Association of Atrial Fibrillation with Incident Probable Dementia and Cognitive Impairment in the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Availability
2.2. Study Design and Participants
2.3. Electrocardiogram and Atrial Fibrillation Diagnosis
2.4. Ascertainment of Probable Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairments
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christiansen, C.B.; Gerds, T.A.; Olesen, J.B.; Kristensen, S.L.; Lamberts, M.; Lip, G.Y.; Gislason, G.H.; Køber, L.; Torp-Pedersen, C. Atrial fibrillation and risk of stroke: A nationwide cohort study. Europace 2016, 18, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Norby, F.L.; Gottesman, R.F.; Mosley, T.H.; Soliman, E.Z.; Agarwal, S.K.; Loehr, L.R.; Folsom, A.R.; Coresh, J.; Alonso, A. Association of atrial fibrillation with cognitive decline and dementia over 20 years: The ARIC-NCS (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Neurocognitive Study). J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e007301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.B.; Lutsey, P.L.; Chen, L.Y.; MacLehose, R.F.; Shao, I.Y.; Alonso, A. Risk factors for dementia in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2022, 174, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, C.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lv, W.; Bai, Y.; Yang, Z. Systolic blood pressure time in target range and incident atrial fibrillation in patients with hypertension: Insights from the SPRINT trial. Hypertension 2023, 80, 2306–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aune, D.; Mahamat-Saleh, Y.; Kobeissi, E.; Feng, T.; Heath, A.K.; Janszky, I. Blood pressure, hypertension and the risk of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2023, 38, 145–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, M.J.; Lam, B.C.P.; Lipnicki, D.M.; Crawford, J.D.; Peters, R.; Schutte, A.E.; Brodaty, H.; Thalamuthu, A.; Rydberg-Sterner, T.; Najar, J. Use of antihypertensives, blood pressure, and estimated risk of dementia in late life: An