Comparison Between Non-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) and Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) for the Detection of Intratumoral Aneurysms in Renal Angiomyolipoma (Renal AML)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Imaging Protocol
2.3. DSA Technique
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Generative AI
3. Results
Introduction to Two False Negative Cases
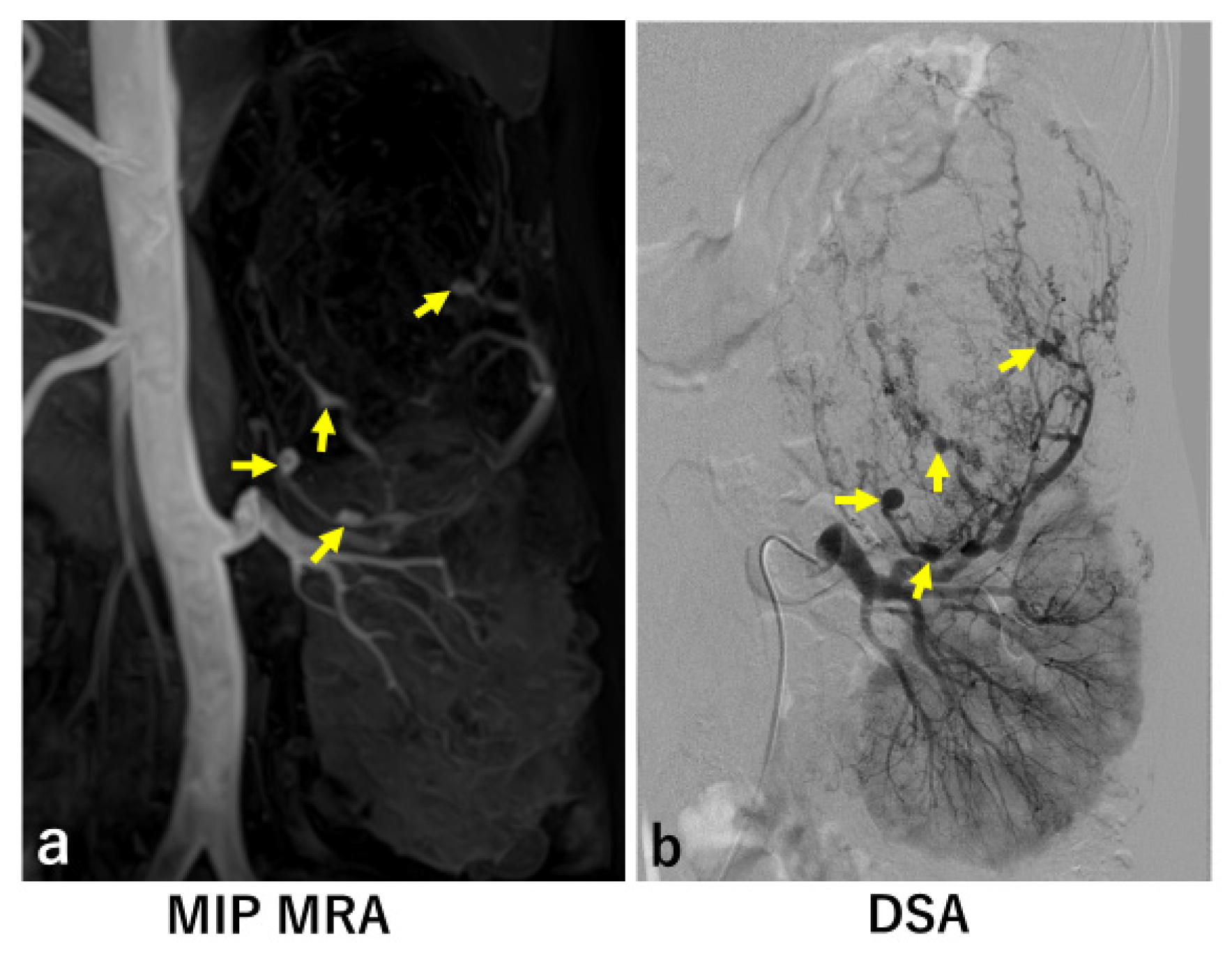
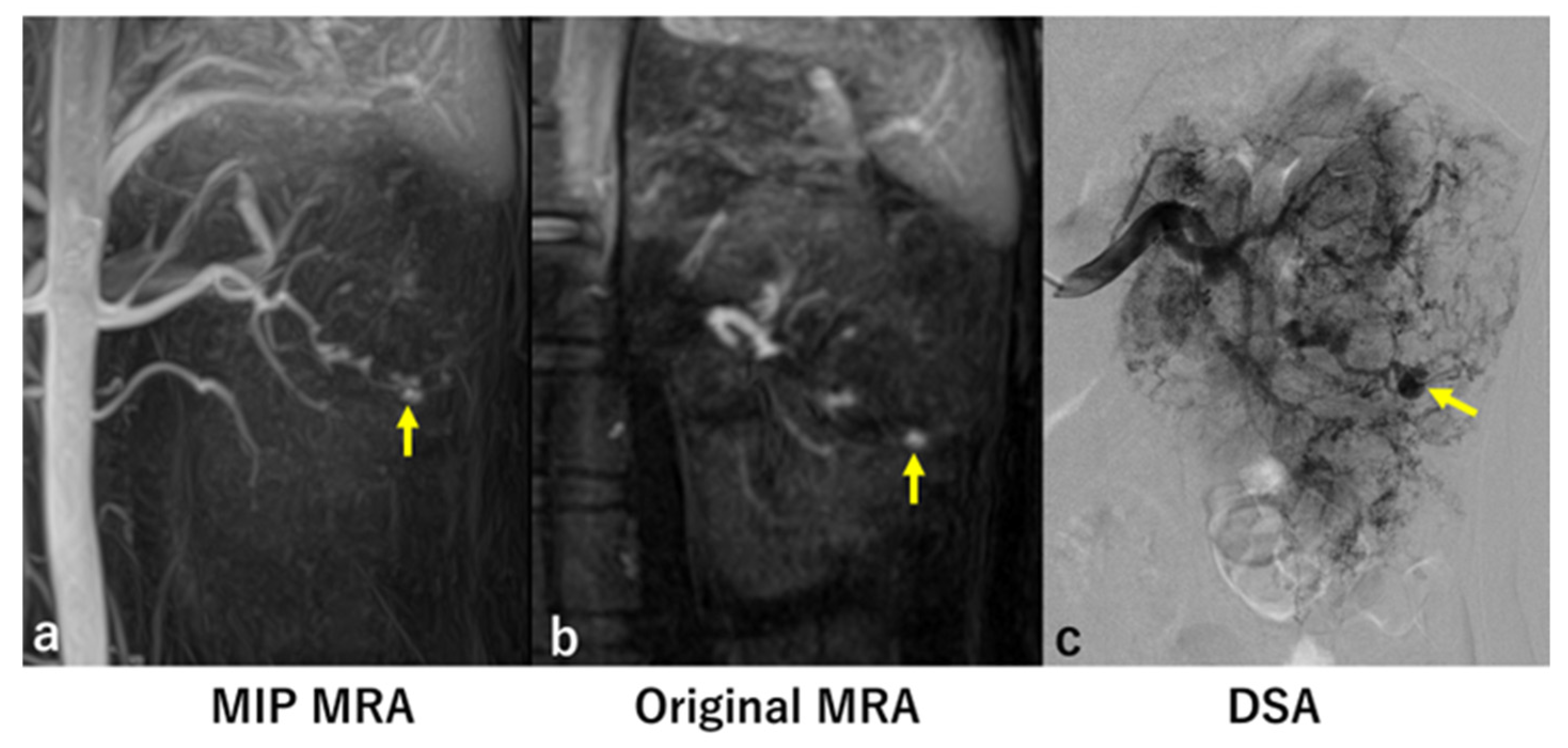
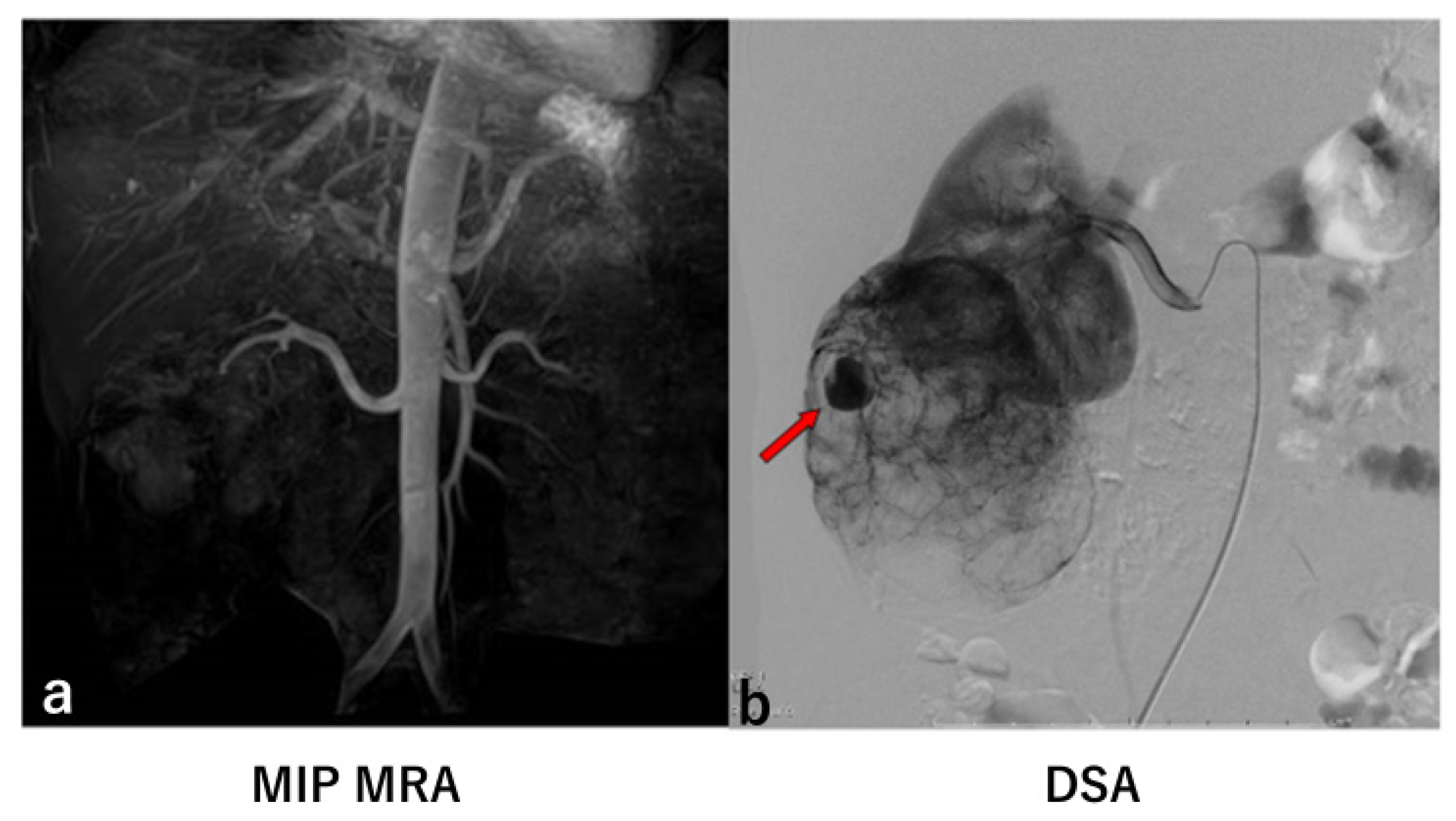

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuwatsuru, R. Renal and Urinary Abnormalities II—Renal Angiomyolipoma. Nephrol. Front. 2003, 2, 136–138. [Google Scholar]
- Omodon, M.; Ayuba, G.; Patel, I.J. Review of Renal Artery Embolization for Treatment of Renal Angiomyolipoma. Clin. Nephrol. Urol. Sci. 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, N.; Kuwatsuru, R.; Kyogoku, S.; Shiraishi, A.; Okada, S.; Tsuge, D.; Yamashiro, Y. Embolization of Spontaneous Intratumoral Hemorrhage with the Hemodynamic Characteristics of Arteriovenous Fistula in Renal Angiomyolipoma. Case Rep. Nephrol. Dial. 2015, 5, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Molen, A.J.; Reimer, P.; Dekkers, I.A.; Bongartz, G.; Bellin, M.F.; Bertolotto, M.; Heckenberg, J.; Jackson, J.; Marckmann, P.; Thomsen, H.S.; et al. Post-contrast Acute Kidney Injury—Part 1: Definition, Clinical Features, Incidence, Role of Contrast Medium and Risk Factors: Recommendations for Updated ESUR Contrast Medium Safety Committee Guidelines. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2845–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Molen, A.J.; Reimer, P.; Dekkers, I.A.; Bongartz, G.; Bellin, M.F.; Bertolotto, M.; Heckenberg, J.; Jackson, J.; Marckmann, P.; Thomsen, H.S.; et al. Post-contrast Acute Kidney Injury—Part 2: Risk Stratification, Role of Hydration and Other Prophylactic Measures, Patients Taking Metformin and Chronic Dialysis Patients: Recommendations for Updated ESUR Contrast Medium Safety Committee Guidelines. