Evaluating Sepsis Mortality Predictions from the Emergency Department: A Retrospective Cohort Study Comparing qSOFA, the National Early Warning Score, and the International Early Warning Score
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
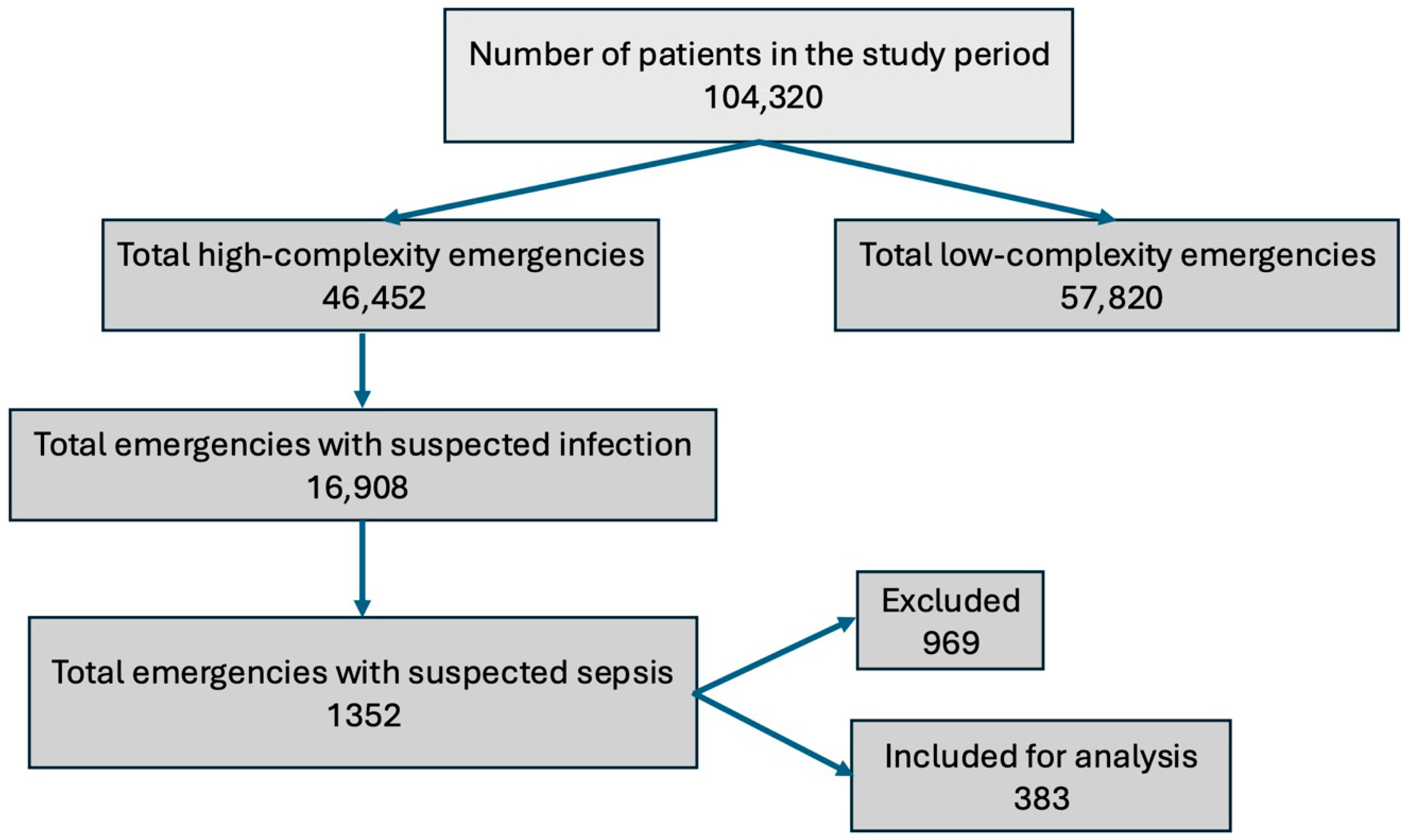
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Definition of Infection
2.3.2. Definition of Sepsis
2.4. Sample Size
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NEWS | the National Early Warning Score |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| AUC | receiver operating characteristic curve |
| NPV | negative predictive value |
| PPV | positive predictive value |
| IEWS | the International Early Warning Score |
References
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Machado, F.R.; Cavalcanti, A.B.; Bozza, F.A.; Ferreira, E.M.; Angotti Carrara, F.S.; Sousa, J.L.; Caixeta, N.; Salomao, R.; Angus, D.C.; Pontes Azevedo, L.C.; et al. The epidemiology of sepsis in Brazilian intensive care units (the Sepsis PREvalence Assessment Database, SPREAD): An observational study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, F.; Barrera, L.; De La Rosa, G.; Dennis, R.; Dueñas, C.; Granados, M.; Londoño, D.; Molina, F.; Ortiz, G.; Jaimes, F. The epidemiology of sepsis in Colombia: A prospective multicenter cohort study in ten university hospitals. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Devia Jaramillo, G.; Menendez Ramirez, S. USER Protocol as a Guide to Resuscitation of the Patient with Septic Shock in the Emergency Department. OAEM. Open Access Emerg. Med. 2021, 13, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, T.M. Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Trials (ProCESS, ARISE, ProMISe): What is Optimal Resuscitation? Crit. Care Clin. 2017, 33, 323–344. [Google Scholar]
- Angus, D.C.; van der Poll, T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 840–851. [Google Scholar]
- Husabø, G.; Nilsen, R.M.; Flaatten, H.; Solligård, E.; Frich, J.C.; Bondevik, G.T.; Braut, G.S.; Walshe, K.; Harthug, S.; Hovlid, E.; et al. Early diagnosis of sepsis in emergency departments, time to treatment, and association with mortality: An observational study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero, R.; Hillman, K.M.; McCarthy, S.; Fatovich, D.M.; Joseph, A.P.; Richardson, D.B. Access block and ED overcrowding. Emerg. Med. Australas. 2010, 22, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Ko, R.E.; Lim, S.Y.; Park, S.; Suh, G.Y.; Lee, Y.J. Sepsis Alert Systems, Mortality, and Adherence in Emergency Departments: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2422823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar]
- Tusgul, S.; Carron, P.-N.; Yersin, B.; Calandra, T.; Dami, F. Low sensitivity of qSOFA, SIRS criteria and sepsis definition to identify infected patients at risk of complication in the prehospital setting and at the emergency department triage. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2017, 25, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Finkelsztein, E.J.; Jones, D.S.; Ma, K.C.; Pabón, M.A.; Delgado, T.; Nakahira, K.; Arbo, J.E.; Berlin, D.A.; Schenck, E.J.; Choi, A.M.K.; et al. Comparison of qSOFA and SIRS for predicting adverse outcomes of patients with suspicion of sepsis outside the intensive care unit. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keep, J.; Messmer, A.; Sladden, R.; Burrell, N.; Pinate, R.; Tunnicliff, M.; Glucksman, E. National early warning score at Emergency Department triage may allow earlier identification of patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: A retrospective observational study. Emerg. Med. J. 2016, 33, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xu, R.