The Role of Guideline’s Threshold Vascular Diameters in Long-Term Radio-Cephalic Arteriovenous Fistula Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Preoperative Vascular Mapping
2.4. RC-AVF Creation
2.5. Follow-Up
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESVS | European Society of Vascular Surgery |
| RA | radial artery |
| CV | cephalic vein |
| RC-AVF | radio-cephalic arteriovenous fistula |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| ESKD | end-stage chronic kidney disease |
| RRT | renal replacement therapy |
| HD | hemodialysis |
| PD | peritoneal dialysis |
| VA | vascular access |
| AVF | arteriovenous fistula |
| AVG | arteriovenous graft |
| CVC | central venous catheter |
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| IHD | ischemic heart disease |
| BUN | blood urea nitrogen |
| SD | standard deviation |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| RCT | randomized controlled trial |
References
- The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Stanifer, J.W.; Muiru, A.; Jafar, T.H.; Patel, U.D. Chronic Kidney Disease in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.-W.; et al. Forecasting Life Expectancy, Years of Life Lost, and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality for 250 Causes of Death: Reference and Alternative Scenarios for 2016–40 for 195 Countries and Territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.; Robinson, B.; Abbott, K.C.; Agodoa, L.Y.C.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Balkrishnan, R.; Bhave, N.; Dietrich, X.; Ding, Z.; Eggers, P.W.; et al. US Renal Data System 2018 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, A7–A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidli, J.; Widmer, M.K.; Basile, C.; de Donato, G.; Gallieni, M.; Gibbons, C.P.; Haage, P.; Hamilton, G.; Hedin, U.; Kamper, L.; et al. Editor’s Choice—Vascular Access: 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2018, 55, 757–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murad, M.H.; Elamin, M.B.; Sidawy, A.N.; Malaga, G.; Rizvi, A.Z.; Flynn, D.N.; Casey, E.T.; McCausland, F.R.; McGrath, M.M.; Vo, D.H.; et al. Autogenous versus Prosthetic Vascular Access for Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 48, S34–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasri, J.; Alsawas, M.; Mainou, M.; Mustafa, R.A.; Wang, Z.; Woo, K.; Cull, D.L.; Murad, M.H. Outcomes of Vascular Access for Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jaishi, A.A.; Liu, A.R.; Lok, C.E.; Zhang, J.C.; Moist, L.M. Complications