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2856–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcos, S.K.; Thomsen, H.S. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: More Questions and Some Answers. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2008, 110, c24–c31; discussion c32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M.; Spuentrup, E.; Stuber, M.; Hoogeveen, R.; Günther, R.W.; Buecker, A. Free-Breathing Renal Magnetic Resonance Angiography with Steady-State Free Precession and Slab-Selective Spin Inversion Combined with Radial K-Space Sampling and Water-Selective Excitation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 53, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herborn, C.U.; Watkins, D.M.; Runge, V.M.; Gendron, J.M.; Montgomery, M.L.; Naul, L.G. Renal Arteries: Comparison of Steady-State Free Precession MR Angiography and Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography. Radiology 2006, 239, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyttenbach, R.; Braghetti, A.; Wyss, M.; Alerci, M.; Briner, L.; Santini, P.; Cozzi, L.; Di Valentino, M.; Katoh, M.; Marone, C.; et al. Renal Artery Assessment with Non-Enhanced Steady-State Free Precession Versus Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography. Radiology 2007, 245, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, J.H.; Wilson, G.J.; Eubank, W.B.; Glickerman, D.J.; Millan, J.A.; Hoogeveen, R.M. Navigator-Gated MR Angiography of the Renal Arteries: A Potential Screening Tool for Renal Artery Stenosis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, W540–W546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parienty, I.; Rostoker, G.; Jouniaux, F.; Piotin, M.; Admiraal-Behloul, F.; Miyazaki, M. Renal Artery Stenosis Evaluation in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: Non-Enhanced Time-Spatial Labeling Inversion-Pulse Three-Dimensional MR Angiography with Regulated Breathing Versus DSA. Radiology 2011, 259, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, I.; Ariff, B.; Quest, R.A.; Moser, S.; Glover, A.; Taube, D.; Gishen, P.; Papalois, V.; Juli, C. Is There a Role for Free-Breathing Non-Contrast Steady-State Free Precession Renal MRA Imaging for Assessing Live Donors? A Preliminary Study. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, e448–e454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajiri, M.; Gentsu, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Sasaki, K.; Ueshima, E.; Okada, T.; Sugimoto, K.; Murakami, T. A Case of Life-threatening Rupture of Small Renal Angiomyolipoma with an Unidentified Intratumoral Aneurysm during Follow-up. Interv. Radiol. 2024, 9, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusk, T.; Biancari, F.; Lane, B.; Tobert, C.; Campbell, S.; Rimon, U.; D’Andrea, V.; Mehik, A.; Vaarala, M.H. Treatment of renal angiomyolipoma: Pooled analysis of individual patient data. BMC Urol. 2015, 15, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelman, R.R.; Carr, M.; Koktzoglou, I. Advances in non-contrast quiescent-interval slice-selective (QISS) magnetic resonance angiography. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaha, M.A.; Jaskolka, J.D.; Tan, K.; Rick, M.; Schmitt, P.; Menezes, R.J.; Wintersperger, B.J. Non-contrast-enhanced MR angiography in critical limb ischemia: Performance of quiescent-interval single-shot (QISS) and TSE-based subtraction techniques. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odudu, A.; Nery, F.; Harteveld, A.A.; Evans, R.G.; Pendse, D.; Buchanan, C.E.; Francis, S.T.; Fernández-Seara, M.A. Arterial spin labelling MRI to measure renal perfusion: A systematic review and statement paper. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2018, 33 (Suppl. S2), ii15–ii21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takehara, Y. Clinical Application of 4D Flow MR Imaging for the Abdominal Aorta. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2022, 21, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, M.; Akahane, M. Non-contrast enhanced MR angiography: Established techniques. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 35, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gietzen, C.; Janssen, J.P.; Görtz, L.; Kaya, K.; Gietzen, T.; Gertz, R.J.; Pennig, H.; Seuthe, K.; Maintz, D.; Rauen, P.S.; et al. Non-contrast-enhanced MR-angiography of the abdominal arteries: Intraindividual comparison between relaxation-enhanced angiography without contrast and triggering (REACT) and 4D contrast-enhanced MR-angiography. Abdom. Radiol. 2025, 50, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga-Szemes, A.; Aherne, E.A.; Schoepf, U.J.; Todoran, T.M.; Koktzoglou, I.; Edelman, R.R. Free-Breathing Fast Low-Angle Shot Quiescent-Interval Slice-Selective Magnetic Resonance Angiography for Improved Detection of Vascular Stenoses in the Pelvis and Abdomen: Technical Development. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. of Cases | Age /Sex | Concurrent Disease | AML Side | Number and Size of Aneurysms (Right) | Number and Size of Aneurysms (Left) | Maximum Size of Angiomyolipoma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRA/DSA | MRA/DSA | |||||
| 1 | 57/F | TSC | Right | 0/0 | N/A *1 | Multiple *2 (153 × 113 × 59 mm) |
| 2 | 29/F | TSC | Bilateral | 0/0 | 1/1 (3 × 2 mm/4 × 2 mm) | Multiple *2 (142 × 119 × 76 mm) |
| 3 | 38/F | sLAM | Left | N/A *1 | 0/0 | 154 × 91 × 71 mm |
| 4 | 37/F | sLAM | Left | N/A *1 | 7/7 (max. 9 × 6 mm, min. 4 × 3 mm /max. 9 × 7 mm, min. 4 × 3 mm) | 110 × 86 × 86 mm |
| 5 | 37/F | TSC | Bilateral | 0/0 | 4/4 (max. 6 × 2 mm, min. 3 × 2 mm /max. 6 × 4 mm, min. 4 × 3 mm) | Multiple *2 (130 × 125 × 85 mm) |
| 6 | 21/F | TSC | Bilateral | 0/0 | 0/0 | Multiple *2 (78 × 74 × 67 mm) |
| 7 | 50/F | sAML | Right | 0/1 (14 × 13 mm) | N/A *1 | 105 × 91 × 77 mm |
| 8 | 55/F | TSC | Bilateral | 8/8 (max. 10 × 7 mm, min.3 × 2 mm /max. 12 × 6 mm, min. 4 × 3 mm) | N/A *1 | Multiple *2 (119 × 102 × 83 mm) |
| 9 | 33/F | TSC | Bilateral | 0/0 | 3/3 (max. 5 × 3 mm, min. 3 × 2 mm /max. 4 × 3 mm, min. 3 × 3 mm) | Multiple *2 (115 × 109 × 67 mm) |
