Comparison of Two Initial Effect-Site Concentrations of Remifentanil with Propofol During Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Under Monitored Anesthesia Care: A Randomized Controlled Study with Titration-Based Adjustment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Randomization
2.3. Anesthesia and Monitoring
2.4. Surgical Procedure
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Power and Sample Size
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data and Surgical Information
3.2. Surgery and Anesthesia-Related Details
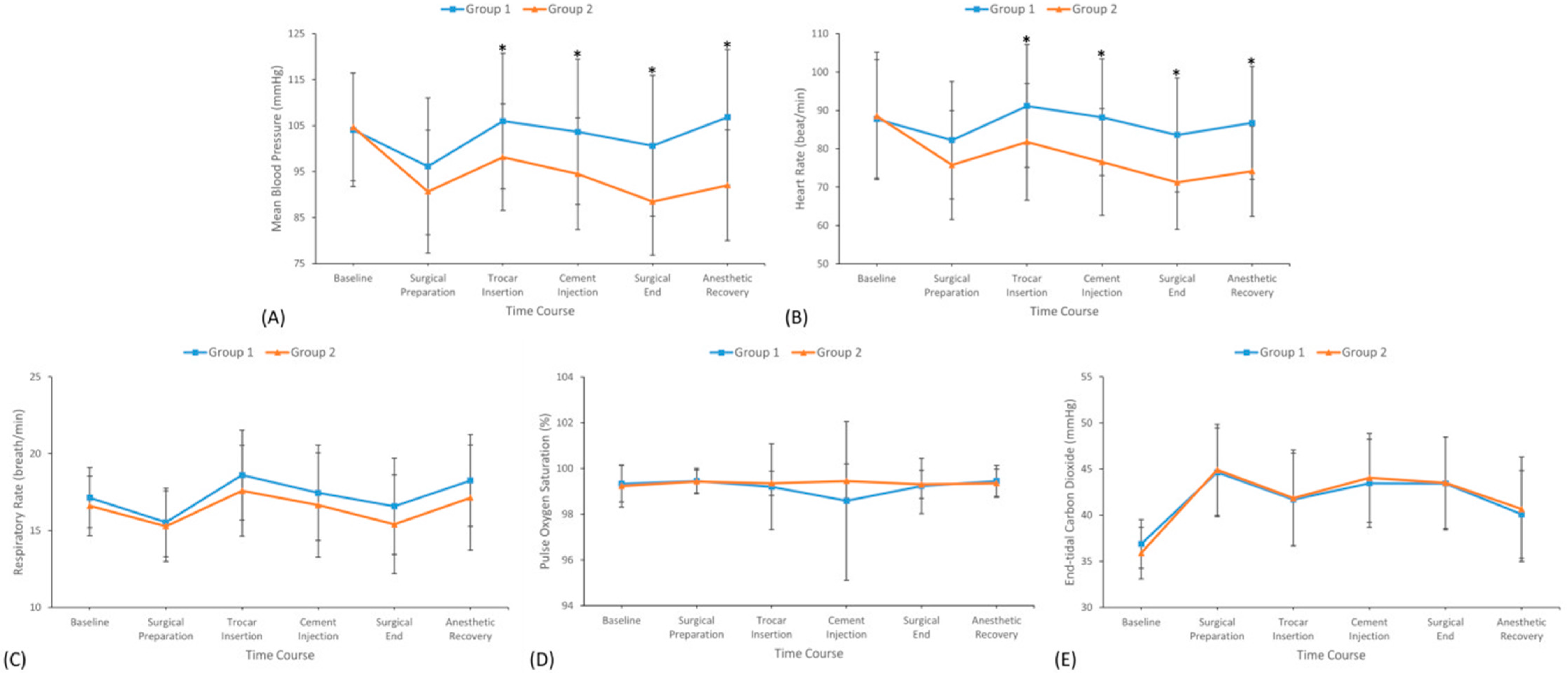
3.3. Hemodynamic and Sedation Profiles During Surgery
3.4. Intraoperative Adverse Events
3.5. Postoperative Assessment and Satisfaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Layton, K.F.; Thielen, K.R.; Koch, C.A.; Luetmer, P.H.; Lane, J.I.; Wald, J.T.; Kallmes, D.F. Vertebroplasty, first 1000 levels of a single center: Evaluation of the outcomes and complications. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goz, V.; Koehler, S.M.; Egorova, N.N.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Guillerme, S.A.; Hecht, A.C.; Qureshi, S.A. Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty: Trends in use in ambulatory and inpatient settings. Spine J. 2011, 11, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klazen, C.A.; Lohle, P.N.; de Vries, J.; Jansen, F.H.; Tielbeek, A.V.; Blonk, M.C.; Venmans, A.; van Rooij, W.J.; Schoemaker, M.C.; Juttmann, J.R.; et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): An open-label randomised trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushchayev, S.V.; Wiener, P.C.; Teytelboym, O.M.; Arrington, J.A.; Khan, M.; Preul, M.C. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A History of Procedure, Technology, Culture, Specialty, and Economics. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2019, 29, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luginbühl, M. Percutaneous vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty and lordoplasty: Implications for the anesthesiologist. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2008, 21, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.M.; Ryu, J.H. Monitored anesthesia care in and outside the operating room. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2016, 69, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.H.; Tran, D.H.; Lam, S.W.; Irwin, M.G. Remifentanil tolerance and hyperalgesia: Short-term gain, long-term pain? Anaesthesia 2016, 71, 1347–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkenstadt, H.; Perel, A.; Hadani, M.; Unofrievich, I.; Ram, Z. Monitored anesthesia care using remifentanil and propofol for awake craniotomy. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2001, 13, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudner, R.; Jalowiecki, P.; Kawecki, P.; Gonciarz, M.; Mularczyk, A.; Petelenz, M. Conscious analgesia/sedation with remifentanil and propofol versus total intravenous anesthesia with fentanyl, midazolam, and propofol for outpatient colonoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2003, 57, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilger, J.A.; Sprung, J.; Maurer, W.; Tetzlaff, J. Remifentanil provides better analgesia than alfentanil during breast biopsy surgery under monitored anesthesia care. Can. J. Anaesth. 2004, 51, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Do, S.H. Remifentanil-propofol versus fentanyl-propofol for monitored anesthesia care during hysteroscopy. J. Clin. Anesth. 2008, 20, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, E.H.; Do, S.H.; Kim, C.S. Randomized double-blind study of remifentanil and dexmedetomidine for flexible bronchoscopy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 108, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlacu, C.L.; McKeating, K.; McShane, A.J. Remifentanil for the insertion and removal of long-term central venous access during monitored anesthesia care. J. Clin. Anesth. 