Tinnitus in Normal-Hearing Individuals: Is Outer Hair Cell Dysfunction the Mechanism?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Clinical Examination and Questionnaires
2.3. Audiometric Examinations
2.4. Evaluated Parameters and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Primary Outcomes
3.2. Secondary Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABR | Auditory Brainstem Response |
| AAO | American Academy of Otolaryngology |
| CG | Control group |
| DPOAEs | Distortion product otoacoustic emissions |
| HNS | Head and Neck Surgery |
| IHCs | Inner Hair Cells |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| MML | Minimum masking level |
| OAEs | Otoacoustic emissions |
| OHCs | Outer hair cells |
| TG | Tinnitus group |
| QR-code | Quick Response Code |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SFR | Spontaneous Firing Rate |
| SNR | Sound-to-noise ratio |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| TEOAEs | Transiently evoked otoacoustic emissions |
| THI | Tinnitus Handicap Inventory |
| THI-G | Tinnitus Handicap Inventory—Greek version |
References
- Henton, A.; Tzounopoulos, T. What’s the buzz? The neuroscience and the treatment of tinnitus. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1609–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, P.C.L.; Sanchez, T.G.; Tomita, S. The impact of gender, age and hearing loss on tinnitus severity. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 76, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; An, S.Y.; Sim, S.; Park, B.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.S.; Hong, S.K.; Choi, H.G. Analysis of the prevalence and associated risk factors of Tinnitus in adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 28, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalrymple, S.N.; Lewis, S.H.; Philman, S. Tinnitus: Diagnosis and management. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 103, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, B.I.; Lee, H.W.; Ryu, S.; Kim, J.S. Tinnitus Update. J. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrogeni, P.; Molnár, A.; Molnár, V.; Tamás, L.; Maihoub, S. Correlation Between the Pitch and Loudness of Tinnitus, Hearing Levels, and Tinnitus Handicap Inventory Scores in Patients with Chronic Subjective Tinnitus. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunkel, D.E.; Bauer, C.A.; Sun, G.H.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Cunningham, E.R., Jr.; Archer, S.M.; Blakley, B.W.; Carter, J.M.; Granieri, E.C.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Tinnitus. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 151, S1–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, M.; Hwang, J.H. Risk of tinnitus in patients with sleep apnea: A nationwide, population-based, case-control study. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 2171–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Ma, W.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, H.; Lin, H. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Association between Hypertension and Tinnitus. Int. J. Hypertens. 2015, 2015, 583493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, A.; Molnár, V.; Mavrogeni, P.; Maihoub, S. Fasting Glucose, Haemoglobin A1C (HbA1c), Blood Lipid, and Triglyceride-Glucose Index Parameters in Relation to Subjective Tinnitus. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilkov, V.; Caswell-Midwinter, B.; Zhao, Y.; de Gruttola, V.; Jung, D.H.; Liberman, M.C.; Maison, S.F. Evidence of cochlear neural degeneration in normal-hearing subjects with tinnitus. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acle-Cervera, L.; Gavilanes-Plasencia, J.; Delgado-Vargas, B.; Sánz-López, L.; Bonet Loscertales, M.; Mata-Castro, N. Effect of Tinnitus in Distortion Products Otoacoustic Emissions (DPOAEs) in Normal Hearing Patients. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 74, 4226–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, T.G.; de Medeiros, Í.R.T.; Levy, C.P.D.; da Rosa Oiticica Ramalho, J.; Bento, R.F. Tinnitus in normally hearing patients: Clinical aspects and repercussions. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2005, 71, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, M.; Cuesta, M.; Sanz, R.; Cobo, P. Comparison of Tinnitus Handicap Inventory and Tinnitus Functional Index as Treatment Outcomes. Audio. Res. 2023, 13, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeman, F.; Koller, M.; Schecklmann, M.; Langguth, B.; Landgrebe, M. TRI database study group. Tinnitus assessment by means of standardized self-report questionnaires: Psychometric properties of the Tinnitus Questionnaire (TQ), the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory (THI), and their short versions in an international and multi-lingual sample. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2012, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papitsi, I.; Balatsouras, D.G.; Makris, I.; Koukoutsis, G.; Kaberos, A.; Tzavara, C.; Nikolopoulos, T.; Sarafis, P. Validation of the Greek version of tinnitus handicap inventory. Audiol. Res. 2020, 10, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ami, M.; Abdullah, A.; Awang, M.A.; Liyab, B.; Saim, L. Relation of distortion product otoacoustic emission with tinnitus. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonsbury-Martin, B.L.; McCoy, M.J.; Whitehead, M.L.; Martin, G.K. Clinical testing of distortion-product otoacoustic emissions. Ear Hear. 1993, 14, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, D.T. Otoacoustic emissions, their origin in cochlear function, and use. Br. Med. Bull. 2002, 63, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.W. Distortion Product and Transient Evoked OAEs: Nonpathologic factors influencing measurement. In Handbook of Otoacoustic Emissions; Hall, J.W., Ed.; Delmar Cengage Learning: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 163–222. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.W. Clinical applications of otoacoustic emissions in adults. In Handbook of Otoacoustic Emissions; Hall, J.W., Ed.; Delmar Cengage Learning: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 481–545. [Google Scholar]
- Shiomi, Y.; Tsuji, J.; Naito, Y.; Fujiki, N.; Yamamoto, N. Characteristics of DPOAE audiogram in tinnitus patients. Hear. Res. 1997, 108, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztuka, A.; Pospiech, L.; Gawron, W.; Dudek, K. DPOAE in estimation of the function of the cochlea in tinnitus patients with normal hearing. Auris Nasus Larynx 2010, 37, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Siburt, H.W.; Lobarinas, E.; Griffiths, S.K.; Spankovich, C. No Reliable Association Between Recreational Noise Exposure and Threshold Sensitivity, Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emission