Body Composition Changes in Hospitalized Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Population
2.2. Pneumonia Severity
2.3. Analysis of Body Composition
2.4. Evaluation of Handgrip and Tongue Strength
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and Their Associations with Disease Severity
3.2. Changes in Variables from Admission to Discharge
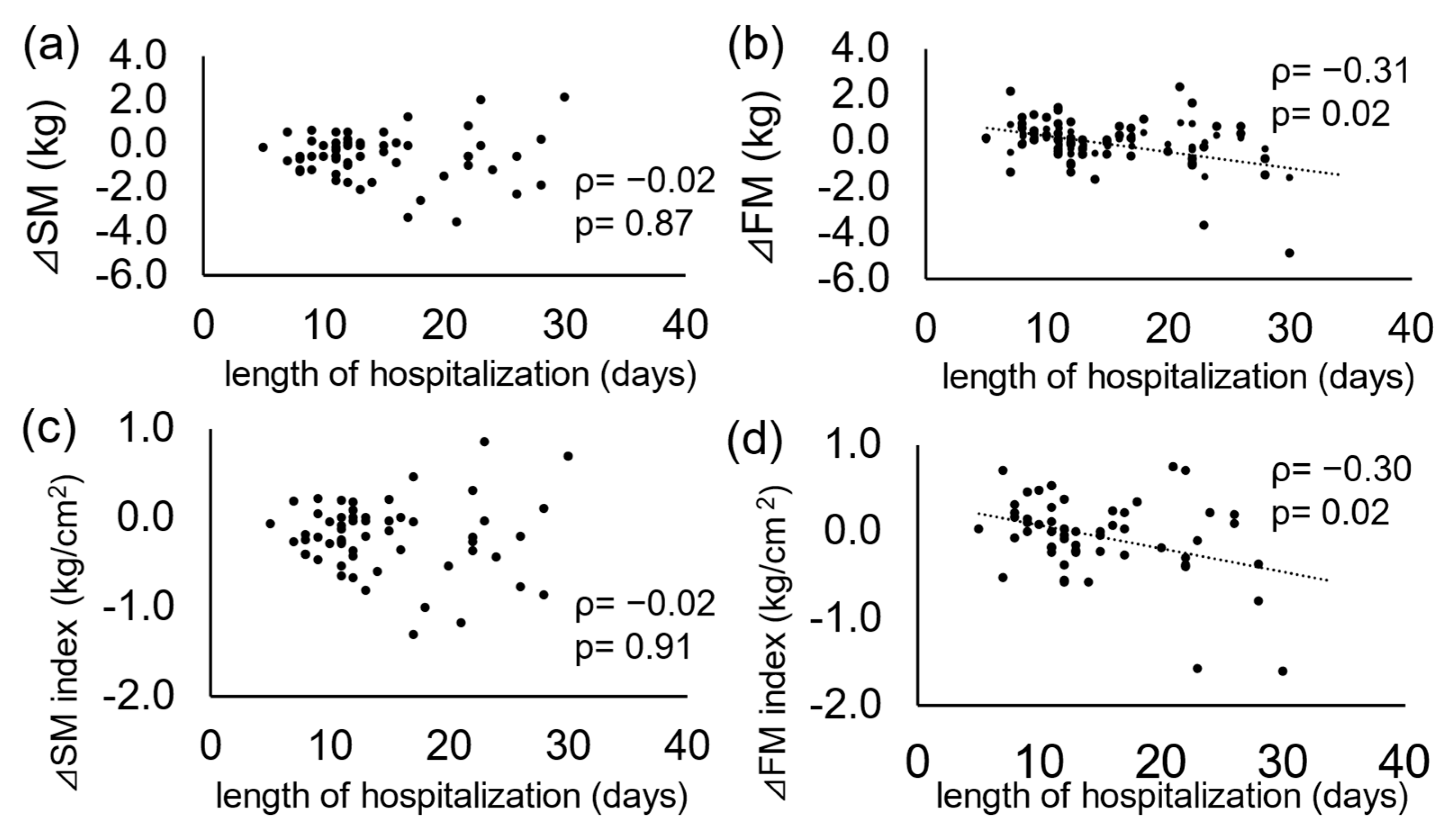
3.3. Characteristics of Patients with Accelerated Decrease in Body Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BIA | bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CAP | community-acquired pneumonia |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| ECOG | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status Scale |
| FFM | fat-free mass |
| FM | fat mass |
| SM | skeletal muscle |
References
- Huang, S.; Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Clinical muscle mass-related biomarkers that predict mortality in older patients with community-acquired pneumonia. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bylova, N.A.; Arutyunov, G.P.; Rylova, A.K.; Simbirtseva, A.S.; Arutyunov, A.G. Prognostic role of body composition in patients with pneumonia associated with decompensated CHF. Kardiologiia 2017, 57, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Committee for the Japanese Respiratory Society. Guidelines in the management of respiratory infections. In The JRS Guidelines for the Management of Pneumonia in Adults; Medical Review Co.: Tokyo, Japan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- José, A.; Dal Corso, S. Inpatient rehabilitation improves functional capacity, peripheral muscle strength and quality of life in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: A randomised trial. J. Physiother. 2016, 62, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Salvador, A.; Colodro-Amores, G.; Torres-Sánchez, I.; Moreno-Ramírez, M.P.; Cabrera-Martos, I.; Valenza, M.C. Physical therapy intervention during hospitalization in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pneumonia: A randomized clinical trial. Med. Clin. 2016, 146, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gassel, R.J.J.; Baggerman, M.R.; van de Poll, M.C.G. Metabolic aspects of muscle wasting during critical illness. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, F.; Zaldivar, F.; Cooper, D.M.; Adams, G.R. IL-6-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 98, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Ebihara, S.; Mori, T.; Izumi, S.; Ebihara, T. Association between sarcopenia and pneumonia in older people. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2020, 20, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, N.; Matsushima, T.; Oka, M.; Japanese Respiratory Society. The JRS guidelines for the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults: An update and new recommendations. Intern. Med. 2006, 45, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.S.; van der Eerden, M.M.; Laing, R.; Boersma, W.G.; Karalus, N.; Town, G.I.; Lewis, S.A.; Macfarlane, J.T. Defining community acquired pneumonia severity on presentation to hospital: An international derivation and validation study. Thorax 2003, 58, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, M.M.; Creech, R.H.; Tormey, D.C.; Horton, J.; Davis, T.E.; McFadden, E.T.; Carbone, P.P. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1982, 5, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crary, M.A.; Mann, G.D.; Groher, M.E. Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, O.; Yamazaki, R.; Sano, H.; Iwanaga, T.; Higashimoto, Y.; Kume, H.; Tohda, Y. Fat-free mass index predicts survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2017, 22, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, S.; Gilliland, J.; O’Connor, C.; Seabrook, J.A.; Mura, M.; Madill, J. Fat-free mass index controlled for age and sex and malnutrition are predictors of survival in interstitial lung disease. Respiration 2021, 100, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Koide, K.; Suzuki, H.; Satoh, Y.; Iwasaki, S.I. Evaluation of reliability of perioral muscle pressure measurements using a newly developed device with a lip piece. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2016, 18, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Salvador, A.; Torres-Sánchez, I.; Sáez-Roca, G.; López-Torres, I.; Rodríguez-Alzueta, E.; Valenza, M.C. Age group analysis of psychological, physical and functional deterioration in patients hospitalized for pneumonia. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2015, 51, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosch, R.; Kattner, S.; Berger, M.M.; Brenner, T.; Haubold, J.; Kleesiek, J.; Koitka, S.; Kroll, L.; Kureishi, A.; Flaschel, N.; et al. Biomarkers extracted by fully automated body composition analysis from chest CT correlate with SARS-CoV-2 outcome severity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, E.; Peghin, M.; De Martino, M.; De Carlo, C.; Da Porto, A.; Bulfone, L.; Casarsa, V.; Sozio, E.; Fabris, M.; Cifu, A.; et al. The impact of body composition on mortality of COVID-19 hospitalized patients: A prospective study on abdominal fat, obesity paradox and sarcopenia. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 51, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besutti, G.; Pellegrini, M.; Ottone, M.; Bonelli, E.; Monelli, F.; Fari, R.; Milic, J.; Dolci, G.; Fasano, T.; Canovi, S.; et al. Modifications of chest CT body composition parameters at three and six months after severe COVID-19 pneumonia: A retrospective cohort study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, T.; Ali, S.H.; Alsadany, M.A.; EI Banouby, M.H. Prevalence of sarcopenia among hospitalized elderly patients. Egypt. J. Geriatr. Gerontol. 2019, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitta, F.; Troosters, T.; Probst, V.S.; Spruit, M.A.; Decramer, M.; Gosselink, R. Physical activity and hospitalization for exacerbation of COPD. Chest 2006, 129, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtin, C.; Van Remoortel, H.; Vrijsen, B.; Langer, D.; Colpaert, K.; Gosselink, R.; Decramer, M.; Dupont, L.; Troosters, T. Impact of exacerbations of cystic fibrosis on muscle strength. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, R.; Menéndez, R.; Reyes, S.; Polverino, E.; Cillóniz, C.; Martínez, A.; Esquinas, C.; Filella, X.; Ramírez, P.; Torres, A. Factors associated with inflammatory cytokine patterns in community-acquired pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, R.; Okazaki, T.; Ebihara, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Tsukita, Y.; Nihei, M.; Sugiura, H.; Niu, K.; Ebihara, T.; Ichinose, M. Aspiration pneumonia induces muscle atrophy in the respiratory, skeletal, and swallowing systems. J. Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momosaki, R.; Yasunaga, H.; Matsui, H.; Horiguchi, H.; Fushimi, K.; Abo, M. Effect of early rehabilitation by physical therapists on in-hospital mortality after aspiration pneumonia in the elderly. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Song, Q.; Huang, X.; Tang, T.; Huang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, T.; Xu, P.; Yu, P.; Yue, J. Sarcopenia and risk of postoperative pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2025, 29, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, A.; Thormann, M.; Kardas, H.; Hinnerichs, M.; Omari, J.; Cingöz, E.; Cingöz, M.; Dursun, M.; Kormaz, İ.; Orhan, Ç.; et al. Visceral to subcutaneous fat ratio predicts short-term mortality in patients with Covid 19. A multicenter study. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20220869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnell, K.M.; Thaweethai, T.; Buckless, C.; Shinnick, D.J.; Torriani, M.; Foulkes, A.S.; Bredella, M.A. Body composition predictors of outcome in patients with COVID-19. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenblock, C.; Schwarz, P.E.H.; Ludwig, B.; Linkermann, A.; Zimmet, P.; Kulebyakin, K.; Tkachuk, V.A.; Markov, A.G.; Lehnert, H.; de Angelis, M.H.; et al. COVID-19 and metabolic disease: Mechanisms and clinical management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darroch, P.; O’Brien, W.J.; Mazahery, H.; Wham, C. Sarcopenia prevalence and risk factors among residents in aged care. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruit, M.A.; Gosselink, R.; Troosters, T.; Kasran, A.; Gayan-Ramirez, G.; Bogaerts, P.; Bouillon, R.; Decramer, M. Muscle force during an acute exacerbation in hospitalised patients with COPD and its relationship with CXCL8 and IGF-I. Thorax 2003, 58, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.E.; Ramirez, J.A.; Oren, E.; Soni, N.J.; Sullivan, L.R.; Restrepo, M.I.; Musher, D.M.; Erstad, B.L.; Pickens, C.; Vaughn, V.M.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Community-acquired Pneumonia. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
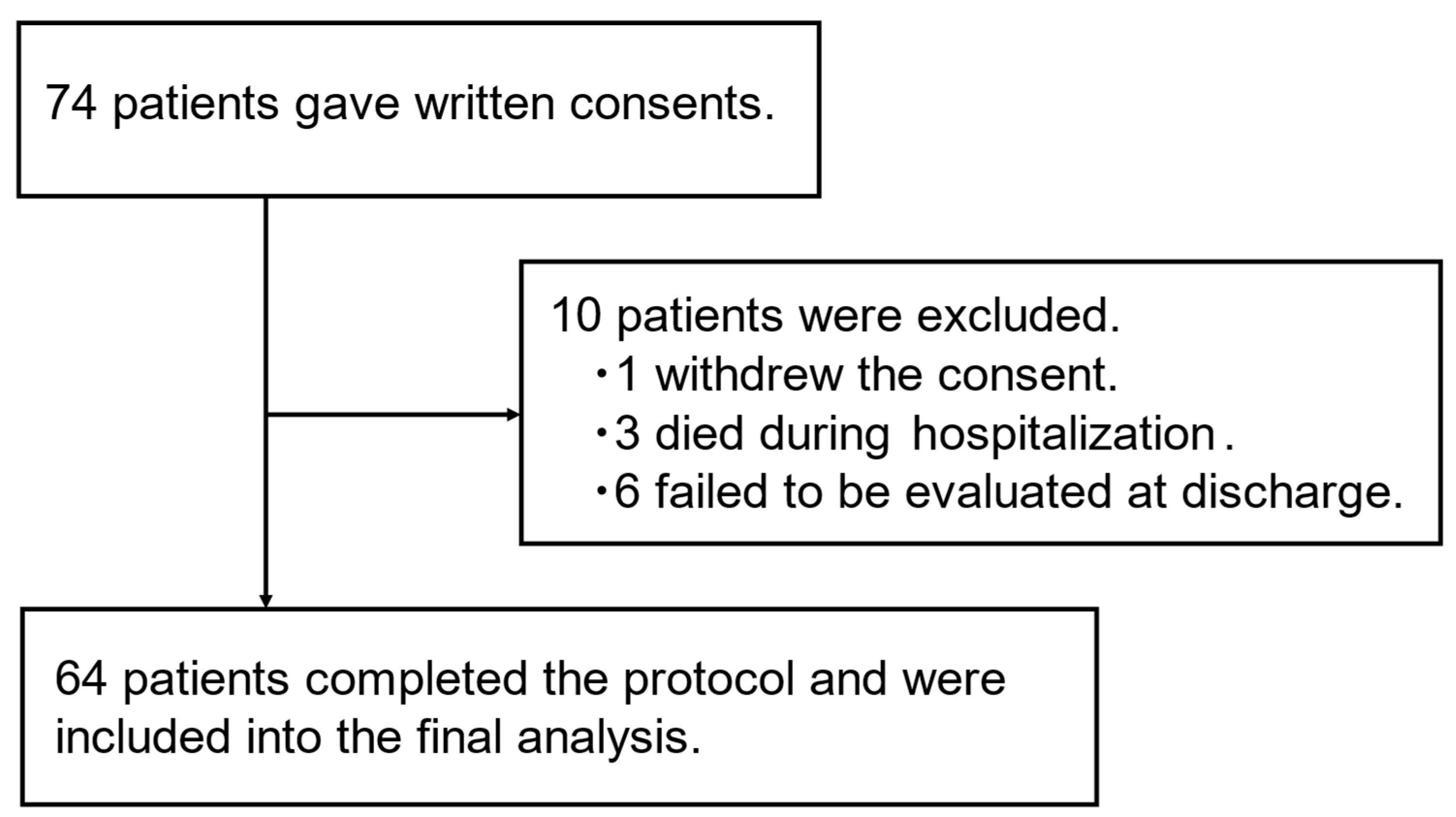
| n= 64 | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 76.1 ± 7.2 |
| Male, n (%) | 50 (78.1) |
| Height (cm) | 161.8 (155.9–167.2) |
| Length of stay (days) | 12.0 (11.0–17.3) |
| Length of treatment by antibiotics (days) | 11.0 (9.0–15.3) |
| A-DROP (score) | 1 (1–2) |
| A-DROP severity class, n (%) | |
| Mild (0) | 9 (14.1) |
| Moderate (1–2) | 49 (76.6) |
| Severe (3–5) | 6 (9.4) |
| CURB-65 (score) | 1 (1–2) |
| CURB-65 severity class, n (%) | |
| Mild (0–1) | 39 (60.9) |
| Moderate (2) | 24 (37.5) |
| Severe (3–5) | 1 (1.6) |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 24 (37.5) |
| Interstitial lung disease | 10 (15.6) |
| Lung cancer (postoperative) | 5 (7.8) |
| Bronchial asthma | 3 (4.7) |
| Non-tuberculous mycobacteria | 2 (3.1) |
| Pulmonary aspergillosis | 1 (1.6) |
| Sarcoidosis | 1 (1.6) |
| Tuberculosis | 1 (1.6) |
| Variables | At Admission | At Discharge | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (×103/mm3) | 11.8 (9.6–14.3) | 6.2 (5.2–7.6) | <0.001 |
| Serum CRP (mg/L) | 9.3 (5.7–17.7) | 0.7 (0.2–1.3) | <0.001 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 3.3 (3.0–3.7) | 3.2 (3.0–3.5) | <0.01 |
| Serum total protein (g/dL) | 6.9 (6.5–7.3) | 6.7 (6.2–7.1) | <0.01 |
| ECOG performance status | 3 (2–3) | 1 (1–2) | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 52.9 (46.6–61.7) | 52.7 (45.3–61.4) | <0.001 |
| Male | 56.0 (48.6–66.1) | 54.2 (47.8–62.2) | <0.001 |
| Female | 44.8 (40.7–51.5) | 44.3 (39.9–50.8) | 0.06 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.5 (18.9–23.0) | 20.2 (18.9–23.0) | <0.001 |
| Male | 20.6 (19.1–23.9) | 20.4 (18.5–23.3) | <0.001 |
