Association of Hepatocyte Growth Factor and Angiopoietin-2 with Systemic Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Patient Recruitment
2.4. Baseline Patient Characteristics
2.5. Plasma Protein Concentration Measurement
2.6. Outcomes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events
3.3. Plasma Concentrations of Angiogenesis-Related Proteins
3.4. Associations Between Angiogenesis-Related Proteins and MACE in PAD Patients
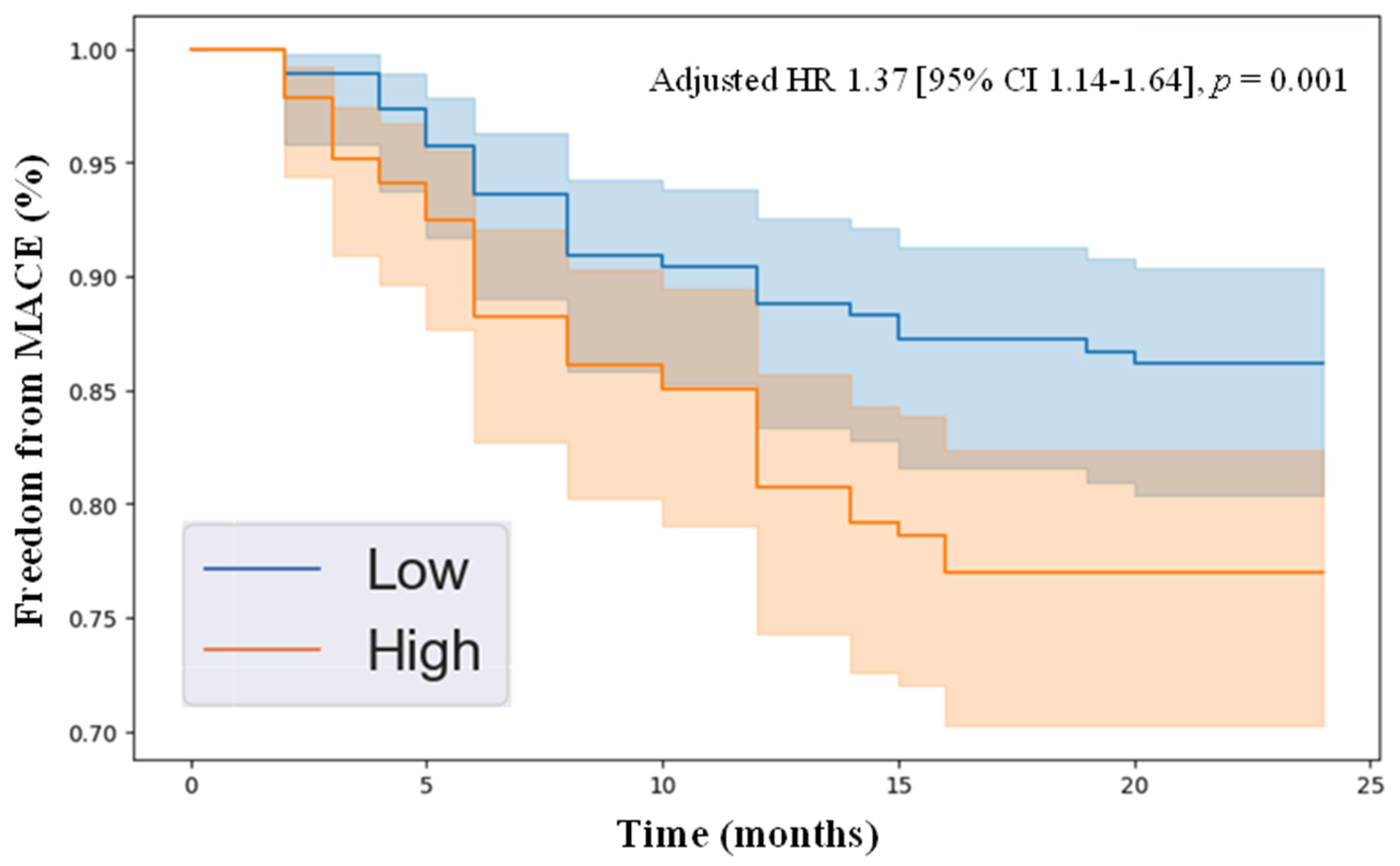
3.5. Kaplan–Meier Analysis of Freedom from MACE in PAD Patients with High vs. Low Levels of HGF and Angiopoietin-2
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Findings
4.2. Comparison to Existing Literature
4.3. Explanation of Findings
4.4. Implications
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olin, J.W.; Sealove, B.A. Peripheral Artery Disease: Current Insight Into the Disease and Its Diagnosis and Management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, L.; Németh, N.; Fehér, G.; Kívés, Z.; Endrei, D.; Boncz, I. Epidemiology of Peripheral Artery Disease: Narrative Review. Life 2022, 12, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenon, S.M.; Vittinghoff, E.; Owens, C.D.; Conte, M.S.; Whooley, M.; Cohen, B.E. Peripheral Artery Disease and Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from the Heart and Soul Study. Vasc. Med. 2013, 18, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikary, D.; Barman, S.; Ranjan, R.; Stone, H. A Systematic Review of Major Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Growing Global Health Concern. Cureus 2022, 14, e30119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, C.; Astin, F. A Multidisciplinary Approach to Prevention. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Djahanpour, N.; Jain, S.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 Has Prognostic Value in Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2023, 78, 719–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shaikh, F.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. A Machine Learning Algorithm for Peripheral Artery Disease Prognosis Using Biomarker Data. iScience 2024, 27, 109081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Nassereldine, R.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Mamdani, M.; Al-Omran, M.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Development and Evaluation of a Prediction Model for Peripheral Artery Disease-Related Major Adverse Limb Events Using Novel Biomarker Data. J. Vasc. Surg. 2024, 80, 490–497.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Djahanpour, N.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Jain, S.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Angiogenesis-Related Proteins as Biomarkers for Peripheral Artery Disease. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, T.H.; Montani, J.-P. Overview of Angiogenesis; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, P.; Schreinlechner, M.; Noflatscher, M.; Engl, C.; Lener, D.; Theurl, M.; Kirchmair, R.; Marschang, P. Hepatocyte Growth Factor as Indicator for Subclinical Atherosclerosis. Vasa 2024, 53, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, G.; Forini, F.; Kusmic, C.; Iervasi, G.; Balzan, S. Angiopoietin 2 Signal Complexity in Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorenoi, V.; Brehm, M.U.; Koch, A.; Hagen, A. Growth Factors for Angiogenesis in Peripheral Arterial Disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, CD011741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.R.; Annex, B.H. Therapeutic Angiogenesis for Peripheral Artery