Is Personalized Mechanical Thrombectomy Based on Clot Characteristics Feasible? A Radiomics Model Using NCECT to Predict FPE in AIS Patients Undergoing Thromboaspiration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Approval
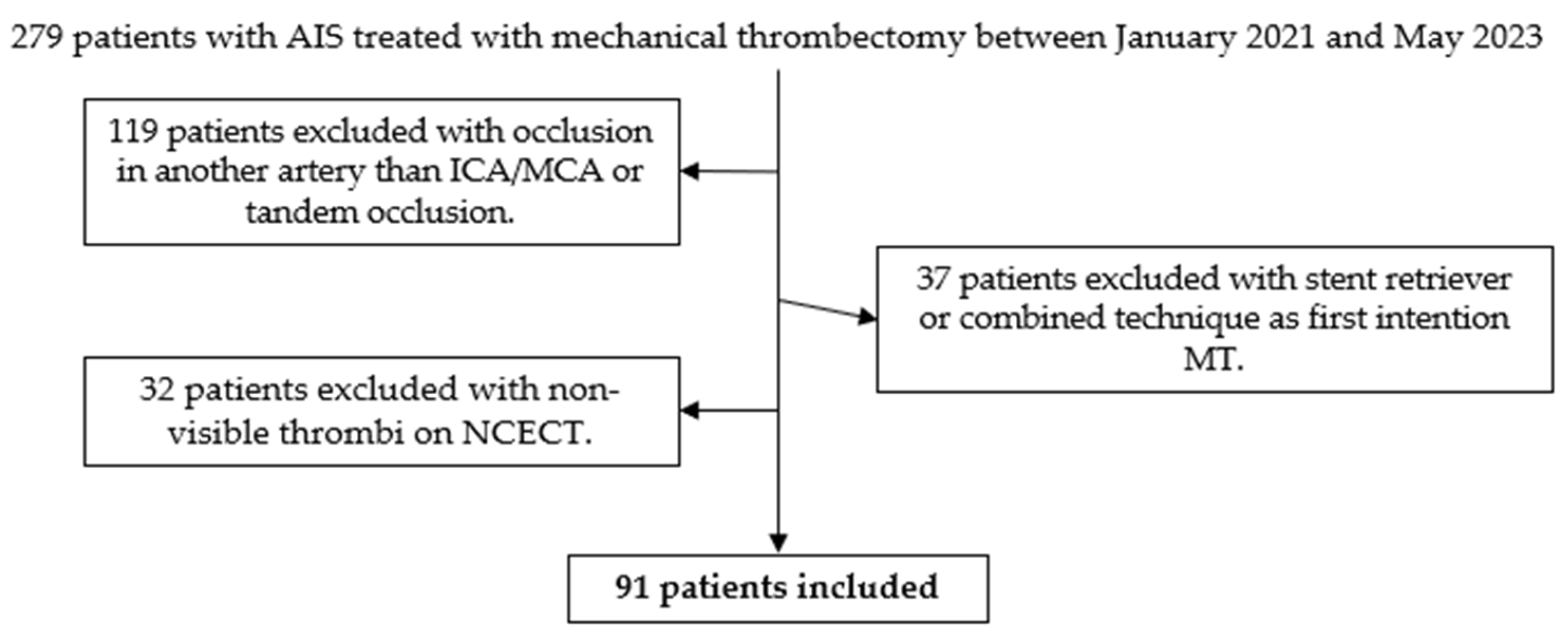
2.2. Patient Selection
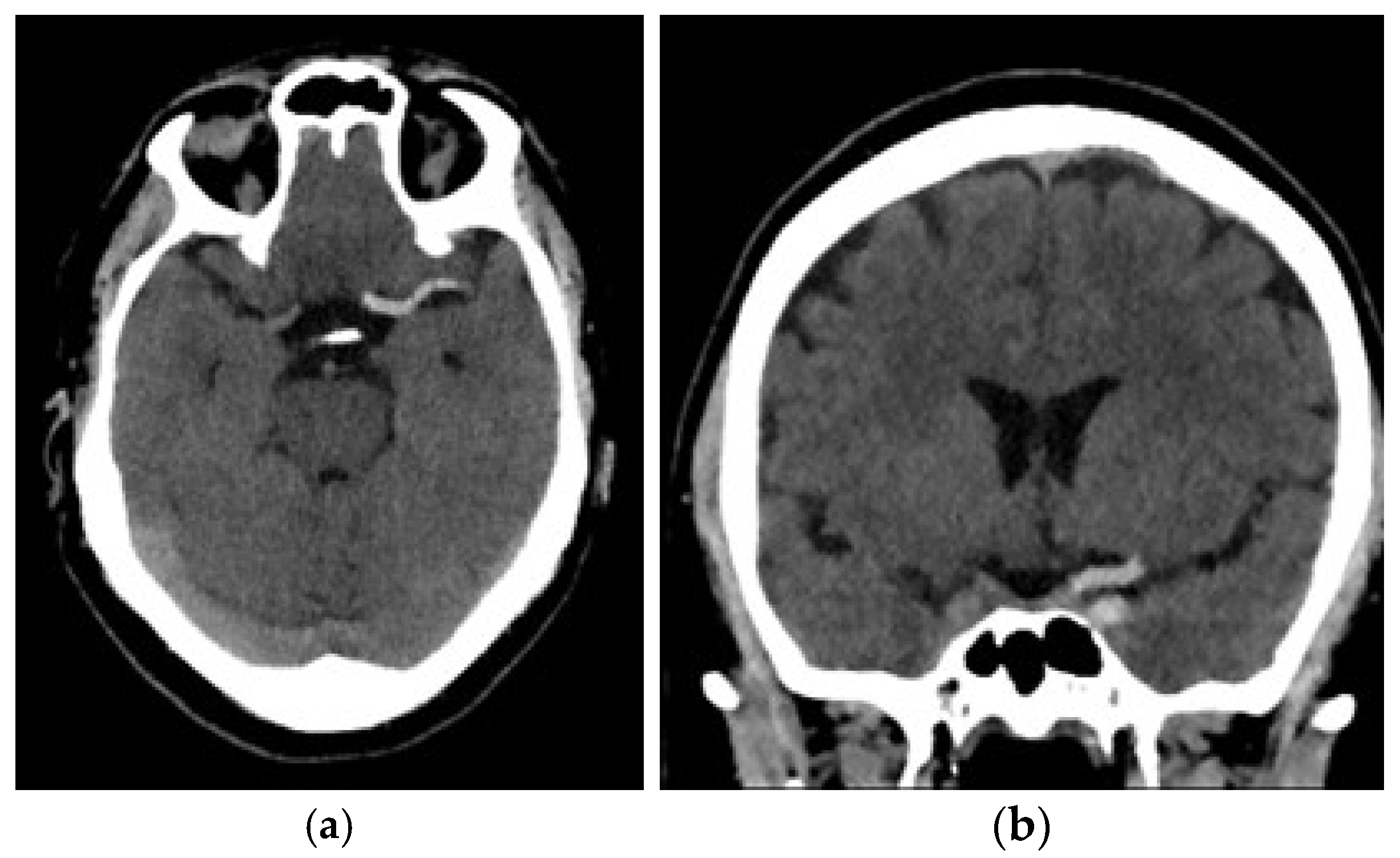
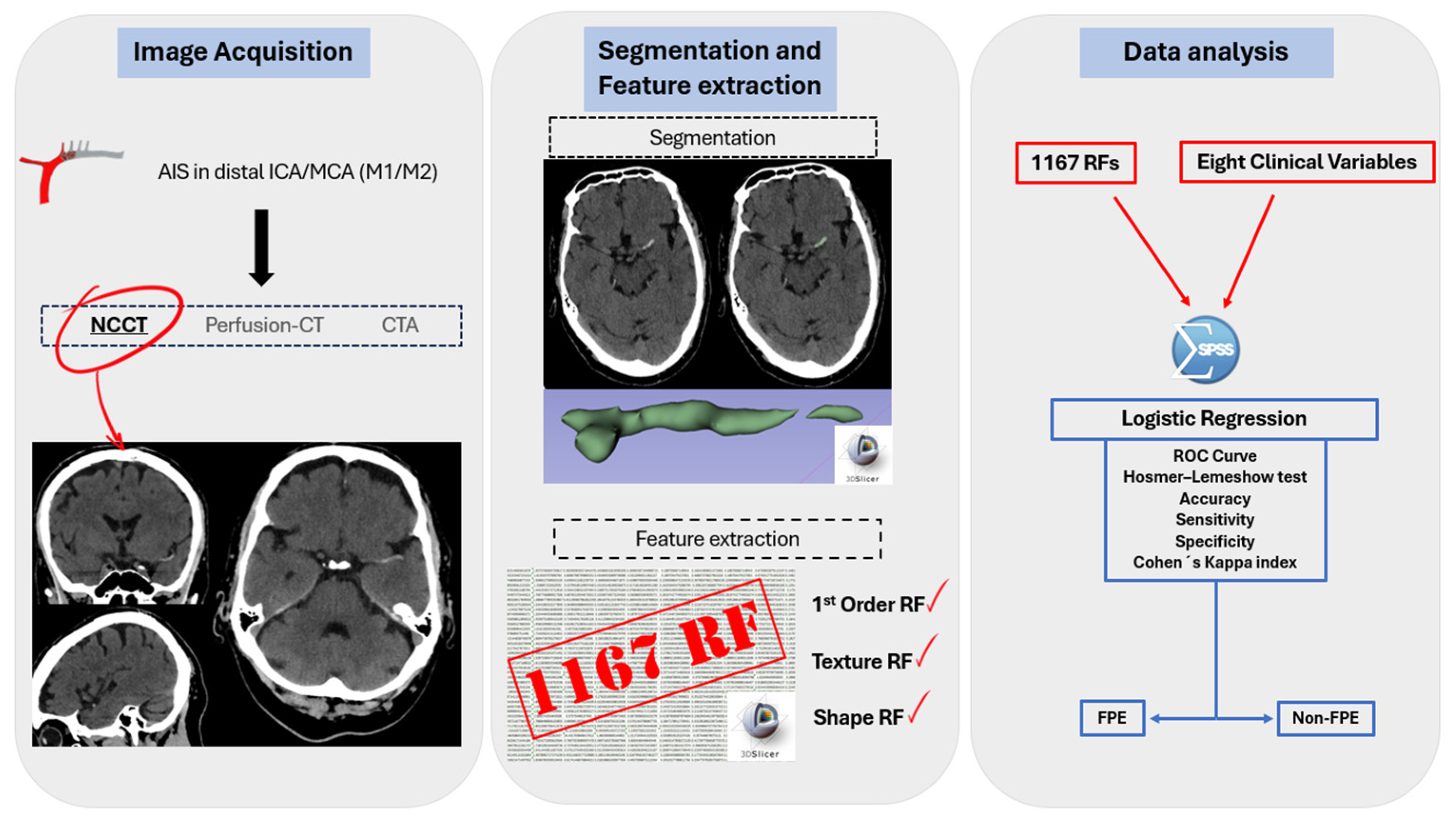
2.3. Image Acquisition
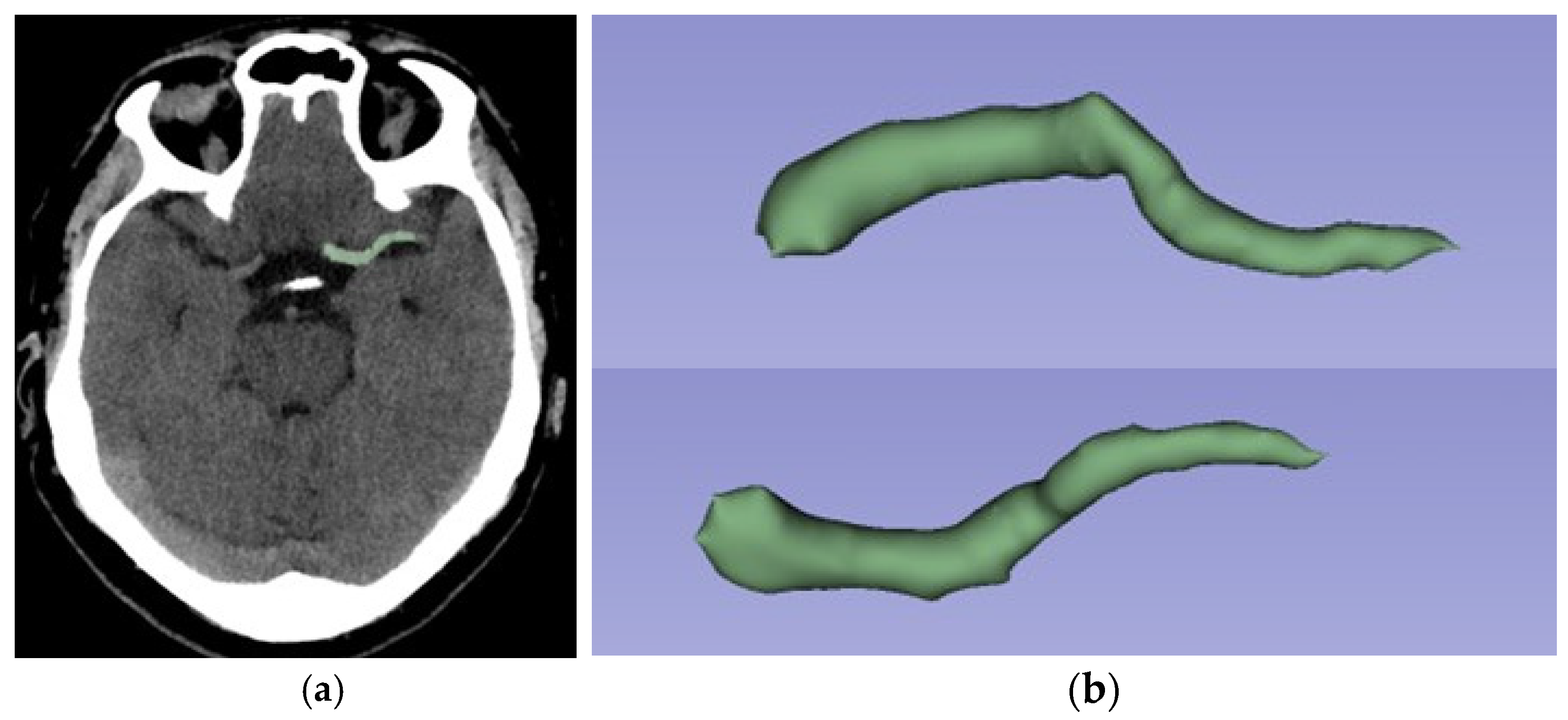
2.4. Segmentation and Feature Extraction
2.5. Clinical Data
2.6. Feature Selection and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Information
3.2. Features Analysis
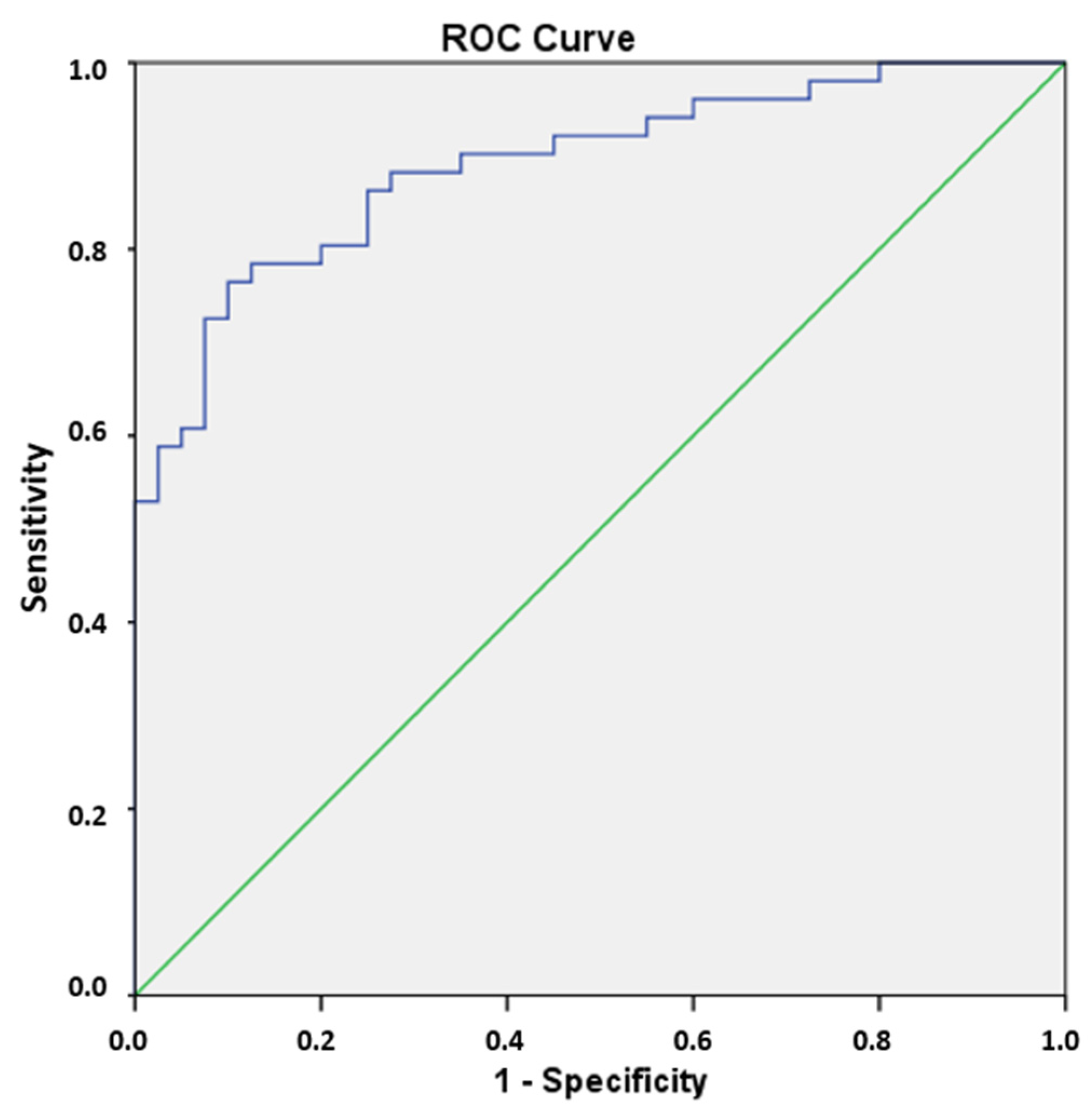
3.3. Prediction of FPE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIS | Acute Ischemic Stroke |
| AUC | Area Under Curve |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine |
| FN | False Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| FPE | First Pass Effect |
| GLCM | Gray-Level Cooccurrence Matrix |
| GLDM | Gray-Level Dependence Matrix |
| GLRLM | Gray-Level Run Length Matrix |
| GLSZM | Gray-Level Size Zone Matrix |
| HU | Hounsfield Units |
| ICA | Internal Carotid Artery |
| MT | Mechanical Thrombectomy |
| MCA | Middle Cerebral Artery |
| NCECT | Non-Contrast Enhanced Computed Tomography |
| NGTDM | Neighboring Gray-Tone Difference Matrix |
| RF | Radiomics Features |
| ROC | Receiver-Operating Characteristic |
| ROI | Region Of Interest |
| RQS | Radiomics Quality Score |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| Se | Sensitivity |
| Sp | Specificity |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| TN | True Negative |
| TP | True Positive |
| TICI | Thrombolysis In Cerebral Infarction |
| tPA | Intravenous Tissue Plasminogen Activator |
Appendix A. Radiomics Quality Score (RQS)
| Questions | Answers |
|---|---|
| Image protocol quality | Protocols well documented and public |
| Multiple segmentations | Yes |
| Phantom study | No |
| Imaging at multiple time points | No |
| Feature reduction | Either measure is implemented |
| Multivariable analysis with non-RFs | Yes |
