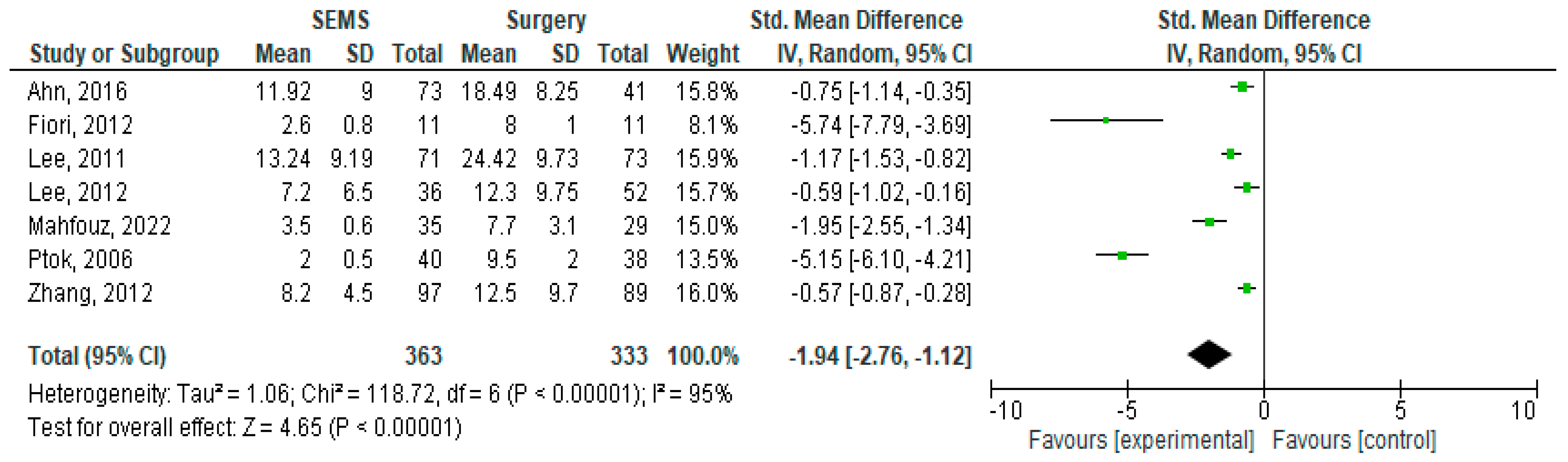Self-Expanding Metal Stents as an Alternative to Palliative Surgery in Advanced Obstructive Colorectal Cancer—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
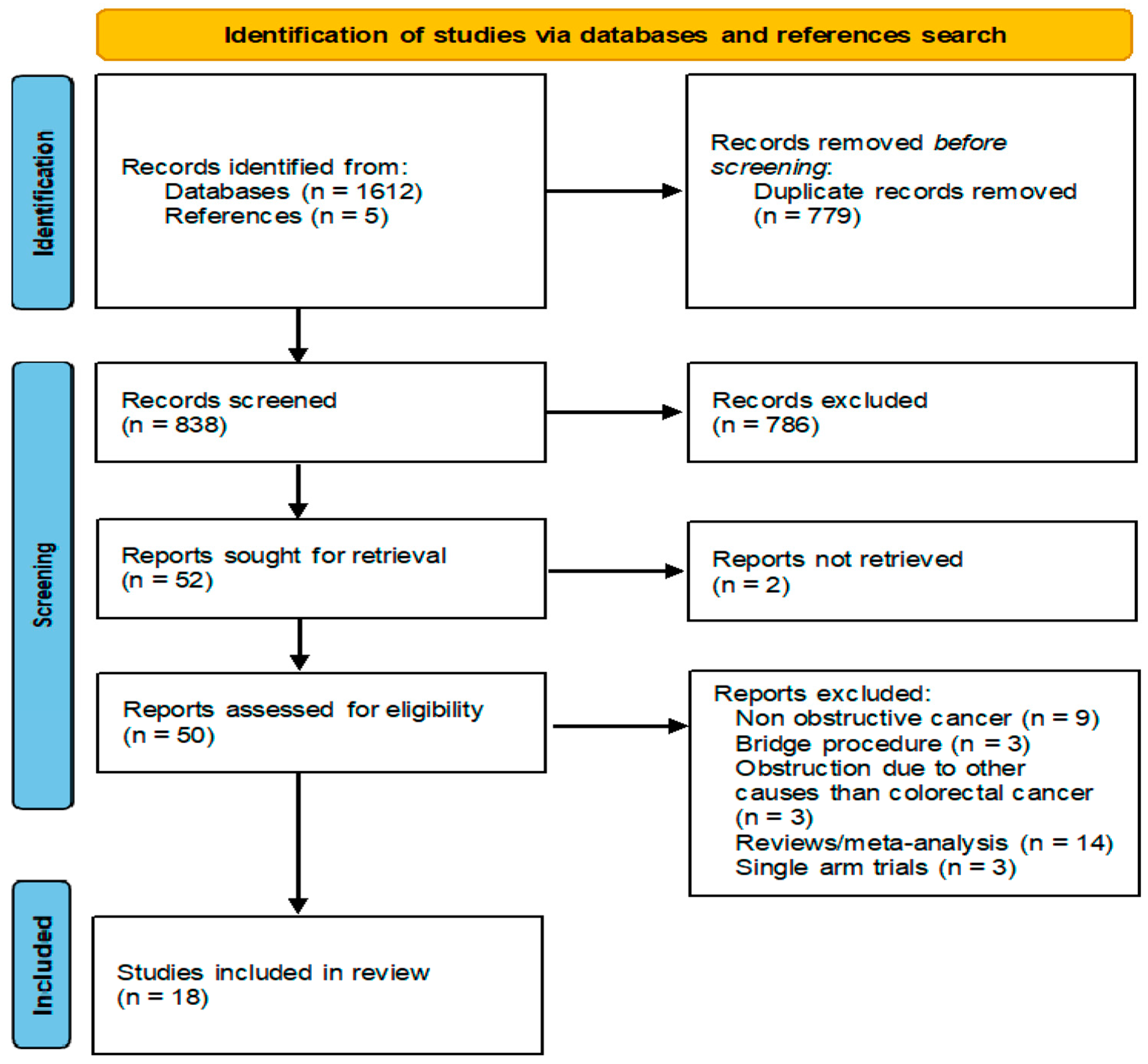
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Bias Assessment of Included Studies
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
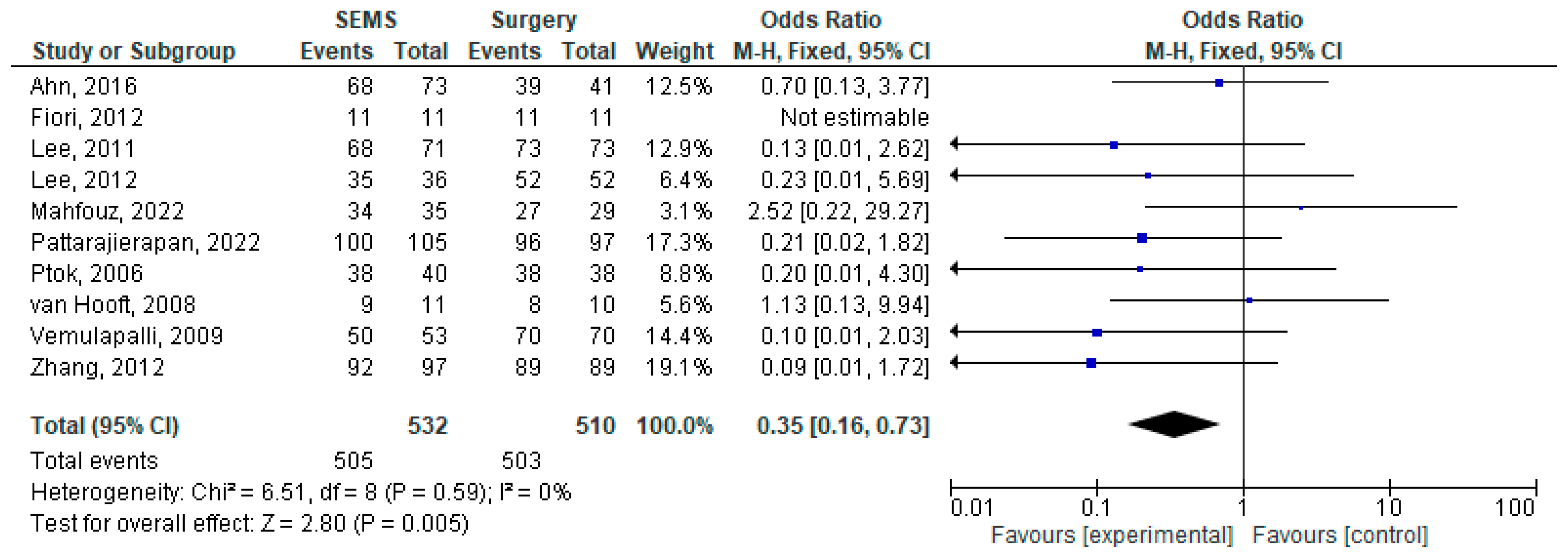
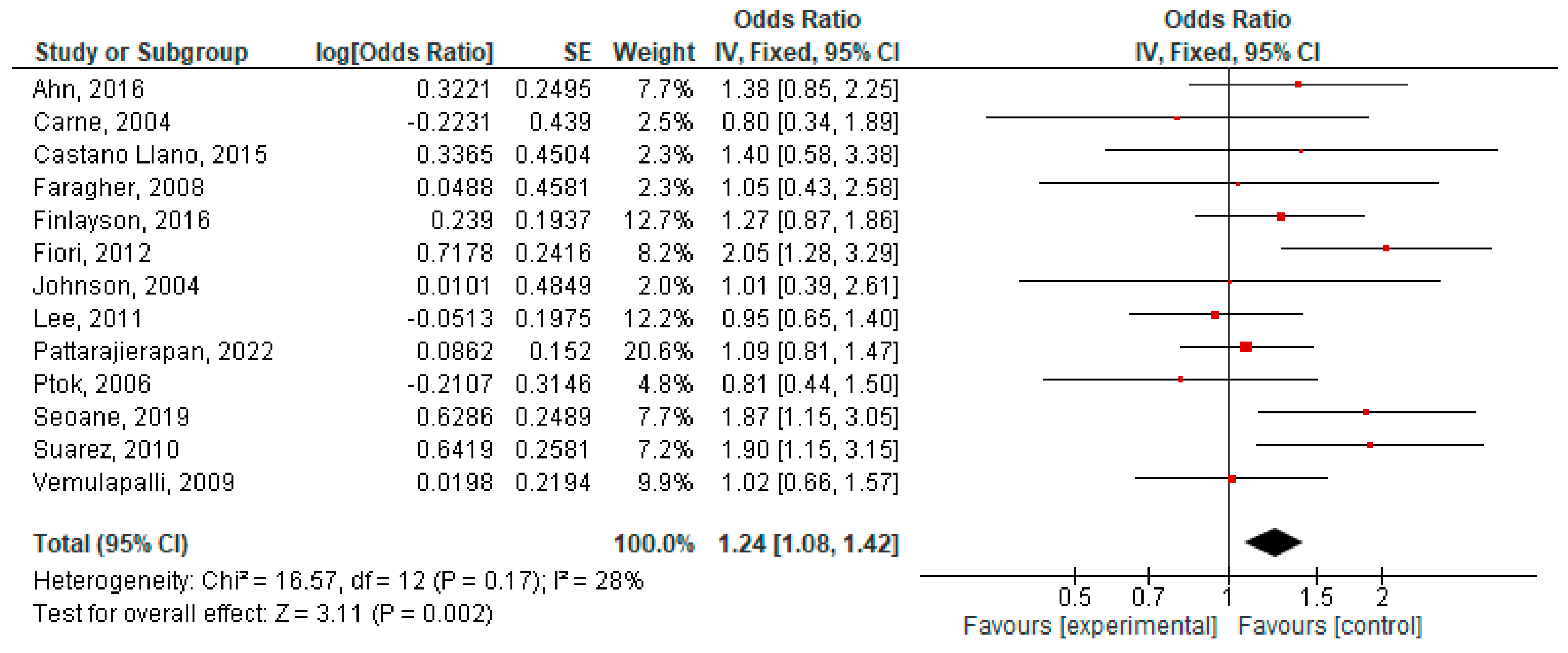
3.1. Outcome Analysis
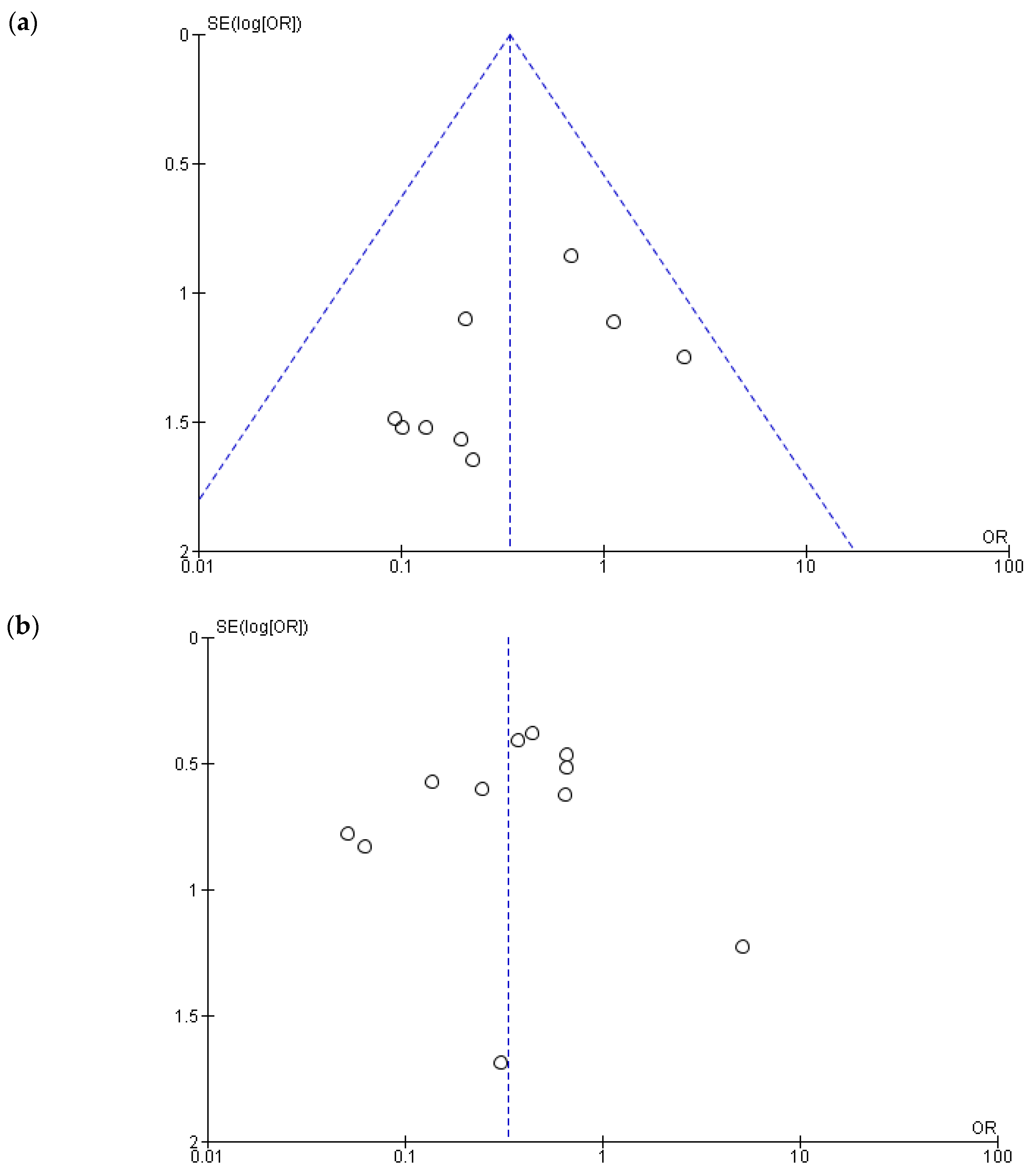
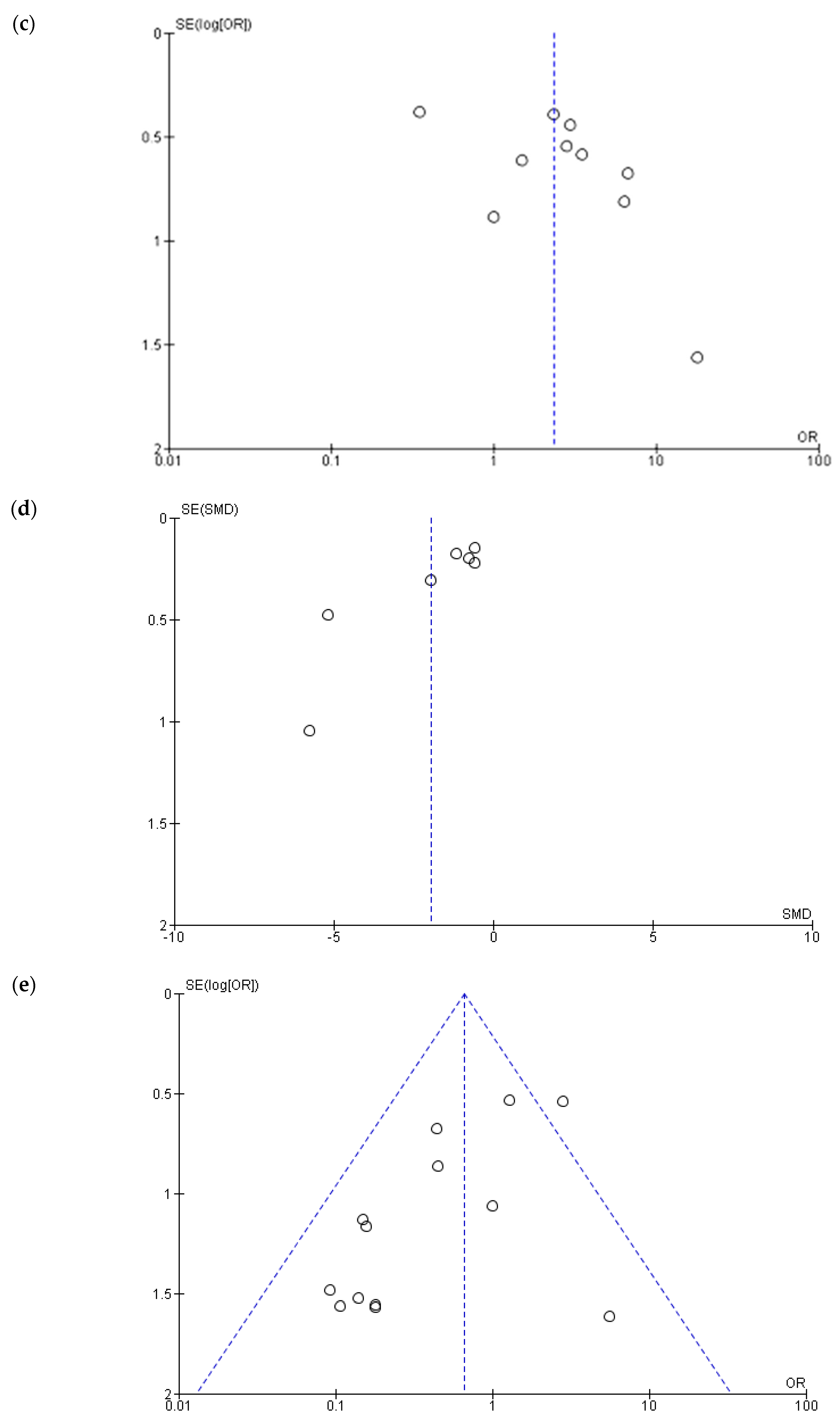
3.2. Heterogeneity, Publication Bias and Sensitivity Analysis
3.3. Subgroup Analysis
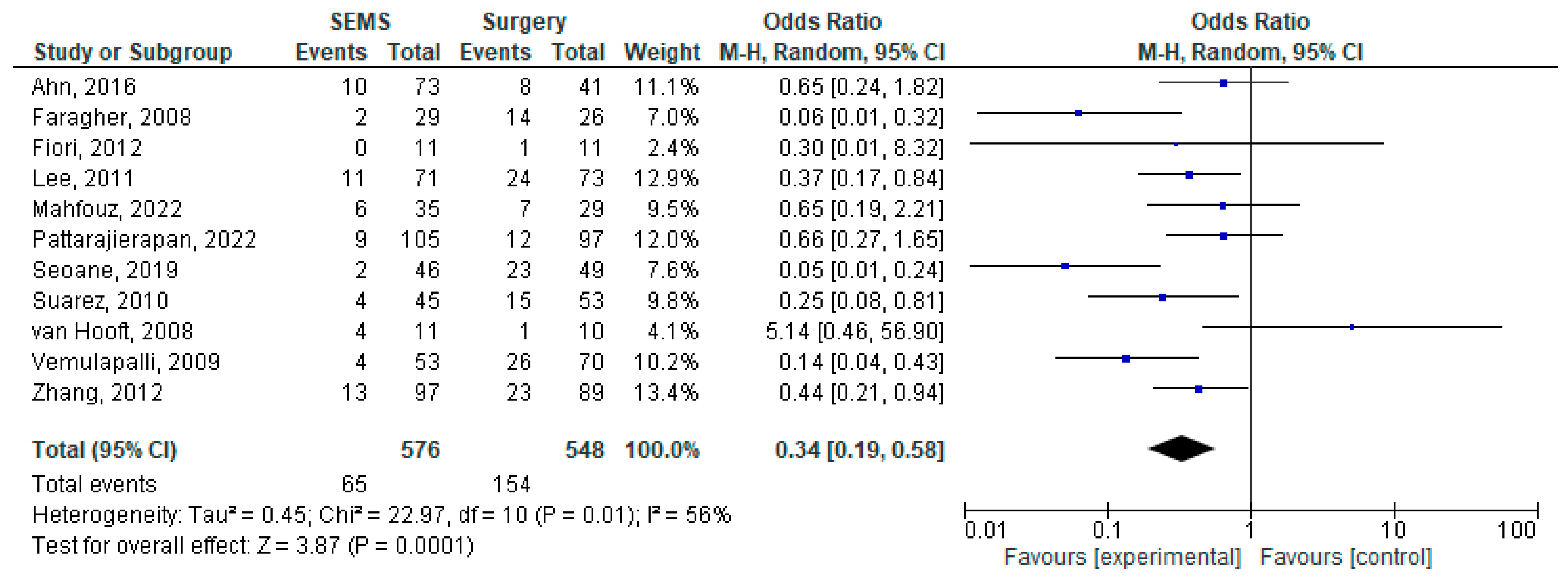
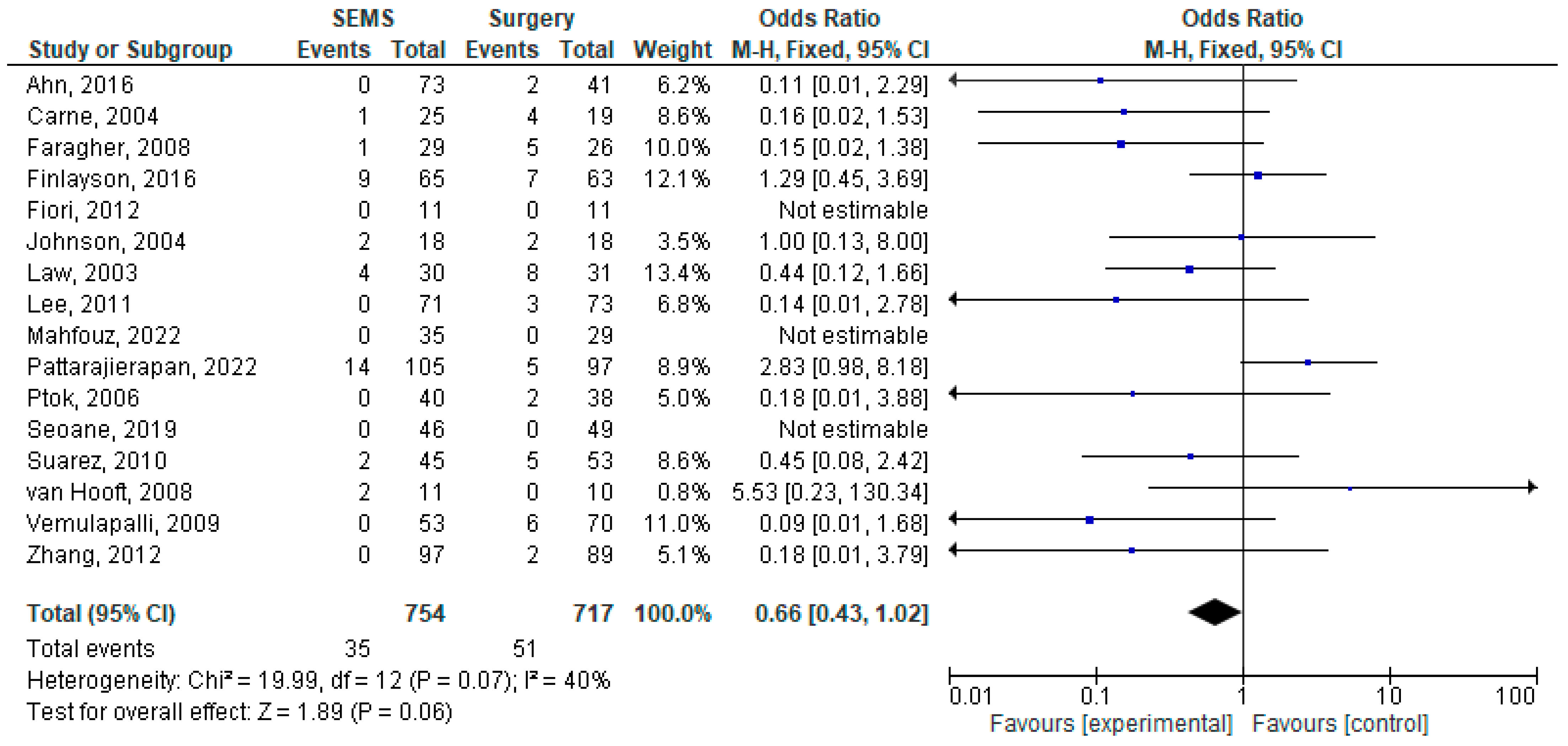
3.4. Early Complications
3.5. Late Complications
3.6. Length of Hospital Stay
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEMS | Self-expanding metal stent |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| AO-CRC | Advanced obstructive colorectal cancer |
| SF/IB | Stoma formation or internal bypass |
| RPT | Resection of primary tumor |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| SMD | Standard mean difference |
| 95%CI | 95% confidence interval |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| NA | Not applicable |
| NOS | Not otherwise specified |
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer Global Cancer Observatory—Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/en/dataviz/pie?mode=cancer&group_populations=1 (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Siegel, R.L.; Wagle, N.S.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagland, H.R.; Søreide, K. Cellular Metabolism in Colorectal Carcinogenesis: Influence of Lifestyle, Gut Microbiome and Metabolic Pathways. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostampoor, Z.; Afrashteh, S.; Mohammadianpanah, M.; Ghaem, H.; Zeegers, M.P.; Fararouei, M. Lifestyle, Dietary Pattern and Colorectal Cancer: A Case-Control Study. BMC Nutr. 2024, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, S.; Conigliaro, R.; Coppini, F.; Dell’Aquila, E.; Grande, G.; Pigò, F.; Mangiafico, S.; Lupo, M.; Marocchi, M.; Bertani, H.; et al. Acute Left-Sided Malignant Colonic Obstruction: Is There a Role for Endoscopic Stenting? World J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 14, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, H.; Yamashita, K.; Wang, G.; Sato, T.; Nakamura, T.; Watanabe, M. Prognostic Significance of Preoperative Bowel Obstruction in Stage III Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 2432–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, Y.; Shimura, T.; Yamada, T.; Hirata, Y.; Yamaguchi, R.; Sakamoto, E.; Kataoka, H. Colorectal Obstruction Is a Potential Prognostic Factor for Stage II Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 23, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Guo, S.B.; Wang, N.F. Decompression of Acute Left-Sided Malignant Colorectal Obstruction: Comparing Transanal Drainage Tube with Metallic Stent. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, e37–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimura, T.; Joh, T. Evidence-Based Clinical Management of Acute Malignant Colorectal Obstruction. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 50, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.W.; Kim, I.Y. The Role of Surgery for Asymptomatic Primary Tumors in Unresectable Stage IV Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Coloproctol. 