Disease. JACC Basic. Transl. Sci. 2017, 2, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Mohler, E.R.; Lederman, R.J.; Mendelsohn, F.O.; Saucedo, J.F.; Goldman, C.K.; Blebea, J.; Macko, J.; Kessler, P.D.; Rasmussen, H.S.; et al. Regional Angiogenesis with Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Peripheral Arterial Disease: A Phase II Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Study of Adenoviral Delivery of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 121 in Patients with Disabling Intermittent Claudication. Circulation 2003, 108, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.S.; Annex, B.H. Growth Factors for Therapeutic Angiogenesis in Peripheral Arterial Disease. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2007, 22, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.S.; Moons, K.G.M.; Dhiman, P.; Riley, R.D.; Beam, A.L.; Calster, B.V.; Ghassemi, M.; Liu, X.; Reitsma, J.B.; van Smeden, M.; et al. TRIPOD+AI Statement: Updated Guidance for Reporting Clinical Prediction Models That Use Regression or Machine Learning Methods. BMJ 2024, 385, e078378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, F.; Janzer, S.F. Peripheral Vascular Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; De Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, e285–e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison, H.C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luminex Assays, Multiplex Immunoassays. Available online: https://www.bio-techne.com/ (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- MAGPIX® System | xMAP Instrument | Luminex Corporation. Available online: https://www.luminexcorp.com/magpix-system/ (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Luminex Assays—CA. Available online: www.thermofisher.com/ca/en/home/life-science/antibodies/immunoassays/procartaplex-assays-luminex.html (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- xPONENT® Software for xMAP® Instruments. Luminex Corporation. Available online: https://us.diasorin.com/en/luminex-ltg/reagents-accessories/software (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D.; The Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018). Circulation 2018, 138, e618–e651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, R.L.; Kasner, S.E.; Broderick, J.P.; Caplan, L.R.; Connors, J.J.; Culebras, A.; Elkind, M.S.V.; George, M.G.; Hamdan, A.D.; Higashida, R.T.; et al. An Updated Definition of Stroke for the 21st Century: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013, 44, 2064–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SPSS Software. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/analytics/spss-statistics-software (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Guo, M.; Shi, J.-H.; Wang, P.-L.; Shi, D.-Z. Angiogenic Growth Factors for Coronary Artery Disease: Current Status and Prospects. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 23, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, P.K.; Buzkova, P.; Wassell, C.L.; Allison, M.; Criqui, M.; Larson, N.B.; Bielinski, S.J. Association of Circulating Hepatocyte Growth Factor and Risk of Incident Peripheral Artery Disease: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Angiology 2020, 71, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Yang, Z.-J.; Kong, F.-X.; Wu, C.-T. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Gene Therapy for Ischemic Diseases. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golledge, J.; Clancy, P.; Yeap, B.B.; Hankey, G.J.; Norman, P.E. Increased Serum Angiopoietin-2 Is Associated with Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Prevalence and Cardiovascular Mortality in Older Men. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.V.; Lim, H.S.; Varughese, G.I.; Hughes, E.A.; Lip, G.Y.H. Angiopoietin-2 Levels as a Biomarker of Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Hypertension. Ann. Med. 2008, 40, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peplinski, B.S.; Houston, B.A.; Bluemke, D.A.; Kawut, S.M.; Kolb, T.M.; Kronmal, R.A.; Lima, J.A.C.; Ralph, D.D.; Rayner, S.G.; Steinberg, Z.L.; et al. Associations of Angiopoietins With Heart Failure Incidence and Severity. J. Card. Fail. 2021, 27, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Mizuno, S. The Discovery of Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) and Its Significance for Cell Biology, Life Sciences and Clinical Medicine. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2010, 86, 588–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. Hepatocyte Growth Factor: Molecular Structure and Implications for a Central Role in Liver Regeneration. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1991, 6, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Morishita, R.; Taniyama, Y.; Kida, I.; Moriguchi, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T.; Kaneda, Y.; Higaki, J.; Ogihara, T. Angiogenesis Induced by Hepatocyte Growth Factor in Non-Infarcted Myocardium and Infarcted Myocardium: Up-Regulation of Essential Transcription Factor for Angiogenesis, Ets. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Morishita, R.; Nakamura, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Moriguchi, A.; Nagano, T.; Taiji, M.; Noguchi, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Potential Role of Hepatocyte Growth Factor, a Novel Angiogenic Growth Factor, in Peripheral Arterial Disease. Circulation 1999, 100, II-301–II-308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, H.G.; Young Koh, G.; Thurston, G.; Alitalo, K. Control of Vascular Morphogenesis and Homeostasis through the Angiopoietin–Tie System. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, W.A.; Tzvetkova, D.; Nikolov, D.B. Structure of the Angiopoietin-2 Receptor Binding Domain and Identification of Surfaces Involved in Tie2 Recognition. Structure 2005, 13, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedler, U.; Scharpfenecker, M.; Koidl, S.; Hegen, A.; Grunow, V.; Schmidt, J.M.; Kriz, W.; Thurston, G.; Augustin, H.G. The Tie-2 Ligand Angiopoietin-2 Is Stored in and Rapidly Released upon Stimulation from Endothelial Cell Weibel-Palade Bodies. Blood 2004, 103, 4150–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Lee, C.-K.; Kang, S.; Park, I.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.K.; Hong, S.P.; Bae, H.; He, Y.; Kubota, Y.; et al. Angiopoietin-2 Exacerbates Cardiac Hypoxia and Inflammation after Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 5018–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhet, M.; Ul-Haq, Z.; Kamalati, T.; Lucas, A.; Majeed, A.; El-Osta, A. Blood Tests in General Practice: The Use of Routine Data to Characterise Venous Blood Testing in North West London, 2016-2018. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2020, 70, bjgp20X711605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.J. Vascular Medicine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 2760–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwood, B.M.; Sayers, R.D. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) in Primary Care-Educational Experiences for PAD Primary Care in England-a Mixed-Method Study. Fam. Pract. 