Usefulness of the Phase Angle in Evaluating Locomotive Syndrome in Cancer Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Measurement Items
2.3. Assessment of Locomotive Syndrome (LS)
2.4. Assessment of PhA
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
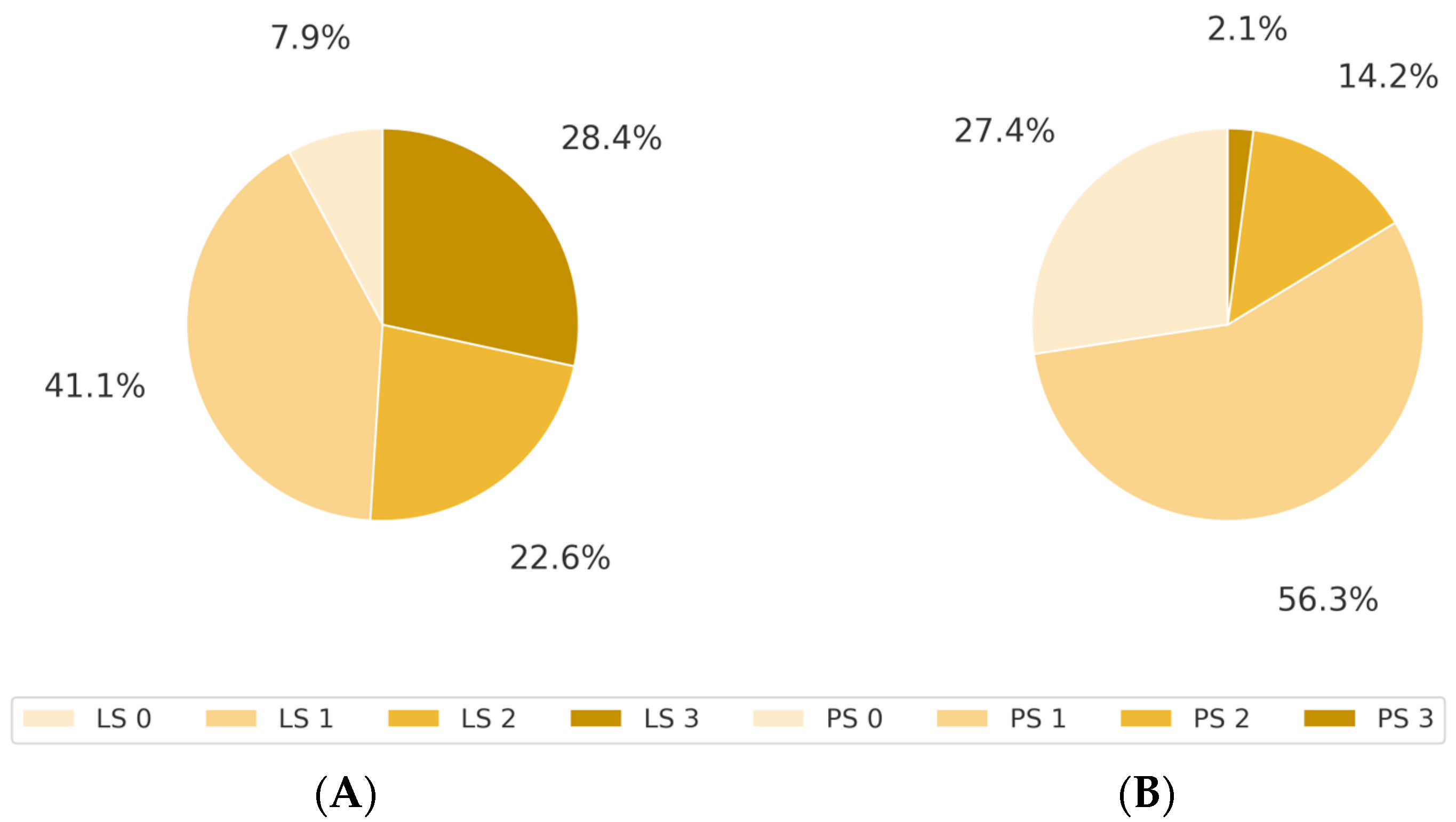
3.2. Association Between LS and ECOG PS
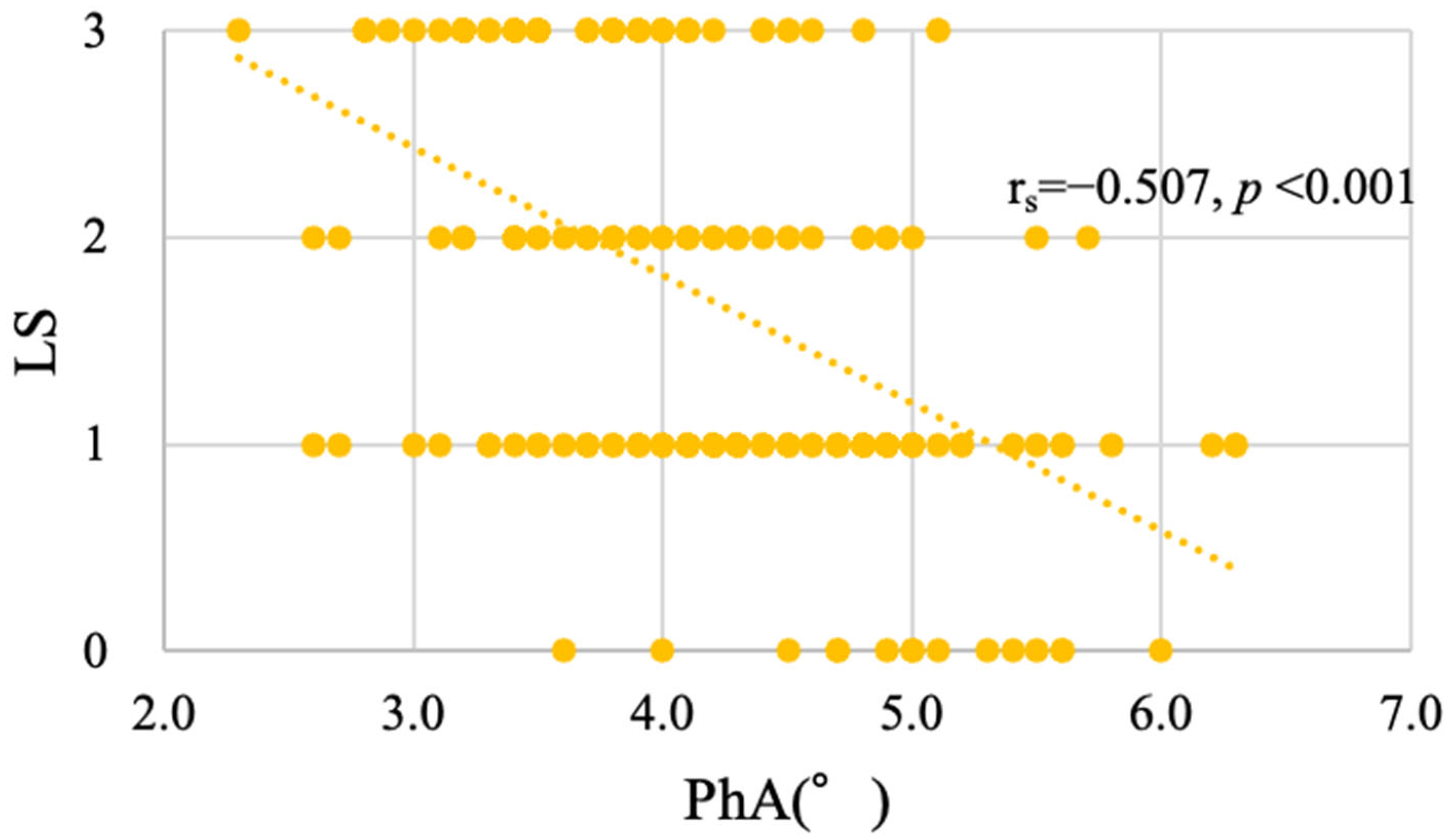
3.3. Distribution of PhA According to LS Stage
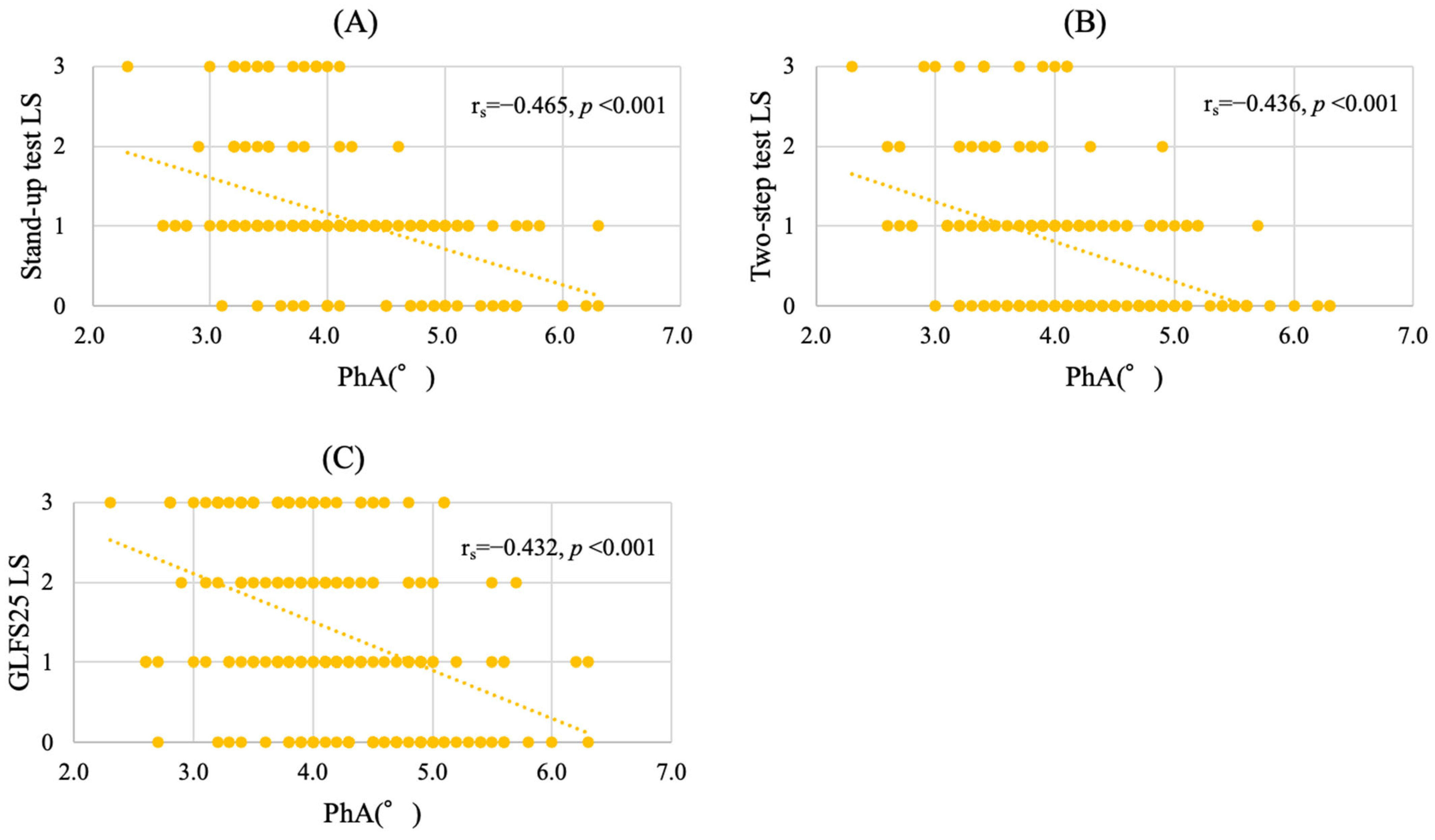
3.4. PhA as an Associated Factor of LS Progression in Cancer Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LS | locomotive syndrome |
| BIA | bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| PhA | phase angle |
| BMI | body mass index |
| GLFS25 | 25-Geriatric Locomotive Function Scale |
| ECOG | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group |
| JOA | Japanese Orthopedic Association |
| PS | performance status |
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, M.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abera, S.F.; Aboyans, V.; Adetokunboh, O.; Afshin, A.; Agrawal, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1151–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, H.; Hirahata, M.; Imanishi, J. Locomotive syndrome in cancer patients: A new role of orthopaedic surgeons as a part of comprehensive cancer care. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 27, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oken, M.M.; Creech, R.H.; Tormey, D.C.; Horton, J.; Davis, T.E.; McFadden, E.T.; Carbone, P.P. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1982, 5, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.M.; Shahrokni, A. Moving beyond Karnofsky and ECOG Performance Status Assessments with New Technologies. J. Oncol. 2016, 2016, 6186543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresham, G.; Hendifar, A.E.; Spiegel, B.; Neeman, E.; Tuli, R.; Rimel, B.J.; Figlin, R.A.; Meinert, C.L.; Piantadosi, S.; Shinde, A.M. Wearable Activity Monitors to Assess Performance Status and Predict Clinical Outcomes in Advanced Cancer Patients. NPJ Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.A. A “super-aged” society and the “locomotive syndrome. ” J. Orthop. Sci. 2008, 13, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirahata, M.; Imanishi, J.; Fujinuma, W.; Abe, S.; Inui, T.; Ogata, N.; Iimuro, S.; Fujita, R.; Sato, K.; Tokizaki, T.; et al. Cancer may accelerate locomotive syndrome and deteriorate quality of life: A single-centre cross-sectional study of locomotive syndrome in cancer patients. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 28, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Ando, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Seki, T.; Hamada, T.; Machino, M.; Ota, K.; Morozumi, M.; Kanbara, S.; Ito, S.; et al. Low bioelectrical impedance phase angle is a significant risk factor for frailty. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6283153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, S.; Gilliland, J.; O’Connor, C.; Chesworth, B.; Madill, J. Is phase angle an appropriate indicator of malnutrition in different disease states? A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 29, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.; Stobäus, N.; Pirlich, M.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Bioelectrical phase angle and impedance vector analysis--Clinical relevance and applicability of impedance parameters. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Kyle, U.G.; Kondrup, J. Assessment of adult malnutrition and prognosis with bioelectrical impedance analysis: Phase angle and impedance ratio. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, N.; Zelnick, L.R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Chertow, G.M. Bioelectrical impedance analysis measures and clinical outcomes in CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, M.; Ogawa, M.; Kondo, H.; Suga, K.; Takahashi, T.; Itoh, H.; Tabata, Y. Bioelectrical impedance analysis-derived phase angle as a determinant of protein-energy wasting and frailty in maintenance hemodialysis patients: Retrospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, C.; Della-Morte, D.; Cacciatore, F.; Gargiulo, G.; Galizia, G.; Roselli, M.; Curcio, F.; Bonaduce, D.; Abete, P. Phase angle as bioelectrical marker to identify elderly patients at risk of sarcopenia. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 58, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, O.; Marra, M.; Di Gregorio, A.; Pasanisi, F.; Scalfi, L. Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA)-derived phase angle in sarcopenia: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3052–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, M.K.; Kizilarslanoglu, M.C.; Arik, G.; Bolayir, B.; Kara, O.; Dogan Varan, H.; Sumer, F.; Kuyumcu, M.E.; Halil, M.; Ulger, Z. Association of bioelectrical impedance analysis-derived phase angle and sarcopenia in older adults. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapel, S.N.; Looijaard, W.G.P.M.; Dekker, I.M.; Girbes, A.R.J.; Weijs, P.J.M.; Oudemans-van Straaten, H.M. Bioelectrical impedance analysis-derived phase angle at admission as a predictor of 90-day mortality in intensive care patients. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, M.G.; Mateus, C.; Capelas, M.L.; Pimenta, N.; Santos, T.; Mäkitie, A.; Ganhão-Arranhado, S.; Trabulo, C.; Ravasco, P. Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) for the assessment of body composition in oncology: A scoping review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Ando, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Seki, T.; Hamada, T.; Machino, M.; Ota, K.; Morozumi, M.; Kanbara, S.; Ito, S.; et al. The decreasing phase angles of the entire body and trunk during bioelectrical impedance analysis are related to locomotive syndrome. J. Orthop. Sci. 2019, 24, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Ando, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Hida, T.; Seki, T.; Hamada, T.; Ito, K.; Tsushima, M.; Morozumi, M.; Machino, M.; et al. The decrease in phase angle measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis reflects the increased locomotive syndrome risk in community-dwelling people: The Yakumo Study. Mod. Rheumatol. 2019, 29, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, T.; Muranaga, S.; Ishibashi, H.; Ohe, T.; Izumida, R.; Yoshimura, N.; Iwaya, T.; Nakamura, K. Development of a screening program to assess motor function in the adult population: A cross-sectional observational study. J. Orthop. Sci. 2015, 20, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-H.; Park, K.S.; Ahn, S.; Ku, E.J.; Jung, K.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.M.; Moon, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Park, K.S.; et al. Comparison of abdominal visceral adipose tissue area measured by computed tomography with that estimated by bioelectrical impedance analysis method in Korean subjects. Nutrients 2015, 7, 10513–10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Furuya, T.; Shiga, Y.; Maki, S.; Takaoka, H.; Miyamoto, T.; Kitamura, M.; Abe, K.; Saito, J.; Fujimoto, K.; et al. Assessment of locomotive syndrome in patients with visceral cancer, the comparison with non-cancer patients using propensity score matching. J. Orthop. Sci. 2022, 27, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa-Silva, M.C.G.; Barros, A.J.D.; Wang, J.