Comparison of Propofol and Dexmedetomidine Infused Overnight to Treat Hyperactive and Mixed ICU Delirium: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trial Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Trial Interventions and Assessments
2.3.1. Study Drugs
2.3.2. Delirium Assessment
2.3.3. Adverse Events
2.4. Study Outcomes
2.5. Sample Size
Early Termination of the Study Because of Slow Recruitment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Deviations from the Original Statistical Plan
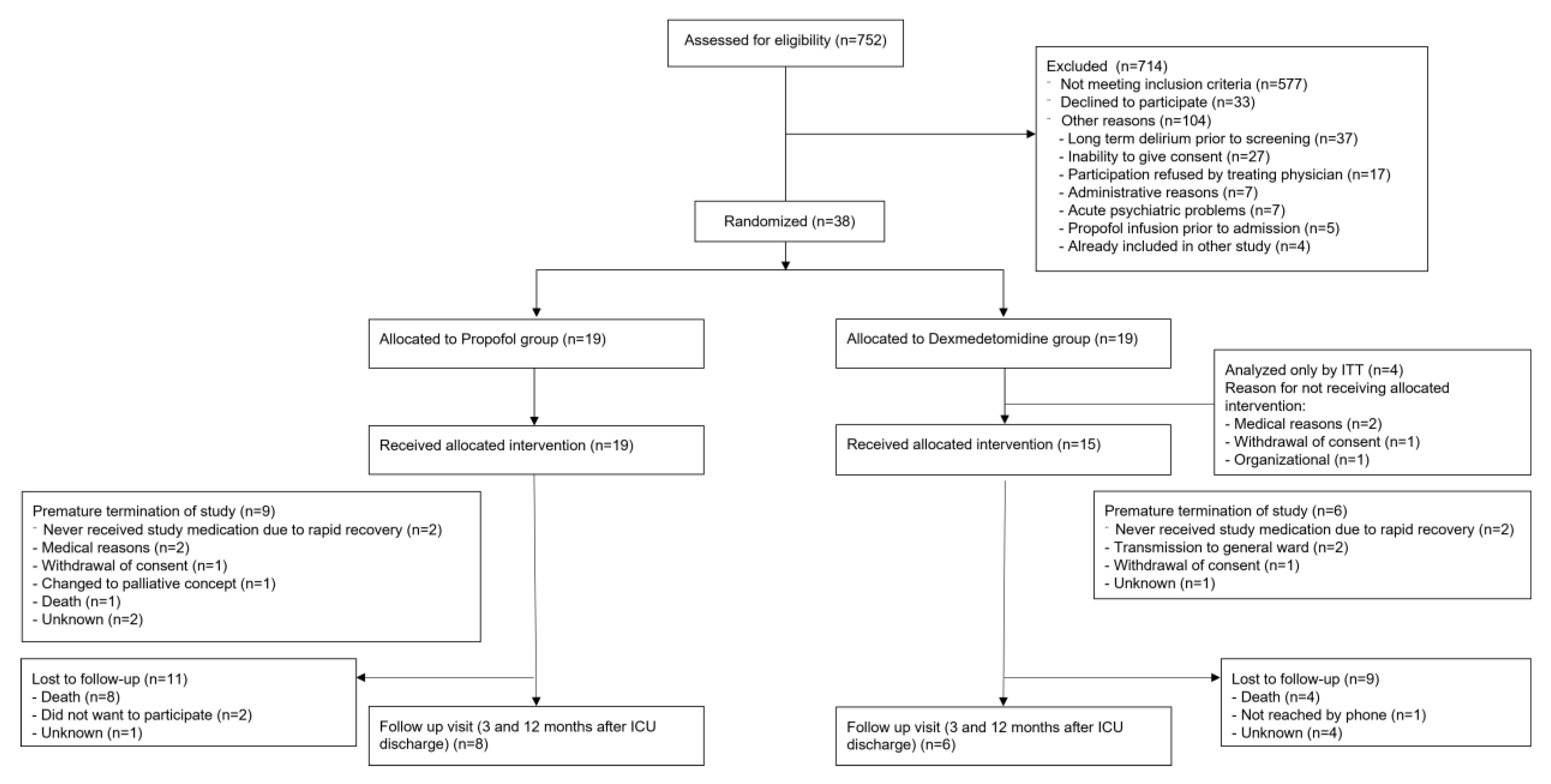
2.7. CONSORT Statement
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Trial Interventions
3.3. Outcomes
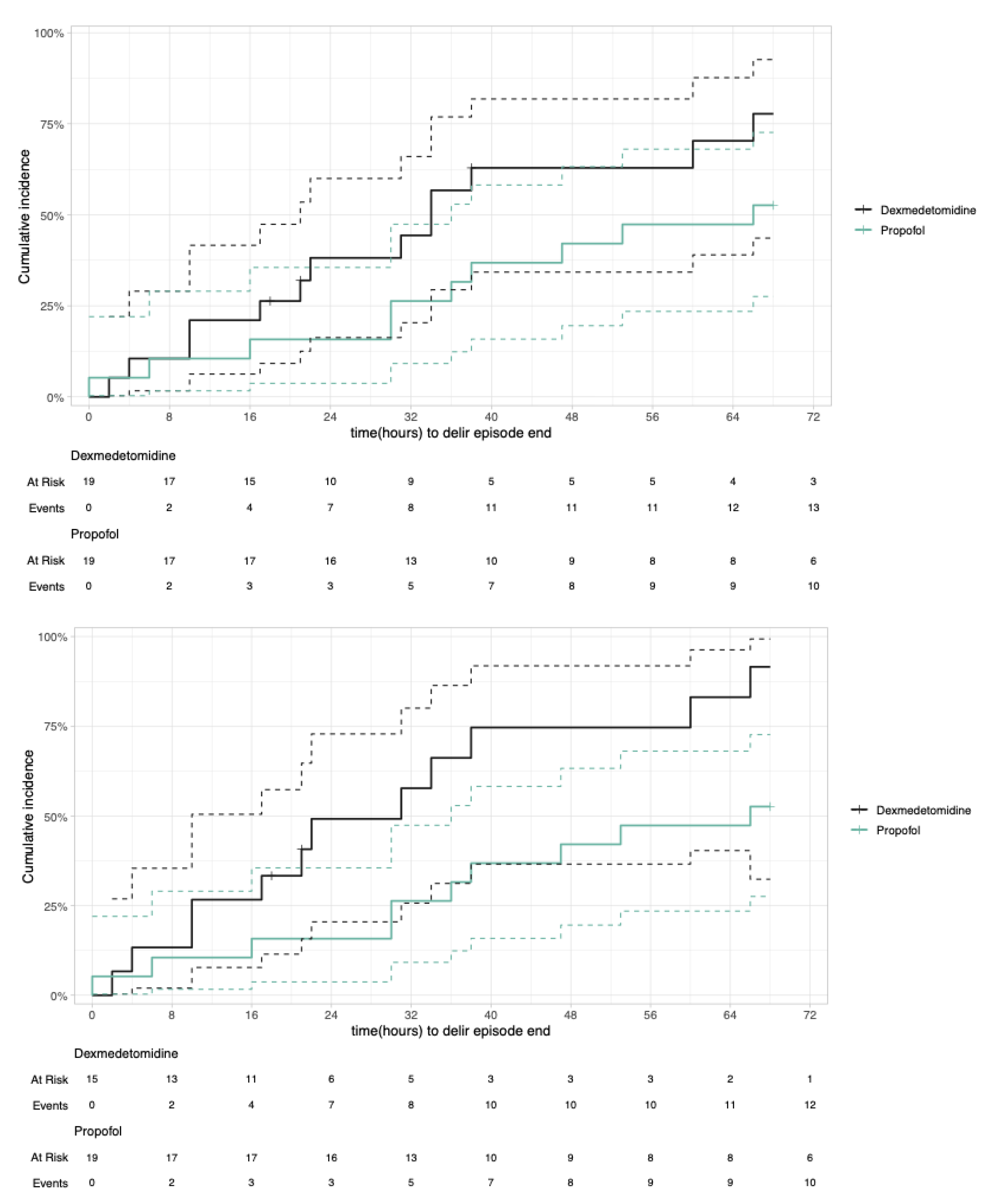
3.3.1. Primary Outcome—Delirium Duration
3.3.2. Secondary Outcomes
Recurrence of Delirium Until 28 Days After ICU Discharge
Death Until Day 28
3.3.3. Additional Endpoints
3.4. Safety End Points
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maclullich, A.M.J.; Hall, R.J. Who understands delirium? Age Ageing 2011, 40, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daou, M.; Telias, I.; Younes, M.; Brochard, L.; Wilcox, M.E. Abnormal Sleep, Circadian Rhythm Disruption, and Delirium in the ICU: Are They Related? Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 549908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krewulak, K.D.; Stelfox, H.T.; Leigh, J.P.; Wesley Ely, E.; Fiest, K.M. Incidence and prevalence of delirium subtypes in an adult ICU: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telias, I.; Wilcox, M.E. Sleep and Circadian Rhythm in Critical Illness. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollinger, A.; Ledergerber, K.; von Felten, S.; Sutter, R.; Rüegg, S.; Gantner, L.; Zimmermann, S.; Blum, A.; Steiner, L.A.; Marsch, S.; et al. Comparison of propofol and dexmedetomidine infused overnight to treat hyperactive and mixed ICU delirium: A protocol for the Basel ProDex clinical trial. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e015783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milbrandt, E.B.; Deppen, S.; Harrison, P.L.; Shintani, A.K.; Speroff, T.; Stiles, R.A.; Truman, B.; Bernard, G.R.; Dittus, R.S.; Ely, E.W. Costs associated with delirium in mechanically ventilated patients. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stollings, J.L.; Kotfis, K.; Chanques, G.; Pun, B.T.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Ely, E.W. Delirium in critical illness: Clinical manifestations, outcomes, and management. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandharipande, P.; Girard, T.; Jackson, J.; Morandi, A.; Thompson, J.; Pun, B.; Brummel, N.; Hughes, C.; Vasilevskis, E.; Shintani, A.; et al. Long-term cognitive impairment after critical illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, J.L.; Boustani, M.; Kamholz, B.; Shaughnessey, M.; Shay, K. Delirium: A strategic plan to bring an ancient disease into the 21st century. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, S237–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.W.; Skrobik, Y.; Gélinas, C.; Needham, D.M.; Slooter, A.J.C.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Watson, P.L.; Weinhouse, G.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; Rochwerg, B.; et al. Executive Summary: Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Pain, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption in Adult Patients in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 1532–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mart, M.F.; Williams Roberson, S.; Salas, B.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Ely, E.W. Prevention and Management of Delirium in the Intensive Care Unit. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 42, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, V.J.; McAuley, D.F. Sedation/drugs used in intensive care sedation. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2015, 28, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozorgi, H.; Zamani, M.; Motaghi, E.; Eslami, M. Dexmedetomidine as an Analgesic Agent with Neuroprotective Properties: Experimental and Clinical Aspects. J. Pain. Palliat. Care Pharmacother. 2021, 35, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huupponen, E.; Maksimow, A.; Lapinlampi, P.; Särkelä, M.; Saastamoinen, A.; Snapir, A.; Scheinin, H.; Scheinin, M.; Meriläinen, P.; Himanen, S.; et al. Electroencephalogram spindle activity during dexmedetomidine sedation and physiological sleep. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2008, 52, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L.E.; Lu, J.; Guo, T.; Saper, C.B.; Franks, N.P.; Maze, M. The α2-adrenoceptor agonist dexmedetomidine converges on an endogenous sleep-promoting pathway to exert its sedative effects. Anesthesiology 2003, 98, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrobik, Y.; Duprey, M.S.; Hill, N.S.; Devlin, J.W. Low-dose nocturnal dexmedetomidine prevents ICU delirium a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.V.; Sanjanwala, R.M.; Mohammed, M.K.; Le, M.L.; Arora, R.C. Dexmedetomidine versus propofol sedation in reducing delirium among older adults in the ICU: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2020, 37, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, A.C.; Hinkley, D.V. Bootstrap Methods and Their Application; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, J.R.; Lemeshow, S.; Saulnier, F. A New Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) Based on a European/North American Multicenter Study. JAMA 1993, 270, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, Y.; Pruna, A.; Turi, S.; Borghi, G.; Lee, T.C.; Zangrillo, A.; Landoni, G.; Pasin, L. Propofol and survival: An updated meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Crit Care 2023, 27, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, N.; Coruh, T.; Kehlibar, T.; Yapici, F.; Tarhan, A.; Can, Y.; Ozler, A.; Aykac, Z. Dexmedetomidine in Cardiac Surgery Patients Who Fail Extubation and Present with a Delirium State. Heart Surg. Forum 2011, 14, E93–E98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reade, M.C.; Eastwood, G.M.; Bellomo, R.; Bailey, M.; Bersten, A.; Cheung, B.; Davies, A.; Delaney, A.; Ghosh, A.; van Haren, F.; et al. Effect of Dexmedetomidine Added to Standard Care on Ventilator-Free Time in Patients With Agitated Delirium: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xie, G.; Zhang, K.; Song, S.; Song, F.; Jin, Y.; Fang, X. Dexmedetomidine vs. propofol sedation reduces delirium in patients after cardiac surgery: A meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Crit. Care 2017, 38, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djaiani, G.; Silverton, N.; Fedorko, L.; Carroll, J.; Styra, R.; Rao, V.; Katznelson, R. Dexmedetomidine versus Propofol Sedation Reduces Delirium after Cardiac Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Anesthesiology 2016, 124, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heybati, K.; Zhou, F.; Ali, S.; Deng, J.; Mohananey, D.; Villablanca, P.; Ramakrishna, H. Outcomes of dexmedetomidine versus propofol sedation in critically ill adults requiring mechanical ventilation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Anaesth. 2022, 129, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.; Alshamsi, F.; Carayannopoulos, K.L.; Granholm, A.; Piticaru, J.; Al Duhailib, Z.; Chaudhuri, D.; Spatafora, L.; Yuan, Y.; Centofanti, J.; et al. Dexmedetomidine vs. other sedatives in critically ill mechanically ventilated adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 811–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabi, Y.; Howe, B.D.; Bellomo, R.; Arabi, Y.M.; Bailey, M.; Bass, F.E.; Bin Kadiman, S.; McArthur, C.J.; Murray, L.; Reade, M.C.; et al. Early Sedation with Dexmedetomidine in Critically Ill Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2506–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabi, Y.; Neto, A.S.; Bellomo, R.; Howe, B.D.; Arabi, Y.M.; Bailey, M.; Bass, F.E.; Bin Kadiman, S.; McArthur, C.J.; Reade, M.C.; et al. Dexmedetomidine and Propofol Sedation in Critically Ill Patients and Dose-associated 90-Day Mortality: A Secondary Cohort Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial (SPICE III). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| (a) Baseline Table BaProDex ITT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propofol (n = 19) | Dexmedetomidine (n = 19) | |||
