Quetiapine Use Is Associated with Longer ICU Stay Compared to Control and Haloperidol: A Propensity Score–Matched Analysis Using the MIMIC-IV Database
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
2.2. Patients, Exposure, Outcome, and Covariates
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
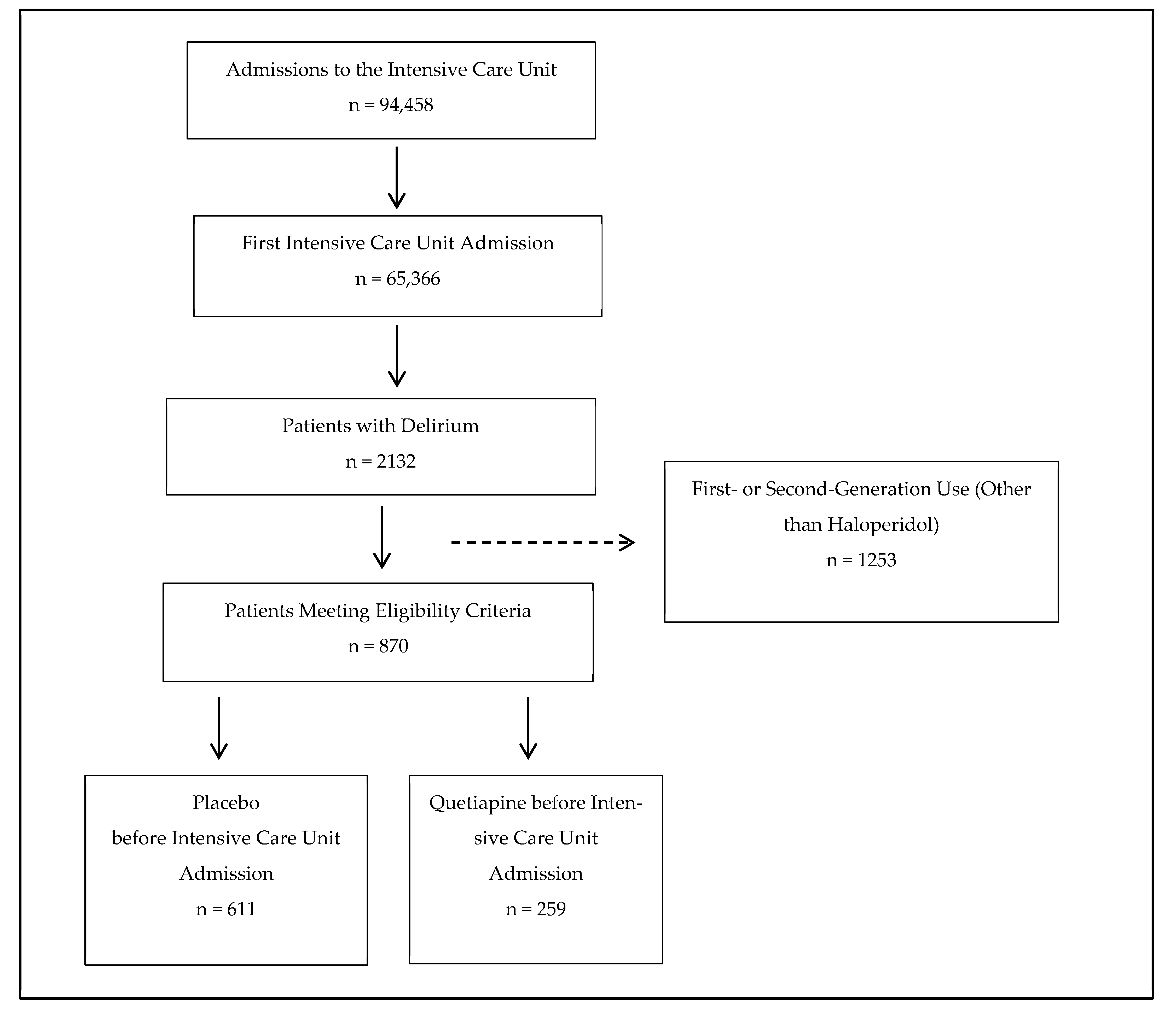
3.1. Participant Flow Diagrams
3.2. Propensity Score Matching—Quetiapine Versus Control
3.3. Propensity Score Matching—Quetiapine Versus Haloperidol
3.4. Generalized Additive Modeling—Quetiapine Versus Control
3.5. Generalized Additive Modeling—Quetiapine Versus Haloperidol
3.6. Sensitivity Analysis—Quetiapine Versus Control
3.7. Sensitivity Analysis—Quetiapine Versus Haloperidol
4. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Slooter, A.J.C.; Otte, W.M.; Devlin, J.W.; Arora, R.C.; Bleck, T.P.; Claassen, J.; Duprey, M.S.; Ely, E.W.; Kaplan, P.W.; Latronico, N.; et al. Updated Nomenclature of Delirium and Acute Encephalopathy: Statement of Ten Societies. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salluh, J.I.F.; Wang, H.; Schneider, E.B.; Nagaraja, N.; Yenokyan, G.; Damluji, A.; Serafim, R.B.; Stevens, R.D. Outcome of Delirium in Critically Ill Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ 2015, 350, h2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hshieh, T.T.; Inouye, S.K.; Oh, E.S. Delirium in the Elderly. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2020, 36, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stollings, J.L.; Kotfis, K.; Chanques, G.; Pun, B.T.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Ely, E.W. Delirium in Critical Illness: Clinical Manifestations, Outcomes, and Management. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-89042-555-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, K.; Balas, M.C.; Stollings, J.L.; McNett, M.; Girard, T.D.; Chanques, G.; Kho, M.E.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Weinhouse, G.L.; Brummel, N.E.; et al. A Focused Update to the Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Pain, Anxiety, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption in Adult Patients in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2025, 53, e711–e727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, J.Y.; Colman, M.A.; Mendu, M.; Shah, S.J.; Fox, M.D.; Rost, N.S.; Kimchi, E.Y. Associations Between Stroke Localization and Delirium: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alıcı, Ş.; Öztürk Birge, A. The Frequency of Sepsis-Associated Delirium in Intensive Care Unit and Its Effect on Nurse Workload. J. Clin. Nurs. 2025, 34, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen-Ranberg, N.C.; Poulsen, L.M.; Perner, A.; Wetterslev, J.; Estrup, S.; Hästbacka, J.; Morgan, M.; Citerio, G.; Caballero, J.; Lange, T.; et al. Haloperidol for the Treatment of Delirium in ICU Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2425–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, L.; Slooter, A.J.C.; Devlin, J.W.; Trogrlic, Z.; Hunfeld, N.G.M.; Osse, R.J.; Ponssen, H.H.; Brouwers, A.J.B.W.; Schoonderbeek, J.F.; Simons, K.S.; et al. Efficacy of Haloperidol to Decrease the Burden of Delirium in Adult Critically Ill Patients: The EuRIDICE Randomized Clinical Trial. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, T.D.; Exline, M.C.; Carson, S.S.; Hough, C.L.; Rock, P.; Gong, M.N.; Douglas, I.S.; Malhotra, A.; Owens, R.L.; Feinstein, D.J.; et al. Haloperidol and Ziprasidone for Treatment of Delirium in Critical Illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2506–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziegielewski, C.; Skead, C.; Canturk, T.; Webber, C.; Fernando, S.M.; Thompson, L.H.; Foster, M.; Ristovic, V.; Lawlor, P.G.; Chaudhuri, D.; et al. Delirium and Associated Length of Stay and Costs in Critically Ill Patients. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 6612187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilevskis, E.E.; Chandrasekhar, R.; Holtze, C.H.; Graves, J.; Speroff, T.; Girard, T.D.; Patel, M.B.; Hughes, C.G.; Cao, A.; Pandharipande, P.P.; et al. The Cost of ICU Delirium and Coma in the Intensive Care Unit Patient. Med. Care 2018, 56, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.E.; Imai, K.; King, G.; Stuart, E.A. MatchIt: Nonparametric Preprocessing for Parametric Causal Inference. J. Stat. Soft. 2011, 42, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürkner, P.-C. Brms: An R. Package for Bayesian Multilevel Models Using Stan. J. Stat. Soft. 2017, 80, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghadeer, S.; Almesned, R.S.; Alshehri, E.A.; Alwhaibi, A. Evaluation of the Efficacy and Safety of Quetiapine in the Treatment of Delirium in Adult ICU Patients: A Retrospective Comparative Study. JCM 2024, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneeton, B.; Maneeton, N.; Srisurapanont, M.; Chittawatanarat, K. Quetiapine versus Haloperidol in the Treatment of Delirium: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2013, 7, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhary, T.; Ahmed, I.; Luttfi, I.; Montasser, M. Quetiapine Versus Haloperidol in the Management of Hyperactive Delirium: Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurocrit Care 2024, 41, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffman, J.A.; Dilsaver, S.C. Cholinergic Mechanisms in Delirium. Am. J. Psychiatry 1988, 145, 382–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassi, T.; Rohrs, E.; Nicholas, M.; Reynolds, S. Meta-Analysis of Serological Biomarkers at Hospital Admission for the Likelihood of Developing Delirium during Hospitalization. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1179243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; McCusker, J.; Cole, M.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Primeau, F.; Elie, M. Use of Medications with Anticholinergic Effect Predicts Clinical Severity of Delirium Symptoms in Older Medical Inpatients. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfistermeister, B.; Tümena, T.; Gaßmann, K.-G.; Maas, R.; Fromm, M.F. Anticholinergic Burden and Cognitive Function in a Large German Cohort of Hospitalized Geriatric Patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salahudeen, M.S.; Duffull, S.B.; Nishtala, P.S. Anticholinergic Burden Quantified by Anticholinergic Risk Scales and Adverse Outcomes in Older People: A Systematic Review. BMC Geriatr. 