2013, 29, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faron, M.; Pignon, J.P.; Malka, D.; Bourredjem, A.; Douillard, J.Y.; Adenis, A.; Elias, D.; Bouché, O.; Ducreux, M. Is Primary Tumour Resection Associated with Survival Improvement in Patients with Colorectal Cancer and Unresectable Synchronous Metastases? A Pooled Analysis of Individual Data from Four Randomised Trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrand, F.; Malka, D.; Bourredjem, A.; Allonier, C.; Bouché, O.; Louafi, S.; Boige, V.; Mousseau, M.; Raoul, J.L.; Bedenne, L.; et al. Impact of Primary Tumour Resection on Survival of Patients with Colorectal Cancer and Synchronous Metastases Treated by Chemotherapy: Results from the Multicenter, Randomised Trial Fédération Francophone de Cancérologie Digestive 9601. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.D.; Cai, B.B.; Cao, R.S.; Shi, R.H. Palliative Treatment for Incurable Malignant Colorectal Obstructions: A Meta-Analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2013, 19, 5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.W.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Y.C.; Yang, D.X. Palliative Treatment of Malignant Colorectal Obstruction Caused by Advanced Malignancy: A Self-Expanding Metallic Stent or Surgery? A System Review and Meta-Analysis. Surg. Today 2014, 44, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Okabayashi, K.; Tsuruta, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Yahagi, M.; Kitagawa, Y. Self-Expanding Metallic Stents Versus Surgical Intervention as Palliative Therapy for Obstructive Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. World J. Surg. 2015, 39, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veld, J.; Umans, D.; van Halsema, E.; Amelung, F.; Fernandes, D.; Lee, M.S.; Stupart, D.; Suárez, J.; Tomiki, Y.; Bemelman, W.; et al. Self-Expandable Metal Stent (SEMS) Placement or Emergency Surgery as Palliative Treatment for Obstructive Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, S.W.; Lim, C.H.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, Y.K.; Park, J.M.; Lee, I.S.; Choi, M.G. Long-Term Outcomes of Palliation for Unresectable Colorectal Cancer Obstruction in Patients with Good Performance Status: Endoscopic Stent versus Surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 4765–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carne, P.W.G.; Frye, J.N.R.; Robertson, G.M.; Frizelle, F.A. Stents or Open Operation for Palliation of Colorectal Cancer: A Retrospective, Cohort Study of Perioperative Outcome and Long-Term Survival. Dis. Colon. Rectum 2004, 47, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño Llano, R.; Restrepo, J.; Carvajal López, A.; Ruiz, M.H.; Puerta, J.D.; Álvarez, Ó.; Rojas, A.; Álvarez, A.; Ruiz, L.M.; Restrepo, D. Estudio Comparativo Del Stent Colónico versus Laparotomía En El Tratamiento de La Obstrucción Intestinal Aguda Por Cáncer Colorrectal. Rev. Colomb. Gastroenterol. 2015, 30, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faragher, I.G.; Chaitowitz, I.M.; Stupart, D.A. Long-Term Results of Palliative Stenting or Surgery for Incurable Obstructing Colon Cancer. Color. Dis. 2008, 10, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, A.; Hulme-Moir, M. Palliative Colonic Stenting: A Safe Alternative to Surgery in Stage IV Colorectal Cancer. ANZ J. Surg. 2016, 86, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, E.; Lamazza, A.; Schillaci, A.; Femia, S.; Demasi, E.; Decesare, A.; Sterpetti, A.V. Palliative Management for Patients with Subacute Obstruction and Stage IV Unresectable Rectosigmoid Cancer: Colostomy versus Endoscopic Stenting: Final Results of a Prospective Randomized Trial. Am. J. Surg. 2012, 204, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hooft, J.E.; Fockens, P.; Marinelli, A.W.; Timmer, R.; van Berkel, A.M.