Medulloblastoma in Adolescents and Young Adults (AYA): Bridging Pediatric Paradigms and Adult Oncology Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiological Characteristics and Tumor Biology
3. Evolution of Pediatric Treatment Protocols
4. Adult-Focused Treatment Approaches
5. Contemporary Research Initiatives and Clinical Trials
6. Unique Challenges in AYA Management
6.1. Clinical Presentation and Diagnostic Delays
6.2. Molecular and Biological Distinctions
6.3. Treatment-Related Toxicity and Long-Term Sequelae
6.4. Clinical Trial Access and Participation Barriers
6.5. Survivorship Care and Care Transition
7. Enhancing Pediatric–Adult Oncology Collaboration
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACNS | A Children’s Oncology Group study designation |
| AMBUSH | Adult Medulloblastoma Study |
| AYA | Adolescents and Young Adults |
| BTG | Brain Tumor Group |
| CCG | Children’s Cancer Group |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| COG | Children’s Oncology Group |
| CSS | Cancer-Specific Survival |
| EORTC | European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer |
| ESMO | European Society for Medical Oncology |
| EURACAN | European Reference Network for Rare Adult Solid Cancers |
| Gy | Gray |
| HIT | Hirntumor (German brain tumor study group) |
| NCT | National Clinical Trial |
| NOA | Neuro-oncology Working Group |
References
- Cushing, H.; Bailey, P. Medulloblastoma cerebelli: A common type of midcerebellar glioma of childhood. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1925, 14, 192–224. [Google Scholar]
- Millard, N.E.; De Braganca, K.C. Medulloblastoma in children: A clinical perspective. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 37, 361–381. [Google Scholar]
- Brandes, A.A.; Franceschi, E.; Tosoni, A.; Reni, M.; Gatta, G.; Vecht, C.; Kortmann, R.D.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Oretti, L.; Spalek, M.; et al. Adult neuroectodermal tumors of posterior fossa (medulloblastoma) and of supratentorial sites (stPNET). Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2009, 71, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fern, L.A.; Whelan, J. National Cancer Research Institute teenage and young adult clinical studies group: The United Kingdom approach to research. Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2010, 22, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, L.A.; Hubbard, A.K.; Scheurer, M.E.; Spector, L.G.; Poynter, J.N. Trends in paediatric central nervous system tumour incidence by global region from 1988 to 2012. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 50, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Gittleman, H.; Patil, N.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2013-2017. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, iv1–iv96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordana, M.T.; Schiffer, P.; Lanotte, M.; Girardi, P.; Chio, A. Epidemiology of adult medulloblastoma. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, F.; Di Carlo, V.; Stiller, C.; Gatta, G.; Woods, R.R.; Visser, O.; Lacour, B.; Tucker, T.C.; Coleman, M.P.; Allemani, C.; et al. Global survival trends for brain tumors, by histology: Analysis of individual records for 67,776 children diagnosed in 61 countries during 2000-2014 (CONCORD-3). Neuro Oncol. 2023, 25, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y. Medulloblastoma: Current Perspectives and Recent Advances. Brain Tumor Res. Treat. 2023, 11, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, M.; Korshunov, A.; Remke, M.; Jones, D.T.; Schlanstein, M.; Northcott, P.A.; Cho, Y.J.; Koster, J.; Schouten-van Meeteren, A.; van Vuurden, D.; et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: An international meta-analysis of transcriptome, genetic aberrations, and clinical data of WNT, SHH, Group 3, and Group 4 medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.D.; Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Remke, M.; Cho, Y.J.; Clifford, S.C.; Eberhart, C.G.; Parsons, D.W.; Rutkowski, S.; Gajjar, A.; et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: The current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.M.G.; Remke, M.; Rampasek, L.; Peacock, J.; Shih, D.J.H.; Luu, B.; Garzia, L.; Torchia, J.; Nor, C.; Morrissy, A.S.; et al. Intertumoral heterogeneity within medulloblastoma subgroups. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 737–754.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vriend, J.; Liu, X.Q. Survival-Related Genes on Chromosomes 6 and 17 in Medulloblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hein, K.H.; Woo, W.L.; Rafiee, G. Integrative Machine Learning Framework for Enhanced Subgroup Classification in Medulloblastoma. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remke, M.; Hielscher, T.; Northcott, P.A.; Witt, H.; Ryzhova, M.; Wittmann, A.; Benner, A.; von Deimling, A.; Scheurlen, W.; Perry, A.; et al. Adult medulloblastoma comprises three major molecular variants. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2717–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalbe, E.C.; Lindsey, J.C.; Nakjang, S.; Crosier, S.; Smith, A.J.; Hicks, D.; Rafiee, G.; Hill, R.M.; Iliasova, A.; Stone, T.; et al. Novel molecular subgroups for clinical classification and outcome prediction in childhood medulloblastoma: A cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, H.J.G.; Wallace, E.N.K.; Henk, J.M. The treatment and prognosis of medulloblastoma in children: A study of 82 verified cases. Am. J. Roentgenol. Radium Ther. Nucl. Med. 1969, 105, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.J.; Sutton, L.N.; Elterman, R.; Lange, B.; Goldwein, J.; Nicholson, H.S.; Mulne, L.; Boyett, J.; D’Angio, G.; Wechsler-Jentzsch, K.; et al. Outcome for children with medulloblastoma treated with radiation and cisplatin, CCNU, and vincristine chemotherapy. J. Neurosurg. 1994, 81, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.E.; Jenkin, R.D.; Sposto, R.; Ortega, J.A.; Wilson, C.B.; Wara, W.; Ertel, I.J.; Kramer, S.; Chang, C.H.; Leikin, S.L.; et al. The treatment of medulloblastoma. Results of a prospective randomized trial of radiation therapy with and without CCNU, vincristine, and prednisone. J. Neurosurg. 