Abstract
Background: The PATHFINDER-CHD Registry is a prospective, multicenter, non-interventional registry across tertiary care centers in Germany. The aim is to analyze real-world data on adults with congenital heart defects (ACHD) or hereditary connective tissue disorders who have manifest heart failure (HF), a history of HF, or are at significant risk of developing HF. This analysis investigates the prevalence and clinical impact of overweight and obesity in this unique population. Methods: As of 1st February, 2025, a total of 1490 ACHD had been enrolled. The mean age was 39.4 ± 12.4 years, and 47.9% were female. Patients were categorized according to Perloff’s functional class and the Munich Heart Failure Classification for Congenital Heart Disease (MUC-HF-Class). Results: The most common congenital heart disease (CHD) in this cohort was Tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the great arteries, and congenital aortic valve disease. Marfan syndrome was the most common hereditary connective tissue disease. Of the patients, 46.1% were classified as overweight (32.8%) or obese (13.3%), while 4.8% were underweight. The highest prevalence of overweight (47.1%) was observed among patients who had undergone palliative surgery, whereas untreated patients showed the highest proportion of normal weight (57.2%). Cyanotic patients were predominantly of normal weight. Patients with univentricular circulation exhibited significantly lower rates of overweight and obesity (35%; p = 0.001). Overweight and obesity were statistically significantly associated with arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and sleep apnea (all p < 0.001). High BMI was linked to increased use of HF-specific medications, including SGLT2 inhibitors (p = 0.040), diuretics (p = 0.014), and angiotensin receptor blockers (p = 0.005). Conclusions: The data highlight the clinical relevance of overweight and obesity in ACHD with HF, emphasizing the need for individualized prevention and treatment strategies. The registry serves as a critical foundation for the optimization of long-term care in this population.
1. Introduction
The management of adults with congenital heart disease poses an increasing challenge in 21st-century cardiovascular medicine, particularly when complicated by heart failure [1,2,3,4]. Advances in pediatric cardiology, congenital cardiac surgery, and improved long-term care have significantly improved the life expectancy of individuals born with CHD. As a result, the population of ACHD is increasing, currently exceeding 350,000 in Germany and 50 million worldwide [5]. These patients present with a unique clinical profile, characterized by a high burden of sequelae from the underlying CHD as well as associated complications, such as heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, arrhythmias, and non-cardiac comorbidities, including metabolic syndrome and obesity.
The PATHFINDER-CHD Registry (“Patients with Heart Failure Due to Congenital Heart Disease”), a prospective, non-interventional, multicenter cohort study aimed at collecting structured real-world data on ACHD with current or previous HF, or those at risk due to structural or functional abnormalities, was established in 2022. In particular, the registry focuses on the epidemiology, risk factors, and management patterns [6]. PATHFINDER-CHD seeks to address key knowledge gaps by providing robust real-world evidence from specialized tertiary care centers in Germany.
Recent studies highlight the high prevalence of cardiometabolic risk factors in ACHD populations. In a meta-analysis including 110,469 ACHD, 33% had hypertension, 18% were obese, and 7% had diabetes mellitus [7]. In a large cohort of 3905 ACHD, the estimated prevalence of heart failure was 6.4%, with a mean BMI of 25.2 ± 4.9 kg/m2 [8].
The role of overweight and obesity in this vulnerable patient group has only rarely been investigated to date [7]. While the relationship between obesity and acquired cardiovascular disease is well documented, little is known about its prevalence and clinical implications in adults with CHD and HF. In adults without congenital heart disease, the co-prevalence of heart failure and obesity is well documented, with obesity contributing significantly to the pathogenesis and progression of heart failure [9]. However, data regarding this association in adults with congenital heart disease remain scarce, despite the growing number of patients reaching adulthood. The unique anatomy and physiology of CHD patients, combined with their lifelong disease burden, require tailored approaches for prevention and management. Obesity may exacerbate symptom burden, reduce functional capacity, and increase the risk of HF and procedural complications. Furthermore, the emergence of new pharmacological treatments in obese patients is often more challenging due to altered drug metabolism and dosing considerations, necessitating individualized therapeutic approaches. Stratification by body mass index (BMI) or body composition is therefore essential to better understand the heterogeneity of comorbidities and treatment patterns within the ACHD cohort [10].
