Clinically Important Decrease in Liver Stiffness Following Treatment for Hepatitis C: Outcome of the TraP HepC Nationwide Elimination Program
Abstract
1. Introduction
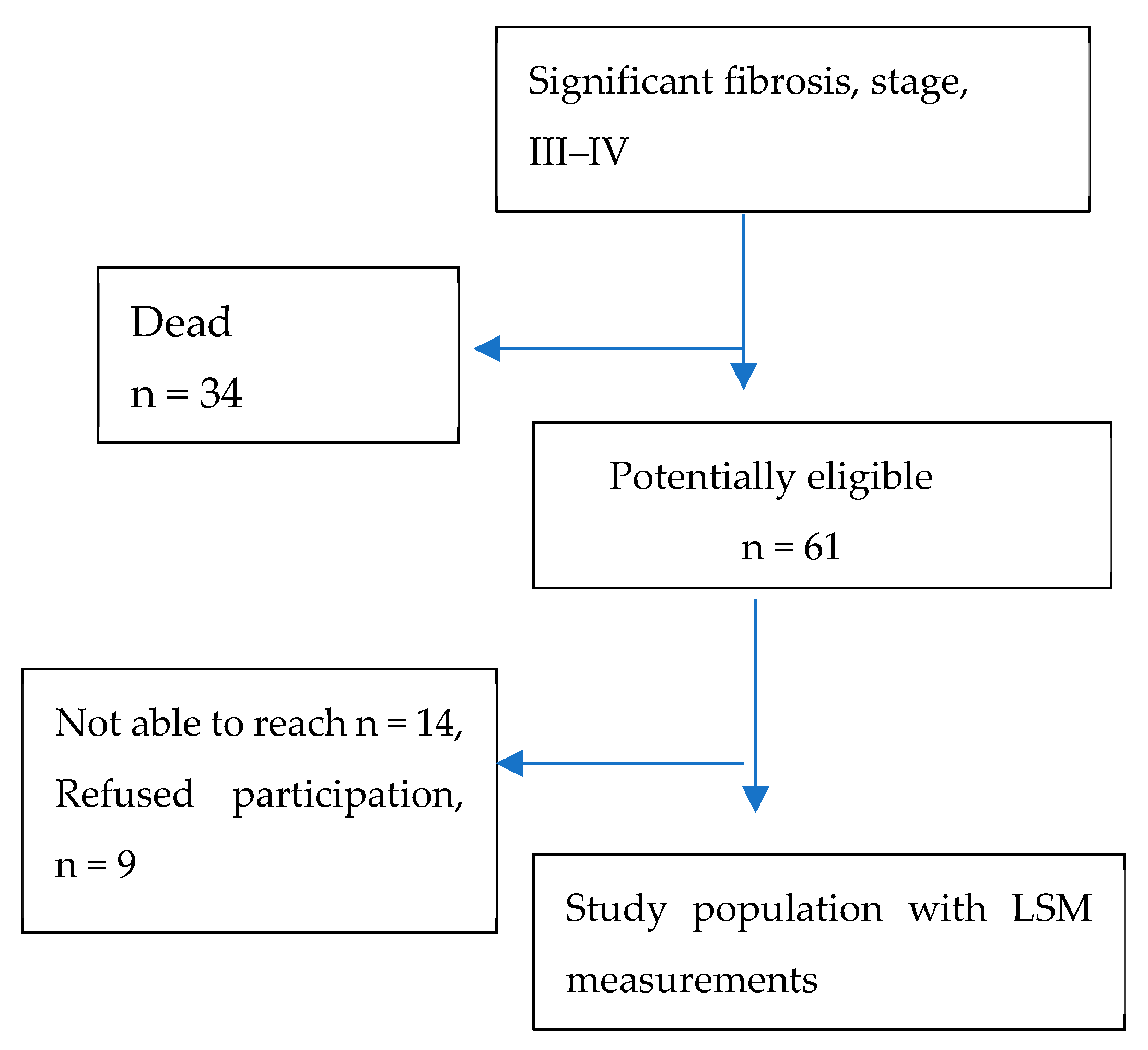
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting and Collection of Baseline Data
2.2. Follow-Up Study
2.3. Liver Stiffness Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics Approval
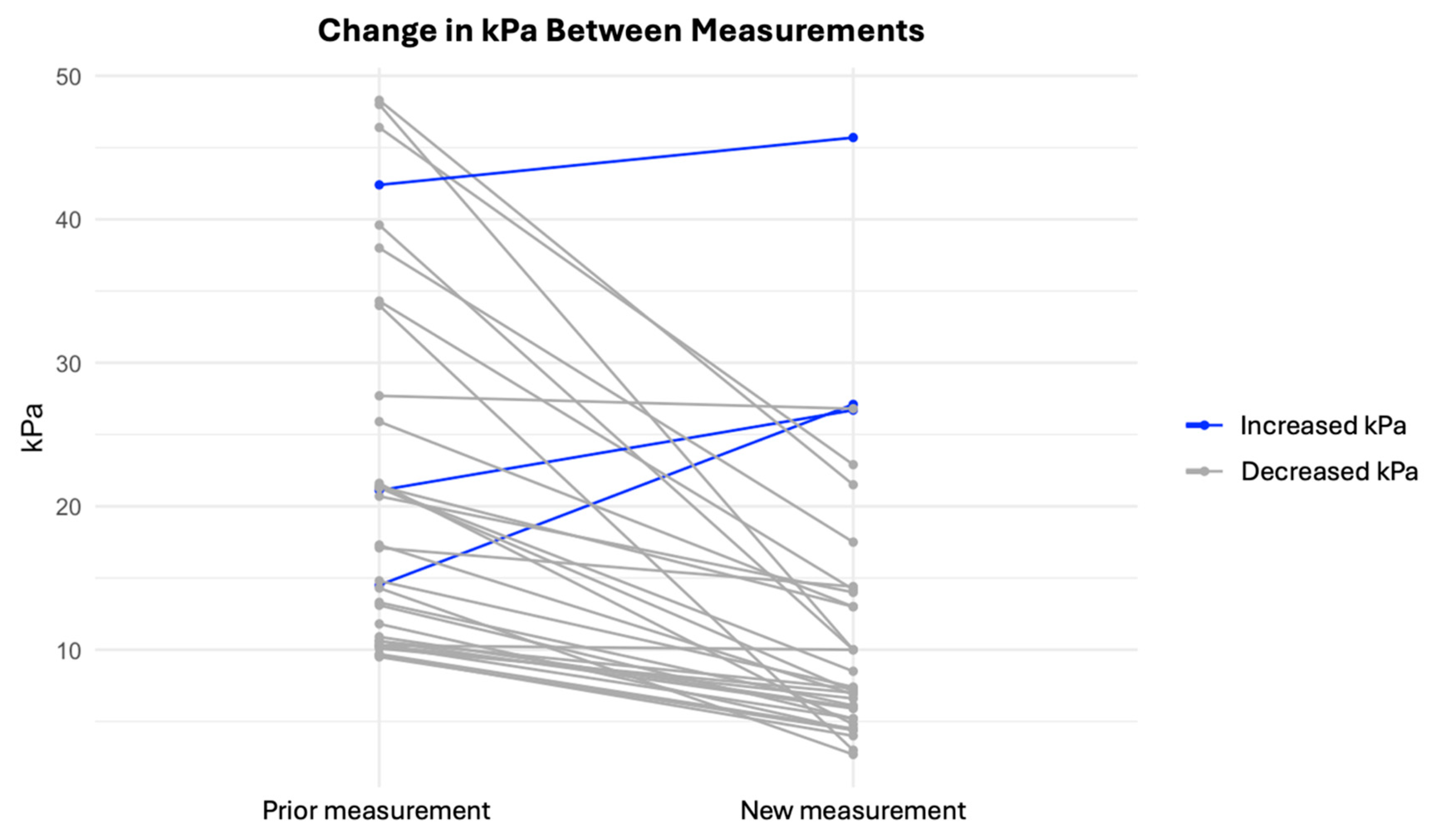
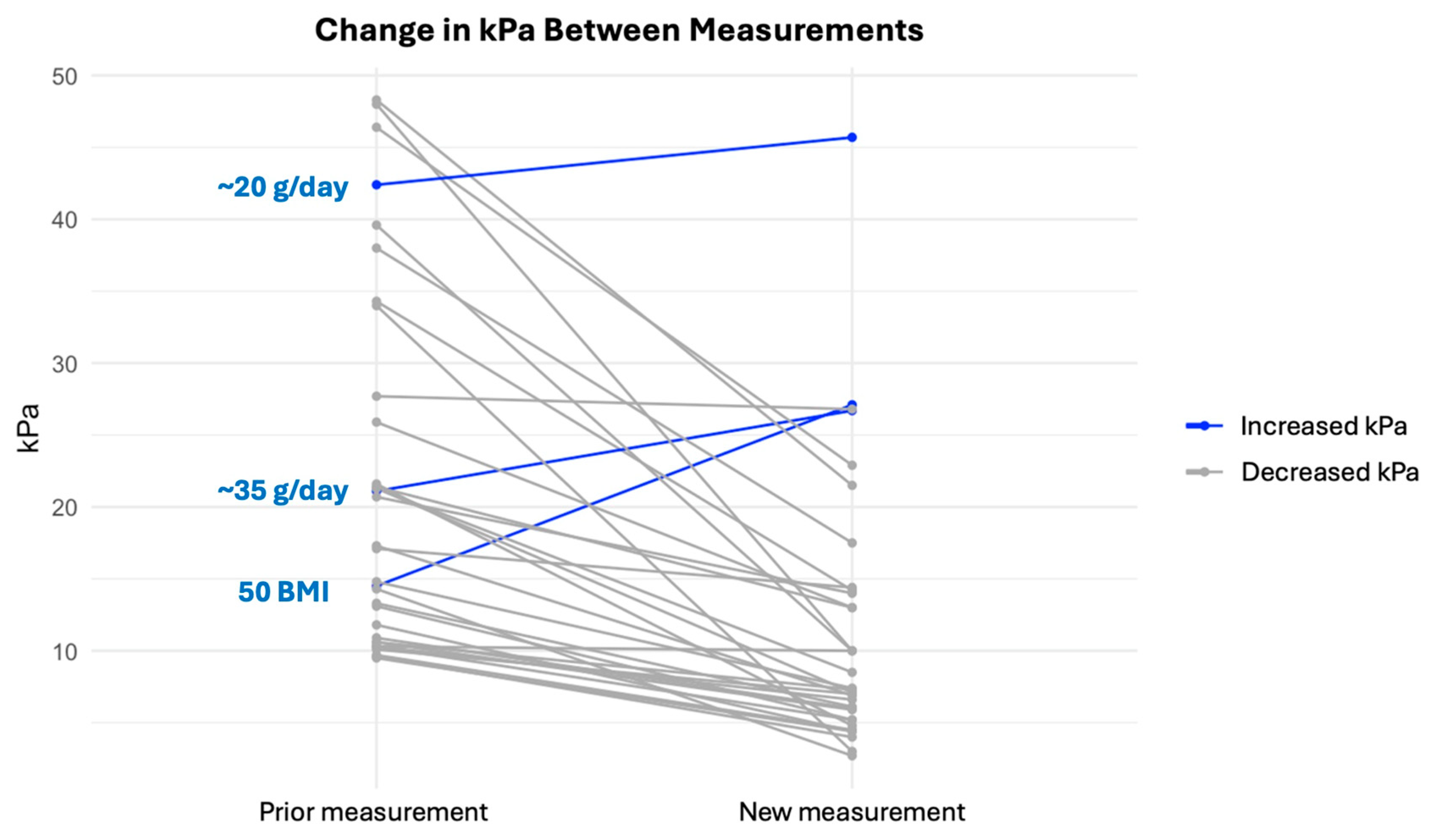
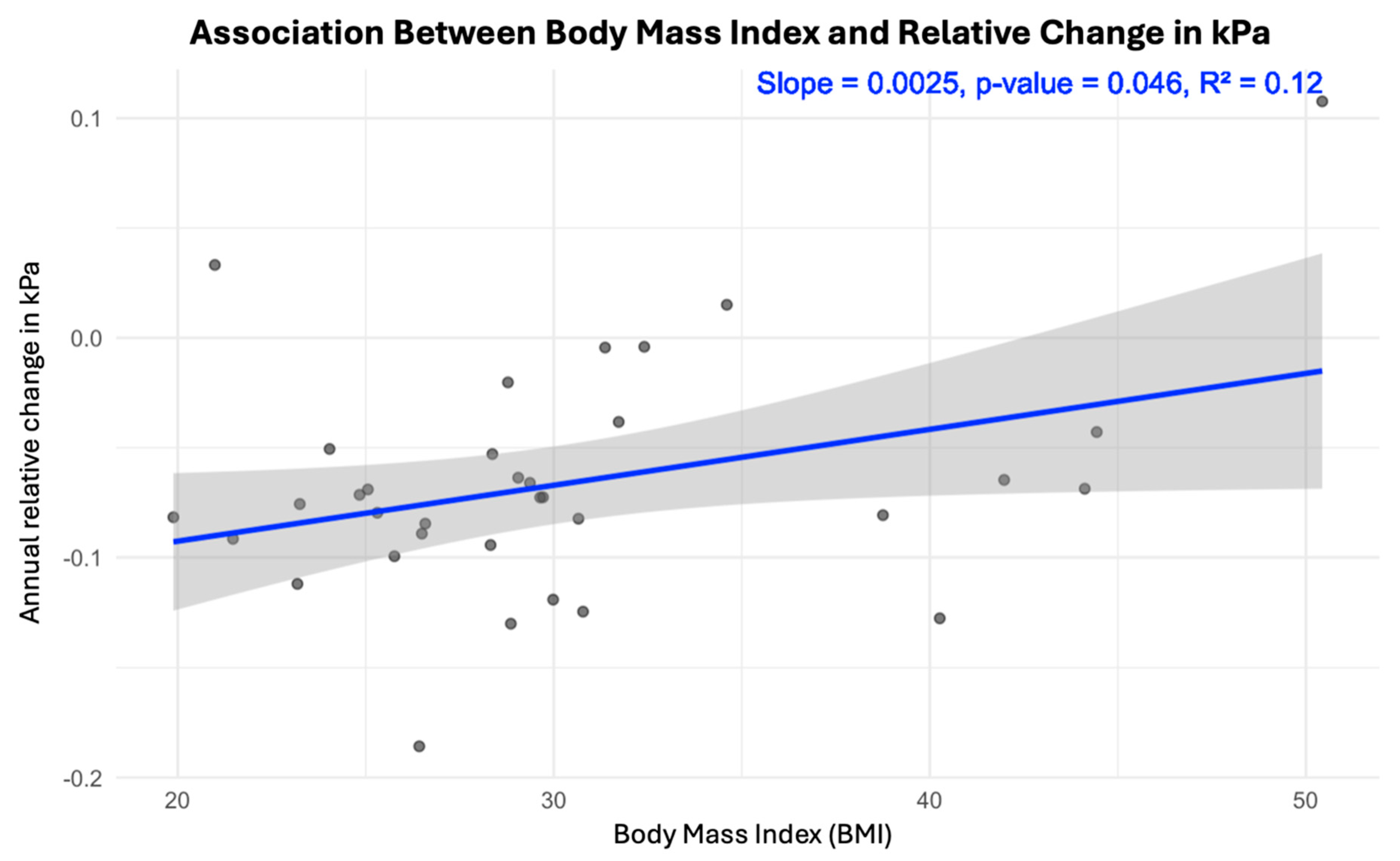
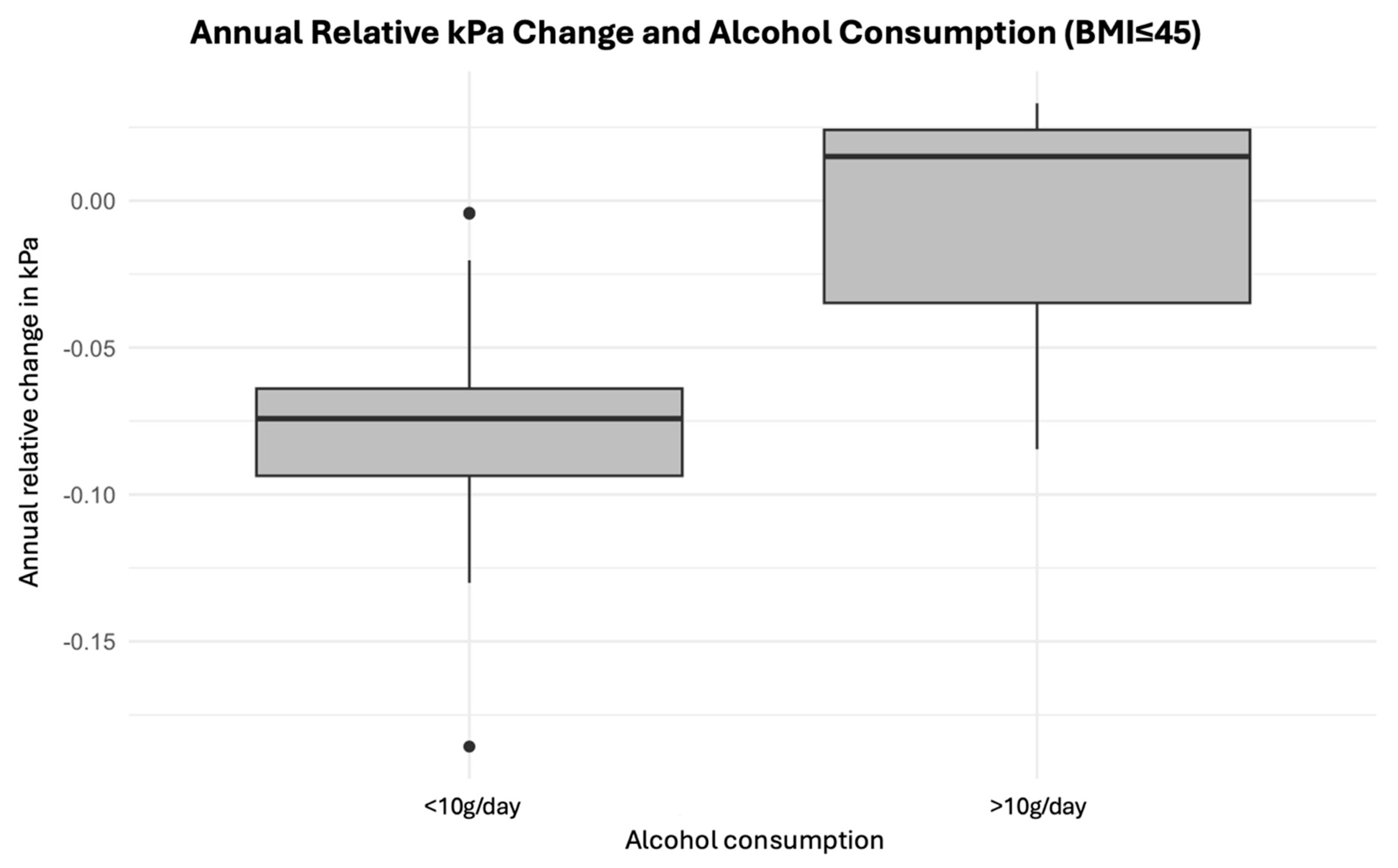
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Cordek, D.G.; Bechtel, J.T.; Maynard, A.T.; Kazmierski, W.M.; Cameron, C.E. Targeting the NS5A protein of HCV: An emerging option. Drugs Future 2011, 36, 691–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, L.; La Mantia, C.; Di Marco, V. Hepatitis C: Standard of Treatment and What to Do for Global Elimination. Viruses 2022, 14, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ólafsson, S.; Tyrfingsson, T.; Rúnarsdóttir, V.; Bergmann, O.M.; Hansdóttir, I.; Björnsson, E.S.; Johannsson, B.; Sigurdardottir, B.; Fridriksdottir, R.H.; Löve, A.; et al. Treatment as Prevention for Hepatitis C (TraP Hep C)—A nationwide elimination programme in Iceland using direct-acting antiviral agents. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 283, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsson, S.; Fridriksdottir, R.H.; Love, T.J.; Tyrfingsson, T.; Runarsdottir, V.; Hansdottir, I.; Bergmann, O.M.; Björnsson, E.S.; Johannsson, B.; Sigurdardottir, B.; et al. Treatment as Prevention for Hepatitis C (TraP HepC). Report on cascade of care during the first 36 months of a nationwide program in Iceland. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Roccarina, D. Update on the role of elastography in liver disease. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 17562848221140657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakareya, T.; Elhelbawy, M.; Elzohry, H.; Eltabbakh, M.; Deif, M.; Abbasy, M. Long-Term Impact of Hepatitis C Virus Eradication on Liver Stiffness in Egyptian Patients. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 2021, 4961919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lens, S.; Baiges, A.; Alvarado-Tapias, E.; LLop, E.; Martinez, J.; Fortea, J.I.; Ibáñez-Samaniego, L.; Mariño, Z.; Rodríguez-Tajes, S.; Gallego, A.; et al. Clinical outcome and hemodynamic changes following HCV eradication with oral antiviral therapy in patients with clinically significant portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Freha, N.; Abu-Kosh, O.; Yardeni, D.; Ashur, Y.; Abu-Arar, M.; Yousef, B.; Monitin, S.; Weissmann, S.; Etzion, O. Liver Fibrosis Regression and Associated Factors in HCV. Patients Treated with Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents. Life 2023, 13, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, H. Alcohol Consumption in Concomitant Liver Disease: How Much is Too Much? Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2017, 16, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajarizadeh, B.; Cunningham, E.B.; Valerio, H.; Martinello, M.; Law, M.; Janjua, N.Z.; Midgard, H.; Dalgard, O.; Dillon, J.; Hickman, M.; et al. Hepatitis C reinfection after successful antiviral treatment among people who inject drugs: A meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, E.S.; Silk, R.; Mathur, P.; Gross, C.; Eyasu, R.; Nussdorf, L.; Hill, K.; Brokus, C.; D’Amore, A.; Sidique, N.; et al. Concurrent Initiation of Hepatitis C and Opioid Use Disorder Treatment in People Who Inject Drugs. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannesson, J.M.; Fridriksdottir, R.H.; Löve, T.J.; Runarsdottir, V.; Hansdóttir, I.; Löve, A.; Thordardottir, M.; Hernandez, U.B.; Olafsson, S.; Gottfredsson, M. High Rate of Hepatitis C Virus Reinfection Among Recently Injecting Drug Users: Results from the TraP Hep C Program—A Prospective Nationwide, Population-Based Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragazzo, T.G.; Zitelli, P.M.Y.; Mazo, D.F.; Oliveira, C.P.; Carrilho, F.J.; Pessoa, M.G. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis can predict clinical outcomes at late follow-up after a sustained virological response in HCV patients? Clinics 2024, 79, 100381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelsgård, A.M.; Mulabecirovic, A.; Leiva, R.A.; Nordaas, I.K.; Mjelle, A.B.; Gilja, O.H.; Havre, R.F. Multiparametric liver assessment in patients successfully treated for hepatitis C: A 4-year follow-up. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.N.; Han, K.H.; Kim, S.U. Clinical application of transient elastography in patients with chronic viral hepatitis receiving antiviral treatment. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.; Asch, S.M.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Cao, Y.; El-Serag, H.B. Risk of Hepatocellular Cancer in HCV Patients Treated with Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraldsson, H.A.; Olafsson, S.; Gottfredsson, M.; Benitez Hernandez, U.; Bjornsson, E.S. Incidence of cirrhosis in Iceland—Impact of the TraP HepC nationwide HCV elimination program. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirinawasatien, A.; Supawan, P. Sustained virological response in chronic hepatitis C patients by direct-acting antiviral treatment significantly reduces liver stiffness over 24 weeks posttreatment. Medicine 2024, 103, e38096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Facciorusso, A.; Loomba, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T. Magnitude and Kinetics of Decrease in Liver Stiffness After Anti-viral Therapy in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, V.; Deterding, K.; Attia, D.; Ringe, K.I.; Heidrich, B.; Cornberg, M.; Gebel, M.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H.; Potthoff, A. Long-term changes in liver elasticity in hepatitis C virus-infected patients with sustained virologic response after treatment with direct-acting antivirals. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tag-Adeen, M.; Sabra, A.M.; Akazawa, Y.; Ohnita, K.; Nakao, K. Impact of hepatitis C virus genotype-4 eradication following direct acting antivirals on liver stiffness measurement. Hepatic Med. Evid. Res. 2017, 9, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Sone, Y.; Takeshima, K.; Ogawa, S.; Goto, T.; Wakahata, A.; Nakashima, M.; Nakamuta, M.; et al. Viral eradication reduces both liver stiffness and steatosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection who received direct-acting anti-viral therapy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.E.; Castera, L.; Al-Ashry, A.; Ghali, S. Impact of HCV eradication following direct-acting antivirals on liver stiffness measurement: A prospective longitudinal study. Egypt. Liver J. 2023, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Bicho, M.; Serejo, F. Effects of HCV Clearance with Direct-Acting Antivirals (DAAs) on Liver Stiffness, Liver Fibrosis Stage and Metabolic/Cellular Parameters. Viruses 2024, 16, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, T.; Nozaki, Y.; Inoue, T.; Suda, T.; Mizumoto, R.; Arimoto, Y.; Ohta, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Ito, Y.; Sudo, Y.; et al. Histological improvement of fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C who achieved a 5-year sustained virological response to treatment with