Effectiveness of Vortioxetine in Relieving Chronic Pain in Patients with Associated Depression in a Spanish Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Study Assessments
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population
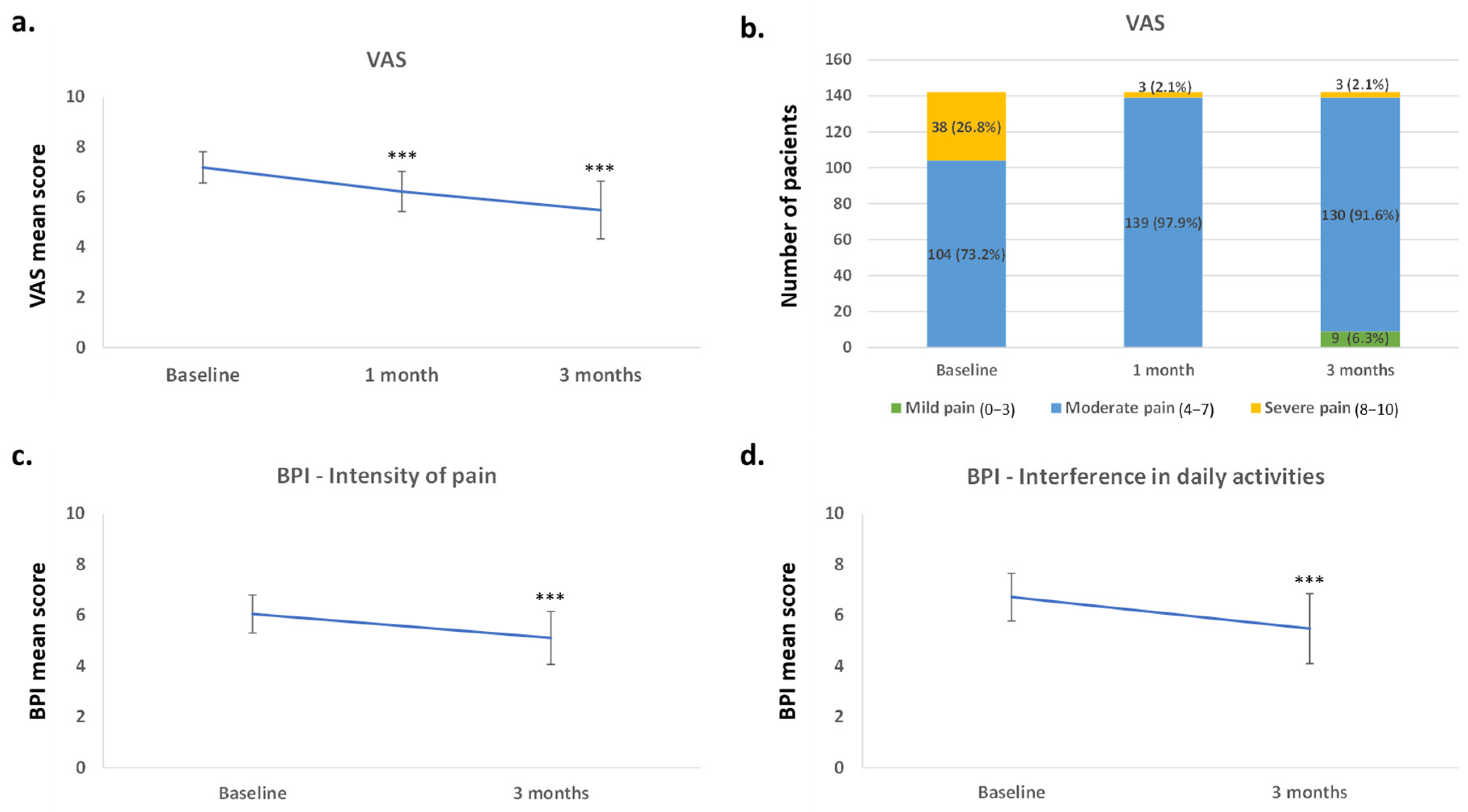
3.2. Effect of Vortioxetine on Pain
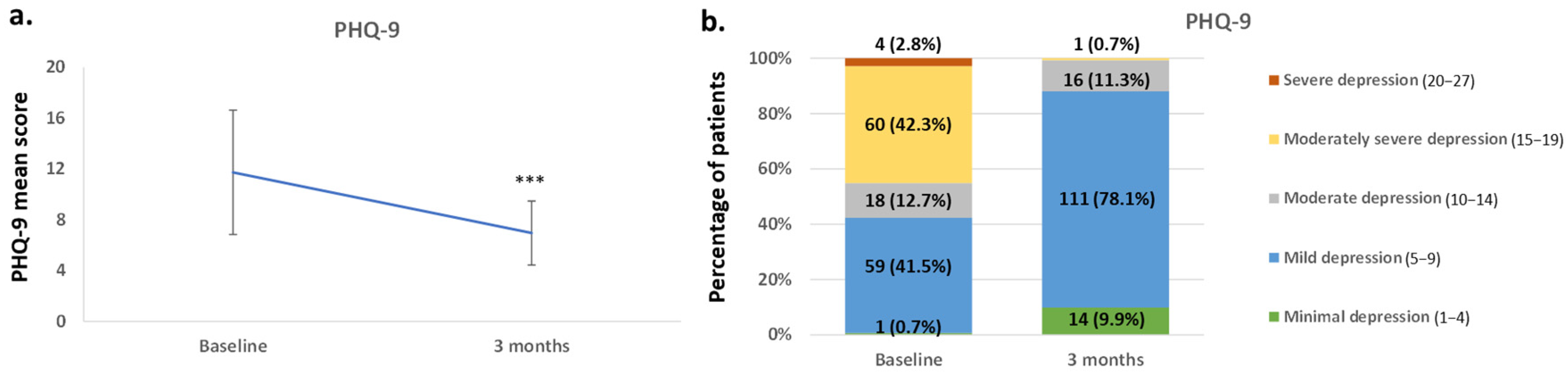
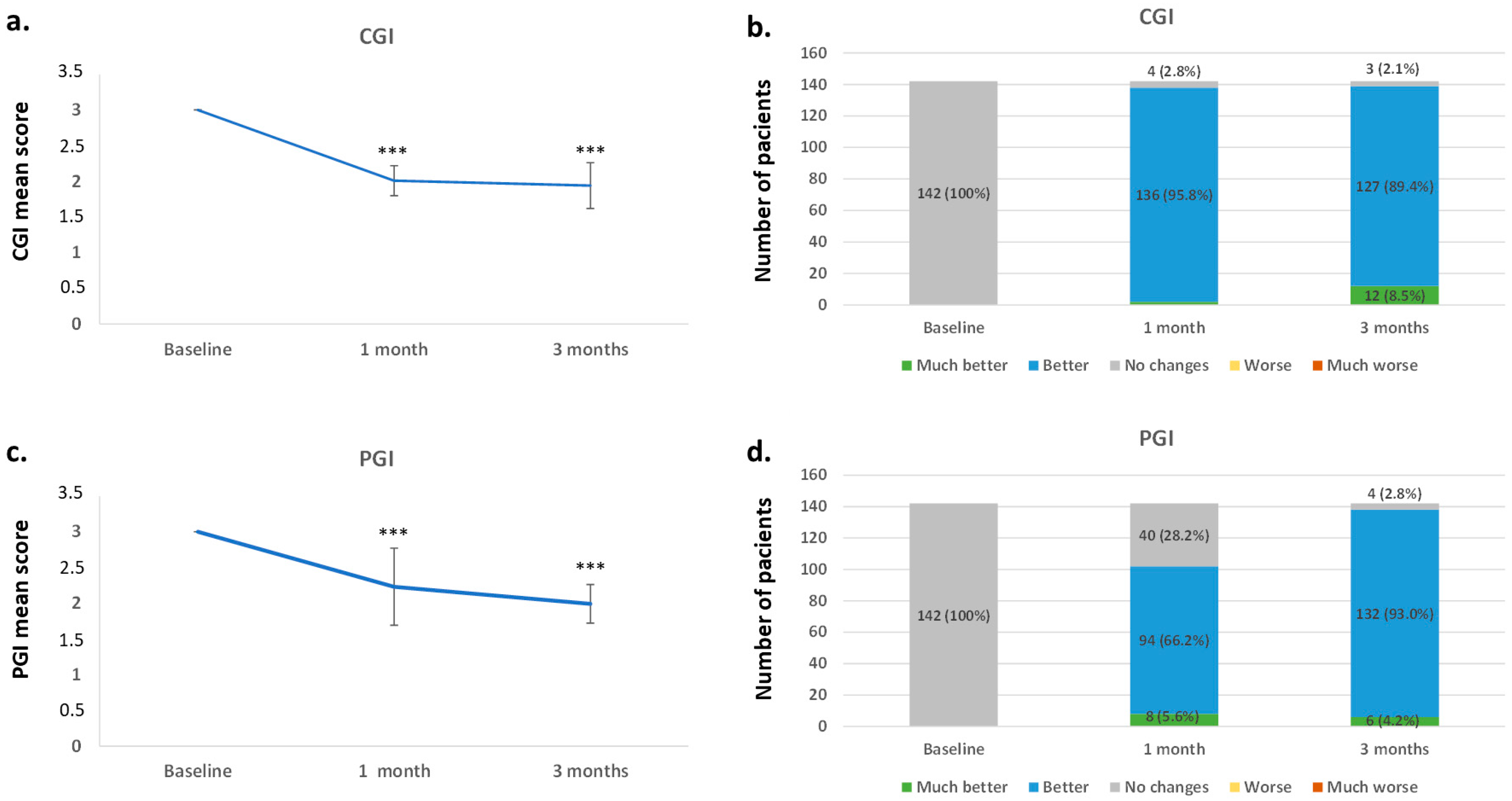
3.3. Effect of Vortioxetine in the Overall Disease Severity and on Depressive Symptoms
3.4. Safety, Tolerability, and Acceptance
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Treede, R.D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. A classification of chronic pain for ICD-11. Pain 2015, 156, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.S.; McGee, S.J. Pain as a global public health priority. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhang, X. The Link between Depression and Chronic Pain: Neural Mechanisms in the Brain. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 9724371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara Montero, A.; Pacheco de Vasconcelos, S.R. Role of vortioxetine in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Rev. Esp. Anestesiol. Reanim. 2022, 69, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrits, M.M.J.G.; Van Oppen, P.; Van Marwijk, H.W.J.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Van Der Horst, H.E. Pain and the onset of depressive and anxiety disorders. Pain 2014, 155, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerwijk, E.L.; Ford, J.M.; Weiss, S.J. Brain regions associated with psychological pain: Implications for a neural network and its relationship to physical pain. Brain Imaging Behav. 2013, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango-Dávila, C.A.; Rincón-Hoyos, H.G. Depressive Disorder, Anxiety Disorder and Chronic Pain: Multiple Manifestations of a Common Clinical and Pathophysiological Core. Rev. Colomb. Psiquiatr. 2018, 47, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, P.; Bitter, I.; Svestka, J.; Seifritz, E.; Karamustafalioglu, O.; Koponen, H.; Sartorius, N. Management of depression in the presence of pain symptoms. Psychiatr. Danub. 2010, 22, 4–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dogrul, A.; Ossipov, M.H.; Porreca, F. Differential mediation of descending pain facilitation and inhibition by spinal 5HT-3 and 5HT-7 receptors. Brain Res. 2009, 1280, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Rygh, L.J.; Dickenson, A.H. Bad news from the brain: Descending 5-HT pathways that control spinal pain processing. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, M.J.; Robinson, R.L.; Katon, W.; Kroenke, K. Depression and Pain Comorbidity. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 2433–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouzam, H.R. Psychopharmacology of chronic pain: A focus on antidepressants and atypical antipsychotics. Postgrad. Med. 2016, 128, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, D.; Pecoraro, G.; Aria, M.; Favia, G.; Mignogna, M.D. Vortioxetine in the treatment of mood disorders associated with burning mouth syndrome: Results of an open-label, flexible-dose pilot study. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 1168–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, P.A.; Martins, C.C.; Miranda, G.; de Souza, M.E.; Silva, E.; Abreu, M.d. Use of antidepressants in dentistry: A systematic review. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2018, 38, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Sindrup, S.H.; Jensen, T.S. The evidence for pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain 2010, 150, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanpää, M.L.; Gourlay, G.K.; Kent, J.L.; Miaskowski, C.; Raja, S.N.; Schmader, K.E.; Wells, C.D. Treatment considerations for patients with neuropathic pain and other medical comorbidities. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saarto, T.; Wiffen, P.J. Antidepressants for neuropathic pain: A Cochrane review. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 1372–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, D.S.; Chrones, L.; Florea, I.; Nielsen, R.; Nomikos, G.G.; Palo, W.; Reines, E. The safety and tolerability of vortioxetine: Analysis of data from randomized placebo-controlled trials and open-label extension studies. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA. Brintellix—Ficha Técnica/Resumen de las Características del Producto [Internet]. European Medical Agency. 2018. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/pdfs/es/p/113891010/P_113891010.html.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- CIMA. PROSPECTO Brintellix 10 mg Comprimidos Recubiertos con Pelicula [Internet]. Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS). 2023. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/dochtml/p/113891010/P_113891010.html (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Alvarez, E.; Perez, V.; Artigas, F. Pharmacology and clinical potential of vortioxetine in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2014, 10, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.C.; Schmidt, S.N.; Grande, I. Effectiveness of vortioxetine in patients with major depressive disorder and early-stage dementia: The MEMORY study. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 338, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattingly, G.W.; Ren, H.; Christensen, M.C.; Katzman, M.A.; Polosan, M.; Simonsen, K.; Hammer-Helmich, L. Effectiveness of Vortioxetine in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder in Real-World Clinical Practice: Results of the RELIEVE Study. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 824831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieta, E.; Sluth, L.B.; Olsen, C.K. The effects of vortioxetine on cognitive dysfunction in patients with inadequate response to current antidepressants in major depressive disorder: A short-term, randomized, double-blind, exploratory study versus escitalopram. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 227, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porreca, F.; Ossipov, M.H.; Gebhart, G.F. Chronic pain and medullary descending facilitation. Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, A.; Furukawa, T.A.; Salanti, G.; Chaimani, A.; Atkinson, L.Z.; Ogawa, Y.; Leucht, S.; Ruhe, H.G.; Turner, E.H.; Higgins, J.P.T.; et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet 2018, 391, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adair, M.; Cronquist Christensen, M.; Florea, I.; Loft, H.; Fagiolini, A. Vortioxetine in patients with major depressive disorder and high levels of anxiety symptoms: An updated analysis of efficacy and tolerability. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 328, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, D.S.; Florea, I.; Jacobsen, P.L.; Zhong, W.; Nomikos, G.G. A meta-analysis of the efficacy of vortioxetine in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) and high levels of anxiety symptoms. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 206, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokka, P.; Ge, H.; Bougie, J.; Ettrup, A.; Clerzius, G. Anxiety symptoms in working patients with major depressive disorder treated with vortioxetine: Associations with clinical and treatment outcomes in the AtWoRC study. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. Orig. 2021, 11, 20451253211013148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baune, B.T.; Sluth, L.B.; Olsen, C.K. The effects of vortioxetine on cognitive performance in working patients with major depressive disorder: A short-term, randomized, double-blind, exploratory study. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 229, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, D.; Pecoraro, G.; Coppola, N.; Calabria, E.; Aria, M.; Mignogna, M. Vortioxetine versus other antidepressants in the treatment of burning mouth syndrome: An open-label randomized trial. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1022–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micov, A.M.; Tomić, M.A.; Todorović, M.B.; Vuković, M.J.; Pecikoza, U.B.; Jasnic, N.I.; Djordjevic, J.D.; Stepanović-Petrović, R.M. Vortioxetine reduces pain hypersensitivity and associated depression-like behavior in mice with oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 103, 109975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuena, A.R.; Maftei, D.; Alemà, G.S.; Dal Moro, F.; Lattanzi, R.; Casolini, P.; Nicoletti, F. Multimodal antidepressant vortioxetine causes analgesia in a mouse model of chronic neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918808987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, S.M. Modes and nodes explain the mechanism of action of vortioxetine, a multimodal agent (MMA): Enhancing serotonin release by combining serotonin (5HT) transporter inhibition with actions at 5HT receptors (5HT1A, 5HT1B, 5HT1D, 5HT7 receptors). CNS Spectr. 2015, 20, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelliny, M.; Croarkin, P.E.; Moore, K.M.; Bobo, W.V. Profile of vortioxetine in the treatment of major depressive disorder: An overview of the primary and secondary literature. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 1193–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch Ibáñez, J.; Vargas Domingo, M.; Coma Alemany, J.; Callao Sánchez, R.; Guitart Vela, J. Effectiveness of Vortioxetine in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Associated with Chronic Pain: An Observational Study in a Spanish Population. Pain Ther. 2024, 13, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couper, M.P.; Tourangeau, R.; Conrad, F.G.; Singer, E. Evaluating the effectiveness of visual analog scales: A web experiment. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 2006, 24, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleeland, C.S. The Brief Pain Inventory. MD Anderson Cancer Center. Available online: https://www.mdanderson.org/research/departments-labs-institutes/departments-divisions/symptom-research/symptom-assessment-tools/brief-pain-inventory.html (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Kroenke, K.; Spitzer, R.L.; Williams, J.B.W. The PHQ-9: Validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2001, 16, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, J.; Monsalve, V. CAD: Cuestionario de afrontamiento ante el dolor crónico. Rev. la Soc. Esp. del Dolor 2002, 9, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Guy, W. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology; Rev. ed. D.; U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare; Public Health Service; Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental HealthAdministration; National Institute of Mental Health; PsychopharmacologyResearch Branch; Division of Extramural Research Programs: Rockville, MD, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Busner, J.; Targum, S.D. Global impressions scale: Applying a research Tool in Clinical Practice. Psychiatry 2007, 4, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, M.A.; Pardo, A.; Rejas, J.; Soto, J.; Villasante, F.; Aranguren, J.L. Development and validation of the “treatment satisfaction with medicines questionnaire” (SATMED-Q)©. Value Health 2008, 11, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Male/Female | 31 (21.8%)/111 (78.2%) |
| Employment status | |
| Total | 142 (100.0%) |
| Active | 58 (40.8%) |
| Unemployed | - |
| Medical leave | 5 (3.5%) |
| Permanent incapacity for work | - |
| Retired | 79 (55.6%) |
| Comorbidities | |
| With any comorbidity | 132 (93.0%) |
| AHT | 94 (66.2%) |
| Osteoporosis | 54 (38.0%) |
| Hypothyroidism | 21 (14.8%) |
| Cardiovascular disease | 19 (13.4%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 16 (11.3%) |
| Prostate pathology | 6 (4.2%) |
| Respiratory disease | 6 (4.2%) |
| Hyperthyroidism | 1 (0.7%) |
| Other | 1 (0.7%) |
| Intensity of the pain | |
| No pain | - |
| Mild | - |
| Moderate | 6 (4.2%) |
| Severe | 132 (93.0%) |
| Unbearable | 3 (2.1%) |
| Missing | 1 (0.7%) |
| Location of the pain | |
| Lower extremities | 98 (69.0%) |
| Lumbar | 92 (64.8%) |
| Shoulders | 19 (13.14%) |
| Head neck | 7 (4.9%) |
| Dorsal | 4 (2.8%) |
| Upper extremities | 4 (2.8%) |
| Type of pain | |
| Somatic | 2 (1.4%) |
| Visceral | - |
| Neuropathic | 6 (4.2%) |
| Mixed | 134 (94.4%) |
| Psychogenic | 2 (1.4%) |
| Others | 3 (2.1%) |
| Main cause of chronic pain | |
| Lumbosciatica | 61 (43.0%) |
| Arthrosis | 58 (40.8%) |
