Proposal for an Expanded “R” Classification: Impact of Positive Surgical Margin Length on Biochemical Recurrence After Robotic Radical Prostatectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCR | Biochemical Recurrence |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| PSA | Prostate-Specific Antigen |
| PSM | Positive Surgical Margin |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| RP | Radical Prostatectomy |
| RARP | Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gultekin, M.; Utku, E.; Ergun, A.; Sevinc, A.; Tutuncu, S.; Dundar, S.; Seymen, E. Türkiye Kanser İstatistikleri (Cancer Statistics in Turkey); Türkiye Halk Sağlığı Kurumu: Ankara, Turkey, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2019. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilt, T.J.; Vo, T.N.; Langsetmo, L.; Dahm, P.; Wheeler, T.; Aronson, W.J.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Taylor, B.C.; Brawer, M.K. Radical Prostatectomy or Observation for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: Extended Follow-up of the Prostate Cancer Intervention Versus Observation Trial (PIVOT). Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.I.; Amin, M.; Boccon-Gibod, L.; Egevad, L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Mikuz, G.; Newling, D.; Nilsson, S.; Sakr, W.; Srigley, J.R.; et al. Prognostic Factors and Reporting of Prostate Carcinoma in Radical Prostatectomy and Pelvic Lymphadenectomy Specimens. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. Suppl. 