1990, 72, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.C.; Gnekow, A.; Wellek, S.; Jones, M.; Round, C.; Brown, J.; Phillips, A.; Neidhardt, M.K. Prospective randomised trial of chemotherapy given before radiotherapy in childhood medulloblastoma. International Society of Paediatric Oncology (SIOP) and the (German) Society of Paediatric Oncology (GPO): SIOP II. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 1995, 25, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.E.; Bailey, C.C.; Robinson, K.; Weston, C.L.; Ellison, D.; Ironside, J.; Lucraft, H.; Gilbertson, R.; Tait, D.M.; Walker, D.A.; et al. Results of a randomized study of preradiation chemotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for nonmetastatic medulloblastoma: The International Society of Paediatric Oncology/United Kingdom Children’s Cancer Study Group PNET-3 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffner, P.K.; Horowitz, M.E.; Krischer, J.P.; Friedman, H.S.; Burger, P.C.; Cohen, M.E.; Sanford, R.A.; Mulhern, R.K.; James, H.E.; Freeman, C.R.; et al. Postoperative chemotherapy and delayed radiation in children less than three years of age with malignant brain tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.J.; Gajjar, A.; Vezina, G.; Rorke-Adams, L.; Burger, P.C.; Robertson, P.L.; Bayer, L.; LaFond, D.; Donahue, B.R.; Marymont, M.H.; et al. Phase III study of craniospinal radiation therapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy for newly diagnosed average-risk medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4202–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, A.; Chintagumpala, M.; Ashley, D.; Kellie, S.; Kun, L.E.; Merchant, T.E.; Woo, S.; Wheeler, G.; Ahern, V.; Krasin, M.J.; et al. Risk-adapted craniospinal radiotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy and stem-cell rescue in children with newly diagnosed medulloblastoma (St Jude Medulloblastoma-96): Long-term results from a prospective, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, C.; Beaugrand, A.; Pizer, B.; Micheli, J.; Aubelle, M.S.; Fourcade, A.; Couanet, D.; Laplanche, A.; Kalifa, C.; Grill, J. Metastatic medulloblastoma in childhood: Chang’s classification revisited. Int. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 245385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimino, M.; Biassoni, V.; Gandola, L.; Garrè, M.L.; Gatta, G.; Giangaspero, F.; Poggi, G.; Rutkowski, S. Childhood medulloblastoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 105, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Remke, M.; Bouffet, E.; Bailey, S.; Clifford, S.C.; Doz, F.; Kool, M.; Dufour, C.; Vassal, G.; Milde, T.; et al. Risk stratification of childhood medulloblastoma in the molecular era: The current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, A.L.; Moding, E.J.; Donaldson, S.S.; Gibbs, I.C.; Soltys, S.G.; Hiniker, S.M.; Pollom, E.L. Survival impact of postoperative radiotherapy timing in pediatric and adolescent medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.J.; Goldwein, J.; Nicholson, H.S.; Vezina, L.G.; Allen, J.C.; Ris, M.D.; Muraszko, K.; Rorke, L.B.; Wara, W.M.; Cohen, B.H.; et al. Treatment of children with medulloblastomas with reduced-dose craniospinal radiation therapy and adjuvant chemotherapy: A Children’s Cancer Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhern, R.K.; Kepner, J.L.; Thomas, P.R.; Armstrong, F.D.; Friedman, H.S.; Kun, L.E. Neuropsychologic functioning of survivors of childhood medulloblastoma randomized to receive conventional or reduced-dose craniospinal irradiation: A Pediatric Oncology Group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, K.R.; Kraemer, D.F.; Neuwelt, E.A. Ototoxicity in children receiving platinum chemotherapy: Underestimating a commonly occurring toxicity that may influence academic and social development. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8588–8596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouladi, M.; Gilger, E.; Kocak, M.; Wallace, D.; Buchanan, G.; Reeves, C.; Robbins, N.; Merchant, T.; Kun, L.E.; Khan, R.; et al. Intellectual and functional outcome of children 3 years old or younger who have CNS malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7152–7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, A.; Robinson, G.W.; Smith, K.S.; Lin, T.; Merchant, T.E.; Chintagumpala, M.; Mahajan, A.; Su, J.; Bouffet, E.; Bartels, U.; et al. Outcomes by clinical and molecular features in children with medulloblastoma treated with risk-adapted therapy: Results of an international phase III trial (SJMB03). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxon-Emre, I.; Bouffet, E.; Taylor, M.D.; Laperriere, N.; Scantlebury, N.; Law, N.; Spiegler, B.J.; Malkin, D.; Janzen, L.; Mabbott, D.J. Impact of craniospinal dose, boost volume, and neurologic complications on intellectual outcome in patients with medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, G.W.; Rudneva, V.A.; Buchhalter, I.; Billups, C.A.; Waszak, S.M.; Smith, K.S.; Bowers, D.C.; Bendel, A.; Fisher, P.G.; Partap, S.; et al. Risk-adapted therapy for young children with medulloblastoma (SJYC07): Therapeutic and molecular outcomes from a multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 768–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mynarek, M.; Milde, T.; Padovani, L.; Janssens, G.O.; Kwiecien, R.; Mosseri, V.; Clifford, S.C.; Doz, F.; Rutkowski, S. SIOP PNET5 MB Trial: History and Concept of a Molecularly Stratified Clinical Trial of Risk-Adapted Therapies for Standard-Risk Medulloblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandola, L.; Massimino, M.; Cefalo, G.; Solero, C.; Spreafico, F.; Pecori, E.; Riva, D.; Collini, P.; Pignoli, E.; Giangaspero, F.; et al. Hyperfractionated accelerated radiotherapy in the Milan strategy for metastatic medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, C.; Kieffer, V.; Varlet, P.; Raquin, M.A.; Dhermain, F.; Puget, S.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Grill, J. Tandem high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell rescue in children with newly diagnosed high-risk medulloblastoma or supratentorial primitive neuro-ectodermic tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, C.; von Bueren, A.O.; von Hoff, K.; Gerber, N.U.; Ottensmeier, H.; Deinlein, F.; Benesch, M.; Kwiecien, R.; Pietsch, T.