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Rostami, A. A comparison of qSOFA, SIRS and NEWS in predicting the accuracy of mortality in patients with suspected sepsis: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, W.L.; Bin Rusli, K.D.; Aitken, L.M. Early warning scores for sepsis identification and prediction of in-hospital mortality in adults with sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Nurs. 2024, 33, 2005–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hincapié-Osorno, C.; van Wijk, R.J.; Postma, D.F.; Koeze, J.; Ter Maaten, J.C.; Jaimes, F.; Bouma, H.R. Validation of MEWS, NEWS, NEWS-2 and qSOFA for different infection foci at the emergency department, the acutelines cohort. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 43, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar]
- Devia Jaramillo, G.; Erazo Guerrero, L. Adjusting EWS scores for altitude above sea level: Is it necessary to predict sepsis mortality in the emergency room? Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2025, 18, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Candel, B.G.J.; Nissen, S.K.; Nickel, C.H.; Raven, W.; Thijssen, W.; Gaakeer, M.I.; Lassen, A.T.; Brabrand, M.; Steyerberg, E.W.; de Jonge, E.; et al. Development and External Validation of the International Early Warning Score for Improved Age- and Sex-Adjusted In-Hospital Mortality Prediction in the Emergency Department. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 51, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Backer, D.; Deutschman, C.S.; Hellman, J.; Myatra, S.N.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; Talmor, D.; Antonelli, M.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; Bauer, S.R.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign Research Priorities 2023. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 52, 268–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Somma, S.; Paladino, L.; Vaughan, L.; Lalle, I.; Magrini, L.; Magnanti, M. Overcrowding in emergency department: An international issue. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2014, 10, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, S.O.B.; Sørensen, R.H.; Nielsen, F.E. Prognostic Accuracy of SOFA, qSOFA, and SIRS for Mortality Among Emergency Department Patients with Infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 2763–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thodphetch, M.; Chenthanakij, B.; Wittayachamnankul, B.; Sruamsiri, K.; Tangsuwanaruk, T. A comparison of scoring systems for predicting mortality and sepsis in the emergency department patients with a suspected infection. Clin. Exp. Emerg. Med. 2021, 8, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brink, A.; Alsma, J.; Verdonschot, R.J.C.G.; Rood, P.P.M.; Zietse, R.; Lingsma, H.F.; Schuit, S.C.E.; Lopez-Delgado, J.C. Predicting mortality in patients with suspected sepsis at the Emergency Department; A retrospective cohort study comparing qSOFA, SIRS and National Early Warning Score. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211133. [Google Scholar]