2005, 39 (Suppl. S216), 34–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, A.; Gandaglia, G.; Fossati, N.; Scuderi, S.; Bravi, C.A.; Mazzone, E.; Stabile, A.; Scarcella, S.; Robesti, D.; Barletta, F.; et al. Defining Clinically Meaningful Positive Surgical Margins in Patients Undergoing Radical Prostatectomy for Localised Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochiai, A.; Sotelo, T.; Troncoso, P.; Bhadkamkar, V.; Babaian, R.J. Natural History of Biochemical Progression after Radical Prostatectomy Based on Length of a Positive Margin. Urology 2008, 71, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sooriakumaran, P.; Ploumidis, A.; Nyberg, T.; Olsson, M.; Akre, O.; Haendler, L.; Egevad, L.; Nilsson, A.; Carlsson, S.; Jonsson, M.; et al. The Impact of Length and Location of Positive Margins in Predicting Biochemical Recurrence after Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy with a Minimum Follow-Up of 5 Years. BJU Int. 2015, 115, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, K.; Cronin, A.M.; Carlino, L.J.; Savage, C.J.; Maschino, A.C.; Al-Ahmadie, H.A.; Gopalan, A.; Tickoo, S.K.; Scardino, P.T.; Eastham, J.A.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Subclassification of Radical Prostatectomy Positive Margins by Linear Extent and Gleason Grade. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Kibel, A.S.; Gao, F.; Tao, Y.; Humphrey, P.A. The Gleason Score of Tumor at the Margin in Radical Prostatectomy Is Predictive of Biochemical Recurrence. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, H.S.; Wiklund, P.; Patel, V.; Parashar, D.; Palmer, K.; Nyberg, T.; Skarecky, D.; Neal, D.E.; Ahlering, T.; Sooriakumaran, P. Surgical Margin Length and Location Affect Recurrence Rates after Robotic Prostatectomy. In Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 33, pp. 109.e7–109.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, K.R.; Hartmann, C.; Reis, S.T.; Viana, N.; Dall’Oglio, M.F.; Sant’Anna, A.C.; Nesrallah, A.; Nesrallah, L.; Antunes, A.A.; Camara-Lopes, L.H.; et al. Biochemical Recurrence Rates Are Similar for pT2-Positive Surgical Margins and pT3a. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2014, 40, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Lim, A.; Catterwell, R.; Selth, L. O’Callaghan, M. Length of positive surgical margins after radical prostatectomy: Does size matter?—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023, 26, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torous, V.F.; Simpson, R.W.; Balani, J.P.; Baras, A.S.; Berman, M.A.; Birdsong, G.G.; Giannico, G.A.; Paner, G.P.; Pettus, J.R.; Sessions, Z.; et al. College of American Pathologists Cancer Protocols: From Optimizing Cancer Patient Care to Facilitating Interoperable Reporting and Downstream Data Use. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2021, 5, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swindle, P.; Eastham, J.A.; Ohori, M.; Kattan, M.W.; Wheeler, T.; Maru, N.; Slawin, K.; Scardino, P.T. Do Margins Matter? The Prognostic Significance of Positive Surgical Margins in Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. J. Urol. 2005, 174, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iczkowski, K.A.; Lucia, M.S. Frequency of Positive Surgical Margin at Prostatectomy and Its Effect on Patient Outcome. Prostate Cancer 2011, 2011, 673021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysenko, I.; Mori, K.; Mostafaei, H.; Enikeev, D.V.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Briganti, A.; Quhal, F.; Janisch, F.; Shariat, S.F. Prognostic Value of Gleason Score at Positive Surgical Margin in Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2020, 18, e517–e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettus, J.A.; Weight, C.J.; Thompson, C.J.; Middleton, R.G.; Stephenson, R.A. Biochemical Failure in Men Following Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy: Impact of Surgical Margin Status and Location. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.H.; Cheng, L.; Srigley, J.R.; Griffiths, D.; Humphrey, P.A.; Van Der Kwast, T.H.; Montironi, R.; Wheeler, T.M.; Delahunt, B.; Egevad, L.; et al. International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Handling and Staging of Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. Working Group 5: Surgical Margins. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavina, R.; Manferrari, F.; Garofalo, M.; Bertaccini, A.; Vagnoni, V.; Guidi, M.; Borghesi, M.; Baccos, A.