This current cross-sectional analysis specifically examines the prevalence of overweight and obesity in the cohort, by type of surgical status, by ventricular morphology, by functional status, and by cardiac and non-cardiac comorbidities, as well as medication usage across different BMI categories. It aims to identify potential disparities in care and to provide a basis for more personalized, preventive, and therapeutic strategies in ACHD.
2. Materials and Methods
The PATHFINDER-CHD Registry is a prospective, multicenter, non-interventional cohort study launched in 2022. It aims to collect structured real-world data on adults (≥18 years) with CHD and either manifest, previous, or preclinical HF. Participating centers are tertiary care institutions across Germany, all certified for their expertise in the management of ACHD [6]. The registry was established with a strong focus on maintaining high-quality standards [11].
The ongoing registry includes data collected between June 2023 and February 2025, with February 2025 serving as the cut-off date for this analysis.
Patients were eligible for inclusion if they were aged 18 years or older, had a confirmed diagnosis of any form of CHD and HF, provided informed consent (either personally or via a legal guardian), and were suitable for long-term follow-up within the registry. The primary exclusion criterion was participation in an interventional clinical trial, as this could compromise the validity of real-world data collection. No additional exclusion criteria were applied in order to reflect the full spectrum of clinical presentations seen in specialized ACHD care. Data collection is performed via a secure, web-based electronic data capture (EDC) system in compliance with the European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). All data are pseudonymized and stored in encrypted form. Ethical approval was granted by the leading ethics committee from the Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nürnberg (Ref: 23-460-Bn) and the Technical University of Munich (Ref: 2022–582-S-KH), with additional further local approvals obtained as required.
The registry captures both mandatory core data and optional extended variables at baseline and follow-up visits. Documented variables include demographics, type and complexity of CHD, prior surgical or interventional procedures, ventricular morphology, functional classification (Perloff and modified ACC/AHA) [2,12], comorbidities, medication use, as well as weight and height to calculate BMI.
Overweight and obesity are categorized according to the World Health Organization classification: normal weight (BMI 18.5–24.9 kg/m2), overweight (BMI 25.0–29.9 kg/m2), and obesity (BMI ≥ 30.0 kg/m2) [13]. Heart failure was classified using the Perloff’s functional class and the ACC/AHA Heart Failure Classification (2022) modified for CHD. Comorbidities such as arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and sleep apnea were documented based on physician diagnosis and standard clinical criteria as routinely applied in participating certified ACHD centers. Surgical status, ventricular morphology, and types of congenital heart disease were recorded in accordance with standard cardiological practice.
The study complies with the principles of Good Pharmacoepidemiology Practice (GPP) [14] and Good Practice in Secondary Data Analysis (GPS) [15]. All statistical evaluations were conducted on pseudonymized, non-personal data. Descriptive and inferential statistical analyses were performed to identify patterns and associations. Methods included frequency analyses, cross-tabulations, and one-sided chi-squared tests for categorical variables, with statistical significance defined as p < 0.05. No imputation or statistical adjustments were applied; missing values were reported as observed. All analyses were performed using SPSS version 29.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Longitudinal analyses are planned for future registry follow-up data.
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
As of 1 February 2025, 1490 ACHD patients with HF were enrolled in the PATHFINDER-CHD Registry. The mean age was 39.4 ± 12.4 years (range: 18–84), with most patients being in the 4th decade (Figure 1). There were 47.9% female patients. A breakdown by the type of CHD is provided in Figure 2. Of the patients, 33.4% had right-sided heart anomalies, followed by 24.7% with complex CHD, 19.5% with left-sided heart anomalies, and 12.8% with septal defects and vascular malformations (Table 1).
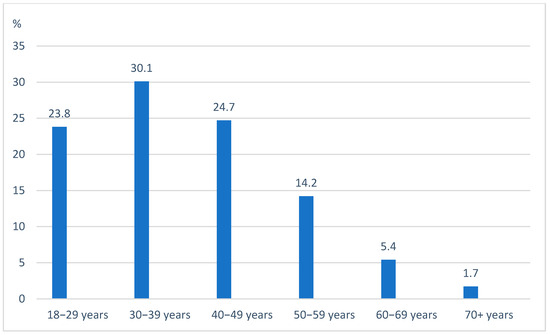
Figure 1.
Age by decades.
