Role of Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling and 4D MR Angiography in the Diagnosis of Neck Paragangliomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Known or suspected head-and-neck paraganglioma (HNPGL):
- ○
- Individuals with a family history, with or without prior surgery or radiotherapy;
- ○
- Subjects undergoing screening because of familial HNPGLs;
- ○
- Patients with neck masses but no known familial predisposition;
- ○
- MRI performed on a 1.5 T scanner (Signa Voyager, GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) that included
- ○
- Conventional, fat-suppressed, T2-weighted fast spin-echo (FS-T2) and post-contrast, fat-suppressed, T1-weighted (CE-FS-T1) sequences;
- ○
- Advanced sequences: pseudo-continuous arterial-spin-labelling (pcASL) and four-dimensional, contrast-enhanced MR angiography (4D-CE-MRA and TRICKS).
- Incomplete MRI protocol.
- Severe motion artefacts precluding image interpretation.
- Patients with base of the skull lesions (including PGLs).
2.1. Advanced Sequence Parameters
- 3D pcASL (acquired before contrast):
- ○
- Labelling duration 1800 ms; post-labelling delay 2025 ms;
- ○
- 3D stack-of-spirals, fast spin-echo read-out (eight spirals × 512 points);
- ○
- FOV 24–26 cm; slice thickness 4 mm; in-plane resolution 3.6–4.5 mm2;
- ○
- TE/TR 10.9/4840 ms; bandwidth 62.5 kHz; acquisition time 4–5 min;
- ○
- A rapid phase-contrast angiogram of the neck vessels was obtained to position the labelling plane;
- 4D-CE-MRA (TRICKS):
- ○
- One mask phase followed by 20 dynamic phases during injection of a gadolinium agent (4 mL s−1) and a 15-mL saline flush;
- ○
- TR/TE 3.3/1.3 ms; flip angle 20°; FOV 24 cm; matrix 220 × 212;
- ○
- Slice thickness 1.6 mm (36-partition slab, sagittal orientation);
- ○
- Temporal resolution 1.8 s per phase, total 37.8 s;
- ○
- Automatic subtraction of the mask to suppress the background signal.
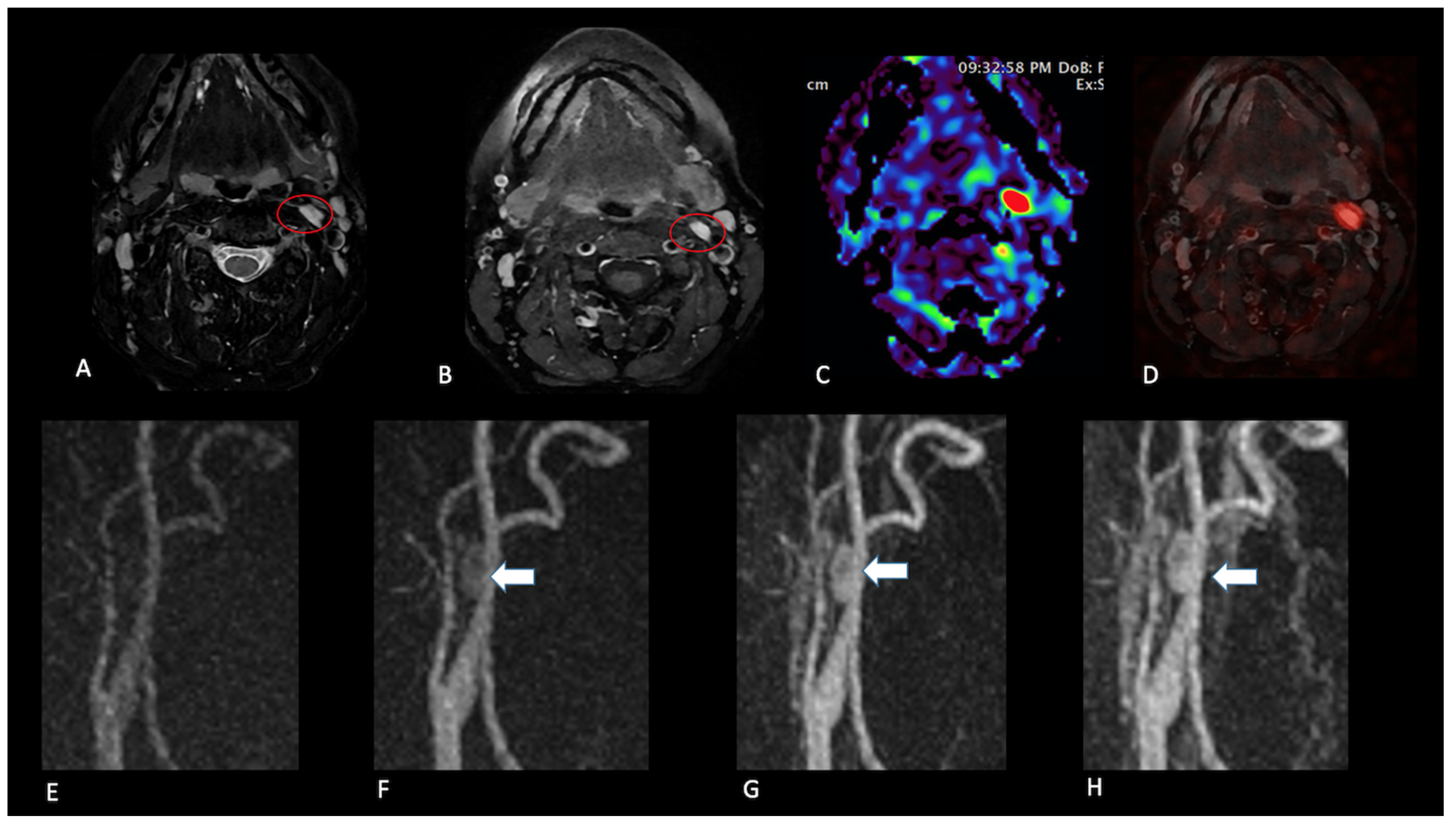
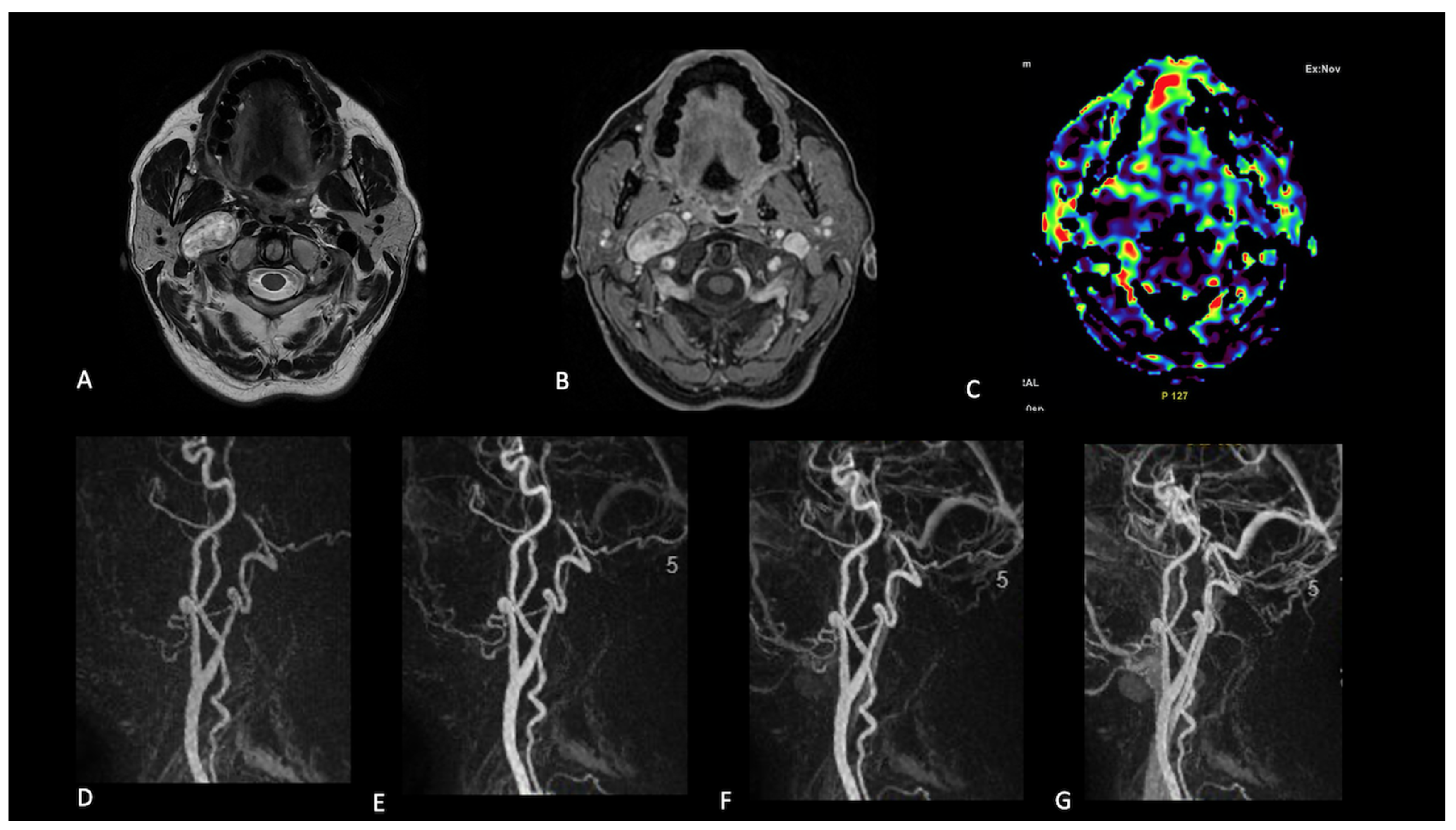
2.2. Image Interpretation
- Presence (present | indeterminate | absent) and site of a lesion.