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Concetti, S.; et al. The Extent of Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection Correlates with the Biochemical Recurrence Rate in Patients with Intermediate- and High-Risk Prostate Cancer. BJU Int. 2011, 108, 1262–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploussard, G.; Agamy, M.A.; Alenda, O.; Allory, Y.; Mouracade, P.; Vordos, D.; Hoznek, A.; Abbou, C.C.; de la Taille, A.; Salomon, L. Impact of Positive Surgical Margins on Prostate-Specific Antigen Failure after Radical Prostatectomy in Adjuvant Treatment-Naïve Patients. BJU Int. 2011, 107, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskas, Y.; Lannes, F.; Branger, N.; Giusiano, S.; Guibert, N.; Pignot, G.; Walz, J.; Rossi, D.; Bastide, C. Extent of Positive Surgical Margins Following Radical Prostatectomy: Impact on Biochemical Recurrence with Long-Term Follow-Up. BMC Urol. 2019, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.I.; Partin, A.W.; Sauvageot, J.; Walsh, P.C. Prediction of Progression Following Radical Prostatectomy: A Multivariate Analysis of 721 Men with Long-Term Follow-Up. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1996, 20, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohori, M.; Wheeler, T.M.; Kattan, M.W.; Goto, Y.; Scardino, P.T. Prognostic Significance of Positive Surgical Margins in Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. J. Urol. 1995, 154, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, M.