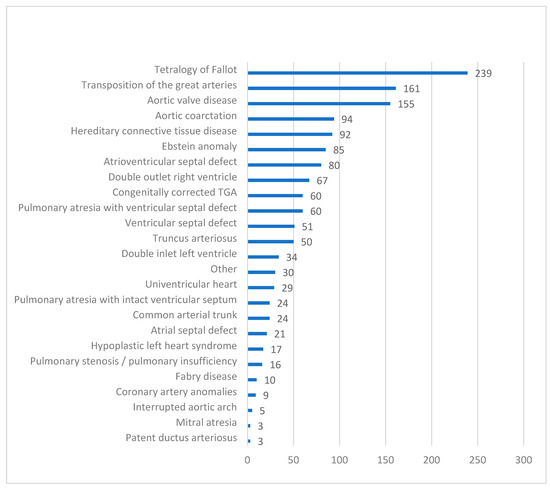
Figure 2.
Types of congenital heart defects. Bars show the number of patients.

Table 1.
Type and demographics of CHD.
3.2. Primary Cyanotic vs. Acyanotic Defects
Acyanotic CHD (n = 651; 45.9%) was slightly less frequent than primary cyanotic CHD (n = 768; 45.9% vs. 54.1%). Acyanotic patients were slightly older (mean 40.9 vs. 38.2 years) and more often female (49.5% vs. 46.9%).
3.3. Functional Status
According to Perloff’s functional classification, 91.5% of patients were in functional class (FC) I or II, indicating preserved daily function. Further, 8.2% were in FC III and 0.3% in FC IV. The modified Munich HF classification placed 0.4% in Class A (at risk), 29.7% in Class B (pre-HF), 68.8% in Class C (symptomatic HF), and 1.1% in Class D (advanced HF).
3.4. BMI Distribution
A total of 188 patients (13.3%) were classified as obese, highlighting a substantial burden of excess weight in this population. Additionally, 466 patients (32.8%) were overweight, 765 (53.9%) had normal weight, and 71 were underweight or cachectic.
3.5. BMI and Treatment Status
Across all treatment groups (treatment-naive, surgically repaired, and interventionally treated), overweight and obesity were prevalent (Table 2). Notably, patients who had undergone palliative surgery exhibited the highest proportion of overweight individuals (47.1%).

Table 2.
Surgical treatment status.
3.6. Systemic Ventricular Morphology
Of the patients, 79.8% exhibited a left-systemic ventricle, while 9.9% had a right-systemic ventricle and 10.3% a univentricular anatomy. Weight distribution varied by the pathologic anatomy of the systemic ventricle. Patients with morphologic right or left systemic ventricles showed higher rates of overweight and obesity, while patients with univentricular circulation had the highest rate of normal weight (Table 3).

Table 3.
Systemic ventricle morphology.
3.7. Cardiac Comorbidities
Cardiac comorbidities were frequent, with aortopathies (manifest or at risk) being the most common, followed by arterial hypertension, arrhythmias, and pulmonary hypertension/Eisenmenger syndrome. Arterial hypertension was statistically significantly (p < 0.001) associated with overweight/obesity (Table 4).

Table 4.
Cardiac comorbidities.
3.8. Non-Cardiac Comorbidities
Non-cardiac comorbidities included in declining order are kidney disease, hypothyroidism, hyperuricemia, liver disease, hyperlipidaemia, neurological disorders, and anemia. A strong association was observed between overweight/obesity and sleep apnea syndrome, as well as with diabetes mellitus (both p < 0.001) (Table 5).

Table 5.
Non-Cardiac comorbidities.
3.9. Pharmacotherapy
A total of 206 patients were not receiving HF-specific medication. In the remaining cohort, overweight or obese patients were treated with angiotensin II receptor blockers (AT1 blockers; p = 0.005), diuretics (p = 0.014), and SGLT2 inhibitors (p = 0.040). Additionally, anticoagulants—such as vitamin K antagonists, non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants (NOACs), and acetylsalicylic acid (ASA)—were more common in overweight/obese patients (Table 6).

Table 6.
Medications.
4. Discussion
The PATHFINDER-CHD Registry was established in response to a notable gap in the scientific and clinical discourse: while obesity is firmly established as a major cardiovascular risk factor in general cardiology, its relevance in the context of adult congenital heart disease has only recently garnered scientific attention. A targeted literature review confirms that this topic has been more intensively addressed within the last decade, with overall limited published evidence to date [16]. Reported prevalence rates for obesity in the ACHD populations vary substantially, ranging from 7% to 26%, while rates of overweight status lie between 22% and 53% depending on study design, patient cohort, and geographic region [7,16,17]. There are no data on obesity in ACHD with different stages of HF.