individual participant data meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2333353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.D.; Pajewski, N.M.; Auchus, A.P.; Bryan, R.N.; Chelune, G.; Cheung, A.K.; Cleveland, M.L.; Coker, L.H.; Crowe, M.G.; Cushman, W.C. Effect of intensive vs standard blood pressure control on probable dementia: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ambrosius, W.T.; Sink, K.M.; Foy, C.G.; Berlowitz, D.R.; Cheung, A.K.; Cushman, W.C.; Fine, L.J.; Goff, D.C., Jr.; Johnson, K.C.; Killeen, A.A. The design and rationale of a multicenter clinical trial comparing two strategies for control of systolic blood pressure: The Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT). Clin. Trials 2014, 11, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, R.F.; Heeringa, J.; Wolters, F.J.; Franco, O.H.; Stricker, B.H.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Ikram, M.A. Association between atrial fibrillation and dementia in the general population. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh-Manoux, A.; Fayosse, A.; Sabia, S.; Canonico, M.; Bobak, M.; Elbaz, A.; Kivimäki, M.; Dugravot, A. Atrial fibrillation as a risk factor for cognitive decline and dementia. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2612–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantarian, S.; Stern, T.A.; Mansour, M.; Ruskin, J.N. Cognitive impairment associated with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; de Larriva, A.P.A. Atrial fibrillation, cognitive decline and dementia. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2016, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunch, T.J. Atrial fibrillation and dementia. Circulation 2020, 142, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasiou, C.A.; Theochari, C.A.; Zareifopoulos, N.; Arfaras-Melainis, A.; Giannakoulas, G.; Karamitsos, T.D.; Palaiodimos, L.; Ntaios, G.; Avgerinos, K.I.; Kapogiannis, D. Atrial fibrillation is associated with cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, vascular dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 3122–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liang, J.; Li, C.; Gao, D.; Ma, Q.