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Ko, K.; Jeong, C.W.; Lee, S.B.; Ku, J.H.; Hong, S.K.; Byun, S.S.; Kwak, C.; Kim, H.H.; et al. Impact of Positive Surgical Margins and Their Locations after Radical Prostatectomy: Comparison of Biochemical Recurrence According to Risk Stratification and Surgical Modality. World J. Urol. 2014, 32, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sooriakumaran, P.; Dev, H.S.; Skarecky, D.; Ahlering, T. The Importance of Surgical Margins in Prostate Cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 113, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to Build a Bridge from a Population-Based to a More “Personalized” Approach to Cancer Staging. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, K.B.; Jo, J.K.; Ho, J.N.; Oh, J.J.; Jeong, S.J.; Hong, S.K.; Byun, S.S.; Choe, G.; Lee, S.E. Prognostic Value of Focal Positive Surgical Margins after Radical Prostatectomy. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2016, 14, e313–e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
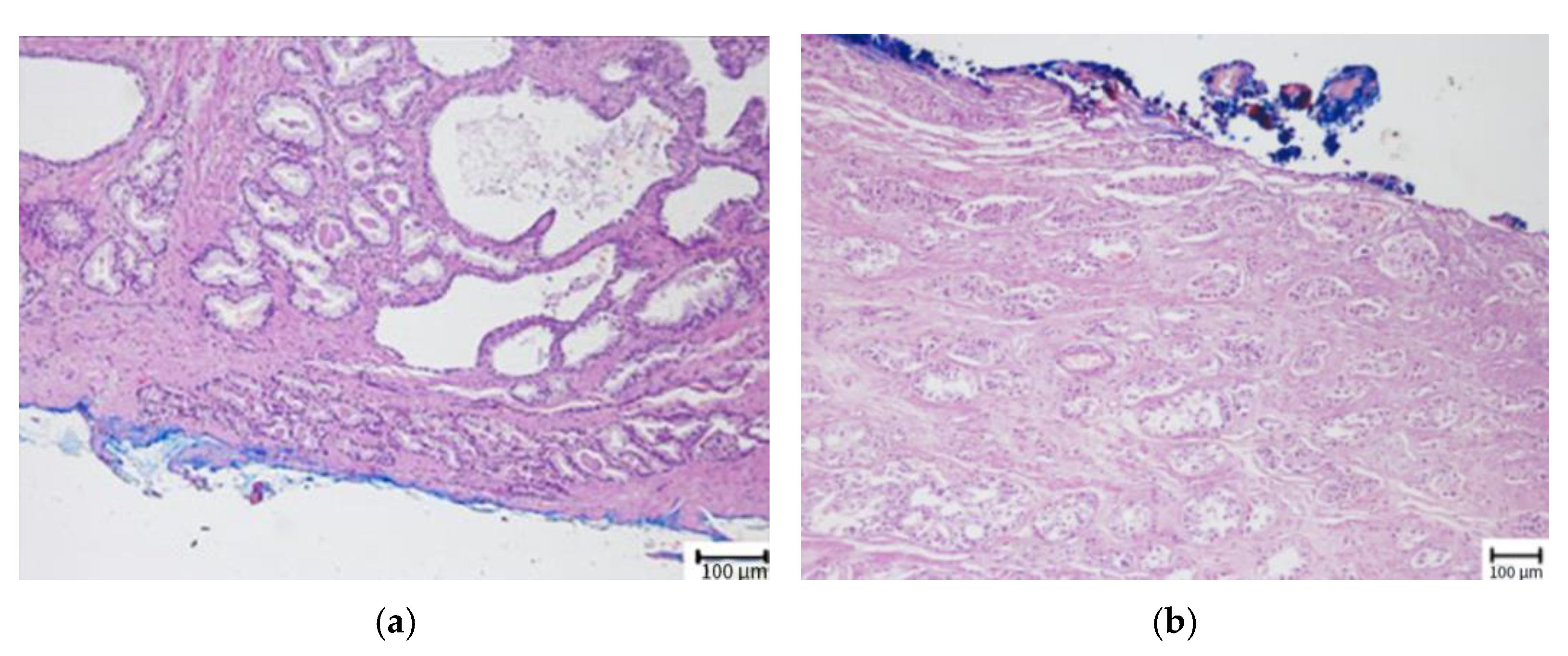
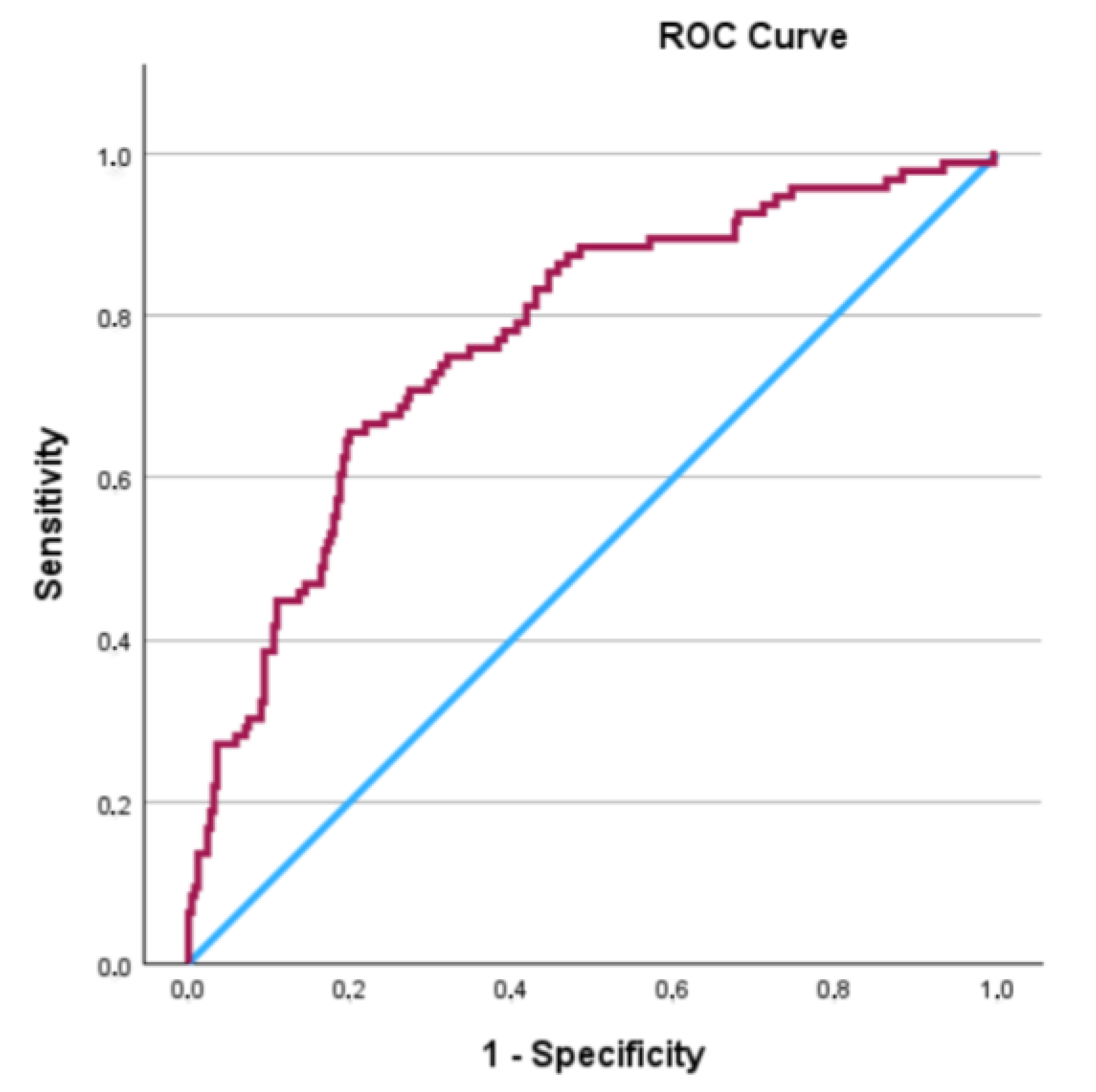
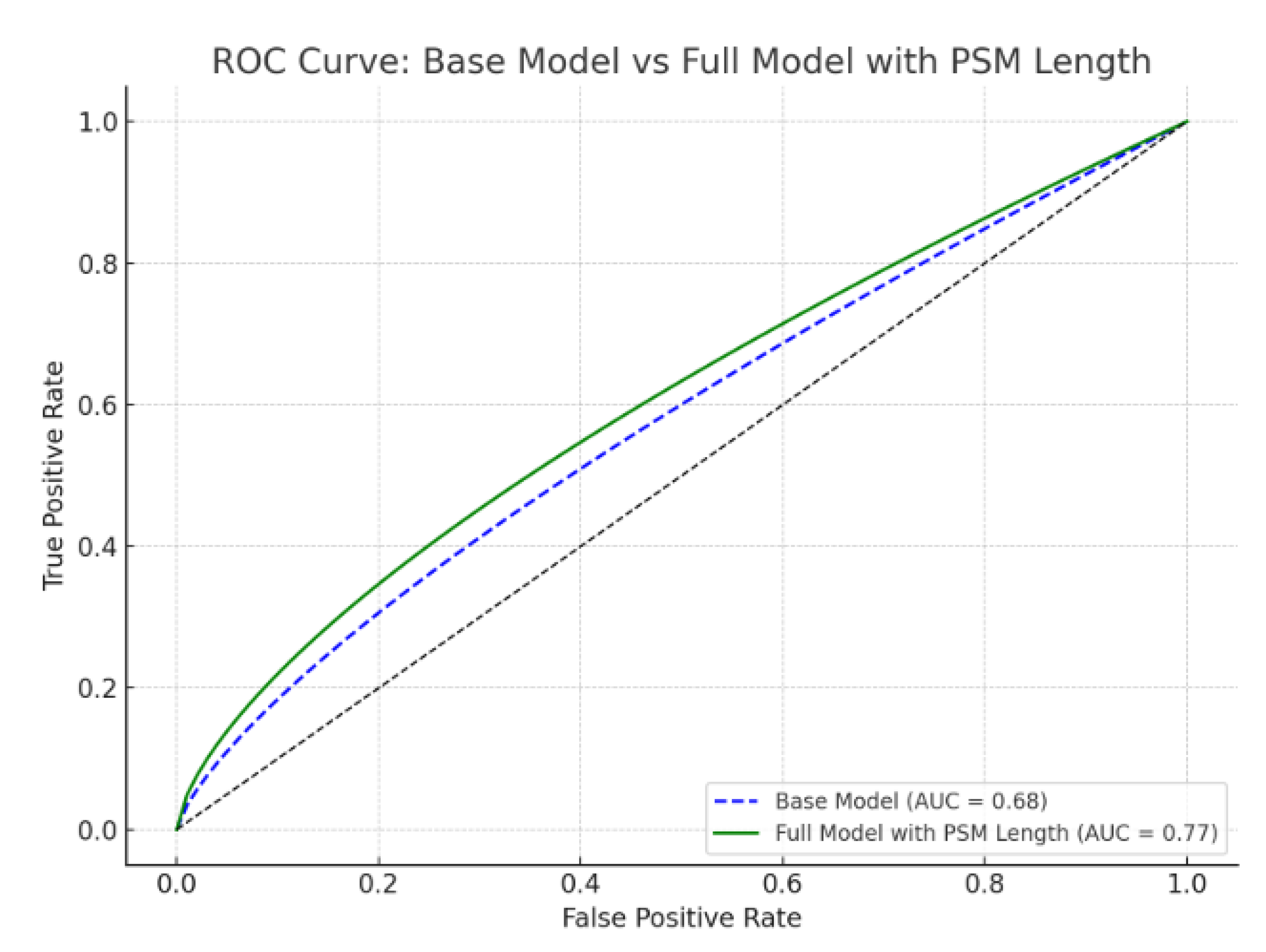
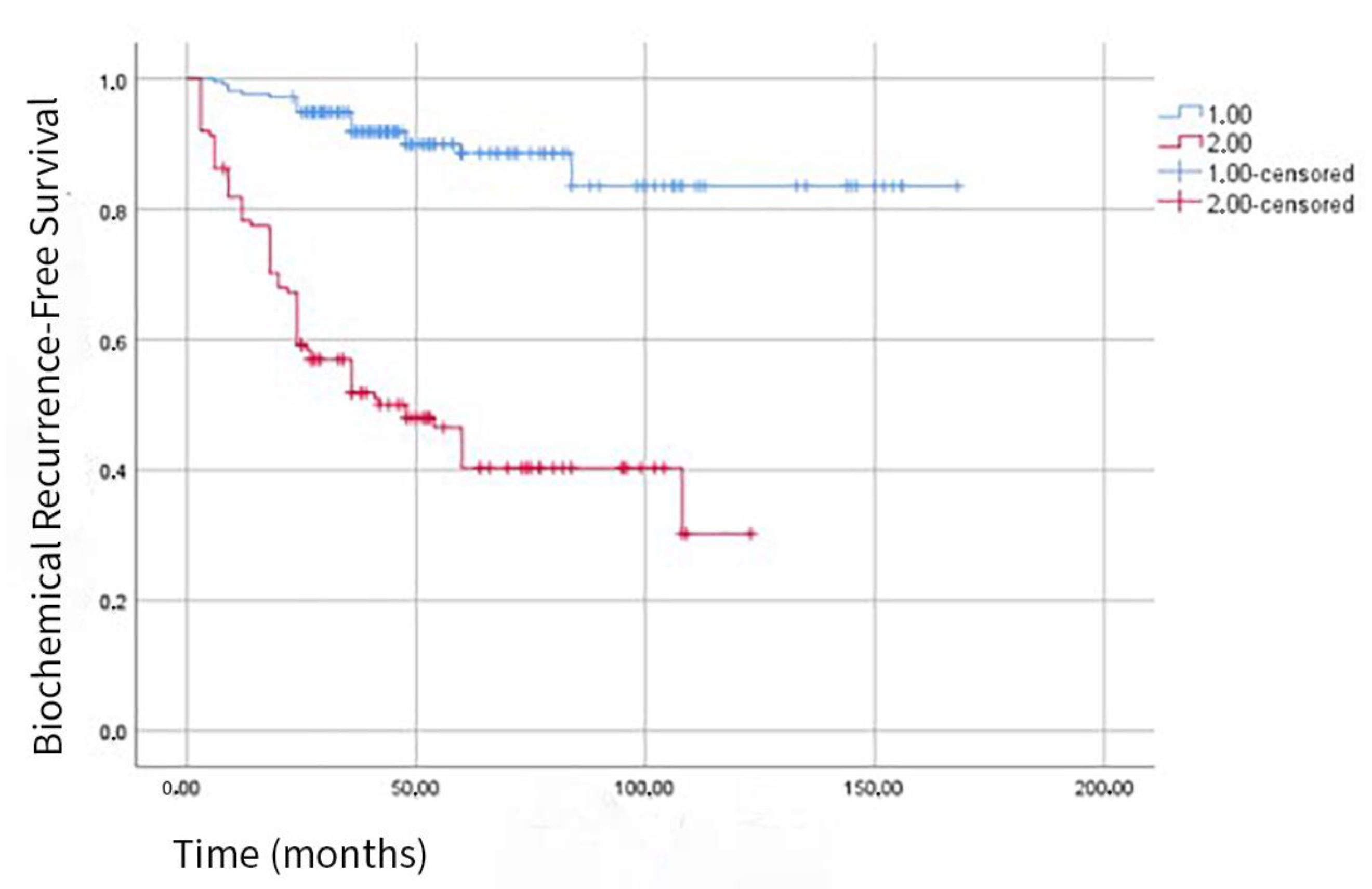
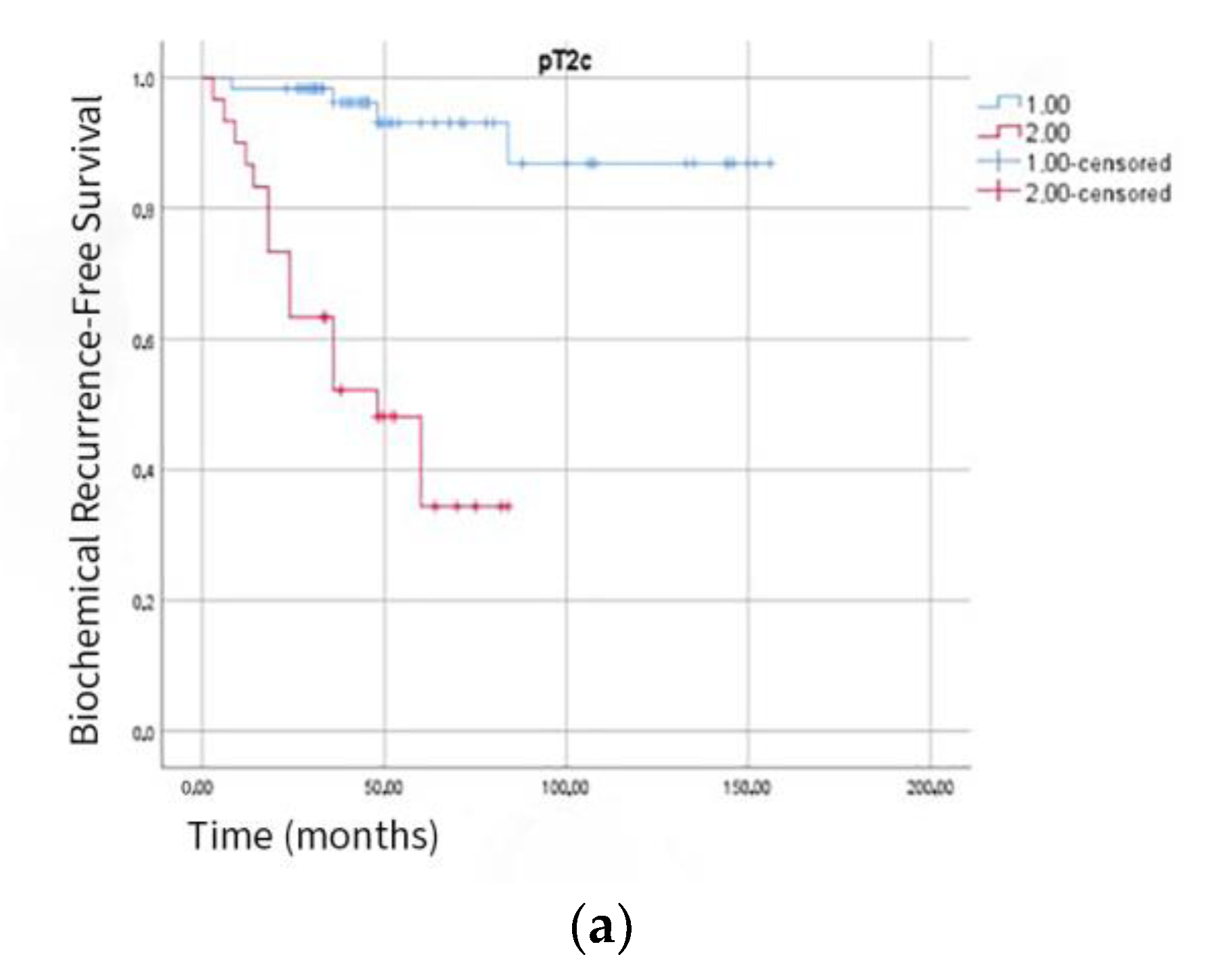
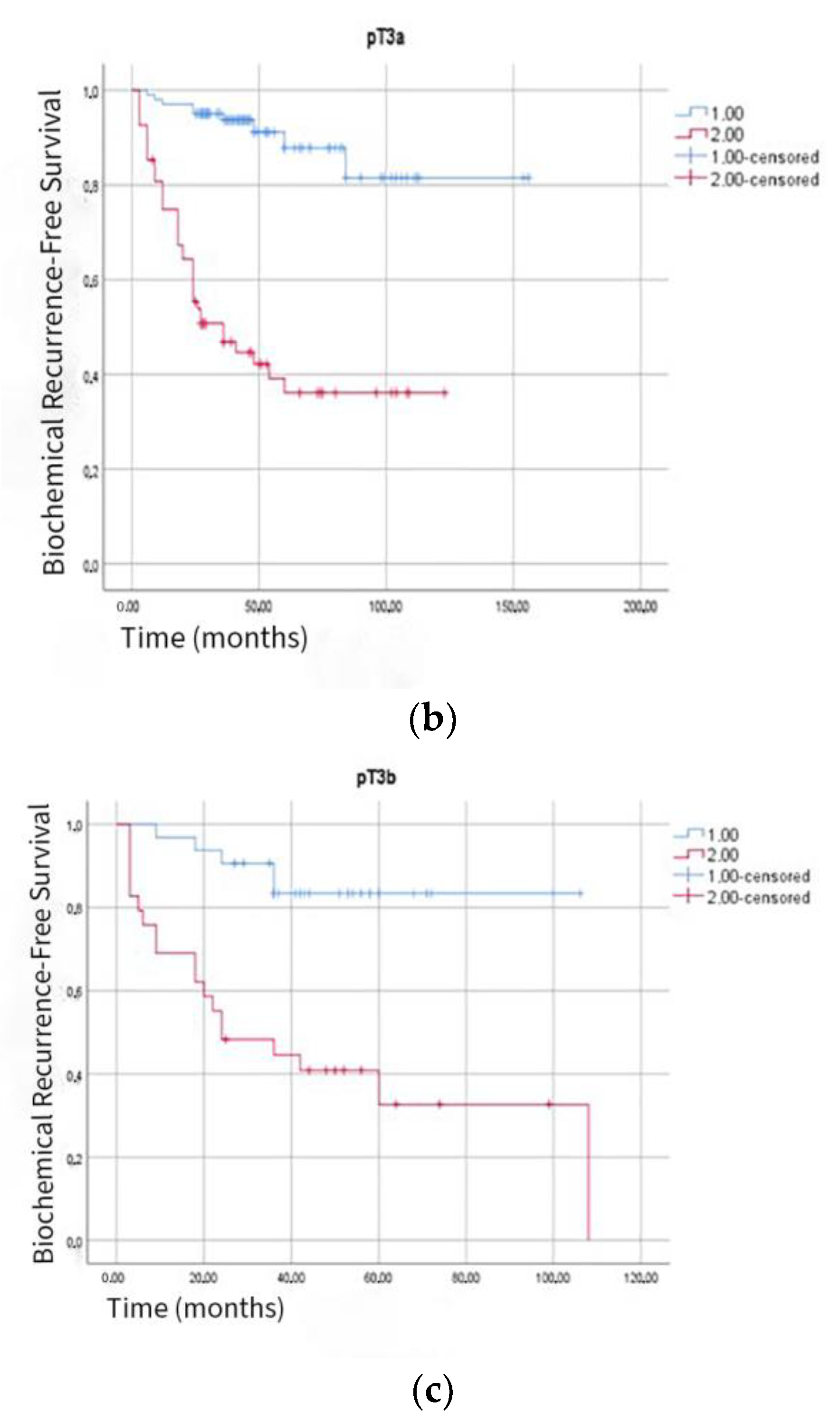
| Variable | All Patients (n = 353) | BCR (−) (n = 257) | BCR (+) (n = 96) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prostate volume (mean ± SD, cc) | 54.4 ± 19.7 | 54.4 ± 20.2 | 54.2 ± 18.5 | 0.936 |
| Tumor volume (mean ± SD, cc) | 7.7 ± 8.2 | 6.8 ± 6.9 | 10.2 ± 10.5 | 0.001 |