In contrast to this emerging epidemiological data, current ACHD guidelines still reflect a surprising lack of engagement with the issue. Neither the 2018 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Adults With Congenital Heart Disease [2] nor the 2020 ESC Guidelines [3] include specific recommendations on the assessment, monitoring, or management of obesity in ACHD patients. At best, obesity is mentioned in passing, without substantive discussion of its implications for pathophysiology, prognosis, or therapy.
This neglect is particularly striking when compared to general HF guidelines, where obesity is consistently recognized as a key modifiable risk factor that influences disease onset, progression, and treatment outcomes [18,19]. In contrast, ACHD care has largely overlooked this issue, likely due to the outdated perception that congenital heart defects are primarily pediatric conditions and that adult survivors form a small, exceptional group. Yet this perspective no longer holds: more than 350,000 ACHD patients live in Germany, and an estimated 50 million worldwide [5], with most surviving into adulthood and accumulating additional comorbidities over time.
Studies from Europe and North America consistently show that ACHD—especially those with simple or moderately complex defects—face a comparable or even elevated burden of obesity and associated cardiometabolic risk factors, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes mellitus [20,21,22]. Yet, lifestyle counselling and structured weight management are rarely incorporated into their routine follow-up. In a large multicenter study from the German National Register for Congenital Heart Defects, over 50% of ACHD were classified as overweight or obese, while targeted preventive measures were inconsistently applied [23].
The findings from the PATHFINDER-CHD Registry corroborate these observations in a systematically documented, real-world cohort. Nearly half of the included ACHD with HF were overweight or obese (46.1%), with overweight alone affecting one-third of the cohort. This prevalence is consistent with prior international reports [17,24] and highlights the need for structured obesity screening and intervention as part of ACHD care.
Importantly, in PATHFINDER-CHD, BMI was significantly associated with cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidities such as arterial hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, and diabetes mellitus—conditions known to aggravate HF and compromise long-term outcomes [7,25].
Pharmacological treatment patterns varied significantly with BMI. Overweight and obese patients were more frequently treated with SGLT2 inhibitors, diuretics, and AT blockers, suggesting a greater therapeutic need and/or proactive clinical management in these patients. However, whether these prescribing patterns translate into improved clinical outcomes remains to be determined and warrants further investigation.
An interesting finding of the present analysis is the lower prevalence of overweight and obesity among patients with cyanotic CHD, who were more frequently of normal weight. This observation may reflect underlying pathophysiological differences, including altered energy expenditure, chronic hypoxemia, or reduced nutritional intake in this subgroup [26]. Similarly, patients with univentricular circulation demonstrated the lowest rates of excess weight, further supporting the notion that anatomical and hemodynamic characteristics may significantly influence metabolic phenotypes in ACHD.
While these cross-sectional associations are noteworthy, their clinical relevance remains to be fully elucidated. It is currently unclear to what extent variations in BMI or body composition impact long-term outcomes such as hospitalization rates, exercise capacity, or mortality in this heterogeneous patient population. To address these questions, prospective longitudinal studies are essential.
5. Limitations
While the PATHFINDER-CHD Registry offers rich data from ACHD-certified tertiary care centers, the generalizability of its findings may be limited to this setting. Patients treated in high-volume, specialized ACHD centers may not reflect the broader population managed in general or less specialized settings. Additionally, the registry lacks direct measurement of body composition; reliance on BMI alone may underestimate adiposity, particularly in patients with altered body habitus, such as those with connective tissue disorders [25]. Future analyses will benefit from including alternative anthropometric indices, such as waist circumference, waist-to-height ratio, or bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) [27], which may offer improved risk stratification [10,28].
Furthermore, the cross-sectional design of the current analysis precludes causal inferences. Longitudinal data are necessary to better understand the impact of weight status on clinical outcomes.
Despite these limitations, this study represents a crucial step toward understanding the burden of obesity in ACHD with HF and offers a foundation for developing targeted interventions to improve long-term outcomes.
6. Conclusions
The PATHFINDER-CHD Registry reveals a high prevalence of overweight and obesity among ACHD and HF. These findings underscore the complex interplay between anatomical, functional, and metabolic factors in this vulnerable patient population. Elevated BMI was significantly associated with a range of cardiac and non-cardiac comorbidities and influenced treatment patterns, suggesting a substantial burden on healthcare systems and individual prognosis.