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, W.; Zheng, F. Age at diagnosis of atrial fibrillation and incident dementia. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2342744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, A.; Breteler, M.M.; De Bruyne, M.C.; Van Harskamp, F.; Grobbee, D.E.; Hofman, A. Atrial fibrillation and dementia in a population-based study: The Rotterdam Study. Stroke 1997, 28, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Qiu, C. Atrial fibrillation, cognitive decline, and dementia: An epidemiologic review. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2018, 5, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinidis, D.G.; Zareifopoulos, N.; Theochari, C.A.; Arfaras-Melainis, A.; Papanastasiou, C.A.; Uppal, D.; Giannakoulas, G.; Kalogeropoulos, A.P.; Fontes, J.D.T. Association between atrial fibrillation and cognitive impairment in individuals with prior stroke: A meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. Stroke 2020, 51, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggesi, A.; Inzitari, D.; Pantoni, L. Atrial fibrillation and cognition: Apidemiological data and possible mechanisms. Stroke 2015, 46, 3316–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.H.; Lew, L.Z.; Franke, K.B.; Elliott, A.D.; Lau, D.H.; Thiyagarajah, A.; Linz, D.; Arstall, M.; Tully, P.J.; Baune, B.T. Predictive role of atrial fibrillation in cognitive decline: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 2.8 million individuals. Europace 2022, 24, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, S.; Conen, D. Mechanisms and clinical manifestations of cognitive decline in atrial fibrillation patients: Potential implications for preventing dementia. Can. J. Cardiol. 