Factors Determining Postoperative Early Continence in Patients Undergoing Robotic Radical Prostatectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
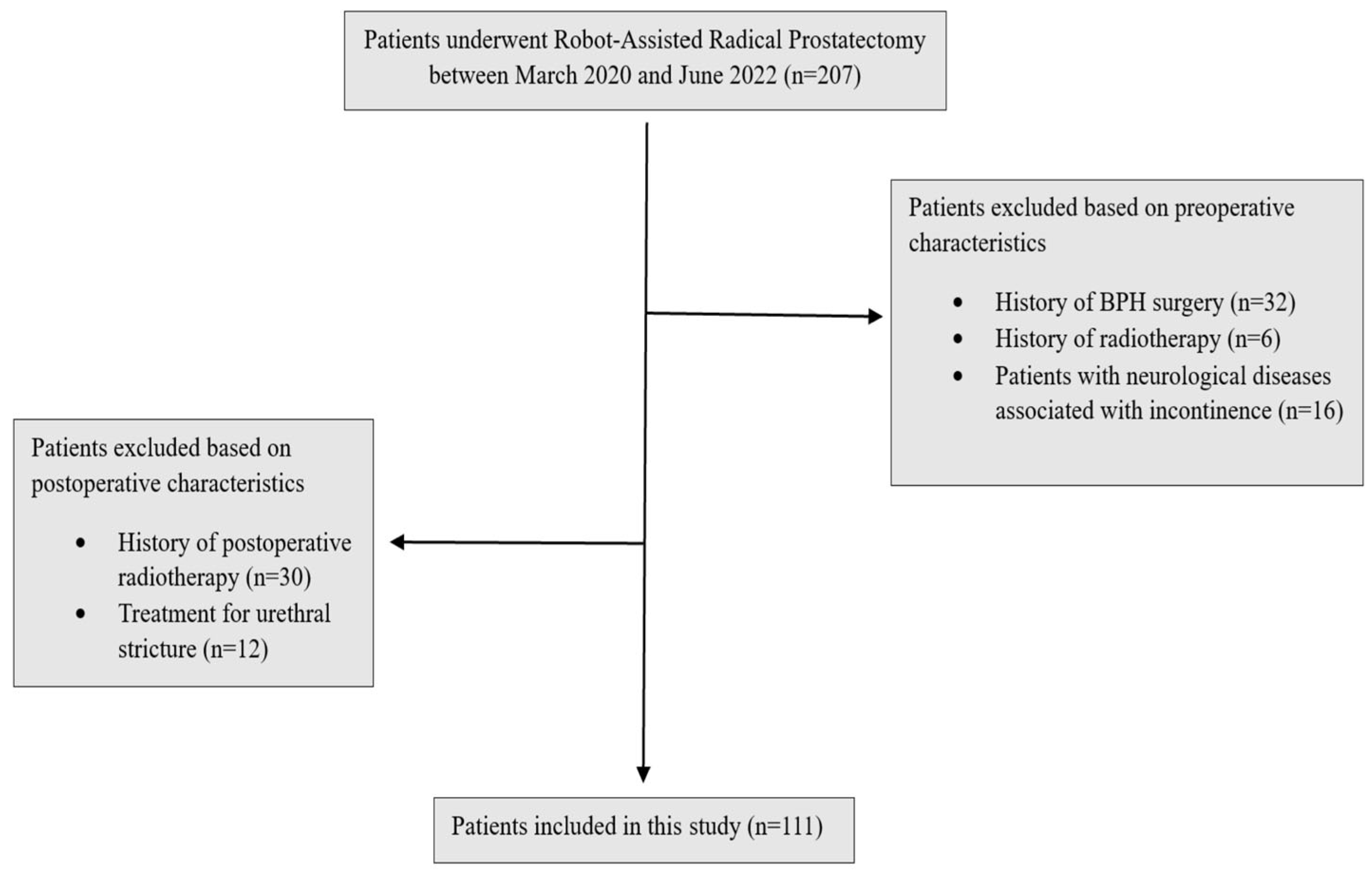
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compliance with Ethical Standards
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Statistical Analysis
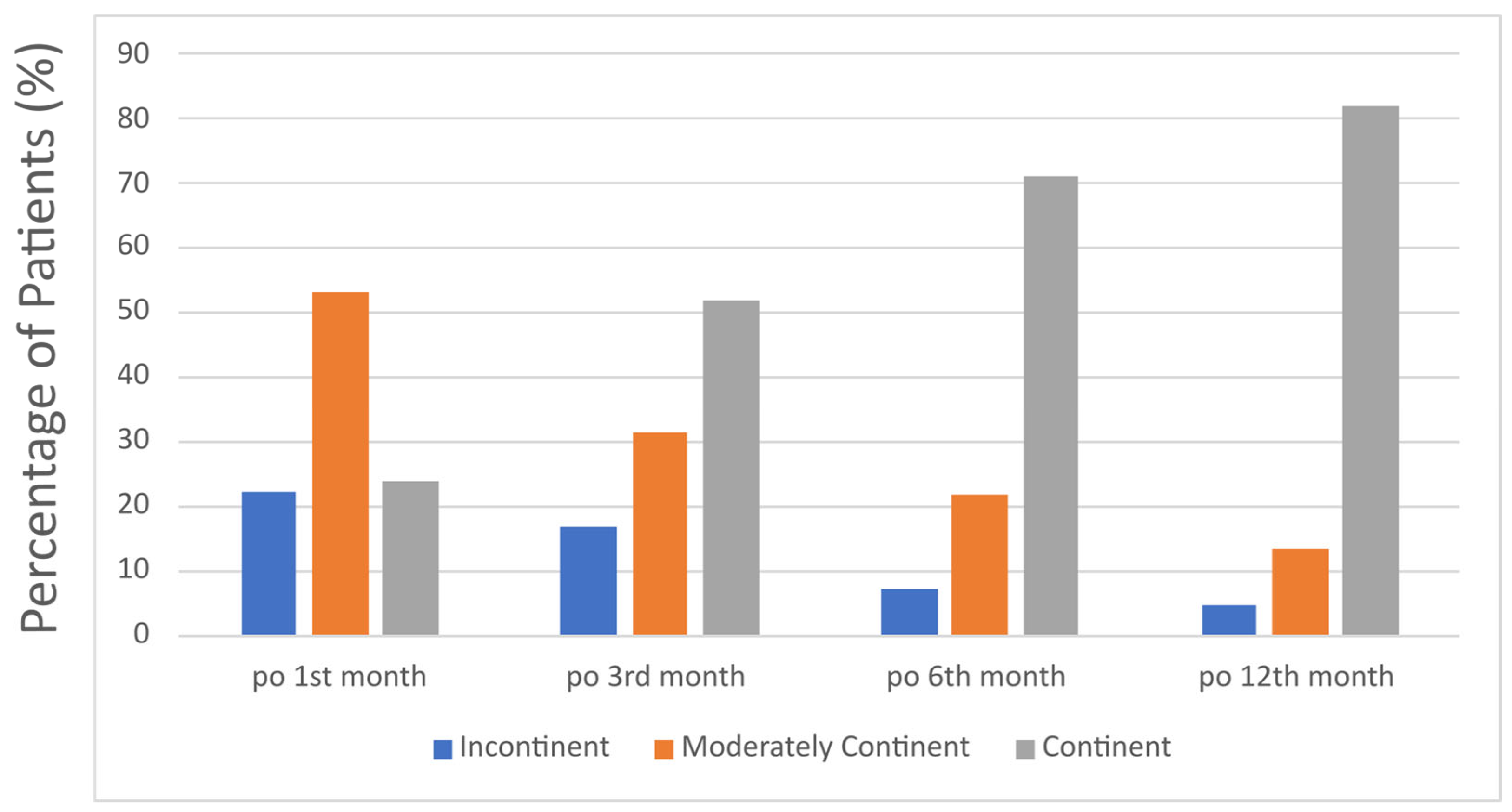
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP | Anterior–Posterior |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| IPSS | International Prostate Symptom Score |
| IIEF | International Index of Erectile Function |
| mpMRI | Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| PCa | Prostate Cancer |
| PSA | Prostate Specific Antigen |
| RARP | Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy |
References
- Bergengren, O.; Pekala, K.R.; Matsoukas, K.; Fainberg, J.; Mungovan, S.F.; Bratt, O.; Bray, F.; Brawley, O.; Luckenbaugh, A.N.; Mucci, L.; et al. 2022 Update on Prostate Cancer Epidemiology and Risk Factors—A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Ahlen, C.; Geissler, A.; Vogel, J. Comparison of the effectiveness of open, laparoscopic, and robotic-assisted radical prostatectomies based on complication rates: A retrospective observational study with administrative data from Switzerland. BMC Urol. 2024, 24, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.R.; Sivaraman, A.; Coelho, R.F.; Chauhan, S.; Palmer, K.J.; Orvieto, M.A.; Camacho, I.; Coughlin, G.; Rocco, B. Pentafecta: A new concept for reporting outcomes of robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vis, A.N.; van der Poel, H.G.; Ruiter, A.E.C.; Hu, J.C.; Tewari, A.K.; Rocco, B.; Patel, V.R.; Razdan, S.; Nieuwenhuijzen, J.A. Posterior, Anterior, and Periurethral Surgical Reconstruction of Urinary Continence Mechanisms in Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy: A Description and Video Compilation of Commonly Performed Surgical Techniques. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schifano, N.; Capogrosso, P.; Tutolo, M.; Dehò, F.; Montorsi, F.; Salonia, A. How to Prevent and Manage Post-Prostatectomy Incontinence: A Review. World J. Men’s Health 2021, 39, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collette, E.R.P.; Klaver, S.O.; Lissenberg-Witte, B.I.; van den Ouden, D.; van Moorselaar, R.J.A.; Vis, A.N. Patient reported outcome measures concerning urinary incontinence after robot assisted radical prostatectomy: Development and validation of an online prediction model using clinical parameters, lower urinary tract symptoms and surgical experience. J. Robot. Surg. 2021, 15, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, M.; Tennstedt, P.; Berliner, C.; Well, L.; Huland, H.; Budäus, L.; Adam, G.; Beyersdorff, D. Predictors of short and long term urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy in prostate MRI: Significance and reliability of standardized measurements. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 120, 108668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, M.E.; Carrozzino, D.; Guidi, J.; Patierno, C. Charlson Comorbidity Index: A Critical Review of Clinimetric Properties. Psychother. Psychosom. 2022, 91, 8–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucuk, E.V.; Sobay, R.; Tahra, A. Ultrapreservation in Robotic Assisted Radical Prostatectomy Provides Early Continence Recovery. JSLS J. Soc. Laparosc. Robot. Surg. 2023, 27, e2022.00077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Liao, L.; Zhang, X. Urinary continence outcomes of four years of follow-up and predictors of early and late urinary continence in patients undergoing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. BMC Urol. 2020, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tienza, A.; Robles, J.E.; Hevia, M.; Algarra, R.; Diez-Caballero, F.; Pascual, J.I. Prevalence analysis