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; et al. Treatment of young children with CNS-primitive neuroectodermal tumors/pineoblastomas in the prospective multicenter trial HIT 2000 using different chemotherapy regimens and radiotherapy. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakacki, R.I.; Burger, P.C.; Zhou, T.; Holmes, E.J.; Kocak, M.; Onar, A.; Goldwein, J.; Mehta, M.; Packer, R.J.; Tarbell, N.; et al. Outcome of children with metastatic medulloblastoma treated with carboplatin during craniospinal radiotherapy: A Children’s Oncology Group Phase I/II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2648–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.W.; Lim, D.H.; Yi, E.S.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, K.H.; Koo, H.H.; Kim, J.H.; Suh, Y.L.; Joung, Y.S.; Shin, H.J. Tandem high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation for atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 48, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, S.N.; Gardner, S.L.; Levy, A.S.; Knopp, E.A.; Miller, D.C.; Wisoff, J.H.; Weiner, H.L.; Finlay, J.L. Feasibility and response to induction chemotherapy intensified with high-dose methotrexate for young children with newly diagnosed high-risk disseminated medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 4881–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortmann, R.D.; Kuhl, J.; Timmermann, B.; Mittler, U.; Urban, C.; Budach, V.; Richter, E.; Willich, N.; Flentje, M.; Berthold, F.; et al. Postoperative neoadjuvant chemotherapy before radiotherapy as compared to immediate radiotherapy followed by maintenance chemotherapy in the treatment of medulloblastoma in childhood: Results of the German prospective randomized trial HIT ’91. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 46, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padovani, L.; Sunyach, M.P.; Perol, D.; Mercier, C.; Alapetite, C.; Haie-Meder, C.; Hoffstetter, S.; Muracciole, X.; Kerr, C.; Wagner, J.P.; et al. Common strategy for adult and pediatric medulloblastoma: A multicenter series of 253 adults. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, A.A.; Franceschi, E.; Tosoni, A.; Blatt, V.; Ermani, M. Long-term results of a prospective study on the treatment of medulloblastoma in adults. Cancer 2007, 110, 2035–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.S.; Gupta, T.; Jalali, R.; Master, Z.; Phurailatpam, R.D.; Sarin, R. High-precision radiotherapy for craniospinal irradiation: Evaluation of three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy and helical TomoTherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2009, 82, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kann, B.H.; Park, H.S.; Lester-Coll, N.H.; Yeboa, D.N.; Benitez, V.; Khan, A.J.; Bindra, R.S.; Marks, A.M.; Roberts, K.B. Postoperative radiotherapy patterns of care and survival implications for medulloblastoma in young children. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassaletta, A.; Ramaswamy, V. Medulloblastoma in adults: They’re not just big kids. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 895–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bueren, A.O.; Friedrich, C.; von Hoff, K.; Kwiecien, R.; Müller, K.; Pietsch, T.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Hau, P.; Benesch, M.; Kuehl, J.; et al. Metastatic medulloblastoma in adults: Outcome of patients treated according to the HIT2000 protocol. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2434–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, E.; Seidel, C.; Sahm, F.; Pajtler, K.W.; Hau, P. How we treat medulloblastoma in adults. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, H.S.; Chamberlain, M.C.; Glantz, M.J.; Wang, S. Adult medulloblastoma: Multiagent chemotherapy. Neuro Oncol. 2001, 3, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, A.A.; Ermani, M.; Amista, P.; Basso, U.; Vastola, F.; Gardiman, M.; Iuzzolino, P.; Turazzi, S.; Rotilio, A.; Volpin, L.; et al. The treatment of adults with medulloblastoma: A prospective study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 57, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, W.; Xu, J. The Role of Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Adult Medulloblastoma. World Neurosurg. 2022, 163, e435–e449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, E.; Hofer, S.; Brandes, A.A.; Frappaz, D.; Kortmann, R.D.; Bromberg, J.; Dangouloff-Ros, V.; Boddaert, N.; Hattingen, E.; Wiestler, B.; et al. EANO-EURACAN clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of post-pubertal and adult patients with medulloblastoma. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e715–e728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocakaya, S.; Beier, C.P.; Beier, D. Chemotherapy increases long-term survival in patients with adult medulloblastoma--a literature-based meta-analysis. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northcott, P.A.; Robinson, G.W.; Kratz, C.P.; Mabbott, D.J.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Clifford, S.C.; Rutkowski, S.; Ellison, D.W.; Malkin, D.; Taylor, M.D.; et al. Medulloblastoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.J.; Vezina, G. Management of and prognosis with medulloblastoma: Therapy at a crossroads. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, G.; Botta, L.; Rossi, S.; Aareleid, T.; Bielska-Lasota, M.; Clavel, J.; Dimitrova, N.; Jakab, Z.; Kaatsch, P.; Lacour, B.; et al. Childhood cancer survival in Europe 1999-2007: Results of EUROCARE-5--a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ris, M.D.; Walsh, K.; Wallace, D.; Armstrong, F.D.; Holmes, E.; Gajjar, A.; Zhou, T.; Packer, R.J. Intellectual and academic outcome following two chemotherapy regimens and radiotherapy for average-risk medulloblastoma: COG A9961. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, J.M.; Janss, A.J.; Vezina, L.G.; Gajjar, A.; Pollack, I.; Merchant, T.E.; FitzGerald, T.J.; Booth, T.; Tarbell, N.J.; Li, Y.; et al. Results of COG ACNS0331: A phase III trial of involved-field radiotherapy (IFRT) and low dose craniospinal irradiation (LD-CSI) with chemotherapy in average-risk medulloblastoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, 937–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, A.; Bowers, D.C.; Karajannis, M.A.; Leary, S.; Witt, H.; Gottardo, N.G. Pediatric brain tumors: Innovative genomic information is transforming the diagnostic and clinical landscape. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2986–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laughton, S.J.; Merchant, T.E.; Sklar, C.A.; Kun, L.E.; Fouladi, M.; Broniscer, A.; Morris, E.B.; Sanders, R.P.; Krasin, M.J.; Shelso, J.; et al. Endocrine outcomes for children with embryonal brain tumors after risk-adapted craniospinal and conformal primary-site irradiation and high-dose chemotherapy with stem-cell rescue on the SJMB-96 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, A.; Remke, M.; Werft, W.; Benner, A.; Ryzhova, M.; Witt, H.; Sturm, D.; Wittmann, A.; Schöttler, A.; Felsberg, J.; et al. Adult and pediatric medulloblastomas are genetically distinct and require different algorithms for molecular risk stratification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3054–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majd, N.; Penas-Prado, M. Updates on management of adult medulloblastoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2019, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, D.; Proescholdt, M.; Reinert, C.; Pietsch, T.; Jones, D.T.W.; Pfister, S.M.; Hattingen, E.; Seidel, C.; Dirven, L.; Luerding, R.; et al. Multicenter pilot study of radiochemotherapy as first-line treatment for adults with medulloblastoma (NOA-07). Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, P.; Frappaz, D.; Hovey, E.; McCabe, M.G.; Pajtler, K.W.; Wiestler, B.; Seidel, C.; Combs, S.E.; Dirven, L.; Klein, M.; et al. Development of Randomized Trials in Adults with Medulloblastoma-The Example of EORTC 1634-BTG/NOA-23. Cancers 2021, 13, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Shih, H.; Penas-Prado, M.; Ligon, K.; Aldape, K.; Hu, L.S.; Loughan, A.R.; Basso, M.R.; Leeper, H.E.; Nahed, B.V.; et al. The Alliance AMBUSH Trial: Rationale and Design. Cancers 2022, 14, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannering, B.; Rutkowski, S.; Doz, F.; Pizer, B.; Gustafsson, G.; Navajas, A.; Massimino, M.; Reddingius, R.; Benesch, M.; Carrie, C.; et al. Hyperfractionated versus conventional radiotherapy followed by chemotherapy in standard-risk medulloblastoma: Results from the randomized multicenter HIT-SIOP PNET 4 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3187–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remke, M.; Ramaswamy, V.; Taylor, M.D. Medulloblastoma molecular dissection: The way toward targeted therapy. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wireko, A.A.; Ben-Jaafar, A.; Kong, J.S.H.; Mannan, K.M.; Sanker, V.; Rosenke, S.L.; Boye, A.N.A.; Nkrumah-Boateng, P.A.; Poornaselvan, J.; Shah, M.H.; et al. Sonic hedgehog signalling pathway in CNS tumours: Its role and therapeutic implications. Mol. Brain 2024, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M. Genomic testing, tumor microenvironment and targeted therapy of Hedgehog-related human cancers. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 953–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutin, L.; Liu, M.; Déchanet Merville, J.; Bedoya-Reina, O.; Wilhelm, M.T. EphA2 and phosphoantigen-mediated selective killing of medulloblastoma by γδT cells preserves neuronal and stem cell integrity. Oncoimmunology 2025, 14, 2485535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chang, M.; Wang, Y.; Xing, B.; Ma, W. B7-H3 in Brain Malignancies: Immunology and Immunotherapy. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 3762–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milde, T.; Lodrini, M.; Savelyeva, L.; Korshunov, A.; Kool, M.; Brueckner, L.M.; Antunes, A.S.; Oehme, I.; Pekrun, A.; Pfister, S.M.; et al. HD-MB03 is a novel Group 3 medulloblastoma model demonstrating sensitivity to histone deacetylase inhibitor treatment. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 110, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leary, S.E.S.; Kilburn, L.; Geyer, J.R.; Kocak, M.; Huang, J.; Smith, K.S.; Hadley, J.; Ermoian, R.; MacDonald, T.J.; Goldman, S.; et al. Vorinostat and isotretinoin with chemotherapy in young children with embryonal brain tumors: A report from the Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium (PBTC-026). Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koravovic, M.; Mayasundari, A.; Tasic, G.; Keramatnia, F.; Stachowski, T.R.; Cui, H.; Chai, S.C.; Jonchere, B.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. From PROTAC to inhibitor: Structure-guided discovery of potent and orally bioavailable BET inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 251, 115246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Fang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Su, T.; Miao, W.; Wang, Z. Self-Assembled Peptide PROTAC Prodrugs Targeting FOXM1 for Cancer Therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2025, 22, 3286–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimini, A.; Ricci, M.; Russo, F.; Egidi, M.; Calabria, F.; Bagnato, A.; Schillaci, O.; Chiaravalloti, A. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy and Primary Brain Tumors: An Overview. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellay, C.N.; Frappaz, D.; Sunyach, M.P.; Franceschi, E.; Brandes, A.A.; Stupp, R. Medulloblastomas in adults: Prognostic factors and lessons from paediatrics. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2011, 24, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, S.F.; Richards, O.; Elliot, M.; Chumas, P. Pediatric-Like Brain Tumors in Adults. Adv. Tech. Stand. Neurosurg. 2024, 50, 147–183. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, A.; Stark, D.; Peccatori, F.A.; Fern, L.; Laurence, V.; Gaspar, N.; Bozovic-Spasojevic, I.; Smith, O.; Munter, J.; Derwich, K.; et al. Adolescents and young adults (AYA) with cancer: A position paper from the AYA Working Group of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) and the European Society for Paediatric Oncology (SIOPE). ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleyer, A.; Budd, T.; Montello, M. Adolescents and young adults with cancer: The scope of the problem and criticality of clinical trials. Cancer 2006, 107, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf von Rohr, L.; Battanta, N.; Vetter, C.; Scheinemann, K.; Otth, M. The Requirements for Setting Up a Dedicated Structure for Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer—A Systematic Review. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsadi, M.O.; Saker, M.; Elias, S.; Kaelooh, T.; Alrefai, A.; Sattouf, M. A rare case of desmoplastic medulloblastoma in a 65-year-old male: A case report on achieving stability post-grade IV surgical resection. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2025, 130, 111294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwalbe, E.C.; Lindsey, J.C.; Danilenko, M.; Hill, R.M.; Crosier, S.; Ryan, S.L.; Williamson, D.; Castle, J.; Hicks, D.; Kool, M.; et al. Molecular and clinical heterogeneity within MYC-family amplified medulloblastoma is associated with survival outcomes: A multicenter cohort study. Neuro Oncol. 2025, 27, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibl, T.; Hammer, A.; Yakubov, E.; Blechschmidt, C.; Kalisch, A.; Steiner, H.H. Medulloblastoma in adults—Reviewing the literature from a surgeon’s point of view. Aging 2021, 13, 3146–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffaud, L.; Saikali, S.; Leray, E.; Hamlat, A.; Haegelen, C.; Vauleon, E.; Lesimple, T. Survival and prognostic factors in a series of adults with medulloblastomas. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreafico, F.; Massimino, M.; Gandola, L.; Cefalo, G.; Mazza, E.; Landonio, G.; Pignoli, E.; Poggi, G.; Terenziani, M.; Pedrazzoli, P.; et al. Survival of adults treated for medulloblastoma using paediatric protocols. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Ye, Q.; Jian, W.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Q. Multifocal medulloblastoma in an adult: A case report and review of the literature. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 151, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.W.; Tarbell, N.J.; Black, P.M.; Louis, D.N.; Frosch, M.P.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Chapman, P.; Loeffler, J.S. Adult medulloblastoma: Prognostic factors and patterns of relapse. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 623–631. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, P.J.; Laperriere, N.J.; Wong, C.S.; Milosevic, M.F.; Simpson, W.J.; Pintilie, M. Medulloblastoma in adults. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1995, 32, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alston, R.D.; Newton, R.; Kelsey, A.; Newbould, M.J.; Birch, J.M.; Lawson, B.; McNally, R.J. Childhood medulloblastoma in northwest England 1954 to 1997: Incidence and survival. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2003, 45, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonm, A.V.; Rutenberg, M.S.; Therkelsen, K.E.; Herbst, J.; Sanaf, A.; Sherwood, M.A.; Rhee, J.Y.; McGranahan, T.M.; Cimino, P.J.; Gonzalez Castro, L.N.; et al. A multi-institutional retrospective cohort of adult-onset medulloblastoma in the modern era. Neurooncol Adv. 2025, 7, vdae231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabori, U.; Sung, L.; Hukin, J.; Laperriere, N.; Crooks, B.; Carret, A.S.; Silva, M.; Odame, I.; Mpofu, C.; Strother, D.; et al. Medulloblastoma in the second decade of life: A specific group with respect to toxicity and management: A Canadian Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium Study. Cancer 2005, 103, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhvaryu, V.V.; Gurav, M.; Deshpande, G.; Rumde, R.; Shetty, O.; Sahay, A.; Sahu, A.; Dasgupta, A.; Chatterji, A.; Gupta, T.; et al. Adult Medulloblastoma: Clinicomolecular Spectrum, An Institutional Experience. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.J.; Hernan, R.; Hollander, A.; Lindsey, J.C.; Lusher, M.E.; Fuller, C.E.; Clifford, S.C.; Gilberston, R.J. The TP53-ARF tumor suppressor pathway is frequently disrupted in large/cell anaplastic medulloblastoma. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2004, 121, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanno, B.; Fratini, E.; Leonardi, S.; Novelli, F.; Pisano, V.; Mancuso, M.; Pazzaglia, S. Dissecting the Impact of Genetic Background on Oncogenic Response to Radiation Exposure in the Ptch1+/− Mouse Model. Cells 2024, 13, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbel, C.; Godbole, S.; Schoof, M.; Holdhof, D.; Kresbach, C.; Loose, C.; Neumann, J.; Schüller, U. MYC overexpression and SMARCA4 loss cooperate to drive medulloblastoma formation in mice. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navickas, S.M.; Giles, K.A.; Brettingham-Moore, K.H.; Taberlay, P.C. The role of chromatin remodeler SMARCA4/BRG1 in brain cancers: A potential therapeutic target. Oncogene 2023, 42, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Shi, W.; Rui, H.; Li, H. BRCA2 deficiency increases sensitivity of medulloblastoma to Olaparib by inhibiting RAD51-mediated DNA damage repair system. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, S. Molecular Diagnostics of Adult Gliomas in Neuropathological Practice. Acta Med. Acad. 2021, 50, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.; Balderson, B.; Jones, K.; Ni, G.; Crawford, J.; Millar, A.; Tolson, E.; Singleton, M.; Kojic, M.; Robertson, T.; et al. Spatial transcriptomic analysis of Sonic hedgehog medulloblastoma identifies that the loss of heterogeneity and promotion of differentiation underlies the response to CDK4/6 inhibition. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.K.; Gwynne, W.D.; Lieng, B.Y.; Quaile, A.T.; Venugopal, C.; Singh, S.K.; Montenegro-Burke, J.R. Protocol for mapping the metabolome and lipidome of medulloblastoma cells using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. STAR Protoc. 2023, 4, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kanchan, R.; Chaturvedi, N.K. Targeting protein synthesis pathways in MYC-amplified medulloblastoma. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatua, S.; Ramaswamy, V.; Bouffet, E. Current therapy and the evolving molecular landscape of paediatric medulloblastoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 94, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Meco, D.; Attinà, G.; Mastrangelo, S.; Navarra, P.; Ruggiero, A. Emerging Perspectives on the Antiparasitic Mebendazole as a Repurposed Drug for the Treatment of Brain Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.W.; Orr, B.A.; Wu, G.; Gururangan, S.; Lin, T.; Qaddoumi, I.; Packer, R.J.; Goldman, S.; Prados, M.D.; Desjardins, A.; et al. Vismodegib exerts targeted efficacy against recurrent sonic hedgehog-subgroup medulloblastoma: Results from phase II pediatric brain tumor consortium studies PBTC-025B and PBTC-032. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2646–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fern, L.A.; Lewandowski, J.A.; Coxon, K.M.; Whelan, J. Available, accessible, aware, appropriate, and acceptable: A strategy to improve participation of teenagers and young adults in cancer trials. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e341–e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltin, H.; Sundaresan, L.; Smith, K.S.; Skowron, P.; Massimi, L.; Eberhart, C.G.; Schreck, K.C.; Gupta, N.; Weiss, W.A.; Tirapelli, D.; et al. Subgroup and subtype-specific outcomes in adult medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 142, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshinyan, D.; Adile, A.A.; Liu, J.; Gwynne, W.D.; Suk, Y.; Custers, S.; Burns, I.; Singh, M.; McFarlane, N.; Subapanditha, M.K.; et al. Temporal profiling of therapy resistance in human medulloblastoma identifies novel targetable drivers of recurrence. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almousa, A.; Erjan, A.; Sarhan, N.; Obeidat, M.; Alshorbaji, A.; Amarin, R.; Alawabdeh, T.; Abu-Hijlih, R.; Mujlli, M.; Kh Ibrahimi, A.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics and Outcome of Adult Medulloblastoma at a Tertiary Cancer Center. Cancers 2024, 16, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, A.; Trombatore, G.; Triarico, S.; Arena, R.; Ferrara, P.; Scalzone, M.; Pierri, F.; Riccardi, R. Platinum compounds in children with cancer: Toxicity and clinical management. Anticancer Drugs 2013, 24, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Ruggiero, A.; Lucidi, D.; De Corso, E.; Sergi, B.; Conti, G.; Paludetti, G. Audiological Monitoring in Children Treated with Platinum Chemotherapy. Audiol. Neurootol. 2016, 21, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, P.R.; Bellman, S.C.; Yeomans, E.C.; Pinkerton, C.R.; Pritchard, J. Cisplatin ototoxicity in children: A practical grading system. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 1991, 19, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia, R.; Melita, V.; De Vita, A.; Ruggiero, A.; Romano, A.; Attinà, G.; Birritella, L.; Lamendola, P.; Lombardo, A.; Lanza, G.A.; et al. Cardiac Surveillance for Early Detection of Late Subclinical Cardiac Dysfunction in Childhood Cancer Survivors After Anthracycline Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 624057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landier, W.; Armenian, S.; Bhatia, S. Late effects of childhood cancer and its treatment. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 2015, 62, 275–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, N.E.; De Braganca, K.C. Medulloblastoma. J. Child Neurol. 2016, 31, 1341–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bueren, A.O.; Kortmann, R.D.; von Hoff, K.; Friedrich, C.; Mynarek, M.; Müller, K.; Goschzik, T.; Zur Mühlen, A.; Gerber, N.; Warmuth-Metz, M. Treatment of children and adolescents with metastatic medulloblastoma and prognostic relevance of clinical and biologic parameters. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4151–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakban, A.; Mohammadi, T.; Lynd, L.D.; Mabbott, D.; Bouffet, E.; Gastonguay, L.; Zafari, Z.; Malkin, D.; Taylor, M.; Marra, C.A. Societal preferences in the treatment of pediatric medulloblastoma: Balancing risk of death and quality of life. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, T.M.; Krasin, M.J.; Liu, W.; Armstrong, G.T.; Ojha, R.P.; Sadighi, Z.S.; Gupta, P.; Kimberg, C.; Srivastava, D.; Merchant, T.E.; et al. Long-term neurocognitive functioning and social attainment in adult survivors of pediatric CNS tumors: Results from the St Jude Lifetime Cohort Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhern, R.K.; Palmer, S.L.; Merchant, T.E.; Wallace, D.; Kocak, M.; Brouwers, P.; Krull, K.; Chintagumpala, M.; Stargatt, R.; Ashley, D.M.; et al. Neurocognitive consequences of risk-adapted therapy for childhood medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5511–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talloa, D.; Triarico, S.; Agresti, P.; Mastrangelo, S.; Attinà, G.; Romano, A.; Maurizi, P.; Ruggiero, A. BRAF and MEK Targeted Therapies in Pediatric Central Nervous System Tumors. Cancers 2022, 14, 4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Thomas, D.; Franklin, A.R.; Hayes-Lattin, B.M.; Mascarin, M.; van der Graaf, W.; Albritton, K.H. Starting an adolescent and young adult program: Some success stories and some obstacles to overcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4850–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, C.; Stout, L.; House, T.; Santana, V.M. Barriers and facilitators of clinical trial enrollment in a network of community-based pediatric oncology clinics. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleyer, A.; O’Leary, M.; Barr, R.; Ries, L.A.G. (Eds.) Cancer Epidemiology in Older Adolescents and Young Adults 15 to 29 Years of Age, Including SEER Incidence and Survival: 1975–2000; NIH Pub. No. 06-5767; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Arnett, J.J. Emerging adulthood: A theory of development from the late teens through the twenties. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribera, J.M.; Oriol, A.; Sanz, M.A.; Tormo, M.; Fernández-Abellán, P.; del Potro, E.; Abella, E.; Bueno, J.; Parody, R.; Bastida, P.; et al. Comparison of the results of the treatment of adolescents and young adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the Programa Español de Tratamiento en Hematología pediatric-based protocol ALL-96. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Lo Vullo, S.; Giardiello, D.; Veneroni, L.; Magni, C.; Clerici, C.A.; Chiaravalli, S.; Casanova, M.; Luksch, R.; Terenziani, M.; et al. The sooner the better? How symptom interval correlates with outcome in children and adolescents with solid tumors: Regression tree analysis of the findings of a prospective study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keegan, T.H.M.; Bleyer, A. Inclusion of adolescent and young adult oncology within distinct research and practice domains. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27318. [Google Scholar]