| Detect and discuss biological correlates | Yes |
| Cut-off analyses | No |
| Discrimination statistics | Discrimination statistic and its significance |
| Calibration statistics | Calibration statistic and its significance |
| Prospective study | No |
| Validation | No validation |
| Comparison to “gold standard” | Yes |
| Potential clinical utility | Yes |
| Cost-effectiveness analysis | No |
| Open science and data | The code is open sourced |
| Total Score | 17 (47.22%) |
References
- Higashida, R.T.; Furlan, A.J.; Roberts, H.; Tomsick, T.; Connors, B.; Barr, J.; Dillon, W.; Warach, S.; Broderick, J.; Tilley, B.; et al. Technology Assessment Committee of the American Society of Interventional and Therapeutic Neuroradiology; Technology Assessment Committee of the Society of Interventional Radiology. Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2003, 34, e109–e137, Erratum in: Stroke 2003, 34, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fugate, J.E.; Klunder, A.M.; Kallmes, D.F. What is meant by “TICI”? AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Castonguay, A.C.; Linfante, I.; Gupta, R.; Martin, C.O.; Holloway, W.E.; Mueller-Kronast, N.; English, J.D.; Dabus, G.; Malisch, T.W.; et al. First Pass Effect: A New Measure for Stroke Thrombectomy Devices. Stroke 2018, 49, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, K.M.; Nam, T.K.; Ko, M.J.; Choi, H.H.; Kwon, J.T.; Park, S.W.; Byun, J.S. Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction Grade 2C or 3 Represents a Better Outcome than 2B for Endovascular Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Network Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2020, 136, e419–e439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Zhai, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, X.; Gao, J.; Kang, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lu, G.; et al. First pass effect in patients undergoing endovascular treatment for posterior circulation acute ischemic stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2024, 33, 107640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducroux, C.; Piotin, M.; Gory, B.; Labreuche, J.; Blanc, R.; Ben Maacha, M.; Lapergue, B.; Fahed, R.; ASTER Trial investigators. First pass effect with contact aspiration and stent retrievers in the Aspiration versus Stent Retriever (ASTER) trial. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2020, 12, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hafeez, M.U.; Kan, P.; Srivatsan, A.; Moore, S.; Jafari, M.; DeLaGarza, C.; Hafeez, K.; Nascimento, F.A.; Srinivasan, V.M.; Burkhardt, J.-K.; et al. Comparison of First-Pass Efficacy Among Four Mechanical Thrombectomy Techniques: A Single-Center Experience. World Neurosurg. 2020, 144, e533–e540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvoye, F.; Di Meglio, L.; Consoli, A.; Nomenjanahary, M.S.; Dupont, S.; Labreuche, J.; Maier, B.; Piotin, M.; Blanc, R.; Escalard, S.; et al. High thrombus platelet content is associated with a lower rate of first pass effect in stroke treated by endovascular therapy. Eur. Stroke J. 2022, 7, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Juega, J.; Requena, M.; Piñana, C.; Rodriguez, M.; Camacho, J.; Vidal, M.; Moliné, T.; Serna, G.; Palacio-Garcia, C.; Rubiera, M.; et al. Intracranial thrombus composition is associated with occlusion location and endovascular treatment outcomes: Results from ITACAT multicenter study. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2024, 17, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viltužnik, R.; Kaučič, A.; Blinc, A.; Vidmar, J.; Serša, I. Comparing CT and MR Properties of Artificial Thrombi According to Their Composition. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Benson, J.C.; Fitzgerald, S.T.; Kadirvel, R.; Johnson, C.; Dai, D.; Karen, D.; Kallmes, D.F.; Brinjikji, W. Clot permeability and histopathology: Is a clot’s perviousness on CT imaging correlated with its histologic composition? J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2020, 12, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fitzgerald, S.T.; Wang, S.; Dai, D.; Douglas, A.; Kadirvel, R.; Gounis, M.J.; Chueh, J.; Puri, A.S.; Layton, K.F.; Thacker, I.C.; et al. Platelet-rich clots as identified by Martius Scarlet Blue staining are isodense on NCCT. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- He, G.; Deng, J.; Lu, H.; Wei, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y. Thrombus enhancement sign on CT angiography is associated with the first pass effect of stent retrievers. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2023, 15, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yue, X.; Cui, J.; Huang, S.; Liu, W.; Qi, J.; He, K.; Li, T. An interpretable radiomics-based machine learning model for predicting reverse left ventricular remodeling in STEMI patients using late gadolinium enhancement of myocardial scar. Eur. Radiol. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Song, F.; Zhang, W.; Gong, T.; Zhao, S.; Lv, F. Prediction of benign and malignant pulmonary nodules using preoperative CT features: Using PNI-GARS as a predictor. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1446511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Porto-Álvarez, J.; Mosqueira Martínez, A.; Martínez Fernández, J.; Sanmartín López, M.; Blanco Ulla, M.; Vázquez Herrero, F.; Pumar, J.M.; Rodríguez-Yáñez, M.; Minguillón Pereiro, A.M.; Bolón Villaverde, A.; et al. How Can Radiomics Help the Clinical Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke? Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manco, L.; Maffei, N.; Strolin, S.; Vichi, S.; Bottazzi, L.; Strigari, L. Basic of machine learning and deep learning in imaging for medical physicists. Phys. Med. 2021, 83, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santo, B.A.; Janbeh Sarayi, S.M.M.; McCall, A.D.; Monteiro, A.; Donnelly, B.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Tutino, V.M. Multimodal CT imaging of ischemic stroke thrombi identifies scale-invariant radiomic features that reflect clot biology. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2023, 15, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hofmeister, J.; Bernava, G.; Rosi, A.; Vargas, M.I.; Carrera, E.; Montet, X.; Burgermeister, S.; Poletti, P.A.; Platon, A.; Lovblad, K.O.; et al. Clot-Based Radiomics Predict a Mechanical Thrombectomy Strategy for Successful Recanalization in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 2488–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sarioglu, O.; Sarioglu, F.C.; Capar, A.E.; Sokmez, D.F.; Mete, B.D.; Belet, U. Clot-based radiomics features predict first pass effect in acute ischemic stroke. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2022, 28, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Romano, D.; Cioni, S.; Leonini, S.; Gennari, P.; Vallone, I.M.; Zandonella, A.; Puliti, A.; Tassi, R.; Casasco, A.; Martini, G.; et al. Manual thromboaspiration technique as a first approach for endovascular stroke treatment: A single-center experience. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2016, 22, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pinter, C.; Lasso, A.; Fichtinger, G. Polymorph segmentation representation for medical image computing. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 171, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, G.M.S.; Jha, A.; Mithun, S.; Panchal, S.; Nath, B.; Nautiyal, A.; Sherkhane, U.K.; Jaiswar, V.; Purandare, N.; Rangarajan, V.; et al. Effect of resampling of voxel size on CT Radiomic features extraction. JNM 2022, 63 (Suppl. S2), 3241. [Google Scholar]
- Shipitko, O.; Grigoryev, A. Gaussian filtering for FPGA based image processing with High-Level Synthesis tools. In Proceedings of the IV International Conference on Information Technology and Nanotechnology, Samara, Russia, 27 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Demsar, J.; Curk, T.; Erjavec, A.; Gorup, C.; Hocevar, T.; Milutinovic, M.; Mozina, M.; Polajnar, M.; Toplak, M.; Staric, A.; et al. Orange: Data Mining Toolbox in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2013, 14, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Casagrande, A.; Fabris, F.; Girometti, R. Beyond kappa: An informational index for diagnostic agreement in dichotomous and multivalue ordered-categorical ratings. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2020, 58, 3089–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.; Deist, T.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, B.; Baessler, B.; Bakas, S.; Cuocolo, R.; Fedorov, A.; Maier-Hein, L.; Mercaldo, N.; Müller, H.; Orlhac, F.; Pinto Dos Santos, D.; et al. CheckList for EvaluAtion of Radiomics research (CLEAR): A step-by-step reporting guideline for authors and reviewers endorsed by ESR and EuSoMII. Insights Imaging 2023, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, A.S., 3rd; Siddiqui, A.; Fifi, J.T.; De Leacy, R.A.; Fiorella, D.J.; Gu, E.; Levy, E.I.; Snyder, K.V.; Hanel, R.A.; Aghaebrahim, A.; et al. Aspiration thrombectomy versus stent retriever thrombectomy as first-line approach for large vessel occlusion (COMPASS): A multicentre, randomised, open label, blinded outcome, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, A.; Boltyenkov, A.; Wu, X.; Matouk, C.C.; Forman, H.P.; Gandhi, D.; Sanelli, P. Endovascular Contact Aspiration versus Stent Retriever for Revascularization in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke and Large Vessel Occlusion: A Cost-Minimization Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2020, 139, e23–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waqas, M.; Li, W.; Patel, T.R.; Chin, F.; Tutino, V.M.; Dossani, R.H.; Ren, Z.; Guerrero, W.R.; Borlongan, C.V.; Pressman, E.; et al. Clot imaging characteristics predict first pass effect of aspiration-first approach to thrombectomy. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2022, 28, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fujimoto, M.; Salamon, N.; Mayor, F.; Yuki, I.; Takemoto, K.; Vinters, H.V.; Viñuela, F. Characterization of Arterial Thrombus Composition by Magnetic Resonance Imaging in a Swine Stroke Model. Stroke 2013, 44, 1463–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahalane, R.; Boodt, N.; Akyildiz, A.C.; Giezen, J.A.; Mondeel, M.; van der Lugt, A.; Marquering, H.; Gijsen, F. A review on the association of thrombus composition with mechanical and radiological imaging characteristics in acute ischemic stroke. J. Biomech. 