Amplitude, or Word-in-Noise Performance in a College Student Population. Ear Hear. 2018, 39, 1057–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimiani, A.; Rouhbakhsh, N.; Zamiri Abdollahi, F.; Jalaie, S. Estimation of outer hair cells function in chronic bilateral tinnitus patients with normal hearing using distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Aud. Vestib. Res. 2021, 30, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrzejczak, W.W.; Pilka, E.; Ganc, M.; Kochanek, K.; Skarzynski, H. Ultra-High Frequency Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions for Detection of Hearing Loss and Tinnitus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrian, H.; Shaibanizadeh, A.; Farahani, S.; Jalaie, S.; Mahdi, P.; Amali, A.; Arian Nahad, H. Evaluation of distortion and transient evoked otoacoustic emission in tinnitus patients with normal hearing. Iran J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 26, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alshabory, H.F.; Gabr, T.A.; Kotait, M.A. Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions (DPOAEs) in Tinnitus Patients. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 26, e046–e057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveris, H.; Maurer, J.; Mann, W. DPOAE-grams in patients with acute tonal tinnitus. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 132, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.; Mertes, I.B.; Chappell, J.; Jeon, C.H.; Husain, F.T. Comparison of otoacoustic emissions in tinnitus and hyperacusis in adults with normal hearing sensitivity. Int. J. Audiol. 2023, 62, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noreña, A.J.; Farley, B.J. Tinnitus-related neural activity: Theories of generation, propagation, and centralization. Hear. Res. 2013, 295, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.E.; Husain, F.T.; Eggermont, J.J. Role of attention in the generation and modulation of tinnitus. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 1754–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehrle, H.M.; Granjeiro, R.C.; Sampaio, A.L.L.; Farias, M.S.; Martins, V.S.; Oliveira, C.A.C.P. Ten Years Follow Up of Patients with Tinnitus and Normal Hearing. Int. Tinnitus J. 2022, 26, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

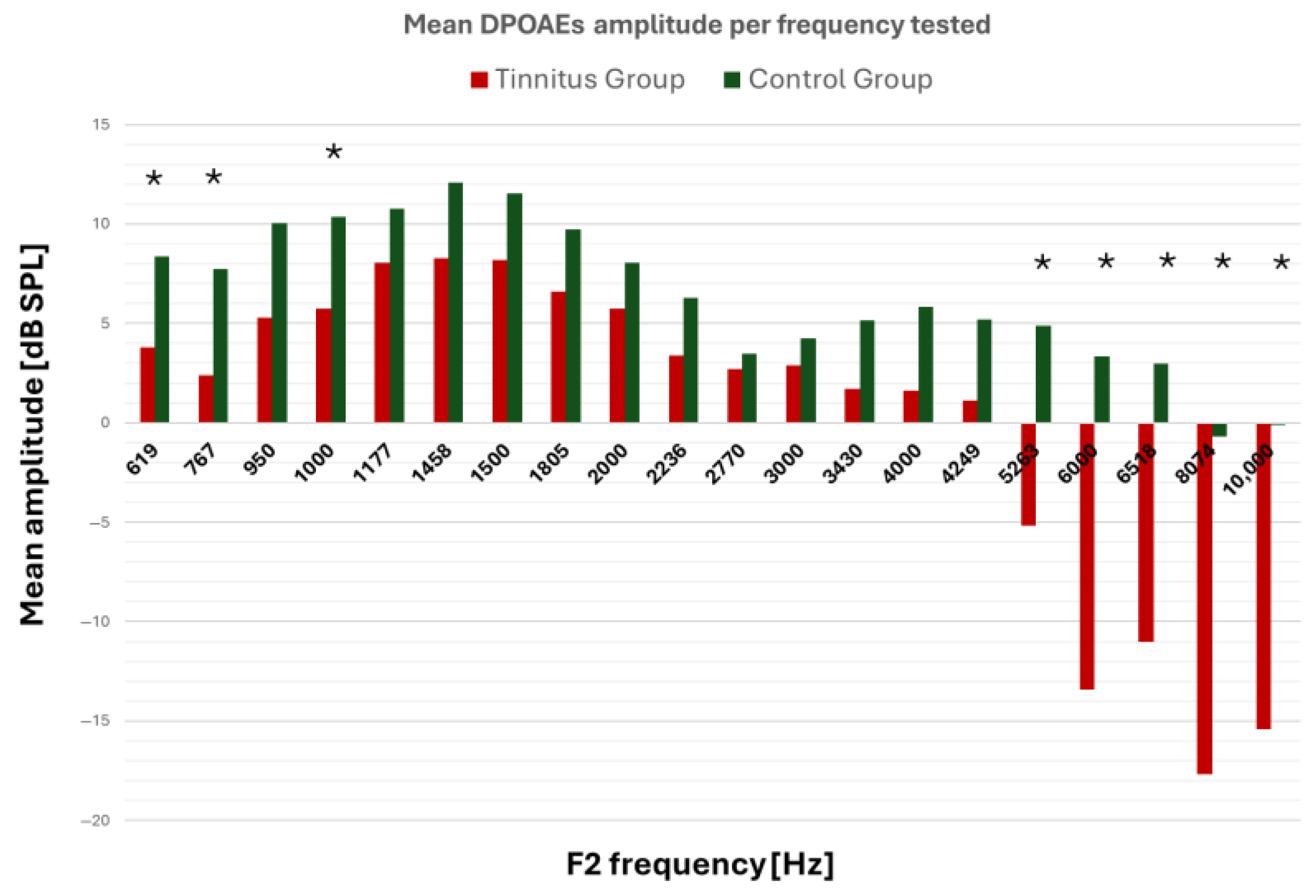
| F2 (Hz) | 619 | 767 | 950 | 1000 | 1177 | 1458 | 1500 | 1805 | 2000 | 2236 |
| F1 (Hz) | 507.37 | 628.68 | 778.68 | 819.67 | 964.75 | 1195.08 | 1229.5 | 1479.5 | 1639.3 | 1832.78 |
| F2 (Hz) | 2770 | 3000 | 3430 | 4000 | 4249 | 5263 | 6000 | 6518 | 8074 | 10,000 |
| F1 (Hz) | 2270.49 | 2459 | 2811.47 | 3278.68 | 3482.78 | 4313.93 | 4918.03 | 5342.62 | 6618.03 | 8.196.72 |
| DPOAEs’ Frequency Recording (F2, Hz) | Group | N | Mean DPOAEs’ Amplitude | SD | Mean Difference | 95% CI | p-Value | Bonferroni-Corrected p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| 619 | TG | 64 | 3.90 | 3.49 | −4.46 | −6.23 | −2.70 | <0.001 | <0.001 * |
| CG | 20 | 8.36 | 3.37 | ||||||
| 767 | TG | 64 | 2.42 | 6.31 | −5.33 | −8.27 | −2.39 | 0.001 | 0.009 * |
| CG | 20 | 7.75 | 3.44 | ||||||
| 950 | TG | 64 | 5.31 | 7.38 | −4.72 | −8.08 | −1.35 | 0.007 | 0.14 |
| CG | 20 | 10.03 | 2.73 | ||||||
| 1000 | TG | 64 | 5.79 | 3.92 | −4.57 | −6.57 | −2.57 | <0.001 | <0.001 * |
| CG | 20 | 10.36 | 3.91 | ||||||
| 1177 | TG | 64 | 8.09 | 5.79 | −2.69 | −5.51 | 0.13 | 0.061 | 1.22 |