of the Arteriovenous Fistula: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.J.; Chen, F.; Pisoni, R.L.; Krishnan, M.; Mapes, D.; Keen, M.; Bradbury, B.D. Hospitalization Risks Related to Vascular Access Type among Incident US Hemodialysis Patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3659–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.B.; Hobson, R.W.; Pappas, P.J.; Jamil, Z.; Araki, C.T.; Goldberg, M.C.; Gwertzman, G.; Padberg, F.T. A Strategy for Increasing Use of Autogenous Hemodialysis Access Procedures: Impact of Preoperative Noninvasive Evaluation. J. Vasc. Surg. 1998, 27, 302–307; discussion 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golledge, J.; Smith, C.J.; Emery, J.; Farrington, K.; Thompson, H.H. Outcome of Primary Radiocephalic Fistula for Haemodialysis. Br. J. Surg. 1999, 86, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbregts, H.J.T.; Bots, M.L.; Wittens, C.H.A.; Schrama, Y.C.; Moll, F.L.; Blankestijn, P.J.; The CIMINO Study Group. Hemodialysis Arteriovenous Fistula Patency Revisited: Results of a Prospective, Multicenter Initiative. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolowczyk, L.; Williams, A.J.; Donovan, K.L.; Gibbons, C.P. The Snuffbox Arteriovenous Fistula for Vascular Access. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2000, 19, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, K.D.; Gillen, D.L.; Caps, M.T.; Kohler, T.R.; Sherrard, D.J.; Stehman-Breen, C.O. Vascular Access Survival and Incidence of Revisions: A Comparison of Prosthetic Grafts, Simple Autogenous Fistulas, and Venous Transposition Fistulas from the United States Renal Data System Dialysis Morbidity and Mortality Study. J. Vasc. Surg. 2001, 34, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allon, M.; Lockhart, M.E.; Lilly, R.Z.; Gallichio, M.H.; Young, C.J.; Barker, J.; Deierhoi, M.H.; Robbin, M.L. Effect of Preoperative Sonographic Mapping on Vascular Access Outcomes in Hemodialysis Patients. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, B.S.; Novak, L.; Fangman, J. Hemodialysis Vascular Access Survival: Upper-Arm Native Arteriovenous Fistula. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravani, P.; Brunori, G.; Mandolfo, S.; Cancarini, G.; Imbasciati, E.; Marcelli, D.; Malberti, F. Cardiovascular Comorbidity and Late Referral Impact Arteriovenous Fistula Survival: A Prospective Multicenter Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooijens, P.P.G.M.; Burgmans, J.P.J.; Yo, T.I.; Hop, W.C.J.; de Smet, A.A.E.A.