2021, 129, 110816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Predicted | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FPE | Non-FPE | ||
| Observed | FPE | TP * | FP * |
| Non-FPE | FN * | TN * | |
| Patient Data | FPE | Non-FPE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female: 36 (70.6% 1) | Female: 24 (60%) | 0.290 |
| Age (mean) | 77.74 (SD 2 12.13) | 77.70 (SD 8.66) | 0.559 |
| Hounsfield Units (mean) | 58.77 (SD 10.17) | 63.38 (SD 26.01) | 0.296 |
| Arterial Hypertension | 41 (80.4%) | 30 (75%) | 0.538 |
| Diabetes | 16 (31.4%) | 9 (22.5%%) | 0.347 |
| Dyslipidemia | 34 (66.7%) | 22 (55%) | 0.256 |
| Smoke | 5 (9.8%) | 6 (15%) | 0.370 |
| Laterality | Left: 27 (53%) | Left: 22 (55%) | 0.845 |
| RFs | Class of RF | OR 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90th Percentile | First order | 0.809 | 0.045 |
| Kurtosis | First order | 0.536 | 0.020 |
| Maximum 2D Diameter Row | Shape | 0.646 | 0.004 |
| Size Zone Non-Uniformity Normalized | GLSZM | 1.848 × 10−4 | 0.010 |
| Zone Entropy | GLSZM | 0.205 | 0.006 |
| Gray-Level Non-Uniformity Normalized | GLRLM | 0.06 | 0.005 |
| Run Entropy | GLRLM | 0.268 | 0.605 |
| Gray-Level Non-Uniformity | GLRLM | 1.383 | 0.240 |
| Large Dependence Low-Gray-Level Emphasis | GLDM | 1.003 | 0.317 |
| Predicted | ∑ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPE | Non-FPE | |||
| Observed | FPE | 44 | 7 | 51 |
| Non-FPE | 10 | 30 | 40 | |
| ∑ | 54 | 37 | 91 | |
| Kappa Value (%) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 0 | Agreement equal to chance |
| 10–20% | Slight agreement |
| 21–40% | Fair agreement |
| 41–60% | Moderate agreement |
| 61–80% | Substantial agreement |
| 81–99% | Near-perfect agreement |
| 100% | Perfect agreement |
| Step | Non-FPE | FPE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed | Predicted | Observed | Predicted | |
| 1 | 8 | 8.899 | 1 | 0.101 |
