Induction or Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Cancer Receiving Chemoradiotherapy? A Turkish Oncology Group Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
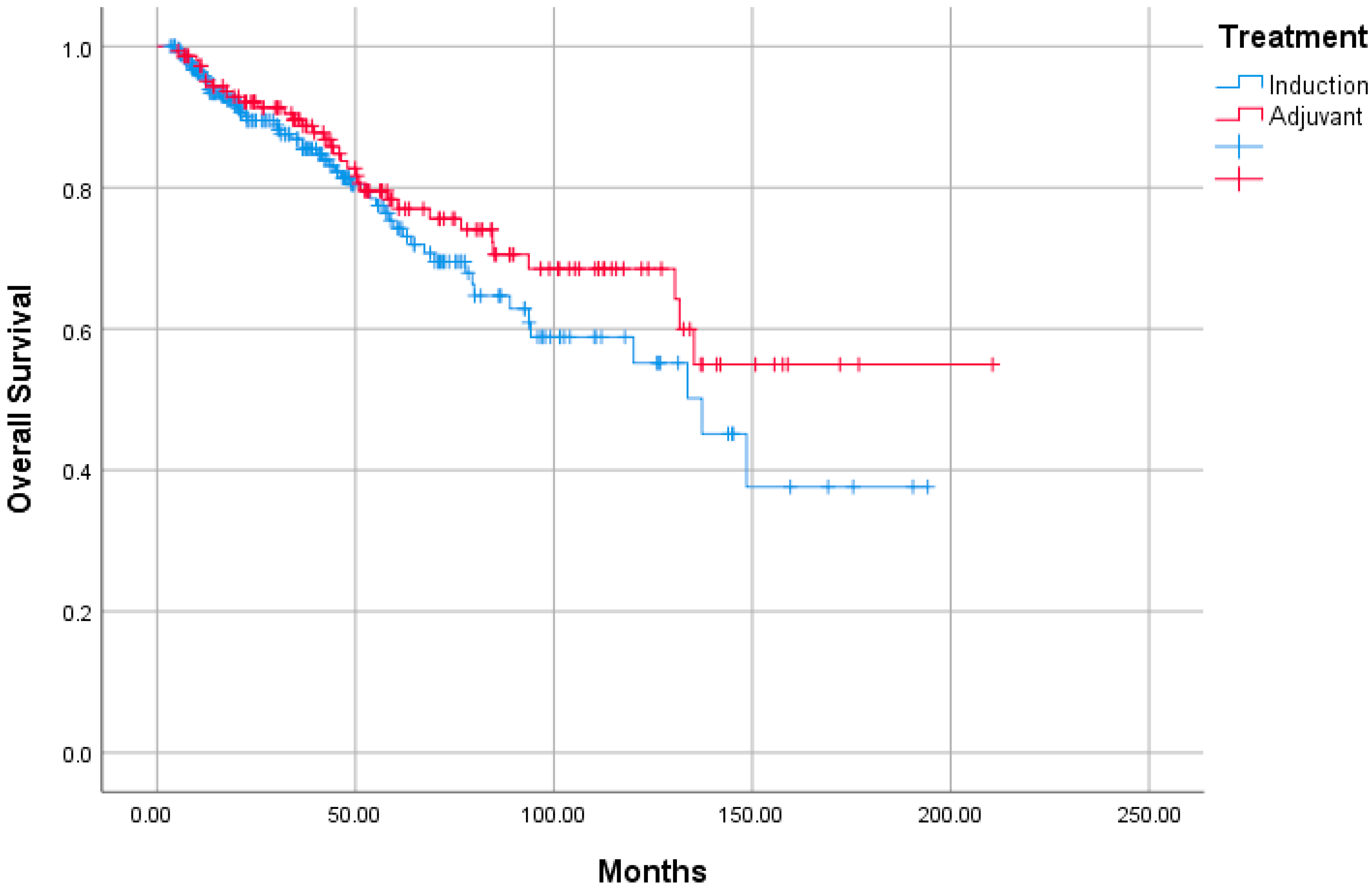
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chua, M.L.K.; Wee, J.T.S.; Hui, E.P.; Chan, A.T.C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2016, 387, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez-Vignon Whaley, J.J.; Afkhami, M.; Onyshchenko, M.; Massarelli, E.; Sampath, S.; Amini, A.; Bell, D.; Villaflor, V.M. Recurrent/Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Treatment from Present to Future: Where Are We and Where Are We Heading? Curr. Treat Options Oncol. 2023, 24, 1138–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantù, G. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. A “different” head and neck tumour. Part B: Treatment, prognostic factors, and outcomes. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2023, 43, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, P.; Chan, A.T.; Licitra, L.; Trama, A.; Orlandi, E.; Hui, E.P.; Halámková, J.; Mattheis, S.; Baujat, B.; Hardillo, J.; et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: ESMO-EURACAN Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up(†). Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sarraf, M.; LeBlanc, M.; Giri, P.G.; Fu, K.K.; Cooper, J.; Vuong, T.; Forastiere, A.A.; Adams, G.; Sakr, W.A.; Schuller, D.E.; et al. Chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal cancer: Phase III randomized Intergroup study 0099. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Wen, Y.F.; Guo, L.; Liu, H.; Huang, P.Y.; Mo, H.Y.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Luo, D.-H.; Huang, P.-Y.; Cao, K.-J.; et al. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy vs radiotherapy alone in stage II nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Phase III randomized trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liang, S.B.; Zong, J.F.; Li, W.F.; Chen, M.; Chen, L.; Mao, Y.-P.; Tang, L.-L.; Guo, Y.; et al. Progress report of a randomized trial comparing long-term survival and late toxicity of concurrent chemoradiotherapy with adjuvant chemotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in patients with stage III to IVB nasopharyngeal carcinoma from endemic regions of China. Cancer 2013, 119, 2230–2238. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, C.; Lee, A.; Ma, J.; Lacas, B.; Ng, W.T.; Chan, A.T.C.; Hong, R.-L.; Chen, M.-Y.; Chen, L.; Li, W.-F.; et al. Role of chemotherapy in patients with nasopharynx carcinoma treated with radiotherapy (MAC-NPC): An updated individual patient data network meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.F.; Chen, N.Y.; Zhang, N.; Hu, G.Q.; Xie, F.Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.-Z.; Li, J.-G.; Zhu, X.-D.; Hu, C.-S.; et al. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy with/without induction chemotherapy in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Long-term results of phase 3 randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, W.F.; Chen, N.Y.; Zhang, N.; Hu, G.Q.; Xie, F.Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.-Z.; Li, J.-G.; Zhu, X.