The Efficacy of Albumin Infusion in Septic Patients with Hypoalbuminemia: An International Retrospective Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
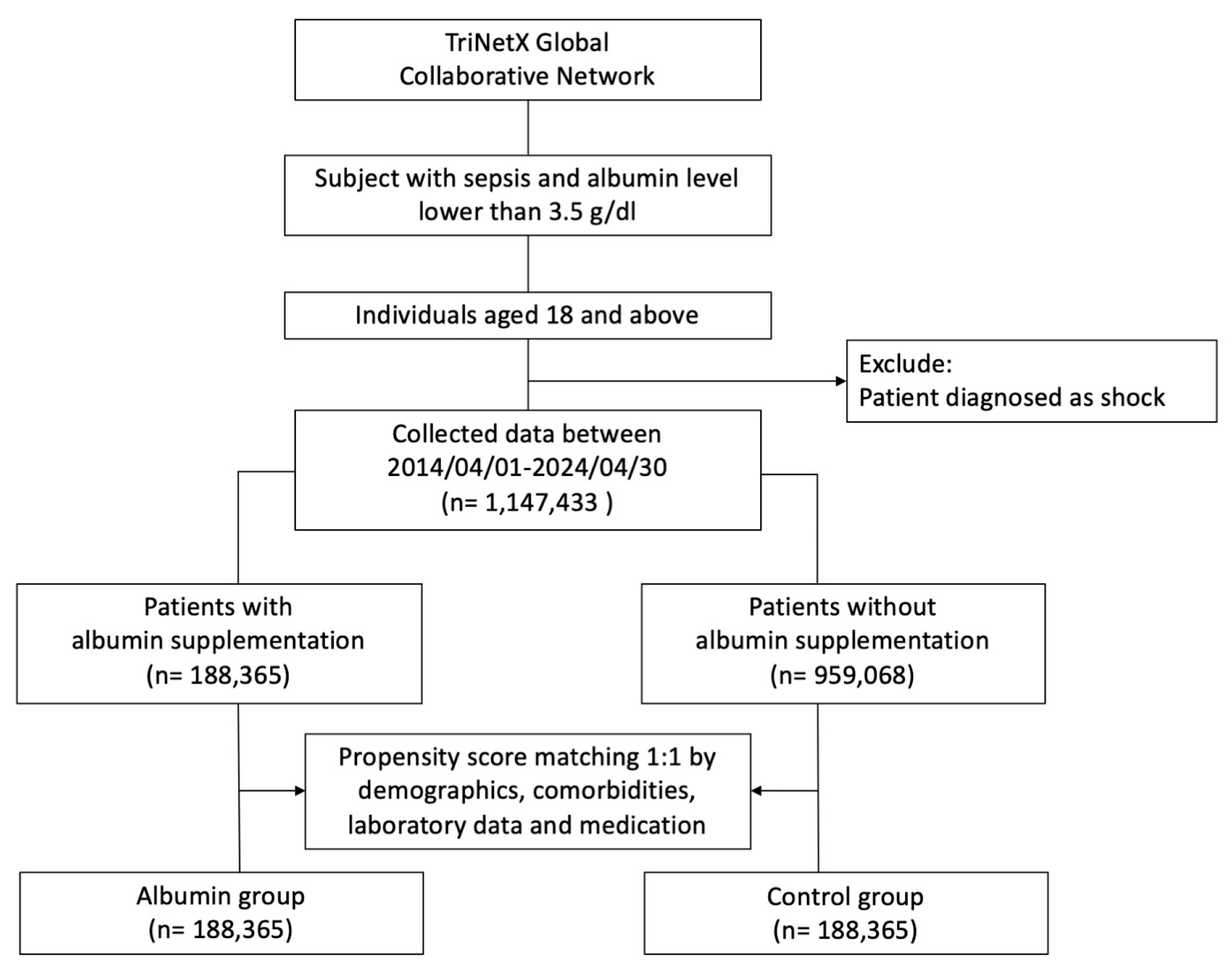
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
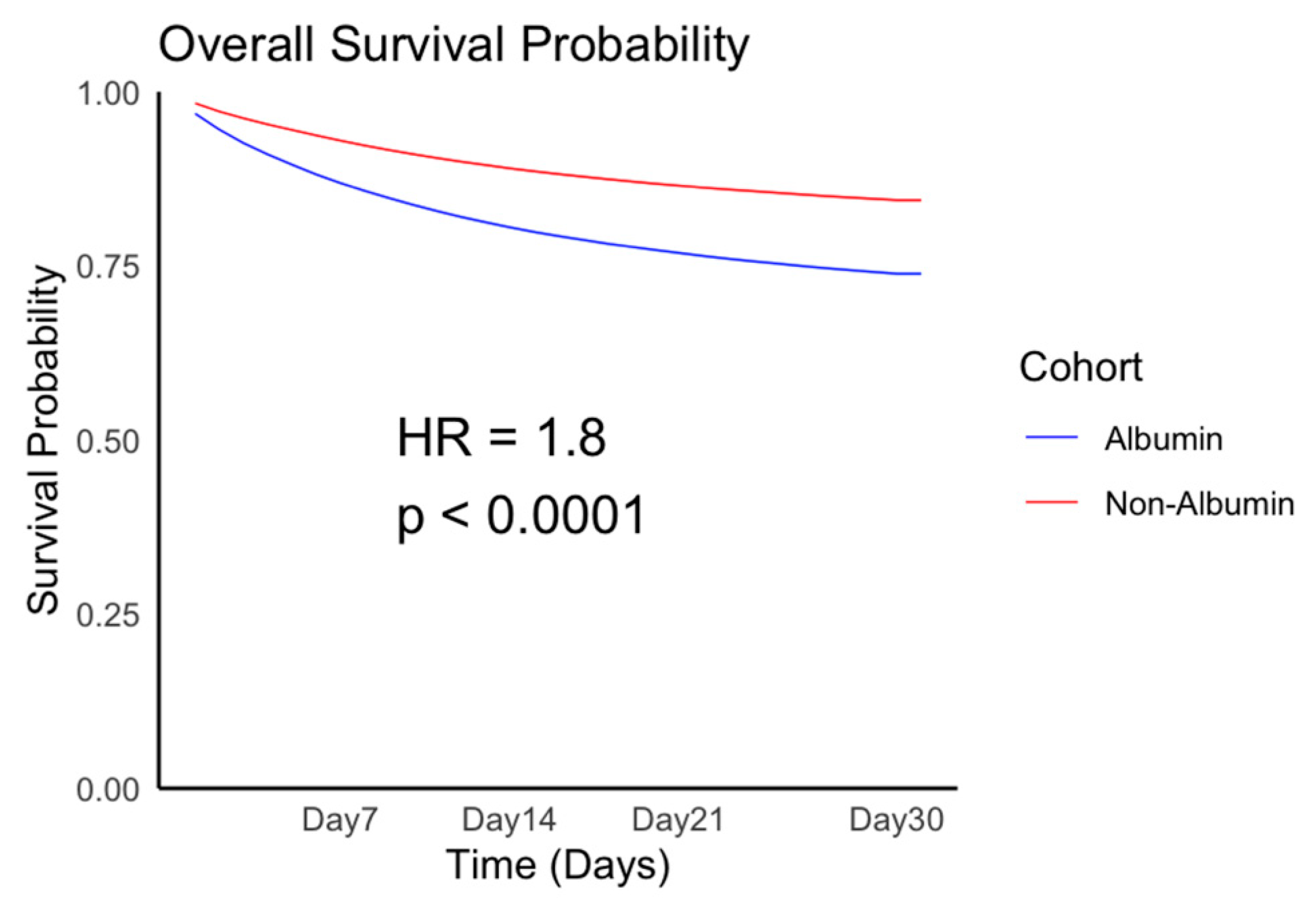
3.1. Patient Population and Outcomes
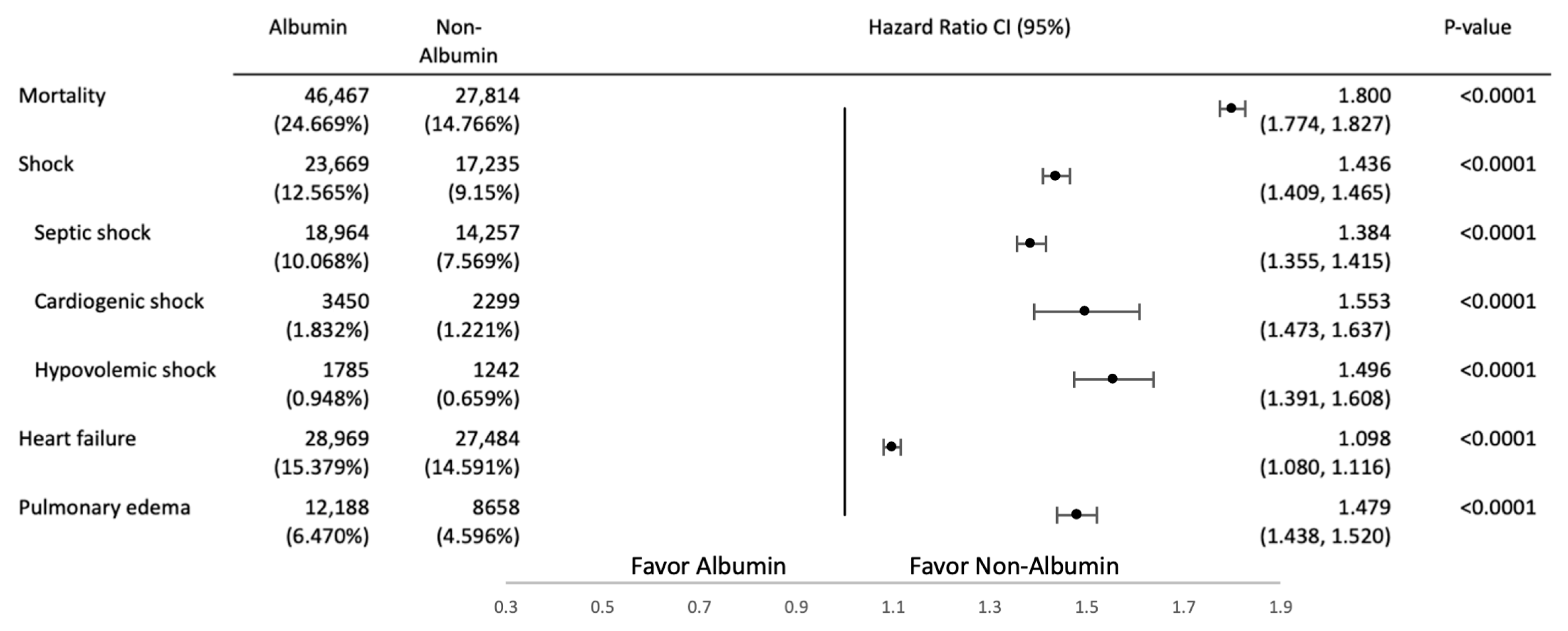
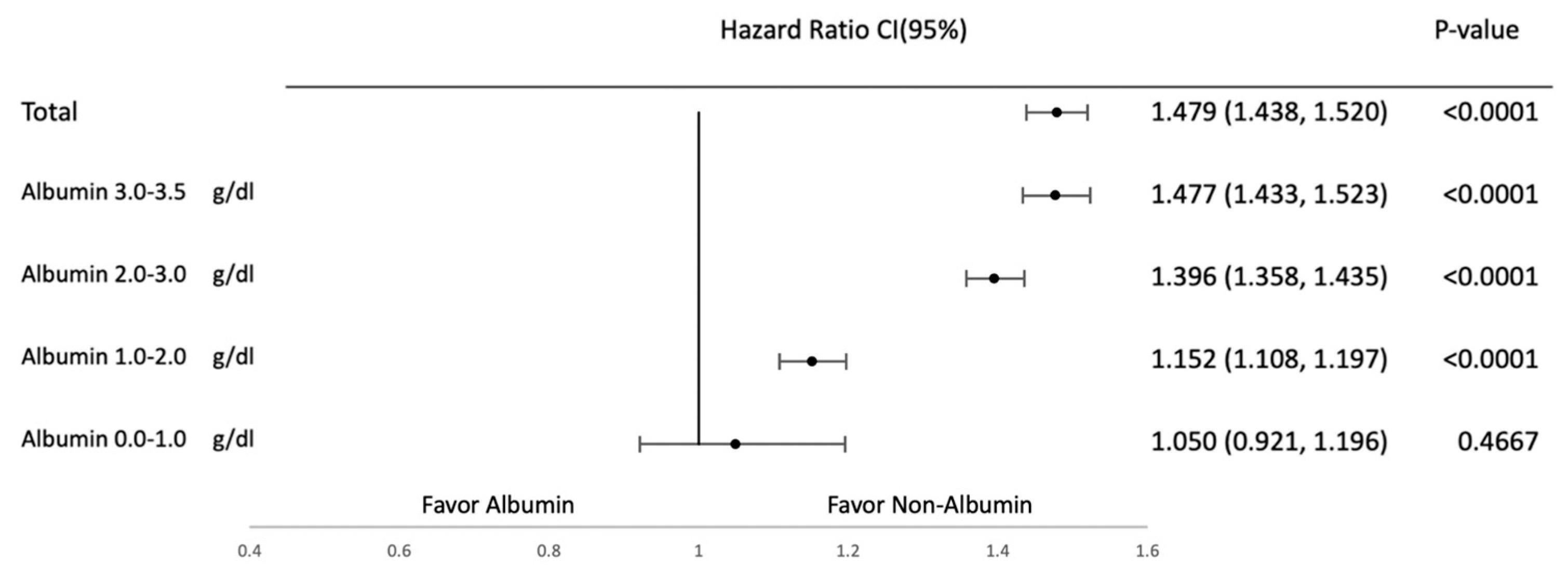
Secondary Outcome
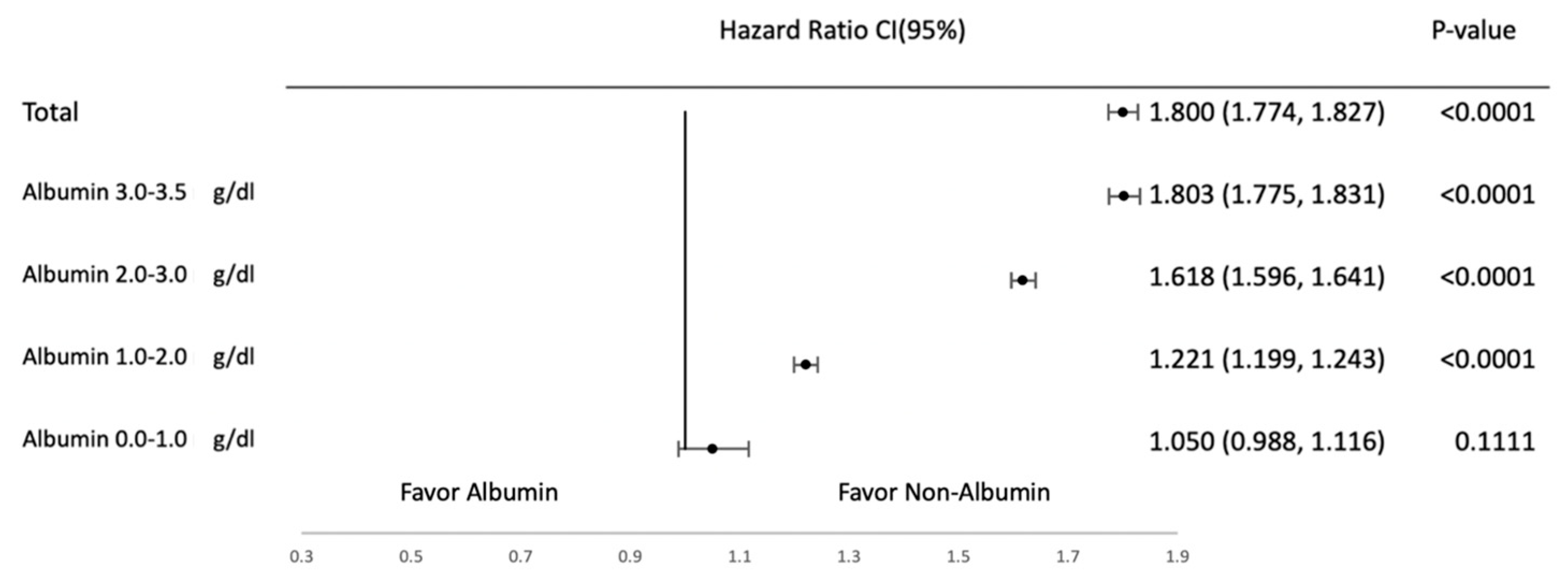
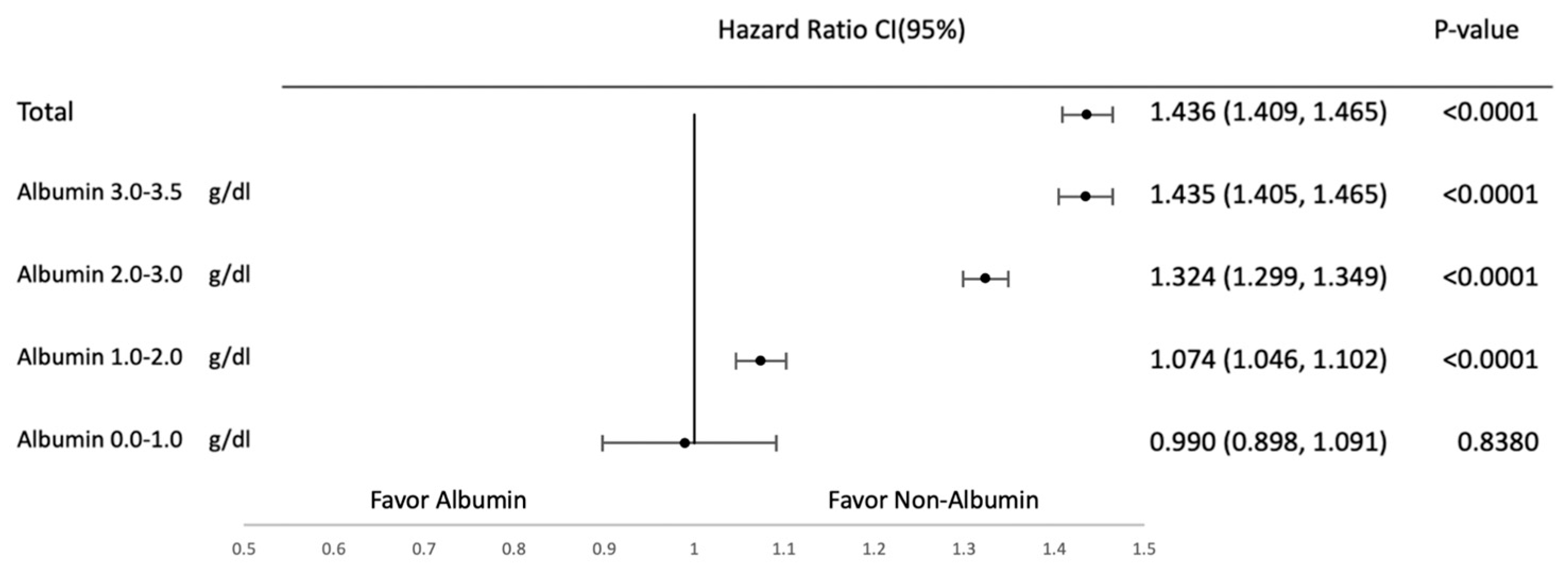
3.2. Subgroup Analysis
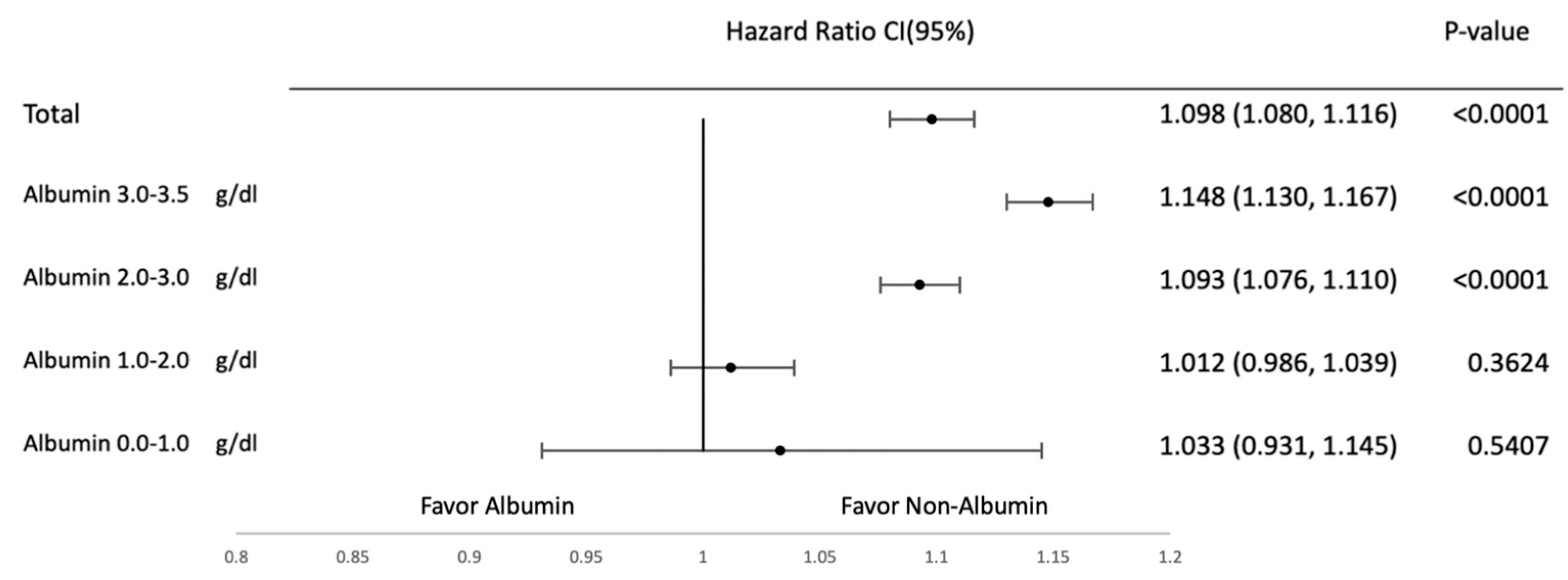
3.3. Sensitivity Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Limitation and Strength
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brock, F.; Bettinelli, L.A.; Dobner, T.; Stobbe, J.C.; Pomatti, G.; Telles, C.T. Prevalence of hypoalbuminemia and nutritional issues in hospitalized elders. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 2016, 24, e2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moramarco, S.; Morciano, L.; Morucci, L.; Messinese, M.; Gualtieri, P.; Carestia, M.; Ciccacci, F.; Orlando, S.; Buonomo, E.; Legramante, J.M.; et al. Epidemiology of Hypoalbuminemia in Hospitalized Patients: A Clinical Matter or an Emerging Public Health Problem? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounden, V.; Vashisht, R.; Jialal, I. Hypoalbuminemia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Melia, D.; Post, B. Human albumin solutions in intensive care: A review. J. Intensive Care Soc. 2021, 22, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Mendez-Sanchez, N.; Romeiro, F.G.; Mancuso, A.; Philips, C.A.; Tacke, F.; Basaranoglu, M.; Primignani, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Wong, Y.J.; et al. Use of albumin infusion for cirrhosis-related complications: An international position statement. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L. Relevance of albumin in modern critical care medicine. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2009, 23, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer-Mikalsen, K.; Vik, A.; Gisvold, S.E.; Skandsen, T.; Hynne, H.; Klepstad, P. Severe head injury: Control of physiological variables, organ failure and complications in the intensive care unit. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2007, 51, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-F.; Ma, H.; Perng, C.-K.; Liao, W.-C.; Shih, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, M.-C.; Hsiao, F.-Y.; Wang, T.-H. Albumin supplementation may have limited effects on prolonged hypoalbuminemia in major burn patients: An outcome and prognostic factor analysis. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2020, 83, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.J.; Myburgh, J.; Heritier, S.; Finfer, S.; Bellomo, R.; Billot, L.; Murray, L.; Vallance, S. Albumin resuscitation for traumatic brain injury: Is intracranial hypertension the cause of increased mortality? J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeters, P.B.; Wolfe, R.R.; Shenkin, A. Hypoalbuminemia: Pathogenesis and Clinical Significance. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2019, 43, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.K.; Sun, F.; Wang, X.; Yuan, S.T.; Zheng, S.Y.; Mu, X.W. Risk factors and prognosis of hypoalbuminemia in surgical septic patients. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caironi, P.; Tognoni, G.; Masson, S.; Fumagalli, R.; Pesenti, A.; Romero, M.; Fanizza, C.; Caspani, L.; Faenza, S.; Grasselli, G.; et al. Albumin replacement in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.; Tian, X.; Gao, Z.; Mao, A.; Feng, L.; He, C. Different Concentrations of Albumin Versus Crystalloid in Patients with Sepsis and Septic Shock: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 38, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; McIntyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e1063–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchuk, M.B.; London, J.W.; Perez-Rey, D.; Drebert, Z.J.; Winer-Jones, J.P.; Thompson, C.N.; Esposito, J.; Claerhout, B. A global federated real-world data and analytics platform for research. JAMIA Open 2023, 6, ooad035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-T.; Liu, J.; Hu, B.; Wang, R.