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; Fritschy, W.M.; de Groot, H.G.W.; Burger, H.; Tordoir, J.H.M. Autogenous Radial-Cephalic or Prosthetic Brachial-Antecubital Forearm Loop AVF in Patients with Compromised Vessels? A Randomized, Multicenter Study of the Patency of Primary Hemodialysis Access. J. Vasc. Surg. 2005, 42, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biuckians, A.; Scott, E.C.; Meier, G.H.; Panneton, J.M.; Glickman, M.H. The Natural History of Autologous Fistulas as First-Time Dialysis Access in the KDOQI Era. J. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 47, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourquelot, P. Vascular Access in Children: The Importance of Microsurgery for Creation of Autologous Arteriovenous Fistulae. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2006, 32, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirozzi, N.; Apponi, F.; Napoletano, A.M.; Luciani, R.; Pirozzi, V.; Pugliese, F. Microsurgery and Preventive Haemostasis for Autogenous Radial–Cephalic Direct Wrist Access in Adult Patients with Radial Artery Internal Diameter below 1.6 Mm. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, B.; Stevenson, K.; Aitken, E.; Jackson, A.; Thomas, S.; Snoeijs, M.; Franchin, M.; Tozzi, M.; Kingsmore, D.B. A Review of Technical Steps in the Performance of Arteriovenous Fistula Creation. J. Vasc. Access 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, E.; Jeans, E.; Aitken, M.; Kingsmore, D. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Interrupted versus Continuous Suturing Techniques for Radiocephalic Fistulas. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 62, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElKassaby, M.; Elsayed, N.; Mosaad, A.; Soliman, M. End-to-Side versus Side-to-Side Anastomosis with Distal Vein Ligation for Arteriovenous Fistula Creation. Vascular 2021, 29, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikam, M.; Chemla, E.S.; Evans, J.; Summers, A.; Brenchley, P.; Tavakoli, A.; Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Mitra, S. Prospective Controlled Pilot Study of Arteriovenous Fistula Placement Using the Novel Optiflow Device. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 61, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karydis, N.; Bevis, P.; Beckitt, T.; Silverberg, D.; Halak, M.; Calder, F. An Implanted Blood Vessel Support Device for Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajek, J.; Malovrh, M. Preoperative Ultrasound Still Valuable for Radio-Cephalic Arteriovenous Fistula Creation? J. Vasc. Access 2017, 18, S5–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordzadeh, A.; Chung, J.; Panayiotopoulos, Y.P. Cephalic Vein and Radial Artery Diameter in Formation of Radiocephalic Arteriovenous Fistula: A Systematic Review. J. Vasc. Access 2015, 16, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaller, R.; Arbănași, E.M.; Mureșan, A.V.; Voidăzan, S.; Arbănași, E.M.; Horváth, E.; Suciu, B.A.; Hosu, I.; Halmaciu, I.; Brinzaniuc, K.; et al. The Predictive Value of Systemic Inflammatory Markers, the Prognostic Nutritional Index, and Measured Vessels’ Diameters in Arteriovenous Fistula Maturation Failure. Life 2022, 12, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindel, P.; Yu, P.; Feliz, J.D.; Hentschel, D.M.; Burke, S.K.; Al-Omran, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Belkin, M.; Ozaki, C.K.; Hussain, M.A. Radiocephalic Arteriovenous Fistula Patency and Use: A Post Hoc Analysis of Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trials. Ann. Surg. Open 2022, 3, e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubensek, J. Doppler Ultrasound Assessment of Calcified Radial Arteries Prior to Radio-Cephalic Arterio-Venous Fistula Placement: An Observational Study. J. Vasc. Access 2024, 25, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordzadeh, A.; Mouhsen, M.I.M.M.; Prionidis, I.; Francesconi, M.; Inston, N. Vessel Diameter and Radiocephalic Arteriovenous Fistula: A Meta-Analysis and Markov Model. J. Vasc. Surg. 2025, 82, 286–294.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaller, R.; Russu, E.; Arbănași, E.M.; Mureșan, A.V.; Jakab, M.; Ciucanu, C.C.; Arbănași, E.M.; Suciu, B.A.; Hosu, I.; Demian, L.; et al. Intimal CD31-Positive Relative Surfaces Are Associated with Systemic Inflammatory Markers and Maturation of Arteriovenous Fistula in Dialysis Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.J.; Gloviczki, P.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, J.D.; Kim, D.-I.; Jang, H.-R.; Heo, W.-S.; Oh, H.-Y. The Influence of Cephalic Vein Diameter and Diabetes on Primary Maturation and Patency of Autogenous Radiocephalic Arteriovenous Fistulas. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 62, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Yan, Y.; Li, G.; Hou, Y.; Sun, X.; Yin, N.; Feng, G. Preoperative Cephalic Vein Diameter and Diabetes Do Not Limit the Choice of Wrist Radio-Cephalic Arteriovenous Fistula. J. Vasc. Access 2020, 21, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-L.; Chan, Y.C.; Cui, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Li, N.; Pai, P.; Cheng, S.W. Predictors of Primary Functional Maturation of Autogenous Radiocephalic Arteriovenous Fistula in a Cohort of Asian Patients. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 66, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbin, M.L.; Chamberlain, N.E.; Lockhart, M.E.; Gallichio, M.H.; Young, C.J.; Deierhoi, M.H.; Allon, M. Hemodialysis Arteriovenous Fistula Maturity: US Evaluation. Radiology 2002, 225, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorzaat, B.M.; van der Bogt, K.E.A.; Janmaat, C.J.; van Schaik, J.; Dekker, F.W.; Rotmans, J.I.; Group, D.V.A.S.; Voorzaat, B.M.; van der Bogt, K.E.A.; Janmaat, C.J.; et al. Arteriovenous Fistula Maturation Failure in a Large Cohort of Hemodialysis Patients in the Netherlands. World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindel, P.; Fitzgibbon, J.J.; Feliz, J.D.; Hentschel, D.M.; Burke, S.K.; Al-Omran, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Belkin, M.; Ozaki, C.K.; Hussain, M.A. Evaluating National Guideline Concordance of Recurrent Interventions after Radiocephalic Arteriovenous Fistula Creation. J. Vasc. Surg. 2023, 77, 1206–1215.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | All Patients n = 110 | RC-AVF Created in Agreement with Guideline Recommendation | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes n = 87 | No n = 23 | |||
| Age, mean ± SD | 62.70 ± 14.46 | 63.39 ± 13.49 | 60.13 ± 17.77 | 0.419 |
| Male, no. (%) | 62 (56.36%) | 52 (59.77%) | 10 (43.48%) | 0.161 |
| Female, no. (%) | 48 (43.64%) | 35 (40.23%) | 13 (56.52%) | |
| Comorbidities and risk factors, no. (%) | ||||
| Hypertension | 99 (90.00%) | 78 (89.66%) | 21 (91.30%) | 0.815 |
| Atrial Fibrillation | 7 (6.36%) | 4 (4.60%) | 3 (13.04%) | 0.140 |
| Diabetes | 44 (40.00%) | 33 (37.93%) | 11 (47.83%) | 0.389 |
| Ischemic Heart Disease | 50 (45.45%) | 37 (42.53%) | 13 (56.52%) | 0.231 |
| History of Myocardial Infarction | 5 (4.55%) | 5 (5.75%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0.236 |
| History of Stroke | 4 (3.64%) | 2 (2.30%) | 2 (8.70%) | 0.145 |
| Active Smoking | 18 (16.36%) | 12 (13.79%) | 6 (26.09%) | 0.156 |
| Laboratory data, median (Q1–Q3) | ||||
| WBC | 7.90 (6.36–9.50) | 8.04 (6.50–9.54) | 7.01 (6.11–9.30) | 0.969 |
| Potassium mmol/l | 5.05 (4.63–5.44) | 5.01 (4.58–5.43) | 5.10 (4.69–5.47) | 0.380 |