2023, 39, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühne, M.; Krisai, P.; Coslovsky, M.; Rodondi, N.; Müller, A.; Beer, J.H.; Ammann, P.; Auricchio, A.; Moschovitis, G.; Hayoz, D. Silent brain infarcts impact on cognitive function in atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2127–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Lopez, F.L.; Gottesman, R.F.; Huxley, R.R.; Agarwal, S.K.; Loehr, L.; Mosley, T.; Alonso, A. Atrial fibrillation and cognitive decline–the role of subclinical cerebral infarcts: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Stroke 2014, 45, 2568–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefansdottir, H.; Arnar, D.O.; Aspelund, T.; Sigurdsson, S.; Jonsdottir, M.K.; Hjaltason, H.; Launer, L.J.; Gudnason, V. Atrial fibrillation is associated with reduced brain volume and cognitive function independent of cerebral infarcts. Stroke 2013, 44, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardarsdottir, M.; Sigurdsson, S.; Aspelund, T.; Rokita, H.; Launer, L.J.; Gudnason, V.; Arnar, D.O. Atrial fibrillation is associated with decreased total cerebral blood flow and brain perfusion. Europace 2018, 20, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, D.; Casuso, A.M.; Maida, A.; Vasumini, N.; Amicone, S.; Canton, L.; Di, L.M.; Basile, M.; Manaresi, T.; Angeli, F.; et al. Prevention of atrial fibrillation with SGLT2 inhibitors across the spectrum of cardiovascular disorders: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2025, pvaf040, Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armillotta, M.; Angeli, F.; Paolisso, P.; Belmonte, M.; Raschi, E.; Di, D.G.; Amicone, S.; Canton, L.; Fedele, D.; Suma, N.; et al. Cardiovascular therapeutic targets of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors beyond heart failure. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 270, 108861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Su, L.; Hou, Y. Statin therapy for the prevention of atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomize controlled trials. Pharmacotherapy 2011, 31, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechocki, M.; Przewłocki, T.; Pieniążek, P.; Trystuła, M.; Podolec, J.; Kabłak-Ziembicka, A.A. Non-Coronary, Peripheral Arterial Atherosclerotic Disease (Carotid, Renal, Lower Limb) in Elderly Patients-A Review PART II Pharmacological Approach for Management of Elderly Patients with Peripheral Atherosclerotic Lesions outside Coronary Territory. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanna, M.G.; Abdullah, A.; Mortensen, M.B.; Navar, A.M. Primary prevention statin therapy in older adults. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2023, 38, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samimisedeh, P.; Kazibwe, R.; Schaich, C.; Hughes, T.; Soliman, E. Abstract P2097: Association of atrial fibrillation with probable dementia in the SPRINT Trial. Circulation 2025, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables n (%) or Mean ± SD | Total Participants (n = 8539) | With AF (n = 264) | Without AF (n = 8275) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 67.9 ± 9.3 | 74.0 ± 8.6 | 67.7 ± 9.2 |
| Female | 3001 (35.1%) | 65 (24.6%) | 2936 (35.5%) |
| Race/Ethnicity | |||
| Black | 2504 (29.3%) | 27 (10.2%) | 2477 (29.9%) |
| Hispanic | 883 (10.3%) | 15 (5.7%) | 868 (10.5%) |
| White | 4997 (58.5%) | 219 (83%) | 4778 (57.7%) |
| Others | 155 (1.8%) | 3 (1.1%) | 152 (1.8%) |
| Non-College graduate | 5075 (59.4%) | 143 (54.2%) | 4932 (59.6%) |
| Intensive treatment arm | 4268 (50.0%) | 133 (50.4%) | 4135 (50.0%) |
| Prior CVD | 1698 (19.8%) | 94 (35.6%) | 1604 (19.4%) |
| Smoking history, n (%) | |||
| Former | 3662/8530 (42.9%) | 163/264 (61.7%) | 3499/8266 (42.3%) |
| Current | 1095/8530 (12.8%) | 16/264 (6.1%) | 1079/8266 (13%) |
| Alcohol use | 331/8534 (3.8%) | 5 (1.9%) | 326 (3.9%) |
| SBP | 139.5 ± 15.5 | 141.5 ± 17.5 | 139.4 ± 15.4 |
| SBP tertiles | |||
| ≤132 mm Hg | 2880 (33.7%) | 92 (34.8%) | 2788 (33.7%) |
| >132 to <145 mm Hg | 2779 (32.5%) | 69 (26.1%) | 2710 (32.7%) |
| ≥145 mm Hg | 2880 (33.7%) | 103 (39.0%) | 2777 (33.6%) |
| No. of BP lowering drugs | 1.83 ± 1.03 | 2.30 ± 0.99 | 1.82 ± 1.03 |
| eGFR | 71.8 ± 20.4 | 65.7 ± 18.1 | 72 ± 20.4 |
| Serum creatinine | 1.07 ± 0.33 | 1.11 ± 0.30 | 1.07 ± 0.33 |