-L.; Yang, X.-H.; Shang, X.-L.; Wang, G.; Wang, C.-S.; Li, B.-L.; Gong, Y.; et al. Expert consensus on the use of human serum albumin in critically ill patients. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 1639–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ling, Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; Wu, B. Impact of albumin infusion on prognosis of intensive care unit patients with congestive heart failure-hypoalbuminemia overlap: A retrospective cohort study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 2235–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, A.; Verardo, A.; Bolognesi, M. Hypoalbuminemia. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2012, 7 (Suppl. S3), S193–S199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; Dubois, M.J.; Navickis, R.J.; Wilkes, M.M. Hypoalbuminemia in acute illness: Is there a rationale for intervention? A meta-analysis of cohort studies and controlled trials. Ann. Surg. 2003, 237, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.J.; Orellana-Jimenez, C.; Melot, C.; De Backer, D.; Berre, J.; Leeman, M.; Brimioulle, S.; Appoloni, O.; Creteur, J.; Vincent, J.L. Albumin administration improves organ function in critically ill hypoalbuminemic patients: A prospective, randomized, controlled, pilot study. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 2536–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callum, J.; Skubas, N.J.; Bathla, A.; Keshavarz, H.; Clark, E.G.; Rochwerg, B.; Fergusson, D.; Arbous, S.; Bauer, S.R.; China, L.; et al. Use of Intravenous Albumin: A Guideline From the International Collaboration for Transfusion Medicine Guidelines. Chest 2024, 166, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saner, F.H.; Stueben, B.O.; Hoyer, D.P.; Broering, D.C.; Bezinover, D. Use or Misuse of Albumin in Critical Ill Patients. Diseases 2023, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wan, J.; He, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Xia, L.; Liu, F.