| Degenerative problems of the spine | 46 (32.4%) |
| Fibromyalgia | 13 (9.2%) |
| Peripheral neuropathy | 7 (4.9%) |
| Herpes zoster | 3 (2.1%) |
| Complex regional syndrome | 1 (0.7%) |
| Tumor | - |
| Visceral | - |
| Other | 1 (0.7%) |
| Time of evolution | |
| >3 months and <12 months | 48 (33.8%) |
| >12 months and <24 months | 30 (21.1%) |
| >2 years and <5 years | 45 (31.7%) |
| >5 years | 19 (13.4%) |
| Previous treatments for depression | |
| Escitalopram | 39 (27.5%) |
| Duloxetine | 31 (21.8%) |
| Citalopram | 19 (13.4%) |
| Venlafaxine | 15 (10.6%) |
| Amitriptyline | 11 (7.7%) |
| Sertraline | 7 (4.9%) |
| Bupropion | 4 (2.8%) |
| Paroxetine | 1 (0.7%) |
| Fluoxetine | 1 (0.7%) |
| Variable | n (%) |
|---|---|
| PHQ-9 | |
| Minimum depression (1–4) | 1 (0.7%) |
| Mild depression (5–9) | 59 (41.5%) |
| Moderate depression (10–14) | 18 (12.7%) |
| Moderately severe depression (15–19) | 60 (42.3%) |
| Severe depression (20–27) | 4 (2.8%) |
| VAS | |
| Mild pain (0–3) | - |
| Moderate pain (4–7) | 104 (73.2%) |
| Severe pain (8–10) | 38 (26.8%) |
| Vortioxetine 5 mg/day n (%) | Vortioxetine 10 mg/day n (%) | Vortioxetine 15 mg/day n (%) | Vortioxetine 20 mg/day n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (n = 142) | - | 142 (100) | - | - |
| 1 month (n = 142) | - | 136 (95.77) | - | 6 (4.23) |
| 3 months (n = 142) | - | 136 (95.77) | - | 6 (4.23) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Folch Ibáñez, J.; Vargas Domingo, M.; Coma Alemany, J.; Callao Sánchez, R.; Guitart Vela, J. Effectiveness of Vortioxetine in Relieving Chronic Pain in Patients with Associated Depression in a Spanish Population. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134487
Folch Ibáñez J, Vargas Domingo M, Coma Alemany J, Callao Sánchez R, Guitart Vela J. Effectiveness of Vortioxetine in Relieving Chronic Pain in Patients with Associated Depression in a Spanish Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134487
Chicago/Turabian StyleFolch Ibáñez, Jordi, Maribel Vargas Domingo, Joan Coma Alemany, Roger Callao Sánchez, and Jordi Guitart Vela. 2025. "Effectiveness of Vortioxetine in Relieving Chronic Pain in Patients with Associated Depression in a Spanish Population" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134487
APA StyleFolch Ibáñez, J., Vargas Domingo, M., Coma Alemany, J., Callao Sánchez, R., & Guitart Vela, J. (2025). Effectiveness of Vortioxetine in Relieving Chronic Pain in Patients with Associated Depression in a Spanish Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134487