2015, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, E.J.; Trivedi, M.H. A Review of Quetiapine in Combination with Antidepressant Therapy in Patients with Depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2007, 3, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Muñoz, F.; Alamo, C. Active Metabolites as Antidepressant Drugs: The Role of Norquetiapine in the Mechanism of Action of Quetiapine in the Treatment of Mood Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2013, 4, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, M.L.; Mulsant, B.H.; Pollock, B.G.; Lehman, M.E.; Greenspan, A.; Kirshner, M.A.; Bies, R.R.; Kapur, S.; Gharabawi, G. A Model of Anticholinergic Activity of Atypical Antipsychotic Medications. Schizophr. Res. 2006, 88, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmarajan, T.S.; Dharmarajan, T.S.; Kanagala, K.; Lebelt, A. Quetiapine Induced Urinary Dysfunction: An Adverse Anticholinergic Effect Needing Recognition. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, B6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, M.B.; Herzig, S.J.; Pekow, P.S.; Avrunin, J.; Lagu, T.; Lindenauer, P.K. Association between Sedating Medications and Delirium in Older Inpatients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2013, 61, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Quetiapine vs. Control Comparison | Quetiapine vs. Haloperidol Comparison | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Means | SMD | Means | SMD | ||
| Quetiapine (n = 259) | Control (n = 259) | Quetiapine (n = 168) | Haloperidol (n = 168) | |||
| Propensity Score | 0.3375 | 0.3361 | 0.0135 | 0.5825 | 0.5723 | 0.0901 |
| Age | 71.7992 | 71.6178 | 0.0125 | 71.4167 | 71.3393 | 0.0053 |
| Antidepressants | 0.2317 | 0.2008 | 0.0732 | 0.2262 | 0.2440 | −0.0423 |
| Benzodiazepines | 0.5676 | 0.5328 | 0.0701 | 0.5238 | 0.5655 | −0.0840 |
| Cancer | 0.2201 | 0.2278 | −0.0186 | 0.2798 | 0.2976 | −0.0431 |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | 0.1776 | 0.1931 | −0.0404 | 0.1667 | 0.1548 | 0.0311 |
| Depression | 0.2432 | 0.2510 | −0.0180 | 0.2024 | 0.1845 | 0.0416 |
| Diabetes | 0.3475 | 0.3591 | −0.0243 | 0.3929 | 0.3750 | 0.0375 |
| Gender | 0.3707 | 0.3552 | 0.0320 | 0.3988 | 0.4048 | −0.0123 |
| Hypertension | 0.4788 | 0.4710 | 0.0155 | 0.4702 | 0.4881 | −0.0357 |
| Myocardial Infarction | 0.2317 | 0.2355 | −0.0092 | 0.2560 | 0.2619 | −0.0141 |
| Opioids | 0.6873 | 0.6680 | 0.0416 | 0.7976 | 0.7976 | 0.0000 |
| Sepsis | 0.2819 | 0.3127 | −0.0687 | 0.2143 | 0.2143 | 0.0000 |
| Stroke | 0.2510 | 0.2432 | 0.0178 | 0.1964 | 0.1905 | 0.0137 |
| Quetiapine vs. Control | Quetiapine vs. Haloperidol | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | Estimated Error | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI | R^ | Bulk Effective Sample Size | Tail Effective Sample Size | Estimate | Estimated Error | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI | R^ | Bulk Effective Sample Size | Tail Effective Sample Size | |