of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy and influential preoperative factors in a single institution. Aging Male 2018, 21, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tienza, A.; Hevia, M.; Benito, A.; Pascual, J.I.; Zudaire, J.J.; Robles, J.E. MRI factors to predict urinary incontinence after retropubic/laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2015, 47, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, S.; Kagebayashi, Y.; Iemura, Y.; Matsumura, Y.; Samma, S. Preoperative MRI Parameters Predict Urinary Continence after Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy in Prostatic Cancer Patients. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ragusa, A.; Brassetti, A.; Prata, F.; Iannuzzi, A.; Callè, P.; Tedesco, F.; Cacciatore, L.; Esperto, F.; Simone, G.; Scarpa, R.M.; et al. Predictors of Urinary Continence Recovery after Laparoscopic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: Is Surgical Urethral Length the Only Key Factor? Life 2023, 13, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrean, C.; Alam, A.; Hickling, D.; Vigil, H.R.; Lavallée, L.T.; Mallick, R.; Shorr, R.; Flaman, A.S.; McInnes, M.; Schieda, N.; et al. Preoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Membranous Urethral Length as a Predictor of Urinary Continence After Radical Prostatectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. Focus 2025, ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boczko, J.; Erturk, E.; Joseph, J.V. Is there a proper pelvic size for an extraperitoneal robot-assisted radical prostatectomy? J. Endourol. 2007, 21, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novara, G.; Ficarra, V.; D’elia, C.; Secco, S.; Cioffi, A.; Cavalleri, S.; Artibani, W. Evaluating urinary continence and preoperative predictors of urinary continence after robot assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. J. Urol. 2010, 184, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Q.