-D.; et al. Induction chemotherapy plus concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A phase 3, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Cao, X.; Xia, W.X.; Liu, K.Y.; Qiang, M.Y.; Guo, L.; Qian, C.-N.; Cao, K.-J.; Mo, H.-Y.; Li, X.-M.; et al. Induction chemotherapy with lobaplatin and fluorouracil versus cisplatin and fluorouracil followed by chemoradiotherapy in patients with stage III–IVB nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An open-label, non-inferiority, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribassin-Majed, L.; Marguet, S.; Lee, A.W.M.; Ng, W.T.; Ma, J.; Chan, A.T.C.; Huang, P.-Y.; Zhu, G.; Chua, D.T.T.; Chen, Y.; et al. What Is the Best Treatment of Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma? An Individual Patient Data Network Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.W.M.; Ngan, R.K.C.; Ng, W.T.; Tung, S.Y.; Cheng, A.A.C.; Kwong, D.L.W.; Lu, T.-X.; Chan, A.T.C.; Sze, H.C.K.; Yiu, H.H.Y.; et al. NPC-0501 trial on the value of changing chemoradiotherapy sequence, replacing 5-fluorouracil with capecitabine, and altering fractionation for patients with advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 2020, 126, 3674–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, K.H.; Ngan, R.K.C.; Ng, A.W.Y.; Poon, D.M.C.; Ng, W.T.; Yuen, K.T.; Lee, V.H.F.; Tung, S.Y.; Chan, A.T.C.; Sze, H.C.K.; et al. Treatment outcomes of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in modern era after intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) in Hong Kong: A report of 3328 patients (HKNPCSG 1301 study). Oral. Oncol. 2018, 77, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, P.; Lee, A.; Marguet, S.; Leclercq, J.; Ng, W.T.; Ma, J.; Chan, A.T.C.; Huang, P.-Y.; Benhamou, E.; Zhu, G.; et al. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An update of the MAC-NPC meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudell, J.J.; Gillison, M.L.; Maghami, E.; Spencer, S.; Pfister, D.G.; Adkins, D.; Birkeland, A.C.; Brizel, D.M.; Busse, P.M.; Cmelak, A.J.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Head and Neck Cancers, Version 1.2022: Featured Updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, C.S.; Chen, X.Z.; Hu, G.Q.; Cheng, Z.B.; Sun, Y.; Li, W.-X.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Xie, F.-Y.; Liang, S.-B.; et al. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy plus adjuvant chemotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A phase 3 multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.W.; Tung, S.Y.; Ngan, R.K.; Chappell, R.; Chua, D.T.; Lu, T.X.; Siu, L.; Tan, T.; Chan, L.K.; Ng, W.T.; et al. Factors contributing to the efficacy of concurrent-adjuvant chemotherapy for locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Combined analyses of NPC-9901 and NPC-9902 Trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitapanarux, I.; Lorvidhaya, V.; Kamnerdsupaphon, P.; Sumitsawan, Y.; Tharavichitkul, E.; Sukthomya, V.; Ford, J. Chemoradiation comparing cisplatin versus carboplatin in locally advanced nasopharyngeal cancer: Randomised, non-inferiority, open trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, G.Q.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, X.D.; Yang, K.Y.; Jin, F.; Shi, M.; Chen, Y.-P.; Hu, W.