- Freyer, D.R.; Felgenhauer, J.; Perentesis, J. Children’s Oncology Group’s 2013 blueprint for research: Adolescent and young adult oncology. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoi, M.A.; Pages, A.; Papageorgiou, L.; Di Meglio, A.; Laparra, A.; Martin, E.; Barbier, A.; Renvoise, N.; Arvis, J.; Scotte, F.; et al. Evaluating the Implementation of Integrated Proactive Supportive Care Pathways in Oncology: Master Protocol for a Cohort Study. J.M.I.R. Res. Protoc. 2024, 13, e52841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.M.; Seymour, J.F.; O’Brien, T.; Sawyer, S.M.; Ashley, D.M. Adolescent and young adult cancer: A revolution in evolution? Intern Med. J. 2006, 36, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebrack, B.; Kent, E.E.; Keegan, T.H.; Kato, I.; Smith, A.W. “Cancer sucks,” and other ponderings by adolescent and young adult cancer survivors. J. Psychosoc. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazak, A.E.; Abrams, A.N.; Banks, J.; Christofferson, J.; DiDonato, S.; Grootenhuis, M.A.; Kabour, M.; Madan-Swain, A.; Patel, S.K.; Zadeh, S.; et al. Psychosocial assessment as a standard of care in pediatric cancer. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, S426–S459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, M.; Greenfield, S.; Stovall, E. (Eds.) From Cancer Patient to Cancer Survivor: Lost in Transition; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein, K.; Spiegler, B.J.; Fung, S.; Panzarella, T.; Mabbott, D.J.; Jewitt, N.; D’Agostino, N.M.; Mason, W.P.; Bouffet, E.; Tabori, U.; et al. Early aging in adult survivors of childhood medulloblastoma: Long-term neurocognitive, functional, and physical outcomes. Neuro Oncol. 2011, 13, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaauwbroek, R.; Groenier, K.H.; Kamps, W.A.; Meyboom-de Jong, B.; Postma, A. Late effects in adult survivors of childhood cancer: The need for life-long follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 1898–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Marino, S.; Gaggiotti, P.; Garavaglia, V.; Silva, M.; Veneroni, L.; Massimino, M. Shout in fury but smile at life: A portrait of an adolescent with cancer on the Youth Project in Milan. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sender, L.; Zabokrtsky, K.B. Adolescent and young adult patients with cancer: A milieu of unique features. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, D.; Bielack, S.; Brugieres, L.; Dirksen, U.; Duarte, X.; Dunn, S.; Erdelyi, D.J.; Grew, T.; Hjorth, L.; Jazbec, J.; et al. Teenagers and young adults with cancer in Europe: From national programmes to a European integrated coordinated project. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2016, 25, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.; Davies, S.; Palmer, S.; Plaster, M. Sex, drugs, and rock ’n’ roll: Caring for adolescents and young adults with cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4825–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebrack, B.; Mathews-Bradshaw, B.; Siegel, S.; LIVESTRONG Young Adult Alliance. Quality cancer care for adolescents and young adults: A position statement. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4862–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, P.F.; Altman, J.; Bhatia, S.; Borinstein, S.C.; Flynn, J.; George, S.; Goldsby, R.; Hayashi, R.; Huang, M.S.; Johnson, R.H.; et al. Adolescent and young adult oncology. Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2012, 10, 1112–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.W.; Seibel, N.L.; Lewis, D.R.; Albritton, K.H.; Blair, D.F.; Blanke, C.D.; Bleyer, W.A.; Freyer, D.R.; Geiger, A.M.; Hayes-Lattin, B.; et al. Next steps for adolescent and young adult oncology workshop: An update on progress and recommendations for the future. Cancer 2016, 122, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albritton, K.H.; Wiggins, C.H.; Nelson, H.E.; Weeks, J.C. Site of oncologic specialty care for older adolescents in Utah. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4616–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffar, R.; Bouchardy, C.; Chappuis, P.O.; Bodmer, A.; Benhamou, S.; Rapiti, E. A population-based cohort of young women diagnosed with breast cancer in Geneva, Switzerland. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trama, A.; Botta, L.; Foschi, R.; Ferrari, A.; Stiller, C.; Desandes, E.; Maule, M.M.; Merletti, F.; Gatta, G.; EUROCARE-5 Working Group. Survival of European adolescents and young adults diagnosed with cancer in 2000-07: Population-based data from EUROCARE-5. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, M.M.; Gupta, S.; Soerjomataram, I.; Ferlay, J.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality among young adults aged 20-39 years worldwide in 2012: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desandes, E.; Lacour, B.; Belot, A.; Molinie, F.; Delafosse, P.; Tretarre, B.; Velten, M.; Sauleau, E.A.; Woronoff, A.S.; Guizard, A.V.; et al. Cancer incidence and survival in adolescents and young adults in France, 2000–2008. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 30, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, L.A.; Hayes, V.E.; Berger, A.M. Oncology nursing in pediatric, adolescent, and young adult cancer care. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2021, 37, 151241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology Progress Review Group. Closing the Gap: Research and Care Imperatives for Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer; Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, and the LiveStrong Young Adult Alliance: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2006.