| 10 | 33/F | sLAM | Bilateral | 0/0 | N/A *1 | Multiple *2 (121 × 84 × 63 mm) |
| 11 | 33/F | TSC | Bilateral | N/A *1 | 1/1 (5 × 3 mm/4 × 3 mm) | Multiple *2 (76 × 59 × 48 mm) |
| 12 | 30/F | TSC | Bilateral | 0/0 | N/A *1 | Multiple *2 (54 × 50 × 32 mm) |
| 13 | 33/F | sLAM | Bilateral | 2/5 (max. 6 × 4 mm, min. 4 × 3 mm /max. 8 × 6 mm, min. 3 × 3 mm) | 0/0 | Multiple *2 (85 × 83 × 75 mm) |
| 14 | 37/F | sAML | Left | N/A *1 | 0/0 | 42 × 39 × 30 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yashiro, D.; Kuwatsuru, Y.; Toei, H.; Udagawa, T.; Okada, S.; Kato, H.; Saito, N.; Kuwatsuru, R. Comparison Between Non-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) and Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) for the Detection of Intratumoral Aneurysms in Renal Angiomyolipoma (Renal AML). J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155276
Yashiro D, Kuwatsuru Y, Toei H, Udagawa T, Okada S, Kato H, Saito N, Kuwatsuru R. Comparison Between Non-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) and Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) for the Detection of Intratumoral Aneurysms in Renal Angiomyolipoma (Renal AML). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155276
Chicago/Turabian StyleYashiro, Daisuke, Yoshiki Kuwatsuru, Hiroshi Toei, Takeshi Udagawa, Shingo Okada, Hitomi Kato, Naoko Saito, and Ryohei Kuwatsuru. 2025. "Comparison Between Non-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) and Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) for the Detection of Intratumoral Aneurysms in Renal Angiomyolipoma (Renal AML)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155276
APA StyleYashiro, D., Kuwatsuru, Y., Toei, H., Udagawa, T., Okada, S., Kato, H., Saito, N., & Kuwatsuru, R. (2025). Comparison Between Non-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) and Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) for the Detection of Intratumoral Aneurysms in Renal Angiomyolipoma (Renal AML). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155276






