Association of Albumin-to-D-Dimer Ratio with Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Intensive Care Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Study Population
2.2. Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nates, J.L.; Pene, F.; Darmon, M.; Mokart, D.; Castro, P.; David, S.; Povoa, P.; Russell, L.; Nielsen, N.D.; Gorecki, G.P.; et al. Septic shock in the immunocompromised cancer patient: A narrative review. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.; Kong, G.; Fu, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Song, F.; Chu, Y.; Meng, M. Impact of Early Administration of Albumin on Mortality Among Severe COVID-19 Patients, China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2025, 18, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabil, M.; Bushi, G.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Alrahbeni, T.; Al-Mugheed, K.; Khatib, M.N.; Gaidhane, S.; Zahiruddin, Q.S.; Kukreti, N.; Rustagi, S.; et al. Hypoalbuminemia as a predictor of severe dengue: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2025, 23, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chu, H.; Zhou, H. Association between hypoalbuminemia and mortality in patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedermann, C.J. Human Albumin Infusion in Critically Ill and Perioperative Patients: Narrative Rapid Review of Meta-Analyses from the Last Five Years. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedermann, C.J.; Wiedermann, W.; Joannidis, M. Causal relationship between hypoalbuminemia and acute kidney injury. World J. Nephrol. 2017, 6, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segmen, F.; Aydemir, S.; Kucuk, O.; Dogu, C.; Dokuyucu, R. Comparison of Oxidative Stress Markers with Clinical Data in Patients Requiring Anesthesia in an Intensive Care Unit. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itagaki, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Banno, M.; Momosaki, R.; Yamada, K.; Hayakawa, M. Efficacy of albumin with diuretics in mechanically ventilated patients with hypoalbuminemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e30276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, B.; Chen, R.; Su, L.; Wu, M.; Liu, Z. Association of D-dimer and acute kidney injury associated with rhabdomyolysis in patients with exertional heatstroke: An over 10-year intensive care survey. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, K.; Fresilli, S.; Paoli, N.; Maiucci, G.; Salvioni, M.; Kotani, Y.; Katzenschlager, S.; Weigand, M.A.; Landoni, G. D-dimer levels in non-COVID-19 ARDS and COVID-19 ARDS patients: A systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0277000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segmen, F.; Aydemir, S.; Kucuk, O.; Dokuyucu, R. The Roles of Vitamin D Levels, Gla-Rich Protein (GRP) and Matrix Gla Protein (MGP), and Inflammatory Markers in Predicting Mortality in Intensive Care Patients: A New Biomarker Link? Metabolites 2024, 14, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Yang, Z.; Liang, H.