| Sodium mmol/l | 139 (137–141) | 139 (137.07–141) | 139.45 (137–140) | 0.239 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 102 (89.42–131.22) | 101 (89–128.9) | 105 (96–174) | 0.080 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 122.40 (99.30–160.20) | 120.60 (92–157.30) | 137.40 (102.42–174.3) | 0.890 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 6.32 (5.26–7.81) | 6.10 (5.25–7.29) | 6.71 (5.66–8.27) | 0.240 |
| Hemoglobin g/dL | 10.00 (8.7–11.4) | 10.00 (8.7–11.41) | 10.35 (8.63–11) | 0.313 |
| Hematocrit % | 30.50 (26.37–35.1) | 30.40 (26.82–35.02) | 30.89 (25.92–35.27) | 0.287 |
| Neutrophils ×103/uL | 5.40 (4.16–7.11) | 5.49 (4.33–7.31) | 4.80 (3.71–6.47) | 0.295 |
| Lymphocytes ×103/uL | 1.51 (1.06–2.07) | 1.44 (1.01–2.07) | 1.72 (1.18–1.96) | 0.555 |
| Monocyte ×103/uL PLT ×103/uL | 0.64 (0.52–0.80) 220.50 (181–296.07) | 0.63 (0.51–0.81) 213.5 (177.77–282.5) | 0.66 (0.56–0.79) 277 (191.25–305.75) | 0.651 0.358 |
| Vascular mapping determinations, mean ± SD | ||||
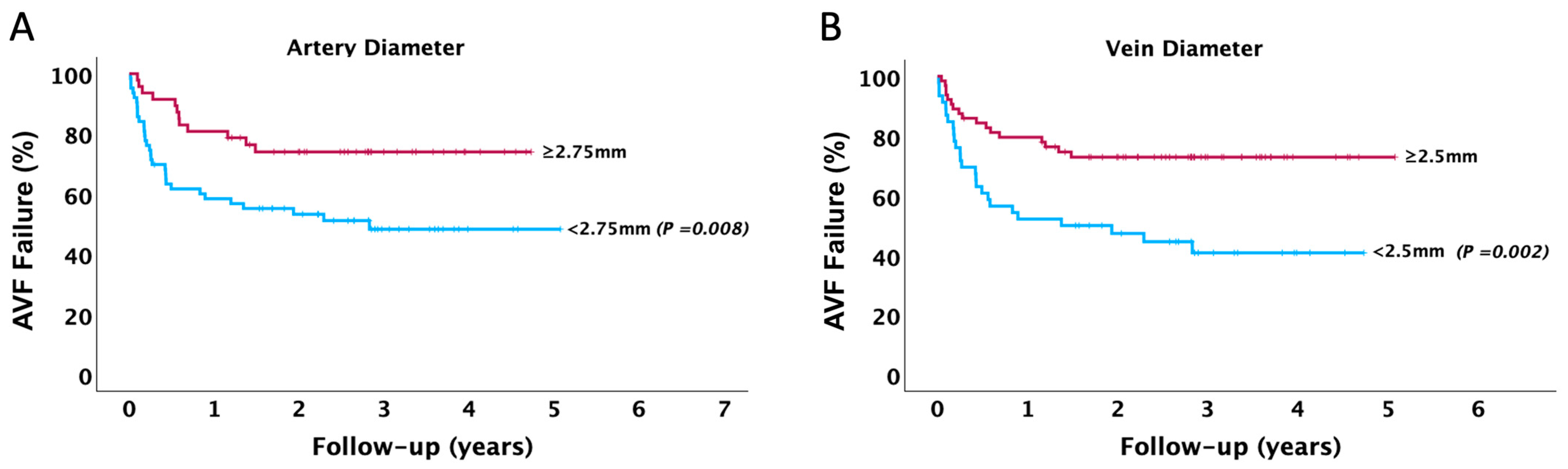
| Arterial Diameter (mm) | 2.71 ± 0.75 | 2.87 ± 0.71 | 2.06 ± 0.48 | <0.001 |
| Vein Diameter (mm) | 2.81 ± 0.61 | 2.96 ± 0.54 | 2.19 ± 0.46 | <0.001 |
| 6-week Arterial Diameter (mm) # | 2.69 ± 0.73 | 2.85 ± 0.73 | 2.24 ± 0.52 | 0.003 |
| 6-week Vein Diameter (mm) # | 5.96 ± 1.51 | 6.05 ± 1.43 | 5.71 ± 1.75 | 0.249 |
| Non-Dominant Upper Limb | 94 (85.45%) | 74 (85.06%) | 20 (86.96%) | 0.818 |
| Out-Patients, no. (%) | 65 (59.09%) | 50 (57.47%) | 15 (65.22%) | 0.502 |
| CVC present, no. (%) | 51 (46.36%) | 36 (41.38%) | 15 (65.22%) | 0.041 |
| 6-week Maturation failure, no. (%) | 23 (20.91%) | 14 (16.09%) | 9 (39.13%) | 0.012 |
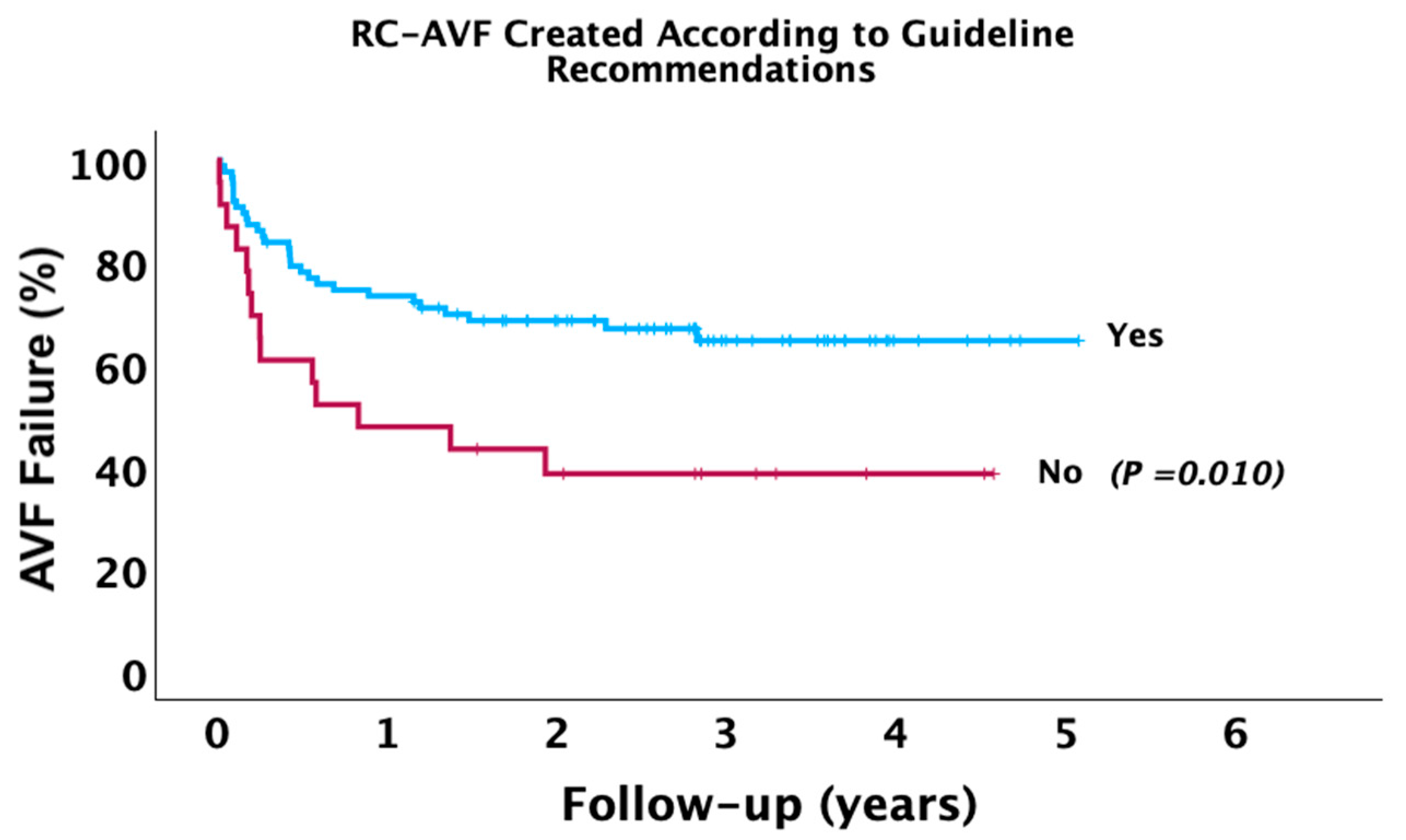
| Long-Term AVF failure | 43 (39.09%) | 29 (33.33%) | 14 (60.87%) | 0.016 |
| Follow-up Period (Years), mean ± SD | 1.98 ± 1.45 | 2.10 ± 1.40 | 1.53 ± 1.55 | 0.083 |
| Radial Artery | Cephalic Vein | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter | Sensitivity | Specificity | Youden’s Index | Diameter | Sensitivity | Specificity | Youden’s Index |
| 2.05 mm | 85.1% | 27.9% | 0.130 | 2.05 mm | 89.6% | 18.6% | 0.082 |
| 2.37 mm | 68.7% | 46.5% | 0.152 | 2.35 mm | 85.1% | 37.2% | 0.223 |
| 2.55 mm | 53.7% | 62.8% | 0.160 | 2.45 mm | 74.6% | 46.5% | 0.211 |
| 2.65 mm | 52.2% | 67.4% | 0.207 | 2.52 mm | 70.1% | 60.5% | 0.306 |
| 2.75 mm | 52.2% | 72.1% | 0.243 | 2.57 mm | 68.7% | 60.5% | 0.291 |
| 2.85 mm | 44.8% | 76.7% | 0.215 | 2.65 mm | 65.7% | 62.8% | 0.285 |
| 2.95 mm | 43.3% | 79.1% | 0.224 | 2.75 mm | 65.7% | 65.1% | 0.304 |
| 3.05 mm | 35.8% | 83.7% | 0.205 | 2.90 mm | 53.7% | 69.8% | 0.235 |
| 3.13 mm | 32.8% | 88.4% | 0.212 | 3.08 mm | 46.3% | 74.4% | 0.207 |
| 3.18 mm | 32.8% | 90.7% | 0.235 | 3.25 mm | 34.3% | 86.0% | 0.204 |