-H.; et al. Final Overall Survival Analysis of Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Induction Chemotherapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Multicenter, Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2420–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorch, J.H.; Goloubeva, O.; Haddad, R.I.; Cullen, K.; Sarlis, N.; Tishler, R.; Tan, M.; Fasciano, J.; Sammartino, D.E.; Posner, M.R.; et al. Induction chemotherapy with cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or in combination with docetaxel in locally advanced squamous-cell cancer of the head and neck: Long-term results of the TAX 324 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.M.; Yang, Q.; Guo, L.; Mai, H.Q.; Mo, H.Y.; Cao, K.J.; Qian, C.-N.; Zhao, C.; Xiang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, X.-P.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A phase III multicentre randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 75, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.T.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.H.; Xie, S.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Guo, S.S.; Qi, B.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, D.P.; et al. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy followed by adjuvant cisplatin-gemcitabine versus cisplatin-fluorouracil chemotherapy for N2–3 nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.W.; Tung, S.Y.; Chan, A.T.; Chappell, R.; Fu, Y.T.; Lu, T.X.; Tang, T.; Chua, D.T.T.; O’Sullivan, B.; Tung, R.; et al. A randomized trial on addition of concurrent-adjuvant chemotherapy and/or accelerated fractionation for locally-advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 98, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Wang, Z.X.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Tang, L.L.; Mao, Y.P.; Li, W.F.; Lin, A.H.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. A Bayesian network meta-analysis comparing concurrent chemoradiotherapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy, concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone and radiotherapy alone in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, G.Q.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, X.D.; Yang, K.Y.; Jin, F.; Ma, J. Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Induction Chemotherapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidova, N.; Sarı, M.; Kahvecioglu, F.A.; Ozcan, E.; Akdag, M.O.; Dogan, A.; Yıldırım, S.; Sonusen, S.D.; Yunusov, E.; Yasar, A.; et al. Clinicopathologic Features and Efficacy of Induction Chemotherapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Real-World Experience. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2024, 47, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Gu, D.; He, X.; Gao, X.; Bian, X. The role of induction and adjuvant chemotherapy in combination with concurrent chemoradiotherapy for nasopharyngeal cancer: A Bayesian network meta-analysis of published randomized controlled trials. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Lim, W.T.; Fong, K.W.; Cheah, S.L.; Soong, Y.L.; Ang, M.K.; Ng, Q.S.; Tan, D.; Ong, W.S.; Tan, S.H.; et al. Concurrent chemo-radiation with or without induction gemcitabine, Carboplatin, and Paclitaxel: A randomized, phase 2/3 trial in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.C.; Jia, Q.J.