2023, 40, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikelboom, J.W.; Connolly, S.J.; Bosch, J.; Dagenais, G.R.; Hart, R.G.; Shestakovska, O.; Diaz, R.; Alings, M.; Lonn, E.M.; Anand, S.S.; et al. Rivaroxaban with or without Aspirin in Stable Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doenst, T.; Haverich, A.; Serruys, P.; Bonow, R.O.; Kappetein, P.; Falk, V.; Velazquez, E.; Diegeler, A.; Sigusch, H. PCI and CABG for Treating Stable Coronary Artery Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockley, M.; Kobewka, D.; Kunkel, E.; Nagpal, S.; McIsaac, D.I.; Thavorn, K.; Forster, A. Characteristics of High-Cost Inpatients with Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 250–258.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patients with PAD (n = 250) | |
|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD, years | 69 ± 9 |
| Female sex | 80 (32%) |
| Hypertension | 193 (77%) |
| Dyslipidemia | 204 (82%) |
| Diabetes | 104 (42%) |
| Past smoker | 131 (53%) |
| Current smoker | 75 (30%) |
| Congestive heart failure | 14 (6%) |
| Coronary artery disease | 105 (42%) |
| Previous stroke | 53 (21%) |
| Patients with PAD (n = 250) | |
|---|---|
| Major adverse cardiovascular event | 48 (19.8%) |
| Myocardial infarction | 37 (15.3%) |
| Stroke | 13 (5.4%) |
| Death | 3 (1.2%) |
| No MACE (n = 202) | MACE (n = 48) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HGF | 300.55 (177.53) | 390.83 (319.16) | <0.001 |
| Angiopoietin-2 | 19.36 (12.06) | 23.67 (17.60) | 0.020 |
| BMP-9 | 160.48 (178.29) | 122.13 (110.64) | 0.091 |
| Leptin | 27.28 (30.00) | 33.77 (46.03) | 0.153 |
| Follistatin | 673.24 (387.61) | 741.93 (339.89) | 0.181 |
| VEGF-D | 389.16 (741.60) | 269.72 (559.28) | 0.210 |
| PLGF | 3.99 (5.66) | 3.12 (3.42) | 0.233 |
| IL-8 | 6.52 (6.08) | 7.42 (5.70) | 0.266 |
| HB-EGF | 41.30 (35.65) | 46.27 (42.09) | 0.322 |
| VEGF-A | 125.10 (158.39) | 135.54 (144.46) | 0.621 |
| EGF | 64.28 (107.36) | 59.00 (59.17) | 0.695 |
| G-CSF | 123.49 (144.57) | 130.74 (169.76) | 0.722 |
| Endothelin-1 | 4.90 (7.56) | 5.15 (8.25) | 0.819 |
| FGF-1 | 10.97 (7.31) | 10.76 (7.68) | 0.830 |
| Endoglin | 1422.07 (727.86) | 1403.68 (764.04) | 0.855 |
| FGF-2 | 111.37 (98.78) | 109.28 (78.08) | 0.874 |
| VEGF-C | 980.10 (637.90) | 989.32 (593.37) | 0.912 |
| Adjusted Hazard Ratio | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HGF | 1.37 | 1.14 | 1.64 | 0.001 |
| Angiopoietin-2 | 1.27 | 1.04 | 1.55 | 0.016 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Khalil, A.M.; Abuhalimeh, L.; Shaikh, F.; Younes, H.; Abuhalimeh, B.; Zamzam, A.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Association of Hepatocyte Growth Factor and Angiopoietin-2 with Systemic Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124031
Li B, Khalil AM, Abuhalimeh L, Shaikh F, Younes H, Abuhalimeh B, Zamzam A, Abdin R, Qadura M. Association of Hepatocyte Growth Factor and Angiopoietin-2 with Systemic Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124031
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ben, Adam M. Khalil, Lina Abuhalimeh, Farah Shaikh, Houssam Younes, Batool Abuhalimeh, Abdelrahman Zamzam, Rawand Abdin, and Mohammad Qadura. 2025. "Association of Hepatocyte Growth Factor and Angiopoietin-2 with Systemic Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124031
APA StyleLi, B., Khalil, A. M., Abuhalimeh, L., Shaikh, F., Younes, H., Abuhalimeh, B., Zamzam, A., Abdin, R., & Qadura, M. (2025). Association of Hepatocyte Growth Factor and Angiopoietin-2 with Systemic Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124031