| (Intercept) | 1.1054 | 0.1517 | 0.8202 | 1.4135 | 1.0002 | 15,050.8 | 9183.7 | 0.8707 | 0.3535 | 0.2448 | 1.6304 | 1.0004 | 9304.9 | 7770.6 |
| Age | −0.2962 | 0.8889 | −1.8913 | 1.5408 | 1.0001 | 6712.4 | 8406.9 | −0.4389 | 0.9614 | −2.2499 | 1.4932 | 1.0004 | 9733.1 | 8959.6 |
| Antidepressants | −0.0262 | 0.1395 | −0.2804 | 0.2655 | 1.0009 | 11,642.8 | 7625.1 | −0.1457 | 0.2733 | −0.6314 | 0.4252 | 1.0000 | 9854.7 | 7752.8 |
| Benzodiazepines | 0.4224 | 0.1145 | 0.2012 | 0.6508 | 1.0002 | 13,847.2 | 9062.8 | 0.4643 | 0.2204 | 0.0326 | 0.9068 | 1.0006 | 8155.2 | 7514.7 |
| Cancer | 0.0529 | 0.1370 | −0.2045 | 0.3298 | 1.0004 | 13,744.6 | 8865.3 | −0.0630 | 0.2152 | −0.4622 | 0.3814 | 1.0003 | 10,877.2 | 8611.4 |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | 0.0522 | 0.1465 | −0.2170 | 0.3567 | 1.0000 | 14,398.4 | 8627.2 | 0.1554 | 0.3290 | −0.3888 | 0.9077 | 1.0007 | 10,220.0 | 6952.2 |
| Depression | −0.0450 | 0.1285 | −0.2868 | 0.2122 | 1.0001 | 12,973.0 | 9017.5 | 0.2824 | 0.3229 | −0.2866 | 0.9845 | 1.0001 | 8208.7 | 7287.8 |
| Diabetes | −0.0921 | 0.1246 | −0.3332 | 0.1600 | 1.0001 | 11,529.1 | 8523.1 | 0.2103 | 0.2291 | −0.2175 | 0.6871 | 1.0003 | 10,038.8 | 8217.5 |
| Gender | −0.0257 | 0.1179 | −0.2536 | 0.2125 | 1.0006 | 11,947.3 | 8742.4 | 0.2107 | 0.2209 | −0.2077 | 0.6638 | 1.0008 | 9340.2 | 8545.4 |
| Hypertension | 0.0732 | 0.1126 | −0.1480 | 0.2969 | 1.0007 | 13,561.5 | 8861.5 | 0.0373 | 0.2186 | −0.3919 | 0.4767 | 1.0001 | 10,571.8 | 8620.8 |
| Myocardial Infarction | 0.0293 | 0.1453 | −0.2491 | 0.3259 | 1.0001 | 11,403.8 | 9372.3 | 0.0575 | 0.2641 | −0.4310 | 0.6068 | 1.0001 | 9124.3 | 7706.8 |
| Opioids | 0.2412 | 0.1148 | 0.0092 | 0.4630 | 1.0001 | 12,971.3 | 8317.5 | 0.3800 | 0.2438 | −0.1260 | 0.8311 | 1.0003 | 10,288.7 | 7068.3 |
| Quetiapine | 0.3598 | 0.1135 | 0.1394 | 0.5881 | 1.0006 | 13,568.9 | 8805.8 | 0.4766 | 0.2037 | 0.0857 | 0.8790 | 1.0001 | 10935.9 | 8509.2 |
| Sepsis | 0.3174 | 0.1352 | 0.0630 | 0.5982 | 1.0003 | 13,171.7 | 8420.9 | 0.6023 | 0.2917 | 0.0891 | 1.2361 | 1.0008 | 9835.7 | 7022.8 |
| Stroke | 0.3502 | 0.1459 | 0.0781 | 0.6549 | 1.0004 | 10,931.9 | 7207.3 | 0.4404 | 0.3018 | −0.0984 | 1.0841 | 1.0006 | 8998.3 | 7678.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamidovic, A. Quetiapine Use Is Associated with Longer ICU Stay Compared to Control and Haloperidol: A Propensity Score–Matched Analysis Using the MIMIC-IV Database. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134438
Hamidovic A. Quetiapine Use Is Associated with Longer ICU Stay Compared to Control and Haloperidol: A Propensity Score–Matched Analysis Using the MIMIC-IV Database. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134438
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamidovic, Ajna. 2025. "Quetiapine Use Is Associated with Longer ICU Stay Compared to Control and Haloperidol: A Propensity Score–Matched Analysis Using the MIMIC-IV Database" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134438
APA StyleHamidovic, A. (2025). Quetiapine Use Is Associated with Longer ICU Stay Compared to Control and Haloperidol: A Propensity Score–Matched Analysis Using the MIMIC-IV Database. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134438