| 2 | 8 | 8.073 | 1 | 0.927 |
| 3 | 6 | 6.576 | 3 | 2.424 |
| 4 | 7 | 5.066 | 2 | 3.934 |
| 5 | 5 | 3.939 | 4 | 5.061 |
| 6 | 3 | 2.859 | 6 | 6.141 |
| 7 | 2 | 2.007 | 7 | 6.993 |
| 8 | 1 | 1.259 | 8 | 7.741 |
| 9 | 0 | 0.823 | 9 | 8.177 |
| 10 | 0 | 0.499 | 10 | 9.501 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porto-Álvarez, J.; Martínez Fernández, J.; Mosqueira Martínez, A.J.; Blanco Ulla, M.; Arias Rivas, S.; Rodríguez Castro, E.; Iglesias Rey, R.; Pumar, J.M.; García-Figueiras, R.; Souto Bayarri, M. Is Personalized Mechanical Thrombectomy Based on Clot Characteristics Feasible? A Radiomics Model Using NCECT to Predict FPE in AIS Patients Undergoing Thromboaspiration. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124027
Porto-Álvarez J, Martínez Fernández J, Mosqueira Martínez AJ, Blanco Ulla M, Arias Rivas S, Rodríguez Castro E, Iglesias Rey R, Pumar JM, García-Figueiras R, Souto Bayarri M. Is Personalized Mechanical Thrombectomy Based on Clot Characteristics Feasible? A Radiomics Model Using NCECT to Predict FPE in AIS Patients Undergoing Thromboaspiration. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124027
Chicago/Turabian StylePorto-Álvarez, Jacobo, Javier Martínez Fernández, Antonio Jesús Mosqueira Martínez, Miguel Blanco Ulla, Susana Arias Rivas, Emilio Rodríguez Castro, Ramón Iglesias Rey, José M. Pumar, Roberto García-Figueiras, and Miguel Souto Bayarri. 2025. "Is Personalized Mechanical Thrombectomy Based on Clot Characteristics Feasible? A Radiomics Model Using NCECT to Predict FPE in AIS Patients Undergoing Thromboaspiration" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124027
APA StylePorto-Álvarez, J., Martínez Fernández, J., Mosqueira Martínez, A. J., Blanco Ulla, M., Arias Rivas, S., Rodríguez Castro, E., Iglesias Rey, R., Pumar, J. M., García-Figueiras, R., & Souto Bayarri, M. (2025). Is Personalized Mechanical Thrombectomy Based on Clot Characteristics Feasible? A Radiomics Model Using NCECT to Predict FPE in AIS Patients Undergoing Thromboaspiration. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124027