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Pierson, R.N. Bioelectrical impedance analysis: Population reference values for phase angle by age and sex. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dutt, A.; Hemraj, S.; Bhat, S.; Manipadybhima, B. Phase angle measurement in healthy human subjects through bio-impedance analysis. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2012, 15, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, L.; Bates, A.; Wootton, S.A.; Levett, D. The use of bioelectrical impedance analysis to predict post-operative complications in adult patients having surgery for cancer: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2914–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.E.; Queiroz, M.D.S.C.; de Albuquerque, N.M.C.; Rodrigues, J.; Wiegert, E.V.M.; Calixto-Lima, L.; de Oliveira, L.C. The prognostic role of phase angle in advanced cancer patients: A systematic review. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2018, 33, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, A.; Karimi, E.; Vingrys, K.; Shirani, F. Is phase angle a valuable prognostic tool in cancer patients’ survival? A systematic review and meta-analysis of available literature. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3182–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detopoulou, P.; Voulgaridou, G.; Papadopoulou, S. Cancer, phase angle and sarcopenia: The role of diet in connection with lung cancer prognosis. Lung 2022, 200, 347–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Park, K.B.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.S.; Kwon, O.K.; Chung, H.Y. Bioelectrical impedance analysis for prediction of early complications after gastrectomy in elderly patients with gastric cancer: The phase angle measured using bioelectrical impedance analysis. J. Gastric Cancer 2019, 19, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 190) | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 62.6 ± 17.2 | |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 57 | 30.0 |
| Male | 133 | 70.0 |
| Primary tumor | ||
| Leukemia | 54 | 28.4 |
| Lymphoma | 31 | 16.3 |
| Esophagus | 29 | 15.3 |
| Gastric | 28 | 14.7 |
| Multiple myeloma | 10 | 5.3 |
| Colorectal | 6 | 3.2 |
