Burmester, G.R.; Hiepe, F. Nucleosomes are major T and B cell autoantigens in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2000, 43, 2307–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzaro, N.; Villalta, D.; Giavarina, D.; Tozzoli, R. Are anti-nucleosome antibodies a better diagnostic marker than anti-dsDNA antibodies for systemic lupus erythematosus? A systematic review and a study of metanalysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 12, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekvig, O.P.; Putterman, C.; Casu, C.; Gao, H.X.; Ghirardello, A.; Mortensen, E.S.; Tincani, A.; Doria, A. Autoantibodies in lupus: Culprits or passive bystanders? Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, U.; Zandman-Goddard, G. Drug-induced lupus: An update. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 10, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Shi, J.; Han, L.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.G. Anti-histones antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: Prevalence and frequency in neuropsychiatric lupus. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2008, 22, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munroe, M.E.; James, J.A. Genetics of Lupus Nephritis: Clinical Implications. Semin. Nephrol. 2015, 35, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenberg, C.G. Anti-C1q autoantibodies. Autoimmun. Rev. 2008, 7, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, M.; Miyachi, K.; Peebles, C.; Fritzler, M.J. The clinical significance of autoantibodies to the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsulami, K.; D’Aoust, J. Not Just Myocarditis: Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) and Overlap Myositis With Anti-Ku Positivity in a Young Male With Shortness of Breath. Cureus 2024, 16, e72310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, Y.; Hosono, Y.; Sugiura, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Mimori, T.; Akiyama, M. Anti-PM/Scl antibodies are found in Japanese patients with various systemic autoimmune conditions besides myositis and scleroderma. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M.; Chan, E.K.; Sobel, E.S.; Kimpel, D.L.; Yamasaki, Y.; Narain, S.; Mansoor, R.; Reeves, W.H. Clinical implication of autoantibodies in patients with systemic rheumatic diseases. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 3, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardena, H.; Betteridge, Z.E.; McHugh, N.J. Myositis-specific autoantibodies: Their clinical and pathogenic significance in disease expression. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruellas, M.G.P.; dos Santos Trindade Viana, V.; Levy-Neto, M.; de Souza, F.H.C.; Shinjo, S.K. Myositis-specific and myositis-associated autoantibody profiles and their clinical associations in a large series of patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Clinics 2013, 68, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavikova, M.; Schmeisser, H.; Kontsekova, E.; Mateicka, F.; Borecky, L.; Kontsek, P. Incidence of autoantibodies against type I and type II interferons in a cohort of systemic lupus erythematosus patients in Slovakia. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2003, 23, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebus-Kardash, J.; Branco, L.; Ribi, C.; Chizzolini, C.; Huynh-Do, U.; Dubler, D.; Roux-Lombard, P.; Dolff, S.; Kribben, A.; Eisenberger, U.; et al. Immune complexes containing serum B-cell activating factor and immunoglobulin G correlate with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Tatouli, I.P.; Rosen, L.B.; Hasni, S.; Alevizos, I.; Manna, Z.G.; Rivera, J.; Jiang, C.; Siegel, R.M.; Holland, S.M.; et al. Distinct Functions of Autoantibodies Against Interferon in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Comprehensive Analysis of Anticytokine Autoantibodies in Common Rheumatic Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpintero, M.F.; Martinez, L.; Fernandez, I.; Romero, A.C.; Mejia, C.; Zang, Y.J.; Hoffman, R.W.; Greidinger, E.L. Diagnosis and risk stratification in patients with anti-RNP autoimmunity. Lupus 2015, 24, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanoni, F.; Lava, S.A.G.; Fossali, E.F.; Cavalli, R.; Simonetti, G.D.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Bozzini, M.A.; Agostoni, C.; Milani, G.P. Neonatal Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 53, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Andreoli, L.; Limper, M.; Amoura, Z.; Cervera, R.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Dörner, T.; Ferrer-Oliveras, R.; Hambly, K.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of antiphospholipid syndrome in adults. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoiseaux, J.; Andrade, L.E.C.; Carballo, O.G.; Conrad, K.; Francescantonio, P.L.C.; Fritzler, M.J.; Garcia de La Torre, I.; Herold, M.; Klotz, W.; de Melo Cruvinel, W.; et al. Clinical relevance of HEp-2 indirect immunofluorescent patterns: The International Consensus on ANA patterns (ICAP) perspective. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.K.L.; Damoiseaux, J.; Carballo, O.G.; Conrad, K.; de Melo Cruvinel, W.; Francescantonio, P.L.C.; Fritzler, M.J.; Garcia-De La Torre, I.; Herold, M.; Mimori, T.; et al. Report of the First International Consensus on Standardized Nomenclature of Antinuclear Antibody HEp-2 Cell Patterns 2014-2015. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S. A short history, principles, and types of ELISA, and our laboratory experience with peptide/protein analyses using ELISA. Peptides 2015, 72, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, H. Monoplex and multiplex immunoassays: Approval, advancements, and alternatives. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 31, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Mendoza, G.; Sansón, S.P.; Rodríguez-Castro, S.; Crispín, J.C.; Rosetti, F. Mechanisms of Tissue Injury in Lupus Nephritis. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, A.; Amelio, J.; Gairy, K.; Kaur, G.; Levy, R.A.; Roth, D.; Bass, D. Systemic lupus erythematosus, lupus nephritis and end-stage renal disease: A pragmatic review mapping disease severity and progression. Lupus 2020, 29, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, A.; Wagner, C.A.; Guthridge, C.J.; Kheir, J.; Macwana, S.; DeJager, W.; Gross, T.; Izmirly, P.; Belmont, H.M.; Diamond, B.; et al. Association of Autoantibody Concentrations and Trajectories With Lupus Nephritis Histologic Features and Treatment Response. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, S.; Chan, T.M. Anti-dsDNA antibodies and resident renal cells—Their putative roles in pathogenesis of renal lesions in lupus nephritis. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 185, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnik, M.D.; Hu, J.Z.; Heilbrunn, K.R.; Strand, V.; Hurley, F.L.; Joh, T. Relationship between anti–double-stranded DNA antibodies and exacerbation of renal disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2005, 52, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatroni, M.; Conte, E.; Stella, M.; De Liso, F.; Reggiani, F.; Moroni, G. Clinical and immunological biomarkers can identify proliferative changes and predict renal flares in lupus nephritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2025, 27, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigler, C.; Schaller, M.; Perahud, I.; Osthoff, M.; Trendelenburg, M. Autoantibodies against complement C1q specifically target C1q bound on early apoptotic cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3512–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trendelenburg, M. Autoantibodies against complement component C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2021, 10, e1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, O.M.; Turner, J.E.; Paust, H.J.; Lindner, M.; Peters, A.; Heiss, K.; Velden, J.; Hopfer, H.; Fehr, S.; Krieger, T.; et al. CXCR3 mediates renal Th1 and Th17 immune response in murine lupus nephritis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4693–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winchester, R.; Wiesendanger, M.; Zhang, H.Z.; Steshenko, V.; Peterson, K.; Geraldino-Pardilla, L.; Ruiz-Vazquez, E.; D’Agati, V. Immunologic characteristics of intrarenal T cells: Trafficking of expanded CD8+ T cell β-chain clonotypes in progressive lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2012, 64, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarilyo, G.; Lourenço, E.V.; Shi, F.D.; La Cava, A. IL-17 promotes murine lupus. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovin, B.H.; Adler, S.G.; Barratt, J.; Bridoux, F.; Burdge, K.A.; Chan, T.M.; Cook, H.T.; Fervenza, F.C.; Gibson, K.L.; Glassock, R.J.; et al. KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Glomerular Diseases. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, S1–S276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Andersen, J.; Aringer, M.; Arnaud, L.; Bae, S.C.; Boletis, J.; Bruce, I.N.; Cervera, R.; Doria, A.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: 2023 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodis, I.; Moroni, G.; Calatroni, M.; Bellis, E.; Gatto, M. Is per-protocol kidney biopsy required in lupus nephritis? Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.M.; Maggiore, U.; Peyronel, F.; Fenaroli, P.; Delsante, M.; Benigno, G.D.; Gianfreda, D.; Urban, M.L.; Manna, Z.; Arend, L.J.; et al. Persistent Isolated C3 Hypocomplementemia as a Strong Predictor of End-Stage Kidney Disease in Lupus Nephritis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosałka-Węgiel, J.; Dziedzic, R.; Siwiec-Koźlik, A.; Spałkowska, M.; Milewski, M.; Wach, A.; Zaręba, L.; Bazan-Socha, S.; Korkosz, M. Comparison of Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics in Lupus Nephritis vs. Non-Lupus Nephritis Patients—A Comprehensive Retrospective Analysis Based on 921 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saegusa, K.; Tsuchida, Y.; Komai, T.; Tsuchiya, H.; Fujio, K. Advances in Targeted Therapy for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Current Treatments and Novel Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturelli, V.; Isenberg, D.A. Targeted Therapy for SLE—What Works, What Doesn’t, What’s Next. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzoo, K.; Sadeghi, S.; Liebman, H.A. Treatment of refractory antibody mediated autoimmune disorders with an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 922–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, J.T.; Neuwelt, C.M.; Wallace, D.J.; Shanahan, J.C.; Latinis, K.M.; Oates, J.C.; Utset, T.O.; Gordon, C.; Isenberg, D.A.; Hsieh, H.J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in moderately-to-severely active systemic lupus erythematosus: The randomized, double-blind, phase II/III systemic lupus erythematosus evaluation of rituximab trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2010, 62, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Furie, R.; Latinis, K.; Looney, R.J.; Fervenza, F.C.; Sanchez-Guerrero, J.; Maciuca, R.; Zhang, D.; Garg, J.P.; Brunetta, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active proliferative lupus nephritis: The Lupus Nephritis Assessment with Rituximab study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2012, 64, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narváez, J.; Ríos-Rodriguez, V.; de la Fuente, D.; Estrada, P.; López-Vives, L.; Gómez-Vaquero, C.; Nolla, J.M. Rituximab therapy in refractory neuropsychiatric lupus: Current clinical evidence. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 41, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.; Petri, M.; Zamani, O.; Cervera, R.; Wallace, D.J.; Tegzová, D.; Sanchez-Guerrero, J.; Schwarting, A.; Merrill, J.T.; Chatham, W.W.; et al. A phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of belimumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B lymphocyte stimulator, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2011, 63, 3918–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarra, S.V.; Guzmán, R.M.; Gallacher, A.E.; Hall, S.; Levy, R.A.; Jimenez, R.E.; Li, E.K.; Thomas, M.; Kim, H.Y.; León, M.G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.; Rovin, B.H.; Houssiau, F.; Malvar, A.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Contreras, G.; Amoura, Z.; Yu, X.; Mok, C.C.; Santiago, M.B.; et al. Two-Year, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Belimumab in Lupus Nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipa, M.; Embleton-Thirsk, A.; Parvaz, M.; Santos, L.R.; Muller, P.; Chowdhury, K.; Isenberg, D.A.; Doré, C.J.; Gordon, C.; Ehrenstein, M.R. Effectiveness of Belimumab After Rituximab in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, H.I.; Abud-Mendoza, C.; Viola, D.O.; Calvo Penades, I.; Levy, D.; Anton, J.; Calderon, J.E.; Chasnyk, V.G.; Ferrandiz, M.A.; Keltsev, V.; et al. Safety and efficacy of intravenous belimumab in children with systemic lupus erythematosus: Results from a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Oganesyan, V.; Wu, H.; Dall’Acqua, W.F.; Damschroder, M.M. Molecular basis for antagonistic activity of anifrolumab, an anti-interferon-α receptor 1 antibody. MAbs 2015, 7, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.; Khamashta, M.; Merrill, J.T.; Werth, V.P.; Kalunian, K.; Brohawn, P.; Illei, G.G.; Drappa, J.; Wang, L.; Yoo, S. Anifrolumab, an Anti-Interferon-α Receptor Monoclonal Antibody, in Moderate-to-Severe Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatham, W.W.; Furie, R.; Saxena, A.; Brohawn, P.; Schwetje, E.; Abreu, G.; Tummala, R. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Anifrolumab in Adults With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Results of a Phase II Open-Label Extension Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.A.; Morand, E.F.; Bruce, I.N.; Manzi, S.; Kalunian, K.C.; Vital, E.M.; Ford, T.L.; Gupta, R.; Hiepe, F.; Santiago, M.; et al. Type I interferon inhibitor anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus (TULIP-1): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019, 1, e208–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, E.F.; Furie, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Bruce, I.N.; Askanase, A.D.; Richez, C.; Bae, S.C.; Brohawn, P.Z.; Pineda, L.; Berglind, A.; et al. Trial of Anifrolumab in Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Planellas, S.; Katsifis-Nezis, D.; Fanouriakis, A. Clinical Trials of Interferon Inhibitors in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Preliminary Real-World Efficacy of Anifrolumab. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2024, 35, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobinai, K.; Klein, C.; Oya, N.; Fingerle-Rowson, G. A Review of Obinutuzumab (GA101), a Novel Type II Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody, for the Treatment of Patients with B-Cell Malignancies. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 324–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinov, A.D.; Wang, H.; Bastacky, S.I.; van Puijenbroek, E.; Schindler, T.; Speziale, D.; Perro, M.; Klein, C.; Nickerson, K.M.; Shlomchik, M.J. The Type II Anti-CD20 Antibody Obinutuzumab (GA101) Is More Effective Than Rituximab at Depleting B Cells and Treating Disease in a Murine Lupus Model. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.A.; Aroca, G.; Cascino, M.D.; Garg, J.P.; Rovin, B.H.; Alvarez, A.; Fragoso-Loyo, H.; Zuta-Santillan, E.; Schindler, T.; Brunetta, P.; et al. B-cell depletion with obinutuzumab for the treatment of proliferative lupus nephritis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.; Dass, S.; Twigg, S.; Jones, C.H.; Rhodes, B.; Hewins, P.; Chakravorty, M.; Courtney, P.; Ehrenstein, M.; Md Yusof, M.Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of obinutuzumab in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with secondary non-response to rituximab. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 4905–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalunian, K.C.; Merrill, J.T.; Maciuca, R.; McBride, J.M.; Townsend, M.J.; Wei, X.; Davis, J.C., Jr.; Kennedy, W.P. A Phase II study of the efficacy and safety of rontalizumab (rhuMAb interferon-α) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (ROSE). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamashta, M.; Merrill, J.T.; Werth, V.P.; Furie, R.; Kalunian, K.; Illei, G.G.; Drappa, J.; Wang, L.; Greth, W. Sifalimumab, an anti-interferon-α monoclonal antibody, in moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, H.A.; Deeks, E.D. Abatacept: A Review in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Drugs 2017, 77, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, J.T.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Westhovens, R.; Chalmers, A.; D’Cruz, D.; Wallace, D.J.; Bae, S.C.; Sigal, L.; Becker, J.C.; Kelly, S.; et al. The efficacy and safety of abatacept in patients with non-life-threatening manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus: Results of a twelve-month, multicenter, exploratory, phase IIb, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2010, 62, 3077–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The ACCESS Trial Group. Treatment of lupus nephritis with abatacept: The Abatacept and Cyclophosphamide Combination Efficacy and Safety Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 3096–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, J.T.; Shevell, D.E.; Duchesne, D.; Nowak, M.; Kundu, S.; Girgis, I.G.; Hu, Y.S.; Nadler, S.G.; Banerjee, S.; Throup, J. An Anti-CD28 Domain Antibody, Lulizumab, in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Results of a Phase II Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70 (Suppl. S9). Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-anti-cd28-domain-antibody-lulizumab-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-results-of-a-phase-ii-study/ (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Furie, R.A.; Bruce, I.N.; Dörner, T.; Leon, M.G.; Leszczyński, P.; Urowitz, M.; Haier, B.; Jimenez, T.; Brittain, C.; Liu, J.; et al. Phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of dapirolizumab pegol in patients with moderate-to-severe active systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 5397–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, D.; Steffgen, J.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Amano, H.; Noppakun, K.; Gomez, H.; Recto, R.; Belsack, V.; Fagan, N.; Padula, S. POS0687 a randomised dose ranging, placebo-controlled, phase II study assessing the efficacy and safety of BI 655064, an antagonistic anti-CD40 antibody, in patients with lupus nephritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 589–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Satoh, T.; Kawai, M.; Hirakata, M.; Kaburaki, J.; Kawakami, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Kuwana, M. Autoantibody to CD40 ligand in systemic lupus erythematosus: Association with thrombocytopenia but not thromboembolism. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarino, A.V.; Kanno, Y.; O’Shea, J.J. Mechanisms and consequences of Jak—STAT signaling in the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, W.J.; O’Shea, J.J. Jaks and STATs: Biological implications. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 293–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysidou, G.S.; Dara, A. JAK Inhibition as a Potential Treatment Target in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2024, 35, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alunno, A.; Padjen, I.; Fanouriakis, A.; Boumpas, D.T. Pathogenic and Therapeutic Relevance of JAK/STAT Signaling in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Integration of Distinct Inflammatory Pathways and the Prospect of Their Inhibition with an Oral Agent. Cells 2019, 8, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C. The Jakinibs in systemic lupus erythematosus: Progress and prospects. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.J.; Furie, R.A.; Tanaka, Y.; Kalunian, K.C.; Mosca, M.; Petri, M.A.; Dörner, T.; Cardiel, M.H.; Bruce, I.N.; Gomez, E.; et al. Baricitinib for systemic lupus erythematosus: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Park, Y.; Jang, S.G.; Hong, S.M.; Song, Y.S.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, S.; Park, S.H.; Kwok, S.K. Baricitinib Attenuates Autoimmune Phenotype and Podocyte Injury in a Murine Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 704526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasni, S.A.; Gupta, S.; Davis, M.; Poncio, E.; Temesgen-Oyelakin, Y.; Carlucci, P.M.; Wang, X.; Naqi, M.; Playford, M.P.; Goel, R.R.; et al. Phase 1 double-blind randomized safety trial of the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agmon-Levin, N.; Mosca, M.; Petri, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Systemic lupus erythematosus one disease or many? Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Tziolos, N.; Bertsias, G.; Boumpas, D.T. Update οn the diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensous, N.; Marti, A.; Barnetche, T.; Blanco, P.; Lazaro, E.; Seneschal, J.; Truchetet, M.E.; Duffau, P.; Richez, C. Predictive biological markers of systemic lupus erythematosus flares: A systematic literature review. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra Sánchez, A.R.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Morand, E.F.; Bruce, I.N.; Kandane-Rathnayake, R.; Weiss, G.; Tummala, R.; Al-Mossawi, H.; Sorrentino, A. Targeting DORIS Remission and LLDAS in SLE: A Review. Rheumatol. Ther. 2023, 10, 1459–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz LeBlanc, B.A.; Gladman, D.D.; Urowitz, M.B. Serologically active clinically quiescent systemic lupus erythematosus--predictors of clinical flares. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 21, 2239–2241. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, A.; Lindblom, J.; Parodis, I.; Bertsias, G. Treat-to-target in SLE: Is serology important? Results from an integrated analysis of five randomized clinical trials of belimumab. Rheumatology 2025, 64, 3598–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teruel, M.; Chamberlain, C.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E. Omics studies: Their use in diagnosis and reclassification of SLE and other systemic autoimmune diseases. Rheumatology 2017, 56, i78–i87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriens, C.; Wren, J.D.; Munroe, M.E.; Mohan, C. Systemic lupus erythematosus biomarkers: The challenging quest. Rheumatology 2017, 56, i32–i45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Qin, H.; Ge, Y.; Du, J.; Lin, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, J. Elevated expression of miR-142-3p is related to the pro-inflammatory function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells in SLE. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavón, E.J.; García-Rodríguez, S.; Zumaquero, E.; Perandrés-López, R.; Rosal-Vela, A.; Lario, A.; Longobardo, V.; Carrascal, M.; Abián, J.; Callejas-Rubio, J.L.; et al. Increased expression and phosphorylation of the two S100A9 isoforms in mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A proteomic signature for circulating low-density granulocytes. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 1778–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, L. Immunometabolism in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Qiu, L.; Wang, H.; Su, D.; Zhang, B.; Chan, K.M.; Han, J. Targeting epigenetic regulators for inflammation: Mechanisms and intervention therapy. MedComm 2022, 3, e173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pagkopoulou, E.; Loutradis, C.; Papaioannou, M.; Daoudaki, M.; Stangou, M.; Dimitroulas, T. Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Diagnostic and Pathogenic Insights. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165714
Pagkopoulou E, Loutradis C, Papaioannou M, Daoudaki M, Stangou M, Dimitroulas T. Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Diagnostic and Pathogenic Insights. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165714
Chicago/Turabian StylePagkopoulou, Eleni, Charalampos Loutradis, Maria Papaioannou, Maria Daoudaki, Maria Stangou, and Theodoros Dimitroulas. 2025. "Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Diagnostic and Pathogenic Insights" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165714
APA StylePagkopoulou, E., Loutradis, C., Papaioannou, M., Daoudaki, M., Stangou, M., & Dimitroulas, T. (2025). Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Diagnostic and Pathogenic Insights. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165714