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Bemelman, W.A.; Bijnen, A.B.; Tuynman, H.; van Coevorden, F.; et al. Early Closure of a Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial of Endoscopic Stenting versus Surgery for Stage IV Left-Sided Colorectal Cancer. Endoscopy 2008, 40, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.; Marsh, R.; Corson, J.; Seymour, K. A Comparison of Two Methods of Palliation of Large Bowel Obstruction Due to Irremovable Colon Cancer. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2004, 86, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, W.L.; Choi, H.K.; Chu, K.W. Comparison of Stenting with Emergency Surgery as Palliative Treatment for Obstructing Primary Left-Sided Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2003, 90, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Hong, S.P.; Cheon, J.H.; Kim, T.I.; Min, B.S.; Kim, N.K.; Kim, W.H. Long-Term Outcome of Palliative Therapy for Malignant Colorectal Obstruction in Patients with Unresectable Metastatic Colorectal Cancers: Endoscopic Stenting versus Surgery. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 73, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Baek, J.H.; Kang, J.M.; Choi, S.; Kwon, K.A. The Outcome after Stent Placement or Surgery as the Initial Treatment for Obstructive Primary Tumor in Patients with Stage IV Colon Cancer. Am. J. Surg. 2012, 203, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouz, M.F.; Saeid Salama, T.M.; Afifi, A.H.; Dabous, H.M.K. Effectiveness and Early Postoperative Outcomes of Palliative Endoluminal Stenting versus Hartmann’s Procedure in Acute Malignant Bowel Obstruction in High-Risk Patients. Ann. Coloproctol. 2022, 38, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattarajierapan, S.; Manomayangoon, C.; Tipsuwannakul, P.; Khomvilai, S. Comparison of Colonic Stenting and Stoma Creation as Palliative Treatment for Incurable Malignant Colonic Obstruction. JGH Open 2022, 6, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptok, H.; Marusch, F.; Steinert, R.; Meyer, L.; Lippert, H.; Gastinger, I. Incurable Stenosing Colorectal Carcinoma: Endoscopic Stent Implantation or Palliative Surgery? World J. Surg. 2006, 30, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, A.; Saperas, E.; O’Callaghan, E.; Pera, M.; Raga, A.; Riu, F.; Barranco, L.; Dedeu, J.M.; Pantaleón, M.; Bessa, X.; et al. Colonic Stent vs Surgical Resection of the Primary Tumor. Effect on Survival from Stage-IV Obstructive Colorectal Cancer. Rev. Esp. Enfermedades Dig. 2020, 112, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Súarez, J.; Jiménez, J.; Vera, R.; Tarifa, A.; Balén, E.; Arrazubi, V.; Vila, J.; Lera, J.M. Stent or Surgery for Incurable Obstructive Colorectal Cancer: An Individualized Decisión. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2009, 25, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemulapalli, R.; Lara, L.F.; Sreenarasimhaiah, J.; Harford, W.V.; Siddiqui, A.A. A Comparison of Palliative Stenting or Emergent Surgery for Obstructing Incurable Colon Cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. Effect of Self-Expanding Metal Stents versus Surgery Therapy for Malignant Colorectal Obstruction in Patients with Advanced Colorectal Cancers. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 2012, 16, 6453. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.J.; Yoon, J.; Oh, E.H.; Kim, J.; Ham, N.S.; Hwang, S.W.; Park, S.H.; Ye, B.D.; Byeon, J.S.; Myung, S.J.; et al. Factors Associated with Clinical Outcomes of Palliative Stenting for Malignant Colonic Obstruction. Gut Liver 2021, 15, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, Y.; Arai, Y.; Yamaura, H.; Sato, Y.; Kato, M.; Saito, H.; Aramaki, T.; Sato, M.; Kumada, T.; Takeuchi, Y. Phase II Clinical Study on Stent Therapy for Unresectable Malignant Colorectal Obstruction (JIVROSG-0206). Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 35, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisner, S.; González-Huix, F.; Vandervoort, J.G.; Repici, A.; Xinopoulos, D.; Grund, K.E.; Goldberg, P. Self-Expanding Metal Stenting for Palliation of Patients with Malignant Colonic Obstruction: Effectiveness and Efficacy on 255 Patients with 12-Month’s Follow-Up. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Rhee, K.; Yoon, J.Y.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Youn, Y.H.; Kim, T.I.; Park, H.; Kim, W.H.; et al. Impact of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis on Clinical Outcomes of Patients Receiving Self-Expandable Metal Stents for Malignant Colorectal Obstruction. Endoscopy 2018, 50, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manes, G.; De Bellis, M.; Fuccio, L.; Repici, A.; Masci, E.; Ardizzone, S.; Mangiavillano, B.; Carlino, A.; Rossi, G.B.; Occhipinti, P.; et al. Endoscopic Palliation in Patients with Incurable Malignant Colorectal Obstruction by Means of Self-Expanding Metal Stent: Analysis of Results and Predictors of Outcomes in a Large Multicenter Series. Arch. Surg. 2011, 146, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargallo, C.J.; Ferrandez, A.; Carrera, P.; Simon, M.A.; Ducons, J.; Lanas, A. Short- and Long-Term Clinical Outcomes of Self-Expandable Metal Stents Inserted for Colorectal Obstruction and Efficacy of Different Insertion Techniques. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 42, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Halsema, E.E.; van Hooft, J.E. Bevacizumab in Patients Treated with Palliative Colonic Stent Placement: Is It Safe? Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 90, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotti, G.B.; Sapienza, P.; Lapolla, P.; Crocetti, D.; Tarallo, M.; Brachini, G.; Mingoli, A.; Fiori, E. Endoscopic Stenting and Palliative Chemotherapy in Advanced Colorectal Cancer: Friends or Foes? An Analysis of the Current Literature. In Vivo 2022, 36, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco-Barcia, V.; Mondéjar, R.; Martínez-Sáez, O.; Longo, F.; Moreno, J.A.; Rogado, J.; Donnay, O.; Santander, C.; Carrato, A.; Colomer, R. Safety and Oncological Outcomes of Bevacizumab Therapy in Patients With Advanced Colorectal Cancer and Self-Expandable Metal Stents. Clin. Color. Cancer 2019, 18, e287–e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, J.P.; Kim, S.W.; Cho, Y.K.; Park, J.M.; Lee, I.S.; Choi, M.G.; Chung, I.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, W.K.; Oh, S.T. Effectiveness of Stent Placement for Palliative Treatment in Malignant Colorectal Obstruction and Predictive Factors for Stent Occlusion. Surg. Endosc. 2010, 24, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugazza, A.; Galtieri, P.A.; Repici, A. Using Stents in the Management of Malignant Bowel Obstruction: The Current Situation and Future Progress. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canena, J.M.; Liberato, M.; Marques, I.; Rodrigues, C.I.; Lagos, A.C.; Patrocínio, S.D.; Tomé, M.J.; Pires, E.N.; Romão, C.; Coutinho, A.P.; et al. Sustained Relief of Obstructive Symptoms for the Remaining Life of Patients Following Placement of an Expandable Metal Stent for Malignant Colorectal Obstruction. Rev. Esp. Enfermedades Dig. 2012, 104, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Khan, Y.; Hu, H.; Lan, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; et al. Intestinal Stents: Structure, Functionalization and Advanced Engineering Innovation. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.C.; Sung, W.C.; Kwang, B.P.; Sung, W.S.; Yoo, S.Y.; Ji, H.K.; Young, S. Do Interventional Management of Malignant Colorectal Obstruction: Use of Covered and Uncovered Stents. Korean J. Radiol. 2007, 8, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirimbei, C.; Rotaru, V.; Chitoran, E.; Cirimbei, S. Laparoscopic Approach in Abdominal Oncologic Pathology. In Proceedings of the 35th Balkan Medical Week, Athens, Greece, 25–27 September 2018; Available online: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/full-record/WOS:000471903700043 (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Rotaru, V.; Chitoran, E.; Cirimbei, C.; Cirimbei, S.; Simion, L. Preservation of Sensory Nerves During Axillary Lymphadenectomy. In Proceedings of the 35th Balkan Medical Week, Athens, Greece, 25–27 September 2018; Available online: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/full-record/WOS:000471903700045 (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Manea, E.; Chitoran, E.; Rotaru, V.; Ionescu, S.; Luca, D.; Cirimbei, C.; Alecu, M.; Capsa, C.; Gafton, B.; Prutianu, I.; et al. Integration of Ultrasound in Image-Guided Adaptive Brachytherapy in Cancer of the Uterine Cervix. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitoran, E.; Rotaru, V.; Mitroiu, M.-N.; Durdu, C.-E.; Bohiltea, R.-E.; Ionescu, S.-O.; Gelal, A.; Cirimbei, C.; Alecu, M.; Simion, L. Navigating Fertility Preservation Options in Gynecological Cancers: A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Inclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Participants | Patients with incurable locally advanced obstructive colorectal cancer |
| Intervention | Self-expanding metal stents (SEMSs) placement as a palliative procedure |
| Comparison | Various alternative surgical approaches to SEMSs |
| Outcomes | Clinical success of the procedure Early and late procedure-related complications Early mortality Overall survival rate Length of hospital stay |
| Study design | Randomized or non-randomized controlled trials |
| Study | Type of Study, Study Population | Observation | Sample Size and Type of Palliative Procedure | Reported Complications | Risk of Bias (Newcastle–Ottawa Scale/Cochrane Tool) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEMS | Surgery | |||||
| Ahn, H.J. (South Korea, 2016) [17] | Retrospective, patients with unresectable CRC obstruction, ECOG 0–3. | Surgery may be preferable to SEMS in ECOG 0–1 patients. No differences in survival were observed in ECOG 2–3 patients. | N = 114 SEMS (n = 73) Surgery (n = 41) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus | Obstruction/ileus Surgery related Infectious complications | 7 |
| Carne, P.W.G. (New Zealand, 2004) [18] | Retrospective, patients with unresectable CRC obstruction, ASA 1–4, SEMS group: median age, 66 (range, 37–88) years, 13 males. Surgery group: median age, 68 (range, 51–85) years, 12 males. | Patients treated with stents were discharged earlier than after surgery Stents did not affect survival. | N = 44 SEMS (n = 25) Surgery (n = 19) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus Functional disorders | - | 5 |
| Castano Llano, R. (Colombia, 2015) [19] | Retrospective, patients with unresectable CRC obstruction in all stages of disease; 49,5% males vs. 50,5% females; median age 60 years (range, 28–87). | Stenting appeared to reduce the need for stoma formation. | N = 47 SEMS (n = 24) Surgery (n = 23) | Stent related Functional disorders | Obstruction/ileus Infectious complications Surgery related Cardiovascular events | 5 |