| Demographics | ||||
| Males (#, %) | 14 (73.7) | 13 (68.4) | ||
| Age (median, IQR) | 72 [64, 77] | 76 [71.5, 78.5] | ||
| Weight (median, IQR) | 80 [77, 91.5] | 85 [72, 90.5] | ||
| BMI (median, IQR) | 28.7 [25.55, 30.45] | 27.7 [25.3, 30.1] | ||
| Reason for Admission | ||||
| Admission Type (# pat, %) | Medical | 8 (42.1) | 5 (26.3) | |
| Scheduled surgical, | 2 (10.5) | 8 (42.1) | ||
| Unscheduled surgical | 9 (47.4) | 5 (26.3) | ||
| Heart surgical | 4 (21.1) | 6 (31.6) | ||
| Admission Information/Scores | ||||
| SAPS II Score (median, IQR) | 57 [47, 64.5] | 45 [40.5, 56] | ||
| Initial ICDSC (# pat, %) | 4 | 5 [26.3] | 2 [10.5] | |
| 5 | 2 [10.5] | 5 [26.3] | ||
| 6 | 7 [36.8] | 4 [21.1] | ||
| 7 | 5 [26.3] | 6 [31.6] | ||
| Inital GCS (median, IQR) | 11 [8, 14] | 13 [11.5, 14] | ||
| Ventilation at admission (# pat, %) | 15 (78.9) | 9 (47.4) | ||
| Noradrenalin at admission [mg] (median, IQR) | 0.1 [0, 0.2] | 0 [0, 0.1] | ||
| Past Medical history (# pat, %) | ||||
| Dementia | 0 (0) | 1 (5.3) | ||
| ADLQ prior to ICU (median, IQR) | 30 [27,32] | 30 [25, 31] | ||
| Substance abuse prior to ICU | Tobacco | 5 (26.3) | 7 (36.8) | |
| Alcohol | 4 (21.1) | 3 (15.8) | ||
| Drugs | ||||
| Diabetes | 6 (31.6) | 8 (42.1) | ||
| Heart rhythm disease | 10 (52.6) | 8 (42.1) | ||
| Severe or multiple infection | 4 (21.1) | 1 (5.3) | ||
| Thyroid disease | 3 (15.8) | 2 (10.5) | ||
| Kidney Disease | 4 (21.1) | 6 (31.6) | ||
| CVI | 3 (15.8) | 5 (26.3) | ||
| Intracranial haemorrhage | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Seizures | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| M. Parkinsons | 0 (0) | 1 (5.3) | ||
| Deliriums | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Hypertensions | 9 (47.4) | 9 (47.4) | ||
| Chronic gastric disease | 1 (5.3) | 1 (5.3) | ||
| Respiratory distress disease | 1 (5.3) | 3 (15.8) | ||
| Cancer, ongoing | 4 (21.1) | 2 (10.5) | ||
| PAD | 3 (15.8) | 2 (10.5) | ||
| Medication at ICU admission (# pat, %) | ||||
| ACE-Inhibitoren | 2 (10.5) | 0 (0) | ||
| Benzodiazepine | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Opiodie | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Narcotics due surgery | 3 (15.8) | 0 (0) | ||
| Glucocorticoide | 1 (5.3) | 2 (10.5) | ||
| Antidepressants | 0 (0) | 1 (5.3) | ||
| NSAID | 1 (5.3) | 2 (10.5) | ||
| Furosemide | 2 (10.5) | 2 (10.5) | ||
| Antibiotic | 3 (15.8) | 3 (15.8) | ||
| Ipratropium bromide | 0 (0) | 1 (5.3) | ||
| Other | 2 (10.5) | 2 (10.5) | ||
| (b) Baseline Table BaProDex PP | ||||
| Propofol (n = 19) | Dexmedetomidine (n = 15) | |||
| Demographics | ||||
| Males (#, %) | 14 (73.7) | 11 (73.3) | ||
| Age (median, IQR) | 72 [64, 77] | 75 [67, 77] | ||