| CG | 20 | 10.78 | 4.58 | ||||||
| 1458 | TG | 64 | 8.28 | 6.77 | −3.82 | −6.90 | −0.73 | 0.016 | 0.32 |
| CG | 20 | 12.09 | 2.53 | ||||||
| 1500 | TG | 64 | 8.23 | 5.79 | −3.32 | −5.98 | −0.67 | 0.015 | 0.3 |
| CG | 20 | 11.56 | 2.40 | ||||||
| 1805 | TG | 64 | 6.60 | 8.40 | −3.15 | −6.95 | 0.66 | 0.10 | 2.0 |
| CG | 20 | 9.75 | 2.71 | ||||||
| 2000 | TG | 64 | 5.71 | 6.81 | −2.34 | −5.49 | 0.81 | 0.143 | 2.86 |
| CG | 20 | 8.06 | 3.36 | ||||||
| 2236 | TG | 64 | 3.50 | 7.37 | −2.77 | −6.12 | 0.57 | 0.103 | 2.06 |
| CG | 20 | 6.27 | 2.42 | ||||||
| 2770 | TG | 64 | 2.77 | 4.90 | −0.70 | −3.10 | 1.70 | 0.639 | 12.7 |
| CG | 20 | 3.47 | 3.97 | ||||||
| 3000 | TG | 64 | 2.97 | 6.27 | −1.30 | −4.23 | 1.64 | 0.563 | 11.26 |
| CG | 20 | 4.27 | 3.63 | ||||||
| 3430 | TG | 64 | 1.78 | 7.98 | −3.36 | −7.01 | 0.29 | 0.383 | 7.6 |
| CG | 20 | 5.14 | 3.29 | ||||||
| 4000 | TG | 64 | 1.11 | 7.08 | −4.72 | −8.02 | −1.42 | 0.071 | 1.42 |
| CG | 20 | 5.83 | 3.87 | ||||||
| 4249 | TG | 64 | −1.97 | 9.07 | −7.15 | −11.32 | −2.99 | 0.006 | 0.12 |
| CG | 20 | 5.18 | 3.93 | ||||||
| 5263 | TG | 64 | −5.22 | 10.98 | −10.11 | −15.15 | −5.07 | 0.001 | 0.02 * |
| CG | 20 | 4.89 | 4.69 | ||||||
| 6000 | TG | 64 | −13.4 | 11.59 | −16.76 | −22.11 | −11.42 | <0.001 | <0.001 * |
| CG | 20 | 3.33 | 5.40 | ||||||
| 6518 | TG | 64 | −11.0 | 11.58 | −14.01 | −19.39 | −8.64 | <0.001 | <0.001 * |
| CG | 20 | 2.99 | 5.90 | ||||||
| 8074 | TG | 29 | −17.7 | 9.20 | −16.99 | −21.29 | −12.68 | <0.001 | <0.001 * |
| CG | 20 | −0.72 | 5.24 | ||||||
| 10,000 | TG | 64 | −15.4 | 8.10 | −15.36 | −19.61 | −11.12 | <0.001 | <0.001 * |
| CG | 20 | −0.10 | 9.04 | ||||||
| Characteristics of TG Participants (64 Ears) | Abnormal DPOAEs, ≤1000 Hz | Abnormal DPOAEs, ~4000 Hz | Abnormal DPOAEs, ≥6000 Hz | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tinnitus onset | Gradual | 2 (3.1%) | p = 0.06 * | 0 | p < 0.001 * | 43 (67.18%) | p < 0.001 * |
| Sudden | 4 (6.25%) | 9 (14.0%) | 6 (9.37%) | ||||
| Tinnitus intensity self-assessment | <70 | 2 (3.1%) | p = 0.06 | 3 (4.68%) | p = 0.17 | 45 (70.3%) | p = 0.002 * |
| >70 | 4 (6.25%) | 6 (9.37%) | 4 (6.25%) | ||||
| Degree of disability | ΤHΙ < 58 | 6 (9.37%) | p = 0.031 * | 2 (3.1%) | p = 0.025 * | 29 (45.3%) | p = 0.456 |
| ΤHΙ > 58 | 0 | 7 (10.9%) | 20 (31.25%) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chimona, T.; Vrentzou, M.; Erotokritakis, E.; Tsakiraki, E.; Asimakopoulou, P.; Papadakis, C. Tinnitus in Normal-Hearing Individuals: Is Outer Hair Cell Dysfunction the Mechanism? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155232
Chimona T, Vrentzou M, Erotokritakis E, Tsakiraki E, Asimakopoulou P, Papadakis C. Tinnitus in Normal-Hearing Individuals: Is Outer Hair Cell Dysfunction the Mechanism? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155232
Chicago/Turabian StyleChimona, Theognosia, Maria Vrentzou, Emmanouel Erotokritakis, Eleni Tsakiraki, Panagiota Asimakopoulou, and Chariton Papadakis. 2025. "Tinnitus in Normal-Hearing Individuals: Is Outer Hair Cell Dysfunction the Mechanism?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155232
APA StyleChimona, T., Vrentzou, M., Erotokritakis, E., Tsakiraki, E., Asimakopoulou, P., & Papadakis, C. (2025). Tinnitus in Normal-Hearing Individuals: Is Outer Hair Cell Dysfunction the Mechanism? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5232. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155232