| Faragher, I.G. (Australia, 2008) [20] | Retrospective, left-sided obstructive unresectable CRC. SEMS group: M/F = 17/12, median age 70 years (range, 44–95). Surgery group: M/F = 16/10, median age 67 years (range, 33–90). | Bowel obstruction due to incurable left-sided CRC can be effectively palliated using SEMSs with a low complication rate. | N = 55 SEMS (n = 29) Surgery (n = 26) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus Functional disorders Cardiovascular events | Infectious complications Cardiovascular events Organ failure Thromboembolic events Stoma related | 6 |
| Finlayson, A. (New Zealand, 2016) [21] | Retrospective, patients with obstructing or near-obstructing stage IV CRC. SEMS group: M/F = 42/23, median age 76 years. Surgery group: M/F = 34/29, median age 71 years. | SEMSs have high clinical success rates and low complications rate. No difference in mortality between groups. | N = 128 SEMS (n = 65) Surgery (n = 63) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus Bleeding/anemia | - | 5 |
| Fiori, E. (Italy, 2012) [22] | RCT, patients with stage IV unresectable rectosigmoid cancer and symptoms of chronic subacute obstruction. | No significant difference in survival between groups. | N = 22 SEMS (n = 11) Surgery SF/IB (n = 11) | Obstruction/ileus Bleeding/anemia | Functional disorders Stoma related | Moderate risk |
| van Hooft, J.E. (Netherlands, 2008) [23] | RCT, stage IV left-sided CRC. | High rate of perforation in the SEMS group. | N = 21 SEMS (n = 11) Surgery (n = 10) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus Functional disorders | Obstruction/ileus | Low risk |
| Johnson, R. (United Kingdom, 2004) [24] | Retrospective, patients with obstructive CRC who underwent SEMS placement. Historical control of patients who underwent surgical stoma formation. Surgical patients were younger (p = 0.0065) and had less co-morbidity (p = 0.04). | Both groups experienced relief of obstructive symptoms. There were no differences in survival or mortality. Selected patients benefit from SEMS with relief of obstructive symptoms and no adverse effect on survival. | N = 36 SEMS (n = 18) Surgery SF/IB (n = 18) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus | Infectious complications | 6 |
| Law, W.L. (Hong Kong, 2003) [25] | Prospective, patients with incurable obstructing left-sided CRC. SEMS group: M/F = 20/10, median age 75 years (range, 36–98). Surgery group: M/F = 20/11, median age 70 years (range, 38–89). Similar medical comorbidities between groups. | SEMSs should be considered in patients with incurable obstructing CRC due to shorter hospital stay and lower incidence of stoma formation. | N = 61 SEMS (n = 30) Surgery (n = 31) | Stent related Functional disorders Cardiovascular events | Infectious complications Cardiovascular events Organ failure Thromboembolic events | 8 |
| Lee, H.J. (South Korea, 2011) [26] | Retrospective, patients with incurable obstructive CRC, with or without previous chemotherapy, ASA I-III. SEMS group: M/F = 47/24, median age 64 years (range, 26–87). Surgery group: M/F = 47/26, median age 62 years (range, 29–88). | Long-term outcomes and complications were comparable between groups. Stent-related late complications were manageable with endoscopic treatment. SEMS should also be recommended to patients with a longer life expectancy. | N = 144 SEMS (n = 71) Surgery (n = 73) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus | Obstruction/ileus Bleeding/anemia Infectious complications Organ failure Thromboembolic events | 7 |
| Lee, W.S. (South Korea, 2012) [27] | Prospective, patients with stage IV obstructive CRC and prior chemotherapy. SEMS was chosen for patients with higher ASA scores (III–IV), liver insufficiency due to diffuse metastatic disease and patient’s refusal of surgery. | SEMS shortened the hospital stays, avoided need for colostomy, and allowed chemotherapy to be administered earlier. | N = 88 SEMS (n = 36) Surgery RPT (n = 52) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus | Obstruction/ileus Bleeding/anemia Surgery related Infectious complications | 7 |