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.J.; Qin, K.; Xu, L.M. The whole-blood Epstein-Barr virus DNA can serve as a valuable molecular marker for diagnosis and prognosis prediction of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 5431–5442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sittitrai, P.; Ruenmarkkaew, D.; Chitapanarux, I.; Muangwong, P.; Kangsadarnwiroon, K.; Benjawongsatien, R.; Srivanitchapoom, C.; Donchalermpak, S.; Asakij, T. Head and Neck Cancer of Unknown Primary: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort study in Northern Thailand, an Endemic Nasopharyngeal Cancer Area. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2024, 25, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Age, years, median | 49.0 (18.2–91.5) |
| <50 years | 215 (53.1%) |
| ≥50 years | 190 (46.9%) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 298 (73.6%) |
| Female | 107 (26.4%) |
| ECOG | |
| 0 | 236 (58.3%) |
| 1 | 163 (40.2%) |
| 2 | 6 (1.5%) |
| T stage | |
| I | 70 (17.3%) |
| II | 162 (40%) |
| III | 103 (25.4%) |
| IV | 70 (17.3%) |
| N stage | |
| 0 | 15 (3.7%) |
| I | 83 (20.5%) |
| II | 263 (64.9%) |
| III | 44 (10.9%) |
| Pathological differentiation | |
| Differentiated | 45 (11.1%) |
| Undifferentiated | 311 (76.8%) |
| No data | 49 (12.1%) |
| Pathological keratinisation | |
| Keratinised | 53 (13.1%) |
| Nonkeratinised | 308 (76.0%) |
| No data | 44 (10.9%) |
| EBER | |
| Positive | 148 (36.5%) |
| Negative | 75 (18.5%) |
| No data | 182 (44.9%) |
| P16 protein | |
| Positive | 11 (2.7%) |
| Negative | 92 (22.7%) |
| No data | 302 (74.6%) |
| Variables | IC (n = 258) | AC (n = 147) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, median | 0.756 | ||
| <50 years | 135 (52.3%) | 80 (54.4%) | |
| ≥50 years | 123 (47.7%) | 67 (45.6%) | |
| Sex | 0.907 | ||
| Male | 189 (73.3%) | 109 (74.1%) | |
| Female | 69 (26.7%) | 38 (25.9%) | |
| T stage | 0.251 | ||
| I–II | 142 (55.0%) | 90 (61.2%) | |
| III–IV | 116 (45.0%) | 57 (32.9%) | |
| N stage | 0.147 | ||
| 0–I | 56 (21.7%) | 42 (28.6%) | |
| II–III | 202 (78.3%) | 105 (71.4%) | |
| Pathological differentiation | 0.067 | ||
| Differentiated | 35 (15.0%) | 10 (8.1%) | |
| Undifferentiated | 198 (85.0%) | 113 (91.9%) | |
| Pathological keratinisation | 0.161 | ||
| Keratinised | 30 (12.7%) | 23 (18.4%) | |
| Nonkeratinised | 206 (87.3%) | 102 (81.6%) | |
| EBER | 0.033 | ||
| Positive | 104 (62.3%) | 44 (78.6%) | |
| Negative | 63 (37.7%) | 12 (21.4%) | |
| P16 protein | 0.999 | ||
| Positive | 9 (11.3%) | 2 (8.7%) | |
| Negative | 71 (88.7%) | 21 (91.3%) | |
| Chemotheraphy during CRT | 0.999 | ||
| Carboplatin | 14 (5.5%) | 8 (5.3%) | |
| Cisplatin | 239 (94.5%) | 144 (94.7%) |
| Chemotherapy | IC (n = 258) | AC (n = 147) |
|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin and fluorouracil | 20 (7.8%) | 103 (70.1%) |
| Docetaxel and cisplatin | 23 (8.9%) | 2 (1.4%) |
| Docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil | 102 (39.5%) | 16 (10.9%) |
| Docetaxel, carboplatin, and fluorouracil | 1 (0.4%) | - |
| Gemcitabine and cisplatin | 101 (39.1%) | 13 (8.8%) |
| Capecitabine | - | 3 (2.1%) |
| Carboplatin and fluorouracil | - | 7 (4.8%) |
| Gemcitabine and carboplatin | 3 (1.2%) | 3 (2.0%) |
| Carboplatin and paclitaxel | 8 (3.1%) | - |