2011, 23, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moerman, A.T.; Struys, M.M.; Vereecke, H.E.; Herregods, L.L.; De Vos, M.M.; Mortier, E.P. Remifentanil used to supplement propofol does not improve quality of sedation during spontaneous respiration. J. Clin. Anesth. 2004, 16, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Absalom, A.R.; Glen, J.I.; Zwart, G.J.; Schnider, T.W.; Struys, M.M. Target-Controlled Infusion: A Mature Technology. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 122, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Tanaka, A. Effect-site concentrations of remifentanil causing bradycardia in hypnotic and non-hypnotic patients. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2016, 30, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.C.; Tsai, Y.T.; Huang, Y.H.; Wu, K.L.; Huang, R.C.; Lin, B.F.; Chan, S.M.; Wu, Z.F. Comparison of 2 effect-site concentrations of remifentanil with midazolam during percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty under monitored anesthesia care: A randomized controlled study. Medicine 2021, 100, e26780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.C.; Chen, C.L.; Huang, Y.H.; Wu, K.L.; Huang, R.C.; Lin, B.F.; Chan, S.M.; Wu, Z.F. Comparison of 2 effect-site concentrations of remifentanil with midazolam during transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy under procedural analgesia and sedation: A randomized controlled study. Medicine 2022, 101, e30466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaizadeh, L.; Hoseyni, M.S.; Shajareh, E.; Heydari, G.; Ardehali, S.H. Use of Bispectral Index Score for Interventional Bronchoscopy Procedures. Tanaffos 2015, 14, 246–251. [Google Scholar]
- Dauri, M.; Coniglione, F.; Faria, S.; Fiori, R.; Frunzo, F.; Massari, F.; Simonetti, G.; Sabato, A.F.; Masala, S. Continuous i.v. infusion of remifentanil and intraosseous lidocaine provide better analgesia than intraosseous lidocaine alone in percutaneous vertebroplasty of osteoporotic fractures. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 103, 901–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, S.J.; Hwang, W.S.; Jang, S.W.; Park, E.Y. Comparison of remifentanil with dexmedetomidine for monitored anaesthesia care in elderly patients during vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. J. Int. Med. Res. 2016, 44, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfouz, A.K.; Ghali, A.M. Combined use of remifentanil and propofol to limit patient movement during retinal detachment surgery under local anesthesia. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2010, 4, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besch, G.; Chopard-Guillemin, A.; Monnet, E.; Causeret, A.; Jurine, A.; Baudry, G.; Lasry, B.; Tavernier, L.; Samain, E.; Pili-Floury, S. Propofol-remifentanil anesthesia for upper airway endoscopy in spontaneous breathing patients: The ENDOTANIL Randomized Trial. Minerva Anestesiol. 2016, 82, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Lobb, D.; MiriMoghaddam, M.; Macalister, D.; Chrisp, D.; Shaw, G.; Lai, H. Safety and efficacy of target controlled infusion administration of propofol and remifentanil for moderate sedation in non-hospital dental practice. J. Dent. Anesth. Pain Med. 2023, 23, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vico, P.; Biasucci, D.G.; Aversano, L.; Polidoro, R.; Zingaro, A.; Millarelli, F.R.; Del Vecchio Blanco, G.; Paoluzi, O.A.; Troncone, E.; Monteleone, G.; et al. Feasibility and safety of deep sedation with propofol and remifentanil in spontaneous breathing