- Sequence(s) providing greatest diagnostic confidence in detecting/localising NPGLs:
- ○
- Single sequences—FS-T2, CE-FS-T1, pcASL, and TRICKS;
- ○
- Combined sequences—FS-T2 + CE-FS-T1, and pcASL + TRICKS.
2.3. Volumetry and Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. pcASL: Evidence and Practical Considerations
4.2. TRICKS and the pcASL + TRICKS Combination
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, E.P.; Chin, B.B.; Fishbein, L.; Moritani, T.; Ellika, S.; Newlands, S. Head and Neck Paragangliomas: An Update on the Molecular Classification, State-of-the-Art Imaging, and Management Recommendations. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2022, 4, e210088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.B.; Koeller, K.K.; Adair, C.F. From the archives of the AFIP. Paragangliomas of the head and neck: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. Radiographics 1999, 19, 1605–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Barich, F.; Karnell, L.H.; Robinson, R.A.; Zhen, W.K.; Gantz, B.J.; Hoffman, H.T. National Cancer Data Base report on malignant paragangliomas of the head and neck. Cancer 2002, 94, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fliedner, S.M.; Lehnert, H.; Pacak, K. Metastatic paraganglioma. Semin. Oncol. 2010, 37, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, R. Imaging and management of head and neck paragangliomas. Eur. Radiol. 2005, 15, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolen, S.; Gemmete, J.J. Paragangliomas of the Head and Neck. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2016, 26, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, R.; Verbist, B.M.; Mertens, B.J.; van der Mey, A.G.; van Buchem, M.A. Head and neck paragangliomas: Improved tumor detection using contrast-enhanced 3D time-of-flight MR angiography as compared with fat-suppressed MR imaging techniques. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 863–870. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, F.; Huwart, L.; Jourdan, G.; Reizine, D.; Herman, P.; Vicaut, E.; Guichard, J.P. Head and neck paragangliomas: Value of contrast-enhanced 3D MR angiography. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.M.; Strecker, R.; Scheffler, K.; Spreer, J.; Schipper, J.; Neumann, H.P.H.; Klisch, J. Dynamic contrast enhancement of paragangliomas of the head and neck: Evaluation with time-resolved 2D MR projection angiography. Eur. Radiol. 2003, 13, 1608–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxerman, J.L.; Shiroishi, M.S.; Ellingson, B.M.; Pope, W.B. Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast MR Imaging in Glioma: Review of Current Clinical Practice. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2016, 24, 649–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Tavanti, F.; Espagnet, M.C.R.; Terenzi, V.; Cassoni, A.; Suma, G.; Boellis, A.; Pierallini, A.; Valentini, V.; Bozzao, A. The role of time-resolved imaging of contrast kinetics (TRICKS) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) in the evaluation of head-neck vascular anomalies: A preliminary experience. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2015, 44, 20140302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geerts, B.; Leclercq, D.; du Montcel, S.T.; Law-Ye, B.; Gerber, S.; Bernardeschi, D.; Galanaud, D.; Dormont, D.; Pyatigorskaya, N. Characterization of Skull Base Lesions Using Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2019, 29, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Et-Tahir, Y.; Merzem, A.; Belgadir, H.; Amriss, O.; Moussali, N.; El Benna, N. Salt and pepper appearance: A characteristic feature of paragangliomas. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2023, 114, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraky, A.M.; Beck, R.T.; Treffy, R.W.; Aaronson, D.M.; Hedayat, H. Role of Advanced MR Imaging in Diagnosis of Neurological Malignancies: Current Status and Future Perspective. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddikeri, S.; Hippe, D.S.; Anzai, Y. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in the Evaluation of Carotid Space Paraganglioma versus Schwannoma. J. Neuroimaging 2016, 26, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, Y.; Liao, E.; Capizzano, A.A.; Baba, A.; Kurokawa, R.; Kurokawa, M.; Srinivasan, A. Intracranial paragangliomas versus schwannomas: Role of dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion and diffusion MRI. J. Neuroimaging 2022, 32, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, S.R.; Bhalla, A.S.; Manchanda, S.; Kandasamy, D.; Kumar, R.; Agarwal, S.; Shamim, S.A.; Kakkar, A. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating head and neck paraganglioma and schwannoma. Head Neck 2021, 43, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, Y.; Liao, E.; Capizzano, A.A.; Kurokawa, R.; Bapuraj, J.R.; Syed, F.; Baba, A.; Moritani, T.; Srinivasan, A. Diagnostic Role of Diffusion-Weighted and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Perfusion MR Imaging in Paragangliomas and Schwannomas in the Head and Neck. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaely, H.J.; Herrmann, K.A.; Dietrich, O.; Reiser, M.F.; Schoenberg, S.O. Quantitative and qualitative characterization of vascularization and hemodynamics in head and neck tumors with a 3D magnetic resonance time-resolved echo-shared angiographic technique (TREAT)--initial results. Eur. Radiol. 2007, 17, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, J.C.; Brunet, J.F.; Carsin-Nicol, B.; Larralde, A.; Godey, B.; Gauvrit, J.Y. Optimized time-resolved 3D contrast-enhanced MRA at 3T: Appreciating the feasibility of assessing cervical paragangliomas. J. Neuroradiol. 