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Albumin infusion may decrease the mortality of hypoalbuminemia patients with severe acute pancreatitis: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, P.; Fan, X.; Xu, Z. Albumin Infusion May Improve the Prognosis of Critical COVID-19 Patients with Hypoalbuminemia in the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 6039–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraceni, P.; Riggio, O.; Angeli, P.; Alessandria, C.; Neri, S.; Foschi, F.G.; Levantesi, F.; Airoldi, A.; Boccia, S.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; et al. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): An open-label randomised trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 2417–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, I.; Blackhall, K.; Alderson, P.; Bunn, F.; Schierhout, G. Human albumin solution for resuscitation and volume expansion in critically ill patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 2011, CD001208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offringa, M. Excess mortality after human albumin administration in critically ill patients. Clinical and pathophysiological evidence suggests albumin is harmful. BMJ 1998, 317, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Finfer, S.; Bellomo, R.; Boyce, N.; French, J.; Myburgh, J.; Norton, R.; Investigators, S.S. A comparison of albumin and saline for fluid resuscitation in the intensive care unit. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SAFE Study Investigators; Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society Clinical Trials Group; Australian Red Cross Blood Service; George Institute for International Health; Myburgh, J.; Cooper, D.J.; Finfer, S.; Bellomo, R.; Norton, R.; Bishop, N.; et al. Saline or albumin for fluid resuscitation in patients with traumatic brain injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulimood, T.B.; Park, G.R. Debate: Albumin administration should be avoided in the critically ill. Crit. Care 2000, 4, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvasto, A.; Ilmakunnas, M.; Raivio, P.; Vlasov, H.; Hiippala, S.; Suojaranta, R.; Wilkman, E.; Petäjä, L.; Helve, O.; Juvonen, T.; et al. Albumin Infusion and Blood Loss After Cardiac Surgery. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2023, 116, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, D.C.; van der Poll, T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.S.; Moss, M.; Wheeler, A.P.; Mealer, M.; Morris, J.A.; Bernard, G.R. A randomized, controlled trial of furosemide with or without albumin in hypoproteinemic patients with acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belayev, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Busto, R.; Ginsberg, M.D. Human albumin therapy of acute ischemic stroke: Marked neuroprotective efficacy at moderate doses and with a broad therapeutic window. Stroke 2001, 32, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Investigators, S.S.; Finfer, S.; McEvoy, S.; Bellomo, R.; McArthur, C.; Myburgh, J.; Norton, R. Impact of albumin compared to saline on organ function and mortality of patients with severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 37, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Bao, J.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, L.; Yu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. The prognostic value of serum albumin levels and respiratory rate for community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective, multi-center study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynor, B.; Huang, A.; Udrea, D.; Montano, N. The Role of Albumin in the Resuscitation of Hypotensive Patients. Curr. Emerg. Hosp. Med. Rep. 2023, 11, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Before Matching | After Matching | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Characteristics | Albumin Group (n = 188,365) | Non-Albumin Group (n = 959,068) | Std Diff | Albumin Group (n = 188,365) | Non-Albumin Group (n = 188,365) | Std Diff |