| 3.25 mm | 28.4% | 93.0% | 0.214 | 3.35 mm | 31.3% | 90.7% | 0.220 |
| Variables | RC-AVF Failure | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Female | 2.12 | 1.15–3.90 | 0.015 |
| Hypertension | 0.45 | 0.20–1.01 | 0.053 |
| Ischemic Heart Disease | 1.24 | 0.76–2.01 | 0.380 |
| Diabetes | 1.96 | 1.08–3.59 | 0.027 |
| Active Smoking | 2.84 | 1.48–5.48 | 0.002 |
| CVC presence | 2.49 | 1.33–4.67 | 0.004 |
| 6-week Maturation Failure | 3.31 | 1.76–6.23 | <0.001 |
| Variables | RC-AVF Failure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p Value | ||
| RC-AVF Created in Agreement with Guideline Recommendation (Yes) | Model 1 | 0.44 | 0.23–0.83 | 0.012 |
| Model 2 | 0.51 | 0.26–0.98 | 0.043 | |
| Model 3 | 0.59 | 0.29–1.19 | 0.146 | |
| Model 4 | 0.69 | 0.34–1.43 | 0.328 | |
| Artery Diameter | Model 1 | 0.56 * | 0.38–0.84 | 0.005 |
| Model 2 | 0.60 * | 0.41–0.89 | 0.013 | |
| Model 3 | 0.68 * | 0.46–1.01 | 0.059 | |
| Model 4 | 0.71 * | 0.48–1.05 | 0.086 | |
| Vein Diameter | Model 1 | 0.61 * | 0.44–0.84 | 0.002 |
| Model 2 | 0.62 * | 0.45–0.85 | 0.004 | |
| Model 3 | 0.67 * | 0.48–0.94 | 0.022 | |
| Model 4 | 0.68 * | 0.49–0.96 | 0.026 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russu, E.; Florea, E.; Asztalos, A.; Ciucanu, C.C.; Arbănași, E.-M.; Bartus, R.; Mureșan, A.V.; Ujlaki-Nagy, A.-A.; Hosu, I.; Arbănași, E.-M. The Role of Guideline’s Threshold Vascular Diameters in Long-Term Radio-Cephalic Arteriovenous Fistula Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134667
Russu E, Florea E, Asztalos A, Ciucanu CC, Arbănași E-M, Bartus R, Mureșan AV, Ujlaki-Nagy A-A, Hosu I, Arbănași E-M. The Role of Guideline’s Threshold Vascular Diameters in Long-Term Radio-Cephalic Arteriovenous Fistula Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134667
Chicago/Turabian StyleRussu, Eliza, Elena Florea, Alexandra Asztalos, Constantin Claudiu Ciucanu, Eliza-Mihaela Arbănași, Réka Bartus, Adrian Vasile Mureșan, Alexandru-Andrei Ujlaki-Nagy, Ioan Hosu, and Emil-Marian Arbănași. 2025. "The Role of Guideline’s Threshold Vascular Diameters in Long-Term Radio-Cephalic Arteriovenous Fistula Failure" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134667
APA StyleRussu, E., Florea, E., Asztalos, A., Ciucanu, C. C., Arbănași, E.-M., Bartus, R., Mureșan, A. V., Ujlaki-Nagy, A.-A., Hosu, I., & Arbănași, E.-M. (2025). The Role of Guideline’s Threshold Vascular Diameters in Long-Term Radio-Cephalic Arteriovenous Fistula Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134667