| Female | 20.2 (18.8–21.8) | 19.9 (18.6–21.4) | 0.06 |
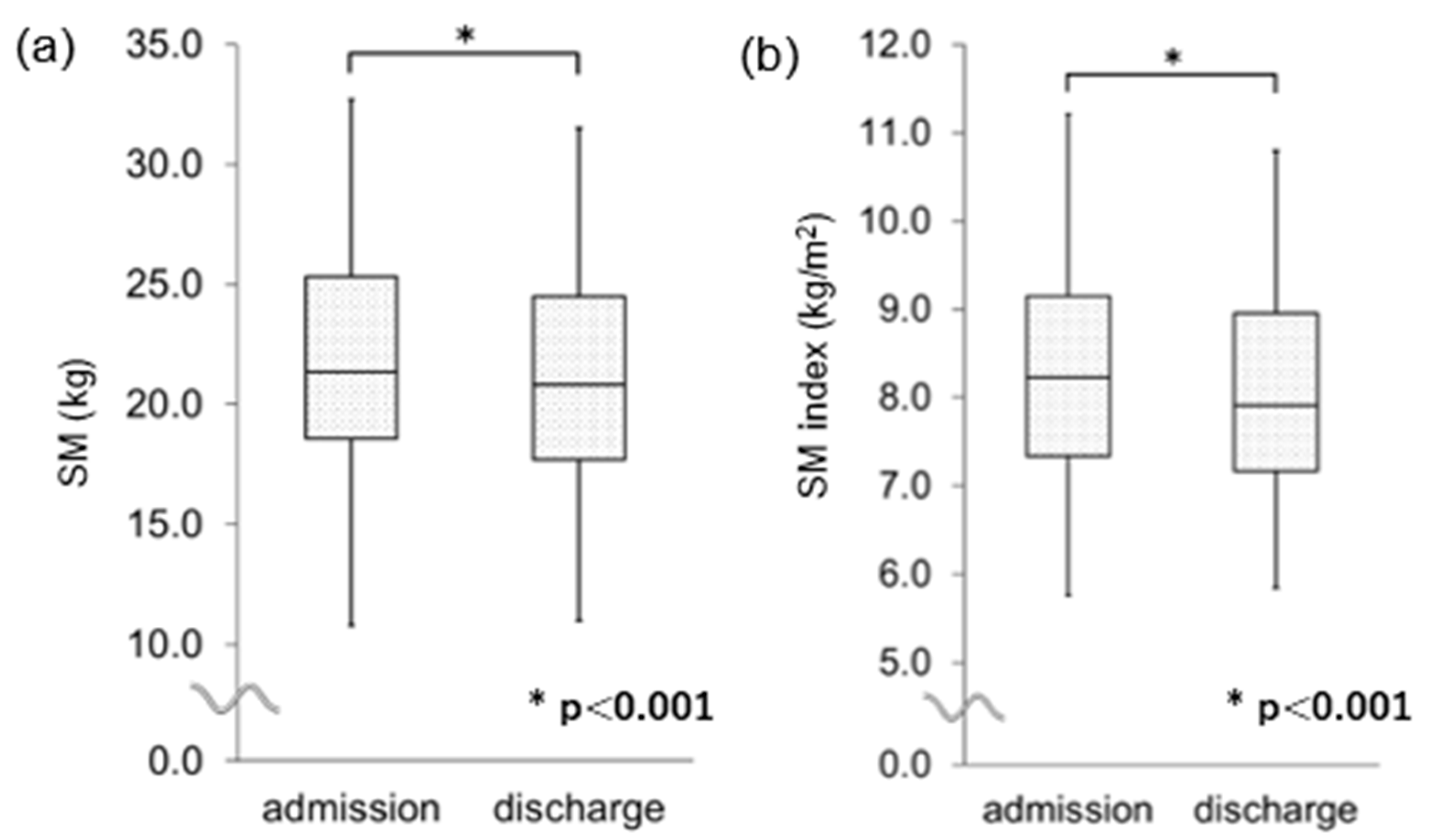
| SM (kg) | 21.4 (18.6–25.3) | 20.7 (17.9–25.2) | <0.001 |
| Male | 22.9 (19.9–26.5) | 22.3 (20.0–26.3) | <0.001 |
| Female | 15.3 (14.2–18.9) | 15.1 (13.8–18.2) | <0.01 |
| SM index (kg/m2) | 8.3 (7.3–9.2) | 8.1 (7.1–9.0) | <0.001 |
| Male | 8.6 (7.8–9.4) | 8.5 (7.6–9.2) | <0.001 |
| Female | 6.9 (6.3–7.9) | 6.7 (6.2–7.5) | 0.01 |
| FM (kg) | 13.2 (9.0–17.3) | 13.2 (9.0–17.3) | 0.32 |
| Male | 12.8 (8.5–17.9) | 11.7 (8.5–18.1) | 0.11 |
| Female | 15.0 (12.3–16.8) | 15.0 (13.3–17.1) | 0.39 |
| FM index (kg/m2) | 5.3 (3.2–6.8) | 5.0 (3.3–6.9) | 0.35 |
| Male | 4.8 (3.1–6.5) | 4.4 (3.2–6.5) | 0.11 |
| Female | 6.7 (6.1–7.1) | 6.7 (5.8–7.1) | 0.37 |
| FFM (kg) | 39.9 (35.4–46.8) | 38.9 (34.4–47.1) | <0.001 |
| Male | 43.3 (37.8–49.5) | 41.5 (37.7–49.3) | <0.01 |
| Female | 30.0 (27.9–36.0) | 29.7 (27.0–35.1) | 0.02 |
| FFM index (kg/m2) | 15.5 (13.8–17.2) | 15.2 (13.9–16.8) | <0.001 |
| Male | 15.9 (14.7–17.5) | 15.9 (14.2–16.9) | <0.01 |
| Female | 13.4 (12.6–15.1) | 13.1 (12.4–14.6) | 0.02 |
| ECW/TBW | 0.396 (0.390–0.403) | 0.395 (0.390–0.401) | 0.56 |
| Male | 0.395 (0.389–0.403) | 0.394 (0.389–0.403) | 0.40 |
| Female | 0.396 (0.393–0.402) | 0.398 (0.391–0.402) | 0.71 |
| Handgrip strength, dominant hand (kg) | 24.0 (19.0–30.3) | 25.2 (18.7–30.7) | 0.08 |
| Male | 26.4 (21.5–31.6) | 27.5 (21.6–33.0) | 0.32 |
| Female | 16.4 (13.1–18.0) | 16.7 (14.5–18.4) | 0.02 |
| Handgrip strength, non-dominant hand (kg) | 22.6 (17.1–28.4) | 22.5 (18.1–29.5) | 0.01 |
| Male | 23.6 (20.2–30.3) | 24.1 (19.6–31.0) | 0.08 |
| Female | 14.9 (12.4–17.1) | 16.0 (13.5–19.0) | <0.01 |
| Maximum tongue strength (kPa) | 27.8 (21.9–33.6) | 28.8 (22.7–35.2) | 0.08 |
| FOIS | 7 (7–7) | 7 (7–7) | 0.57 |
| ΔSM Index < −0.4 (n = 16) | ΔSM Index ≥ −0.4 (n = 48) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | 56.9 (52.2–66.3) | 50.8 (44.1–61.1) | 0.07 |
| Age (years) | 74.9 ± 8.1 | 77.0 ± 6.8 | 0.46 |
| Sex (male/female) | 14/2 | 36/12 | 0.30 |
| Length of hospitalization (days) | 13.5 (11.0–20.3) | 12.0 (11.0–16.3) | 0.43 |