| Age at index | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 67.8 ± 15.7 | 68.6 ± 17.2 | 0.049 | 67.8 ± 15.7 | 67.6 ± 16.7 | 0.015 |
| Gender | ||||||
| Female | 81,722 (43.4%) | 445,488 (46.5%) | 0.062 | 81,722 (43.4%) | 80,666 (42.8%) | 0.011 |
| Male | 99,107 (52.6%) | 484,002 (50.5%) | 0.043 | 99,107 (52.6%) | 99,750 (53.0%) | 0.007 |
| Race | ||||||
| White | 113,392 (60.2%) | 581,668 (60.6%) | 0.009 | 113,392 (60.2%) | 113,736 (60.4%) | 0.004 |
| Black or African American | 30,850 (16.3%) | 157,990 (16.5%) | 0.003 | 30,850 (16.3%) | 29,322 (15.6%) | 0.022 |
| Asian | 15,313 (8.1%) | 55,469 (5.8%) | 0.092 | 15,313 (8.1%) | 16,647 (8.8%) | 0.025 |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 602 (0.3%) | 2749 (0.3%) | 0.006 | 602 (0.3%) | 639 (0.3%) | 0.003 |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 2052 (1.1%) | 8668 (0.9%) | 0.019 | 2052 (1.1%) | 1980 (1.1%) | 0.004 |
| Other races | 7685 (4.1%) | 36,185 (3.8%) | 0.016 | 7685 (4.1%) | 7653 (4.1%) | <0.001 |
| Unknown Ethnicity | 30,758 (16.3%) | 203,373 (21.2%) | 0.125 | 30,758 (16.3%) | 29,730 (15.8%) | 0.015 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases | 170,936 (90.7%) | 734,633 (76.6%) | 0.390 | 170,936 (90.7%) | 167,920 (89.1%) | 0.053 |
| Disease of the digestive system | 157,787 (83.8%) | 620,842 (64.7%) | 0.446 | 157,787 (83.8%) | 158,442 (84.1%) | 0.009 |
| Disease of the circulatory system | 168,750 (89.6%) | 725,709 (75.7%) | 0.374 | 168,750 (89.6%) | 166,680 (88.5%) | 0.035 |
| Disease of the genitourinary system | 156,778 (83.2%) | 629,362 (65.6%) | 0.412 | 156,778 (83.2%) | 155,279 (82.4%) | 0.021 |
| Disease of the respiratory system | 151,860 (80.6%) | 586,127 (61.1%) | 0.440 | 151,860 (80.6%) | 150,787 (80.1%) | 0.014 |
| Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | 130,595 (69.3%) | 593,420 (61.9%) | 0.157 | 130,595 (69.3%) | 128,866 (68.4%) | 0.020 |
| Certain infectious and parasitic disease | 169,408 (89.9%) | 562,844 (58.7%) | 0.766 | 169,408 (89.9%) | 167,730 (89.0%) | 0.029 |