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Bi, Y. Predictive value of D-dimer to albumin ratio for severe illness and mortality in patients with COVID-19. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1410179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Deng, G.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, M.; Chen, L.; Han, D.; Li, W.; Guo, K.; Chen, X.; et al. A predictive model for the severity of COVID-19 in elderly patients. Aging 2020, 12, 20982–20996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yang, X.; Cao, B.; Su, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, C. Retrospective study of the impact of diabetes on the severity and prognosis of COVID-19. Exp. Ther. Med. 2024, 27, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzych, L.J.; Putowski, Z.; Czok, M.; Hofman, M. What Is the Role of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange as an Adjunctive Treatment in Severe COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Viruses 2021, 13, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ren, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J. The predictive value of the preoperative albumin-to-fibrinogen ratio for postoperative hospital length of stay in liver cancer patients. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 20321–20331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Khorobrykh, T.V.; He, M.; et al. Albumin-to-D-dimer ratios: A novel prognostic factor for evaluating first-line chemotherapy efficacy in advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients. Neoplasma 2024, 71, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaiti, Z.; Xu, C.; Fu, J.; Tianyu Li, W.; Chai, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J. A Novel Biomarker to Screen for Malnutrition: Albumin/Fibrinogen Ratio Predicts Septic Failure and Acute Infection in Patients Who Underwent Revision Total Joint Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 3282–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Prognostic Value of Albumin to D-Dimer Ratio in Advanced Gastric Cancer. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 9973743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Abdul-Aziz, M.H.; Lipman, J.; Mouton, J.W.; Vinks, A.A.; Felton, T.W.; Hope, W.W.; Farkas, A.; Neely, M.N.; Schentag, J.J.; et al. Individualised antibiotic dosing for patients who are critically ill: Challenges and potential solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulla, A.; Dijkstra, A.; Hunfeld, N.G.M.; Endeman, H.; Bahmany, S.; Ewoldt, T.M.J.; Muller, A.E.; van Gelder, T.; Gommers, D.; Koch, B.C.P. Failure of target attainment of beta-lactam antibiotics in critically ill patients and associated risk factors: A two-center prospective study (EXPAT). Crit. Care 2020, 24, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Survivors (n = 101) | Non-Survivors (n = 61) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) or Mean ± SD | |||