| A-DROP (score) | 1.5 (1.0–2.0) | 1.0 (1.0–2.0) | 0.52 |
| CURB-65 (score) | 1.0 (1.0–2.0) | 1.0 (1.0–2.0) | 0.24 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 16.5 (8.3–19.7) | 8.4 (5.5–15.3) | 0.15 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 3.3 (3.0–3.6) | 3.4 (3.0–3.7) | 0.48 |
| Serum total protein (g/dL) | 6.6 (6.3–7.0) | 7.0 (6.7–7.3) | <0.05 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.6 (20.4–24.1) | 20.4 (18.3–22.9) | 0.13 |
| FM index (kg/m2) | 6.5 (4.4–7.2) | 4.8 (3.0–6.8) | 0.27 |
| Variables | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 1.08 | 0.98–1.19 | 0.14 |
| Sex (female) | 1.70 | 0.25–11.46 | 0.58 |
| Serum total protein at admission (g/dL) | 7.88 | 1.70–36.62 | 0.008 |
| Weight at admission (kg) | 0.95 | 0.90–1.01 | 0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sugiya, R.; Nishiyama, O.; Shiraishi, M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Gose, K.; Yamazaki, R.; Oomori, T.; Sano, A.; Arizono, S.; Uchiyama, Y.; et al. Body Composition Changes in Hospitalized Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5460. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155460
Sugiya R, Nishiyama O, Shiraishi M, Yoshikawa K, Gose K, Yamazaki R, Oomori T, Sano A, Arizono S, Uchiyama Y, et al. Body Composition Changes in Hospitalized Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5460. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155460
Chicago/Turabian StyleSugiya, Ryuji, Osamu Nishiyama, Masashi Shiraishi, Kazuya Yoshikawa, Kyuya Gose, Ryo Yamazaki, Takashi Oomori, Akiko Sano, Shinichi Arizono, Yasushi Uchiyama, and et al. 2025. "Body Composition Changes in Hospitalized Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5460. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155460
APA StyleSugiya, R., Nishiyama, O., Shiraishi, M., Yoshikawa, K., Gose, K., Yamazaki, R., Oomori, T., Sano, A., Arizono, S., Uchiyama, Y., Higashimoto, Y., & Matsumoto, H. (2025). Body Composition Changes in Hospitalized Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5460. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155460