| Weight (median, IQR) | 80 [77, 91.5] | 85 [73.5, 90] | ||
| BMI (median, IQR) | 28.7 [25.55, 30.45] | 27.7 [25.3, 30.1] | ||
| Reason for Admission | ||||
| Admission Type (# pat, %) | Medical | 8 (42.1) | 5 (33.3) | |
| Scheduled surgical, | 2 (10.5) | 6 (40) | ||
| Unscheduled surgical | 9 (47.4) | 4 (26.7) | ||
| Heart surgical | 4 (21.1) | 4 (26.7) | ||
| Admission Information/Scores | ||||
| SAPS II Score (median, IQR) | 57 [47, 64.5] | 46 [41, 58.5] | ||
| Initial ICDSC (# pat, %) | 4 | 5 [26.3] | 2 [13.3] | |
| 5 | 2 [10.5] | 3 [20] | ||
| 6 | 7 [36.8] | 3 [20] | ||
| 7 | 5 [26.3] | 5 [33.3] | ||
| Inital GCS (median, IQR) | 11 [8, 14] | 13 [11.5, 13.5] | ||
| Ventilation at admission (# pat, %) | 15 (78.9) | 8 (53.3) | ||
| Noradrenalin at admission [mg] (median, IQR) | 0.1 [0, 0.2] | 0 [0, 0.1] | ||
| Type of delirium | hyperactive | |||
| mixed | ||||
| Past Medical history (# pat, %) | ||||
| Dementia | 0 (0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| ADLQ prior to ICU (median, IQR) | 30 [27, 32] | 30 [25, 31] | ||
| Substance abuse prior to ICU | Tobacco | 5 (26.3) | 5 (33.3) | |
| Alcohol | 4 (21.1) | 3 (20) | ||
| Drugs | ||||
| Diabetes | 6 (31.6) | 7 (46.7) | ||
| Heart rhythm disease | 10 (52.6) | 6 (40) | ||
| Severe or multiple infection | 4 (21.1) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Thyroid disease | 3 (15.8) | 2 (13.3) | ||
| Kidney Disease | 4 (21.1) | 4 (26.7) | ||
| CVI | 3 (15.8) | 3 (20) | ||
| Intracranial haemorrhage | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Seizures | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| M. Parkinsons | 0 (0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Deliriums | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Hypertensions | 9 (47.4) | 7 (46.7) | ||
| Chronic gastric disease | 1 (5.3) | 0 (0) | ||
| Respiratory distress disease | 1 (5.3) | 3 (20) | ||
| Cancer, ongoing | 4 (21.1) | 2 (13.3) | ||
| PAD | 3 (15.8) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Medication at ICU admission (# pat, %) | ||||
| ACE-Inhibitoren | 2 (10.5) | 0 (0) | ||
| Benzodiazepine | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Opiodie | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Narcotics due surgery | 3 (15.8) | 0 (0) | ||
| Glucocorticoide | 1 (5.3) | 2 (13.3) | ||
| Antidepressants | 0 (0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| NSAID | 1 (5.3) | 2 (13.3) | ||
| Furosemide | 2 (10.5) | 2 (13.3) | ||
| Antibiotic | 3 (15.8) | 3 (20) | ||
| Ipratropium bromide | 0 (0) | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Other | 2 (10.5) | 2 (13.3) | ||
| Dexmedetomidine Group n = 15 | Propofol Group n = 19 | |
|---|---|---|
| Death at day 28 | 1 (7) | 5 (26) |
| Severity of ICU delirium (ICDSC) | 4.9 [4.0–5.2] | 4.7 [4.0–5.3] |