| Mahfouz, M.F. (Egypt, 2022) [28] | Retrospective, emergency intervention for acute malignant left-sided colonic obstruction and metastatic disease. SEMS group: M/F = 26/9, median age 69 years (range, 63–79). Surgery group: M/F = 21/8, median age 67 years (range, 61–75). | SEMS provided comparable efficacy and safety to surgery and faster recovery. | N = 64 SEMS (n = 35) Surgery RPT (n = 29) | Obstruction/ileus Bleeding/anemia Infectious complications | Obstruction/ileus Bleeding/anemia Infectious complications | 7 |
| Pattarajierapan, S. (Thailand, 2022) [29] | Retrospective, patients with incurable stage IV CRC. | SEMS was safe and effective. | N = 202 SEMS (n = 105) Surgery SF/IB (n = 97) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus | Functional disorders Bleeding/anemia Infectious complications Surgery related Stoma related | 7 |
| Ptok, H. (Germany, 2006) [30] | Prospective, non-randomized, patients with unresectable CRC. Study groups differed significatively in terms of age (p = 0.020) and ASA score (p = 0.012). | In comparison with SEMS, surgical palliative intervention for incurable CRC, especially in older patients, provided no significant advantages. | N = 78 SEMS (n = 40) Surgery (n = 38) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus | - | 8 |
| Seoane, A. (Spain, 2019) [31] | Prospective, patients with stage IV obstructive CRC. SEMS group: M/F = 29/17, median age 68.9 years. Surgery group: M/F = 28/21, median age 65.2 years. Surgical group had a higher proportion of prior chemotherapy (89.4% vs. 69.8%, p = 0.02). No differences between groups in ASA scores. | The key to treatment resided in assessing cases on an individual basis. SEMS may be considered for patients with a higher ASA score who are not eligible for chemotherapy due to a shorter life expectancy. | N = 95 SEMS (n = 46) Surgery RPT (n = 49) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus Functional disorders | Obstruction/ileus Bleeding/anemia Infectious complications | 6 |
| Suarez, J. (Spain, 2010) [32] | Retrospective, patients with stage IV obstructive CRC. Both groups were comparable regarding age, ASA score, prior chemotherapy, tumor location and presence of metastatic disease. | SEMS should be considered when tumors are non-resectable or when the patient is not a candidate for systemic therapy due to co-morbidities. | N = 98 SEMS (n = 45) Surgery (n = 53) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus Functional disorders | Bleeding/anemia Infectious complications Surgery related Stoma related Cardiovascular events Organ failure | 7 |
| Vemulapalli, R. (United States, 2009) [33] | Retrospective, patients with incurable obstructive CRC. No differences between groups in age. | SEMS should be first-line therapy in patients with acute malignant obstruction due to lower complication and mortality rates and shorter hospital stay. Surgery was an option for patients in whom SEMS was unsuccessful or contraindicated. | N = 123 SEMS (n = 53) Surgery (n = 70) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus | Obstruction/ileus Infectious complications Surgery related Cardiovascular events Organ failure Thromboembolic events | 5 |