| Disease of the nervous system | 135,290 (71.8%) | 541,817 (56.5%) | 0.324 | 135,290 (71.8%) | 134,285 (71.3%) | 0.012 |
| Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders | 115,170 (61.1%) | 492,546 (51.4%) | 0.200 | 115,170 (61.1%) | 114,291 (60.7%) | 0.010 |
| Neoplasms | 85,052 (45.2%) | 355,606 (37.1%) | 0.165 | 85,052 (45.2%) | 85,085 (45.2%) | <0.001 |
| External causes of morbidity | 78,730 (41.8%) | 305,7635 (31.9%) | 0.206 | 78,730 (41.8%) | 78,703 (41.8%) | <0.001 |
| Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities | 22,924 (12.2%) | 83,702 (8.7%) | 0.113 | 22,924 (12.2%) | 22,849 (12.1%) | 0.001 |
| Medication | ||||||
| Central nervous system medications | 178,513 (94.8%) | 797,469 (83.2%) | 0.377 | 178,513 (94.8%) | 175,837 (93.3%) | 0.060 |
| Respiratory tract medications | 177,141 (94.0%) | 757,689 (79.0%) | 0.452 | 177,141 (94.0%) | 174,945 (92.87%) | 0.047 |
| Gastrointestinal medications | 176,099 (93.5%) | 753,901 (78.6%) | 0.440 | 176,099 (93.5%) | 174,072 (92.4%) | 0.042 |
| Antimicrobials | 173,956 (92.4%) | 739,684 (77.1%) | 0.433 | 173,956 (92.4%) | 171,382 (91.0%) | 0.050 |
| Cardiovascular medications | 172,644 (91.7%) | 743,815 (77.6%) | 0.398 | 172,644 (91.7%) | 171,190 (90.9%) | 0.027 |
| Hormones/synthetics/modifiers | 170,538 (90.5%) | 717,420 (74.8%) | 0.425 | 170,538 (90.5%) | 168,895 (89.7%) | 0.029 |
| Genitourinary medications | 157,804 (83.8%) | 626,166 (65.3%) | 0.434 | 157,804 (83.8%) | 157,741 (83.7%) | <0.001 |
| Musculoskeletal medications | 134,090 (71.2%) | 549,287 (57.3%) | 0.293 | 134,090 (71.2%) | 134,825 (71.6%) | 0.009 |
| Antiparasitics | 10,564 (5.6%) | 38,241 (4.0%) | 0.076 | 10,564 (5.6%) | 10,377 (5.6%) | 0.002 |
| Antineoplastics | 33,939 (18.0%) | 135,261 (14.1%) | 0.107 | 33,939 (18.0%) | 33,991 (18.0%) | <0.001 |
| Laboratory | ||||||
| Sodium [Moles/volume] in Serum, Plasma or Blood | 137 ± 5.82 | 137 ± 4.77 | 0.161 | 137 ± 5.82 | 137 ± 4.91 | 0.116 |
| Potassium [Moles/volume] in Serum, Plasma or Blood | 4.04 ± 0.677 | 4.06 ± 0.592 | 0.036 | 4.04 ± 0.677 | 4.06 ± 0.605 | 0.033 |