| Treatment results | ||
| Completed | 253 (98.1%) | 129 (87.8%) |
| Dose reduction due to toxicity | 32 (12.4%) | 10 (6.8%) |
| Early withdrawal due to toxicity | 5 (1.9%) | 18 (12.2%) |
| Adverse Event | IC (n = 258) | AC (n = 147) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1–2 | Grade 3–4 | Grade 1–2 | Grade 3–4 | |
| Anaemia | 31 (12.0%) | 1 (0.4%) | 5 (3.4%) | 4 (2.7%) |
| Neutropenia | 48 (18.6%) | 11 (4.3%) | 3 (2.0%) | 10 (6.8%) |
| Thrombocytopenia | 22 (8.5%) | 2 (0.8%) | 2 (1.4%) | 4 (2.7%) |
| Nausea, vomiting | 22 (8.5%) | 2 (0.8%) | 7 (4.8%) | 4 (2.7%) |
| Diarrhoea | 6 (2.3%) | 2 (0.8%) | 2 (1.4%) | - |
| Fatigue, asthenia | 5 (1.9%) | 2 (0.8%) | 9 (6.1%) | 8 (5.4%) |
| Neuropathy | - | - | 2 (1.4%) | - |
| Mucositis, stomatitis | 8 (3.1%) | 4 (1.6%) | 6 (4.1%) | 2 (1.4%) |
| Rash | 2 (0.8%) | - | - | - |
| Hearing loss | 2 (0.8%) | 2 (0.8%) | 2 (1.4%) | - |
| Arrhythmia | - | - | - | 4 (2.7%) |
| Elevated liver function test | 5 (1.9%) | - | - | - |
| Alopecia | 1 (0.4%) | - | - | - |
| Febrile neutropenia | - | 4 (1.6%) | - | 6 (4.1%) |
| Acute kidney injury | 4 (1.6%) | 1 (0.1%) | 6 (4.1%) | 2 (1.4%) |
| Total | 156 (60.5%) | 31 (12.0%) | 44 (29.9%) | 44 (29.9%) |
| p Value | ||
|---|---|---|
| Variables | OS | PFS |
| Age, <50 years vs. ≥50 years | 0.073 | 0.614 |
| Sex, male vs. female | 0.107 | 0.158 |
| T stage, I–II vs. III–IV | 0.744 | 0.570 |
| N stage, 0–I vs. II–III | 0.380 | 0.947 |
| Pathological differentiation, differentiated vs. undifferentiated | 0.129 | 0.347 |
| Pathological keratinisation, keratinised vs. nonkeratinised | 0.805 | 0.665 |
| EBER, positive vs. negative | 0.179 | 0.469 |
| P16 protein, positive vs. negative | 0.149 | 0.345 |
| Chemotheraphy during CRT, carboplatin vs. cisplatin | 0.600 | 0.801 |
| Treatment, IC vs. AC | 0.209 | 0.248 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sekmek, S.; Oguz, A.; Karakurt Eryilmaz, M.; Araz, M.; Biter, S.; Kıdı, M.M.; Bayram, E.; Erdat, E.C.; Yasar, A.; Colak, R.; et al. Induction or Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Cancer Receiving Chemoradiotherapy? A Turkish Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124189
Sekmek S, Oguz A, Karakurt Eryilmaz M, Araz M, Biter S, Kıdı MM, Bayram E, Erdat EC, Yasar A, Colak R, et al. Induction or Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Cancer Receiving Chemoradiotherapy? A Turkish Oncology Group Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124189
Chicago/Turabian StyleSekmek, Serhat, Aysel Oguz, Melek Karakurt Eryilmaz, Murat Araz, Sedat Biter, Mehmet Mutlu Kıdı, Ertugrul Bayram, Efe Cem Erdat, Arzu Yasar, Rumeysa Colak, and et al. 2025. "Induction or Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Cancer Receiving Chemoradiotherapy? A Turkish Oncology Group Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124189
APA StyleSekmek, S., Oguz, A., Karakurt Eryilmaz, M., Araz, M., Biter, S., Kıdı, M. M., Bayram, E., Erdat, E. C., Yasar, A., Colak, R., Yilmaz, M., Bakir Kahveci, G., Divriklioglu, D., Chalabiyev, E., Aksoy, S., Ozsan Celebi, S. N., Kosku, H., Yılmaz, M., Hacibekiroglu, I., ... Ucar, G. (2025). Induction or Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Cancer Receiving Chemoradiotherapy? A Turkish Oncology Group Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124189