2010, 37, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razek, A.A.; Gaballa, G.; Megahed, A.S.; Elmogy, E. Time resolved imaging of contrast kinetics (TRICKS) MR angiography of arteriovenous malformations of head and neck. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Chandler, A.; Borzykowski, R.; Thornhill, B.; Taragin, B.H. Maximizing time-resolved MRA for differentiation of hemangiomas, vascular malformations and vascularized tumors. Pediatr. Radiol. 2012, 42, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
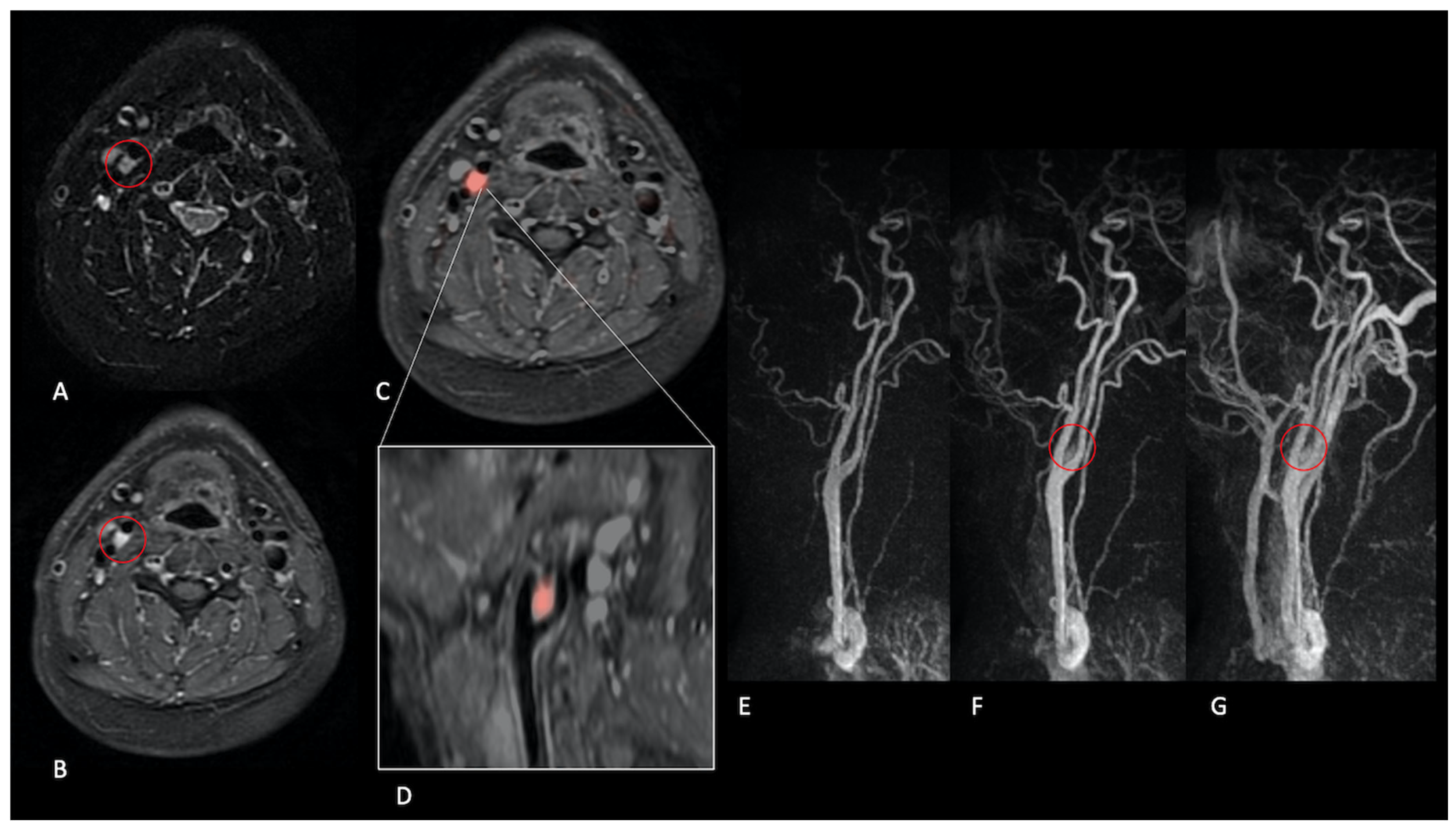
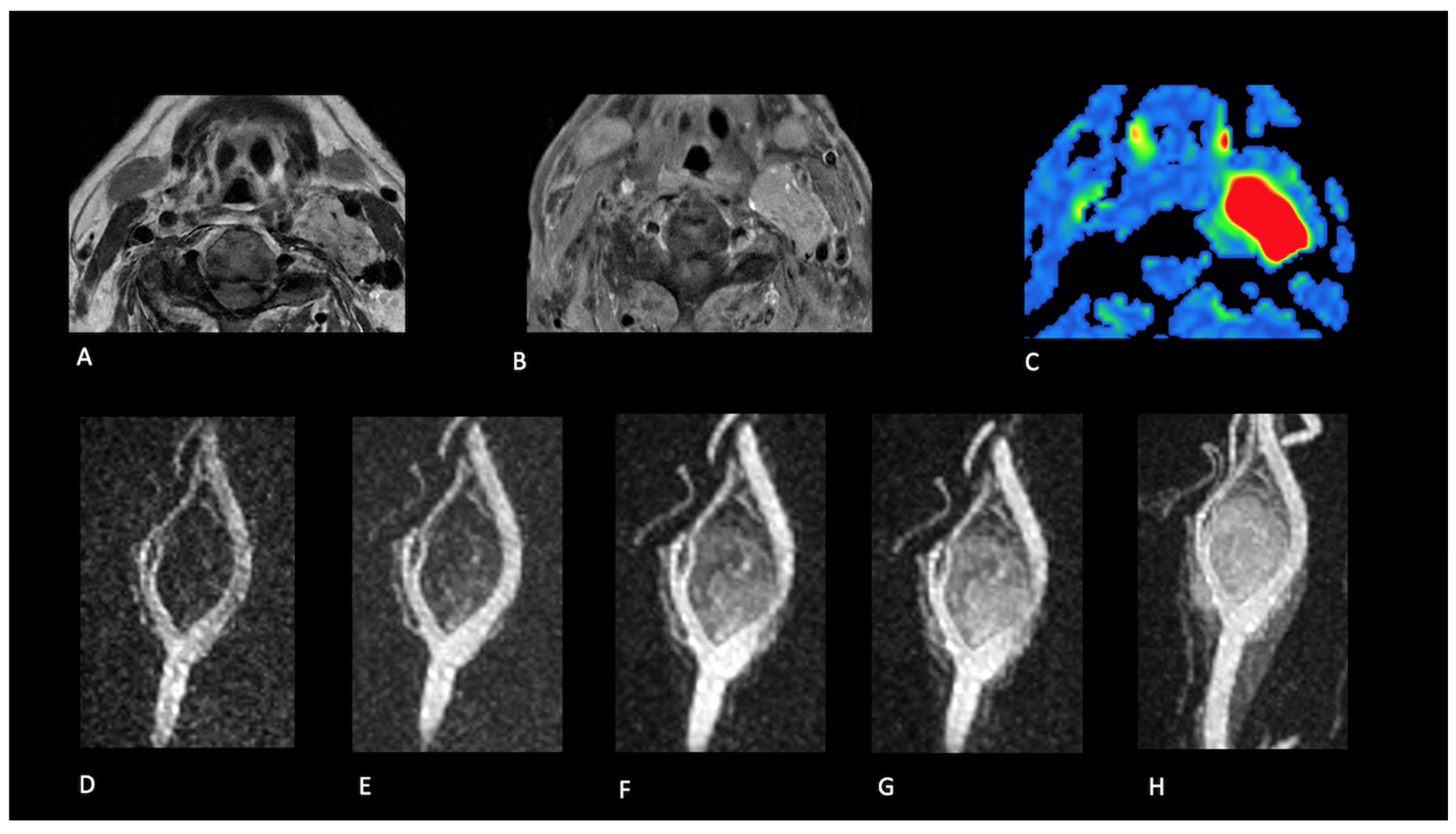
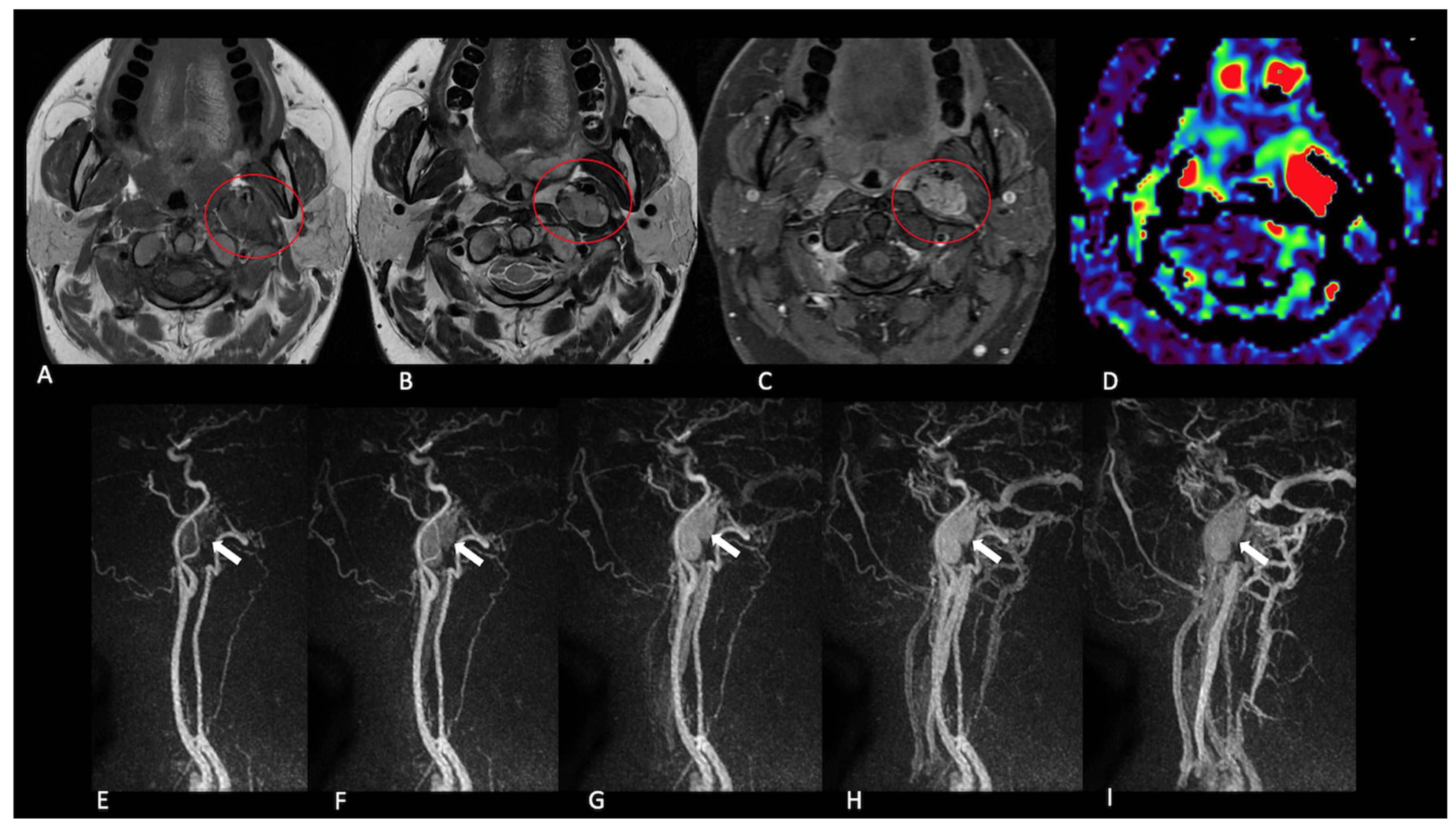
| Patient No. | Age (Years) | Sex | Lesion Type | Location | Volume (cm3) | Treatment | Surgery | Recurrence | Radiotherapy | Familial Predisposition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 4.112 | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| 2 | 53 | M | PARAGANGLIOMA | CAROTID | 0.659 | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| 3 | 38 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 4.221 | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO |
| 4 | 58 | M | PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 3.558 | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| 5 | 53 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | CAROTID | 0.456 | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO |
| 6 | 45 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 5.656 | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO |
| 7 | 48 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 3.995 | NO | NO | NO | NO | YES |
| 8 | 62 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 1.287 | NO | NO | NO | NO | YES |
| 9 | 79 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 2.457 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES |
| 10 | 50 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | CAROTID | 0.943 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES |
| 11 | 59 | M | PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 4.956 | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 4.821 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES | |||
| 12 | 74 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | CAROTID | 0.599 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES |
| 13 | 66 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 6.955 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES |
| 14 | 54 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | CAROTID | 0.541 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES |
| 15 | 79 | M | PARAGANGLIOMA | CAROTID | 1.788 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES |
| 16 | 83 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 4.218 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES |
| 17 | 54 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | VAGAL | 2.659 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES |
| PARAGANGLIOMA | CAROTID | 0.398 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES | |||
| 18 | 65 | M | PARAGANGLIOMA | CAROTID | 4.266 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES |
| 19 | 59 | F | PARAGANGLIOMA | CAROTID | 1.522 | NO | NO | - | NO | YES |
| 20 | 35 | M | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | YES |
| 21 | 29 | M | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | YES |
| 22 | 44 | M | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | YES |
| 23 | 48 | F | SCHWANNOMA | NECK | 6.544 | YES | YES | - | NO | - |
| 24 | 55 | F | SCHWANNOMA | NECK | 4.877 | YES | YES | - | NO | - |
| 25 | 68 | F | SCHWANNOMA | NECK | 6.764 | YES | YES | - | NO | - |
| 26 | 62 | M | SCHWANNOMA | NECK | 4.832 | YES | YES | - | NO | - |
| 27 | 71 | F | SCHWANNOMA | NECK | 4.521 | YES | YES | - | NO | - |
| 28 | 59 | M | SCHWANNOMA | NECK | 5.961 | YES | YES | - | NO | - |
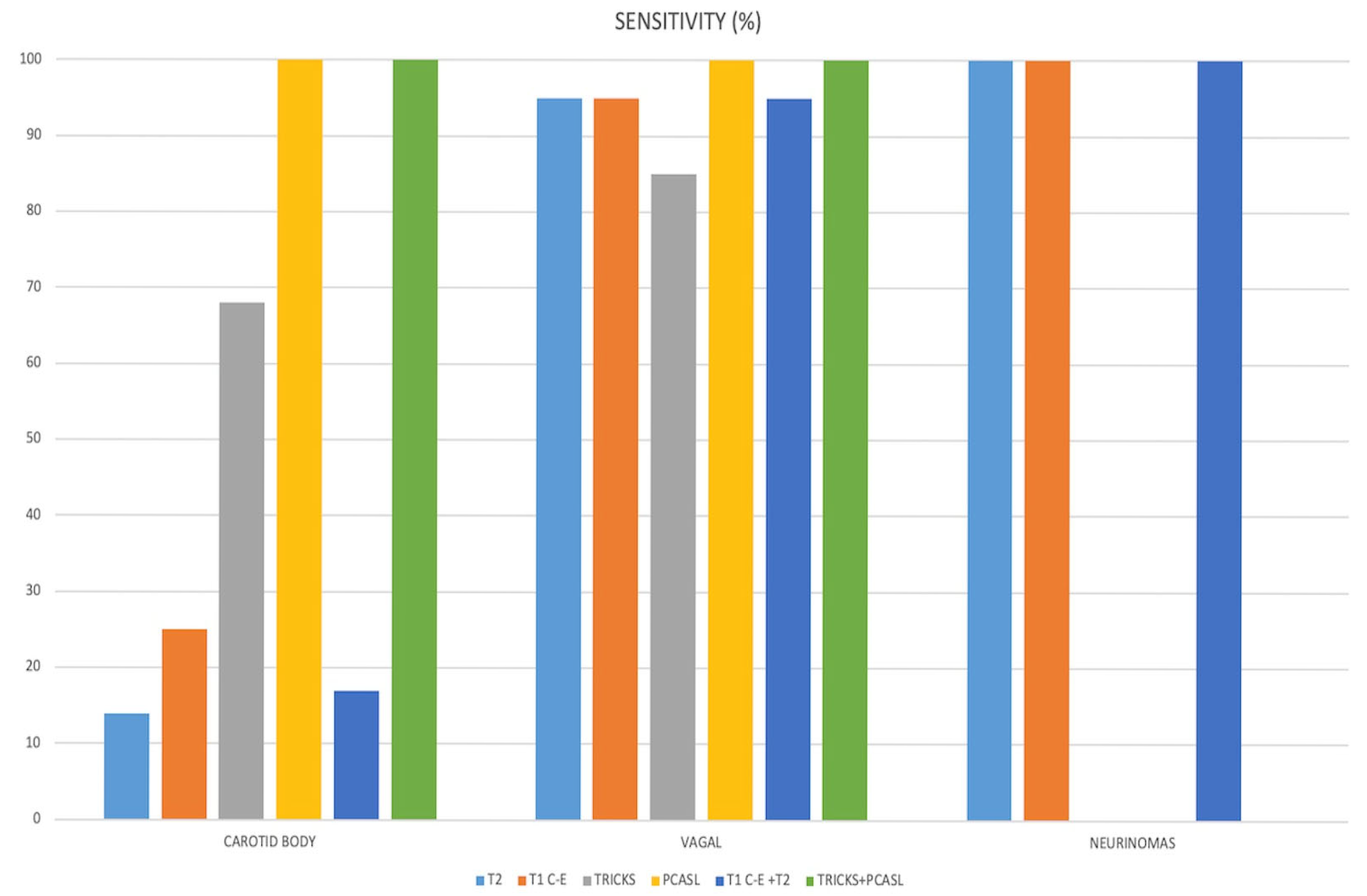