during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: An observational prospective study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tănase, N.V.; Hainăroșie, R.; Brîndușe, L.A.; Cobilinschi, C.; Dutu, M.; Corneci, D.; Zainea, V. Study of Two Sedative Protocols for Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy: Propofol versus Propofol-Remifentanil Combination, Delivered in Target-Controlled Infusion Mode. Medicina 2024, 60, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannata, F.; Spinoglio, A.; Di Marco, P.; Luzi, M.; Canneti, A.; Ricciuti, G.; Reale, C. Total intravenous anesthesia using remifentanil in extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). Comparison of two dosages: A randomized clinical trial. Minerva Anestesiol. 2014, 80, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lizano-Díez, I.; Poteet, S.; Burniol-Garcia, A.; Cerezales, M. The burden of perioperative hypertension/hypotension: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, M.; Aslan, B.; Arikan, O.; But, A.; Horasanli, E. Comparison of propofol-remifentanil and propofol-ketamine combination for dilatation and currettage: A randomized double blind prospective trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 3522–3527. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Chen, W.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Comparison of remifentanil and esketamine in combination with propofol for patient sedation during fiberoptic bronchoscopy. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, Y.S.; Hong, J.Y. Effects of remifentanil on propofol requirements for loss of consciousness in target-controlled infusion. Minerva Anestesiol. 2008, 74, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schnider, T.W.; Minto, C.F.; Struys, M.M.; Absalom, A.R. The Safety of Target-Controlled Infusions. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 122, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moerman, A.T.; Herregods, L.L.; De Vos, M.M.; Mortier, E.P.; Struys, M.M. Manual versus target-controlled infusion remifentanil administration in spontaneously breathing patients. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 108, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variables | Group 1 (n = 40) | Group 2 (n = 40) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male/female (n [%]) | 9/31 (22.5%/77.5%) | 12/28 (30.0%/70.0%) | 0.446 |
| Age (years old) | 70.03 ± 7.46 | 68.50 ± 7.87 | 0.377 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.42 ± 4.34 | 23.89 ± 4.34 | 0.587 |
| Cigarette smoking, n (%) | 5 (12.5%) | 6 (15.0%) | 0.745 |
| Alcohol consumption, n (%) | 4 (10.0%) | 1 (2.5%) | 0.166 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |||
| Hypertension | 23 (57.5%) | 24 (60.0%) | 0.820 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 13 (32.5%) | 8 (20.0%) | 0.204 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 14 (35.0%) | 16 (40.0%) | 0.644 |
| Cardiac disease | 7 (17.5%) | 5 (12.5%) | 0.531 |
| Respiratory disease | 3 (7.5%) | 1 (2.5%) | 0.305 |
| Neurological disease | 3 (7.5%) | 5 (12.5%) | 0.456 |
| Hepatic disease | 3 (7.5%) | 3 (7.5%) | 1.000 |
| Renal disease | 3 (7.5%) | 2 (5.0%) | 0.644 |
| Thyroid disease | 3 (7.5%) | 2 (5.0%) | 0.644 |
| Rheumatic disease | 3 (7.5%) | 3 (7.5%) | 1.000 |
| Psychiatric disease | 4 (10.0%) | 6 (15.0%) | 0.499 |
| Malignancy | 8 (20.0%) | 10 (25.0%) | 0.592 |
| ASA class, II/III (n [%]) | 25/15 (62.5%/37.5%) | 19/21 (47.5%/52.5%) | 0.178 |
| ≥4 METs, n (%) | 37 (92.5%) | 35 (87.5%) | 0.456 |
| Surgical site, T/L spine (n [%]) | 17/23 (42.5%/57.5%) | 17/23 (42.5%/57.5%) | 1.000 |
| Variables | Group 1 (n = 40) | Group 2 (n = 40) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operation time (min) | 31.80 ± 14.54 | 30.73 ± 14.14 | 0.738 |