| Patients needed ventilation | 7 (47) | 15 (79) |
| Ventilation days [days] | 0.5 [0–1.8]; total = 30 | 4 [1–6]; total = 102 |
| Patients received rescue medicaitons | 4 (27) | 6 (32) |
| Rescue medication, nr of administrations | 11 | 71 |
| Haloperidol | ||
| Number of patients | 5 (33) | 9 (47) |
| Numer of administrations | 2 [1–4] | 3 [2–9] |
| Amount of haloperidol [mg] | 4 [2–4]; total 18.5 | 5 [2–9]; total 139 |
| Quetiapine | ||
| Number of patients | 8 (53) | 11 (58) |
| Number of administrations | 4 [2–7] | 8 [2–9] |
| Amount of oral quetiapine [mg] | 44 [12–84]; total 740 | 80 [74–140]; total 4695 |
| Depth of sedation [RASS] | 1.0 [0.0–1.5] | 1.0 [0.5–2.0] |
| Total costs of medication [CHF] | 58 [39–242] | 16 [6–23] |
| ICU length of stay [hours] | 43 [35–133] | 128 (72–330) |
| Length of hospital stay [days] | 10 [6–17] | 22 [15–37] |
| Survival three months after ICU discharge (number of patients died) | 2 (13) | 7 (37) |
| Survival twelve months after ICU discharge (number of patients died) | 2 (13) | 8 (42) |
| ADLQ | ||
| Patients with baseline | 15 (100) | 18 (95) |
| Baseline Score | 29.0 [26.1–30.4] | 30.4 [27.5–31.9] |
| Patients participated in 3-month follow-up | 11 (73) | 9 (47) |
| Score at 3-month follow-up | 29.9 [26.8–30.4] | 23.2 [16.0–30.4] |
| Patients participated in 1-year follow-up | 6 (40) | 8 (42) |
| Score at 1-year follow-up | 28.3 [23.2–31.2] | 21.0 [17.8–30.4] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zimmermann, S.; Hollinger, A.; Achermann, R.; von Felten, S.; Sutter, R.; Rüegg, S.; Abdelhamid, S.; Glatz, S.; Steiner, L.A.; Siegemund, M. Comparison of Propofol and Dexmedetomidine Infused Overnight to Treat Hyperactive and Mixed ICU Delirium: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124348
Zimmermann S, Hollinger A, Achermann R, von Felten S, Sutter R, Rüegg S, Abdelhamid S, Glatz S, Steiner LA, Siegemund M. Comparison of Propofol and Dexmedetomidine Infused Overnight to Treat Hyperactive and Mixed ICU Delirium: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124348
Chicago/Turabian StyleZimmermann, Stefan, Alexa Hollinger, Rita Achermann, Stefanie von Felten, Raoul Sutter, Stephan Rüegg, Salim Abdelhamid, Simon Glatz, Luzius A. Steiner, and Martin Siegemund. 2025. "Comparison of Propofol and Dexmedetomidine Infused Overnight to Treat Hyperactive and Mixed ICU Delirium: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124348
APA StyleZimmermann, S., Hollinger, A., Achermann, R., von Felten, S., Sutter, R., Rüegg, S., Abdelhamid, S., Glatz, S., Steiner, L. A., & Siegemund, M. (2025). Comparison of Propofol and Dexmedetomidine Infused Overnight to Treat Hyperactive and Mixed ICU Delirium: A Prospective Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124348