direct-acting antivirals. J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 60, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.S.; Mei, C.Y.; Thompson, A.J.; Christensen, B.; Cunningham, G.; McDonald, L.; Bell, S.; Iser, D.; Nguyen, T.; Desmond, P.V. Sustained virological response halts fibrosis progression: A long-term follow-up study of people with chronic hepatitis C infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185609. [Google Scholar]
- Ravaioli, F.; Conti, F.; Brillanti, S.; Andreone, P.; Mazzella, G.; Buonfiglioli, F.; Serio, I.; Verrucchi, G.; Reggiani, M.L.B.; Colli, A.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma risk assessment by the measurement of liver stiffness variations in HCV cirrhotics treated with direct-acting antivirals. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HCV Patients n = 38 | |
|---|---|
| Age, median, IQR, | 58 (55–65), |
| Gender, males (%) | 31 (82%) |
| Time interval between measurements (years) | 7.2 (6.4–17.9) |
| LSM at baseline (kPa) | 17.2 (10.5–26.3) |
| LSM at follow-up (kPa) | 7.3 (5.4–14.1) |
| LSM decrease, | 35/38 (92%) |
| LSM increase | 3/38 (8%) |
| BMI | 29 (25–32) |
| Waist circumference | 101 (93–112) |
| Alcohol use g/day | 0 (0–1.4) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 21(38%) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 6 (16%) |
| Sleep apnea | 6 (16%) |
| ALT (U/L) | 25 (16–34) |
| AST (U/L) | 26 (21–31) |
| ALP (IU/L) | 80 (66–95) |
| GGT (U/L) | 39 (23–55) |