| Fleiss k | Sensitivity | Specificity | NPV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2 | 0.611 | 0.6 (0.14–0.95) | 0.3 (0.12–0.62) | 0.85 |
| C-E | 0.766 | 0.71 (0.25–0.95) | 0.28 (0.14–0.69) | 0.87 |
| TRICKS | 0.587 | 0.82 (0.68–0.94) | 1 (1.00–1.00) | 0.93 |
| PCASL | 1 | 1 (1.00–1.00) | 1 (0.00–1.00) | 1 |
| T2+C-E | 0.572 | 0.6 (0.17–0.95) | 0.32 (0.14–0.71) | 0.86 |
| TRICKS+PCASL | 1 | 1 (1.00–1.00) | 1 (1.00–1.00) | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romano, A.; Romano, A.; Moltoni, G.; Palizzi, S.; Muscoli, A.; D’Eufemia, S.; Parri, E.; Faggiano, A.; Ciddio, A.B.; Guarnera, A.; et al. Role of Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling and 4D MR Angiography in the Diagnosis of Neck Paragangliomas. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134725
Romano A, Romano A, Moltoni G, Palizzi S, Muscoli A, D’Eufemia S, Parri E, Faggiano A, Ciddio AB, Guarnera A, et al. Role of Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling and 4D MR Angiography in the Diagnosis of Neck Paragangliomas. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134725
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomano, Andrea, Allegra Romano, Giulia Moltoni, Serena Palizzi, Andrea Muscoli, Silvia D’Eufemia, Emanuela Parri, Antongiulio Faggiano, Alessia Bernardo Ciddio, Alessia Guarnera, and et al. 2025. "Role of Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling and 4D MR Angiography in the Diagnosis of Neck Paragangliomas" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134725
APA StyleRomano, A., Romano, A., Moltoni, G., Palizzi, S., Muscoli, A., D’Eufemia, S., Parri, E., Faggiano, A., Ciddio, A. B., Guarnera, A., Suma, G., & Bozzao, A. (2025). Role of Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling and 4D MR Angiography in the Diagnosis of Neck Paragangliomas. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134725