Given the limited evidence base in this field, our data provide an important foundation for future interventional studies, for example, those investigating pharmacological therapies now available to support weight loss. They also support the urgent need for individualized preventive strategies, lifestyle interventions, and multidisciplinary care models that address weight-related issues in ACHD. The implementation of structured weight management should become a standard component of ACHD follow-up, particularly in patients with additional risk factors for cardiovascular deterioration.
The underrepresentation of obesity in current clinical guidelines and the scarcity of dedicated interventions reflect a broader deficiency in integrating cardiometabolic risk management into congenital cardiology. Addressing this gap requires both a paradigm shift in clinical care and a stronger scientific focus on the intersection between CHD, obesity, and heart failure in adult populations. The present study contributes to this emerging field and highlights the urgent need for updated clinical guidelines, targeted research, and individualized therapeutic strategies. Prophylactic measures to avoid obesity should be implemented much earlier in the patient’s life course.
In sum, PATHFINDER-CHD offers critical insights into the real-world health profiles of ACHD with HF and should stimulate the development of new standards of care that incorporate metabolic health as a central therapeutic goal.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.D.P., H.K., S.F., L.B.P. and B.A.P.; data curation, S.F. and M.N.S.; formal analysis, F.K.; funding acquisition, H.K.; investigation, R.D.P., H.K., A.F., S.A., G.B., O.D., P.E., A.E., S.F., J.H., S.F., M.H., A.-S.K.-S., L.B.P., R.K., F.M., N.N., R.C.N., W.S., B.A.P., E.U., F.v.S., F.H. and M.N.S.; methodology, R.D.P., H.K., A.F., S.F., F.K. and M.N.S.; project administration, H.K.; resources, H.K., S.A., G.B., O.D., P.E., A.E., J.H., S.H., M.H., A.-S.K.-S., R.K., F.M., N.N., W.S., E.U., R.C.N., F.v.S. and F.H.; software, F.K.; supervision, H.K.; writing—original draft, R.D.P.; writing—review and editing, H.K., A.F., S.A., G.B., O.D., P.E., A.E., S.F., J.H., S.H., M.H., A.-S.K.-S., L.B.P., R.K., F.K., F.M., N.N., R.C.N., W.S., B.A.P., E.U., F.v.S., F.H. and M.N.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the German Heart Foundation (“Deutsche Herzstiftung e.V.”), the patient organization “Herzkind e.V.”, the “Förderverein Deutsches Herzzentrum München e.V.”, and “Gesellschaft für Prävention e.V. (GPeV)”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committees of Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nürnberg (Ref: 23-460-Bn) and the Technical University of Munich (Ref: 2022–582-S-KH, 21 November 2022), with additional further local approvals obtained as required.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Researchers or clinical centers interested in accessing the dataset for collaborative analyses are encouraged to contact the principal investigators. Data sharing will be considered in accordance with applicable data protection regulations and study governance.
Acknowledgments
This article is a revised and expanded version of a paper entitled “Overweight and Obesity in Operated and Unoperated Adults with Congenital Heart Disease and Heart Failure (ACHD-HF)”, which was presented at Congress of the German Society for Cardiac and Thoracic Surgery, Hamburg, Germany on 15 February 2025 [29] and at the Annual Meeting of the German Society of Cardiology on 24 April 2025 [30]. We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the dedicated study team at the German Heart Center Munich and the other participating centers for their important contributions and the provision of high-quality data that made this analysis possible. We gratefully acknowledge the generous support of the German Heart Foundation, Herzkind e.V., the Association for the Promotion of the German Heart Center Munich, the Axe Foundation, the Manfred Roth Foundation in Fürth, and the German Pension Insurance Rheinland. Their contributions have been instrumental in advancing academic research and education in the field of congenital heart defects in adulthood.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ACHD | Adult Congenital Heart Disease |
| ASA | Acetylsalicylic Acid |
| AT1 blockers | Angiotensin II Receptor Type 1 Blockers |
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| ACC | American College of Cardiology |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CHD | Congenital Heart Disease |
| EDC | Electronic Data Capture |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| FC | Functional Class (Perloff Classification) |