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Bai, Y.; Qin, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, B.; Xie, L. Preoperative risk factors for early postoperative urinary continence recovery after non-nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy in Chinese patients: A single institute retrospective analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 14105–14109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Demographics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age | 61.5 ± 6.7 | mean ± SD |
| BMI | 27.7 (20.1–39) | median (min–max) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 4 (2–6) | median (min–max) |
| Prostate Specific Antigen (ng/mL) | 6.5 (2.44–24) | median (min–max) |
| IIEF | 16 (5–25) | median (min–max) |
| IPSS | 15 (1–35) | median (min–max) |
| Briganti Score | 3.1 (1–45.9) | median (min–max) |
| Prostate Volume (ml) | 50 (12–238) | median (min–max) |
| Final Pathological Outcomes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| pT Stage | pN Stage | ISUP Grade | Surgical Margin |
| T2a (n = 20) T2b (n = 18) T2c (n = 32) T3a (n = 32) T3b (n = 9) | Nx (n = 71) N0 (n = 37) N1 (n = 3) | Grade Group 1 (n = 15) Grade Group 2 (n = 84) Grade Group 3 (n = 10) Grade Group 4 (n = 0) Grade Group 5 (n = 2) | R0 (n = 88) R1 (n = 23) |
| Total Continent (n = 62) | Moderately Continent (n = 30) | Incontinent (n = 19) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative IPSS | 9 (1–18) | 18 (2–36) | 17 (1–34) | 0.033 a |
| Postoperative 3rd month IPSS | 5 (0–21) | 8 (0–16) | 9 (5–13) | 0.001 a |
| Postoperative 1st year IPSS | 3 (0–26) | 3 (0–12) | 6 (1–11) | 0.007 a |
| Difference between preoperative and postoperative 3rd IPSS | 4 (12–32) | 10 (6–32) | 9 (6–29) | 0.369 a |
| p | 0.002 b | 0.001 b | 0.001 b |
| Total Continent (n = 62) | Moderately Continent (n = 30) | Incontinent (n = 19) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