| Total cholesterol | 190.0 ± 41.1 | 176.9 ± 38.5 | 190.5 ± 41.1 |
| Statin use, n (%) | 3736/8486 (44%) | 141/262 (53.8%) | 3595/8224 (43.7%) |
| HDL-Cholesterol | 52.7 ± 14.3 | 52.1 ± 13.9 | 52.8 ± 14.3 |
| BMI | 29.8 ± 5.7 | 30.2 ± 5.6 | 29.8 ± 5.7 |
| Outcome | Events/Participants n (%) | Model 1 | Model 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With AF (n = 264) | Without AF (n = 8275) | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
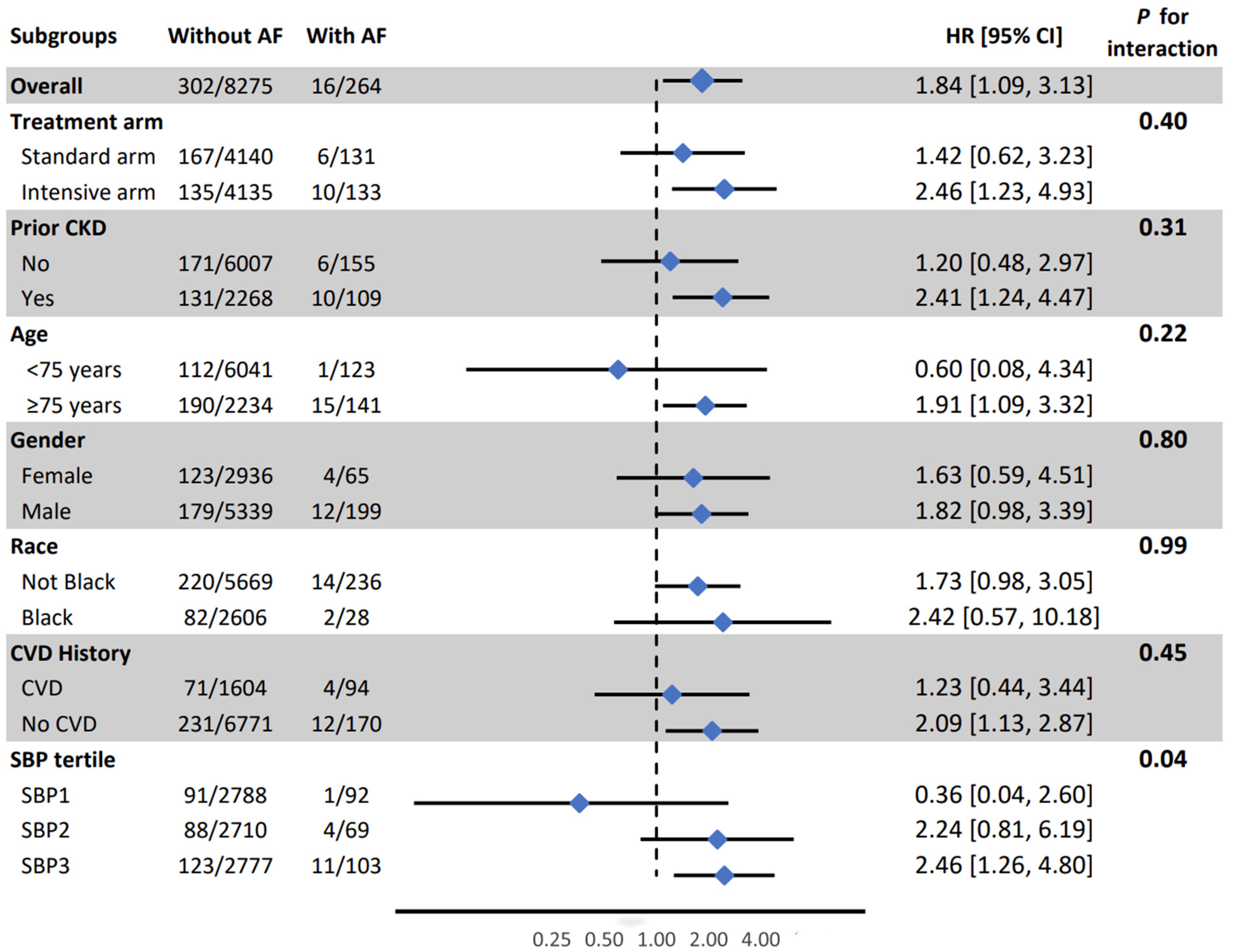
| Probable Dementia (PD) | 16/264 (6.1%) | 302/8275 (3.6%) | 1.98 (1.19, 3.29) | 0.007 | 1.84 (1.09, 3.13) | 0.02 |
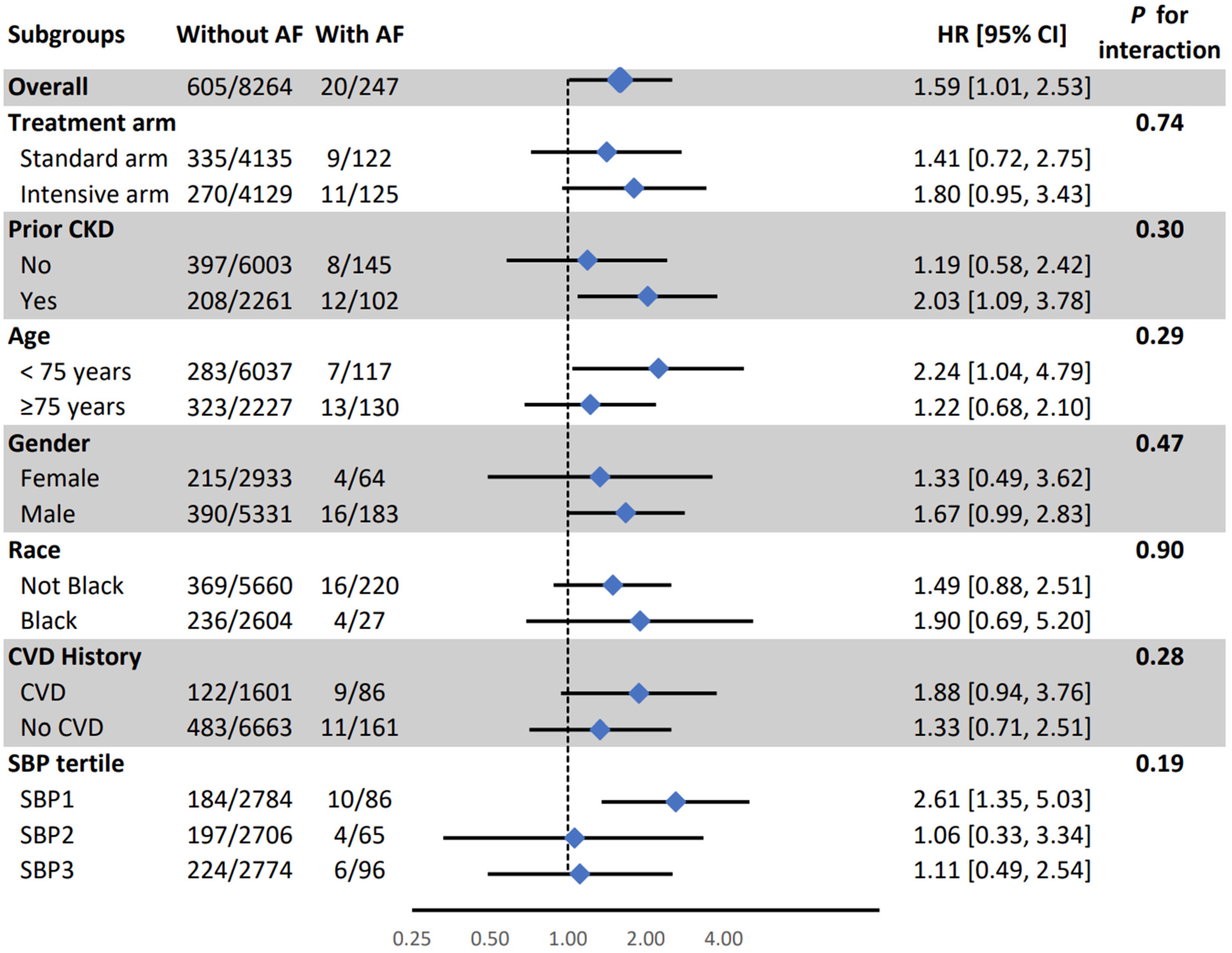
| Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) | 20/247 (8.1%) | 605/8264 (7.3%) | 1.64 (1.04, 2.57) | 0.03 | 1.59 (1.01, 2.53) | 0.04 |
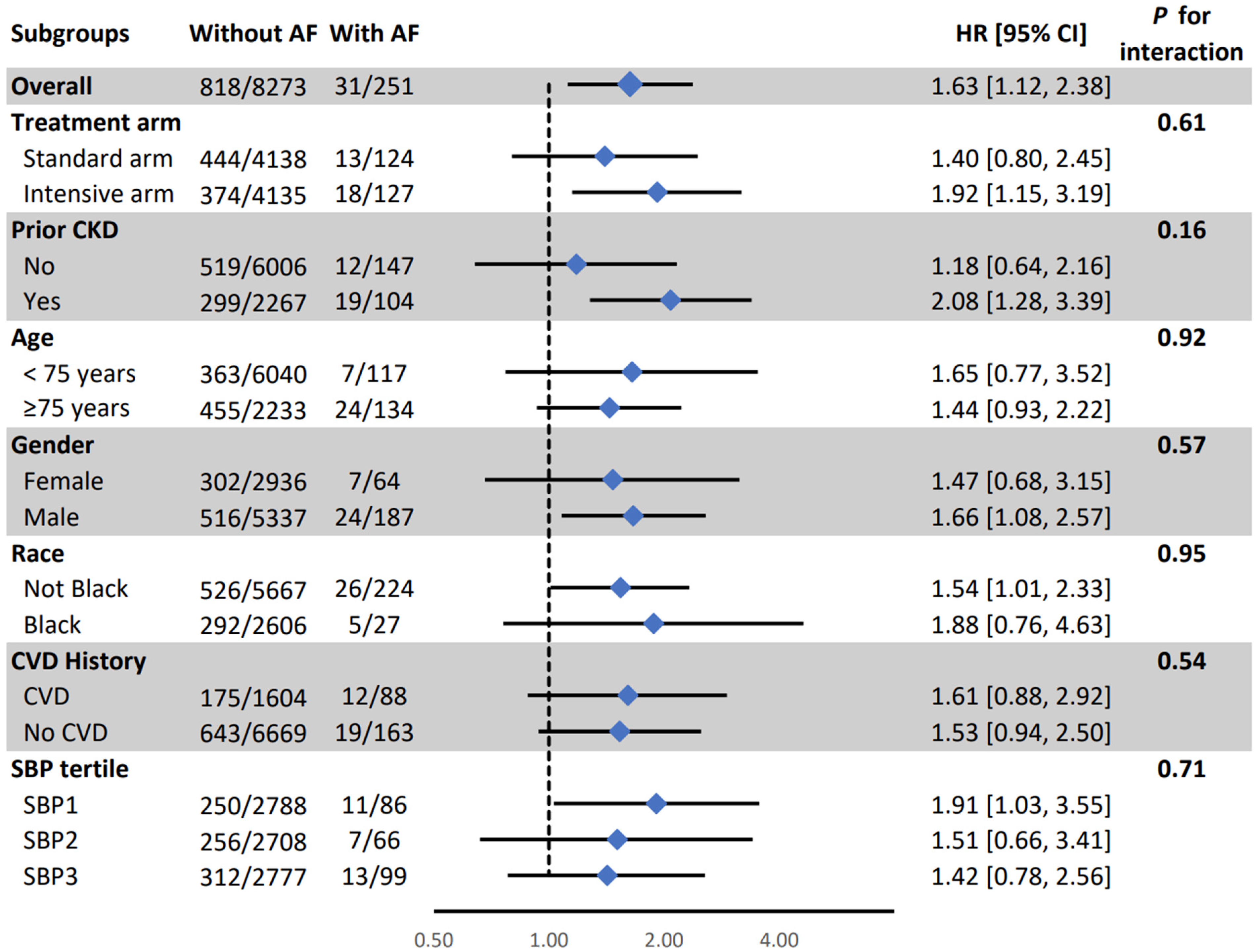
| Composite MCI/PD | 31/251 (12.3%) | 818/8273 (9.8%) | 1.74 (1.21, 2.50) | 0.002 | 1.63 (1.12, 2.38) | 0.009 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samimisedeh, P.; Kazibwe, R.; Schaich, C.L.; Hughes, T.M.; Soliman, E.Z. Association of Atrial Fibrillation with Incident Probable Dementia and Cognitive Impairment in the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT). J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134791
Samimisedeh P, Kazibwe R, Schaich CL, Hughes TM, Soliman EZ. Association of Atrial Fibrillation with Incident Probable Dementia and Cognitive Impairment in the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134791
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamimisedeh, Parham, Richard Kazibwe, Christopher L. Schaich, Timothy M. Hughes, and Elsayed Z. Soliman. 2025. "Association of Atrial Fibrillation with Incident Probable Dementia and Cognitive Impairment in the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134791
APA StyleSamimisedeh, P., Kazibwe, R., Schaich, C. L., Hughes, T. M., & Soliman, E. Z. (2025). Association of Atrial Fibrillation with Incident Probable Dementia and Cognitive Impairment in the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134791