| Others | 32 | 16.8 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.7 ± 3.5 | |
| Underweight < 18.5 | 33 | 17.4 |
| Standard 18.5–25.0 | 123 | 64.7 |
| Obesity > 25.0 | 34 | 17.9 |
| Gait speed (m/s) | 1.15 ± 0.34 | |
| Grip strength (kg) | 27.9 ± 8.7 | |
| Phase angle (°) | 4.16 ± 0.78 |
| LS 0 | LS 1 | LS 2 | LS 3 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS 0 | 12 | 28 | 6 | 6 | 52 |
| PS 1 | 3 | 44 | 33 | 27 | 107 |
| PS 2 | 0 | 6 | 4 | 17 | 27 |
| PS 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| PS 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 15 | 78 | 43 | 54 | 190 |
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase angle | 0.361 | 0.221–0.588 | <0.001 |
| Gait speed | 0.235 | 0.086–0.642 | 0.005 |
| Grip strength | 0.931 | 0.880–0.984 | 0.012 |
| Age | 1.003 | 0.986–1.021 | 0.704 |
| Sex | |||
| Female | 0.635 | 0.285–1.413 | 0.266 |
| Male | 1.000 | - | - |
| BMI | |||
| Underweight | 1.358 | 0.447–4.124 | 0.59 |
| Standard | 0.946 | 0.430–2.081 | 0.89 |
| Obesity | 1.000 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kashima, R.; Yoshikawa, R.; Saho, W.; Fujii, Y.; Harada, R.; Makiura, D.; Tatebayashi, D.; Fujiwara, K.; Mizuta, M.; Inoue, J.; et al. Usefulness of the Phase Angle in Evaluating Locomotive Syndrome in Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3980. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113980
Kashima R, Yoshikawa R, Saho W, Fujii Y, Harada R, Makiura D, Tatebayashi D, Fujiwara K, Mizuta M, Inoue J, et al. Usefulness of the Phase Angle in Evaluating Locomotive Syndrome in Cancer Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3980. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113980
Chicago/Turabian StyleKashima, Ryoga, Ryo Yoshikawa, Wataru Saho, Yasumitsu Fujii, Risa Harada, Daisuke Makiura, Daisuke Tatebayashi, Katsuya Fujiwara, Mayu Mizuta, Junichiro Inoue, and et al. 2025. "Usefulness of the Phase Angle in Evaluating Locomotive Syndrome in Cancer Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3980. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113980
APA StyleKashima, R., Yoshikawa, R., Saho, W., Fujii, Y., Harada, R., Makiura, D., Tatebayashi, D., Fujiwara, K., Mizuta, M., Inoue, J., & Sakai, Y. (2025). Usefulness of the Phase Angle in Evaluating Locomotive Syndrome in Cancer Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3980. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113980