- Dadeh, A.-A.; Kulparat, M. Predictive Performance of the NEWS—Lactate and NEWS Towards Mortality or Need for Critical Care Among Patients with Suspicion of Sepsis in the Emergency Department: A Prospective Observational Study. Open Access Emerg. Med. 2022, 14, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Yoon, J.; Lee, J.B.; Jin, Y.; Jeong, T.; Park, B. Predictive value of the National Early Warning Score–Lactate for mortality and the need for critical care among general emergency department patients. J. Crit. Care 2016, 36, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Lei, Y.-P.; Zhou, R.-X. SIRS, SOFA, qSOFA, and NEWS in the diagnosis of sepsis and prediction of adverse outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2023, 21, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRISM Investigators; Rowan, K.M.; Angus, D.C.; Bailey, M.; Barnato, A.E.; Bellomo, R.; Canter, R.R.; Coats, T.J.; Delaney, A.; Gimbel, E.; et al. Early, Goal-Directed Therapy for Septic Shock—A Patient-Level Meta-Analysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, D.C.; Barnato, A.E.; Bell, D.; Bellomo, R.; Chong, C.-R.; Coats, T.J.; Davies, A.; Delaney, A.; Harrison, D.A.; Holdgate, A.; et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of early goal-directed therapy for septic shock: The ARISE, ProCESS and ProMISe Investigators. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Gerlach, H.; Vogelmann, T.; Preissing, F.; Stiefel, J.; Adam, D. Mortality in sepsis and septic shock in Europe, North America and Australia between 2009 and 2019—Results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, M.C.; Scherag, A.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Hartog, C.S.; Tsaganos, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K.; International Forum of Acute Care Trialists. Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Current Estimates and Limitations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, G.; Ospina-Tascón, G.A.; Damiani, L.P.; Estenssoro, E.; Dubin, A.; Hurtado, J.; Friedman, G.; Castro, R.; Alegría, L.; Teboul, J.-L.; et al. Effect of a Resuscitation Strategy Targeting Peripheral Perfusion Status vs Serum Lactate Levels on 28-Day Mortality Among Patients with Septic Shock: The ANDROMEDA-SHOCK Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Devia Jaramillo, G.; Ibáñez Pinilla, M. Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment, and Procalcitonin for Early Diagnosis and Prediction of Death in Elderly Patients with Suspicion of Sepsis in the Emergency Department, Based on Sepsis-3 Definition. Gerontology 2022, 68, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Variable | Survivors (%) | No Survivors (%) | OR | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n = 383) | 304 (79.4) | 79 (20.6) | ||
| Sex(male) | 168 (55.3) | 43 (54.4) | 0.96 (0.58–1.59) | 0.995 |
| Age (median (IQ)) | 72 (57–79) | 76 (68–86) | <0.001 | |
| Septic shock | 101 (33.2) | 55 (69.6) | 4.57 (2.70–7.94) | <0.001 |
| Glasgow score (median (IQ)) | 15 (15–15) | 15 (14–15) | 0.001 | |
| Heart rate (mean (sd)) | 101.16 (23.2) | 102.03 (28.8) | 0.805 | |
| Respiratory rate (median (IQ)) | 20 (18–22) | 22 (19.5–26) | 0.028 | |
| Oxygen saturation (median (IQ)) | 92 (88–94) | 90 (86–92) | 0.015 | |
| Systolic pressure (median (IQ)) | 106 (90–125.2) | 98 (70–120) | 0.001 | |
| Diastolic pressure (median (IQ)) | 65 (55–75) | 59 (41.5–72) | 0.009 | |
| Temperature (median (IQ)) | 37.2 (36.5–38.1) | 37.1 (36.4–38.4) | 0.934 | |
| Po2 (median (IQ)) | 66 (57.3–75.4) | 68.5 (58–83.5) | 0.07 | |
| PaFi (mean (sd)) | 278.9 (80.3) | 225.2 (105.9) | <0.001 | |
| Platelet count (median (IQ)) | 209 (140–335) | 243 (143–404) | 0.466 | |
| Bilirubin (median (IQ)) | 1 (0.7–1.4) | 1 (0.7–1.4) | 0.61 | |