| Creatinine [Mass/volume] in Serum, Plasma or Blood | 1.94 ± 2.64 | 1.48 ± 3.86 | 0.151 | 1.94 ± 2.64 | 1.58 ± 3.23 | 0.120 |
| Hematocrit [Volume Fraction] of Blood | 30.9 ± 7.46 | 33.9 ± 8.73 | 0.372 | 30.9 ± 7.46 | 34 ± 7.64 | 0.415 |
| Neutrophils [#/volume] in Blood | 347 ± 2242 | 142 ± 1273 | 0.113 | 347 ± 2242 | 276 ± 1871 | 0.034 |
| Lymphocytes/100 leukocytes in Blood | 13.2 ± 11.8 | 16.7 ± 12.5 | 0.286 | 13.2 ± 11.8 | 16 ± 12.5 | 0.227 |
| Monocytes/100 leukocytes in Blood | 7.21 ± 4.57 | 7.88 ± 4.22 | 0.153 | 7.21 ± 4.57 | 7.79 ± 4.34 | 0.130 |
| Eosinophils/100 leukocytes in Blood | 1.57 ± 2.63 | 1.84 ± 2.6 | 0.101 | 1.57 ± 2.63 | 1.8 ± 2.67 | 0.083 |
| Basophils/100 leukocytes in Blood | 0.38 ± 0.546 | 0.445 ± 0.567 | 0.116 | 0.38 ± 0.546 | 0.432 ± 0.53 | 0.097 |
| Clinical Outcomes | After Matching | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |||
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Overall Survival | 2.162 (2.134, 2.192) | <0.0001 | 1.800 (1.774, 1.827) | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Liu, J.-F.; Hsu, P.-S.; Cheng, W.-P.; Lin, S.-S. The Efficacy of Albumin Infusion in Septic Patients with Hypoalbuminemia: An International Retrospective Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134790
Liu H-Y, Chen Y-C, Liu J-F, Hsu P-S, Cheng W-P, Lin S-S. The Efficacy of Albumin Infusion in Septic Patients with Hypoalbuminemia: An International Retrospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134790
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hsin-Yu, Yu-Ching Chen, Ju-Fang Liu, Pei-Sung Hsu, Wen-Pin Cheng, and Shih-Sen Lin. 2025. "The Efficacy of Albumin Infusion in Septic Patients with Hypoalbuminemia: An International Retrospective Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134790
APA StyleLiu, H.-Y., Chen, Y.-C., Liu, J.-F., Hsu, P.-S., Cheng, W.-P., & Lin, S.-S. (2025). The Efficacy of Albumin Infusion in Septic Patients with Hypoalbuminemia: An International Retrospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134790