| Age (years) | 65.1 ± 13.8 | 71.2 ± 14.2 | 0.008 |
| Sex (male) | 56 (55.4%) | 38 (62.3%) | 0.402 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 27.3 ± 4.1 | 28.9 ± 4.9 | 0.031 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 34 (33.7%) | 35 (57.4%) | 0.003 |
| Hypertension | 64 (63.4%) | 44 (72.1%) | 0.092 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 15 (14.9%) | 15 (24.6%) | 0.132 |
| Coronary artery disease | 29 (28.7%) | 25 (41.0%) | 0.048 |
| Others | 26 (25.7%) | 19 (31.1%) | 0.177 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 2.3 ± 1.1 | 3.6 ± 1.4 | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 82 ± 47 | 120 ± 56 | <0.001 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 31.4 ± 13.1 | 42.1 ± 15.0 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.6 | <0.001 |
| Platelet count (×103/μL) | 223 ± 70 | 197 ± 74 | 0.022 |
| INR | 1.22 ± 0.16 | 1.33 ± 0.21 | 0.041 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 2.7 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| D-dimer (μg/mL) | 1.7 ± 1.1 | 2.6 ± 1.3 | <0.001 |
| Albumin-to-D-dimer ratio (ADR) | 1.56 ± 0.52 | 1.02 ± 0.43 | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | 41 (40.6%) | 35 (57.4%) | 0.029 |
| Multiple organ failure | 17 (16.8%) | 27 (44.3%) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis/Organ failure rate | 29 (28.7%) | 37 (60.7%) | <0.001 |
| ICU length of stay (days) | 8.3 ± 4.2 | 11.7 ± 5.3 | <0.001 |
| Mechanical ventilation duration (days) | 6.2 ± 3.5 | 9.1 ± 4.2 | <0.001 |
| 30-day mortality rate | 0 (0%) | 61 (100%) | – |
| Parameter | Albumin-to-D-Dimer Ratio (ADR) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High (n = 50) (>1.45) | Intermediate (n = 54) (0.95–1.45) | Low (n = 58) (<0.95) | ||
| Age (years) | 64.3 ± 13.5 | 67.9 ± 13.7 | 70.5 ± 14.8 | 0.041 |
| Male sex (%) | 28 (56%) | 32 (59.3%) | 34 (58.6%) | 0.942 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 27.2 ± 4.0 | 28.0 ± 4.5 | 28.5 ± 5.2 | 0.187 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 16 (32%) | 22 (40.7%) | 31 (53.4%) | 0.029 |
| Hypertension (%) | 30 (60%) | 36 (66.7%) | 42 (72.4%) | 0.364 |
| Chronic kidney disease (%) | 6 (12%) | 11 (20.4%) | 13 (22.4%) | 0.228 |
| Coronary artery disease (%) | 13 (26%) | 16 (29.6%) | 23 (39.7%) | 0.243 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 2.1 ± 1.0 | 2.7 ± 1.2 | 3.5 ± 1.4 | 0.002 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 72 ± 38 | 94 ± 49 | 119 ± 56 | <0.001 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 29.1 ± 12.7 | 34.7 ± 13.3 | 42.1 ± 14.7 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 0.001 |
| Platelet count (×103/μL) | 226 ± 68 | 211 ± 70 | 198 ± 78 | 0.043 |
| INR | 1.19 ± 0.15 | 1.25 ± 0.17 | 1.34 ± 0.20 | 0.002 |
| Sepsis (%) | 15 (30%) | 26 (48.1%) | 35 (60.3%) | 0.011 |
| Multiple organ failure (%) | 6 (12%) | 14 (25.9%) | 24 (41.4%) | 0.001 |
| Sepsis/Organ failure (%) | 13 (26%) | 23 (42.6%) | 32 (55.2%) | 0.005 |
| ICU stay (days) | 7.1 ± 3.2 | 9.1 ± 3.7 | 12.3 ± 5.2 | <0.001 |