| Mean art. Pressure (median (IQ)) | 78.3 (67.2–90.7) | 71 (52–89.5) | 0.01 | |
| Creatinine (median (IQ)) | 1.2 (0.8–1.6) | 1.3 (1.0–1.8) | 0.066 | |
| Oxygen saturation (median (IQ)) | 92 (88–94) | 90 (86–92) | 0.015 | |
| Lactate levels (median (IQ)) | 1.6 (1–2.5) | 3 (1.6–5.5) | <0.001 | |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Cardiovascular | 136 (44.7) | 47 (59.5) | 1.80 (1.09–3.01) | 0.027 |
| Diabetes | 76 (25) | 20 (25.3) | 1.02 (0.56–1.78) | 1 |
| Renal insufficiency | 22 (7.2) | 17 (21.5) | 3.50 (1.73–7.00) | <0.001 |
| Immunosuppression | 58 (91.1) | 12 (15.2) | 0.76 (0.37–1.47) | 0.526 |
| COPD | 24 (7.9) | 13 (16.5) | 2.30 (1.08–4.72) | 0.034 |
| Sepsis origin (%) | 0.923 | |||
| Pulmonary (29.0) | 89 (29.3) | 22 (27.8) | ||
| Urinal (26.1) | 77 (25.3) | 23 (29.1) | ||
| Biliary (11.7) | 35 (11.5) | 10 (12.7) | ||
| Abdominal (6.8) | 23 (7.6) | 3 (3.8) | ||
| Soft tissues (5.7) | 17 (5.6) | 5 (6.3) | ||
| Gastroenteritis (5.0) | 15 (4.9) | 4 (5.1) | ||
| Endocarditis (1.0) | 4 (1.3) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Osteomyelitis (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Hospital stay (median (IQ)) | 9 (6–14.2) | 7 (3–13) | 0.154 | |
| Stay in ICU (median (IQ)) | 3 (0–6) | 4 (2–8) | 0.045 | |
| qSOFA (median (IQ)) | 1 (0–1) | 1 (1–2) | <0.001 | |
| NEWS (median (IQ)) | 7 (4–9) | 9 (7–12.5) | <0.001 | |
| IEWS (mean (SD)) | 11.2 (3.8) | 14.8 (3.8) | <0.001 | |
| IEWS_L (median (IQ)) | 13 (10.1–15.9) | 19.2 (15.5–22.7) | <0.001 |
| Score | Threshold | Spec | Sens | NPV | PPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qSOFA | 1.5 | 0.80 | 0.46 | 0.85 | 0.38 |
| NEWS | 7.5 | 0.57 | 0.72 | 0.88 | 0.30 |
| IEWS | 13.5 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.88 | 0.36 |
| IEWS_L | 15.6 | 0.73 | 0.74 | 0.91 | 0.41 |
| NEWS_L | 11.05 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.90 | 0.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devia-Jaramillo, G.A.; Erazo-Guerrero, L.; Laguado-Castro, V.; Alfonso-Parada, J.M. Evaluating Sepsis Mortality Predictions from the Emergency Department: A Retrospective Cohort Study Comparing qSOFA, the National Early Warning Score, and the International Early Warning Score. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144869
Devia-Jaramillo GA, Erazo-Guerrero L, Laguado-Castro V, Alfonso-Parada JM. Evaluating Sepsis Mortality Predictions from the Emergency Department: A Retrospective Cohort Study Comparing qSOFA, the National Early Warning Score, and the International Early Warning Score. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(14):4869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144869
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevia-Jaramillo, German Alberto, Lilia Erazo-Guerrero, Vivian Laguado-Castro, and Juan Manuel Alfonso-Parada. 2025. "Evaluating Sepsis Mortality Predictions from the Emergency Department: A Retrospective Cohort Study Comparing qSOFA, the National Early Warning Score, and the International Early Warning Score" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 14: 4869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144869
APA StyleDevia-Jaramillo, G. A., Erazo-Guerrero, L., Laguado-Castro, V., & Alfonso-Parada, J. M. (2025). Evaluating Sepsis Mortality Predictions from the Emergency Department: A Retrospective Cohort Study Comparing qSOFA, the National Early Warning Score, and the International Early Warning Score. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(14), 4869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144869