- Lim-Fat, M.J.; Bennett, J.; Ostrom, Q.; Touat, M.; Franceschi, E.; Schulte, J.; Bindra, R.S.; Fangusaro, J.; Dhall, G.; Nicholson, J.; et al. Central nervous system tumors in adolescents and young adults: A Society for Neuro-Oncology Consensus Review on diagnosis, management, and future directions. Neuro Oncol. 2025, 27, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nass, S.J.; Beaupin, L.K.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Fasciano, K.; Ganz, P.A.; Hayes-Lattin, B.; Hudson, M.M.; Nevidjon, B.; Oeffinger, K.C.; Rechis, R.; et al. Identifying and addressing the needs of adolescents and young adults with cancer: Summary of an Institute of Medicine workshop. Oncologist 2015, 20, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, P.C.; Hayes-Lattin, B.; Sisler, J.J.; Hudson, M.M. Critical issues in transition and survivorship for adolescents and young adults with cancers. Cancer 2011, 117, 2335–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, R.D.; Ferrari, A.; Ries, L.; Whelan, J.; Bleyer, W.A. Cancer in adolescents and young adults: A narrative review of the current status and a view of the future. JAMA Pediatr. 2016, 170, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebrack, B.; Bleyer, A.; Albritton, K.; Meyers, S.; Casillas, J. Assessing the health care needs of adolescent and young adult cancer patients and survivors. Cancer 2006, 107, 2915–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.; Zebrack, B.J.; Meeske, K.A.; Embry, L.; Aguilar, C.; Block, R.; Hayes-Lattin, B.; Li, Y.; Butler, M.; Cole, S. Prevalence and predictors of post-traumatic stress symptoms in adolescent and young adult cancer survivors: A 1-year follow-up study. Psychooncology 2013, 22, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saloustros, E.; Stark, D.P.; Michailidou, K.; Mountzios, G.; Brugieres, L.; Peccatori, F.A.; Jezdic, S.; Essiaf, S.; Douillard, J.Y.; Bielack, S. The care of adolescents and young adults with cancer: Results of the ESMO/SIOPE survey. ESMO Open 2017, 2, e000252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desandes, E.; Stark, D.P. Epidemiology of adolescents and young adults with cancer in Europe. Prog. Tumor Res. 2016, 43, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akre, C.; Ramelet, A.S.; Berchtold, A.; Suris, J.C. Educational intervention for parents of adolescents with chronic illness: A pre-post test pilot study. Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2015, 27, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, A.G.; Dreyzin, A.; Miller, K.D.; Seynnaeve, B.K.N.; Rapkin, L.B. Adolescent and young adult oncology-past, present, and future. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
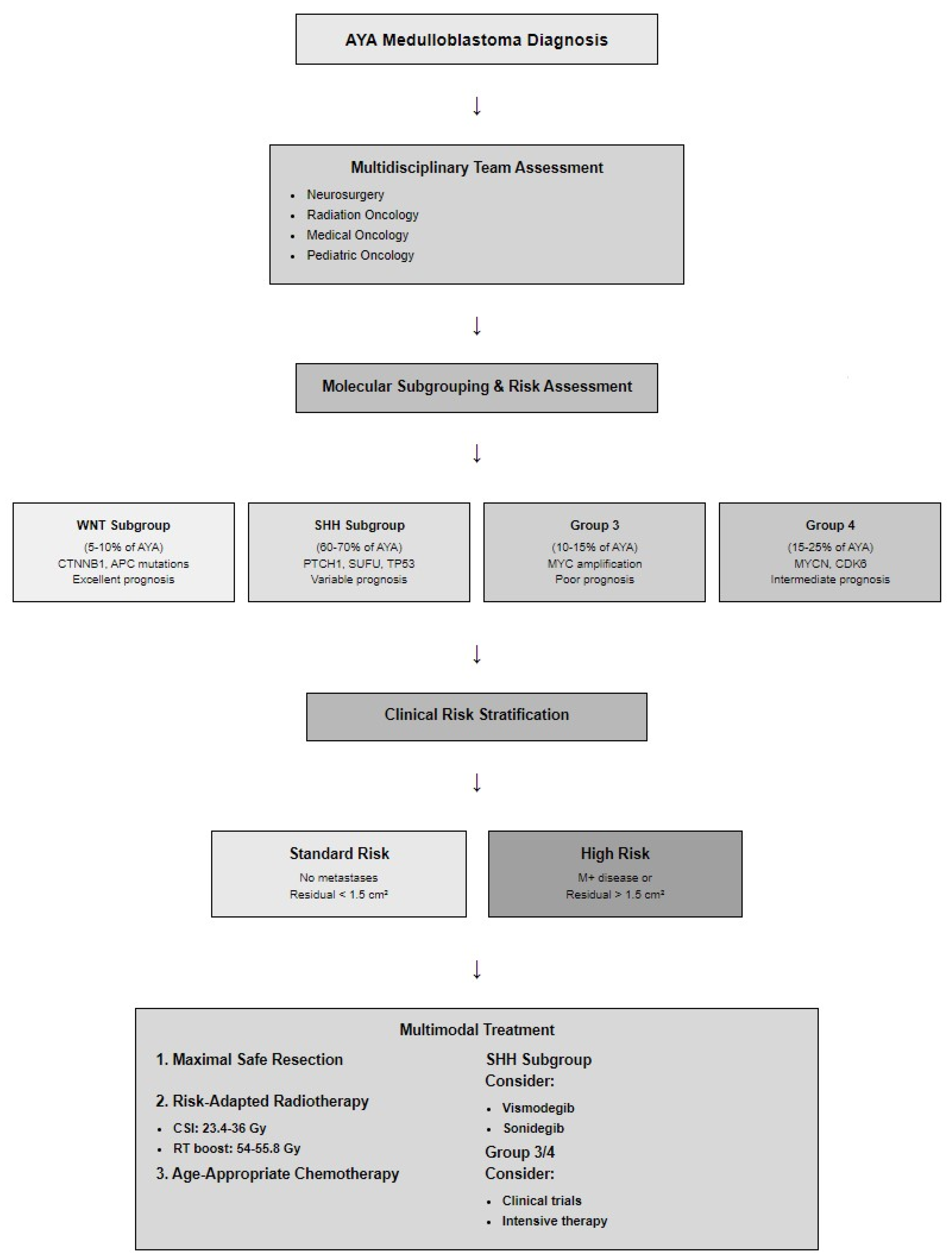
| Subgroup | AYA Frequency (%) | Key Genetic Alterations | Therapeutic Targets | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WNT | 5–10 | CTNNB1, APC, SMARCA4 | β-catenin inhibitors | Excellent |
| SHH | 60–70 | PTCH1, SUFU, SMO, TP53 | Hedgehog inhibitors | Intermediate |
| Group 3 | 10–15 | MYC, SMARCA4, KBTBD4 | BET inhibitors, PROTACs | Poor-Intermediate |
| Group 4 | 15–25 | MYCN, CDK6, SNCAIP | CDK inhibitors | Intermediate |
| Trial | Phase | Population | Intervention | Primary Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SJMB12 | II | Pediatric/AYA | Vismodegib maintenance | Event-free survival |
| PNOC015 | I/II | Pediatric | Neoantigen vaccines | Safety/Immunogenicity |
| PNOC017 | I | Pediatric | Epigenetic therapy | Maximum tolerated dose |
| EORTC-1634 | III | Adult | Radiotherapy optimization | Overall survival |
| AMBUSH | II | Adult SHH | Sonidegib + radiotherapy | Progression-free survival |
| Trial | Age Range | Design | Key Findings | AYA Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric Trials | ||||
| COG A9961 | 3–21 years | Randomized Phase III | Reduced CSI non-inferior (23.4 vs. 36 Gy), >80% 5-year EFS | Moderate—Upper age included some AYAs |
| SJMB12 | 3–21 years | Phase II | Molecular stratification improves outcomes | High—Includes adolescents, targeted therapy for SHH |
| SIOP PNET-5 | 3–18 years | Phase III | Risk-adapted therapy based on molecular subgroups | Limited—Excludes most AYAs |
| Adult Trials | ||||
| HIT-2000 | >18 years | Retrospective | 68% 4-year EFS with pediatric-derived protocols | High—Direct relevance to young adults |
| EORTC 1634 | >18 years | Phase II/III | Ongoing molecular stratification study | High—Includes AYA population |
| AYA-Focused Trials | ||||
| AMBUSH | 16–65 years | Phase II | Targeting SHH subgroup with SMO inhibitors | Very High—AYA-specific design |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruggiero, A.; Attinà, G.; Talloa, D.; Mastrangelo, S.; Romano, A.; Maurizi, P.; Chiesa, S.; Tamburrini, G.; Olivi, A.; Albanese, A. Medulloblastoma in Adolescents and Young Adults (AYA): Bridging Pediatric Paradigms and Adult Oncology Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134472
Ruggiero A, Attinà G, Talloa D, Mastrangelo S, Romano A, Maurizi P, Chiesa S, Tamburrini G, Olivi A, Albanese A. Medulloblastoma in Adolescents and Young Adults (AYA): Bridging Pediatric Paradigms and Adult Oncology Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134472
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuggiero, Antonio, Giorgio Attinà, Dario Talloa, Stefano Mastrangelo, Alberto Romano, Palma Maurizi, Silvia Chiesa, Gianpiero Tamburrini, Alessandro Olivi, and Alessio Albanese. 2025. "Medulloblastoma in Adolescents and Young Adults (AYA): Bridging Pediatric Paradigms and Adult Oncology Practice" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134472
APA StyleRuggiero, A., Attinà, G., Talloa, D., Mastrangelo, S., Romano, A., Maurizi, P., Chiesa, S., Tamburrini, G., Olivi, A., & Albanese, A. (2025). Medulloblastoma in Adolescents and Young Adults (AYA): Bridging Pediatric Paradigms and Adult Oncology Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134472