| Anesthesia time (min) | 53.33 ± 19.90 | 48.03 ± 16.60 | 0.200 |
| Time to LOC (min) | 3.19 ± 1.20 | 2.69 ± 1.26 | 0.074 |
| Time to ROC (min) | 4.64 ± 1.15 | 4.52 ± 1.00 | 0.606 |
| Propofol consumption (mg) | 328.63 ± 135.61 | 281.13 ± 111.84 | 0.091 |
| Propofol pump adjustment (n) | |||
| Total times | 5.0 (4.5–7.5) | 4.5 (4.0–6.0) | 0.101 |
| Upward times | 2.0 (1.0–3.0) | 2.0 (1.0–2.0) | 0.069 |
| Downward times | 3.0 (3.0–4.0) | 3.0 (3.0–4.0) | 0.603 |
| Remifentanil consumption (mcg) | 141.40 ± 75.25 | 208.50 ± 78.61 | <0.001 |
| Remifentanil pump adjustment (n) | |||
| Total times | 2.0 (1.0–3.0) | 2.0 (1.0–2.0) | 0.193 |
| Upward times | 1.0 (0.0–1.0) | 0.0 (0.0–1.0) | <0.001 |
| Downward times | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) | 1.0 (1.0–2.0) | 0.063 |
| Fluid administration (mL) | 202.50 ± 80.02 | 197.50 ± 81.61 | 0.783 |
| Intraoperative adverse events, n (%) | |||
| Pulmonary episodes | 2 (5.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.152 |
| Cardiovascular episodes | 3 (7.5%) | 3 (7.5%) | 1.000 |
| Patient movement | 17 (42.5%) | 4 (10.0%) | 0.001 |
| Ephedrine administration, n (%) | 3 (7.5%) | 3 (7.5%) | 1.000 |
| Atropine administration, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.000 |
| Variables | Group 1 (n = 40) | Group 2 (n = 40) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Postoperative adverse events, n (%) | |||
| Pulmonary episodes | 1 (2.5%) | 1 (2.5%) | 1.000 |
| Cardiovascular episodes | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.000 |
| Postoperative nausea and vomiting | 1 (2.5%) | 2 (5.0%) | 0.556 |
| Remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.000 |
| VAS at PACU | 1.30 ± 0.97 | 0.90 ± 0.38 | 0.018 |
| Rescue tramadol, n (%) | 3 (7.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.077 |
| Postoperative hospital stay (day) | 1.85 ± 1.89 | 1.88 ± 2.28 | 0.958 |
| Total hospital stay (day) | 3.58 ± 3.15 | 4.28 ± 5.49 | 0.486 |
| Patient satisfaction | 4.0 (4.0–5.0) | 4.0 (4.0–5.0) | 1.000 |
| Surgeon satisfaction | 4.0 (4.0–4.0) | 4.5 (4.0–5.0) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.-S.; Wu, Z.-F.; Lai, H.-C.; Ko, C.-L.; Sun, T.-Y.; Hong, K.-T.; Lo, K.-L.; Yeh, T.-H.; Tseng, W.-C. Comparison of Two Initial Effect-Site Concentrations of Remifentanil with Propofol During Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Under Monitored Anesthesia Care: A Randomized Controlled Study with Titration-Based Adjustment. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134669
Lin S-S, Wu Z-F, Lai H-C, Ko C-L, Sun T-Y, Hong K-T, Lo K-L, Yeh T-H, Tseng W-C. Comparison of Two Initial Effect-Site Concentrations of Remifentanil with Propofol During Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Under Monitored Anesthesia Care: A Randomized Controlled Study with Titration-Based Adjustment. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134669
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shih-Syuan, Zhi-Fu Wu, Hou-Chuan Lai, Ching-Lung Ko, Ting-Yi Sun, Kun-Ting Hong, Kai-Li Lo, Tzu-Hsuan Yeh, and Wei-Cheng Tseng. 2025. "Comparison of Two Initial Effect-Site Concentrations of Remifentanil with Propofol During Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Under Monitored Anesthesia Care: A Randomized Controlled Study with Titration-Based Adjustment" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134669
APA StyleLin, S.-S., Wu, Z.-F., Lai, H.-C., Ko, C.-L., Sun, T.-Y., Hong, K.-T., Lo, K.-L., Yeh, T.-H., & Tseng, W.-C. (2025). Comparison of Two Initial Effect-Site Concentrations of Remifentanil with Propofol During Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Under Monitored Anesthesia Care: A Randomized Controlled Study with Titration-Based Adjustment. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134669