| Bilirubin umol/L | 12 (8–16) |
| INR | 1.0 (0.9–1.1) |
| Platelets | 243 (175–311) |
| Blood sugar, fasting | 5.9 (5.5–6.3) |
| HbA1c | 35 (31–40) |
| Cholesterol | 4.7 (4–5.4) |
| HDL | 1.3 (1.1–1.5) |
| Triglycerides | 1.2 (0.8–1.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kristjánsson, S.F.; Olafsson, S.; Gottfredsson, M.; Love, T.J.; Björnsson, E.S. Clinically Important Decrease in Liver Stiffness Following Treatment for Hepatitis C: Outcome of the TraP HepC Nationwide Elimination Program. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113982
Kristjánsson SF, Olafsson S, Gottfredsson M, Love TJ, Björnsson ES. Clinically Important Decrease in Liver Stiffness Following Treatment for Hepatitis C: Outcome of the TraP HepC Nationwide Elimination Program. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113982
Chicago/Turabian StyleKristjánsson, Smári Freyr, Sigurdur Olafsson, Magnús Gottfredsson, Thorvardur Jon Love, and Einar Stefán Björnsson. 2025. "Clinically Important Decrease in Liver Stiffness Following Treatment for Hepatitis C: Outcome of the TraP HepC Nationwide Elimination Program" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113982
APA StyleKristjánsson, S. F., Olafsson, S., Gottfredsson, M., Love, T. J., & Björnsson, E. S. (2025). Clinically Important Decrease in Liver Stiffness Following Treatment for Hepatitis C: Outcome of the TraP HepC Nationwide Elimination Program. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113982