| Tumor density (mean ± SD, cc/cc) | 0.14 ± 0.14 | 0.13 ± 0.12 | 0.18 ± 0.17 | 0.002 |
| ISUP Grade Group: | <0.001 | |||
| 1 (Gleason ≤ 6) | 43 | 29 (67.4%) | 14 (32.6%) | |
| 2 (Gleason 3 + 4 = 7) | 165 | 134 (81.2%) | 31 (18.8%) | |
| 3 (Gleason 4 + 3 = 7) | 101 | 73 (72.3%) | 28 (27.7%) | |
| 4 (Gleason 8) | 26 | 15 (57.7%) | 11 (42.3%) | |
| 5 (Gleason ≥ 9) | 18 | 6 (33.3%) | 12 (66.7%) | |
| Lymph Node Dissection: | 0.005 | |||
| pNx, pN0 | 340 | 252 (74.1%) | 88 (25.9%) | |
| pN1 | 13 | 5 (38.5%) | 8 (61.5%) | |
| Clavien Complication Score: | 0.638 | |||
| 1 | 289 | 208 (72%) | 81 (28%) | |
| 2 | 52 | 39 (75%) | 13 (25%) | |
| 3 | 12 | 10 (83.3%) | 2 (16.7%) | |
| Pathological Stage: | 0.02 | |||
| T2a | 20 | 19 (95%) | 1 (5%) | |
| T2b | 13 | 11 (84.6%) | 2 (15.4%) | |
| T2c | 89 | 68 (76.4%) | 21 (23.6%) | |
| T3a | 170 | 122 (71.8%) | 48 (28.2%) | |
| T3b | 61 | 37 (60.7%) | 24 (39.3%) | |
| PSM Location: | 0.3 | |||
| Posterior | 162 | 116 (71.6%) | 46 (28.4%) | |
| Apex | 69 | 53 (76.8%) | 16 (23.2%) | |
| Bladder neck | 27 | 20 (74.1%) | 7 (25.9%) | |
| Anterior | 28 | 24 (85.7%) | 4 (14.3%) | |
| Multiple | 67 | 44 (65.7%) | 23 (34.3%) | |
| PSM Length (mm): | 4.1 ± 4.03 | 3.1 ± 3.2 | 6.6 ± 4.8 | <0.001 |
| <3.5 mm | 215 | 194 (75.5%) | 21 (21.9%) | |
| ≥3.5 mm | 138 | 63 (24.5%) | 75 (78.1%) |
| Factors | HR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-biopsy PSA | 1.016 | 0.995–1.038 | 0.142 |
| Clinical Stage | 1.333 | 0.873–2.036 | 0.183 |