| GDPR | General Data Protection Regulation |
| GPP | Good Pharmacoepidemiology Practice |
| GPS | Good Practice in Secondary Data Analysis |
| HF | Heart Failure |
| MUC-HF-Class | Munich Heart Failure Classification for Congenital Heart Disease |
| NOACs | Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants |
| PATHFINDER-CHD | Patients with Heart Failure Due to Congenital Heart Disease (Registry) |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors |
References
- Bhatt, A.B.; Foster, E.; Kuehl, K.; Alpert, J.; Brabeck, S.; Crumb, S.; Davidson, W.R.; Earing, M.G.; Ghoshhajra, B.B.; Karamlou, T.; et al. Congenital Heart Disease in the Older Adult. Circulation 2015, 131, 1884–1931. [Google Scholar]
- Stout, K.K.; Daniels, C.J.; Aboulhosn, J.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Broberg, C.S.; Colman, J.M.; Crumb, S.R.; Dearani, J.A.; Fuller, S.; Gurvitz, M.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Adults with Congenital Heart Disease: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1494–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, H.; De Backer, J.; Babu-Narayan, S.V.; Budts, W.; Chessa, M.; Diller, G.P.; Lung, B.; Kluin, J.; Lang, I.M.; Meijboom, F.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of adult congenital heart disease: The Task Force for the management of adult congenital heart disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 563–645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaemmerer, H.; Diller, G.P.; Dähnert, I.; Eichstaedt, C.A.; Eicken, A.; Freiberger, A.; Freilinger, S.; Geiger, R.; Gorenflo, M.; Grünig, E.; et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in congenital heart disease—Part I. Pneumol. Stuttg. Ger. 2023, 77, 956–961. [Google Scholar]
- Henning, R.J. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with congenital heart disease. Future Cardiol. 2020, 16, 317–342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freilinger, S.; Kaemmerer, H.; Pittrow, R.D.; Achenbach, S.; Baldus, S.; Dewald, O.; Ewert, P.; Freiberger, A.; Gorenflo, M.; Harig, F.; et al. PATHFINDER-CHD: Prospective registry on adults with congenital heart disease, abnormal ventricular function, and/or heart failure as a foundation for establishing rehabilitative, prehabilitative; preventive, and health-promoting measures: Rationale, aims, design and methods. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2024, 24, 181. [Google Scholar]
- Papazoglou, A.S.; Kyriakoulis, K.G.; Barmpagiannos, K.; Moysidis, D.V.; Kartas, A.; Chatzi, M.; Baroutidou, A.; Kamperidis, V.; Ziakas, A.; Dimopoulos, K.; et al. Atherosclerotic risk factor prevalence in adults with congenital heart disease: A meta-analysis. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2024, 3, 101359. [Google Scholar]
- Arnaert, S.; De Meester, P.; Troost, E.; Droogne, W.; Van Aelst, L.; Van Cleemput, J.; Voros, G.; Gewillig, M.; Cools, B.; Moons, P.; et al. Heart failure related to adult congenital heart disease: Prevalence; outcome and risk factors. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 2940–2950. [Google Scholar]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar]
- Freilinger, S.; Suleiman, M.N.; Bischoff, G.; Ewert, P.; Freiberger, A.; Huntgeburth, M.; Kaemmerer, A.S.; Schopen, J.; Meierhofer, C.; Nagdyman, N.; et al. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis as a Contemporary Biomarker of Obesity in Adults with Marfan- or Loeys-Dietz-Syndrome. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittrow, R.D.; Dewald, O.; Harig, F.; Kaemmerer-Suleiman, A.S.; Suleiman, M.; Pittrow, L.B.; Achenbach, S.; Freiberger, A.; Freilinger, S.; Pittrow, B.A.; et al. Establishing a cardiology registry: Navigating quality and regulatory challenges with a focus on congenital heart disease. Cardiovasc. Diagn Ther. 2025, 15, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perloff, J.K.; Child, J.S.; Aboulhosn, J. Congenital Heart Disease in Adults, 3rd ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Report of a WHO Consultation on Obesity. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- Public Policy Committee IS of, P. Guidelines for good pharmacoepidemiology practice (GPP). Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2016, 25, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alegria, E.; Gothe, H.; Geyer, S.; Jaunzeme, J.; Maier, M.; Grobe, T.; Ihle, P. [Good Practice of Secondary Data Analysis (GPS): Guidelines and recommendations]. Das Gesundheitswesen 2015, 77, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Willinger, L.; Brudy, L.; Meyer, M.; Oberhoffer-Fritz, R.; Ewert, P.; Müller, J. Overweight and Obesity in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9931. [Google Scholar]