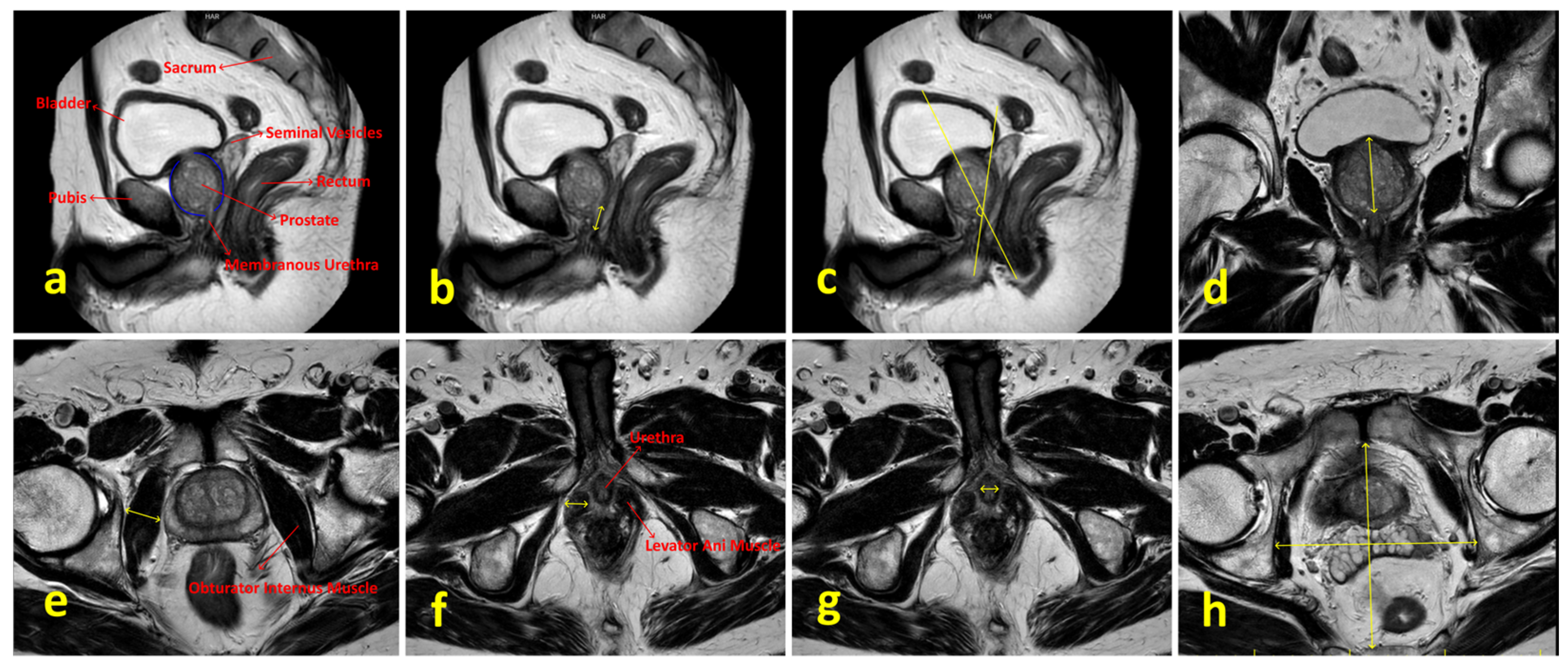
| Membranous urethral length (mm) | 14.5 (10.6–24.8) | 15.6 (10.6–21.4) | 15.8 (11.8–21.4) | 0.101 c |
| Membranous urethra–prostate axis angle | 56.6 (33.6–77.5) | 55.2 (32.7–86.6) | 59.4 (44.3–76.4) | 0.531 c |
| Obturator internus muscle thickness (mm) | 19.9 (13.4–25.9) | 20.3 (15.4–27.4) | 20.3 (13–27.7) | 0.900 c |
| Levator ani muscle thickness (mm) | 9.9 (6.3–14.9) | 10.5 (6.8–12.2) | 10.4 (8.5–12.4) | 0.825 c |
| Urethral width (mm) | 10.8 (6.7–13.9) | 9.6 (7–12.4) | 10.1 (8.3–14.1) | 0.012 c |
| Intraprostatic urethral Length (mm) | 32.4 (20.7–56.6) | 36.1 (19–57.6) | 35.2 (29–52.5) | 0.079 a |
| Pelvis AP diameter (mm) | 124.9 (101.5–141.6) | 128.4 (119–139.8) | 121.2 (80.5–134.7) | 0.033 a |
| Pelvis transverse diameter (mm) | 117.4 (96.5–146.1) | 121.2 (103.1–151.3) | 114 (96.8–132.8) | 0.002 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mod, M.; Güngör, H.S.; Karaca, H.; Tahra, A.; Sobay, R.; İnkaya, A.; Küçük, E.V. Factors Determining Postoperative Early Continence in Patients Undergoing Robotic Radical Prostatectomy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134405
Mod M, Güngör HS, Karaca H, Tahra A, Sobay R, İnkaya A, Küçük EV. Factors Determining Postoperative Early Continence in Patients Undergoing Robotic Radical Prostatectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134405
Chicago/Turabian StyleMod, Metin, Hasan Samet Güngör, Hakan Karaca, Ahmet Tahra, Resul Sobay, Abdurrahman İnkaya, and Eyüp Veli Küçük. 2025. "Factors Determining Postoperative Early Continence in Patients Undergoing Robotic Radical Prostatectomy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134405
APA StyleMod, M., Güngör, H. S., Karaca, H., Tahra, A., Sobay, R., İnkaya, A., & Küçük, E. V. (2025). Factors Determining Postoperative Early Continence in Patients Undergoing Robotic Radical Prostatectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134405