| Specimen Tumor Density | 2.047 | 0.484–8.661 | 0.33 |
| Specimen ISUP Grade Group | 1.228 | 0.987–1.527 | 0.065 |
| Pathological Tumor Stage | 1.123 | 0.862–1.463 | 0.391 |
| pN Positivity | 1.282 | 0.994–1.654 | 0.056 |
| PSM Length | 1.113 | 1.076–1.152 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aksoy, A.K.; Tahra, A.; Sobay, R.; Kumcu, A.; Tosun, İ.; Boylu, U.; Küçük, E.V. Proposal for an Expanded “R” Classification: Impact of Positive Surgical Margin Length on Biochemical Recurrence After Robotic Radical Prostatectomy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124310
Aksoy AK, Tahra A, Sobay R, Kumcu A, Tosun İ, Boylu U, Küçük EV. Proposal for an Expanded “R” Classification: Impact of Positive Surgical Margin Length on Biochemical Recurrence After Robotic Radical Prostatectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124310
Chicago/Turabian StyleAksoy, Alper Kerem, Ahmet Tahra, Resul Sobay, Ali Kumcu, İlkay Tosun, Uğur Boylu, and Eyüp Veli Küçük. 2025. "Proposal for an Expanded “R” Classification: Impact of Positive Surgical Margin Length on Biochemical Recurrence After Robotic Radical Prostatectomy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124310
APA StyleAksoy, A. K., Tahra, A., Sobay, R., Kumcu, A., Tosun, İ., Boylu, U., & Küçük, E. V. (2025). Proposal for an Expanded “R” Classification: Impact of Positive Surgical Margin Length on Biochemical Recurrence After Robotic Radical Prostatectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124310