- Vangedal, M.S.K.; Thuraiaiyah, J.; Joergensen, T.H.; Solis, A.; Langsted, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Kistorp, C.; Raunsoe, J.; Schmiegelow, S.S.; Aplin, M.; et al. Prevalence of obesity among adult patients with congenital heart disease: A population-based study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2025, 431, 133247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhmm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4901. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.D.; Ryan, D.H.; Apovian, C.M.; Ard, J.D.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Donato, K.A.; Hu, F.B.; Hubbard, V.S.; Jakicic, J.M.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS Guideline for the Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2985–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, J.B.; Parness, I.A.; Shenoy, R.U. Body Weights in Adults With Congenital Heart Disease and the Obesity Frequency. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 119, 638–642. [Google Scholar]
- Deen, J.F.; Krieger, E.V.; Slee, A.E.; Arslan, A.; Arterburn, D.; Stout, K.K.; Portman, M.A. Metabolic Syndrome in Adults With Congenital Heart Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e001132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cruz, E.; Manzur-Sandoval, D.; Gopar-Nieto, R.; Plata-Corona, J.C.; Montalvo-Ocotoxtle, I.G.; Navarro-Martinez, D.A.; Mier Y Terán-Morales, E.; Rivera-Buendía, F.; Antonio-Villa, N.E.; García-González, N.E.; et al. Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Mexican Adults With Congenital Heart Disease. JACC Adv. 2023, 2, 100596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, U.M.M.; Körten, M.-A.; Diller, G.-P.; Helm, P.; Baumgartner, H.; Ewert, P.; Tutarel, O. Cardiovascular risk factors in adults with congenital heart defects—Recognised but not treated? An analysis of the German National Register for Congenital Heart Defects. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 277, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.; Rodriquez, E.; Fernandes, S. Prevalence of obesity in adults with congenital heart disease [abstract]. In Proceedings of the Fifth National Conference Adult Congenital Heart Association, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1–4 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton, V.L.; McCrindle, B.W.; Barkin, S.; Daniels, S.R.; Barlow, S.E.; Binns, H.J.; Cohen, M.S.; Economos, C.; Faith, M.S.; Gidding, S.S.; et al. Report of the National Heart; Lung; and Blood Institute’s Working Group on Obesity and Other Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Congenital Heart Disease Pemberton-Obesity in CHD WG Report. Circulation 2010, 121, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brida, M.; Dimopoulos, K.; Kempny, A.; Liodakis, E.; Alonso-Gonzalez, R.; Swan, L.; Uebing, A.; Baumgartner, H.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Diller, G.P.; et al. Body mass index in adult congenital heart disease. Heart Br. Card. Soc. 2017, 103, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Maïmoun, L.; Alonso, S.; Mahadea, K.K.; Dubois, J.; Paunet, T.; Kucharczak, F.; Nande, L.M.; Boudousq, V.; Mura, T.; Mariano-Goulart, D.; et al. Cross-calibration of areal bone mineral densities and body composition between DMS Stratos and Hologic Horizon A dual-energy X-ray absorptiometers: The effect of body mass index. J. Clin. Densitom. Off. J. Int. Soc. Clin. Densitom. 2024, 28, 101553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.; Cummings, D.E.; Eckel, R.H.; Cohen, R.V.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Brown, W.A.; Stanford, F.C.; Batterham, R.L.; Farooqi, I.S.; Farpour-Lambert, N.J.; et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of clinical obesity. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittrow, R.D.; Harig, F.; Dewald, O.; Pittrow, L.B.; Kaemmerer, H.; Achenbach, S.; Bischoff, G.; Ewert, P.; Freiberger, A.; Hörer, J.; et al. Overweight and Obesity in Operated and Unoperated Adults with Congenital Heart Disease and Heart Failure (ACHD-HF). In Proceedings of the Congress of the German Society for Cardiac and Thoracic Surgery, Hamburg, Germany, 15 February 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Pittrow, R.D.; Harig, F.; Dewald, O.; Pittrow, L.B.; Kaemmerer, H.; Achenbach, S.; Bischoff, G.; Ewert, P.; Freiberger, A.; Hörer, J.; et al. Übergewicht und Adipositas bei operierten und nicht operierten Erwachsenen mit angeborenen Herzfehlern und Herzinsuffizienz (ACHD-HF). In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the German Society of Cardiology, Mannheim, Germany, 24 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).