| Mechanical ventilation (days) | 4.8 ± 2.7 | 6.6 ± 3.2 | 9.6 ± 4.3 | <0.001 |
| 30-day mortality (%) | 9 (18%) | 20 (37%) | 32 (55.2%) | <0.001 |
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 1.04 | 1.01–1.08 | 0.032 |
| Sex (male) | 1.20 | 0.65–2.30 | 0.602 |
| Body mass index | 1.06 | 0.99–1.14 | 0.074 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.72 | 1.02–3.24 | 0.039 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 1.65 | 1.13–2.41 | 0.005 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 1.02 | 1.01–1.03 | 0.021 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 1.05 | 1.02–1.09 | 0.010 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.82 | 1.16–2.98 | 0.013 |
| Platelet count (×103/μL) | 0.87 | 0.78–0.98 | 0.049 |
| INR | 2.76 | 1.35–5.67 | 0.003 |
| Albumin-to-D-dimer ratio | 0.39 | 0.26–0.58 | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | 1.91 | 1.03–3.55 | 0.041 |
| Multiple organ failure | 3.04 | 1.52–6.10 | 0.001 |
| ICU stay (days) | 1.09 | 1.01–1.18 | 0.014 |
| Mechanical ventilation (days) | 1.11 | 1.02–1.20 | 0.008 |
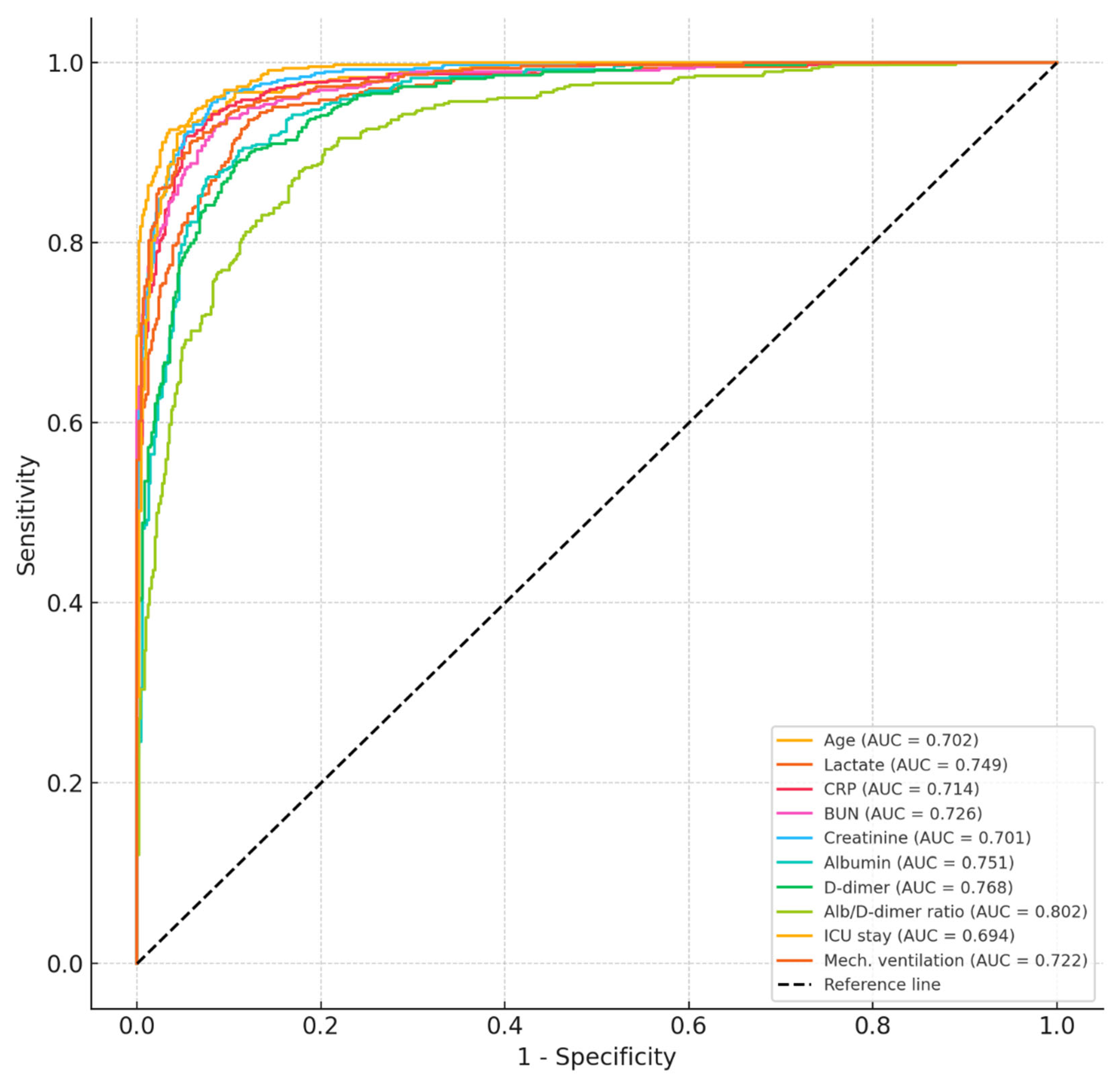
| Variable | Cut-Off | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | AUC (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | >68.5 | 72.1 | 63.2 | 0.702 (0.625–0.778) | 0.001 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | >2.6 | 76.5 | 68.4 | 0.749 (0.675–0.822) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | >105 | 69.4 | 66.7 | 0.714 (0.638–0.790) | 0.002 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | >38.5 | 74.2 | 62.3 | 0.726 (0.655–0.797) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | >1.4 | 71.8 | 69.2 | 0.701 (0.628–0.774) | 0.002 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | <2.9 | 74.6 | 67.1 | 0.751 (0.675–0.827) | <0.001 |
| D-dimer (μg/mL) | >2.2 | 73.4 | 65.5 | 0.768 (0.661–0.812) | <0.001 |
| Albumin-to-D-dimer ratio | <1.05 | 78.7 | 71.4 | 0.802 (0.728–0.875) | <0.001 |
| ICU stay (days) | >10.5 | 68.3 | 64.8 | 0.694 (0.619–0.768) | 0.003 |
| Mechanical ventilation (days) | >7.0 | 75.6 | 65.9 | 0.722 (0.648–0.795) | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eygi, E.; Bayrakci, S. Association of Albumin-to-D-Dimer Ratio with Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Intensive Care Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113917
Eygi E, Bayrakci S. Association of Albumin-to-D-Dimer Ratio with Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Intensive Care Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113917
Chicago/Turabian StyleEygi, Elif, and Sinem Bayrakci. 2025. "Association of Albumin-to-D-Dimer Ratio with Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Intensive Care Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113917
APA StyleEygi, E., & Bayrakci, S. (2025). Association of Albumin-to-D-Dimer Ratio with Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Intensive Care Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113917