| Zhang, Y.X. (China, 2012) [34] | Retrospective, patients with incurable obstructive CRC. No differences between groups in age. | SEMS was suitable for patients with poor general condition. No significant difference in the main complications between SEMS and surgery. The long-term efficacy of SEMS was worse than that of surgery. | N = 186 SEMS (n = 97) Surgery (n = 89) | Stent related Obstruction/ileus Infectious complications Thromboembolic events | Bleeding/anemia Infectious complications Surgery related Organ failure Thromboembolic events | 6 |
| Outcome | Variable for Subgroup Analysis | Nr. of Studies | Nr. of Patients SEMS/Surgery | I2 | OR/SMD [95%CI] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early Complications | ||||||
| Year of publication | ≤2010 | 4 | 138/159 | 68% | 0.25 [0.07, 0.94] | 0.04 |
| >2010 | 7 | 438/389 | 39% | 0.42 [0.25, 0.71] | 0.001 | |
| Type of study | Prospective | 2 | 151/146 | 88% | 0.20 [0.02, 2.57] | 0.22 |
| Retrospective | 7 | 403/381 | 41% | 0.33 [0.19, 0.55] | <0.0001 | |
| RCT | 2 | 22/21 | 46% | 1.59 [0.10, 24.41] | 0.74 | |
| Location of CRC | Left-sided CRC | 4 | 86/76 | 70% | 0.47 [0.08, 2.76] | 0.40 |
| NOS CRC | 7 | 490/472 | 54% | 0.32 [0.18, 0.56] | <0.0001 | |
| Type of surgical intervention | SF/IB | 2 | 116/108 | 0% | 0.63 [0.26, 1.51] | 0.3 |
| RPT | 2 | 106/102 | 0% | 0.44 [0.23, 0.87] | 0.02 | |
| NOS Surgery | 7 | 354/338 | 69% | 0.26 [0.11, 0.61] | 0.002 | |
| Late Complications | ||||||
| Year of publication | ≤2010 | 4 | 138/159 | 14% | 3.03 [1.39, 6.56] | 0.005 |
| >2010 | 6 | 403/360 | 80% | 1.92 [0.76, 4.86] | 0.17 | |
| Type of study | Prospective | 2 | 151/146 | 93% | 1.46 [0.08, 26.78] | 0.8 |
| Retrospective | 6 | 368/352 | 0% | 2.73 [1.79, 4.15] | <0.00001 | |
| RCT | 2 | 22/21 | 63% | 3.21 [0.19, 54.97] | 0.42 | |
| Location of CRC | Left-sided CRC | 3 | 51/47 | 28% | 1.83 [0.55, 6.09] | 0.32 |
| NOS CRC | 7 | 490/472 | 79% | 2.47 [1.08, 5.65] | 0.03 | |
| Type of surgical intervention | SF/IB | 2 | 116/108 | 14% | 0.44 [0.19, 1.00] | 0.05 |
| RPT | 1 | 71/73 | NA | 2.36 [1.09, 5.12] | 0.03 | |
| NOS Surgery | 7 | 354/338 | 0% | 3.34 [2.11, 5.29] | <0.00001 | |
| Length of Hospital Stay | ||||||
| Year of publication | ≤2010 | 1 | 40/38 | NA | −5.15 [−6.10, −4.21] | <0.00001 |
| >2010 | 6 | 323/217 | 88% | −1.23 [−1.85, −0.62] | <0.00001 | |
| Type of study | Prospective | 2 | 76/49 | 99% | −2.63 [−7.55, 2.28] | 0.29 |
| Retrospective | 4 | 276/195 | 82% | −1.08 [−1.56, −0.60] | <0.00001 | |
| RCT | 1 | 11/11 | NA | −5.74 [−7.79, −3.69] | <0.00001 | |
| Location of CRC | Left-sided CRC | 2 | 46/40 | 92% | −3.71 [−7.41, −0.01] | 0.05 |
| NOS CRC | 5 | 317/215 | 95% | −1.48 [−2.45, −0.51] | 0.003 | |
| Type of surgical intervention | SF/IB | 1 | 11/11 | NA | −5.74 [−7.79, −3.69] | <0.00001 |
| RPT | 2 | 71/40 | 93% | −1.05 [−2.82, 0.73] | 0.25 | |
| NOS Surgery | 4 | 281/255 | 96% | −1.82 [−2.94, −0.69] | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rotaru, V.; Chitoran, E.; Gullo, G.; Mosoiu, D.V.; Simion, L. Self-Expanding Metal Stents as an Alternative to Palliative Surgery in Advanced Obstructive Colorectal Cancer—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124339
Rotaru V, Chitoran E, Gullo G, Mosoiu DV, Simion L. Self-Expanding Metal Stents as an Alternative to Palliative Surgery in Advanced Obstructive Colorectal Cancer—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124339
Chicago/Turabian StyleRotaru, Vlad, Elena Chitoran, Giuseppe Gullo, Daniela Viorica Mosoiu, and Laurentiu Simion. 2025. "Self-Expanding Metal Stents as an Alternative to Palliative Surgery in Advanced Obstructive Colorectal Cancer—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124339
APA StyleRotaru, V., Chitoran, E., Gullo, G., Mosoiu, D. V., & Simion, L. (2025). Self-Expanding Metal Stents as an Alternative to Palliative Surgery in Advanced Obstructive Colorectal Cancer—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124339